Emerging Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Phenolics: Opportunities and Challenges
Abstract
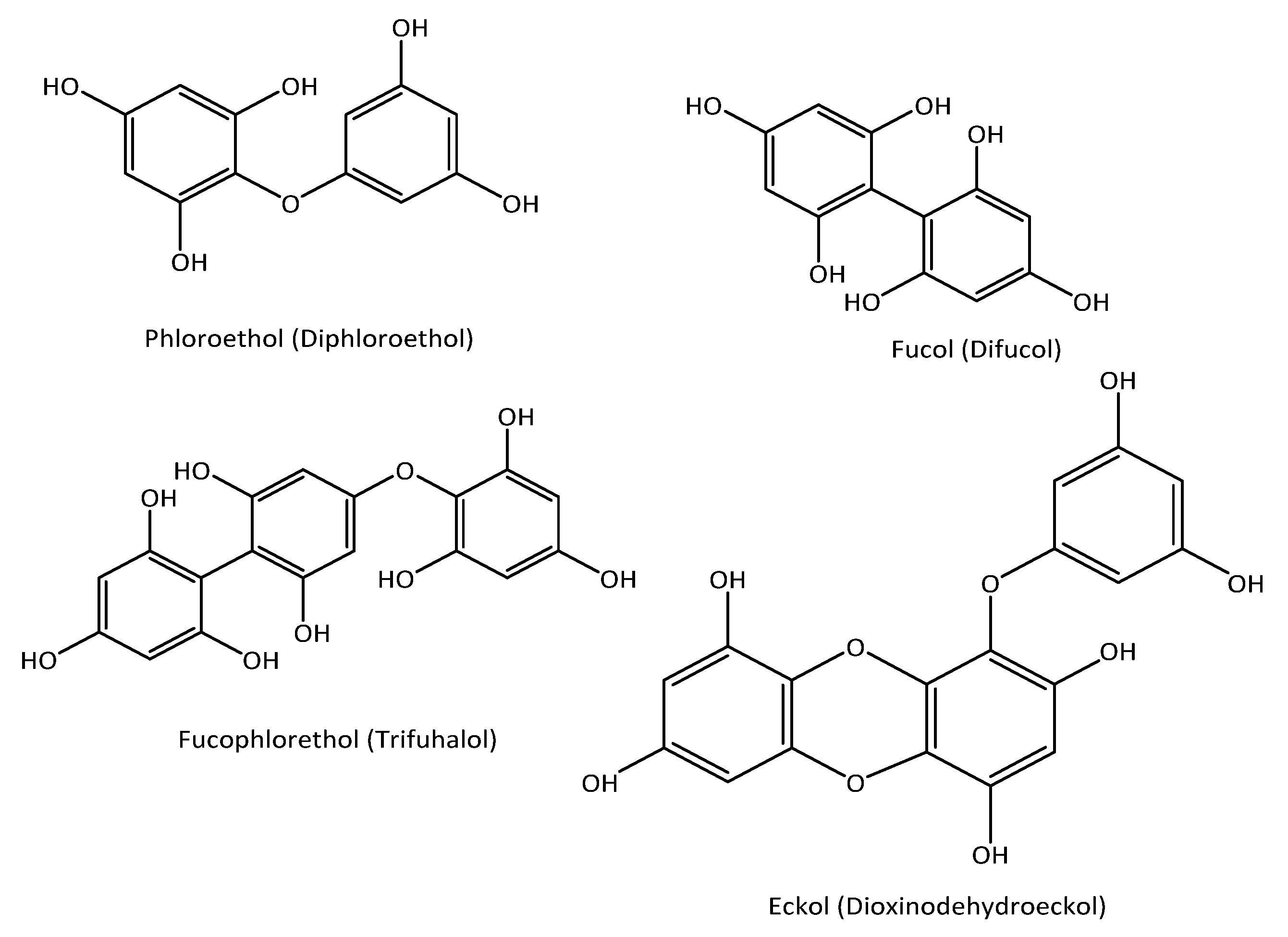
1. Introduction
2. Traditional Extraction of Marine Phenolics
3. Emerging Technologies for Extraction of Marine Phenolics
3.1. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction (EAE)
3.2. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
3.3. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
3.4. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
3.5. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
3.6. Other Emerging Technologies
3.7. Combination of Different Emerging Technologies
4. Opportunities and Challenges with Emerging Technologies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiménez-Escrig, A.; Gómez-Ordóñez, E.; Rupérez, P. Brown and red seaweeds as potential sources of antioxidant nutraceuticals. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, C.A. Size and survival of intertidal plants in response to wave action: A case study with fucus gardneri. Ecology 1997, 78, 1563–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parys, S.; Rosenbaum, A.; Kehraus, S.; Reher, G.; Glombitza, K.W.; König, G.M. Evaluation of quantitative methods for the determination of polyphenols in algal extracts. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, G.S.; Sørensen, A.D.M.; Safafar, H.; Pedersen, A.H.; Holdt, S.L. Antioxidant content and activity of the seaweed Saccharina latissima: A seasonal perspective. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steevensz, A.J.; MacKinnon, S.L.; Hankinson, R.; Craft, C.; Connan, S.; Stengel, D.B.; Melanson, J.E. Profiling phlorotannins in brown macroalgae by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gager, L.; Connan, S.; Molla, M.; Couteau, C.; Arbona, J.F.; Coiffard, L.; Cérantola, S.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V. Active phlorotannins from seven brown seaweeds commercially harvested in Brittany (France) detected by 1H NMR and in vitro assays: Temporal variation and potential valorization in cosmetic applications. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirke, D.A.; Rai, D.K.; Smyth, T.J.; Stengel, D.B. An assessment of temporal variation in the low molecular weight phlorotannin profiles in four intertidal brown macroalgae. Algal Res. 2019, 41, 101550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.; Sørensen, A.-D.M.; Holdt, S.L.; Akoh, C.C.; Hermund, D.B. Source, extraction, characterization, and applications of novel antioxidants from seaweed. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 541–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jónsdóttir, R.; Ólafsdóttir, G. Total phenolic compounds, radical scavenging and metal chelation of extracts from Icelandic seaweeds. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeena Farvin, K.H.; Jacobsen, C. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of selected species of seaweeds from Danish coast. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machu, L.; Misurcova, L.; Vavra Ambrozova, J.; Orsavova, J.; Mlcek, J.; Sochor, J.; Jurikova, T. Phenolic content and antioxidant capacity in algal food products. Molecules 2015, 20, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajauria, G.; Foley, B.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Identification and characterization of phenolic antioxidant compounds from brown Irish seaweed Himanthalia elongata using LC-DAD–ESI-MS/MS. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 37, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshie, Y.; Wang, W.; Petillo, D.; Suzuki, T. Distribution of catechins in Japanese seaweeds. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.P.; Sidana, J. Phlorotannins. In Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2013; Volume 256, pp. 181–204. ISBN 9780857095121. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, I.; Huovinen, P. Brown algal phlorotannins: An overview of their functional roles. In Antarctic Seaweeds; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 365–388. [Google Scholar]
- Holdt, S.L.; Kraan, S. Bioactive compounds in seaweed: Functional food applications and legislation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 543–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinteus, S.; Silva, J.; Alves, C.; Horta, A.; Fino, N.; Rodrigues, A.I.; Mendes, S.; Pedrosa, R. Cytoprotective effect of seaweeds with high antioxidant activity from the Peniche coast (Portugal). Food Chem. 2017, 218, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Fu, X.; Duan, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, X.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of bioactivity of phenolic compounds from the brown seaweed of Sargassum fusiforme and development of their stable emulsion. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1955–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, A.; Jouini, M.; Bel Haj Amor, H.; Mzoughi, Z.; Dridi, M.; Ben Said, R.; Bouraoui, A. Phytochemical analysis and evaluation of the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antinociceptive potential of phlorotannin-rich fractions from three mediterranean brown seaweeds. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio-Rodríguez, P.A.; Esquivel-Solis, H.; Murillo-Álvarez, J.I.; Ascencio, F.; Campa-Córdova, Á.I.; Angulo, C. Biosprospecting potential of kelp (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae) from Baja California Peninsula: Phenolic content, antioxidant properties, anti-inflammatory, and cell viability. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3115–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.P.; Suganthy, N.; Kesika, P.; Pandian, S.K. Bioprotective properties of seaweeds: In vitro evaluation of antioxidant activity and antimicrobial activity against food borne bacteria in relation to polyphenolic content. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubayed, N.M.S.; Al Houri, H.J.; Al Khulaifi, M.M.; Al Farraj, D.A. Antimicrobial, antioxidant properties and chemical composition of seaweeds collected from Saudi Arabia (Red Sea and Arabian Gulf). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaoui, B.; Ghalem, B.R. The phenolic contents and antimicrobial activities of some marine algae from the mediterranean sea (Algeria). Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2017, 43, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Manigandan, V.; Sheeba, R.; Saravanan, R.; Rajesh, P.R. Structural characterization and comparative biomedical properties of phloroglucinol from Indian brown seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3561–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Górka, B.; Wieczorek, P.P.; Rój, E.; Lipok, J.; Łęska, B.; Messyasz, B.; Wilk, R.; Schroeder, G.; Dobrzyńska-Inger, A.; et al. Supercritical fluid extraction of algae enhances levels of biologically active compounds promoting plant growth. Eur. J. Phycol. 2016, 51, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Yuan, G.; Fan, Y.; Chen, K. Optimization of the microwave-assisted extraction of phlorotannins from Saccharina japonica Aresch and evaluation of the inhibitory effects of phlorotannin-containing extracts on HepG2 cancer cells. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, A.; Lajili, S.; Elkaibi, M.A.; Ben Salem, Y.; Abdelhamid, A.; Muller, C.D.; Majdoub, H.; Kraiem, J.; Bouraoui, A. Optimized extraction, preliminary characterization and evaluation of the in vitro anticancer activity of phlorotannin-rich fraction from the Brown Seaweed, Cystoseira sedoides. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2019, 28, 892–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Molina, A.; Fernández, K. Comparison of different extraction techniques for obtaining extracts from brown seaweeds and their potential effects as angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tiller, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, C.; Girouard, G.S.; Dennis, D.; Barrow, C.J.; Miao, M.; Ewart, H.S. Antidiabetic properties of polysaccharide- and polyphenolic-enriched fractions from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 85, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.V.; Walsh, N.A. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of extracts from a variety of edible seaweeds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantidos, N.; Boath, A.; Lund, V.; Conner, S.; McDougall, G.J. Phenolic-Rich extracts from the edible seaweed, ascophyllum nodosum, inhibit α-amylase and α-glucosidase: Potential anti-hyperglycemic effects. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.T.H.; Bangoura, I.; Kang, J.Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Joo, J.; Choi, Y.S.; Hwang, D.S.; Hong, Y.K. Comparison of ecklonia cava, ecklonia stolonifera and eisenia bicyclis for phlorotannin extraction. J. Environ. Biol. 2014, 35, 713–719. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, G.; Sousa, C.; Silva, L.R.; Pinto, E.; Andrade, P.B.; Bernardo, J.; Mouga, T.; Valentão, P. Can phlorotannins purified extracts constitute a novel pharmacological alternative for microbial infections with associated inflammatory conditions? PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parys, S.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Glombitza, K.W.; Carmeli, S.; Klimo, K.; Gerhäuser, C.; König, G.M. In vitro chemopreventive potential of fucophlorethols from the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus L. by anti-oxidant activity and inhibition of selected cytochrome P450 enzymes. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, R.; Chitra, L.; Penislusshiyan, S.; Palvannan, T. Exploring bioactive fraction of Sargassum wightii: In vitro elucidation of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibition and antioxidant potential. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.; Silva, A.; Mateus, N.; Cardoso, S. Optimization of phlorotannins extraction from fucus vesiculosus and evaluation of their potential to prevent metabolic disorders. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, M.S.; Smyth, T.J.; Rai, D.K.; Soler-Vila, A.; Croft, A.K.; Brunton, N. Enrichment of polyphenol contents and antioxidant activities of Irish brown macroalgae using food-friendly techniques based on polarity and molecular size. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, K.S.; Aznar, R.; O’Donnell, C.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound technology for the extraction of biologically active molecules from plant, animal and marine sources. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Sousa, S.; Silva, A.; Amorim, M.; Pereira, L.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Gomes, A.M.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Freitas, A.C. Impact of enzyme- and ultrasound-assisted extraction methods on biological properties of red, brown, and green seaweeds from the Central West Coast of Portugal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3177–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Ummat, V.; Tiwari, B.; Rajauria, G. Exploring ultrasound, microwave and ultrasound–microwave assisted extraction technologies to increase the extraction of bioactive compounds and antioxidants from brown macroalgae. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gligor, O.; Mocan, A.; Moldovan, C.; Locatelli, M.; Crișan, G.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Enzyme-Assisted extractions of polyphenols—A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniaud-Bouët, E.; Kervarec, N.; Michel, G.; Tonon, T.; Kloareg, B.; Hervé, C. Chemical and enzymatic fractionation of cell walls from Fucales: Insights into the structure of the extracellular matrix of brown algae. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, G.; Czjzek, M. Polysaccharide-Degrading enzymes from marine bacteria. In Marine Enzymes for Biocatalysis: Sources, Biocatalytic Characteristics and Bioprocesses of Marine Enzymes; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2013; pp. 429–464. ISBN 9781907568800. [Google Scholar]
- Ihua, M.W.; Guihéneuf, F.; Mohammed, H.; Margassery, L.M.; Jackson, S.A.; Stengel, D.B.; Clarke, D.J.; Dobson, A.D.W. Microbial population changes in decaying ascophyllum nodosum result in macroalgal-polysaccharide-degrading bacteria with potential applicability in enzyme-assisted extraction technologies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardouin, K.; Bedoux, G.; Burlot, A.S.; Donnay-Moreno, C.; Bergé, J.P.; Nyvall-Collén, P.; Bourgougnon, N. Enzyme-Assisted extraction (EAE) for the production of antiviral and antioxidant extracts from the green seaweed Ulva armoricana (Ulvales, Ulvophyceae). Algal Res. 2016, 16, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeena, S.F.; Alagarsamy, S.; Sattari, Z.; Al-Haddad, S.; Fakhraldeen, S.; Al-Ghunaim, A.; Al-Yamani, F. Enzyme-Assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from brown seaweeds and characterization. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 615–629. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, C.-B.; Park, P.-J.; Je, J.-Y. Preparation and biological evaluation of enzyme-assisted extracts from edible seaweed (Enteromorpha prolifera) as antioxidant, anti-acetylcholinesterase and inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in murine macrophages. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Camargo, A.D.P.; Montero, L.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Tanniou, A.; Cifuentes, A.; Herrero, M.; Ibáñez, E. Considerations on the use of enzyme-assisted extraction in combination with pressurized liquids to recover bioactive compounds from algae. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Zill-e-Huma; Khan, M.K. Applications of ultrasound in food technology: Processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-García, J.L.; Luque De Castro, M.D. Ultrasound: A powerful tool for leaching. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, M.; Gourdon, C. Investigation in solid-liquid extraction: Influence of ultrasound. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 87, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.A.; Vinatoru, M.; Mason, T.J.; Abdel-Azim, N.S.; Aboutabl, E.A.; Hammouda, F.M. A possible general mechanism for ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) suggested from the results of UAE of chlorogenic acid from Cynara scolymus L. (artichoke) leaves. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinatoru, M. An overview of the ultrasonically assisted extraction of bioactive principles from herbs. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2001, 8, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.; Sineiro, J.; Chenlo, F.; Arufe, S.; Díaz-Varela, D. Aqueous extracts of Ascophyllum nodosum obtained by ultrasound-assisted extraction: Effects of drying temperature of seaweed on the properties of extracts. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.; Chenlo, F.; Sineiro, J.; Arufe, S.; Sexto, S. Drying temperature effect on powder physical properties and aqueous extract characteristics of Fucus vesiculosus. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, O.K.; Gokoglu, N.; Yerlikaya, P.; Ucak, I.; Gumus, B. Optimization of antioxidant activity and phenolic compound extraction conditions from red seaweed (Laurencia obtuse). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.T.; Van Vuong, Q.; Schreider, M.J.; Bowyer, M.C.; Van Altena, I.A.; Scarlett, C.J. Optimisation of ultrasound-assisted extraction conditions for phenolic content and antioxidant activities of the alga Hormosira banksii using response surface methodology. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 3161–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Rodríguez, B.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A.; Antunes-Ricardo, M.; Santos-Zea, L.; Cruz-Suárez, L.E. Ultrasound-Assisted extraction of phlorotannins and polysaccharides from Silvetia compressa (Phaeophyceae). J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Clark, J.; Shen, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C. Microwave assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from four economic brown macroalgae species and evaluation of their antioxidant activities and inhibitory effects on α-amylase, α-glucosidase, pancreatic lipase and tyrosinase. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, M.; Yuen, A.K.L.; Zhang, R.; Wright, J.T.; Taylor, R.B.; Maschmeyer, T.; de Nys, R. A comparative assessment of microwave assisted (MAE) and conventional solid-liquid (SLE) techniques for the extraction of phloroglucinol from brown seaweed. Algal Res. 2017, 23, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, G. Preparation and antioxidant property of extract and semipurified fractions of Caulerpa racemosa. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.T.; Bowyer, M.C.; Van Altena, I.A.; Scarlett, C.J. Optimum conditions of microwave-assisted extraction for phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of the brown alga Sargassum vestitum. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.; Diop, A.; Rainville, L.-C.; Barnabé, S. Bioextracting polyphenols from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum from Québec’s North Shore Coastline. Ind. Biotechnol. 2019, 15, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, P.; Rezaei, M.; Shaviklo, A.R. The optimum conditions for the extraction of antioxidant compounds from the Persian gulf green algae (Chaetomorpha sp.) using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2974–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.; O’Donnell, C.; Rai, D.; Hossain, M.; Burgess, C.; Walsh, D.; Tiwari, B. Laminarin from Irish Brown Seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum and Laminaria hyperborea: Ultrasound assisted extraction, characterization and bioactivity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4270–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kang, M.C.; Moon, S.H.; Jeon, B.T.; Jeon, Y.J. Potential use of ultrasound in antioxidant extraction from Ecklonia cava. Algae 2013, 28, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, A.T.; Chun, B.S. Influence of hydrothermal process on bioactive compounds extraction from green coffee bean. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 38, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; Sánchez-Camargo, A.d.P.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E. Plants, seaweeds, microalgae and food by-products as natural sources of functional ingredients obtained using pressurized liquid extraction and supercritical fluid extraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; López-Martínez, M.I.; García-Risco, M.R. Application of pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) to obtain bioactive fatty acids and phenols from Laminaria ochroleuca collected in Galicia (NW Spain). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.; Marina, M.L. Pressurized hot water extraction of bioactives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangestuti, R.; Getachew, A.T.; Siahaan, E.A.; Chun, B.S. Characterization of functional materials derived from tropical red seaweed Hypnea musciformis produced by subcritical water extraction systems. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gereniu, C.R.N.; Saravana, P.S.; Getachew, A.T.; Chun, B.-S. Characteristics of functional materials recovered from Solomon Islands red seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) using pressurized hot water extraction. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, B.; Yu, C.; Xu, Y. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenols from enteromorpha prolifra by orthogonal test. Chin. Herb. Med. 2010, 2, 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, E.; Zhang, Y. Supercritical fluid extraction of flavonoids from Maydis stigma and its nitrite-scavenging ability. Food Bioprod. Process. 2011, 89, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messyasz, B.; Michalak, I.; Łęska, B.; Schroeder, G.; Górka, B.; Korzeniowska, K.; Lipok, J.; Wieczorek, P.; Rój, E.; Wilk, R.; et al. Valuable natural products from marine and freshwater macroalgae obtained from supercritical fluid extracts. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, M.K.; Uddin, M.S.; Chun, B.S. Extraction of fucoxanthin and polyphenol from Undaria pinnatifida using supercritical carbon dioxide with co-solvent. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2008, 13, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina, M.; Castro-Vargas, H.I.; Parada-Alfonso, F. Antioxidant capacity of Colombian seaweeds: 1. Extracts obtained from Gracilaria mammillaris by means of supercritical fluid extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 128, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klejdus, B.; Lojková, L.; Vlcek, J. Hyphenated solid phase extraction/supercritical fluid extraction methods for extraction of phenolic compounds from algae. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2014, 10, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, E.; Moure, A.; Domínguez, H. Supercritical CO2 extraction of fatty acids, phenolics and fucoxanthin from freeze-dried Sargassum muticum. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corato, U.; Salimbeni, R.; De Pretis, A.; Avella, N.; Patruno, G. Antifungal activity of crude extracts from brown and red seaweeds by a supercritical carbon dioxide technique against fruit postharvest fungal diseases. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2017, 131, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaëlle, T.; Serrano Leon, E.; Laurent, V.; Elena, I.; Mendiola, J.A.; Stéphane, C.; Nelly, K.; Stéphane, L.B.; Luc, M.; Valérie, S.P. Green improved processes to extract bioactive phenolic compounds from brown macroalgae using Sargassum muticum as model. Talanta 2013, 104, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.N.; Getachew, A.T.; Haque, A.S.M.T.; Saravana, P.S.; Cho, Y.J.; Nkurunziza, D.; Chun, B.S. Physicochemical characterization and deodorant activity of essential oil recovered from Asiasarum heterotropoides using supercritical carbon dioxide and organic solvents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 69, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Das, S.; Bhattacharjee, P. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of eugenol-rich fraction from Ocimum sanctum Linn and a comparative evaluation with other extraction techniques: Process optimization and phytochemical characterization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 47, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, R.; Bueno, M.; Herrero, M. Sub- and supercritical fluid extraction of bioactive compounds from plants, food-by-products, seaweeds and microalgae—An update. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Pintos, N.; Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Buschmann, A.H.; Vergara-Salinas, J.R.; Pérez-Correa, J.R.; Saura-Calixto, F. Macromolecular antioxidants and dietary fiber in edible seaweeds. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo Dinh, T.; Saravana, P.S.; Woo, H.C.; Chun, B.S. Ionic liquid-assisted subcritical water enhances the extraction of phenolics from brown seaweed and its antioxidant activity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 196, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, N.; Smyth, T.J.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Soler-Vila, A.; Brunton, N. Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of pressurised liquid and solid-liquid extracts from four Irish origin macroalgae. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, M.S.; Smyth, T.J.; Hayes, M.; Soler-Vila, A.; Croft, A.K.; Brunton, N. Influence of pressurised liquid extraction and solid-liquid extraction methods on the phenolic content and antioxidant activities of Irish macroalgae. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Týskiewicz, K.; Konkol, M.; Rój, E. The application of supercritical fluid extraction in phenolic compounds isolation from natural plant materials. Molecules 2018, 23, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lebovka, N.; Marchal, L.; Vorobiev, E.; Grimi, N. Pulsed electric energy and ultrasonication assisted green solvent extraction of bio-molecules from different microalgal species. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 62, 102358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, T.; Frey, W.; Sack, M.; Haberl Meglič, S.; Peterka, M.; Miklavčič, D. Electroporation-Based applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.M.R.; Genisheva, Z.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Rodrigues, R.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pereira, R.N. Electric field-based technologies for valorization of bioresources. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, K.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Kwon, J.-H. Green extraction methods for polyphenols from plant matrices and their byproducts: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.-G.; He, L.; Xi, J. High intensity pulsed electric field as an innovative technique for extraction of bioactive compounds—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2877–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaosa, Y.; Wang, T. High performance centrifugal partition chromatographic separation of alkaline earth metal ions with bis-2-ethylhexylphosphinic acid. J. Sep. Sci. 2003, 26, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.Y.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.; Jeon, Y.J. Preparative isolation and purification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava using centrifugal partition chromatography by one-step. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.Y.; Samarakoon, K.; Oh, J.Y.; Heo, S.J.; Kim, C.Y.; Nah, J.W.; Jang, M.K.; Lee, J.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Preparative isolation of sargachromanol E from Sargassum siliquastrum by centrifugal partition chromatography and its anti-inflammatory activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.Y.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, C.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Nah, J.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Efficient approach to purification of octaphlorethol A from brown seaweed, Ishige foliacea by centrifugal partition chromatography. Algal Res. 2017, 22, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kori, S.; Parmar, A. Surfactant mediated extraction of total phenolic contents (TPC) and antioxidants from fruits juices. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümüş Yılmaz, G.; Gómez Pinchetti, J.L.; Cifuentes, A.; Herrero, M.; Ibáñez, E. Comparison of extraction techniques and surfactants for the isolation of total polyphenols and phlorotannins from the brown algae lobophora variegata. Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 2724–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Qiu, H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S. 1-Hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquid as a new cationic surfactant for separation of phenolic compounds by MEKC. Chromatographia 2009, 69, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Ferreira, A.M.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Optimization of the gallic acid extraction using ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.Y.; Xiao, X.H.; Luo, X.J.; Li, G.K. Application of ionic liquids in the microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenolic compounds from medicinal plants. Talanta 2009, 78, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. Ionic liquids based simultaneous ultrasonic and microwave assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from burdock leaves. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 716, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Zhu, T.; Row, K.H. Ultrasonic extraction of phenolic compounds from laminaria japonica aresch using ionic liquid as extraction solvent. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 2212–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal-Abidin, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Jayakumar, N.S. New horizons in the extraction of bioactive compounds using deep eutectic solvents: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 979, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.F.; Wang, X.Q.; Peng, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Fu, Y.J. Fast and green extraction and separation of main bioactive flavonoids from Radix Scutellariae. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 63, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as a new extraction media for phenolic metabolites in carthamus tinctorius L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Qi, X.; Li, T.; Luo, M.; Wang, W.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y. Application of natural deep eutectic solvents for extraction and determination of phenolics in Cajanus cajan leaves by ultra performance liquid chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesgas-Ramón, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of deep eutectic solvents (DES) for phenolic compounds extraction: Overview, challenges, and opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Sharma, M.; Mondal, D.; Prasad, K. Deep eutectic solvents as efficient solvent system for the extraction of κ-carrageenan from Kappaphycus alvarezii. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwal, T.; Chemat, F.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Cravotto, G.; Jaiswal, D.K.; Bhatt, I.D.; Devkota, H.P.; Luo, Z. Recent advances in scaling-up of non-conventional extraction techniques: Learning from successes and failures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Seaweed Type | State of the Seaweed (Wet/Dry/Particle Size) | Type of Enzyme Used | Extraction Conditions Enzyme Conc./Temperature (°C)/Time (min)/pH | Yield (mg GAE/g DW) | Application of the Extract | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sargassum boveanum, Sargassum angustifolium Padina gymnospora, Canistrocarpus cervicornis Colpomenia sinuosa, Iyengaria stellata Feldmannia irregularis | Freeze dried/powdered | Viscozyme AMG 300 L Cellucclast Termamyl Ultraflo L Flavourzyme Alcalase Neutrase | 0.1%/50/1200/4.5 0.1%/60/1200/4.5 0.1%/50/1200/4.5 0.1%/60/1200/6 0.1%/40/1200/6 0.1%/50/1200/7 0.1%/50/1200/8 0.1%/50/1200/8 | 32.4–74.8 * 50.0–84.0 22.3–63.8 26.1–43.0 16.7–32.0 9.5–38.4 28.2–82.5 | Antioxidant Antimicrobial | [46] |
| Lessonia nigrescens Macrocystis pyrifera Durvillaea antarctica | Air dried/powdered (100 µm) | Cellulase α-Amylase | 10%/50/1020/4.5 | 17.38–19.31 21.3 ~13 | Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) activity | [28] |
| Enteromorpha prolifera | Dried/pulverized | AMG 300 L Celluclast Dextrozyme, Maltogenase, Promozyme, Viscozyme Termamyl Alcalase Flavourzyme Neutrase Protamex | 2% (w/w, DW)/-/480/- | 2.47 1.5 2.02 1.24 1.83 2.53 2.02 8.44 6.43 6.98 1.83 | Antioxidant Anti-acetylcholinesterase Anti-Inflammatory | [47] |
| Sargassum muticum, Osmundea pinnatifida Codium tomentosum | Oven dried (60 °C)/Powdered (<1.0 mm) | Alcalase Flavourzyme Cellulase Viscozyme L | 5% (w/w, DW)/50/8.0 5% (w/w, DW)/50/7.0 5% (w/w, DW)/50/4.5 5% (w/w, DW)/50/4.5 | 0.2–0.3 mg CE/g LE 0.1–0.12 mg CE/g LE 0.11–0.16 mg CE/g LE | Antioxidant Antidiabetic | [39] |
| Ulva armoricana | Wet/grounded | Neutral endo-protease A mix of neutral and alkaline endo-proteases A multiple-mix of carbohydrases Mix of endo-1,4-β-xylanase/endo-1,3(4)-β-glucanase Cellulase Exo-β-1,3(4)-glucanase | 6% (w/w, DW)/50/240/6.2 | 9 11 7 6 4 7 | Antioxidant and antiviral | [45] |
| Seaweed Type | State of the Seaweed (Wet/Dry/Particle Size) | Extraction Conditions Power (W)/Temperature (°C)/Time (min) | Solvent Used | Yield (TPC mg GAE/g DW) | Application of the Extract | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascophyllum nodosum, Laminaria hyperborea | Freeze dried/powdered | 750/-/15 | Distilled water | 0.365 mg PGE/g DW 0.156 mg PGE/g DW | Antioxidant | [65] |
| Ecklonia cava | Far infrared radiation dried (40 °C)/grounded (300 µm) | 200/30/720 | Water Methanol: water 50:50 Methanol | 47.7 63.5 57.9 | Antioxidant | [66] |
| Laurencia obtuse | Oven dried (50 °C)/Powdered (1.55 mm) | 250/30–50/30–60 | 95% ethanol | 26.23 | Antioxidant | [56] |
| Hormosira banksii | Freeze dried/powdered (≤0.6 mm) | 150–200/30–50/20–60 | 70% (v/v) Ethanol | 23.12 | Antioxidant | [57] |
| Sargassum muticum, Osmundea pinnatifida, Codium tomentosum | Oven dried (60 °C)/powdered (<1.0 mm) | 400/50/60 | Deionized water | 235.0 ± 5.57 µg CE/g LE 103.7 ± 1.67 µg CE/g LE 141.1 ± 9.79 µg CE/g LE | antioxidant | [39] |
| Seaweed Type | State of the Seaweed (Wet/Dry/Particle Size) | Extraction Conditions Power (W) Temperature (°C)/Time (min) | Solvent Used/Solid:Solvent Ratio (g/mL) | Yield * (TPC mg GAE/g DW) | Application of the Extract | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sargassum vestitum | Freeze dried/powdered (≤600 µm) | 720–1200/-/0.42–1.25 | Ethanol: water (30–70%)/1:50 | 58.2 | Antioxidant | [62] |
| Cystoseira sedoides | Shade dried/Powdered (200–500 µm) | -/-/0.17–3 | Ethanol: water (0–100%)/1:10–1:60 | 0.38 mg PGE/g DW | Anticancer Activity | [27] |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | Oven dried/Powdered (1 mm) | 250,600,1000/-/2–5 | 0.1 M HCl/1:10 | 17.9 | Antioxidant | [40] |
| Chaetomorpha sp. | Shade dried/powdered (60µm) | 200–600/-/4–12 | Acetone: water (0–100%)/1:20 | 0.98 mg TAE/g DW | [64] | |
| Enteromorpha prolifera | Shade dried (40 °C)/powdered | 300–700/-/5–40 (1–4 cycles) | Ethanol: water (10–60%)/1:10–1:35 | 0.923 | Antioxidant | [73] |
| Saccharina japonica | Dried/powdered (40 µm) | 400–600/45–65/5–25 | Ethanol: water (50–70%)/1:8–1:12 | 0.644 mg PGE/g DW | Inhibitory effects on HepG2 cancer cells | [26] |
| Caulerpa racemose | Oven dried (35 ± 2 °C)/Powdered | 100–600/20–70/5–60 | Ethanol: water (20–100%)/1:10–1:50 | 6.8 | Antioxidant | [61] |
| Seaweed Type | State of the Seaweed (Wet/Dry/Particle Size) | Extraction Solvent | Extraction Temperature (°C)/Pressure (MPa)/Time (min) | Solid: Liquid Ratio (g/mL) | Yield (mg GAE/g DW) | Application of the Extract | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sargassum muticum | Freeze dried/powdered (250 µm) | Ethanol: water (25:75, and 75:25) | 120/10.3/20 | 1:5 | 101.8 | Antioxidant | [81] |
| Gracilaria chilensis | Oven dried (50 °C)/Powdered (0.5 mm) | Water | 100/-/5 (3 extraction cycles) 150/-/5 (3 extraction cycles) 200/-/30 (3 extraction cycles) | - | 2.06 0.78 10.17 | Antioxidant | [85] |
| Saccharina japonica | Freeze dried/Powdered (710 µm) | Water + 0.25 M 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate | 175/5/5 | 1:32 | 58.92 mg PGE/g DW | Antioxidant | [86] |
| Laminaria ochroleuca | Freeze dried/Powdered (<500 µm) | Hexane Ethyl Acetate Ethanol Ethanol: Water (1:1) | 80,120,160/10/10 | 1:20 | 6 - 83 173.65 | Bioactive | [69] |
| Fucus serratus, Laminaria digitata, Gracilaria gracilis, Codium fragile | Freeze dried/powdered | Ethanol: water (80:20) Methanol: water (70:30) Ethanol: water (80:20) Methanol: water (70:30) Ethanol: water (80:20) Methanol: water (70:30) Ethanol: water (80:20) Methanol: water (70:30) | 100/6.9/25 90/6.9/25 100/6.9/25 90/6.9/25 100/6.9/25 90/6.9/25 100/6.9/25 90/6.9/25 | - | 75.96 80.70 1.39 2.93 2.40 0.93 4.76 5.36 | Antioxidant | [87] |
| Ascophyllum nodosum, Pelvetia canaliculata, Fucus spiralis Ulva intestinalis | Freeze dried/powdered | Water Ethanol: water (80:20) Acetone: water (80:20) Water Ethanol: water (80:20) Acetone: water (80:20) Water Ethanol: water (80:20) Acetone: water (80:20) Water Ethanol: water (80:20) Acetone: water (80:20) | 120/10.3/60 120/10.3/60 60/6.9/60 120/10.3/60 120/10.3/60 60/6.9/60 120/10.3/60 120/10.3/60 60/6.9/60 120/10.3/60 120/10.3/60 60/6.9/60 | - | 70.4 mg PGE/g DW 66.26 155.95 41.13 40.07 168.82 90.79 124.30 204.40 33.75 20.95 48.56 | Antioxidant | [88] |
| Seaweed Type | State of the Seaweed (wet/dry/particle size) | Co-Solvent Used/Co-Solvent Flow Rate (mL/min/%CO2 flow rate) | Extraction Conditions Temperature (°C)/Pressure (MP)/CO2 Flow Rate (g/min)/Time | Yield (mg GAE/g DW) | Application of the Extract | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gracilaria mammillaris | Vacuum oven dried (45 °C)/Powdered (0.15–0.6 mm) | Ethanol (2–8%, w/w) | 40–60/15–30/6.7/240 | 3.79 | Antioxidant | [77] |
| Sargassum muticum | Freeze dried/powdered (250 µm) | Ethanol (12% w/w) | 60/15.2/-/90 | 34.5 mg PGE/g DE | Antioxidant | [81] |
| Sargassum muticum | Freeze dried/Powdered (<0.5 mm) | Ethanol (0.5–10%, w/w) | 30–50/10–30/25/60 | - | Antioxidant | [79] |
| Undaria pinnatifida | Freeze dried/Powdered (500 µm) | Ethanol/2 | 30–60/10–30/28.17/60 | - | - | [76] |
| Laminaria digitata Undaria pinnatifida Porphyra umbilicalis Eucheuma denticulatum Gelidium pusillum | Dried/Powdered | - | 50/37.9/56.7/120 | 23 mg GAE/g DE 4 3 2 15 | Antifungal | [80] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Getachew, A.T.; Jacobsen, C.; Holdt, S.L. Emerging Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Phenolics: Opportunities and Challenges. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080389
Getachew AT, Jacobsen C, Holdt SL. Emerging Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Phenolics: Opportunities and Challenges. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(8):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080389
Chicago/Turabian StyleGetachew, Adane Tilahun, Charlotte Jacobsen, and Susan Løvstad Holdt. 2020. "Emerging Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Phenolics: Opportunities and Challenges" Marine Drugs 18, no. 8: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080389
APA StyleGetachew, A. T., Jacobsen, C., & Holdt, S. L. (2020). Emerging Technologies for the Extraction of Marine Phenolics: Opportunities and Challenges. Marine Drugs, 18(8), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080389







