Electrochemical Approach for Isolation of Chitin from the Skeleton of the Black Coral Cirrhipathes sp. (Antipatharia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
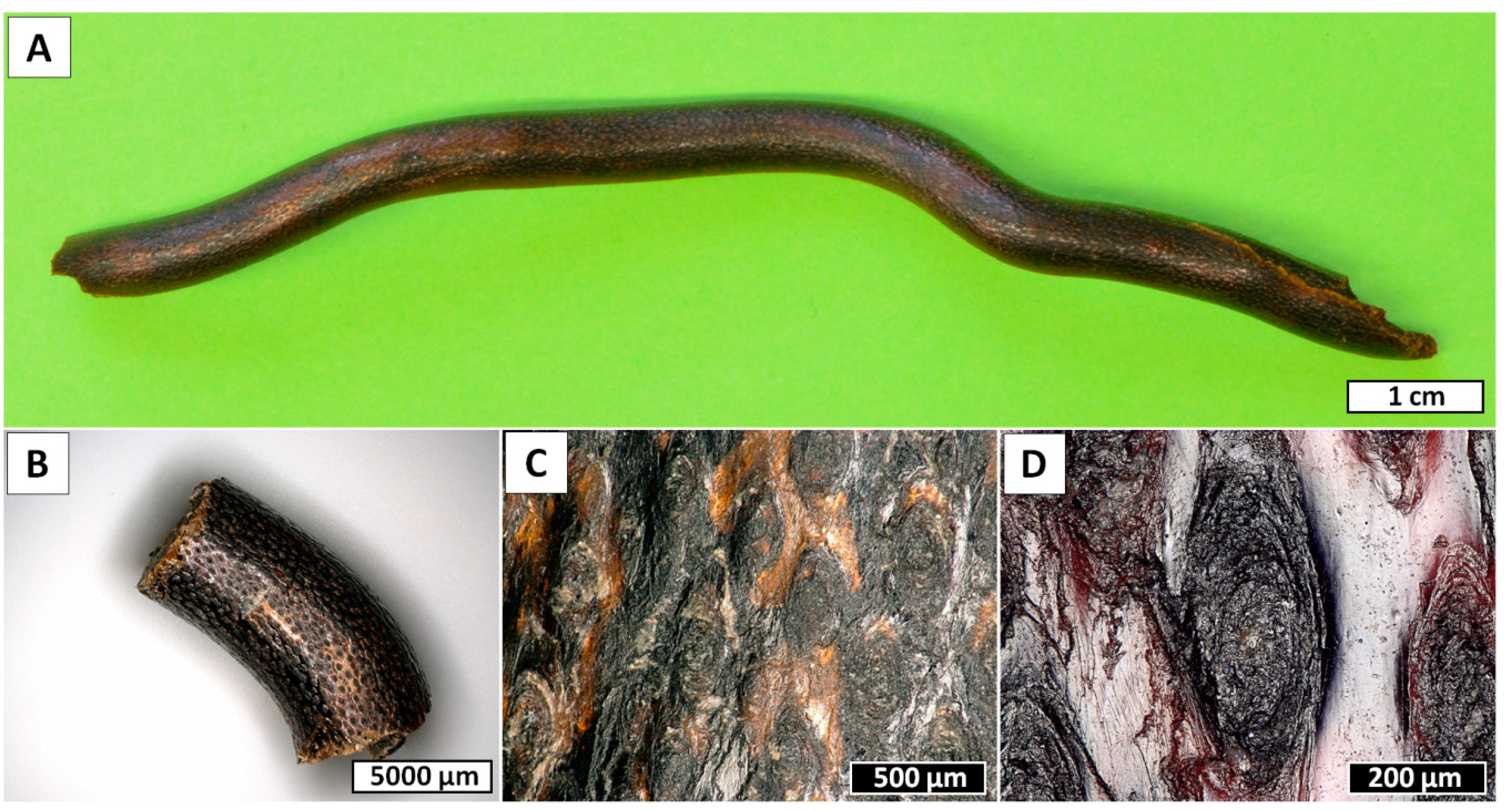
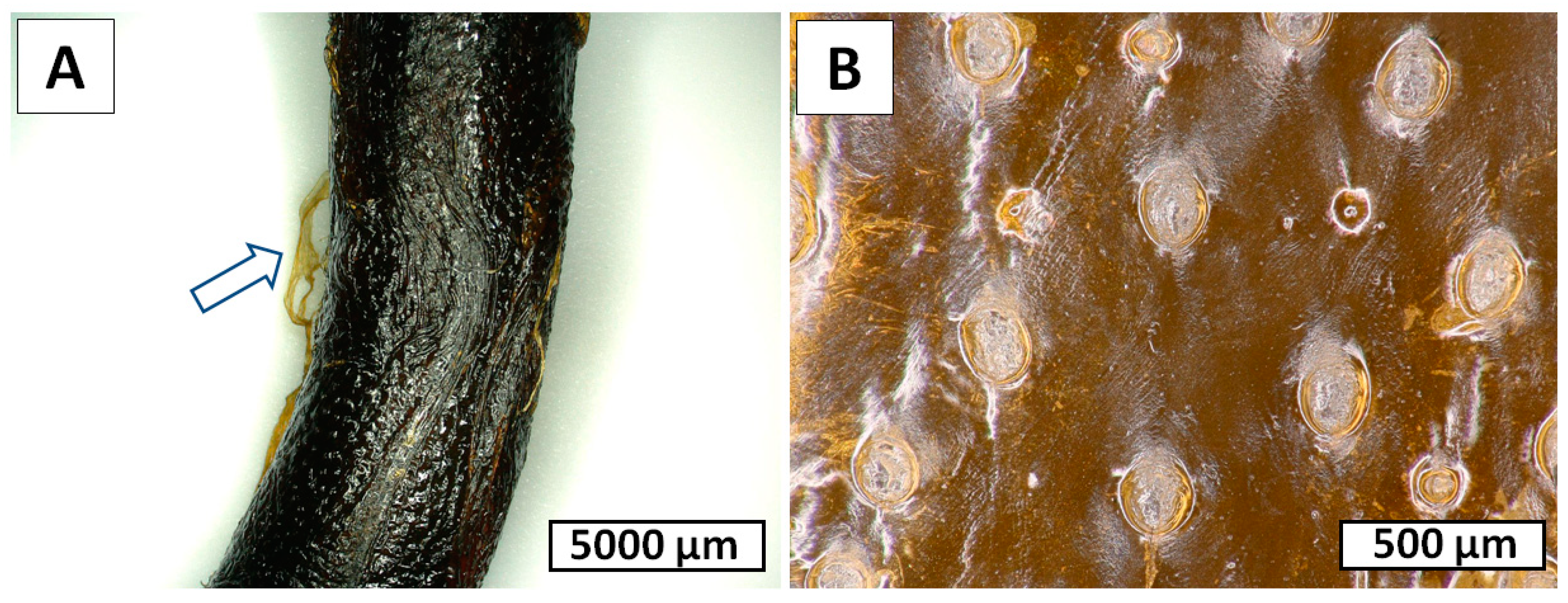
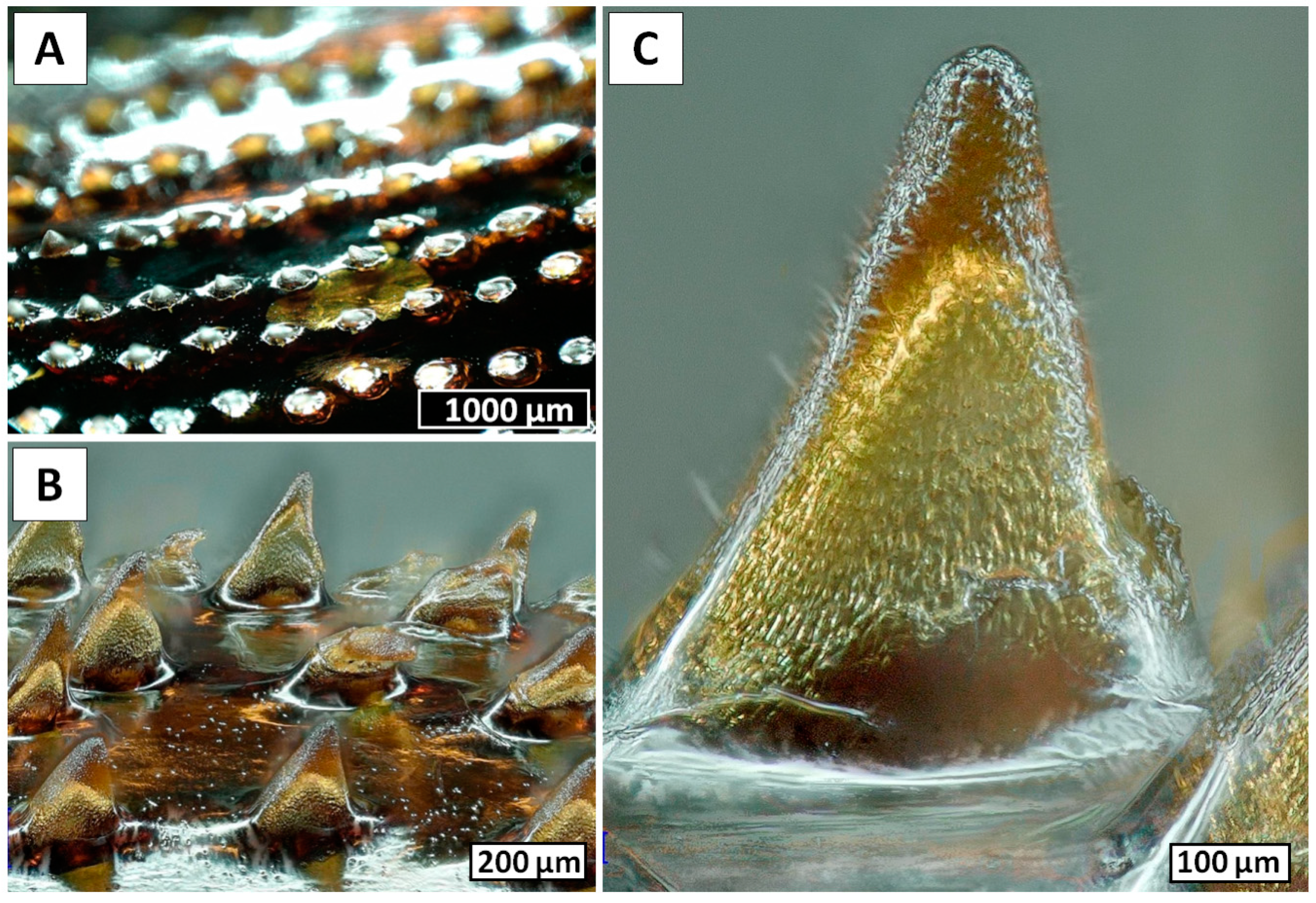
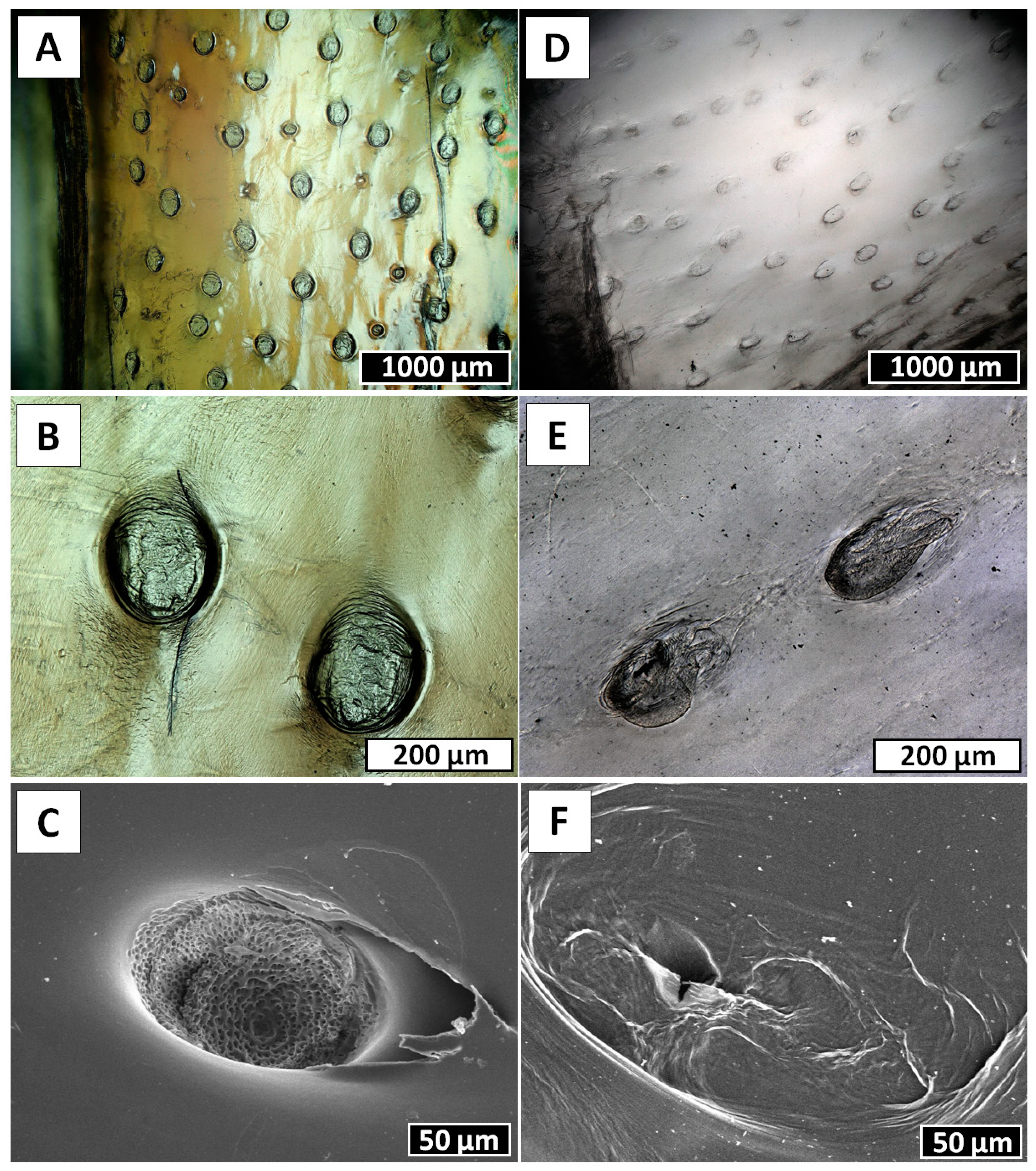
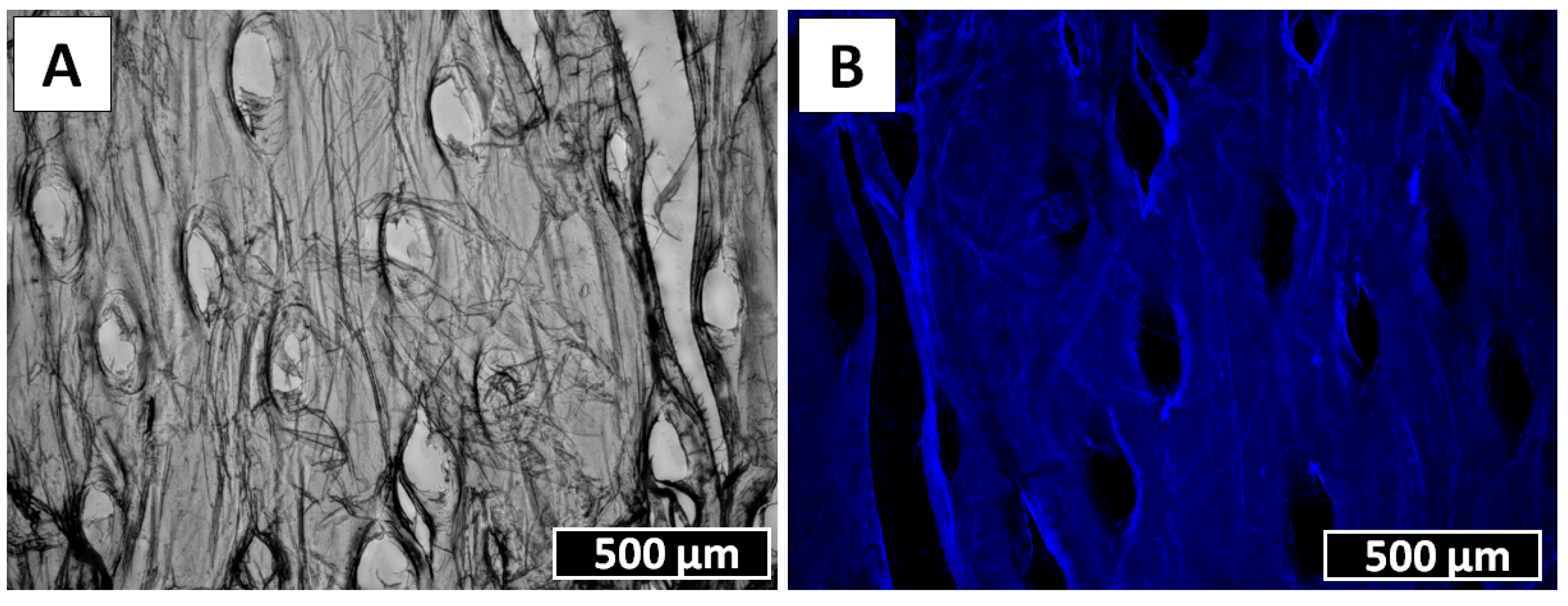
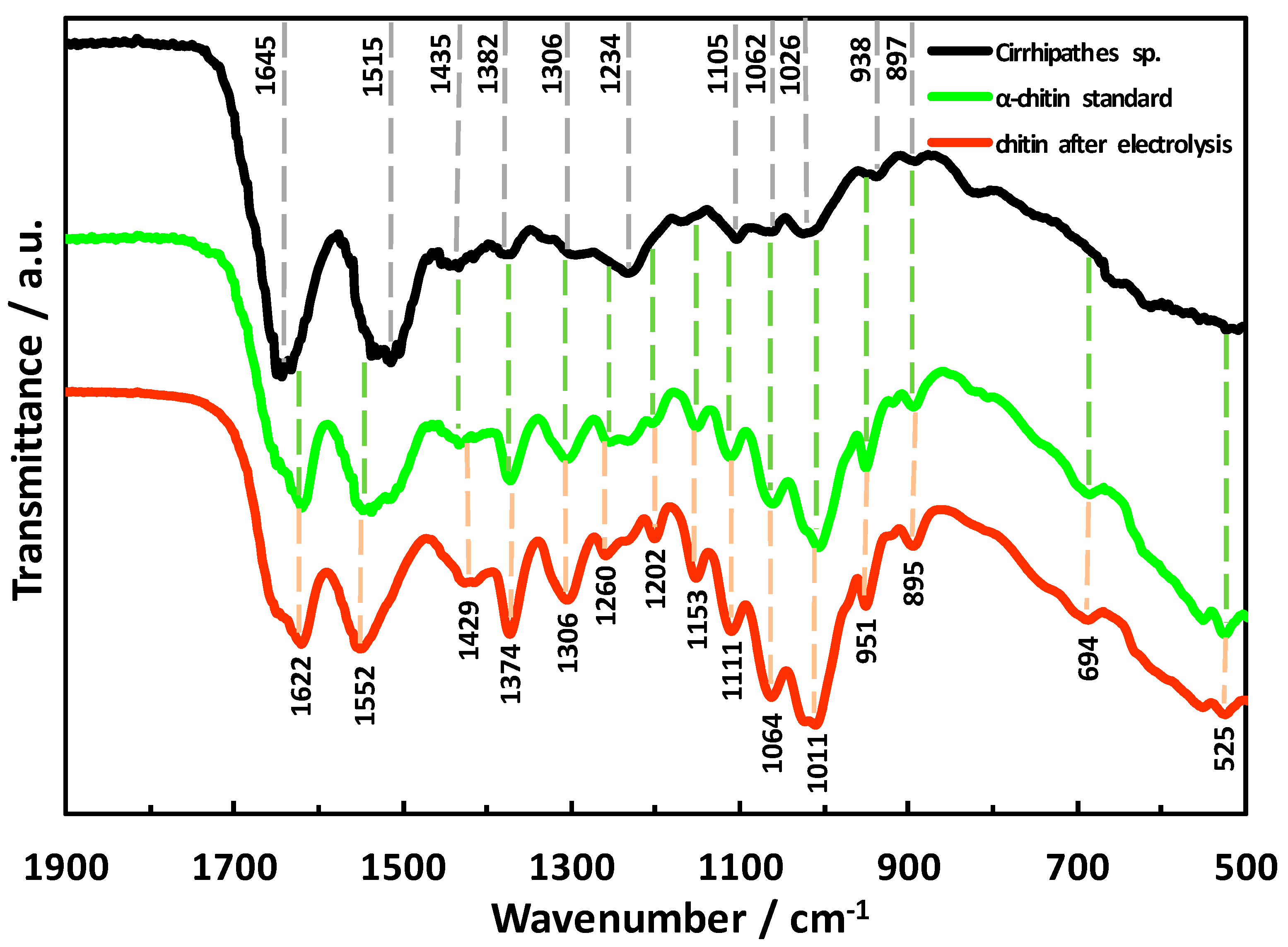
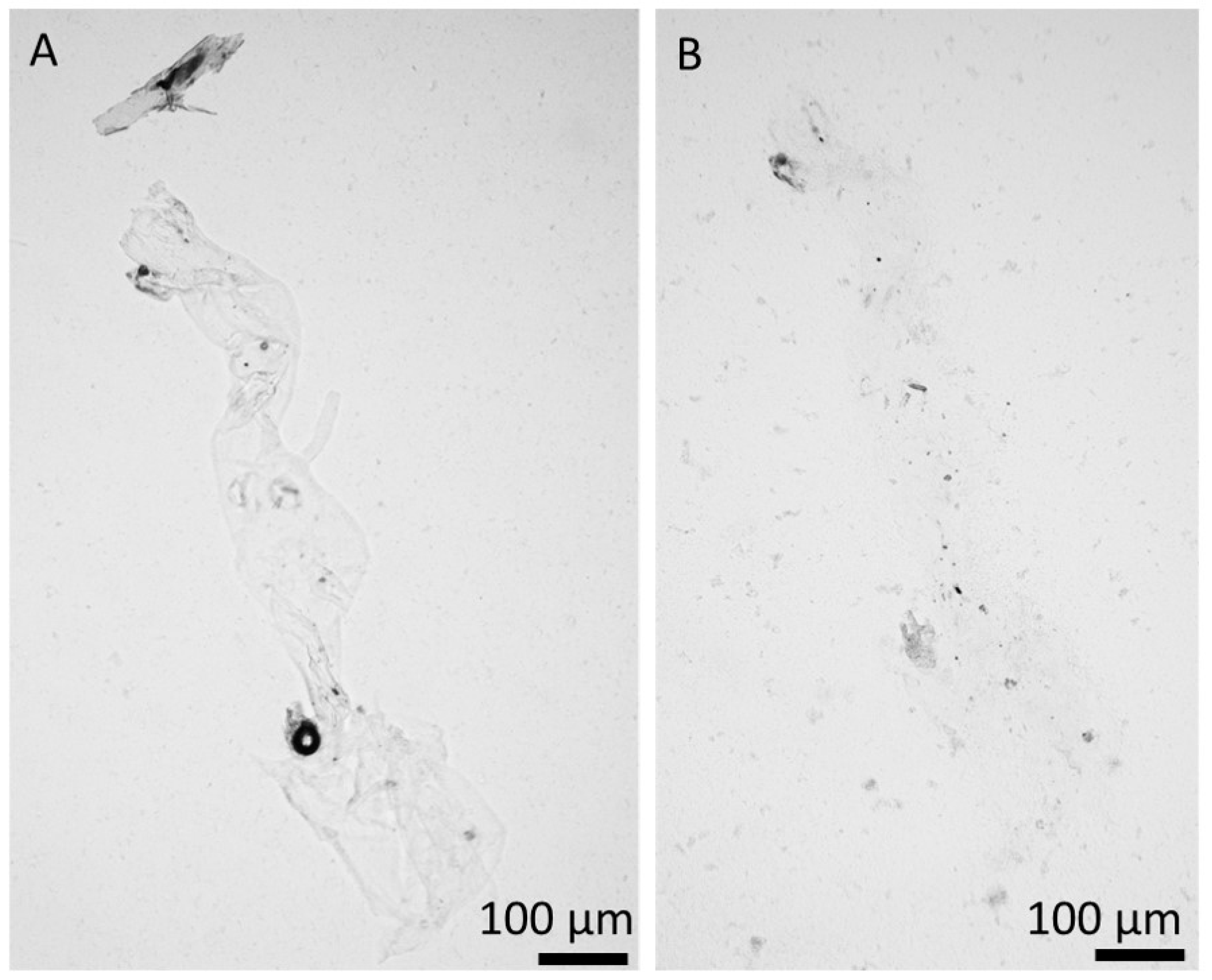
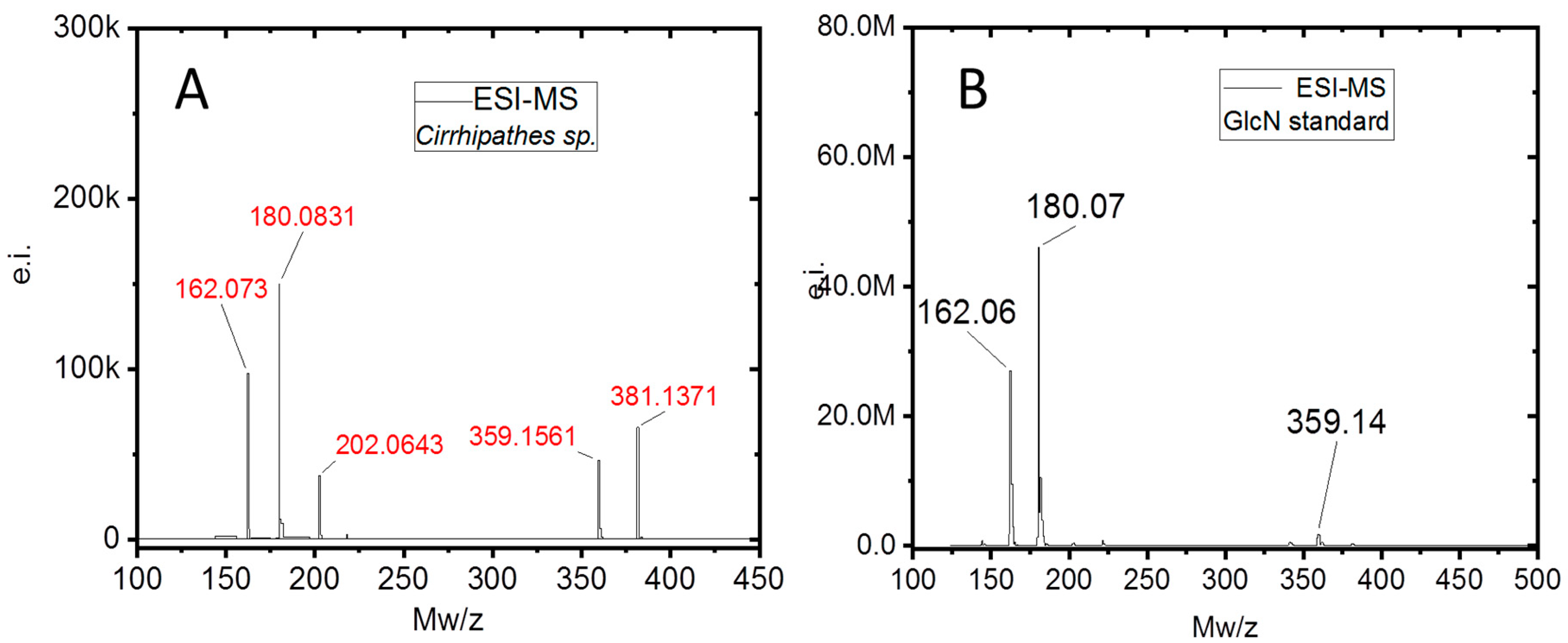
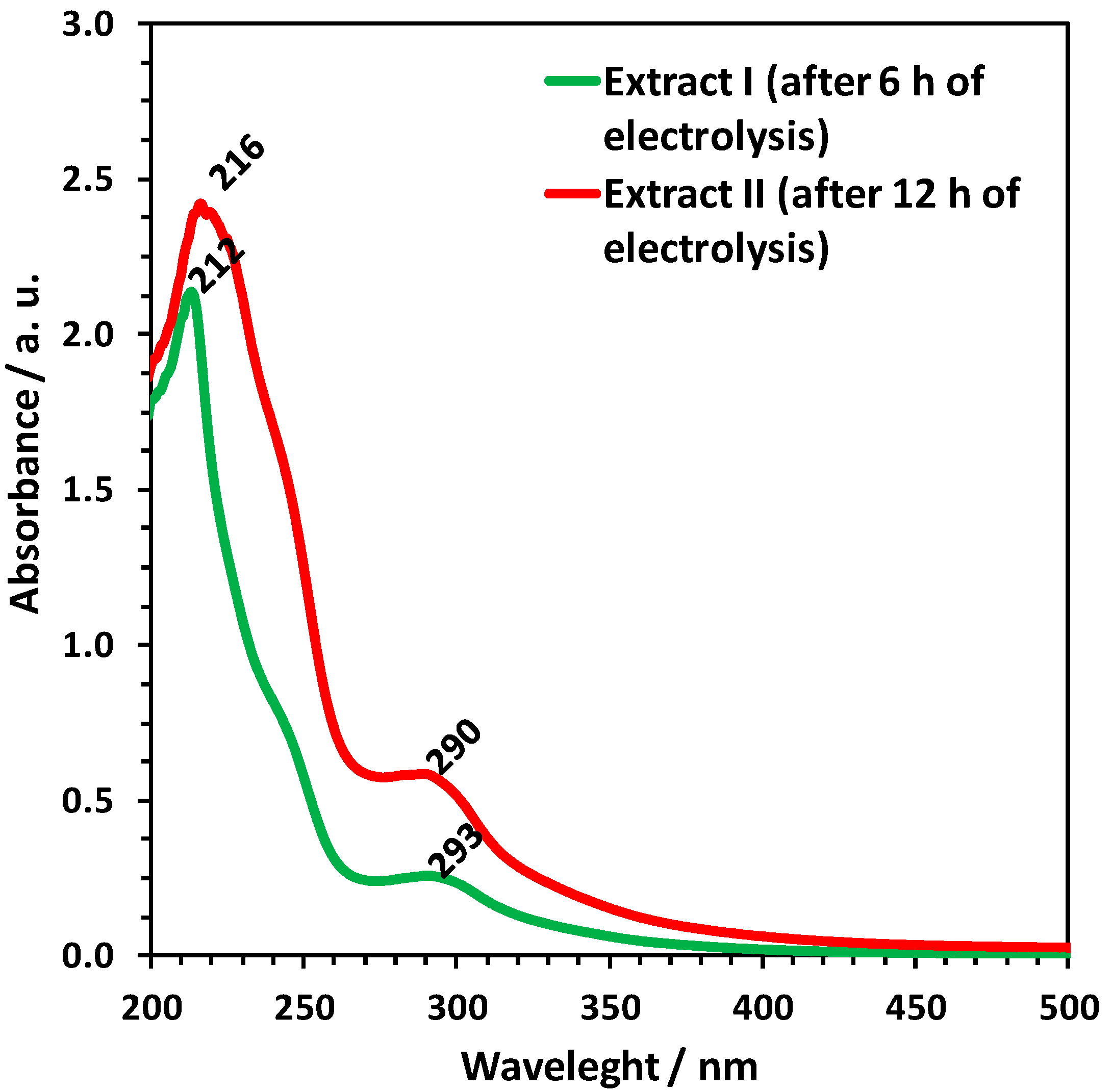
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Samples and Chemicals
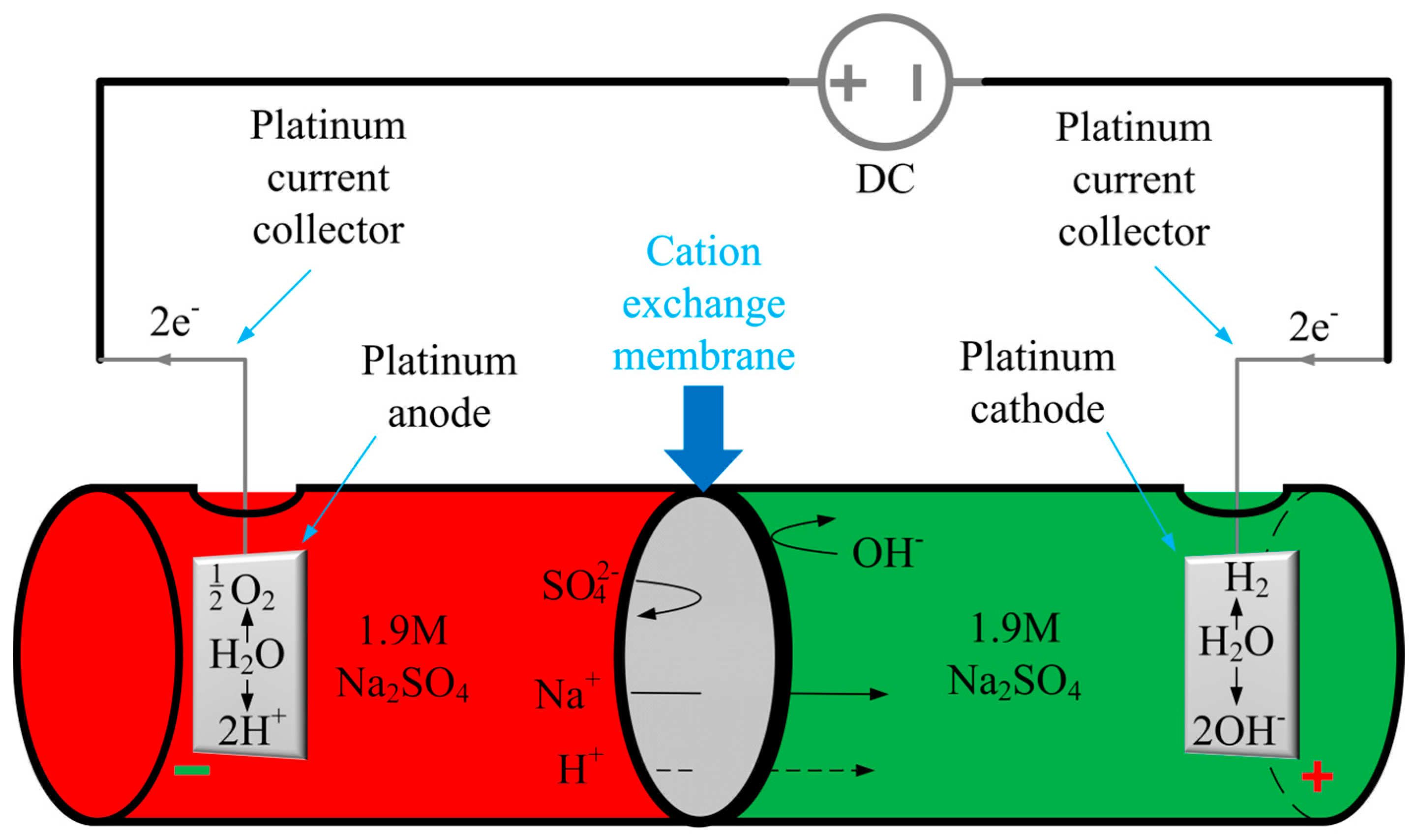
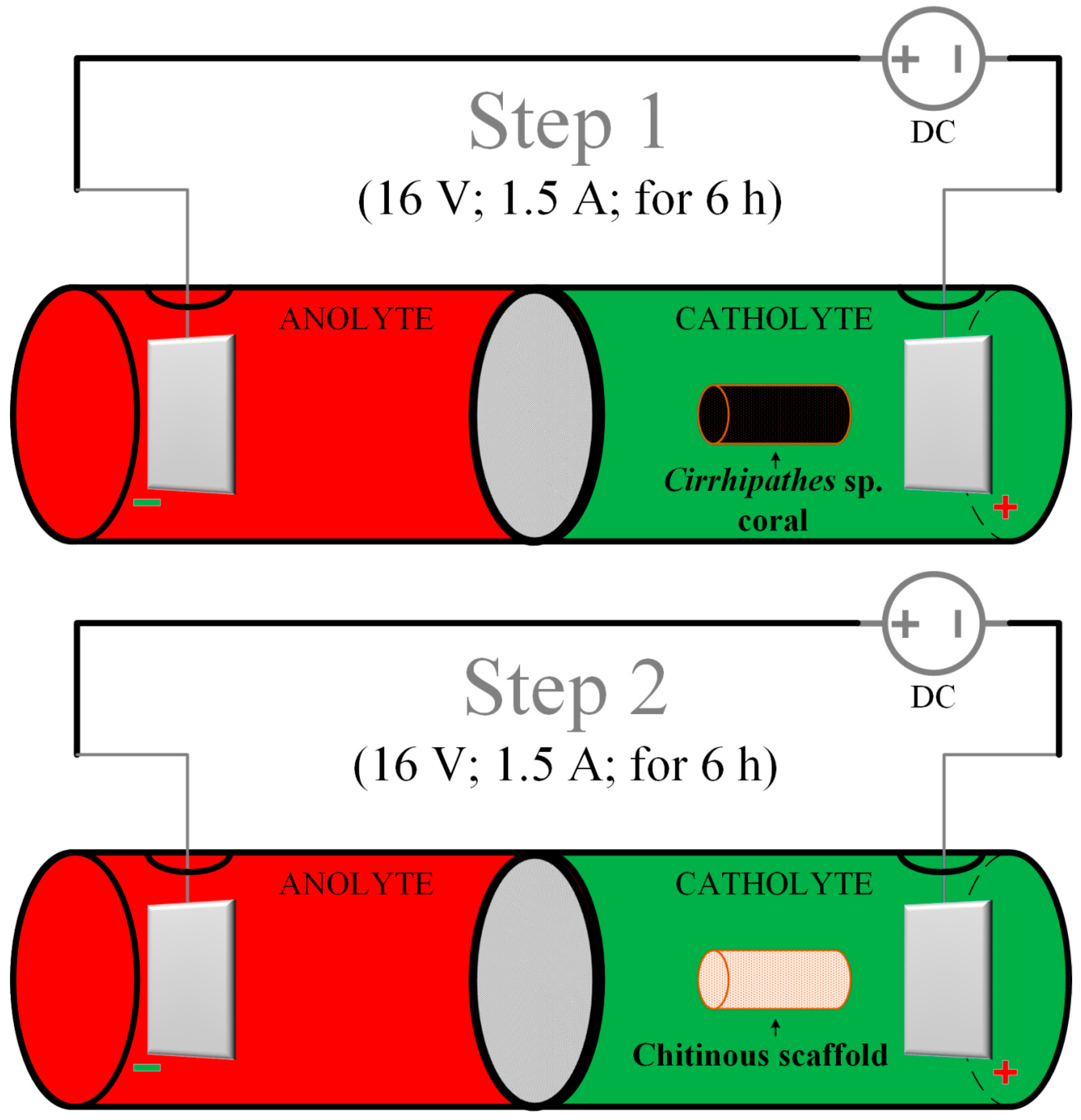
4.2. Electrolytic Cell Setup
4.3. Electrochemically-Assisted Isolation of Chitin
4.4. Calcofluor White Staining
4.5. Chitinase Digestion Test
4.6. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.7. Estimation of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (NAG) Contents
4.8. Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS)
4.9. UV-VIS Spectroscopy
4.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Halfar, J. First evidence of chitin in calcified coralline algae: New insights into the calcification process of Clathromorphum compactum. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, E.; Ehrlich, H.; Schupp, P.; Hedrich, R.; Hunoldt, S.; Kammer, M.; Machill, S.; Paasch, S.; Bazhenov, V.; Kurek, D.; et al. Chitin-based scaffolds are an integral part of the skeleton of the marine demosponge Ianthella basta. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 168, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Maldonado, M.; Spindler, K.-D.; Eckert, C.; Hanke, T.; Born, R.; Goebel, C.; Simon, P.; Heinemann, S.; Worch, H. First evidence of chitin as a component of the skeletal fibers of marine sponges. Part I. Verongidae (demospongia: Porifera). J. Exp. Zoöl. Part B: Mol. Dev. Evol. 2007, 308, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Krautter, M.; Hanke, T.; Simon, P.; Knieb, C.; Heinemann, S.; Worch, H. First evidence of the presence of chitin in skeletons of marine sponges. Part II. Glass sponges (Hexactinellida: Porifera). J. Exp. Zoöl. Part B: Mol. Dev. Evol. 2007, 308, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Ilan, M.; Maldonado, M.; Muricy, G.; Bavestrello, G.; Kljajic, Z.; Carballo, J.L.; Schiaparelli, S.; Ereskovsky, A.; Schupp, P.; et al. Three-dimensional chitin-based scaffolds from Verongida sponges (Demospongiae: Porifera). Part I. Isolation and identification of chitin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Bi, J.; Zhu, F.; Qu, M.; Jiang, C.; Yang, Q. Extraction and Characterization of Chitin from the Beetle Holotrichia parallela Motschulsky. Molecules 2012, 17, 4604–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Seyyar, O.; Baran, T.; Erdogan, S.; Kar, M. A physicochemical characterization of fully acetylated chitin structure isolated from two spider species: With new surface morphology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machałowski, T.; Wysokowski, M.; Tsurkan, M.; Galli, R.; Schimpf, C.; Rafaja, D.; Brendler, E.; Viehweger, C.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Petrenko, I.; et al. Spider Chitin: An Ultrafast Microwave-Assisted Method for Chitin Isolation from Caribena versicolor Spider Molt Cuticle. Molecules 2019, 24, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machałowski, T.; Wysokowski, M.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Bechmann, N.; Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Guan, K.; Bornstein, S.R.; Czaczyk, K.; Pokrovsky, O.; et al. Spider Chitin. The biomimetic potential and applications of Caribena versicolor tubular chitin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolesa, L.D.; Gupta, B.S.; Lee, M.-J. Chitin and chitosan production from shrimp shells using ammonium-based ionic liquids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, K.; Ravichandran, S.; Muralisankar, T.; Uthayakumar, V.; Chandirasekar, R.; Rajeevgandhi, C.; Rajan, D.K.; Seedevi, P. Extraction and characterization of chitin from sea snail Conus inscriptus (Reeve, 1843). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Bazhenov, V.; Debitus, C.; De Voogd, N.; Galli, R.; Tsurkan, M.; Wysokowski, M.; Meissner, H.; Bulut, E.; Kaya, M.; et al. Isolation and identification of chitin from heavy mineralized skeleton of Suberea clavata (Verongida: Demospongiae: Porifera) marine demosponge. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H. Marine Biological Materials of Invertebrate Origin; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Klinger, C.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Wysokowski, M.; Tsurkan, M.; Galli, R.; Petrenko, I.; Machałowski, T.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Martinovic, R.; Muzychka, L.; et al. Express Method for Isolation of Ready-to-Use 3D Chitin Scaffolds from Aplysina archeri (Aplysineidae: Verongiida) Demosponge. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacki, K.; Stępniak, I.; Machałowski, T.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Schimpf, C.; Rafaja, D.; Langer, E.; Richter, A.; Ziętek, J.; et al. Electrochemical method for isolation of chitinous 3D scaffolds from cultivated Aplysina aerophoba marine demosponge and its biomimetic application. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, C.Y.; Tee, Y.B.; Tan, C.H.; Rosnita, A.T.; Khalina, A. Extraction and physicochemical characterization of chitin and chitosan from Zophobas morio larvae in varying sodium hydroxide concentration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan Preparation from Marine Sources. Structure, Properties and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Tsurkan, M.; Galli, R.; Meissner, H.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Tabachnick, K.R.; et al. Discovery of chitin in skeletons of non-verongiid Red Sea demosponges. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percot, A.; Viton, C.; Domard, A. Optimization of Chitin Extraction from Shrimp Shells. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafari, A.; Marandi, R.; Sanatei, S. Recovery of chitin and chitosan from shrimp waste by chemical and microbal methods. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2008, 5, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Knidri, H.; Dahmani, J.; Addaou, A.; Laajeb, A.; Lahsini, A. Rapid and efficient extraction of chitin and chitosan for scale-up production: Effect of process parameters on deacetylation degree and molecular weight. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuprina, E.E.; Maslova, G.V.; Bachische, E.V. Electrochemical method for obtaining water-soluble oligomers of chitin in the presence of NaCl. In Proceedings of the IXth International Conference: Modern Perspectives in Chitin and Chitosan Studies, Stavropol, Russia, 13–17 October 2008; pp. 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Lu, L.; Zhang, S. Direct conversion of shrimp shells to O-acylated chitin with antibacterial and anti-tumor effects by natural deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuprina, E.E.; Vodolazhskaya, S.V.; Nyanikova, G.G.; Timofeeva, K.G. Development of technology for obtaining biologically active chitin sorbents based on the electrochemical conversion of crustaceans. In Proceedings of the VIth International Conference: New Achievements in Study of Chitin and Chitosan, Shchelkovo, Russia, 22–24 October 2001; pp. 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kuprina, E.E.; Timofeeva, K.G.; Kozlova, I.; Pimenov, A. Electrochemical method extracting sorbitol from chitin-containing raw material with strengthened anitimicrobal properties. In Proceedings of the VIIth International Conference: Modern Perspectives in Chitin and Chitosan Studies, St. Petersburg, Russia, 15–18 September 2003; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kuprina, E.E.; Timofeeva, K.G.; Krasavtsev, V.E.; Boykov, I.O.A. Experimental producing unit for getting chitin-mineral complex “chizitel” by electrochemical method. In Proceedings of the VIIIth International Conference: Modern Perspectives in Chitin and Chitosan Studies, Kazan, Russia, 13–17 June 2006; pp. 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kuprina, E.É.; Timofeeva, K.G.; Vodolazhskaya, S.V. Electrochemical Preparation of Chitin Materials. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2002, 75, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennakone, K. Hydrogen from brine electrolysis: A new approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1989, 14, 681–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, B.J.-D.; Ardisson, P.-L.; Azamar-Barrios, J.; Quintana, P.; Alvarado-Gil, J.J. Optical, thermal, and structural characterization of the sclerotized skeleton of two antipatharian coral species. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.; Florek, M.; Nowak, J.; Kwiatek, W.M.; Lekki, J.; Chevallier, P.; Hacura, A.; Wrzalik, R.; Ben-Nissan, B.; Van Grieken, R.; et al. Morphology and the chemical make-up of the inorganic components of black corals. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Goldberg, W.M.; Taylor, G.T. Architectural and Mechanical Properties of the Black Coral Skeleton (Coelenterata: Antipatharia): A Comparison of Two Species. Biol. Bull. 1992, 182, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Kurek, D.; Paasch, S.; Brunner, E.; Born, R.; Galli, R.; Stelling, A.L.; Sivkov, V.N.; Petrova, O.V.; et al. Isolation and identification of chitin in black coral Paranthipates larix (Anthozoa: Cnidaria). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuprina, E.E.; Krasavtsev, V.; Kozlova, I.; Vodolazhskaya, S.; Bogeruk, A.; Ezhov, V. Electrochemical method of chitinous products with enhanced ecology rehabilitation ability. In Proceedings of the Vth International Conference: New Prospects in Study of Chitin and Chitosan, Shchelkovo, Russia, 25–27 May 1999; pp. 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pletcher, D.; Walsh, F.C. Industrial Electrochemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann, H. Ion-Exchange Membrane Separation Processes. Membr. Sci. Tech. 2004, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Savari, S.; Sachdeva, S.; Kumar, A. Electrolysis of sodium chloride using composite poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene) cation exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppilli, M.; Lai, A.; Villano, M.; Majone, M. Anion vs. cation exchange membrane strongly affect mechanisms and yield of CO2 fixation in a microbial electrolysis cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holze, R.; Ahn, J. Advances in the use of perfluorinated cation exchange membranes in integrated water electrolysis and hydrogen/oxygen fuel cell systems. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Kang, S.Y.; Oh, S.-H.; Kim, J.K.; Lim, M.S.; Ahn, C.-Y.; Cho, Y.-H.; Sung, Y.-E. High-performance anion-exchange membrane water electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 295, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, D.A.; Weekes, D.M.; He, J.; Dettelbach, K.E.; Li, Y.C.; Mallouk, T.E.; Berlinguette, C.P. Electrolysis of Gaseous CO2 to CO in a Flow Cell with a Bipolar Membrane. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 3, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, B.; Wicher, I.; Dylewski, R. Studies on the parameters for membrane-electrolysis conversion of sodium sulfate solutions. Przemysł Chem. 2004, 83, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Holze, S.; Jörissen, J.; Fischer, C.; Kalvelage, H. Hydrogen consuming anodes for energy saving in sodium sulphate electrolysis. Chem. Eng. Technol. 1994, 17, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörissen, J.; Simmrock, K.H. The behavior of ion exchange membranes in electrolysis and electrodialysis of sodium sulfate. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1991, 21, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumirska, J.; Czerwicka, M.T.; Kaczynski, Z.; Bychowska, A.; Brzozowski, K.; Thöming, J.; Stepnowski, P. Application of Spectroscopic Methods for Structural Analysis of Chitin and Chitosan. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1567–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Rigby, J.K.; Botting, J.P.; Tsurkan, M.; Werner, C.; Schwille, P.; Petrásek, Z.; Pisera, A.; Simon, P.; Sivkov, V.N.; et al. Discovery of 505-million-year old chitin in the basal demosponge Vauxia gracilenta. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Kaluzhnaya, O.V.; Tsurkan, M.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Tabachnick, K.R.; Ilan, M.; Stelling, A.; Galli, R.; Petrova, O.V.; Nekipelov, S.V.; et al. First report on chitinous holdfast in sponges (Porifera). Proc. R. Soc. B 2013, 280, 20130339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Kaluzhnaya, O.V.; Brunner, E.; Tsurkan, M.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Ilan, M.; Tabachnick, K.R.; Bazhenov, V.; Paasch, S.; Kammer, M.; et al. Identification and first insights into the structure and biosynthesis of chitin from the freshwater sponge Spongilla lacustris. J. Struct. Biol. 2013, 183, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, B.S.; Garcia, E.S.; Azambuja, P.; Genta, F.A. Determination of Chitin Content in Insects: An Alternate Method Based on Calcofluor Staining. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, G.; Khanna, R.; Hornstra, I.; Kwatra, S.G.; Grossberg, A.L. Rapid detection of fungal elements using calcofluor white and handheld ultraviolet illumination. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1000–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connors, M.J.; Ehrlich, H.; Hog, M.; Godeffroy, C.; Araya, S.; Kallai, I.; Gazit, D.; Boyce, M.; Ortiz, C. Three-dimensional structure of the shell plate assembly of the chiton Tonicella marmorea and its biomechanical consequences. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 177, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysokowski, M.; Motylenko, M.; Walter, J.; Lota, G.; Wojciechowski, J.; Stöcker, H.; Galli, R.; Stelling, A.L.; Himcinschi, C.; Niederschlag, E.; et al. Synthesis of nanostructured chitin–hematite composites under extreme biomimetic conditions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61743–61752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Tsurkan, M.; Lim, S.; Meissner, H.; Tabachnick, K.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Ivanenko, V.N.; Petrenko, I.; Wysokowski, M.; et al. The demosponge Pseudoceratina purpurea as a new source of fibrous chitin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Elhady, S.S.; Tsurkan, M.; Petrenko, I.; Wysokowski, M.; Tabachnick, K.; Meißner, H.; Ivanenko, V.N.; et al. First Report on Chitin in a Non-Verongiid Marine Demosponge: The Mycale euplectellioides Case. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromont, J.; Zoltowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Galli, R.; Meissner, H.; Erpenbeck, D.; Vacelet, J.; Diaz, C.; Tsurkan, M.V.; Petrenko, I.; Youssef, D.; et al. New family and genus of a Dendrilla-like sponge with characters of Verongiida. Part II. Discovery of chitin in the skeleton of Ernstilla lacunosa. Zoologischer Anzeiger 2019, 280, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Asfour, H.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Wysokowski, M.; Tsurkan, M.; Galli, R.; Meißner, H.; Petrenko, I.; Tabachnick, K.; et al. New Source of 3D Chitin Scaffolds: The Red Sea Demosponge Pseudoceratina arabica (Pseudoceratinidae, Verongiida). Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Binnewerg, B.; Voronkina, A.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Kovalchuk, V.; Tsurkan, M.; Martinovic, R.; Bechmann, N.; et al. Naturally Prefabricated Marine Biomaterials: Isolation and Applications of Flat Chitinous 3D Scaffolds from Ianthella labyrinthus (Demospongiae: Verongiida). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, V.; Voronkina, A.; Binnewerg, B.; Schubert, M.; Muzychka, L.; Wysokowski, M.; Tsurkan, M.; Bechmann, N.; Petrenko, I.; Fursov, A.; et al. Naturally Drug-Loaded Chitin: Isolation and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Mujtaba, M.; Ehrlich, H.; Salaberria, A.M.; Baran, T.; Amemiya, C.T.; Galli, R.; Akyuz, L.; Sargin, I.; Labidi, J. On chemistry of γ-chitin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillar, E.A.; Zhou, R.; Guzman, M. Heterogeneous Oxidation of Catechol. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 10349–10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holl, S.M.; Schaefer, J.; Goldberg, W.M.; Kramer, K.J.; Morgan, T.D.; Hopkins, T.L. Comparison of black coral skeleton and insect cuticle by a combination of carbon-13 NMR and chemical analyses. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 292, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Haga, A.; Sekiguchi, H.; Hirano, S. Structure of insect chitin isolated from beetle larva cuticle and silkworm (Bombyx mori) pupa exuvia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2000, 27, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, S.D. Deep-water corals: An overview with special reference to diversity and distribution of deep-water scleractinian corals. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2007, 81, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Farfan, G.A.; Cordes, E.E.; Waller, R.G.; Decarlo, T.M.; Hansel, C.M. Mineralogy of Deep-Sea Coral Aragonites as a Function of Aragonite Saturation State. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugler, M.R.; Opresko, D.M.; France, S. The evolutionary history of the order Antipatharia (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Hexacorallia) as inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA: Implications for black coral taxonomy and systematics. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 169, 312–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molodtsova, T.N.; Opresko, D.M. Black corals (Anthozoa: Antipatharia) of the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.; Brugler, M.R.; Cartwright, P.; Collins, A.G.; Dawson, M.N.; Fautin, D.G.; France, S.; McFadden, C.S.; Opresko, D.M.; Rodriguez, E.; et al. The phylum Cnidaria: A review of phylogenetic patterns and diversity 300 years after Linnaeus*. Zootaxa 2007, 1668, 127–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Di Camillo, C.; Addamo, A.M.; Valisano, L.; Bavestrello, G. Growth strategies of whip black corals (Cnidaria: Antipatharia) in the Bunaken Marine Park (Celebes Sea, Indonesia). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2009, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Angiolillo, M.; Calcagnile, L.; Canese, S.; Cannas, R.; Cau, A.; D’Elia, M.; D’Oriano, F.; Follesa, M.C.; et al. Persistence of Pristine Deep-Sea Coral Gardens in the Mediterranean Sea (SW Sardinia). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roark, E.B.; Guilderson, T.; Dunbar, R.; Ingram, B. Radiocarbon-based ages and growth rates of Hawaiian deep-sea corals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 327, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouty, N.; Roark, E.B.; Buster, N.; Ross, S. Growth rate and age distribution of deep-sea black corals in the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 423, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Luck, D.G.; Toonen, R.J. The Biology and Ecology of Black Corals (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Hexacorallia: Antipatharia). Adv. Mar. Biol. 2012, 63, 67–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Shuler, A. The black coral fauna (Cnidaria: Antipatharia) of Bermuda with new records. Zootaxa 2017, 4344, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gąsiorek, P.; Cordeiro, R.T.S.; Perez, C.D. Black Corals (Anthozoa: Antipatharia) from the Southwestern Atlantic. Zootaxa 2019, 4692, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, W.M. Chemical changes accompanying maturation of the connective tissue skeletons of gorgonian and antipatharian corals. Mar. Biol. 1978, 49, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazioli, S.; Bo, M.; Boyer, M.; Rotinsulu, H.; Bavestrello, G. Ecological observations of some common antipatharian corals in the marine park of Bunaken (North Sulawesi, Indonesia). Zool. Stud. 2007, 46, 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, W.M.; Hopkins, T.L.; Holl, S.M.; Schaefer, J.; Kramer, K.J.; Morgan, T.D.; Kim, K. Chemical composition of the sclerotized black coral skeleton (Coelenterata: Antipatharia): A comparison of two species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B: Comp. Biochem. 1994, 107, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, W.M. Chemistry and structure of skeletal growth rings in the black coral Antipathes fiordensis (Cnidaria, Antipatharia). Hydrobiologia 1991, 216, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, N.; Sommer, U.; Spindler, K.-D. Demonstration and characterization of chitinases in the Drosophila-K-cell Line. Insect Biochem. 1985, 15, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowacki, K.; Stępniak, I.; Langer, E.; Tsurkan, M.; Wysokowski, M.; Petrenko, I.; Khrunyk, Y.; Fursov, A.; Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; et al. Electrochemical Approach for Isolation of Chitin from the Skeleton of the Black Coral Cirrhipathes sp. (Antipatharia). Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060297
Nowacki K, Stępniak I, Langer E, Tsurkan M, Wysokowski M, Petrenko I, Khrunyk Y, Fursov A, Bo M, Bavestrello G, et al. Electrochemical Approach for Isolation of Chitin from the Skeleton of the Black Coral Cirrhipathes sp. (Antipatharia). Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(6):297. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060297
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowacki, Krzysztof, Izabela Stępniak, Enrico Langer, Mikhail Tsurkan, Marcin Wysokowski, Iaroslav Petrenko, Yuliya Khrunyk, Andriy Fursov, Marzia Bo, Giorgio Bavestrello, and et al. 2020. "Electrochemical Approach for Isolation of Chitin from the Skeleton of the Black Coral Cirrhipathes sp. (Antipatharia)" Marine Drugs 18, no. 6: 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060297
APA StyleNowacki, K., Stępniak, I., Langer, E., Tsurkan, M., Wysokowski, M., Petrenko, I., Khrunyk, Y., Fursov, A., Bo, M., Bavestrello, G., Joseph, Y., & Ehrlich, H. (2020). Electrochemical Approach for Isolation of Chitin from the Skeleton of the Black Coral Cirrhipathes sp. (Antipatharia). Marine Drugs, 18(6), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060297









