Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Depolymerized Glycosaminoglycan from Holothuria fuscopunctata, a Novel Anticoagulant Candidate, in Rats by Bioanalytical Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Establishment and Validation of Anti-iXase Method
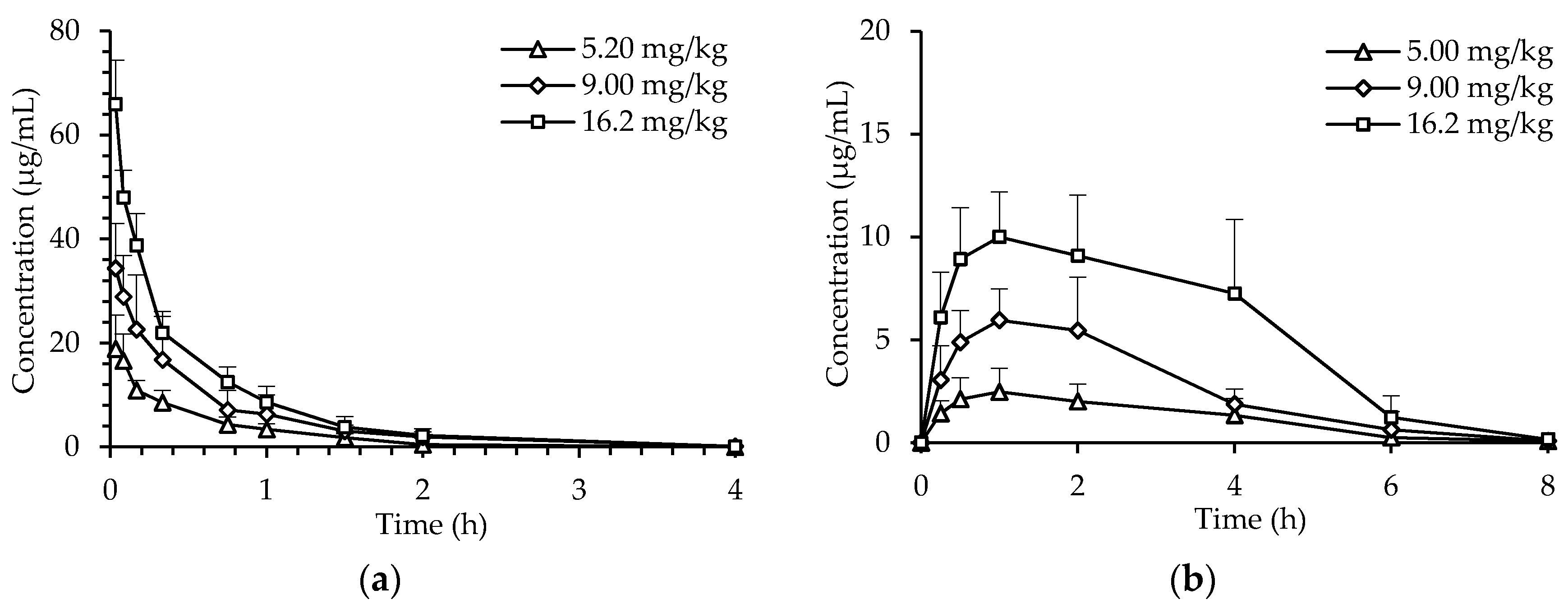
2.2. Pharmacokinetics of dHG-5
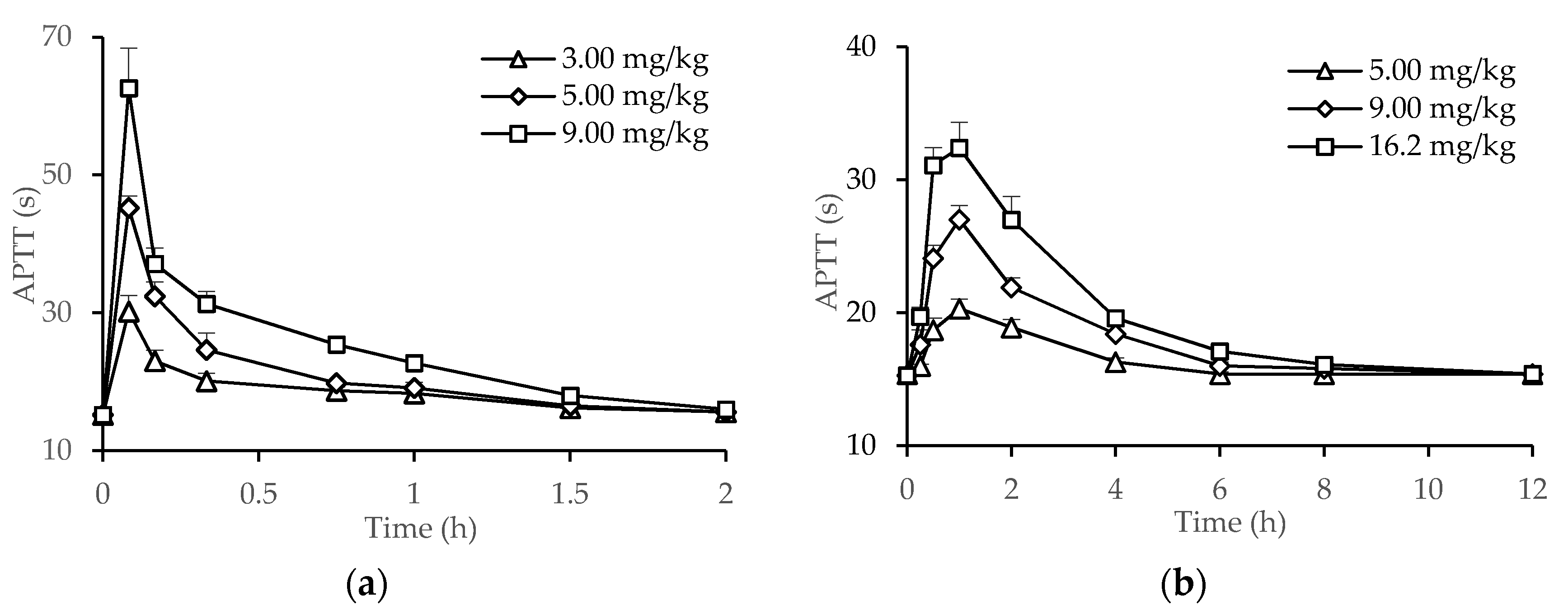
2.3. PK/PD Correlation Analysis of dHG-5
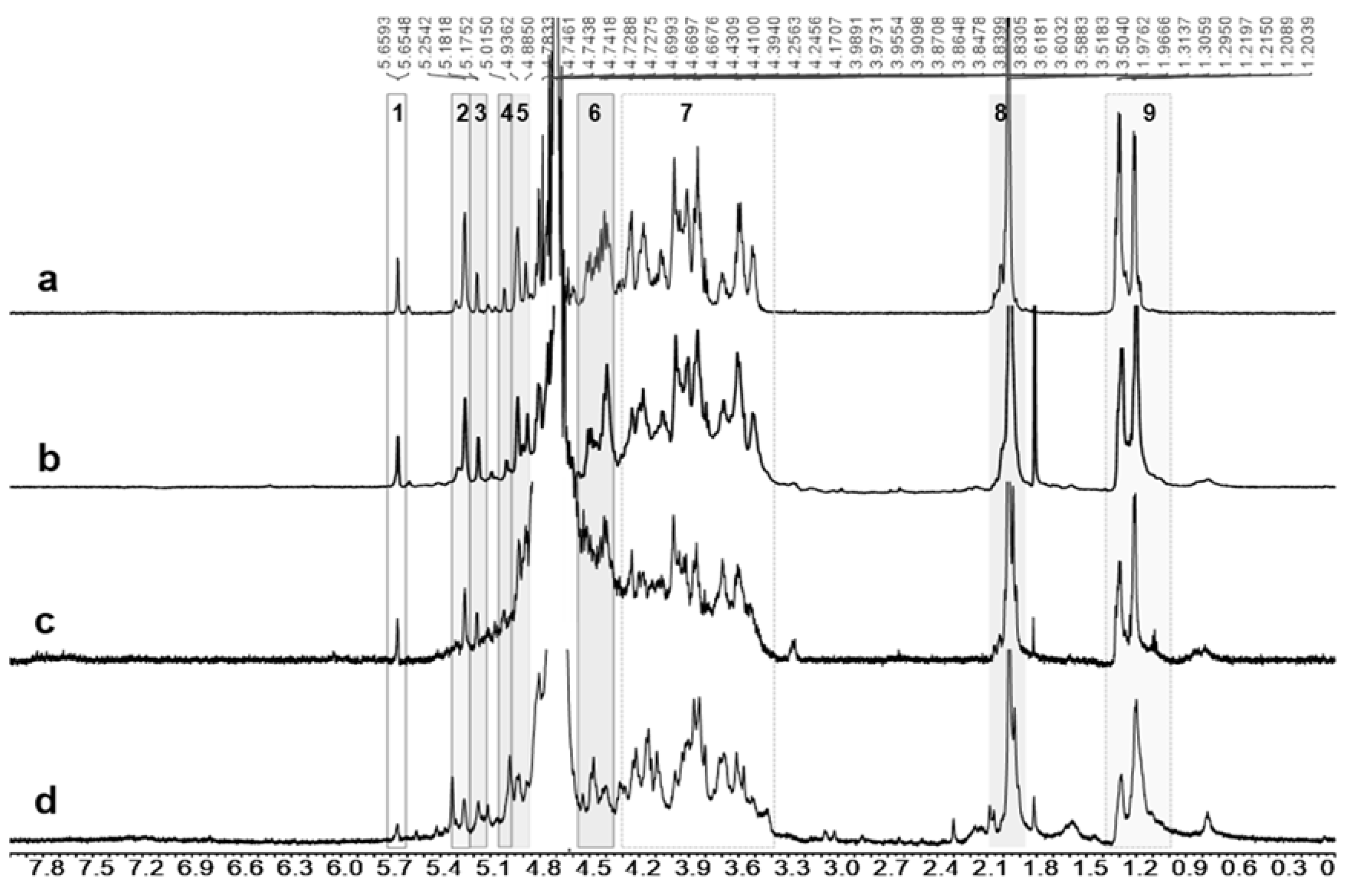
2.4. Metabolite Identification
2.5. Establishment and Validation of APTT Prolongation Method
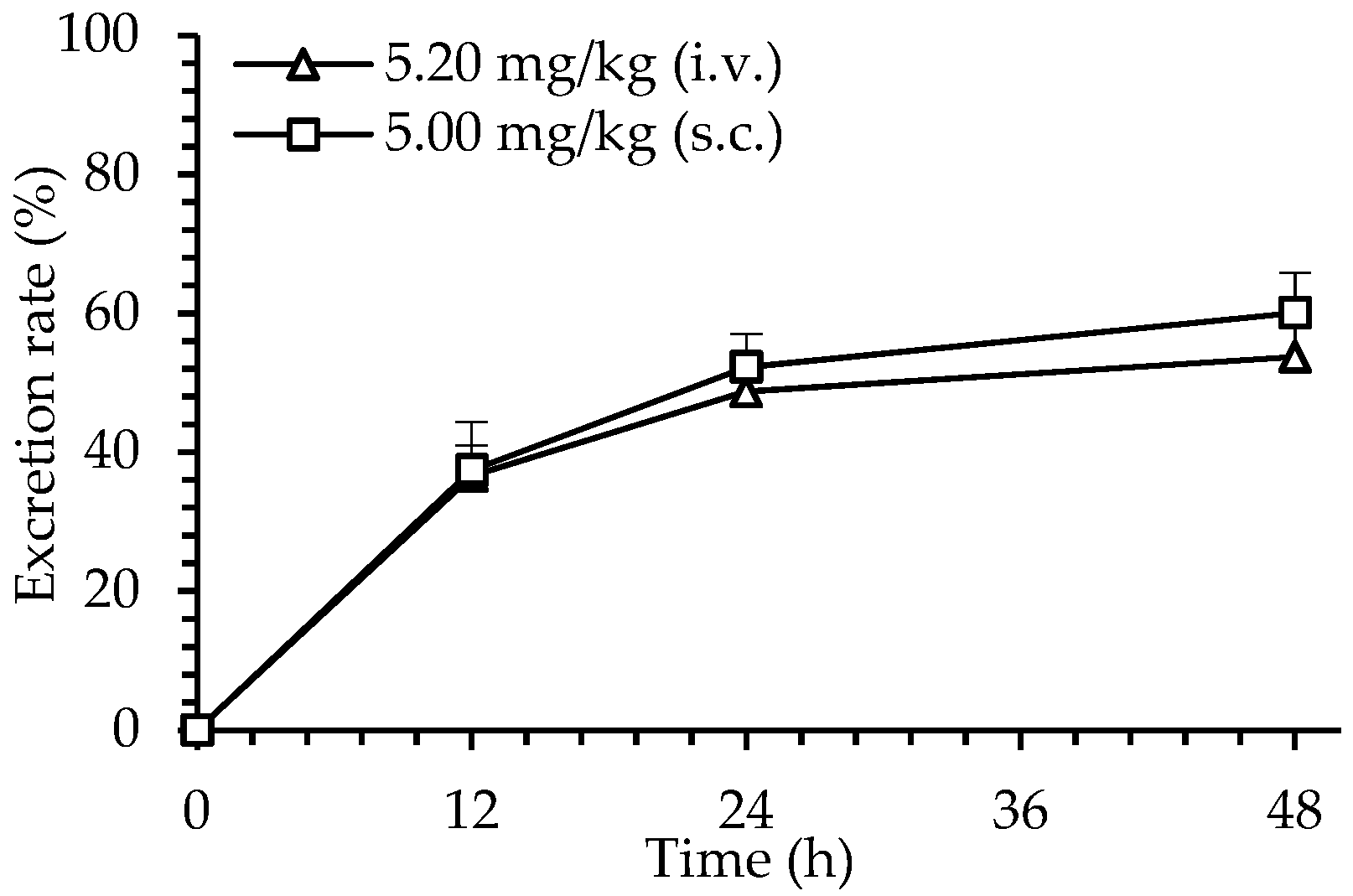
2.6. Excretion of dHG-5
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) of dHG-5
4.3.1. Anti-IXase Method for dHG-5 Plasma Concentration Analysis
4.3.2. Pharmacokinetics of dHG-5
4.3.3. Pharmacodynamics of dHG-5
4.4. Metabolites and Excretion Analysis
4.4.1. Metabolite Identification
4.4.2. APTT Prolongation Method for dHG-5 Urine Concentration Analysis
4.4.3. Excretion Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timmis, A.; Townsend, N.; Gale, C.P.; Torbica, A.; Lettino, M.; Petersen, S.E.; Mossialos, E.A.; Maggioni, A.P.; Kazakiewicz, D.; May, H.T.; et al. European society of cardiology: Cardiovascular disease statistics 2019. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 12–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskob, G.E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A.N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S.V.; McCumber, M.; et al. Thrombosis: A major contributor to the global disease burden. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, J.; Anand, S.S.; Halperin, J.L.; Fuster, V. Guide to anticoagulant therapy: Heparin: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American heart association. Circulation 2001, 103, 2994–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, G.; Naggi, A. Heparin centenary—An ever-young life-saving drug. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 212S1, S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.K.; Manithody, C.; Rezaie, A.R. Heparin-activated antithrombin interacts with the autolysis loop of target coagulation proteases. Blood 2004, 104, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluwala, I.; Favaloro, E.; Pasalic, L. Therapeutic monitoring of unfractionated heparin-trials and tribulations. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumaine, R.; Borentain, M.; Bertel, O.; Bode, C.; Gallo, R.; White, H.D.; Collet, J.P.; Steinhubl, S.R.; Montalescot, G. Intravenous low-molecular-weight heparins compared with unfractionated heparin in percutaneous coronary intervention quantitative review of randomized trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eikelboom, J.W.; Weitz, J.I. Update on antithrombotic therapy new anticoagulants. Circulation 2010, 121, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, I.Y.; Schwarz, U.I.; Crown, N.; Dresser, G.K.; Lazo-Langner, A.; Zou, G.Y.; Roden, D.M.; Stein, C.M.; Rodger, M.; Wells, P.S.; et al. Clinical and genetic determinants of warfarin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics during treatment initiation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrasciotta, Y.; Crisafulli, S.; Pizzimenti, V.; Marcianò, I.; Mancuso, A.; Andò, G.; Corrao, S.; Capranzano, P.; Trifirò, G. Pharmacokinetics of new oral anticoagulants: Implications for use in routine care. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, A.P.; Gailani, D. The Intrinsic Pathway of Coagulation as a Target for Antithrombotic Therapy. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, S.C. Direct oral anticoagulants in cirrhosis-safe and effective alternative to traditional anticoagulants. QJM Int. J. Med. 2019, 112, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, G.; Cotruzzola, A.M.; Battaglia, V. Thrombophilias and new oral anticoagulants, a safe alternative to warfarin? Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 220, 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.F.; Gao, N.; Ren, L.; Liu, S.; Lin, L.S.; Zheng, W.Q.; Zhou, L.T.; Yin, R.H.; Zhao, J.H. The components and activities analysis of a novel anticoagulant candidate dHG-5. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 207, 112796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.T.; Gao, N.; Sun, H.F.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Lin, L.S.; Yin, R.H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.B.; Ji, X.; et al. Effects of native fucosylated glycosaminoglycan, Its depolymerized derivatives on intrinsic factor Xase, coagulation, thrombosis, and hemorrhagic risk. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Lu, F.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, K.; Wen, D.D.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.Y.; Jiang, J.M.; et al. β-eliminative depolymerization of the fucosylated chondroitin sulfate and anticoagulant activities of resulting fragments. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Wang, Z.J.; Sun, G.L.; Shen, L.; Xu, D.S.; Feng, Y. A sensitive and specific HPGPC-FD method for the study of pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of radix ophiopogonis polysaccharide in rats. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Ma, F.G.; Yu, W.J.; Jiang, T.F.; Lv, Z.H. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion study of fluorescein labeled PS916 in rats. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 391–399. [Google Scholar]
- Balogh, L.; Polyak, A.; Mathe, D.; Kiraly, R.; Thuroczy, J.; Terez, M.; Janoki, G.; Ting, Y.T.; Bucci, L.R.; Schauss, A.J. Absorption, uptake and tissue affinity of high-molecular-weight hyaluronan after oral administration in rats and dogs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10582–10593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforest, M.D.; Colas-Linhart, N.; Guiraud-Vitaux, F.; Bok, B.; Bara, L.; Samama, M.; Marin, J.; Imbault, F.; Uzan, A. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of technetium 99m labelled standard heparin and a low molecular weight heparin (enoxaparin) after intravenous injection in normal volunteers. Br. J. Haematol. 1991, 77, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alban, S.; Welzel, D.; Hemker, H.C. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characterization of a medium-molecular-weight heparin in comparison with UFH and LMWH. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 28, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischke, R.; Schmitt, J.; Wolken, S.; Böhm, C.; Wolf, P.; Kietzmann, M. Pharmacokinetics of the low molecular weight heparin dalteparin in cats. Vet. J. 2012, 192, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikov, A.N.; Flisyuk, E.V.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N. Pharmacokinetics of marine-derived drugs. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.J.C.; Mourao, P.A.S. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate as a new oral antithrombotic agent. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 96, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanari, T.; Washio, Y.; Huang, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Suzuki, A.; Toida, T. Oral absorption and clearance of partially depolymerized FCS from sea cucumber. Thromb. Res. 1999, 93, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Faustova, N.M.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Kosman, V.M.; Vuorela, H.; Makarov, V.G. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus after oral administration to rats. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.Y.; Wu, M.Y.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L.T.; Gao, N.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, J.K.; et al. Discovery of an intrinsic tenase complex inhibitor: Pure nonasaccharide from fucosylated glycosaminoglycan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8284–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Xu, S.M.; Zhao, J.H.; Kang, H.; Ding, H. Physicochemical characteristics and anticoagulant activities of low molecular weight fractions by free-radical depolymerization of a fucosylated chondroitin sulphate from sea cucumber Thelenata ananas. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, J.P.; Kobbervig, C.E.; Kirkpatrick, H.M. Heparin inhibits the intrinsic tenase complex by interacting with an exosite on factor IXa. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 11316–11325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Xu, L.; Lian, W.; Peng, W.L.; Jiang, J.M.; Zhao, J.H. Anticoagulant and antithrombotic evaluation of native fucosylated chondroitin sulfates and their derivatives as selective inhibitors of intrinsic factor Xase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Drug Evaluation, National Medical Products Administration. Available online: http://www.cde.org.cn/zdyz.do?method=largePage&id=21e45c8c5bacf662 (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Gao, N.; Wu, M.Y.; Liu, S.; Lian, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.H. Preparation and characterization of O-acylated fucosylated chondroitin Sulfate from sea cucumber. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Nominal Concentration (µg/mL) | Intra-Day Accuracy (%, n = 5) | Intra-Day Precision (RSD%, n = 5) | Inter-Day Precision (RSD%, n = 15) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.131 | 99.8 | 14.5 | 13.6 |
| 0.819 | 109.0 | 12.6 | 11.4 |
| 12.8 | 96.9 | 9.6 | 12.1 |
| Nominal Concentration (μg/mL) | Recovery Rate (%) of dHG-5 after 30 d at −20 °C |
|---|---|
| 0.131 | 101.4 ± 11.1 |
| 0.819 | 115.4 ± 3.8 |
| 12.8 | 109.4 ± 9.0 |
| Parameters 1 | 5.2 mg/kg | 5 mg/kg | 9 mg/kg | 16.2 mg/kg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i.v. | s.c. | i.v. | s.c. | i.v. | s.c. | ||
| T1/2α (h) | 0.25 ± 0.20 | 0.94 ± 0.33 | 0.29 ± 0.20 | 0.64 ± 0.10 | 0.07± 0.05 | 1.08 ± 0.94 | |
| T1/2β (h) | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 1.15 ± 0.34 | 0.44 ± 0.11 | 0.80 ± 0.10 | 0.48 ± 0.05 | 1.25 ± 1.00 | |
| Cmax (μg/mL) | 19.08 ± 6.23 | 2.70 ± 1.22 | 34.40 ± 8.56 | 6.50 ± 2.10 | 65.98 ± 8.36 | 10.11 ± 2.22 | |
| Tmax (h) | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.22 | 0.03 ± 0.00 * | 1.00 ± 0.61 # | 0.03 ± 0.00 * | 1.10 ± 0.55 # | |
| V1(L/kg) | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.82 ± 0.32 | 0.23 ± 0.03 * | 0.56 ± 0.19 # | 0.19 ± 0.04 * | 0.26 ± 0.23 # | |
| CL (L/h/kg) | 0.52 ± 0.12 | 0.40 ± 0.20 | 0.54 ± 0.30 * | 0.50 ± 0.17 # | 0.49 ± 0.03 * | 0.43 ± 0.21 # | |
| AUC0-t (μg/mL∙h) | 9.51± 2.21 | 9.17 ± 1.38 | 19.59 ± 10.48 | 17.93 ± 6.15 | 30.88 ± 2.15 | 34.52 ± 9.50 | |
| AUC0-∞ (μg/mL∙h) | 10.53 ± 2.40 | 9.95 ± 1.41 | 21.07 ± 10.67 | 19.89 ± 6.64 | 33.23 ± 1.94 | 34.43 ± 10.51 | |
| F (%) | / | 98.3 | / | 94.4 | / | 104.0 | |
| Nominal Concentration (µg/mL) | Intra-Day Accuracy (%, n = 5) | Intra-Day Precision (RSD%, n = 5) | Inter-Day Precision (RSD%, n = 15) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 115.0 | 4.4 | 10.7 |
| 45 | 110.0 | 11.2 | 11.8 |
| 180 | 115.0 | 13.1 | 10.5 |
| Nominal Concentration (µg/mL) | Recovery Rate (%) of dHG-5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Short-Term (r.t., 1 d) | Medium-Term (r.t., 3 d) | Long-Term (−20 °C, 7 d) | |
| 15 | 89.5 ± 0.05 | 754.0 ± 0.86 | 112.0 ± 2.57 |
| 45 | 104.0 ± 0.07 | 560.0 ± 0.62 | 128.0 ± 5.73 |
| 180 | 123.0 ± 0.05 | 191.0 ± 0.26 | 109.0 ± 15.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Lin, L.; Gao, N.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Zhao, J. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Depolymerized Glycosaminoglycan from Holothuria fuscopunctata, a Novel Anticoagulant Candidate, in Rats by Bioanalytical Methods. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040212
Liu S, Zhang T, Sun H, Lin L, Gao N, Wang W, Li S, Zhao J. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Depolymerized Glycosaminoglycan from Holothuria fuscopunctata, a Novel Anticoagulant Candidate, in Rats by Bioanalytical Methods. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(4):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040212
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuang, Taocui Zhang, Huifang Sun, Lisha Lin, Na Gao, Weili Wang, Sujuan Li, and Jinhua Zhao. 2021. "Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Depolymerized Glycosaminoglycan from Holothuria fuscopunctata, a Novel Anticoagulant Candidate, in Rats by Bioanalytical Methods" Marine Drugs 19, no. 4: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040212
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhang, T., Sun, H., Lin, L., Gao, N., Wang, W., Li, S., & Zhao, J. (2021). Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Depolymerized Glycosaminoglycan from Holothuria fuscopunctata, a Novel Anticoagulant Candidate, in Rats by Bioanalytical Methods. Marine Drugs, 19(4), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040212





