The Geographic Distribution, Venom Components, Pathology and Treatments of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Venom
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Disease Burden of Stonefish Envenomation
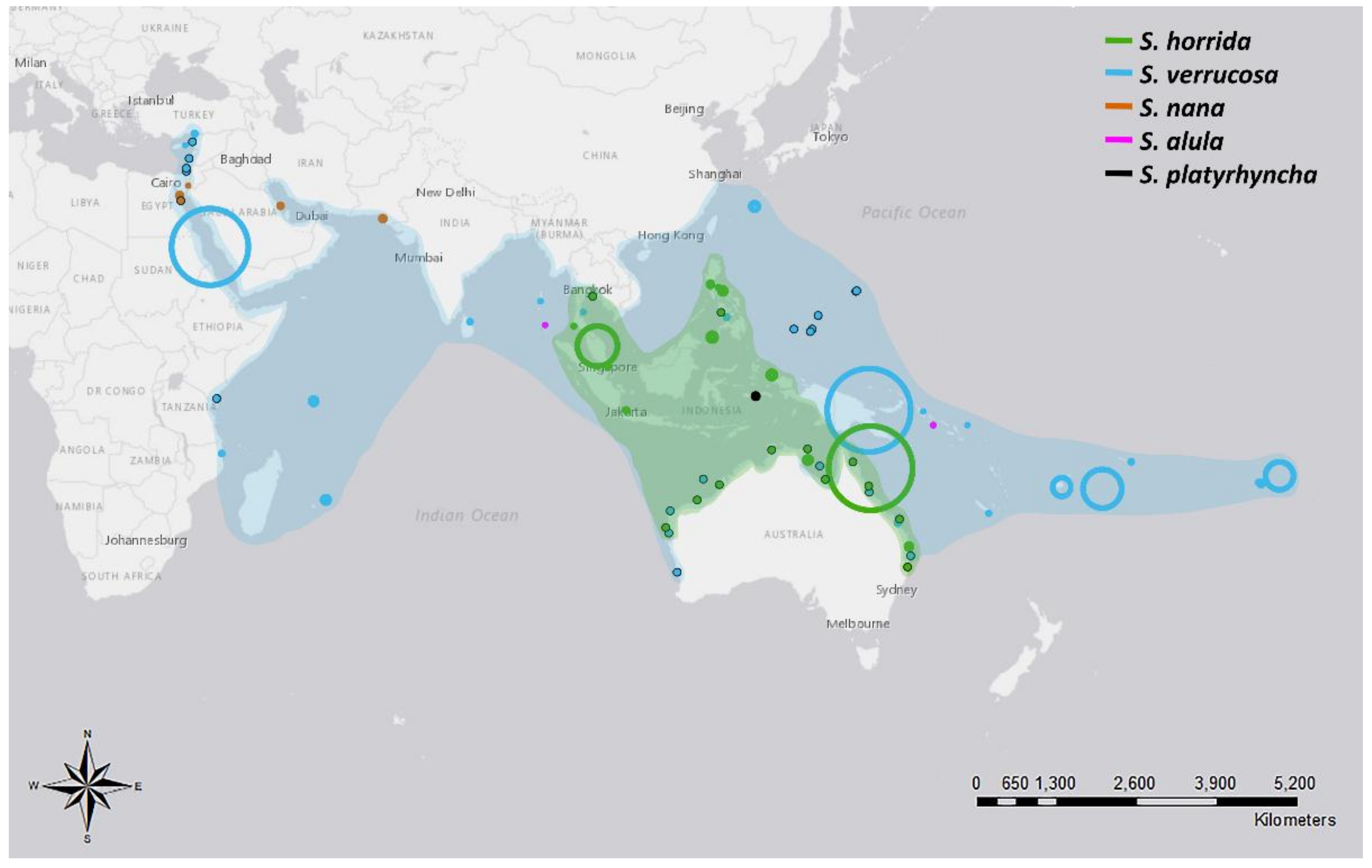
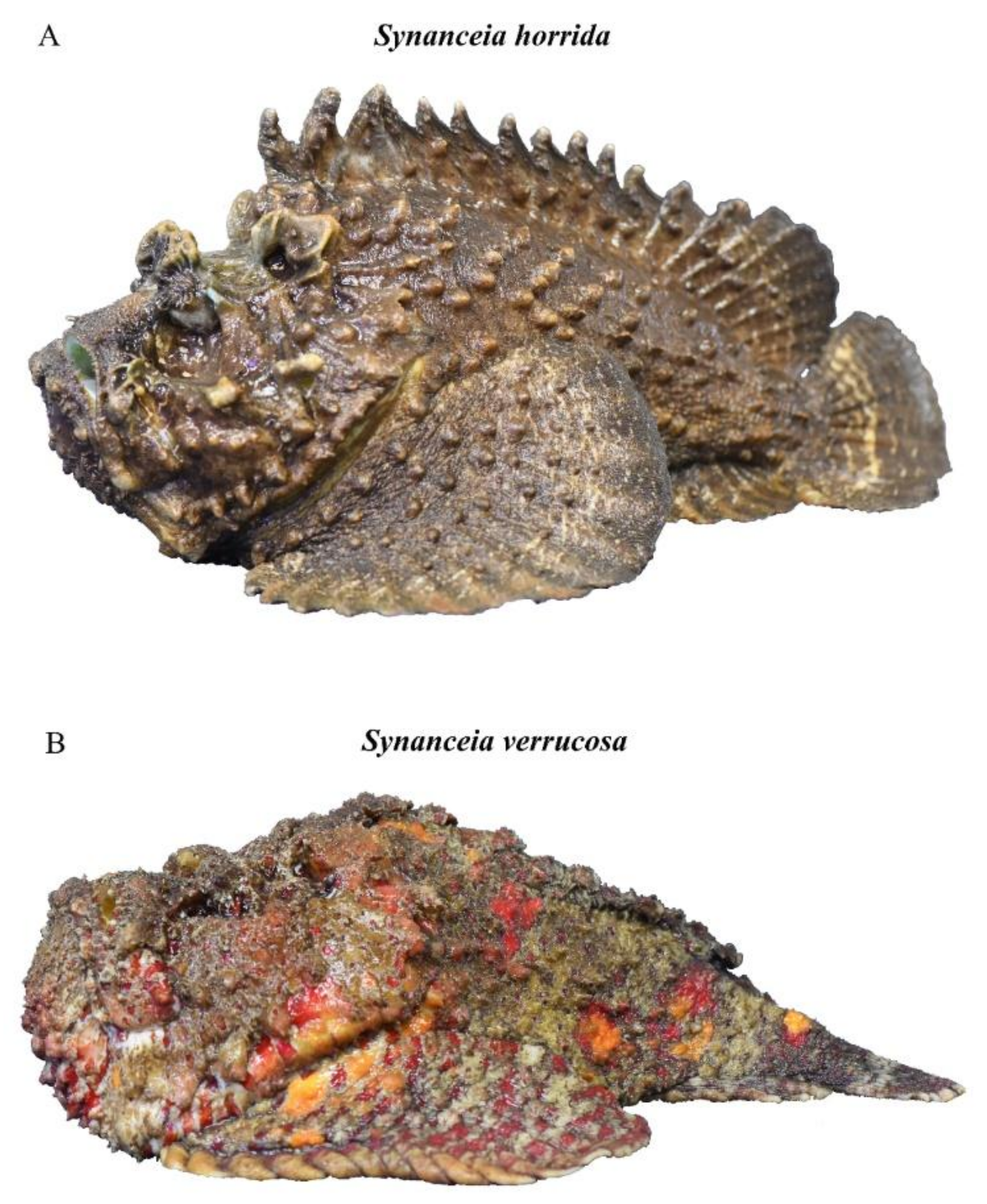
3. Geographic Distribution of Synanceia spp.
4. Envenomation
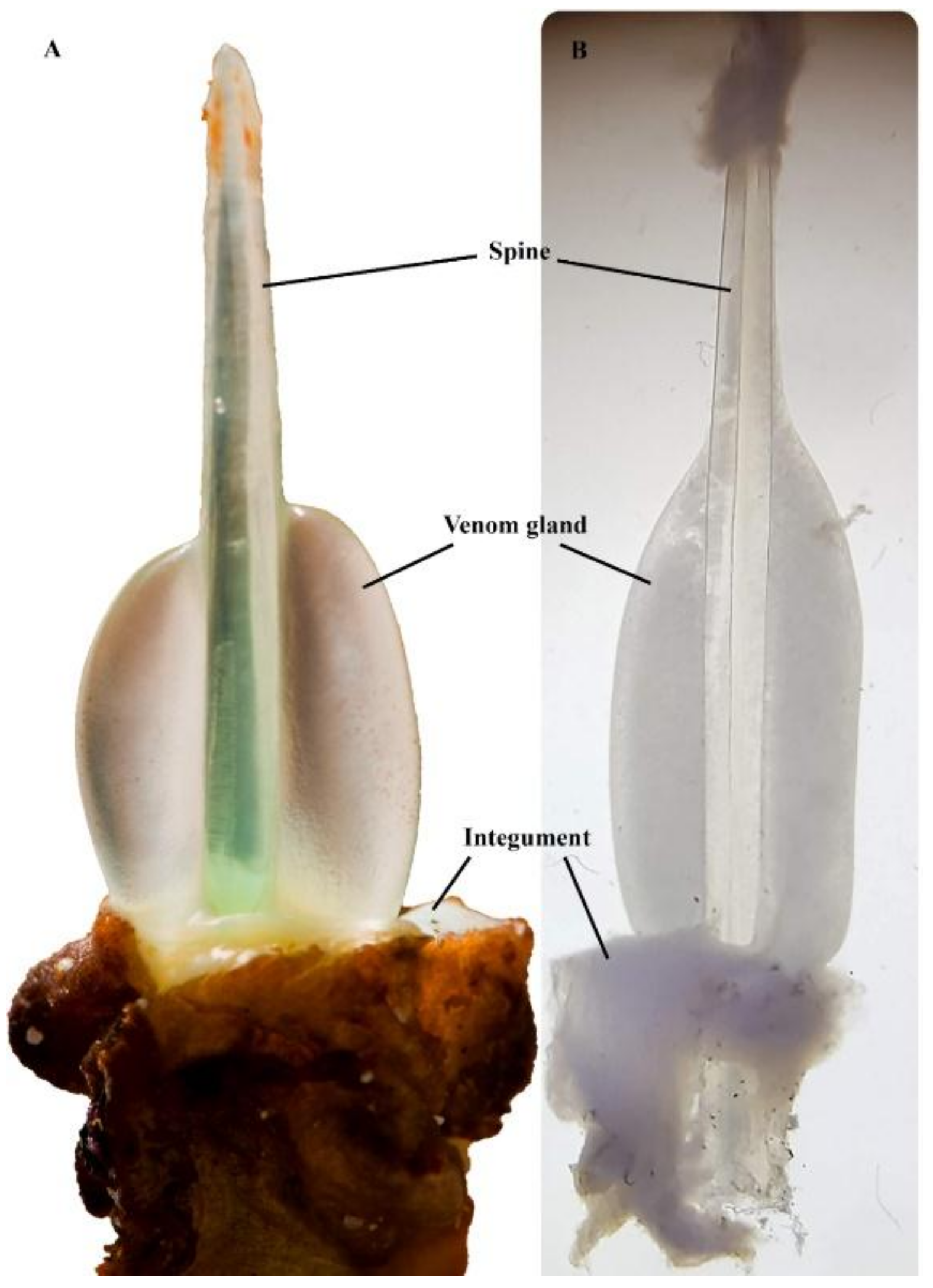
4.1. Venom Apparatus
4.2. First Aid, Clinical and Systemic Features of Stonefish Stings
4.3. Antivenom
5. Composition of Synanceia spp. Venoms
6. Cardiovascular and Respiratory Effects of Synanceia Envenomation
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors
7. Vascular Permeability and Cytolytic Effects of Synanceia Envenomation
8. Neuromuscular Effects of Synanceia Envenomation
9. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Location | Number of Cases | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | |||
| Cairns | 1 | [123] | |
| Cooktown | 1 | [123] | |
| Western Australia | 1 | [124] | |
| Tropical northern Australia | 1 | [125] | |
| Cook Islands | 1 | [31] | |
| Egypt | |||
| Taba | 1 | [126] | |
| French Polynesia | |||
| Bora Bora | 1 | 2018 | [27] |
| Tubuai Island | 1 | 2014 | [27] |
| Guam | 2 | [99,127] | |
| Indonesia | |||
| Lembeh, North Sulawesi | 1 | [128] | |
| Indo-Pacific region | 1 | [32] | |
| Japan | |||
| Okinawa | 15 | 2013–2017 | [6] |
| Kingdom of Bahrain | 1 | [30] | |
| Malaysia | |||
| Kota Kinabalu, Sabah | 1 | [129] | |
| Mozambique | |||
| Pinda | 1 | 1956 | [34] |
| New Caledonia | 1 | 2008 | [27] |
| Papua New Guinea | |||
| Trobriand Islands | 12 | [130] | |
| People’s Republic of China | |||
| Hong Kong | 1 | 2002 | [131] |
| Hong Kong | 1 | 2003 | [131] |
| Hong Kong | 7 | 2005–2008 | [5] |
| Not clearly stated—possibly Hong Kong | 1 | 2008 | [28] |
| Hong Kong | 32 | 2008–2018 | [4] |
| Not clearly stated | 1 | [26] | |
| Seychelles | |||
| Pont Larue, Mahe | 1 | 1956 | [34] |
| Singapore | |||
| Pulau Bukom | 81 | 4 years | [25] |
| Location not stated | 1 | 2001–2003 | [11] |
| Location not stated | 7 | 1.25 years | [11] |
| Location not stated | 30 | 2004–2006 | [9] |
| Location per Continent | Number of Specimens | Coordinates | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. verrucosa | |||
| AFRICA | |||
| Kenya–Andromache Reef, S of Port Kilindini of Mombasa Harbor | 1 | 4°05′ 05″ S, 39°40′ 39″ E | [2] |
| Mauritius—location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| Mozambique—Pinda Peninsula | 1 | 14°14°12″ S | [132] |
| Seychelles—location not stated | 2 | [2] | |
| ASIA | |||
| Ceylon—Trincomalee, inside base of Royal Navy of Ceylon | 3 | [2] | |
| Cyprus—Kumyali | 1 | [133] | |
| Japan—Okinawa | 1 | [2] | |
| Mediterranean Sea | |||
| Gaza City, State of Palestine | 1 | 31°31′ 3.32″ N, 34°25′ 18.66″ E | [134] |
| Israel—Palmakhim | 1 | 31°56.36′ N, 34°42.16′ E | [135] |
| Lebanon—Tyr | 1 | 33.290657° N, 35.184459° E | [136] |
| Syria—Lattakia city | 1 | 35°31.5′ 5.97″ N, 35°42′ 48.57″ E | [137] |
| Turkey—Yumurtalik, Iskenderum Bay | 1 | [138] | |
| Phillipines | |||
| Dumaguette | 1 | [2] | |
| Sitankai, Sulu Province | 2 | [2] | |
| Location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| Red Sea | |||
| Location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| Thailand—Ko Tao, Sairee Beach, Gulf of Thailand | 1 | [139] | |
| Western Indian Ocean | |||
| Southern Andaman Islands, S of Corbyn’s Cove, Port Blair | 1 | [2] | |
| OCEANIA | |||
| Australia | |||
| Capricorn Islands, One Tree Island, W side, QLD | 1 | [2] | |
| Exmouth, WA | 1 | −21.958648, 114.141082 | [140] |
| Fairfax Island, QLD | 1 | [2] | |
| Gulf of Carpentaria, QLD | 1 | 15°1′ 30″ S, 138°41′ 30″ E | [141] |
| Heron Island, QLD | 1 | [13] | |
| Lancelin, WA | 1 | 31°0′ S, 115°19′ E | [142] |
| Magnetic Island, Townsville, QLD | 1 | 19°08′ 00″ S, 146°50’00ʺ E | [143] |
| Mermaid Reef, Rowley Shoals, WA | 1 | −17.083, 119.583 | [144] |
| Shark Bay, New Beach, 45 km S of Carnarvon | 1 | 25°20′ S, 113°56′ E | [145] |
| Tallow Beach, 300 m S of the southern boundary of Arakwal NP, NSW | 1 | 28°39′ 54″ S, 153°37’ 32″ E | [146] |
| Melanesia | |||
| Solomon Islands | |||
| Bougainville, E side of Puk Puk Island, outside Poison Lagoon | 1 | [2] | |
| Sikaiana Island | 1 | [2] | |
| Micronesia | |||
| Caroline Islands | |||
| Yap Island, inlet E side of Yap Island | 1 | 9°29′ 48″ N, 138°26′ 57″ E | [2] |
| Location not stated | 4 | [2] | |
| Mariana Islands | |||
| Guam, Hagatna | 1 | [2] | |
| Guam, N of Tringhera Beach in Hagatna Bay | 3 | 13°28′ 53″ N, 144°45′ 45″ E | [2] |
| Guam, SW of Agat village, N side of Bangi Point | 1 | 13°22′ 36″ N, 144°38′ 53″ E | [2] |
| Location not stated | 3 | [2] | |
| Palau Islands | |||
| Angaur Island, in Garangaoi Cove, S of Cape Nagaramudel | 1 | 6°53′ 50″ N, 137°7′ 49″ E | [2] |
| Auluptagel Island, Crocodile Cove | 1 | 7°17′ N, 137°29′ E | [2] |
| Ngadarak Reef SW of Auluptagel Island | 2 | 7°17′ 48″ N, 134°28′ 37″ E | [2] |
| Location not stated | 5 | [2] | |
| New Caledonia—Noumea | 1 | [2] | |
| New Guinea—location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| Polynesia | |||
| Society Islands | |||
| Moorea, Faatoai village at Papetoai Bay | 1 | [2] | |
| Tahiti | 1 | [2] | |
| Location not stated | 4 | [2] | |
| Fiji | |||
| Location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| Samoa | |||
| Pago Pago | 2 | [2] | |
| Location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| Location not stated | 4 | [2] | |
| Tonga Islands | |||
| Location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| Tuamotu Islands | |||
| Location not stated | 3 | [2] | |
| S. horrida | |||
| ASIA | |||
| Batavia (Jakarta) | 1 | [2] | |
| Malasia—location not stated | [147] | ||
| Phillipines | |||
| Atimonan, Tayabas | 1 | [2] | |
| Calaogao, Cauayan, Negros Island | 1 | 10°N, 122°30′ E | [2] |
| Manila Bay | 1 | [2] | |
| Ragay Gulf, Luzon | 1 | [2] | |
| Stankai, Sulu Island | 1 | [2] | |
| Location not stated | 2 | [2] | |
| Singapore | |||
| Pacific Expedition—location not stated | 5 | [2] | |
| Punggol—location not stated | 1 | [25] | |
| Singapore Market | 1 | [2] | |
| Location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| Thailand | |||
| Patong Bay, Patong Phuket | 2 | [2] | |
| Rayong Province, SE of Ban Phe Fisheries Station | 1 | 12°35′ 40″ N, 101°25′43″ E | [2] |
| Location not stated | 1 | [2] | |
| OCEANIA | |||
| New Guinea—Waigeo Island | 1 | [2] | |
| Australia | |||
| Between Moreton Bay and Cairns, Queensland, Australia | 52 | [13] | |
| Britomart Reef, QLD | 1 | 18°10′ S, 146°43′ E | [148] |
| Coffs Harbor, NSW | 1 | 30°15′ S, 153°8′ E | [149] |
| East coast of Northern Queensland | 25-30 | [150] | |
| Melville Bay and Cape Arnhem area, NT | 1 | 12°15′ S, 136°43′ E | [151] |
| Moreton Bay | [13] | ||
| N side of Main Wharf, Broome, WA | 1 | −17.967, 122.233 | [152] |
| Northern Territory, Groote Eylandt | 5 | [2] | |
| Port Darwin, NT | 1 | 12°27′ S, 130°48′ E | [153] |
| Port Hedland, WA | 1 | 20°18′ S, 118°35′ E | [154] |
| Princess Charlotte Bay, QLD | 1 | −14.333333, 144.116667 | [155] |
| Shark Bay, blow holes, N of Carnarvon | 1 | −24.483333, 113.416667 | [156] |
| Sweers Island, Gulf of Carpentaria, QLD | 1 | 17°6′ S, 139°37′ E | [157] |
| Tryon Island, Capricorn Group, QLD | 1 | 23°15′ S, 151°47′ E | [158] |
| S. nana | |||
| ASIA | |||
| Pakistan—Karachi Fish Harbor | 1 | [159] | |
| Red Sea | |||
| Gulf of Suez—Et-Tur, Sinai Peninsula | 1 | [2] | |
| Gulf of Suez—off Port Safaga | 1 | 27°16′ 15″ N, 33°47′ 30″ E | [2] |
| Israel—Gulf of Aqaba, between Marset Mahash el Ala and Marset Abu Samra | 1 | [2] | |
| Israel—NW coast of the Gulf of Aqaba, bay at Al Himeira | 5 | [2] | |
| Saudi Arabia—Persian Gulf, Tarut Bay, Near Ras Tanura spit | 1 | [2] | |
| S. alula | |||
| OCEANIA | |||
| Nicobar Islands—Nancowry Island | 2 | 8°N, 93°40′ E | [2] |
| Solomon Islands—New Georgia, Munda Lagoon | 1 | [2] | |
| Solomon Islands—New Georgia, Munda Pier | 2 | [2] | |
| S. platyrhyncha | |||
| ASIA | |||
| Ambon Island | 1 | [2] |
References
- Smith, M.M.; Heemstra, P.C. Smith’s Sea Fishes; Macmillan: Johannesburg, South Africa, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Eschmeyer, W.N.; Rao, K.V.R. Two new stonefishes (pisces, Scorpaeniidae) from the Indo-West Pacific with a synopsis of the Subfamily Synanceiinae. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 1973, 39, 337–382. [Google Scholar]
- Halstead, B.W.; Chitwood, M.J.; Modglin, F.R. Stonefish stings, and the venom apparatus of Synanceja horrida (Linnaeus). Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1956, 75, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, K.M.; Ng, C.H.V.; Tse, M.L. A 10-year retrospective review of stonefish sting injury in Hong Kong. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 27, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.Y.; Chan, Y.C.; Tse, M.L.; Lau, F.L. Venomous fish sting cases reported to Hong Kong Poison Information Centre: A three-year retrospective study on epidemiology and management. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 17, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hifumi, T.; Fukuchi, Y.; Otani, N.; Kondo, Y.; Kitamoto, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Nakaya, N.; Tomioka, J. Clinical characteristics of stonefish ‘Oni-daruma-okoze’ envenomation in Japan. Acute Med. Surg. 2020, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, C. Venomous Bites and Stings in Australia to 2005; Injury Research and Statistics Series Number 40; Australian Institute of Health and Welfare: Canberra, Australia, 2008; pp. 1–104. [Google Scholar]
- Pointer, S.; Harrison, J. Venomous Bites and Stings, 2017–2018; Injury Research and Statistics Series Number 134; Australian Institute of Health and Welfare: Canberra, Australia, 2021; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, S.Y.A.; Ong, S.H.J.; Ponampalam, R. Stonefish envenomation presenting to a Singapore hospital. Singap. Med. J. 2009, 50, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E. Bioactive proteins from stonefish venom. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.L.; Teoh, L.C.; Leo, S.P.M. Stonefish envenomations of the hand—A local marine hazard: A series of 8 cases and review of the literature. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2004, 33, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, J.H. Marine Scorpaenidae Envenomation in Travelers: Epidemiology, Management, and Prevention. J. Travel Med. 2015, 22, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endean, B.R. A study of distribution, habitat, behaviour, venom apparatus, and venom of the stone-fish. Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1961, 12, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobecker, D.B. The ‘lie-in-wait’ feeding mode of a cryptic teleost, Synanceia verrucose. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1983, 8, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southcott, R.V. Australian venomous and poisonous fishes. Clin. Toxicol. 1977, 10, 291–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, J.A.; Fenner, P.J.; Burnett, J.W.; Rifkin, J. Venomous and Poisonous Marine Animals; University of New South Wales Press: Sydney, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, S. The production and assay of stone-fish antivenene. Med. J. Aust. 1959, 46, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tintinalli, J.E.; Stapczynski, S.; John Ma, O.; Cline, D.; Cydulka, R.; Meckler, G. Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 7th ed.; McGraw-Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, P.R.T.; Boyle, A.; Hartin, D.; McAuley, D. Is hot water immersion an effective treatment for marine envenomation? Emerg. Med. J. 2006, 23, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbeak, K.B.; Auerbach, P.S. Marine envenomation. Emerg. Med. Clin. North Am. 2017, 35, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, S.; Saggiomo, S.; Smout, M.; Seymour, J. Heat deactivation of the stonefish Synanceia horrida venom—Implications for first-aid management. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2017, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwee, M.C.E.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Yuen, R.; Khoo, H.E.; Low, K.S.Y. A review of stonefish venoms and toxins. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 64, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.R. Venom of the stonefish Synanceja horrida (Linnaeus). Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 1959, 123, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach, P.S. Marine envenomations. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 486–493. [Google Scholar]
- Phoon, W.O.; Alfred, E.R. A study of stonefish (Synanceja) stings in Singapore with a review of the venomous fishes of Malaysia. Singap. Med. J. 1965, 6, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.F.; Hardy, J.C. Stonefish envenomation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillaud, C.; Hoang-Oppermann, T.; Hoang-Oppermann, V.; Rigot, H.; Girardot, S.; Nour, M. Is stonefish Synanceia verrucosa envenomation potentially lethal? Toxicon 2020, 184, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.K.K.; Cheng, S.C.; Yen, C.H. Stonefish envenomation with acute carpal tunnel syndrome. Hong Kong Med. J. 2009, 15, 471–473. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, T.K.W.; Chan, H.Z.; Ahmad, T.S.T.; Teh, K.K.; Low, T.H.; Wahab, N.A. Stonefish envenomation of hand with impending compartment syndrome. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, H.; Khan, M.T.; Al-Ghanem, S.; Al-Qasem, G. Stonefish (Synanceiea verrucosa) envenomation in the Kingdom of Bahrain. J. Bahrain Med. Soc. 2019, 31, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dall, G.F.; Barclay, K.L.; Knight, D. Severe sequelae after stonefish envenomation. Surgeon 2006, 4, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, A.; Giè, O.; Biegger, P.; Fusetti, C.; Lucchina, S. Surgical vacuum-assisted closure for treatment of dramatic case of stonefish envenomation. Chin. J. Traumatol. Engl. Ed. 2010, 13, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téot, L.; Meaume, S.; Akita, S.; Ennis, W.J.; del Marmol, V. Skin Necrosis; Springer-Verlag: Wien, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.B. Two rapid fatalities from stonefish stabs. Am. Soc. Ichthyol. Herpetol. 1957, 3, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiomi, K.; Hosaka, M.; Fujita, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Kikuchi, T. Venoms from six species of marine fish: Lethal and hemolytic activities and their neutralization by commercial stonefish antivenom. Mar. Biol. 1989, 103, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, S.K. Antivenom use in Australia. Med. J. Aust. 1992, 157, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. Stonefish (Synanceia trachynis) antivenom: In vitro efficacy and clinical use. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2003, 22, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, B.J. Marine antivenoms. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RTheakston, D.G.; Warrell, D.A.; Griffiths, E. Report of a WHO workshop on the standardization and control of antivenoms. Toxicon 2003, 41, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledsgaard, L.; Jenkins, T.P.; Davidsen, K.; Krause, K.E.; Martos-Esteban, A.; Engmark, M.; Andersen, M.R.; Lund, O.; Laustsen, A.H. Antibody cross-reactivity in antivenom research. Toxins 2018, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciscotto, P.H.C.; Rates, B.; Silva, D.A.F.; Richardson, M.; Silva, L.P.; Andrade, H.; Donato, M.F.; Cotta, G.A.; Maria, W.S.; Rodrigues, R.J.; et al. Venomic analysis and evaluation of antivenom cross-reactivity of South American Micrurus species. J. Proteomics 2011, 74, 1810–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. The pharmacological activity of fish venoms. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.L.; Menezes, T.N.; Carnielli, J.B.T.; Andrich, F.; Evangelista, K.S.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Vassallo, D.V.; Figueiredo, S.G. Stonefish antivenom neutralises the inflammatory and cardiovascular effects induced by scorpionfish Scorpaena plumieri venom. Toxicon 2011, 57, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, S.T.; Connor, J.M.O. An investigation of the biological activity of bullrout (Notesthes robusta) venom. Toxicon 2000, 38, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, S. Observations on the venom of the stone fish (Synanceja trachynis). Med. J. Aust. 1959, 46, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.R.; Tokes, L. Purification and properties of the lethal fraction of the venom of the stonefish Synanceia horrida (Linnaeus). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1961, 52, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.J.; Youngman, N.J.; Chan, W.; Bosmans, F.; Cheney, K.L.; Fry, B.G. Getting stoned: Characterisation of the coagulotoxic and neurotoxic effects of reef stonefish (Synanceia verrucosa) venom. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. Dose-dependent cardiovascular and neuromuscular effects of stonefish (Synanceja trachynis) venom. Toxicon 2000, 38, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, P.; Goudey-Perrière, F.; Breton, P.; Dewulf, C.; Petek, F.; Perrière, C. Enzymatic properties of the stonefish (Synanceia verrucosa Bloch and Schneider, 1801) venom and purification of a lethal, hypotensive and cytolytic factor. Toxicon 1995, 33, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggiomo, S.L.; Zelenka, C.; Seymour, J. Relationship between food and venom production in the estuarine stonefish Synanceia horrida. Toxicon 2017, 125, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P.; Williams, V.; White, J. Snake venom variability: Methods of study, results and interpretation. Toxicon 1991, 29, 1279–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, K.L.; Isbister, G.K.; McGowan, S.; Konstantakopoulos, N.; Seymour, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. A pharmacological and biochemical examination of the geographical variation of Chironex fleckeri venom. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 192, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, L.H.; Rymer, T.L.; Wilson, D.T. Variation in venom composition in the Australian funnel-web spiders Hadronyche valida. Toxicon X 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapothakis, E.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C. Venom variability among several Tityus serrulatus specimens. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.E. Marine toxins and venomous and poisonous marine animals. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1965, 3, 255–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, C.H.; Yuen, R.; Khoo, H.E.; Chung, M.; Gwee, M.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Purification and partial characterization of stonustoxin (lethal factor) from Synanceja horrida venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. 1991, 99, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadessy, F.J.; Chen, D.; Kini, R.M.; Chung, M.C.M.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Khoo, H.E.; Yuen, R. Stonustoxin is a novel lethal factor from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom. cDNA cloning and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 25575–25581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreger, A.S. Detection of a cytolytic toxin in the venom of the stonefish (Synanceia trachynis). Toxicon 1991, 29, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, C.H.; Yuen, R.; Chung, M.C.M.; Khoo, H.E. Purification and partial characterization of hyaluronidase from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. 1992, 101, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegman, R.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Baillie, G.; Jones, A.; Alewood, P.F. Investigation of the estuarine stonefish (Synanceia horrida) venom composition. J. Proteom. 2019, 201, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, A.; Suzuki, M.; Honma, T.; Nagai, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Purification, properties and cDNA cloning of neoverrucotoxin (neoVTX), a hemolytic lethal factor from the stonefish Synanceia verrucosa venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2006, 1760, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Sumatora, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Yoshihara, J.; Shimamura, Y.; Fukami, J. Purification and properties of a cardioactive toxin, cardioleputin, from stonefish, Synanceja verrucose. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins 1996, 2, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Shinohara, M.; Ohura, K. Purification of a novel lectin from the dorsal spines of the stonefish, Synanceia verrucose. J. Osaka Dent. Univ. 2016, 50, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madokoro, M.; Ueda, A.; Kiriake, A.; Shiomi, K. Properties and cDNA cloning of a hyaluronidase from the stonefish Synanceia verrucosa venom. Toxicon 2011, 58, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, P.; Sauviat, M.P.; Goudey-Perriere, F.; Perriere, C. Cardiotoxicity of verrucotoxin, a protein isolated from the venom of Synanceia verrucose. Toxicon 1997, 35, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, P.; Ducancel, F.; Ogawa, T.; Boulain, J.; Goudey-Perrière, F.; Perrière, C.; Ménez, A. Complete amino-acid sequence of the β-subunit of VTX from venom of the stonefish (Synanceia verrucosa) as identified from cDNA cloning experiments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1997, 1337, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakins, D.E.; Saunders, P.R. Purification of the lethal fraction of the venom of the stonefish Synanceja horrida (Linnaeus). Toxicon 1967, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.R.; Rothman, S.; Medrano, V.A.; Chin, H.P. Cardiovascular actions of venom of the stonefish Synanceja horrida. Am. J. Physiol. 1962, 203, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.E.; Yuen, R.; Poh, C.H.; Tan, C.H. Biological activities of Synanceja horrida (stonefish) venom. Nat. Toxins 1992, 1, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiomi, K.; Hosaka, M.; Kikuchi, T. Properties of a lethal factor in stonefish Synanceia verrucosa venom. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi Jpn. Ed. 1993, 59, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wahsha, M.A.; Al-Najjar, T.H.; Al-Tarawneh, H.; Khalaf, M.A.; Saad, A. Biochemical and histological observations of lung injury after stonefish (Synanceia verrucosa) envenom in BALB/c mice. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 7204–7208. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.M.; Wahsha, M.A.; Khadra, K.M.A.; Khalaf, M.A.; Al-Najjar, T.H. Biochemical and histopathological effects of the stonefish (Synanceia verrucosa) venom in rats. Toxicon 2018, 142, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Fasoli, E.; Sanz, L.; Boschetti, E.; Righetti, P.G. Exploring the venom proteome of the western diamondback rattlesnake, Crotalus atrox, via snake venomics and combinatorial peptide ligand library approaches. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3055–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Snake venom hyaluronidase: A therapeutic target. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2006, 24, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A.T.; Hendon, R.R. Characterization of lizard venom hyaluronidase and evidence for its action as a spreading factor. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1983, 76, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, K.; Yamada, S.; Sugiura, M.; Takeda, K.; Yuen, R.; Khoo, H.E.; Poh, C.H. Identification of the reaction products of the purified hyaluronidase from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom,” Biochem. J. 1992, 283, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.C.; Ranganathan, S.; Chua, K.L.; Khoo, H.E. Cloning and molecular characterization of the first aquatic hyaluronidase, SFHYA1, from the venom of stonefish (Synanceja horrida). Gene 2005, 346, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, P.; Grosclaude, J.; Goudey-Perrière, F.; Gervat, V.; Gayral, P.; Jacquot, C.; Perrière, C. Presence of norepinephrine and other biogenic amines in stonefish venom. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1996, 685, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.J.; Hodgson, W.C.; Sutherland, S.K. Pharmacological studies of stonefish (Synanceja trachynis) venom. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijavan, M.; Chandra, N. Lectins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999, 9, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauviat, M.P.; Garnier, P.; Goudey-Perriere, F.; Perriere, C. Does crude venom of the stonefish (Synanceia verrucosa) activate β-adrenoceptors in the frog heart muscle? Toxicon 1995, 33, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Yazawa, K.; Hao, L.Y.; Onoue, Y.; Kameyama, M. Verrucotoxin inhibits KATP channels in cardiac myocytes through a muscarinic M3 receptor-PKC pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 563, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, S.R.; Wanstall, J.C. Pharmacological experiments demonstrate that toad (Bufo marinus) atrial beta-adrenoceptors are not identical with mammalian beta2- or beta1-adrenoceptors. Life Sci. 1982, 31, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, L.; Cairncross, K.D.; McCallum, I.A. Some pharmacological actions of the venom of the stonefish ‘Synanceja horrida’. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn 1961, 131, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.J.; Hodgson, W.C.; Sutherland, S.K. Evidence for adrenergic and tachykinin activity in venom of the stonefish (Synanceia trachynis). Toxicon 1996, 34, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.S.Y.; Gwee, M.C.E.; Yuen, R.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Khoo, H.E. Stonustoxin: A highly potent endothelium-dependent vasorelaxant in the rat. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, H.C.; Khoo, H.E.; Moore, P.K.; Bhatia, M.; Lu, J.; Moochhala, S.M. Synergism between hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and nitric oxide (NO) in vasorelaxation induced by stonustoxin (SNTX), a lethal and hypotensive protein factor isolated from stonefish Synanceja horrida venom. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1664–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.M.L.; Low, K.S.Y.; Khoo, H.E. Characterization of the mechanism underlying stonustoxin-mediated relaxant response in the rat aorta in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, M.H.; Liu, H.L.C.; Zajchowski, D.A.; Whitlow, M. Protein fold analysis of the B30.2-like domain. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 1999, 35, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.; Ribouchon, M.T.; Offer, C.; Pontarotti, P. B30.2-like domain proteins: A growing family. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 235, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Kobilka, B.K. The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 2009, 459, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazawa, K.; Wang, J.W.; Hao, L.Y.; Onoue, Y.; Kameyama, M. Verrucotoxin, a stonefish venom, modulates calcium channel activity in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madamanchi, A. Β-adrenergic receptor signaling in cardiac function and heart failure. McGill J. Med. 2007, 10, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, A.; Gobeil, F.; Calo, G.; Inamura, N.; Regoli, D. FR 173657: A new, potent, nonpeptide kinin B2 receptor antagonist. An in vitro study. Hypertension 1997, 29, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, J.B.; Medeiros, R.; Fernandes, E.S.; Ferreira, J.; Cabrini, D.A.; Campos, M.M. Kinin B1 receptors: Key G-protein-coupled receptors and their role in inflammatory and painful processes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.P. Plasma kinins and inflammation. Metabolism 1964, 13, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauviat, M.P.; Meunier, F.A.; Kreger, A.; Molgó, J. Effects of trachynilysin, a protein isolated from stonefish (Synanceia trachynis) venom, on frog atrial heart muscle. Toxicon 2000, 38, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieglgänsberger, W. Substance P and pain chronicity. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 375, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.A.J.; Magee, C.A.J.; Belyea, C.C.M.; Gumboc, L.R.D.L. Finger Flexor Tenosynovitis from Stonefish Envenomation Injury. JAAOS Glob. Res. Rev. 2019, 3, e024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, L.; Gillis, R.G.; Youatt, G. Stonefish venom: Some biochemical and chemical observations. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 1965, 43, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E.; Hon, W.M.; Lee, S.H.; Yuen, R. Effects of stonustoxin (lethal factor from Synanceja horrida venom) on platelet aggregation. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Kini, R.M.; Yuen, R.; Khoo, H.E. Haemolytic activity of stonustoxin from stonefish (Synanceia horrida) venom: Pore formation and the role of cationic amino acid residues. Biochem. J. 1997, 325, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouanounou, G.; Mattei, C.; Meunier, F.A.; Kreger, A.S.; Molgó, J. Trachynilysin, a protein neurotoxin isolated from stonefish (Synanceia trachynis) venom, increases spontaneous quantal acetylcholine release from Torpedo marmorata neuromuscular junctions. Cybium Int. J. Ichthyol. 2000, 24 (Suppl. 3), 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Wahsha, M.; Al-Tarawneh, H.; Khalaf, M.; Al-Najjar, T.; Al-Zyoud, W. Histological and functional renal alterations caused by Synanceia verrucosa venom in mice. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 5294–5300. [Google Scholar]
- Ellisdon, A.M.; Reboul, C.F.; Panjikar, S.; Huynh, K.; Oellig, C.A.; Winter, K.L.; Dunstone, M.A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Seymour, J.; Dearden, P.K.; et al. Stonefish toxin defines an ancient branch of the perforin-like superfamily. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15360–15365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouanounou, G.; Malo, M.; Stinnakre, J.; Kreger, A.S.; Molgó, J. Trachynilysin, a neurosecretory protein isolated from stonefish (Synanceia trachynis) venom, forms nonselective pores in the membrane of NG108-15 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39119–39127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Jackowski, S. Membrane phospholipid synthesis and endoplasmic reticulum function. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S311–S316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.E.; Chen, D.; Yuen, R. Role of free thiol groups in the biological activities of stonustoxin, a lethal factor from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom. Toxicon 1998, 36, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E.; Chen, D.; Yuen, R. The role of cationic amino acid residues in the lethal activity of stonustoxin from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1998, 44, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, W.S.; Khoo, H.E. The role of tryptophan residues in the hemolytic activity of stonustoxin, a lethal factor from stonefish (Synanceja horrida) venom. Biochimie 2000, 82, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, R.; Cai, B.; Khoo, H.E. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against stonustoxin from Synanceja horrida. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.S.Y.; Gwee, M.C.E.; Yuen, R. Neuromusclar effects of the venom of the stonefish synanceja horrida. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 183, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.S.Y.; Gwee, M.C.E.; Yuen, R.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Khoo, H.E. Stonustoxin: Effects on neuromuscular function in vitro and in vivo. Toxicon 1994, 32, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreger, A.S.; Molgó, J.; Comella, J.X.; Hansson, B.; Thesleff, S. Effects of stonefish (Synanceia trachynis) venom on murine and frog neuromuscular junctions. Toxicon 1993, 31, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, F.A.; Mattei, C.; Chameau, P.; Lawrence, G.; Colasante, C.; Kreger, A.S.; Dolly, J.O.; Molgó, J. Trachynilysin mediates SNARE-dependent release of catecholamines from chromaffin cells via external and stored Ca2+. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, L.; Meldolesi, J. A-Latrotoxin and Related Toxins. Pharmacol. Ther. 1989, 42, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, P.; Caratsch, C.G.; Waser, P.G.; Lazarovici, P.; Primor, N. Presynaptic effects of the Pardaxins, polypeptides isolated from the gland secretion of the flatfish Pardachirus marmoratus. Neuroscience 1987, 23, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spira, M.E.; Klein, M.; Yarom, Y.; Castel, M. Ultrastructural changes accompanying the disturbances of neuromuscular transmission caused by Pardachirus toxin. Neuroscience 1976, 1, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shai, Y. Pardaxin: Channel formation by a shark repellant peptide from fish. Toxicology 1994, 87, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopian, A.N.; Sivilotti, L.; Wood, J.N. A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature 1996, 379, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, S.; Benn, S.; Hick, C.; Trezise, D.; John, V.; Mannion, R.J.; Costigan, M.; Plumpton, C.; Grose, D.; Gladwell, Z.; et al. Two sodium channels contribute to the TTX-R sodium current in primary sensory neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jami, S.; Erickson, A.; Brierley, S.M.; Vetter, I. Pain-causing venom peptides: Insights into sensory neuron pharmacology. Toxins 2018, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flecker, H. Injuries from stone fish. Med. J. Aust. 1956, 43, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurat, D.R.; Copson, D.G.; Wood, F.M. First aid protocols for Stonefish stings: A burn’s risk case study. Burn. Open 2019, 3, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K. Venomous fish stings in tropical Northern Australia. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2001, 19, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishpon, A.; Cohen, Z.; Brenner, S. Neuroma formation and toe amputation resulting from stonefish envenomation. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 1076–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, O.; Fernandez, W.G.; Luyber, T.J.; McMonicle, T.L.; Simmons, M.D. Stonefish envenomation. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 26, 972.e1–972.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenneke, F.; Hatz, C. Stonefish envenomation-A lucky outcome. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2006, 4, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongkili, D.F.; Cheah, P.K. Hot water immersion as a treatment for stonefish sting: A case report. Malays. Fam. Physician 2013, 8, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Phleps, D.R. Stone-fish poisoning. Med. J. Aust. 1960, 47, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.M.; Fung, K.K.; Cheng, V.C.; Lucke, L. Rapidly progressive necrotising fasciitis following a stonefish sting: A report of two cases. J. Orthop. Surg. 2006, 14, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.L.B. A case of poisoning by the stonefish, Synanceja verrucose. Copeia 1951, 1951, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbora, H.D.; Çiçek, B.A.; Ayas, D. The first record of Synanceia verrucosa Bloch & Schneider, 1801 and Pagrus auriga Valencienne, 1843 from Cyprus. J. Black Sea Mediterr. Environ. 2021, 27, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bariche, M.; Sayar, N.; Balistreri, P. Records of two non-indigenous fish species Synanceia verrucosa Bloch and Schneider, 1801 and Acanthurus sohal (Forsskål, 1775) from the Gaza strip (eastern Mediterranean Sea). BioInvasions Rec. 2019, 8, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelist, D.; Spanier, E.; Golani, D. Evidence for the occurrence of the indo-pacific stonefish, synanceia verrucosa (actinopterygii: Scorpaeniformes: Synanceiidae), in the mediterranean sea. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2011, 41, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crocetta, F.; Agius, D.; Balistreri, P.; Bariche, M.; Bayhan, Y.; Çakir, M.; Ciriaco, S.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Deidun, A.; el Zrelli, R.; et al. New Mediterranean biodiversity records. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 682–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Alshawy, F.; Hussein, C. Stonefish synanceia verrucosa bloch & schneider, 1801 (Actinopterygii: Synanceiidae): The first record in the syrian coast and the fourth in the Mediterranean. Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2019, 7, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilecenoglu, M. First sighting of the Red Sea originated stonefish (Synanceia verrucosa) from Turkey. J. Black Sea Mediterr. 2012, 18, 76–82. Available online: http://www.blackmeditjournal.org/blackmeditjournal.org/pdf/vol18no1pdf6.pdf.
- Scaps, P.; Scott, C. An update to the list of coral reef fishes from Koh Tao, Gulf of Thailand. Check List 2014, 10, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Atlas of Living Australia 1. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/408ab640-e9a8-4d6b-9340-8371f18aae01 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 2. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/22ab93f9-e34c-4eed-8728-badb908c9af3%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 3. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/ad41b508-6131-45d7-99df-6d36d780cfaf%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 4. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/e3049247-20ff-45d9-bb50-94feda199fe3%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 5. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/ecf347a1-8215-4af1-8fe5-f0c7f54cee30%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 6. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/8df2d35b-5b6b-4e83-8813-21d43c4aadad%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 7. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/c0278e8d-6dd5-495c-8e0b-a1bb1191743a%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Le Mare, D.W. Poisonous Malayan fish. Med. J. Malaya 1952, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Atlas of Living Australia 8. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/653b360f-f020-4992-8e66-efe9cd07e93a%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 9. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/2b163cff-f83d-4b51-8ef7-8ab31850e7a2%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Fewings, D.; Squire, L. Notes on reproduction in the estuarine stonefish Synanceia horrida. Live Reef Fish Inf. Bull. 1999, 5, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Atlas of Living Australia 10. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/908d3ae4-6444-497a-8dcc-15b5ee62b7ff%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 11. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/ff697ff5-b456-43fe-8d9a-5614f9efad64%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 12. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/697561b2-08f0-46b1-9be0-bf6487f8b86f%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 13. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/45855fa1-dab5-4f4d-a354-79c037226bbb%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 14. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/88c67a38-2fba-4003-8993-d10707e02565%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 15. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/1fbf2735-0b70-4d7b-8c0e-63889ea3cced%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 16. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/14668e49-de69-4423-9f39-587d04223e47%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Atlas of Living Australia 17. Available online: https://biocache.ala.org.au/occurrences/e2b1138c-b361-4f19-a8fa-17364e7440df%0A (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Osmany, H.B.; Moazzam, M. Review of stonefishes of family Synanceidae from Pakistan with a new record of Synanceia nana Eschmeyer and Rama-Rao, 1973. Int. J. Biol. Biotechnol. 2018, 15, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
| Fish Species | Neutralizing Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Synanceia verrucosa | Lethal and hemolytic | [35] |
| Inimicus japonicus | Lethal and hemolytic | [35] |
| Pterois lunulata | Lethal and hemolytic | [35] |
| Pterois antennata | Lethal and hemolytic | [35] |
| Dendrochirus zebra | Lethal and hemolytic | [35] |
| Pterois volitans | Lethal, hemolytic and pharmacological | [35,42] |
| Gymnapistes marmoratus | Pharmacological | [42] |
| Scorpaena plumieri | Inflammatory and cardiovascular | [43] |
| Notesthes robusta | No effect | [44] |
| Synanceia Species | Toxins | MW (kDa) | Subunit MW (kDa) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. horrida | SNTX | 148 | α-subunit—79 | [57] |
| β-subunit—79 | ||||
| Cytolysin | 158 | - | [58] | |
| SFHYA1 | 62 | - | [59] | |
| Peroxiredoxin-6 | 24 | - | [60] | |
| S. verrucosa | VTX | 322 | 2x α-subunit—83 | [49] |
| 2x β-subunit—78 | ||||
| NeoVTX | 166 | α-subunit—79 | [61] | |
| β-subunit—79 | ||||
| Cardioleputin | 46 | - | [62] | |
| Con A-I-PS-I | 42.1 | - | [63] | |
| 100 | ||||
| 110 | ||||
| 45 kDa lectin | 45 | - | [63] | |
| Hyaluronidase | 59 | - | [64] |
| Synanceia Species | Toxic Component | Route | LD50 (µg/kg) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. horrida | Crude venom | IV | 0.4–0.6 | [67] |
| Reconstituted venom | IV | 220 | [68] | |
| 300–666 | [45,56,69] | |||
| SC | 2666–4000 | [45] | ||
| IC | 266 | [45] | ||
| IP | 1333–2000 | [45,58] | ||
| Fraction 1 | IV | 35 | [56] | |
| SNTX | IV | 17 | [56] | |
| S. verrucosa | Crude venom | IV | 360 | [70] |
| 180 | [35] | |||
| 125 (estimated) | [49] | |||
| Crude venom | IM | 107 | [71] | |
| 38 | [72] | |||
| NeoVTX | IV | 47 | [70] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saggiomo, S.L.; Firth, C.; Wilson, D.T.; Seymour, J.; Miles, J.J.; Wong, Y. The Geographic Distribution, Venom Components, Pathology and Treatments of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Venom. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060302
Saggiomo SL, Firth C, Wilson DT, Seymour J, Miles JJ, Wong Y. The Geographic Distribution, Venom Components, Pathology and Treatments of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Venom. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(6):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060302
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaggiomo, Silvia L., Cadhla Firth, David T. Wilson, Jamie Seymour, John J. Miles, and Yide Wong. 2021. "The Geographic Distribution, Venom Components, Pathology and Treatments of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Venom" Marine Drugs 19, no. 6: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060302
APA StyleSaggiomo, S. L., Firth, C., Wilson, D. T., Seymour, J., Miles, J. J., & Wong, Y. (2021). The Geographic Distribution, Venom Components, Pathology and Treatments of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Venom. Marine Drugs, 19(6), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060302






