Shallow Hydrothermal Vent Bacteria and Their Secondary Metabolites with a Particular Focus on Bacillus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bacterial Diversity Studies
2.2. Characteristics of the Isolated Bacterial Colonies
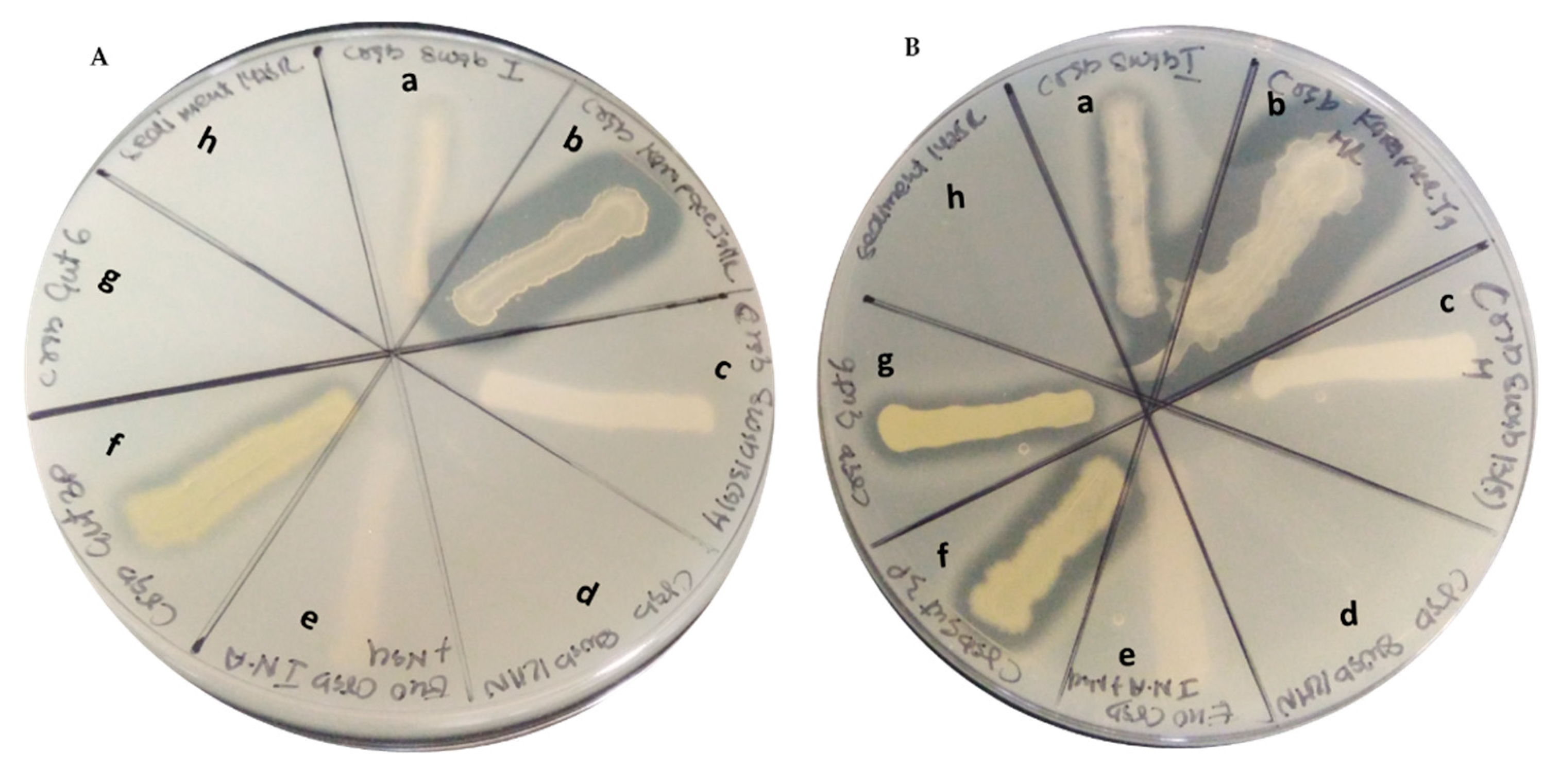
2.3. Products from Marine Isolates
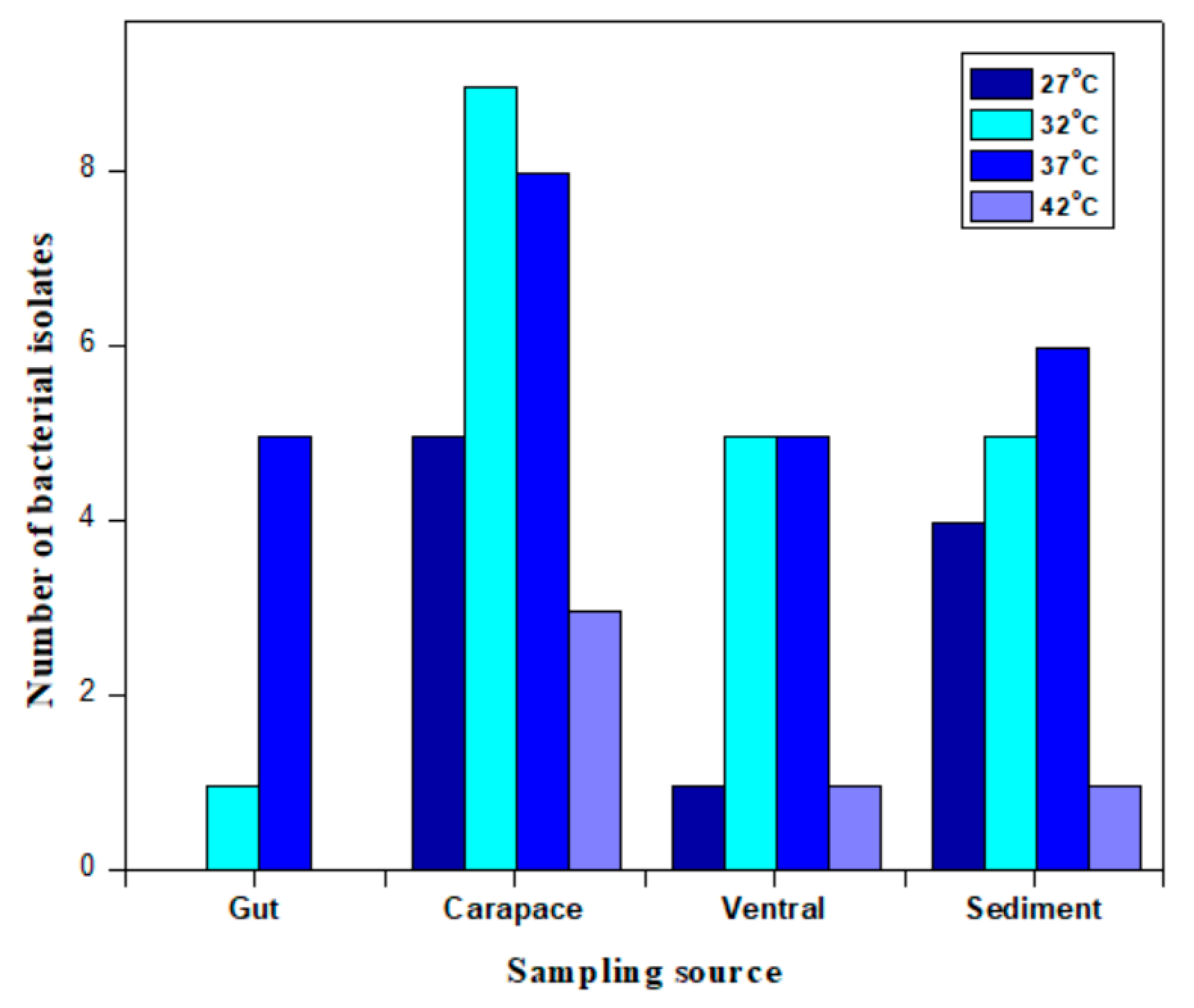
2.4. The Identification of Differences in Bacterial Colony Occurrence from the Sampling Source
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Colony Isolation
3.2. DNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Phylogenetic Tree
3.4. Protease Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rampelotto, P. Extremophiles and Extreme Environments. Life 2013, 3, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahms, H.-U.; Schizas, N.V.; James, R.A.; Wang, L.; Hwang, J.-S. Marine hydrothermal vents as templates for global change scenarios. Hydrobiologia 2018, 818, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahms, H.U.; Peterson, T.R.; Baveye, P.C. Editorial: Innovative Approaches to Learning in Environmental Science. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, R.; Huang, B.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Hwang, J.-S.; Dahms, H.-U. Novel recombinant keratin degrading subtilisin like serine alkaline protease from Bacillus cereus isolated from marine hydrothermal vent crabs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, T.D. Life at High Temperatures. Science 1985, 230, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, T.D. The road to yellowstone and beyond. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, K.V.; Doan, K.L.U.; Doan, N.X.; Pham, H.Q.; Le, T.H.O.; Le, M.-H.; Vu, M.T.T.; Dahms, H.-U.; Truong, K.N. Parental exposures increase the vulnerability of copepod offspring to copper and a simulated marine heatwave. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetter, K.O. History of discovery of the first hyperthermophiles. Extremophiles 2006, 10, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, F.W. Priminary Investigation of the Hydrothermal Activities off Kueishantao Island; National Sun Yat-Sen University: Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-G.; Wu, W.-S.; Chen, C.-H.; Liu, T.-K. A date for volcanic eruption inferred from a siltstone xenolith. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2001, 20, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, V.G.; Gebruk, A.V.; Mironov, A.N.; Moskalev, L.I. Deep-sea and shallow-water hydrothermal vent communities: Two different phenomena? Chem. Geol. 2005, 224, 5–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Wang, X.M.; Zeng, Z.G.; Yin, X.B.; Chen, C.T.A.; Zhang, S.W. Origin of the hydrothermal fluid of the shallow sea near Kueishantao Island. Mar. Sci. 2010, 34, 61–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Franco, P.; Dahms, H.-U.; Hwang, J.-S. Pelagic tunicates at shallow hydrothermal vents of Kueishantao. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.A.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Lou, J.; Kuo, F.; Tu, Y.; Tsai, H. Investigation into extremely acidic hydrothermal fluids off Kueishan Tao, Taiwan, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2005, 24, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Zeng, Z.; Kuo, F.-W.; Yang, T.F.; Wang, B.-J.; Tu, Y.-Y. Tide-influenced acidic hydrothermal system offshore NE Taiwan. Chem. Geol. 2005, 224, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-G.; Lyu, S.-S.; Garbe-Schönberg, D.; Lebrato, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Zhang, P.-P.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Ye, Y. Heavy metals from Kueishantao shallow-sea hydrothermal vents, offshore northeast Taiwan. J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 180, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrato, M.; Wang, Y.V.; Tseng, L.-C.; Achterberg, E.P.; Chen, X.-G.; Molinero, J.-C.; Bremer, K.; Westernströer, U.; Söding, E.; Dahms, H.-U.; et al. Earthquake and typhoon trigger unprecedented transient shifts in shallow hydrothermal vent biogeochemistry. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, M.-S.; Ng, N.K.; Ng, P.K.L. Feeding behaviour: Hydrothermal vent crabs feast on sea “snow”. Nature 2004, 432, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.-L.; Guo, S.-Y.; Chen, I.-A.; Burgaud, G.; Luo, Z.-H.; Dahms, H.U.; Hwang, J.-S.; Lin, Y.-L.; Huang, J.-S.; Ho, T.-W.; et al. Insights into fungal diversity of a shallow-water hydrothermal vent field at Kueishan Island, Taiwan by culture-based and metabarcoding analyses. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hough, D.W.; Danson, M.J. Extremozymes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999, 3, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hencyia, S.; Vengateshwarana, T.D.; Gokul, M.S.; Rajasabapathy, R.; Vignesh, S.; Krishnan Muthukumar, K.; Kaviarasan, M.; Veeramania, T.; Dahms, H.-U.; James, R.A. Solar saltern bacteria as an effective inhibitor of diabetic foot drug resistant pathogens. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3711–3723. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, K.-L.; Chiang, M.W.-L.; Guo, S.-Y.; Shih, C.-Y.; Dahms, H.U.; Hwang, J.-S.; Cha, H.-J. Growth study under combined effects of temperature, pH and salinity and transcriptome analysis revealed adaptations of Aspergillus terreus NTOU4989 to the extreme conditions at Kueishan Island Hydrothermal Vent Field, Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Adebisi, W.A.; Ahmad, F.; Sethupathy, S.; Danso, B.; Sun, J. Recent Development of Extremophilic Bacteria and Their Application in Biorefinery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.F.; Ouddane, B.; Hwang, J.-S.; Dahms, H.-U. In silico assessment of health risks mediated by marine cyanobacteria. Biocell 2021, 45, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jia, Q.Y.; Jing, W.; Dahms, H.-U.; Wang, L. Screening strains for microbial biosorption technology of cadmium. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.S.; Roberts, N.; Singleton, F.L.; Attwell, R.W.; Grimes, D.J.; Colwell, R.R. Survival and viability of nonculturable Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae in the estuarine and marine environments. Microb. Ecol. 1982, 8, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simu, K.; Holmfeldt, K.; Zweifel, U.L.; Hagström, A. Culturability and Coexistence of Colony-Forming and Single-Cell Marine Bacterioplankton. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4793–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerf, O.; Carpentier, B.; Sanders, P. Tests for determining in-use concentrations of antibiotics and disinfectants are based on entirely different concepts: “Resistance” has different meanings. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 136, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasotti, L.; Zucca, S.; Lupotto, M.; Cusella De Angelis, M.; Magni, P. Characterization of a synthetic bacterial self-destruction device for programmed cell death and for recombinant proteins release. J. Biol. Eng. 2011, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prieto-Barajas, C.M.; Alfaro-Cuevas, R.; Valencia-Cantero, E.; Santoyo, G. Effect of seasonality and physicochemical parameters on bacterial communities in two hot spring microbial mats from Araró, Mexico. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2017, 88, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Su, X.; Chen, F.; Holland, M.; Yang, S.; Liang, J.; Su, P.; Dong, H.; Hou, W. Microbial diversity of two cold seep systems in gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the South China Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 144, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, A.; Jha, B. Bacterial community structure and functional diversity in subsurface seawater from the western coastal ecosystem of the Arabian Sea, India. Gene 2019, 701, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Dombard, D.R.; Amend, J.P.; Osburn, M.R. Microbial diversity and potential for arsenic and iron biogeochemical cycling at an arsenic rich, shallow-sea hydrothermal vent (Tutum Bay, Papua New Guinea). Chem. Geol. 2013, 348, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, V.L.; Meena, R.M.; Shenoy, B.D. Phylogenetic characterization of culturable bacteria and fungi associated with tarballs from Betul beach, Goa, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vipindas, P.V.; Mujeeb, R.K.M.; Jabir, T.; Thasneem, T.R.; Mohamed Hatha, A.A. Diversity of sediment bacterial communities in the South Eastern Arabian Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Schlingloff, A.; Bernhard, M.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Antagonistic activity of bacteria isolated from organic aggregates of the German Wadden Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamo, M.T.; Gugliandolo, C.; Zammuto, V.; Magazù, S. Thermal properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by a marine thermotolerant Bacillus licheniformis by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandeparker, R.; Verma, P.; Deobagkar, D. A novel halotolerant xylanase from marine isolate Bacillus subtilis cho40: Gene cloning and sequencing. New Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shofiyah, S.S.; Yuliani, D.; Widya, N.; Sarian, F.D.; Puspasari, F.; Radjasa, O.K.; Ihsanawati; Natalia, D. Isolation, expression, and characterization of raw starch degrading α-amylase from a marine lake Bacillus megaterium NL3. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, Y.; Alrumman, S.; Alamri, S.; Hashem, M.; Al-izran, K.; Alfaifi, M.; Elbehairi, S.E.; Taha, T. Enhanced production of glutaminase-free l-asparaginase by marine Bacillus velezensis and cytotoxic activity against breast cancer cell lines. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 42, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamiche, S.; Mechri, S.; Khelouia, L.; Annane, R.; El Hattab, M.; Badis, A.; Jaouadi, B. Purification and biochemical characterization of two keratinases from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S13 isolated from marine brown alga Zonaria tournefortii with potential keratin-biodegradation and hide-unhairing activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandas, S.P.; Balan, L.; Jayanath, G.; Anoop, B.S.; Philip, R.; Cubelio, S.S.; Bright Singh, I.S. Biosynthesis and characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoate from marine Bacillus cereus MCCB 281 utilizing glycerol as carbon source. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Farraj, D.A.; Kumar, T.S.J.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Elshikh, M.S.; Alkufeidy, R.M.; Alkubaisi, N.A.; Alshammari, M.K. Enhanced production, purification and biochemical characterization of therapeutic potential fibrinolytic enzyme from a new Bacillus flexus from marine environment. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 3174–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, N.; Gupta, V.; Kumar, M.; Kumari, P.; Reddy, C.R.K.; Jha, B. Solvent tolerant marine bacterium Bacillus aquimaris secreting organic solvent stable alkaline cellulase. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Sen, R. Antimicrobial potential of a lipopeptide biosurfactant derived from a marine Bacillus circulans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Zhu, P.; Chen, J.; Yang, R. Preparative isolation and purification of macrolactin antibiotics from marine bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens using high-speed counter-current chromatography in stepwise elution mode. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1272, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, G.S.; Priyadharsini, S.; Sajayan, A.; Ravindran, A.; Selvin, J. An antibiotic agent pyrrolo [1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro isolated from a marine bacterium Bacillus tequilensis MSI45 effectively controls multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17837–17846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saggese, A.; Culurciello, R.; Casillo, A.; Corsaro, M.; Ricca, E.; Baccigalupi, L. A Marine Isolate of Bacillus pumilus secretes a Pumilacidin Active against Staphylococcus aureus. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nisha, P.; John, N.; Mamatha, C.; Thomas, M. Characterization of bioactive compound produced by microfouling actinobacteria (Micrococcus luteus) isolated from the ship hull in Arabian Sea, Cochin. Kerala. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 25, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Michailidou, S.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Koromilas, S.; Kios, K.; Pasentsis, K.; Psomopoulos, F.; Argiriou, A.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Boziaris, I.S. Bacterial communities and potential spoilage markers of whole blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) stored under commercial simulated conditions. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kwon, T.-H.; Jung, S.-M.; Cho, S.-H.; Jin, S.Y.; Park, N.-H.; Kim, C.-G.; Kim, J.-S. Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria Isolated from the Internal Organs of Edible Snow Crabs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.R.; Wicks, T.C.; Tubiash, H.S. A comparative study of the bacterial flora of the hemolymph of Callinectes sapidus. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1975, 37, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore, R.K.; Colwell, R.R.; Tubiash, H.S.; Lovelace, T.E. Bacterial Flora of the Hemolymph of the Blue Crab, Callinectes sapidus: Numerical Taxonomy. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 29, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S. No. | Media | No. of Different CFUs Obtained |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nutrient media supplemented with NaCl | 7 |
| 2 | Nutrient media without NaCl | 12 |
| 3 | Tryptic soy media | 8 |
| 4 | Zobell marine media | 18 |
| 5 | Seawater complete | 2 |
| 6 | Casamino acid seawater | 2 |
| No. | Bacteria | Optimal Media | Temperature (°C) | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bacillus aerius | Lb without and with NaCl, NA, ZMA | 30–37 | White, irregular, raised |
| 2 | Staphylococcus haemolyticus | NA, LB, TSA | 37 | Light yellow |
| 3 | Bacillus aryabhattai | MA, Nutrient and Lb with NaCl | 37 | Opaque, white, raised, irregular |
| 4 | Bacillus ginsengi | NA, LB, TSA | 37 | Light yellow |
| 5 | Bacillus aquimaris | MA, Nutrient and Lb with NaCl | 30–37, 42 | Yellow pale, circular to slightly irregular and raised |
| 6 | Bacillus iocasae | Nutrient agar with 2% NaCl, Zobell marine agar | 32–37 | Off-white |
| 7 | Bacillus firmus | TSA, LB, NB with NaCl, MA | 37 | Shiny, circular, semi-transparent, flat colonies |
| 8 | Kocuria subflava | MA | 37 | Yellow colonies |
| 9 | Bacillus marisflavis | Marine agar, LB with and without NaCl | 27 | Pale yellow, smooth, circular to slightly irregular |
| 10 | Bacillus safensis | TSA, with and without NaCl | 32–37, 42 | Irregular margins, off-white/cream |
| 11 | Exiguobacterium aurantiacum | MA | 27–37,42 | Orange colonies, flat |
| 12 | Bacillus subterraneus | TSA | 37 | Transparent, irregular colonies |
| 13 | Staphylococcus sciuri | TSA, NA, MA | 37 | Yellow, circular |
| 14 | Micrococcus luteus | NA with NaCl, MA | 37 | Light yellow, regular circular colony |
| 15 | Bacillus megaterium | NA without and with NaCl | 32 | Foamy white colonies, irregular |
| 16 | Jeotgalicoccus haukii | MA, NA with NaCl | 37 | Round, smooth, circular, white |
| 17 | Bacillus cereus | MA, LB, NA | 27–32 | Irregular, opaque, white cream, little fuzzy appearance |
| 18 | Brevibacillus parabrevis | Trypticase soy agar, MA | 32–37 | Pale yellow, circular |
| 19 | Bacillus vallismortis | NA, MA | 27–32 | Opaque, smooth circular |
| 20 | Psychrobacter pulmonis | MA | 37 | White and opaque |
| 21 | Bacillus licheniformis | MA, LB, NA | 27–42 | Opaque, hair-like outgrowths, whitish, colonies round to irregular |
| 22 | Paenibacillus silvae | MA, NA | 32 | Shiny, smooth, beige color, irregular |
| 23 | Exiguobacterium mexicanum | MA | 37 | Orange, circular |
| 24 | Bacillus jeotgali | MA, NA 2% NaCl | 32 | Smooth and flat, irregular colony, cream yellow to light yellow |
| 25 | Bacillus boroniphilus | MA, NA, LB 2% NaCl | Opaqe, smooth surface | |
| 26 | Bacillus halasaccharovorans | MA | 32 | Circular, smooth, creamy |
| 27 | Bacillus flexus | 10% NaCl, 2%NaCl, MA lb | 32 | Creamish white, smooth and opaque |
| 28 | Bacillus velezensis | Tryptic soy agar (TSA or tryptic soy broth (TSB) | 27 | Creamish white, irregular |
| 29 | Bacillus albus | LB medium with and without NaCl NA MA | 32 | White regular |
| 30 | Bacillus tequilensis | TSA, MA | 37 | Round, smooth, yellowish in colour |
| 31 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | MA | 37 | Irregular, raised, white mucous, filled and sticky |
| S. No. | Bacterial Strain | Protease Assay in the Presence of ZnSO4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 µM | 100 µM | 500 µM | 1 mM | 10 mM | ||
| 1 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | + | + | + | + | − |
| 2 | Bacillus aquimaris | + | + | + | + | − |
| 3 | Micrococcus luteus | + | + | − | − | − |
| 4 | Bacillus jeotgali | − | − | − | − | − |
| 5 | Bacillus firmus | − | − | − | − | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gurunathan, R.; Rathinam, A.J.; Hwang, J.-S.; Dahms, H.-U. Shallow Hydrothermal Vent Bacteria and Their Secondary Metabolites with a Particular Focus on Bacillus. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120681
Gurunathan R, Rathinam AJ, Hwang J-S, Dahms H-U. Shallow Hydrothermal Vent Bacteria and Their Secondary Metabolites with a Particular Focus on Bacillus. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(12):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120681
Chicago/Turabian StyleGurunathan, Revathi, Arthur James Rathinam, Jiang-Shiou Hwang, and Hans-Uwe Dahms. 2021. "Shallow Hydrothermal Vent Bacteria and Their Secondary Metabolites with a Particular Focus on Bacillus" Marine Drugs 19, no. 12: 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120681
APA StyleGurunathan, R., Rathinam, A. J., Hwang, J.-S., & Dahms, H.-U. (2021). Shallow Hydrothermal Vent Bacteria and Their Secondary Metabolites with a Particular Focus on Bacillus. Marine Drugs, 19(12), 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120681






