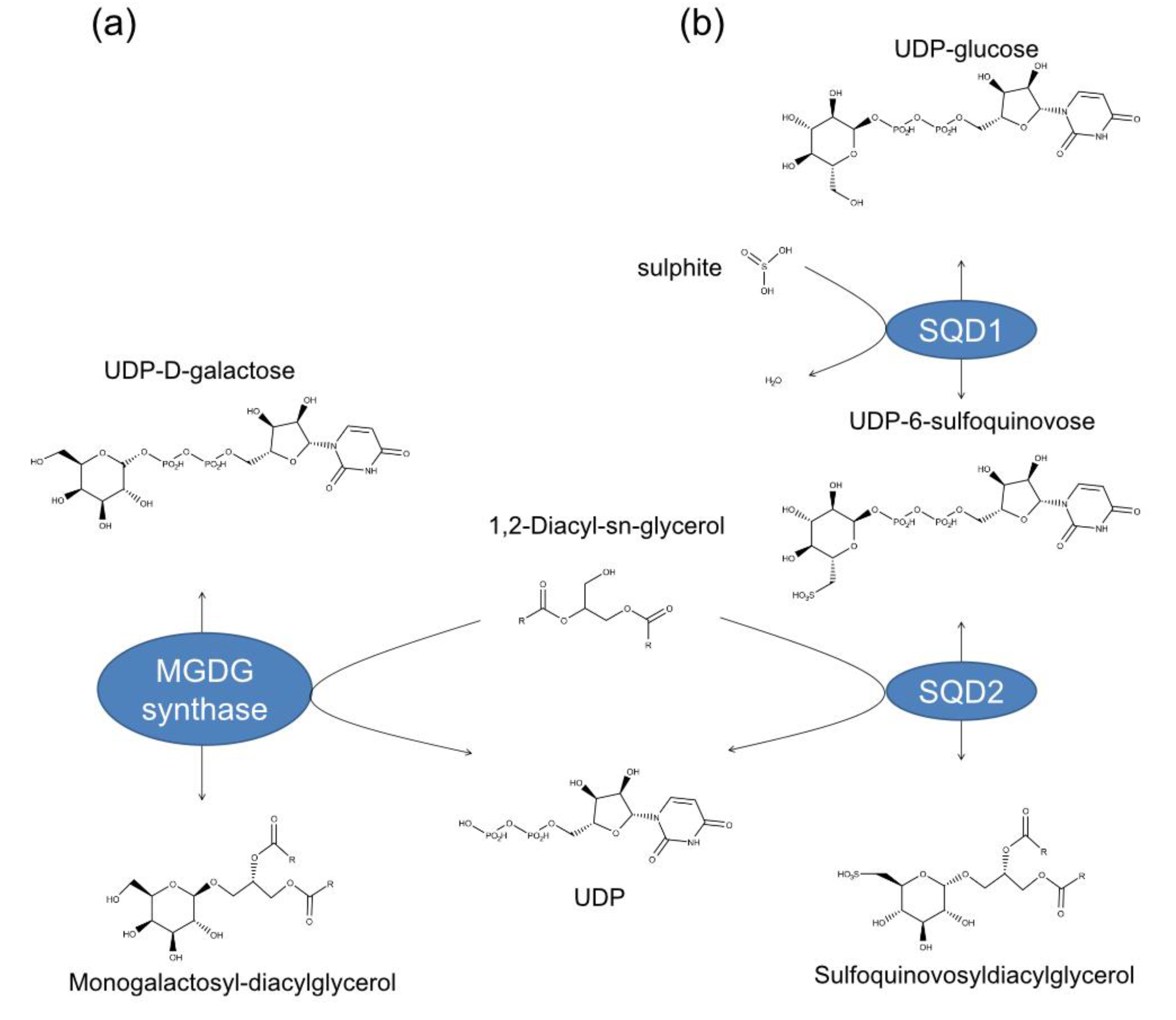
Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol and Sulfolipid Synthesis in Microalgae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
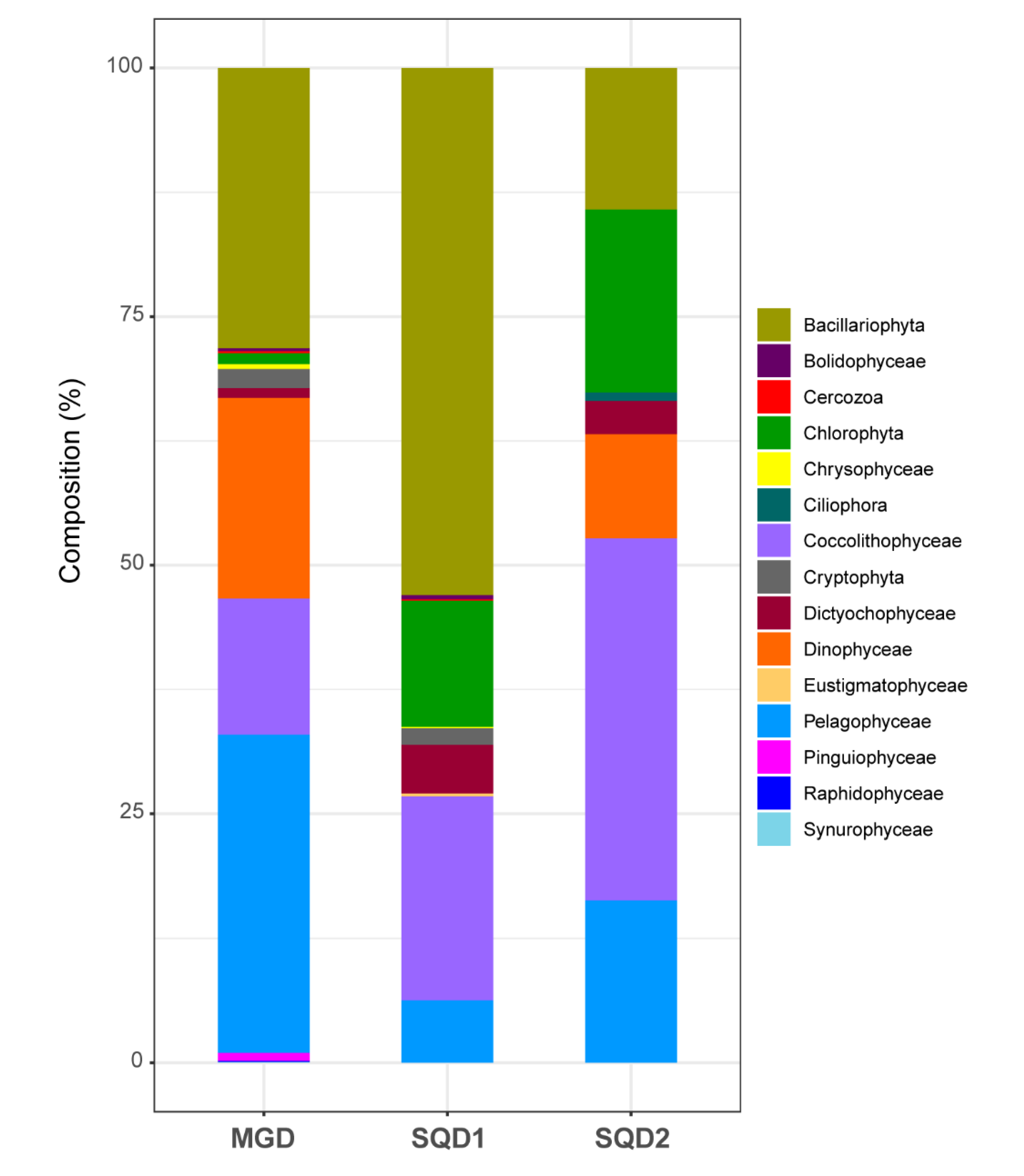
2.1. Identification and Taxonomic Assignation of MGD, SQD1, and SQD2 Homologous Sequences
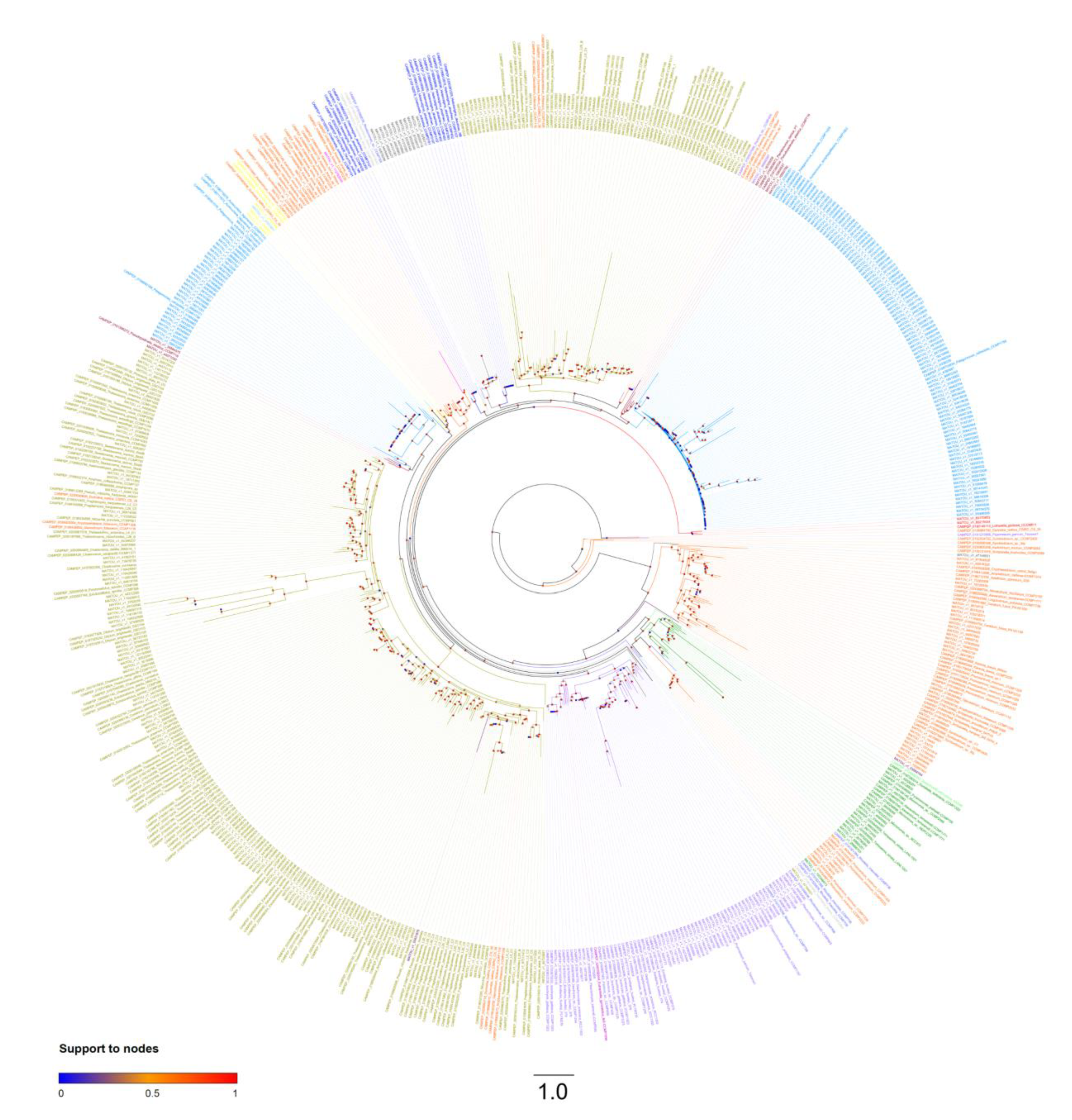
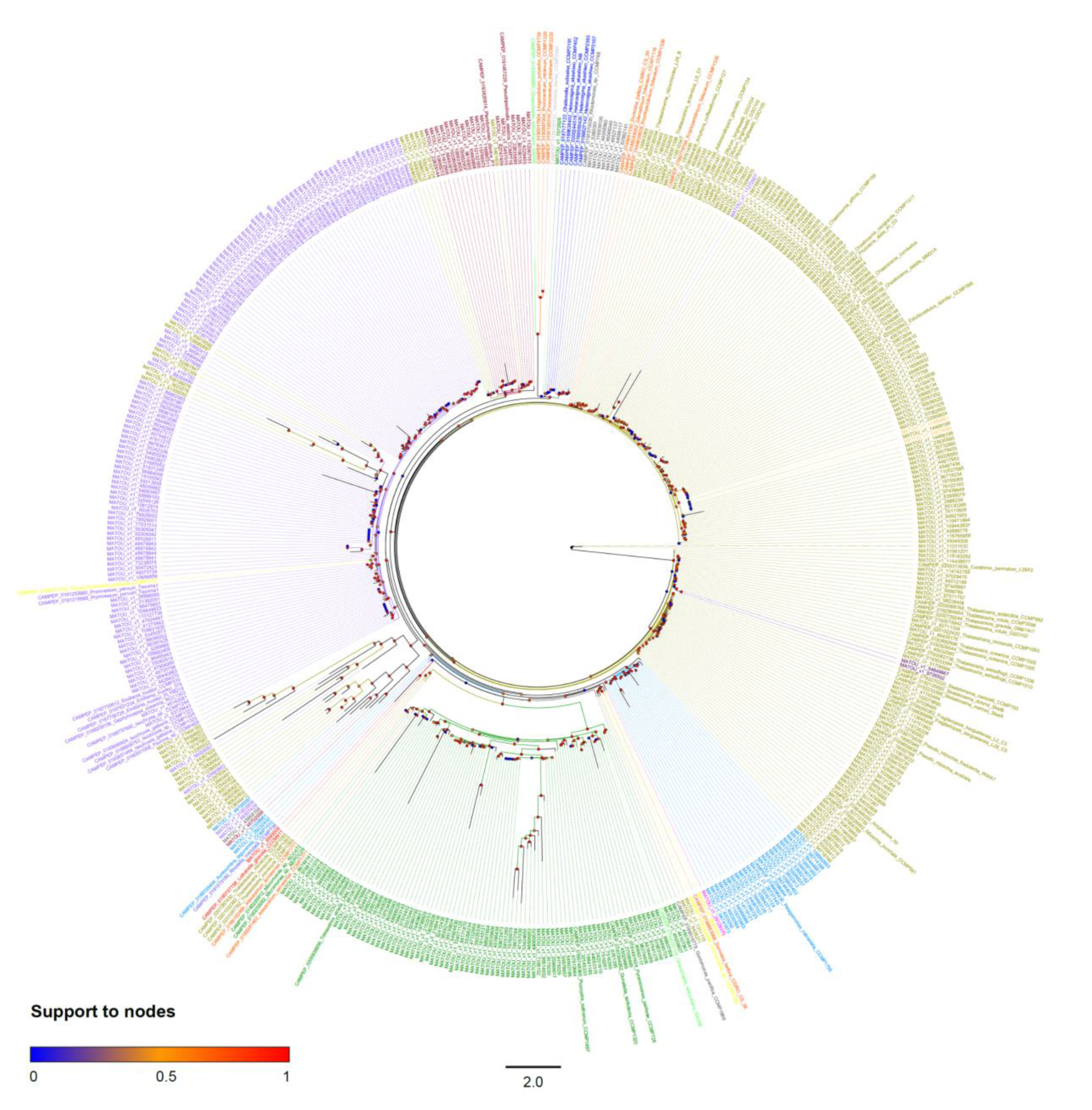
2.2. Final Dataset and Phylogenetic Inferences
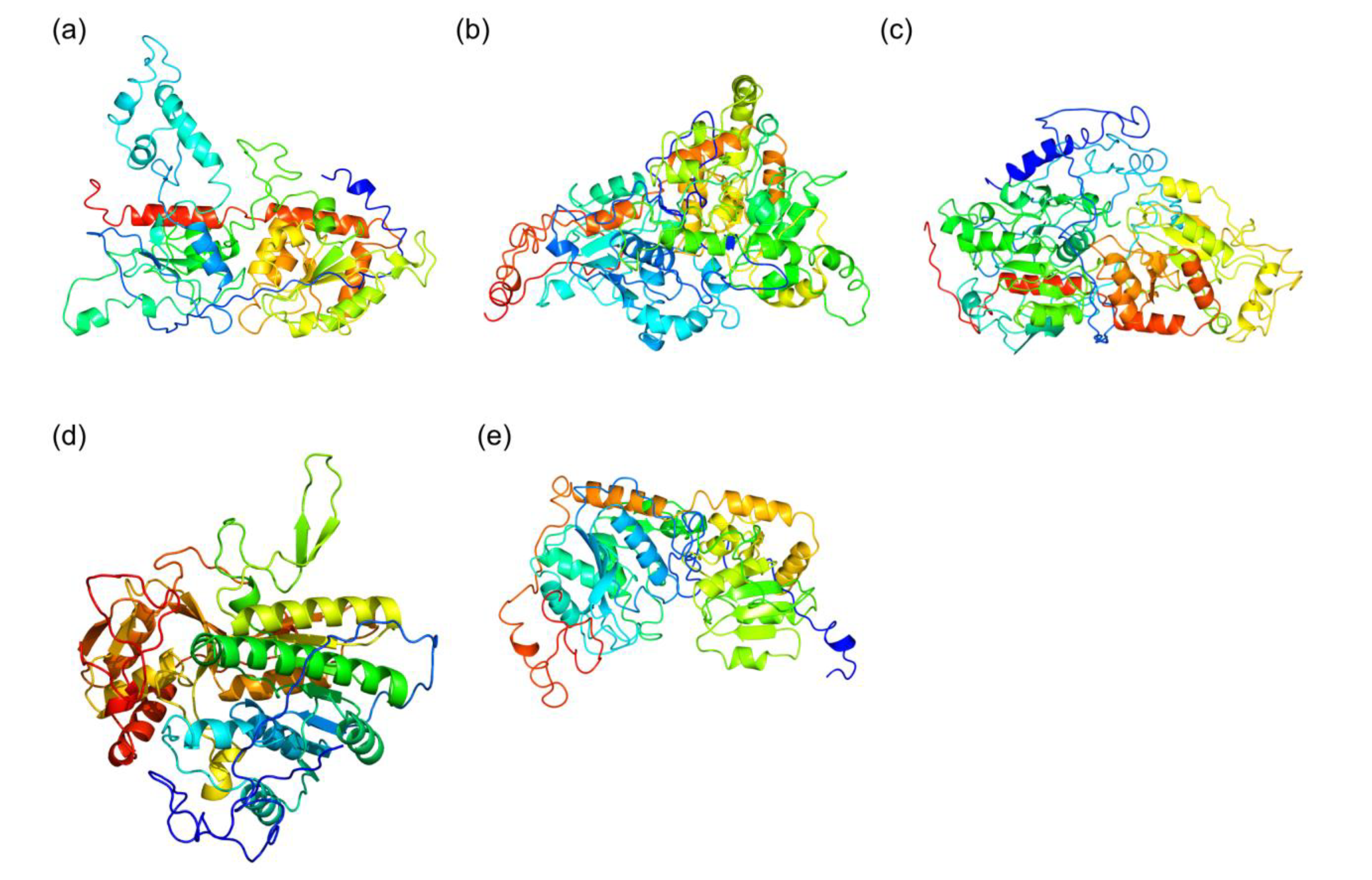
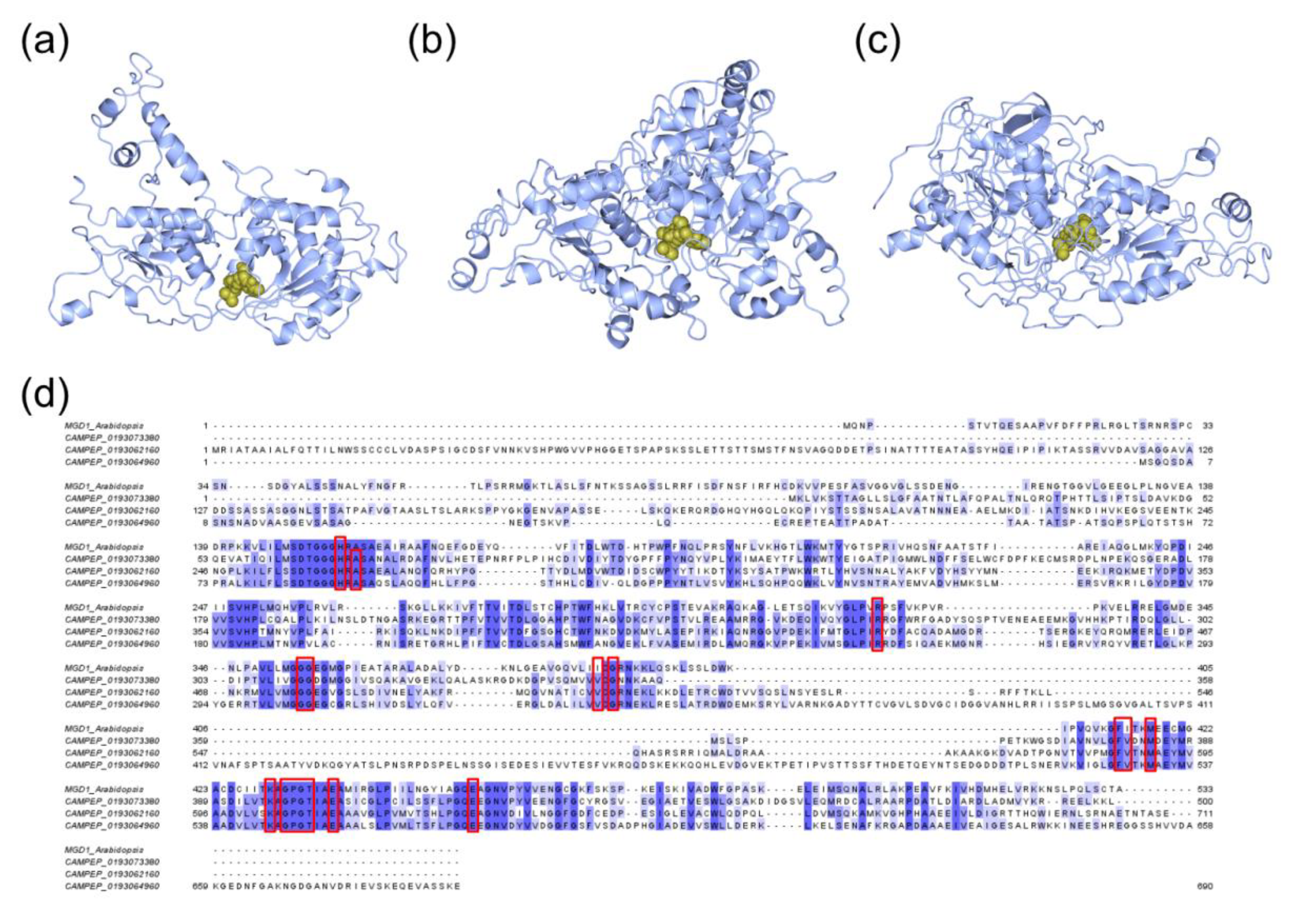
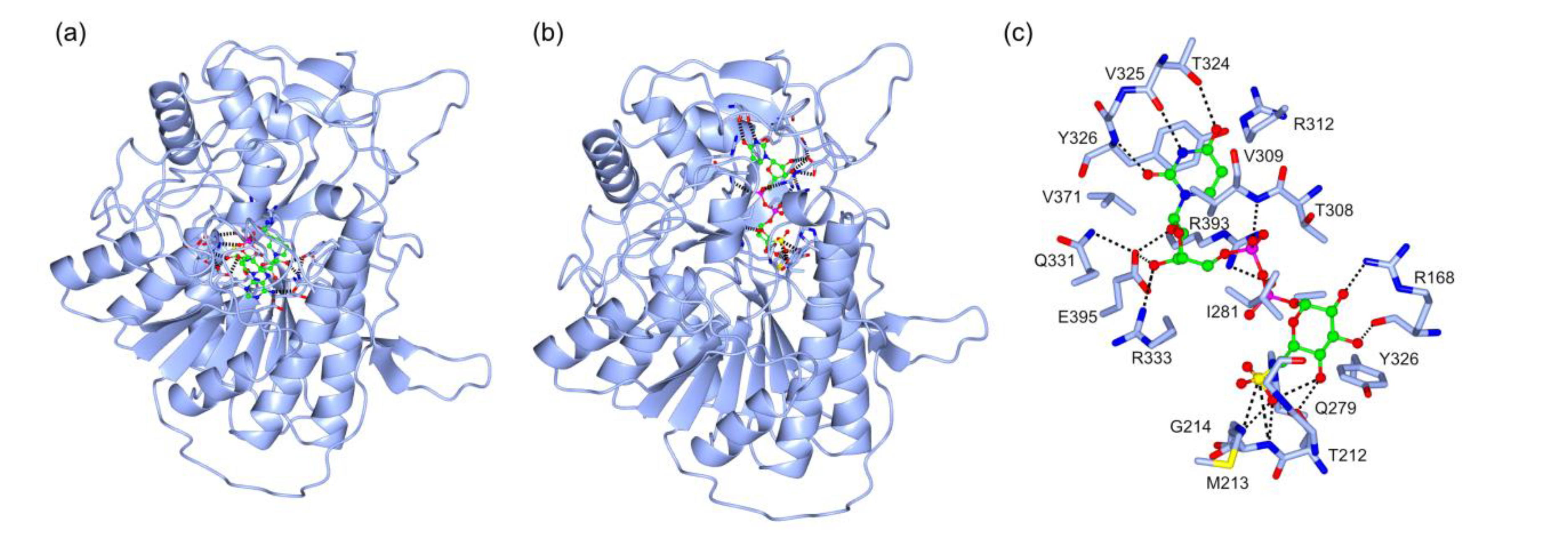
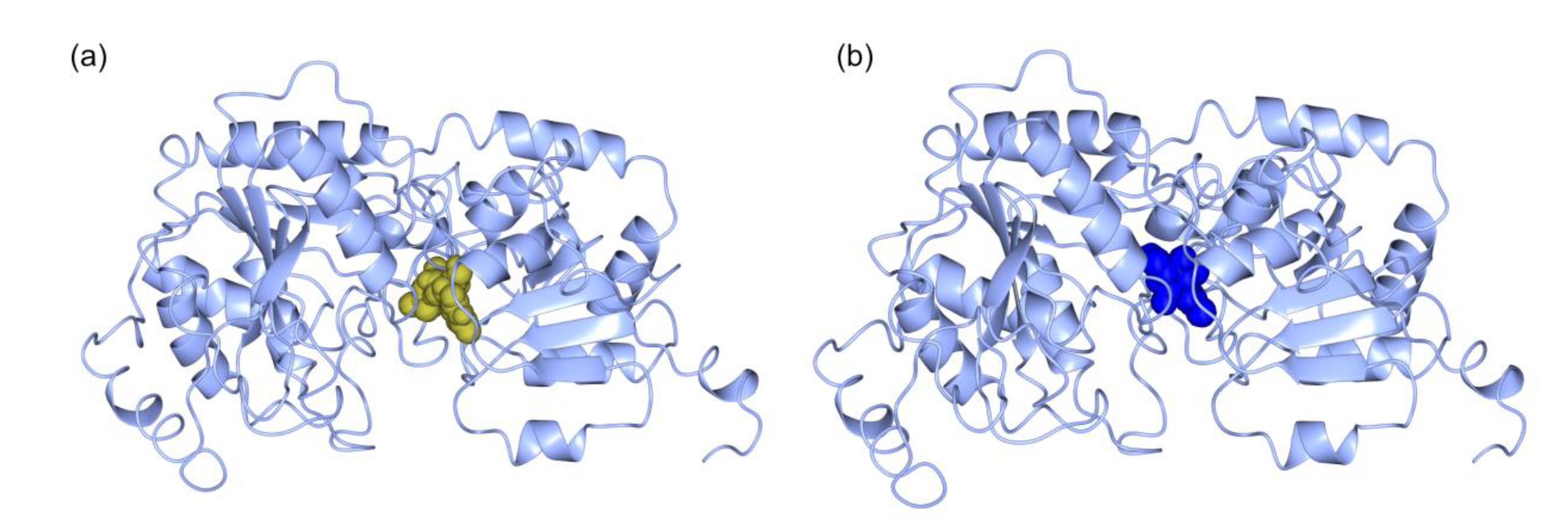
2.3. Structural Details of MDGs, SQD1, and SQD2 from Thalassiosira Weissflogii CCMP1336 (Conticriba weissflogii)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Identification of MGD, SQD1, and SQD2 Homologous Sequences
3.2. Taxonomic Overview
3.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Inference
3.4. In Silico Protein Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plaza, M.; Herrero, M.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibanez, E. Innovative natural functional ingredients from microalgae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7159–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspars, M.; De Pascale, D.; Andersen, J.H.; Reyes, F.; Crawford, A.D.; Ianora, A. The marine biodiscovery pipeline and ocean medicines of tomorrow. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2016, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimouni, V.; Ulmann, L.; Pasquet, V.; Mathieu, M.; Picot, L.; Bougaran, G.; Cadoret, J.P.; Morant-Manceau, A.; Schoefs, B. The potential of microalgae for the production of bioactive molecules of pharmaceutical interest. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 2733–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyande, A.K.; Chew, K.W.; Rambabu, K.; Tao, Y.; Chu, D.-T.; Show, P.-L. Microalgae: A potential alternative to health supplementation for humans. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourelle, M.L.; Gómez, C.P.; Legido, J.L. The potential use of marine microalgae and cyanobacteria in cosmetics and thalassotherapy. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; Ferrante, M.I.; Rogato, A. Marine natural products from microalgae: An -omics overview. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; De Luca, D.; Ferrarini, A.; Avanzato, C.; Minio, A.; Esposito, F.; Ianora, A. De novo transcriptome of the cosmopolitan dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae to identify enzymes with biotechnological potential. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dato, V.; Di Costanzo, F.; Barbarinaldi, R.; Perna, A.; Ianora, A.; Romano, G. Unveiling the presence of biosynthetic pathways for bioactive compounds in the Thalassiosira rotula transcriptome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; De Luca, D.; Amoroso, M.; Benfatto, S.; Maestri, S.; Racioppi, C.; Esposito, F.; Ianora, A. New molecular insights on the response of the green alga Tetraselmis suecica to nitrogen starvation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagoz, A.M.; Ambrosino, L.; Lauritano, C. De novo transcriptome of the diatom Cylindrotheca closterium identifies genes involved in the metabolism of anti-inflammatory compounds. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingiani, G.M.; De Luca, P.; Ianora, A.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Lauritano, C. Microalgal enzymes with biotechnological applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junpeng, J.; Xupeng, C. Monogalactosyldiacylglycerols with High PUFA Content From Microalgae for Value-Added Products. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Andrade, K.A.; Lauritano, C.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. Marine Microalgae with Anti-Cancer Properties. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, E.; Silva, J.; Mendonça, S.H.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, M.R. Lipidomic approaches towards deciphering glycolipids from microalgae as a reservoir of bioactive lipids. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasaka, H.; Sasaki, R.; Yoshida, K.; Takayama, I.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yoshida, H.; Mizushina, Y. Monogalactosyl diacylglycerol, a replicative DNA polymerase inhibitor, from spinach enhances the anti-cell proliferation effect of gemcitabine in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianasolo, E.H.; Haramaty, L.; Vardi, A.; White, E.; Lutz, R.; Falkowski, P. Apoptosis-inducing galactolipids from a cultured marine diatom, Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.H.; Gallant, P.; Stefanova, R.; Melanson, R.; Oleary, S.J.B. Monogalactosyldiacylglycerols, potent nitric oxide inhibitors from the marine microalga Tetraselmis chui. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 23, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.H.; Stefanova, R.; Gallant, P.; McGinn, P.J. Mono- and digalactosyldiacylglycerols: Potent nitric oxide inhibitors from the marine microalga Nannochloropsis granulata. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 27, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K. Role of membrane glycerolipids in photosynthesis, thylakoid biogenesis and chloroplast development. J. Plant. Res. 2016, 129, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hielscher-Michael, S.; Griehl, C.; Buchholz, M.; Demuth, H.U.; Arnold, N.; Wessjohann, L.A. Natural Products from Microalgae with Potential against Alzheimer’s Disease: Sulfolipids Are Potent Glutaminyl Cyclase Inhibitors. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, E.; Cutignano, A.; Pagano, D.; Gallo, C.; Barra, G.; Nuzzo, G.; Sansone, C.; Ianora, A.; Urbanek, K.; Fenoglio, D.; et al. A new marine-derived sulfoglycolipid triggers dendritic cell activation and immune adjuvant response. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawski, M.; Schilling, S.; Kreuzberger, M.; Waniek, A.; Jäger, C.; Koch, B.; Cynis, H.; Kehlen, A.; Arendt, T.; Hartlage-Rübsamen, M.; et al. Glutaminyl cyclase in human cortex: Correlation with (pGlu)-amyloid-β load and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 39, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyard, J.; Maréchal, E.; Miège, C.; Block, M.A.; Dorne, A.-J.; Douce, R. Structure, Distribution and Biosynthesis of Glycerolipids from Higher Plant Chloroplasts. In Lipids in Photosynthesis: Structure, Function and Genetics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 21–52. [Google Scholar]
- Benning, C.; Ohta, H. Three enzyme systems for galactoglycerolipid biosynthesis are coordinately regulated in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2397–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Ohta, H. Type A and type B monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthases are spatially and functionally separated in the plastids of higher plants. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Ling, J.; Kawano, N.; Li, D.; Tanaka, K. Cloning of a putative monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase gene from rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants and its expression in response to submergence and other stresses. Planta 2004, 219, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.M.; James, M.G.; Lin, Q.; Yi, G.; Stinard, P.S.; Hennen-Bierwagen, T.A.; Becraft, P.W. Maize opaque5 encodes monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase and specifically affects galactolipids necessary for amyloplast and chloroplast function. Plant. Cell 2011, 23, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubots, E.; Audry, M.; Yamaryo, Y.; Bastien, O.; Ohta, H.; Breton, C.; Maréchal, E.; Block, M.A. Activation of the chloroplast monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase MGD1 by phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylglycerol. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 6003–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, R.; Zhang, J.; Hussain, N.; Shu, Q. Characterization and Mutational Analysis of a Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol Synthase Gene OsMGD2 in Rice. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 10, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awai, K.; Maréchal, E.; Block, M.A.; Brun, D.; Masuda, T.; Shimada, H.; Takamiya, K.I.; Ohta, H.; Joyard, J. Two types of MGDG synthase genes, found widely in both 16:3 and 18:3 plants, differentially mediate galactolipid syntheses in photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic tissues in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10960–10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frentzen, M. Phosphatidylglycerol and sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol: Anionic membrane lipids and phosphate regulation. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2004, 7, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.B.; Hewlins, M.J.; Ellis, A.J.; Harwood, J.L.; White, G.F. Glycolytic breakdown of sulfoquinovose in bacteria: A missing link in the sulfur cycle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6434–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speciale, G.; Jin, Y.; Davies, G.J.; Williams, S.J.; Goddard-Borger, E.D. YihQ is a sulfoquinovosidase that cleaves sulfoquinovosyl diacylglyceride sulfolipids. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanda, S.; Leustek, T.; Theisen, M.J.; Garavito, R.M.; Benning, C. Recombinant Arabidopsis SQD1 converts UDP-glucose and sulfite to the sulfolipid head group precursor UDP-sulfoquinovose in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Xu, C.C.; Benning, C. Arabidopsis disrupted in SQD2 encoding sulfolipid synthase is impaired in phosphate-limited growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5732–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, C.; Martín, J.; De La Cruz, M.; Reyes, F.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. First identification of marine diatoms with anti-tuberculosis activity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillatz, T.; Lauritano, C.; Jacmin, M.; Khamma, S.; Marcourt, L.; Righi, D.; Romano, G.; Esposito, F.; Ianora, A.; Queiroz, E.F.; et al. Zebrafish-based identification of the antiseizure nucleoside inosine from the marine diatom Skeletonema marinoi. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; Andersen, J.H.; Hansen, E.; Albrigtsen, M.; Escalera, L.; Esposito, F.; Helland, K.; Hanssen, K.O.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. Bioactivity Screening of Microalgae for Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Anticancer, Anti-Diabetes, and Antibacterial Activities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, G.; Lauritano, C. Microalgae with Immunomodulatory Activities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, D.; Costantini, M.; Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Núñez Pons, L.; Ruocco, N.; di Prisco, G.; Ianora, A.; Verde, C. Biotechnological Applications of Bioactive Peptides From Marine Sources. In Advances in Microbial Physiology; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 171–220. ISBN 9780128151907. [Google Scholar]
- Keeling, P.J. The endosymbiotic origin, diversification and fate of plastids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 729–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Katz, M.E.; Knoll, A.H.; Quigg, A.; Raven, J.A.; Schofield, O.; Taylor, F.J.R. The evolution of modern eukaryotic phytoplankton. Science 2004, 305, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, E.; Gallo, C.; Sartorius, R.; Nuzzo, G.; Sardo, A.; De Berardinis, P.; Fontana, A.; Cutignano, A. Immunostimulatory Phosphatidylmonogalactosyldiacylglycerols (PGDG) from the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii: Inspiration for a novel synthetic toll-like receptor 4 agonist. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Anderson, S.; Zhang, Y.; Garavito, R.M. The structure of sucrose synthase-1 from Arabidopsis thaliana and its functional implications. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 36108–36118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, J.; Sarkis, J.; Thomas, A.; Pitou, L.; Radzimanowski, J.; Audry, M.; Chazalet, V.; de Sanctis, D.; Palcic, M.M.; Block, M.A.; et al. Structural insights and membrane binding properties of MGD1, the major galactolipid synthase in plants. Plant. J. 2016, 85, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulichak, A.M.; Theisen, M.J.; Essigmann, B.; Benning, C.; Garavito, R.M. Crystal structure of SQD1, an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the plant sulfolipid headgroup donor UDP-sulfoquinovose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13097–13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Otsuki, H.; Narisawa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Sawai, S.; Kamide, Y.; Kusano, M.; Aoki, T.; Hirai, M.Y.; Saito, K. A new class of plant lipid is essential for protection against phosphorus depletion. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Shen, Q.; Wang, X.; Hong, Y. The Sulfoquinovosyltransferase-like Enzyme SQD2.2 is Involved in Flavonoid Glycosylation, Regulating Sugar Metabolism and Seed Setting in Rice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Shen, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, P.; Wang, X.; Hong, Y. Rice sulfoquinovosyltransferase SQD2.1 mediates flavonoid glycosylation and enhances tolerance to osmotic stress. Plant. Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 2215–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, E.; Vannier, T.; Vernette, C.; Lescot, M.; Cuenca, M.; Alexandre, A.; Bachelerie, P.; Rosnet, T.; Pelletier, E.; Sunagawa, S.; et al. The Ocean Gene Atlas: Exploring the biogeography of plankton genes online. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W289–W295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, P.J.; Burki, F.; Wilcox, H.M.; Allam, B.; Allen, E.E.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Armbrust, E.V.; Archibald, J.M.; Bharti, A.K.; Bell, C.J.; et al. The Marine Microbial Eukaryote Transcriptome Sequencing Project (MMETSP): Illuminating the Functional Diversity of Eukaryotic Life in the Oceans through Transcriptome Sequencing. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradec, Q.; Pelletier, E.; Da Silva, C.; Alberti, A.; Seeleuthner, Y.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Lima-Mendez, G.; Rocha, F.; Tirichine, L.; Labadie, K.; et al. A global ocean atlas of eukaryotic genes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, G.; Paoli, L.; Alberti, A.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Cuenca, M.; Field, C.M.; Coelho, L.P.; Cruaud, C.; Engelen, S.; et al. Gene Expression Changes and Community Turnover Differentially Shape the Global Ocean Metatranscriptome. Cell 2019, 179, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusch, D.B.; Halpern, A.L.; Sutton, G.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Williamson, S.; Yooseph, S.; Wu, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Hoffman, J.M.; Remington, K.; et al. The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling expedition: Northwest Atlantic through eastern tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. 2019: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Found. Stat. Comput. Vienna, Austria. Available online: http//.r-project.org/ (accessed on 18 November 2019).
- Wickham, H. Package ‘scales’—Scale Functions for Visualization. CRAN Repos. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2 Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24275-0. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, J.S.; Agarwala, R. COBALT: Constraint-based alignment tool for multiple protein sequences. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A Simple, Fast, and Accurate Algorithm to Estimate Large Phylogenies by Maximum Likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 596–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, V.; Longueville, J.E.; Gascuel, O. SMS: Smart Model Selection in PhyML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2422–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, M.; Gascuel, O. Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: A fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Y. BioLiP: A semi-manually curated database for biologically relevant ligand-protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D1096–D1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Y. Protein-ligand binding site recognition using complementary binding-specific substructure comparison and sequence profile alignment. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholas, S.; Potterton, E.; Wilson, K.S.; Noble, M.E.M. Presenting your structures: The CCP4mg molecular-graphics software. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
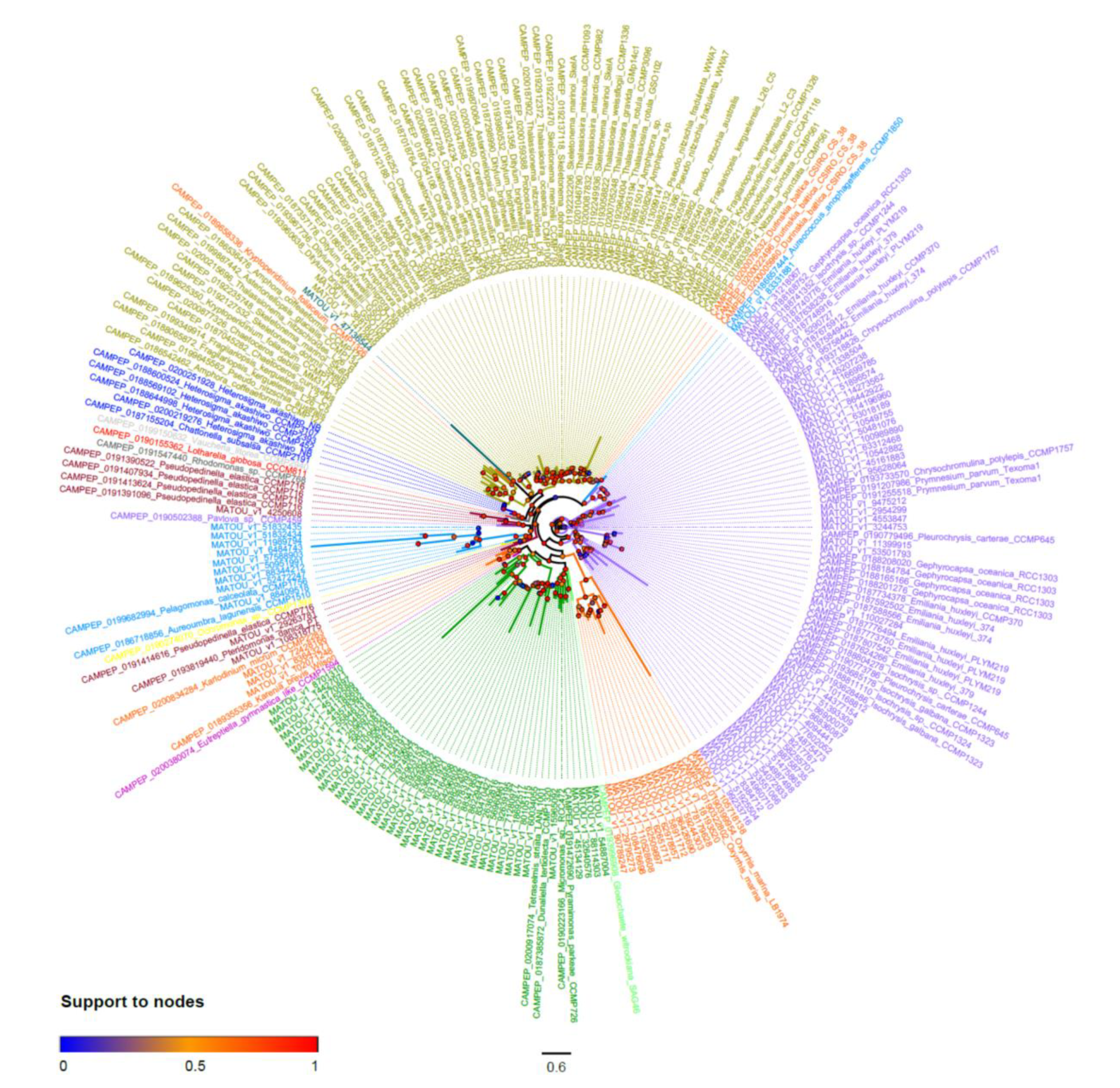
| Color Legend | Taxonomic Group | Species/Strain Surveyed | Accepted Synonym | MGD | SQD1 | SQD2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dinophyceae | Alexandrium monilatum CCMP3105 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Alexandrium tamarense CCMP1771 | P | P | |||
| Dinophyceae | Amphidinium carterae CCMP1314 | P | ||||
| Bacillariophyta | Amphiprora sp. | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Amphora coffeaeformis CCMP127 | Halamphora coffeiformis | P | P | P | |
| Bacillariophyta | Asterionellopsis glacialis CCMP134 | P | P | P | ||
| Pelagophyceae | Aureococcus anophagefferens CCMP1850 | P | P | |||
| Pelagophyceae | Aureoumbra lagunensis CCMP1510 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Azadinium spinosum 3D9 | P | ||||
| Bacillariophyta | Ceratium fusus PA161109 | Tripos fusus | P | |||
| Bacillariophyta | Chaetoceros affinis CCMP159 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Chaetoceros curvisetus | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Chaetoceros debilis MM31A 1 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Chaetoceros neogracile CCMP1317 | P | P | P | ||
| Raphidophyceae | Chattonella subsalsa CCMP2191 | P | P | P | ||
| Coccolithophyceae | Chrysochromulina polylepis CCMP1757 | Prymnesium polylepis | P | P | P | |
| Bacillariophyta | Corethron pennatum L29A3 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Crypthecodinium cohnii Seligo | P | ||||
| Bacillariophyta | Ditylum brightwellii GSO103 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Ditylum brightwellii GSO104 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Ditylum brightwellii GSO105 | P | P | P | ||
| Chlorophyta | Dunaliella tertiolecta CCMP1320 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Durinskia baltica CSIRO CS 38 | Durinskia dybowskii | P | P | P | |
| Coccolithophyceae | Emiliania huxleyi 374 | P | P | |||
| Coccolithophyceae | Emiliania huxleyi 379 | P | P | P | ||
| Coccolithophyceae | Emiliania huxleyi CCMP370 | P | P | P | ||
| Coccolithophyceae | Emiliania huxleyi PLYM219 | P | P | P | ||
| Euglenophyceae | Eutreptiella gymnastica like CCMP1594 | P | P | |||
| Bacillariophyta | Extubocellulus spinifer CCMP396 | P | P | |||
| Bacillariophyta | Fragilariopsis kerguelensis L26 C5 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Fragilariopsis kerguelensis L2 C3 | P | P | P | ||
| Coccolithophyceae | Gephyrocapsa oceanica RCC1303 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Glenodinium foliaceum CCAP1116 3 | Kryptoperidinium foliaceum | P | P | P | |
| Glaucophyceae | Gloeochaete wittrockiana SAG46 84 | P | P | P | ||
| Cryptophyta | Goniomonas pacifica CCMP1869 | P | ||||
| Raphidophyceae | Heterosigma akashiwo CCMP2393 | P | P | P | ||
| Raphidophyceae | Heterosigma akashiwo CCMP3107 | P | P | P | ||
| Raphidophyceae | Heterosigma akashiwo CCMP452 | P | P | P | ||
| Raphidophyceae | Heterosigma akashiwo NB | P | P | P | ||
| Coccolithophyceae | Isochrysis galbana CCMP1323 | P | P | P | ||
| Coccolithophyceae | Isochrysis sp. CCMP1244 | P | P | P | ||
| Coccolithophyceae | Isochrysis sp. CCMP1324 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Karenia brevis CCMP2229 | P | ||||
| Dinophyceae | Karenia brevis SP1 | P | ||||
| Dinophyceae | Karenia brevis SP3 | P | ||||
| Dinophyceae | Karenia brevis Wilson | P | P | |||
| Dinophyceae | Karlodinium micrum CCMP2283 | Karlodinium veneficum | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Kryptoperidinium foliaceum CCMP1326 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Lingulodinium polyedra CCMP1738 | P | P | |||
| Cercozoa | Lotharella globosa CCCM811 | P | P | P | ||
| Chlorophyta | Micromonas sp. CCMP2099 | P | ||||
| Chlorophyta | Micromonas sp. NEPCC29 | P | P | |||
| Chlorophyta | Micromonas sp. RCC472 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Nitzschia punctata CCMP561 | Tryblionella punctata | P | P | P | |
| Chrysophyceae | Ochromonas sp. CCMP1393 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Oxyrrhis marina | P | P | |||
| Dinophyceae | Oxyrrhis marina LB1974 | P | ||||
| Pavlovophyceae | Pavlova sp. CCMP459 | P | P | P | ||
| Pelagophyceae | Pelagococcus subviridis CCMP1429 | P | ||||
| Pelagophyceae | Pelagomonas calceolata CCMP1756 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Peridinium aciculiferum PAER 2 | Apocalathium aciculiferum | P | |||
| Chlorophyta | Picocystis salinarum CCMP1897 | P | ||||
| Coccolithophyceae | Pleurochrysis carterae CCMP645 | Chrysotila carterae | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Proboscia alata PI D3 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Prorocentrum minimum CCMP1329 | Prorocentrum cordatum | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Prorocentrum minimum CCMP2233 | Prorocentrum cordatum | P | P | ||
| Coccolithophyceae | Prymnesium parvum Texoma1 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Pseudo-nitzschia australis 10249 10 AB | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Pseudo-nitzschia fradulenta WWA7 | P | P | P | ||
| Dictyochophyceae | Pseudopedinella elastica CCMP716 | P | P | P | ||
| Dictyochophyceae | Pteridomonas danica PT | P | P | P | ||
| Chlorophyta | Pyramimonas parkeae CCMP726 | P | P | P | ||
| Rhodophyta | Rhodella maculata CCMP736 | Rhodella violacea | P | P | ||
| Cryptophyta | Rhodomonas sp. CCMP768 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Scrippsiella hangoei SHTV5 | Apocalathium malmogiense | P | |||
| Dinophyceae | Scrippsiella hangoei like SHHI 4 | P | ||||
| Dinophyceae | Scrippsiella trochoidea CCMP3099 | P | ||||
| Bacillariophyta | Skeletonema dohrnii SkelB | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Skeletonema marinoi SkelA | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Skeletonema menzelii CCMP793 | P | P | P | ||
| Dinophyceae | Symbiodinium sp. C1 | P | ||||
| Dinophyceae | Symbiodinium sp. CCMP2430 | P | ||||
| Dinophyceae | Symbiodinium sp. Mp | P | ||||
| Chlorophyta | Tetraselmis striata LANL1001 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassionema nitzschioides L26 B | P | P | |||
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiosira antarctica CCMP982 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiosira gravida GMp14c1 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiosira miniscula CCMP1093 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiosira oceanica CCMP1005 | P | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiosira rotula CCMP3096 | Thalassiosira gravida | P | P | P | |
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiosira rotula GSO102 | Thalassiosira gravida | P | P | P | |
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiosira weissflogii CCMP1010 | Conticribra weissflogii | P | P | ||
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiosira weissflogii CCMP1336 | Conticribra weissflogii | P | P | P | |
| Bacillariophyta | Thalassiothrix antarctica L6 D1 | P | P | |||
| Xanthophyceae | Vaucheria litorea CCMP2940 | P | P | P |
| Thalassiosira (Conticribra) weissflogii CCMP1336 Proteins | Template (PDB Code) | Confidence | % id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGD CAMPEP 0193073380 | MGD1 from A. thaliana (4X1T) | 100 | 46 | |
| MGD CAMPEP 0193064960 | MGD1 from A. thaliana (4X1T) | 100 | 47 | |
| MGD CAMPEP 0193062160 | MGD1 from A. thaliana (4X1T) | 100 | 40 | |
| SQD1 CAMPEP_0193062736 | SQD1 from A. thaliana (1I24) | 100 | 45 | |
| SQD2 CAMPEP_0193058822 | SUS1 from A. thaliana (3S29) | 100 | 18 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riccio, G.; De Luca, D.; Lauritano, C. Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol and Sulfolipid Synthesis in Microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050237
Riccio G, De Luca D, Lauritano C. Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol and Sulfolipid Synthesis in Microalgae. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(5):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050237
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiccio, Gennaro, Daniele De Luca, and Chiara Lauritano. 2020. "Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol and Sulfolipid Synthesis in Microalgae" Marine Drugs 18, no. 5: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050237
APA StyleRiccio, G., De Luca, D., & Lauritano, C. (2020). Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol and Sulfolipid Synthesis in Microalgae. Marine Drugs, 18(5), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050237







