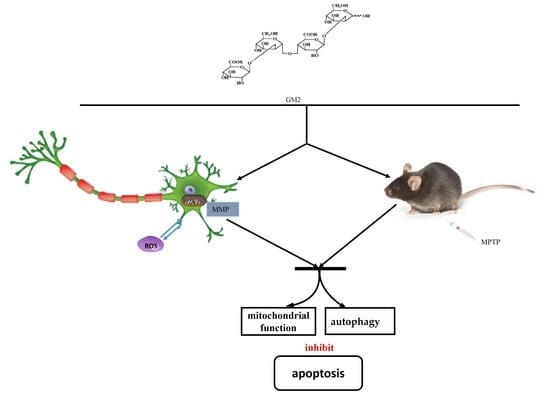
Glucuronomannan GM2 from Saccharina japonica Enhanced Mitochondrial Function and Autophagy in a Parkinson’s Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. GM2 Improves Cell Viability and Suppresses Apoptosis in PC12 Cells
2.2. GM2 Ameliorates MMP and Improves Antioxidant Capacity in PC12 Cells
2.3. GM2 Inhibits Apoptosis in PC12 Cells
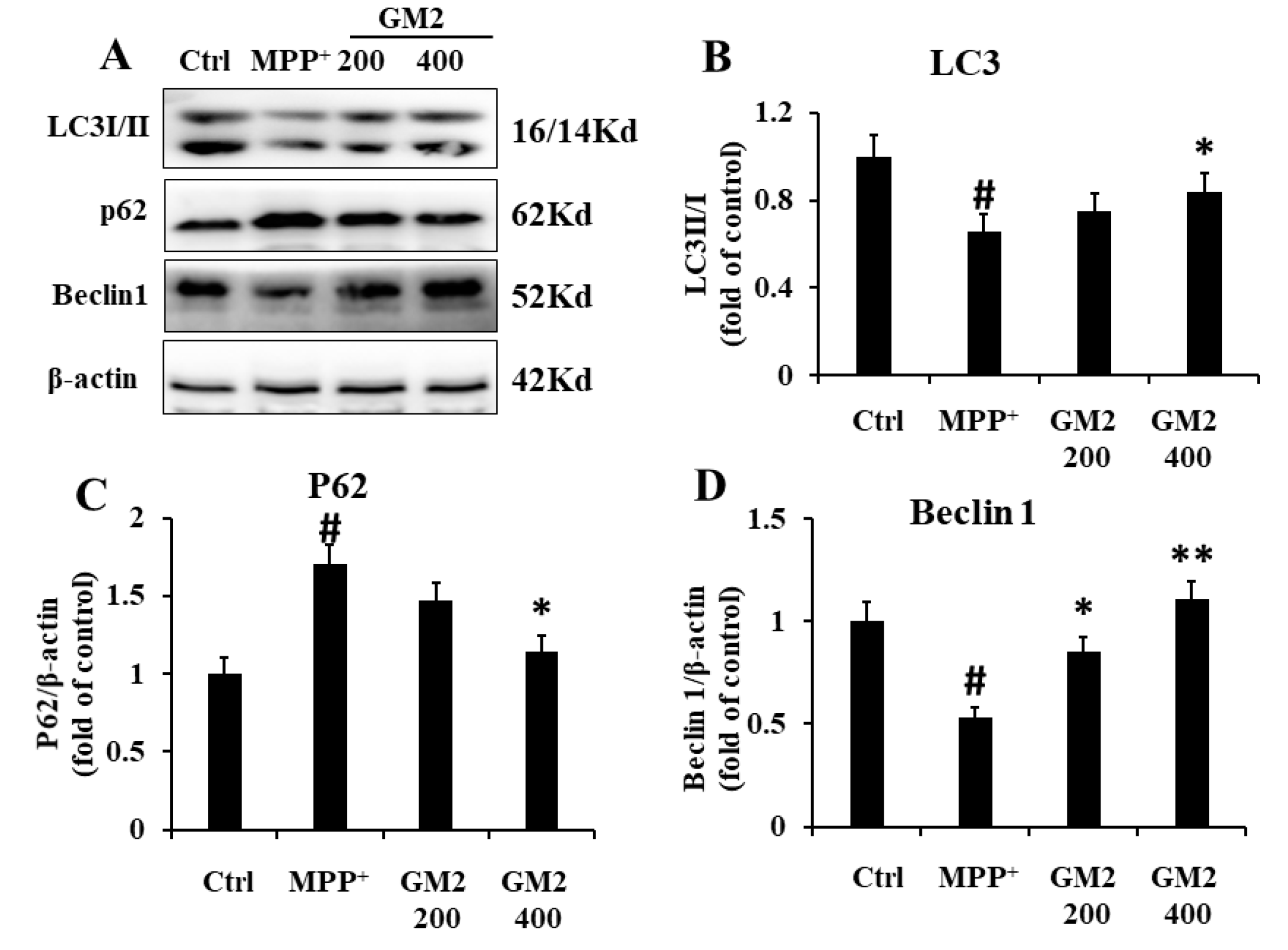
2.4. GM2 Enhances Autophagy in PC12 Cells
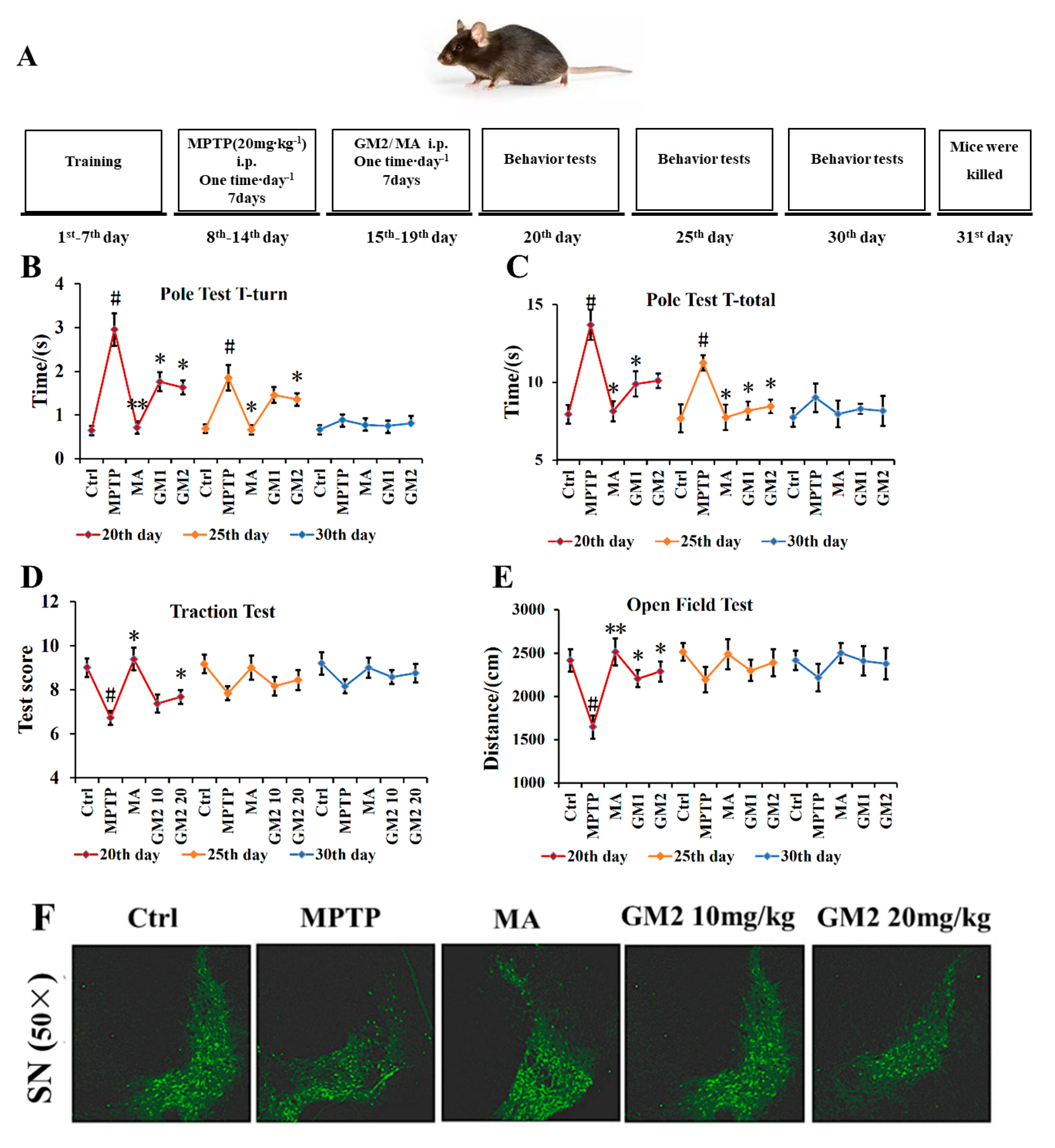
2.5. GM2 Prevents TH Loss
2.6. GM2 Enhanced Autophagy in PD Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
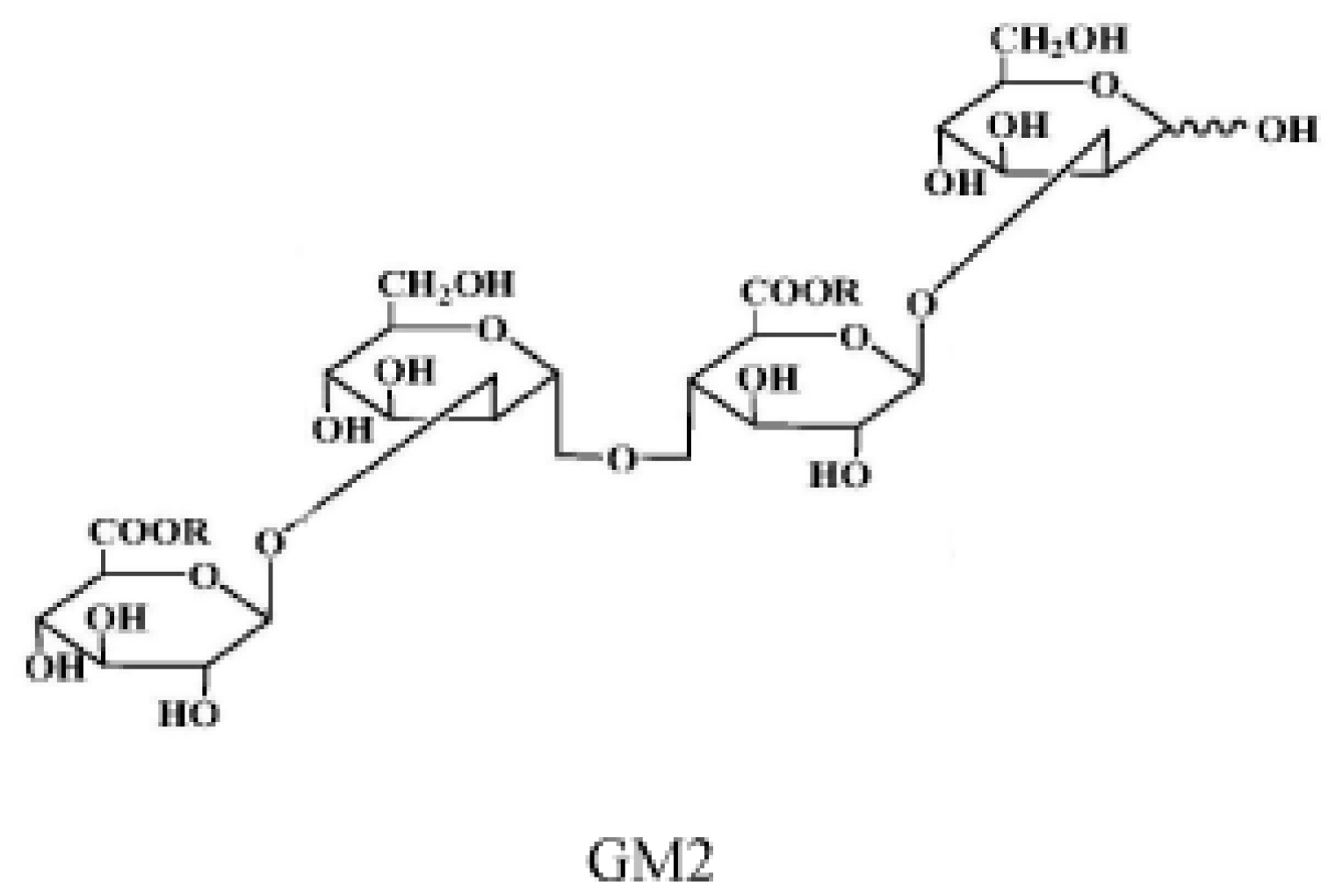
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining
4.4. Measurement of MMP
4.5. Measurement of ROS
4.6. Antioxidant Systems Assay
4.7. Determination of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 Activity
4.8. Drug Administration
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Tissue Collection and Preparation: Immunostaining
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kin, K.; Yasuhara, T.; Kameda, M.; Date, I. Animal Models for Parkinson’s Disease Research: Trends in the 2000s. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, S.J.; Tan, E.-K.; Chao, Y.X. Historical Perspective: Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Xie, J. Dopamine, and alpha-synuclein interactions in at-risk dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Tanimura, A.; Graves, S.M.; Shen, W.; Surmeier, D.J. Striatal synapses, circuits, and Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 48, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Kinoshita, K.-I.; Muroi, Y. Serotonin 5-HT4 Receptor Agonists Improve Facilitation of Contextual Fear Extinction in An MPTP-Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Rong, H.; Zhang, X.; Dong, M. Ferulic acid ameliorates MPP(+)/MPTP-induced oxidative stress via ERK1/2-dependent Nrf2 activation: Translational implications for Parkinson Disease treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 2981–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filomeni, G.; Graziani, I.; de Zio, D.; Dini, L.; Centonze, D.; Rotilio, G.; Ciriolo, M.R. Neuroprotection of kaempferol by autophagy in models of rotenone-mediated acute toxicity: Possible implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 767–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xuan, M.; Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. Neurochemical effects of the R form of α-lipoic acid and its neuroprotective mechanism in cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 87, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentillier, N.; Etzerodt, A.; Olesen, M.N.; Rizalar, F.S.; Jacobsen, J.; Bender, D.; Moestrup, S.K.; Romero-Ramos, M. Anti-inflammatory modulation of microglia via CD163-targeted glucocorticoids protects dopaminergic neurons in the 6-OHDA Parkinson’s Disease model. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 9375–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-González, M.; Padilla-Zambrano, H.S.; Tomás-Zapico, C.; Fernández-García, B. Clearing Extracellular Alpha-Synuclein from Cerebrospinal Fluid: A New Therapeutic Strategy in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-B.; Kim, H.T.; Yang, H.O.; Jang, W. Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation prevents methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced neurotoxicity by modulating autophagy in an in vivo mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Gao, W.; Shan, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Shao, Z.; Dou, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Cheng, B. Apelin-36 mediates neuroprotective effects by regulating oxidative stress, autophagy and apoptosis in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model mice. Brain Res. 2020, 1726, 146493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Karin, M. Autophagy, Inflammation, and Immunity: A Troika Governing Cancer and Its Treatment. Cell 2016, 166, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.Y.; Lee, P.H. Mesenchymal stem cells modulate misfolded α-synuclein in parkinsonian disorders: A multitarget disease-modifying strategy. Stem Cell Res. 2020, 47, 101908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Rabiee, N.; Zabihnejad, S.; Roghani, M. Ellagic acid exerts protective effect in intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Possible involvement of ERbeta/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Brain Res. 2017, 1662, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, G.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Bae, H. Neuro-protective effects of bee venom by suppression of neuroinflammatory responses in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: Role of regulatory T cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, S.; Umayaparvathi, S.; Saravanan, R.; Manivasagam, T.; Balasubramanian, T. Neuroprotective effect of fucoidan from Turbinaria decurrens in MPTP intoxicated Parkinsonic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, C.; Fan, Y.; Yan, P.; Shi, D.; Zhang, Y. Neuroprotection by Paeoniflorin in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2017, 116, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, F. Polysaccharides: Candidates of promising vaccine adjuvants. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Qi, M.; Li, N.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.-X. Natural products and their derivatives: Promising modulators of tumor immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gopal, S.; Pocock, R.; Xiao, Z.-C. Glycan Mimetics from Natural Products: New Therapeutic Opportunities for Neurodegenerative Disease. Molecules 2019, 24, 4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Geng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Sulfated Hetero-Polysaccharides Protect SH-SY5Y Cells from H2O2-Induced Apoptosis by Affecting the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, W.-H.; Deng, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and Neuroprotective Activity of Glucuronomannan Oligosaccharides in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Model. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Kang, K.; El-Sayed, M.A. Real-time tracking of the autophagy process in living cells using plasmonically enhanced Raman spectroscopy of fucoidan-coated gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5460–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Z. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 mediates the toxic of Parkinson’s disease induced by MPTP /MPP+ via regulation of gene expression. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.; Banik, S.; Akter, M.; Rahman, M.; Sikder, T.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. Curcumin alleviates arsenic-induced toxicity in PC12 cells via modulating autophagy/apoptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200, 110756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Jiang, C.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhou, S.; Liang, J.; Lao, Y.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1,2,4-triazole derivatives as potential neuroprotectant against ischemic brain injury. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 190, 112114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mao, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Xie, C.-H. Allicin Protects PC12 Cells Against 6-OHDA-Induced Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction via Regulating Mitochondrial Dynamics. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.Y.; Panchal, H.V.; Ghribi, O.; Benzeroual, K.E. The neuroprotective effect of fisetin in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2012, 2, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, T.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, W.; Mei, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, M.; Pan, H.; Li, W.; et al. FA-97, a New Synthetic Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Derivative, Protects against Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neuronal Cell Apoptosis and Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impairment by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Jiang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Gu, X.; Sun, C. Achyranthes bidentata polypeptide protects dopaminergic neurons from apoptosis in Parkinson’s disease models both in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Di, L.; Li, J.-L.; Li, N. Erxian decoction, a famous Chinese medicine formula, antagonizes corticosterone-induced injury in PC12 cells, and improves depression-like behaviours in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Yu, C.; Gao, J. Trilobatin Protects Against Abeta25-35-Induced Hippocampal HT22 Cells Apoptosis Through Mediating ROS/p38/Caspase 3-Dependent Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, M.F. Experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, D.W.; Ali, A.; Thornberry, N.A.; Vaillancourt, J.P.; Ding, C.K.; Gallant, M.; Gareau, Y.; Griffin, P.R.; Labelle, M.; Lazebnik, Y.A.; et al. Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 1995, 376, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, R.B.; Teismann, P. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: Pathogenesis and neuroprotection. Parkinsons Dis. 2010, 2011, 617472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, S.; Shojaei, S.; Yeganeh, B.; Ande, S.R.; Jangamreddy, J.R.; Mehrpour, M.; Christoffersson, J.; Chaabane, W.; Moghadam, A.R.; Kashani, H.H.; et al. Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 112, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tang, P.; Tu, N.; Wang, K.; Wu, G. Overexpression of miR185 inhibits autophagy and apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons by regulating the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Dehay, B.; Bove, J.; Rodriguez-Muela, N.; Perier, C.; Recasens, A.; Boya, P.; Vila, M. Pathogenic lysosomal depletion in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 12535–12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, A.R.; Larrick, J.W. Rapamycin as an Antiaging Therapeutic? Targeting Mammalian Target of Rapamycin to Treat Hutchinson–Gilford Progeria and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Rejuvenat. Res. 2011, 14, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, D.; Barth, S.; MacLeod, K.F. Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosp, J.A.; Pekanovic, A.; Rioult-Pedotti, M.S.; Luft, A.R. Dopaminergic projections from midbrain to primary motor cortex mediate motor skill learning. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 2481–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winogrodzka, A.; Bergmans, P.; Booij, J.; van Royen, E.; Stoof, J.C.; Wolters, E.C. 123I]β-CIT SPECT is a 43useful method for monitoring dopaminergic degeneration in early stage Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry Investig. 2017, 74, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Jin, W.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. Glucuronomannan GM2 from Saccharina japonica Enhanced Mitochondrial Function and Autophagy in a Parkinson’s Model. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020058
Liu Y, Jin W, Deng Z, Zhang Q, Wang J. Glucuronomannan GM2 from Saccharina japonica Enhanced Mitochondrial Function and Autophagy in a Parkinson’s Model. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(2):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020058
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yingjuan, Weihua Jin, Zhenzhen Deng, Quanbin Zhang, and Jing Wang. 2021. "Glucuronomannan GM2 from Saccharina japonica Enhanced Mitochondrial Function and Autophagy in a Parkinson’s Model" Marine Drugs 19, no. 2: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020058
APA StyleLiu, Y., Jin, W., Deng, Z., Zhang, Q., & Wang, J. (2021). Glucuronomannan GM2 from Saccharina japonica Enhanced Mitochondrial Function and Autophagy in a Parkinson’s Model. Marine Drugs, 19(2), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020058