Antiproliferative Activity and Potential Mechanism of Marine-Sourced Streptoglutarimide H against Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
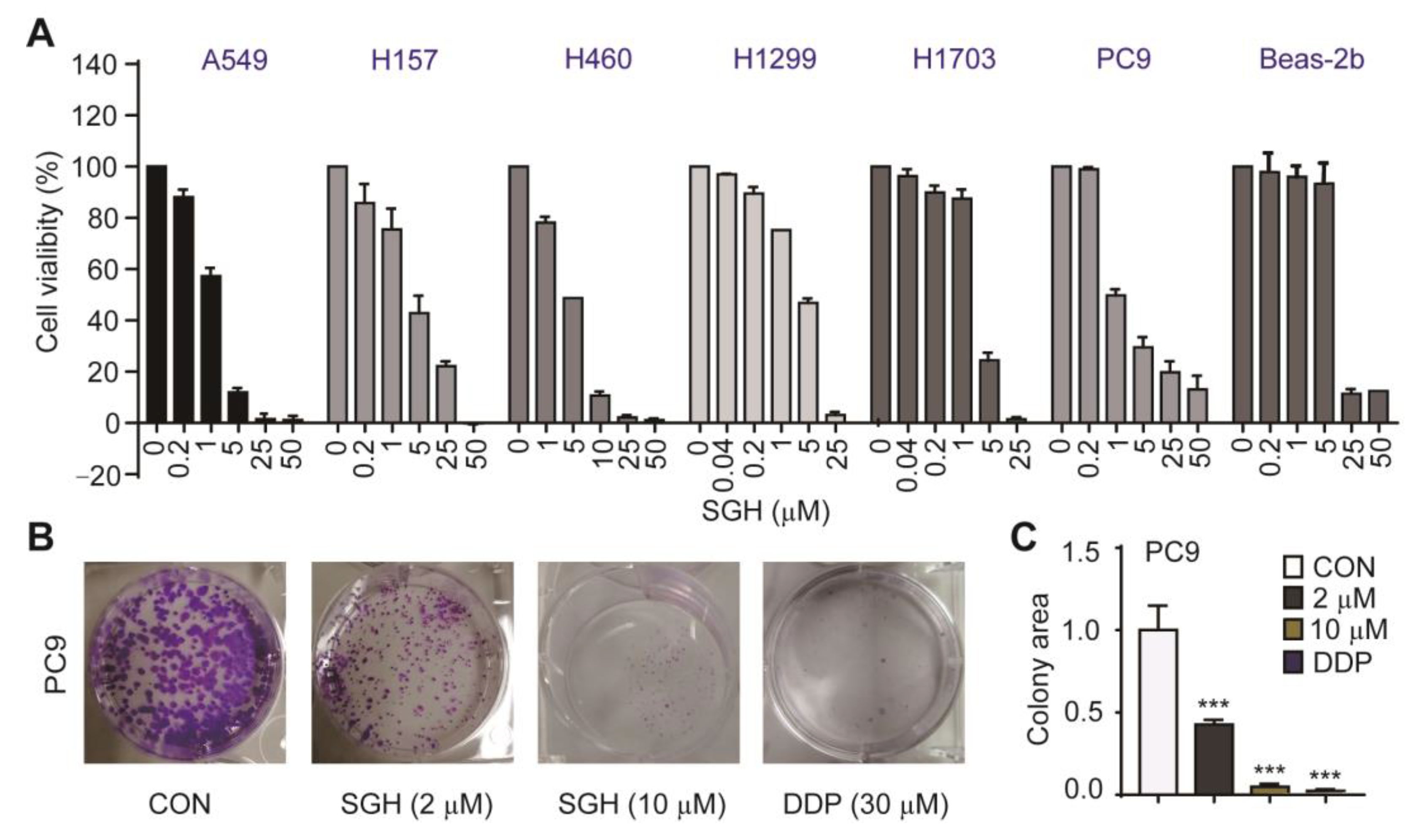
2.1. Streptoglutarimide H (SGH) Inhibited the Proliferation and Colony Formation of Lung Cancer Cells
2.2. Streptoglutarimide H (SGH) Blocked Cell Cycle at G0/G1 Phase by Downregulating the Cell Cycle- and Nucleotide Synthesis-related Proteins in Lung Cancer Cells
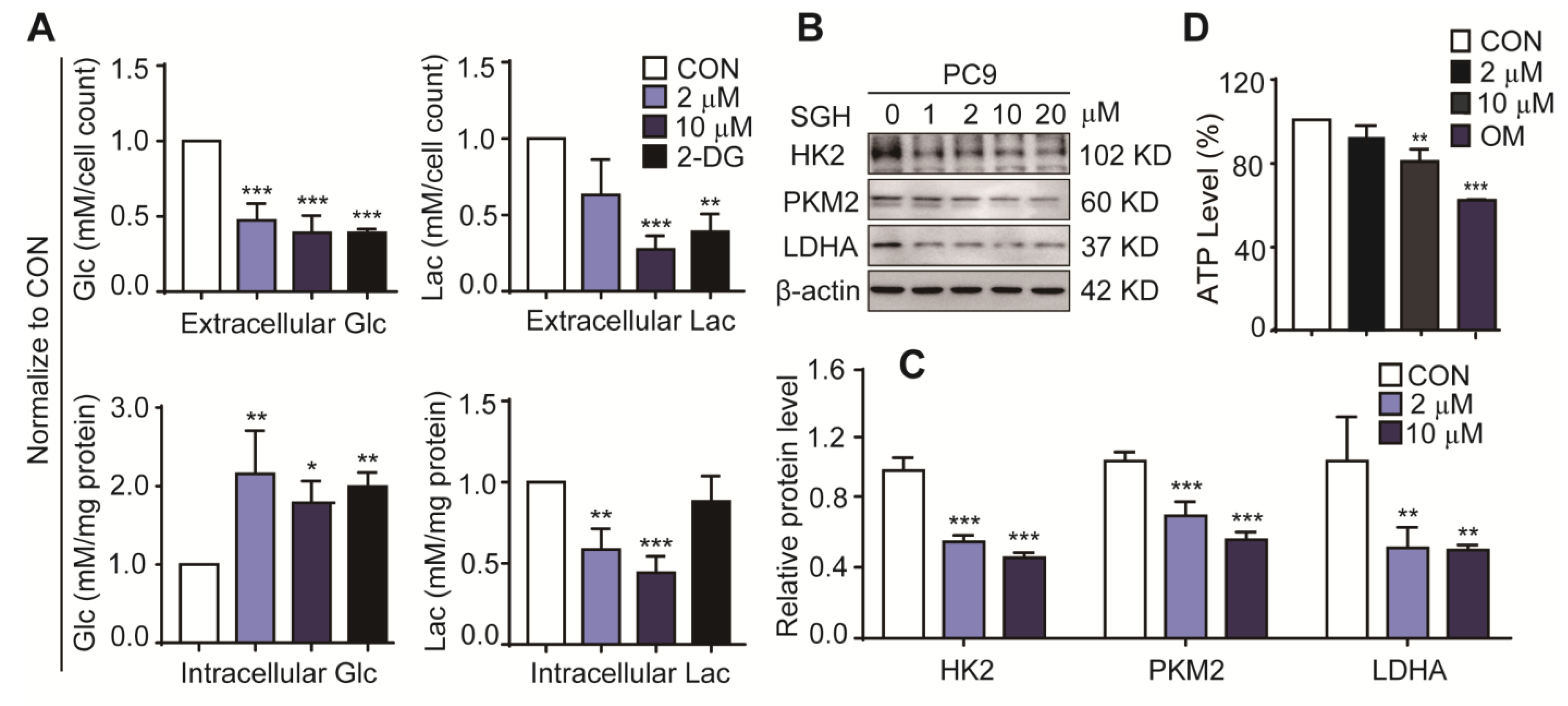
2.3. Streptoglutarimide H (SGH) Inhibited Glycolysis in Lung Cancer Cells
2.4. Streptoglutarimide H (SGH) Downregulated Deubiquitinase USP28 and Cancer Transcription Factor c-Myc
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Lung Cancer Cells and Cell Culture
4.2. Agents
4.3. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
4.4. Colony Formation Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.6. Cell Transfection
4.7. Measure of Glucose, Lactate, and ATP
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Society, A.C. Global Cancer Facts & Figures, 4th ed.; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 192–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelatti, A.C.Z.; Drilon, A.; Santini, F.C. Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer 2019, 137, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.H.; Lu, J.J. Osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cancer Lett. 2018, 420, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senft, D.; Qi, J.; Ronai, Z.A. Ubiquitin ligases in oncogenic transformation and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Zhou, Z.; Mei, X.; Yu, X.; Shao, Z.; et al. Targeting deubiquitinase USP28 for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Han, X. miR-3940-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting cyclin D1 and ubiquitin specific peptidase-28. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.B.; Evdokimov, N.M.; Lefranc, F.; Valentão, P.; Kornienko, A.; Pereira, D.M.; Andrade, P.B.; Gomes, N.G.M. Marine-derived anticancer agents: Clinical benefits, innovative mechanisms, and new targets. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yi, W.; Ge, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, B. Bioactive streptoglutarimides A-J from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. ZZ741. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.M.; He, M.Y.; Liu, Y.W.; Lu, Y.J.; Hong, Y.Q.; Luo, H.H.; Ren, Z.L.; Zhao, S.C.; Jiang, Y. AGE/RAGE/Akt pathway contributes to prostate cancer cell proliferation by promoting Rb phosphorylation and degradation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G. Targeting cancer metabolism: A therapeutic window opens. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Kroemer, G. Metabolic targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seliger, C.; Leukel, P.; Moeckel, S.; Jachnik, B.; Lottaz, C.; Kreutz, M.; Proescholdt, M.; Bogdahn, U.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Vollmann-Zwerenz, A.; et al. Lactate-modulated induction of THBS-1 activates transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta2 and migration of glioma cells in vitro. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8, e78935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Agnihotri, S.; Guha, A. Targeting metabolic remodeling in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 5521557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.P.; Schulze, A. Targeting cancer metabolism-aiming at a tumour’s sweet-spot. Drug Discov. 2012, 17, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billiard, J.; Dennison, J.B.; Briand, J.; Annan, R.S.; Chai, D.; Colón, M.; Dodson, C.S.; Gilbert, S.A.; Greshock, J.; Jing, J.; et al. Quinoline 3-sulfonamides inhibit lactate dehydrogenase A and reverse aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells. Cancer Metab. 2013, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Agnihotri, S.; Micallef, J.; Mukherjee, J.; Sabha, N.; Cairns, R.; Hawkins, C.; Guha, A. Hexokinase 2 is a key mediator of aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor growth in human glioblastoma multiforme. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefas, B.; Comeau, L.; Erdle, N.; Montgomery, E.; Amos, S.; Purow, B. Pyruvate kinase M2 is a target of the tumor-suppressive microRNA-326 and regulates the survival of glioma cells. Neuro. Oncol. 2010, 12, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Peiris-Pagés, M.; Pestell, R.G.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Cancer metabolism: A therapeutic perspective. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, B.; Qiang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Qian, J. Overexpression of deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 promoted non-small cell lung cancer growth. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, N.; Wanzel, M.; Madiredjo, M.; Zhang, D.; Beijersbergen, R.; Bernards, R.; Moll, R.; Elledge, S.J.; Eilers, M. The ubiquitin-specific protease USP28 is required for MYC stability. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Qing, G. Targeting oncogenic MYC as a strategy for cancer treatment. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretones, G.; Delgado, M.D.; León, J. Myc and cell cycle control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Tu, R.; Liu, H.; Qing, G. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism: Oncogenic MYC in the driver’s seat. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.S.; Sears, R.C. MYC degradation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley, J.D.; Gavory, G.; Simpson, I.; Preston, M.; Plant, H.; Bradley, J.; Goeppert, A.U.; Rozycka, E.; Davies, G.; Walsh, J.; et al. Identification and characterization of dual inhibitors of the USP25/28 deubiquitinating enzyme subfamily. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 3113–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, Q.; Ding, Y.; Xiong, M.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Y.; Su, H.; Gu, L.; Xu, Y.; Shi, L.; et al. USP28 and USP25 are downregulated by vismodegib in vitro and in colorectal cancer cell lines. FEBS J. 2020, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Li, Z.; Sun, K.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Guo, J.; Yu, B.; Shi, X.; Liu, H. Discovery of [1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives as highly potent, selective, and cellularly active USP28 inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2020, 10, 1476–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Koga, Y.; Su, C.; Waterbury, A.L.; Johnny, C.L.; Liau, B.B. Versatile synthetic route to cycloheximide and analogues that potently inhibit translation elongation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 5387–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, J.B. Clinical evaluation of streptovitacin A. Cancer Chemother. Rep. 1963, 31, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, H.; Oritani, T.; Yamashita, K. Syntheses and biological activities of (+/-)-streptovitacin A and E-73. Agri. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, W.; Ye, X.; Yu, S.; Lian, X.; Zhang, Z. New capoamycin-type antibiotics and polyene acids from marine Streptomyces fradiae PTZ0025. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2388–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Liang, J.; Ye, Y.; Lu, J.; Lin, T.; Wang, N.; Do, J.; Pan, J. FUT4siRNA augments the chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer to cisplatin through activation of FOXO1-induced apoptosis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ye, X.; Huang, H.; Peng, R.; Su, Z.; Lian, X.; Zhang, Z. Bioactive sulfated saponins from sea cucumber Holothuria moebii. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, H.; Zhang, D.; Shi, M.; Lian, X.; Zhang, Z. Antiproliferative Activity and Potential Mechanism of Marine-Sourced Streptoglutarimide H against Lung Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020079
Ge H, Zhang D, Shi M, Lian X, Zhang Z. Antiproliferative Activity and Potential Mechanism of Marine-Sourced Streptoglutarimide H against Lung Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(2):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020079
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Hengju, Di Zhang, Muran Shi, Xiaoyuan Lian, and Zhizhen Zhang. 2021. "Antiproliferative Activity and Potential Mechanism of Marine-Sourced Streptoglutarimide H against Lung Cancer Cells" Marine Drugs 19, no. 2: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020079
APA StyleGe, H., Zhang, D., Shi, M., Lian, X., & Zhang, Z. (2021). Antiproliferative Activity and Potential Mechanism of Marine-Sourced Streptoglutarimide H against Lung Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs, 19(2), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020079






