Assessment of the Allelochemical Activity and Biochemical Profile of Different Phenotypes of Picocyanobacteria from the Genus Synechococcus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Allelopathic Effect of Different Synechococcus sp. Phenotypes on the Growth of Targeted Species of Phytoplankton
2.2. Allelopathic Effect of Different Synechococcus sp. Phenotypes on the Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Studied Species of Phytoplankton
2.3. Allelopathic Effect of Different Synechococcus sp. Phenotypes on the Photosynthetic Pigments of Studied Species of Phytoplankton
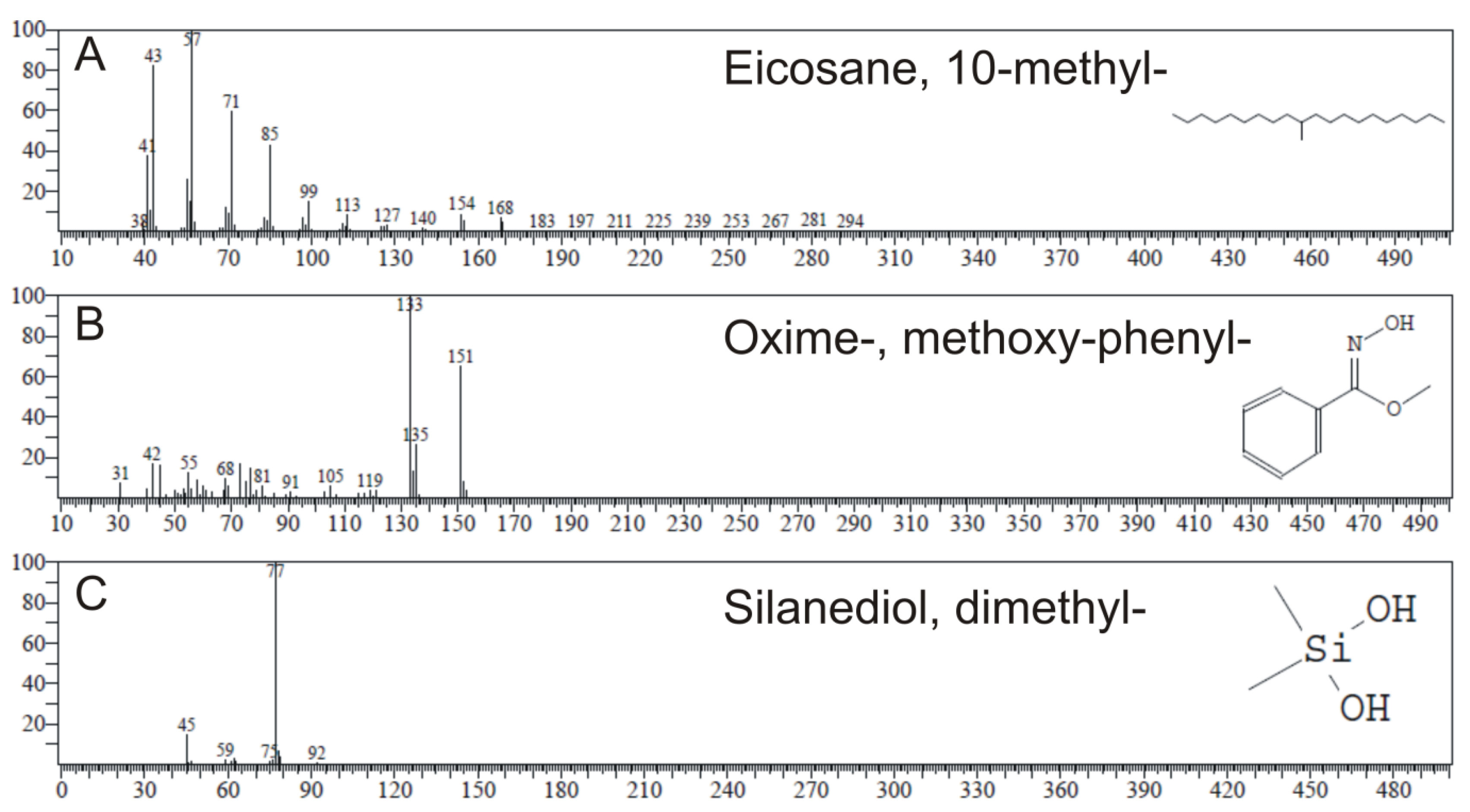
2.4. GC-MS Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Studied Species
3.2. Culture Condition
3.3. Determination of the Allelopathic Effect of Cell-Free Filtrates
3.4. Cell Density Assays
3.5. Fluorescence Assay
3.6. Pigments Assay
3.7. GC–MS Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorokin, P.Y.; Sorokin, Y.I.; Boscolo, R.; Giovanardi, O. Bloom of picocyanobacteria in the Venice lagoon during summer–autumn 2001: Ecological sequences. Hydrobiologia 2004, 523, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Maculewicz, J.; Barreiro, A.; Latała, A. Allelopathic and bloom-forming picocyanobacteria in a changing world. Toxins 2018, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Cai, Y.; Xiao, M.; Zhu, L. Temporal variation of major nutrients and probabilistic eutrophication evaluation based on stochastic-fuzzy method in Honghu Lake, Middle China. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flombaum, P.; Gallegos, J.L.; Gordillo, R.A.; Rincon, J.; Zabala, L.L.; Jiao, N.; Karl, D.M.; Li, W.K.; Lomas, M.W.; Veneziano, D. Present and future global distributions of the marine Cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. PNAS 2013, 110, 9824–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutkiewicz, S.; Morris, J.J.; Follows, M.J.; Scott, J.; Levitan, O.; Dyhrman, S.T.; Berman-Frank, I. Impact of ocean acidification on the structure of future phytoplankton communities. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, A.; Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Klin, M.; Konarzewska, Z.; Vasconcelos, V. Temperature-dependent impacts of allelopathy on growth, pigment, and lipid content between a subpolar strain of Synechocystis sp. CCBA MA-01 and coexisting microalgae. Hydrobiologia 2019, 835, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Mazur-Marzec, H.; Sutryk, K.; Kobos, J.; Hebel, A.; Hohlfeld, N.; Błaszczyk, A.; Toruńska, A.; Kaczkowska, M.J.; Łysiak-Pastuszak, E.; Kraśniewski, W.; et al. Occurrence of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxin in the Southern Baltic Proper. Filamentous cyanobacteria versus single-celled picocyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 2013, 701, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, C.; Thomas, J.C.; Thion, L.; Lemoine, Y.; Zal, F.; Partensky, F. Two novel phycoerythrin-associated linker proteins in the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain WH8102. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, C.; Thomas, J.C.; Garczarek, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Dufresne, A.; Blot, N.; Scanlan, D.J.; Partensky, F. Diversity and evolution of phycobilisomes in marine Synechococcus spp.: A comparative genomics study. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, J.; Celepli, N.; Ininbergs, K.; Dupont, C.L.; Yooseph, S.; Bergman, B.; Ekman, M. Picocyanobacteria containing a novel pigment gene cluster dominate the brackish water Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, T.H.; Schouten, D.; Doeleman, M.; Wollenzien, U.; Huisman, J.; Stal, L.J. Colorful microdiversity of Synechococcus strains (picocyanobacteria) isolated from the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2009, 3, 34–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Cieszyńska, A.; Maculewicz, J.; Latała, A. Ecophysiological characteristics of red, green, and brown strains of the Baltic picocyanobacterium Synechococcus sp.—a laboratory study. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, C.; Rengefors, K.; Fistarol, G.O.; Graneli, E. Allelopathy in phytoplankton-biochemical, ecological and evolutionary aspects. Phycologia 2003, 42, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, M.; Castenholz, R.W.; Waterbury, J.B.; Rippka, R. Form-genus XIII. The Archaea and the Deeply Branching and Phototrophic Bacteria. In Synechococcus. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed; Boone, D.R., Castenholz, R.W., Garrity, G.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 508–512. [Google Scholar]
- Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Pniewski, F.; Latała, A. Allelopathic activity of the picocyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. under varied light, temperature and salinity conditions. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2016, 101, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Maculewicz, J.; Barreiro, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Latała, A. Allelopathic activity of picocyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. on filamentous cyanobacteria. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 496, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, A.; Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Złoch, I.; Vasconcelos, V. Light-dependent cytolysis in the allelopathic interaction between picoplanktic and filamentous cyanobacteria. J. Plankton R. 2018, 40, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Barreiro, A.; Maculewicz, J.; Sobczyk, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Latała, A. Allelopathic activity of the picocyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. on unicellular eukaryote planktonic microalgae. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suikkanen, S.; Fistarol, G.O.; Granéli, E. Allelopathic effects of the Baltic Cyanobacteria Nodularia spumigena, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and Anabaena lemmermannii on algal monocultures. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 308, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suikkanen, S.; Engström-Öst, J.; Jokela, J.; Sivonen, K.; Viitasalo, M. Allelopathy of Baltic Sea cyanobacteria: No evidence for the role of nodularin. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchow, H. Spatio-temporal pattern formation in nonlinear non-equilibrium plankton dynamics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. 1993, 251, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, J.; Jonker, R.R.; Zonneveld, C.; Weissing, F.J. Competition for light between phytoplankton species: Experimental tests of mechanistic theory. Ecology 1999, 80, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, A.; Roy, S.; Vasconcelos, V. Allelopathy prevents competitive exclusion and promotes phytoplankton biodiversity. Oikos 2018, 127, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Suikkanen, S.; Fistarol, G.O.; Grane´li, E. Effects of cyanobacterial allelochemicals on a natural plankton community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 287, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Yosef, Y.; Sukenik, A.; Hadas, O.; Viner-Mozzini, Y.; Kaplan, A. Enslavement in the water body by toxic Aphanizomenon ovalisporum, inducing alkaline phosphatase in phytoplanktons. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, E.K.; Myers, T.L.; Kubanek, J. Effects of harmful algal blooms on competitors: Allelopathic mechanisms of the red tide dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, A.W.; Tóth, V.R.; Pálffy, K. The effects of interspecific interactions between bloom forming cyanobacteria and Scenedesmus quadricauda (chlorophyta) on their photophysiology. Acta Biol. Hung. 2018, 69, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Dahms, H.U.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, W.C.; Shin, K.H. Algal photosynthetic responses to toxic metals and herbicides assessed by chlorophyll a fluorescence. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 104, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.D.; Lopes, A.R.; Soares, E.V. Responses of the alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata to long-term exposure to metal stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 296, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2001–2002: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2005, 140, 265–286. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Meizoso, I.; Jaime, L.; Santoyo, S.; Cifuentes, A.; García-Blairsy Reina, G.; Senorans, F.J.; Ibáñez, E. Pressurized fluid extraction of bioactive compounds from Phormidium species. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3517–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.; Santoyo, S.; Jaime, L.; García-Blairsy Reina, G.; Herrero, M.; Señoráns, F.J.; Ibáñez, E. Screening for bioactive compounds from algae. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güven, K.C.; Coban, B.; Erdugan, H. A Chemical Research on Three Red Algae Gracilaria bursa-pastoris, Phyllophora crispa and Laurencia obtusa var. pyramidata. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 6118–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, S.; Sujatha, K.; Velmurugan, D. The Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Turbinaria ornata (Turner) J. Agaradh and Computational Studies. Pharmacogn. J. 2019, 11, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, G.; Horzum, Z.; Sukatar, A.; Karabay-Yavasoglu, N.U. Antimicrobial activities of volatile components and various extracts of Dictyopteris membranaceae and Cystoseira barbata from the coast of Izmir, Turkey. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Tao, W.Y.; Sun, J. Identification of volatile compounds released by myxobacteria Sorangium cellulosum AHB103-1. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 353–358. [Google Scholar]
- Altaee, N.; Kadhim, M.J.; Hameed, I.H. Detection of volatile compounds produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from UTI patients by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2017, 7, 8–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, G.J.; Kadhim, M.J.; Hussein, H.M. Characterization of bioactive chemical compounds from Aspergillus terreus and evaluation of antibacterial and antifungal activity. IJPPR 2016, 8, 889–905. [Google Scholar]
- Swamy, N.T.; Rosaiah, G.; Babu, K.; Kumar, K.V. A study on phytochemical composition, GC-MS analysis and anti-microbial potential of methanolic leaf extract of Alstonia scholaris (l.) R. BR. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 10, 747–755. [Google Scholar]
- Sieburth, S.M.; Chen, C.A. Silanediol protease inhibitors: From conception to validation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 2, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, A.S.; Kristensen, H.M.; Lanz, G.; Olsen, C.A. The effect of various zinc binding groups on inhibition of histone deacetylases 1–11. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latała, A.; Jodłowska, S.; Pniewski, F. Culture Collection of Baltic Algae (CCBA) and characteristic of some strains by factorial experiment approach. Algol. Stud. 2006, 122, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, R.R.; Sieracki, M.S. Counting cells in cultures with the light microscope. Algal Cult. Tech. 2005, 239–252. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, D.; Hurry, V.; Clarke, A.K.; Gustafsson, P.; Öquist, G. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis of cyanobacterial photosynthesis and acclimation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 1998, 62, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S.T.; Humphrey, G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 1975, 167, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.; Parsons, T.R. A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1972, 167, 1–310. [Google Scholar]
- Paranthaman, R.; Praveen, K.P.; Kumaravel, S. GC-MS analysis of phytochemicals and simultaneous determination of flavonoids in Amaranthus caudatus (Sirukeerai) by RP-HPLC. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2012, 3, 147. [Google Scholar]
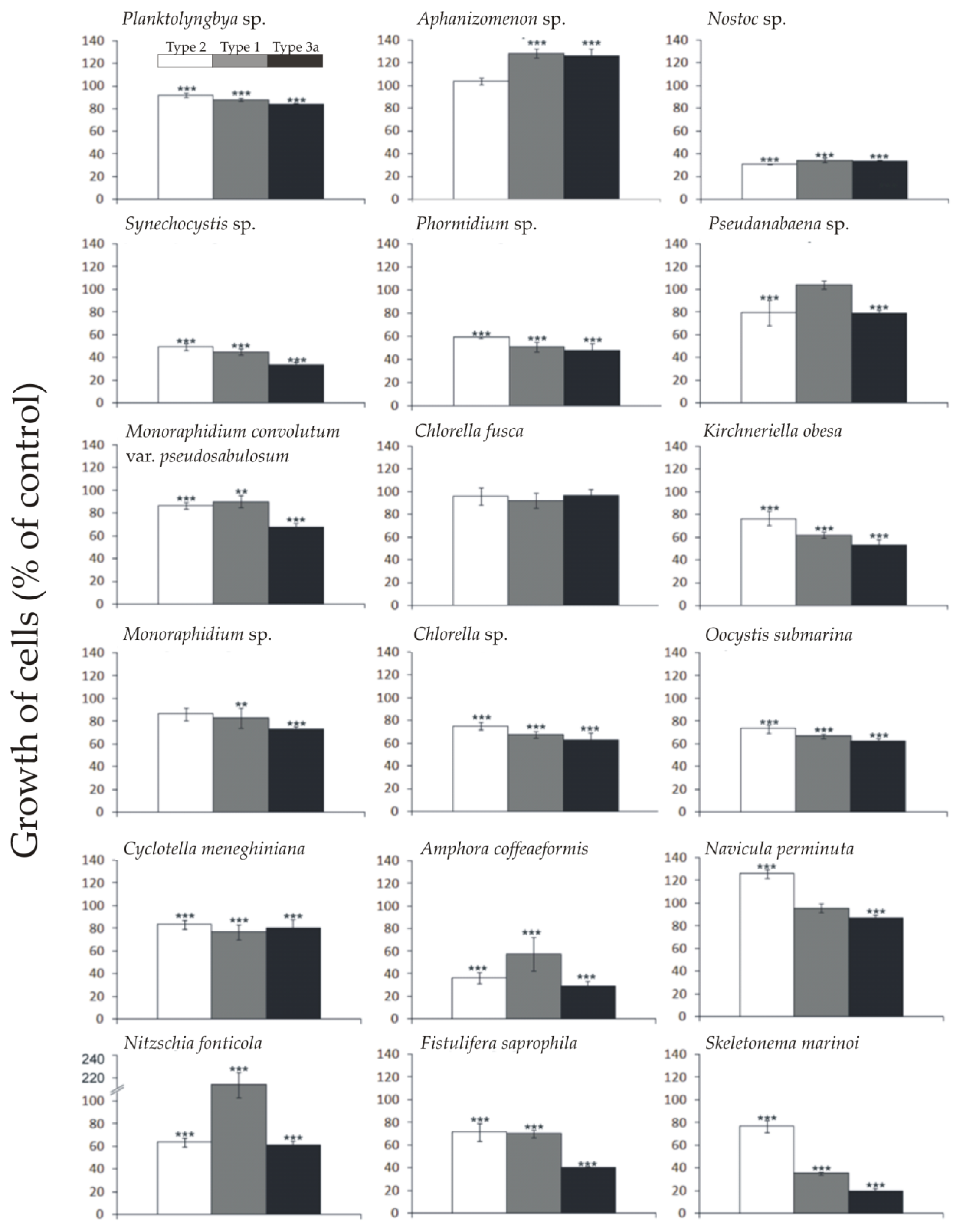
| Target Species | Effect on Phenotypes of Synechococcus sp. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3a | |
| Cyanobacteria | |||
| Planktolyngbya sp. | + * | 0 | 0 |
| Aphanizomenon sp. | + ** | + *** | + *** |
| Nostoc sp. | − *** | − *** | − *** |
| Synechocystis sp. | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Phormidium sp. | + *** | + *** | + *** |
| Pseudanabaena sp. | − *** | − *** | 0 |
| Green algae | |||
| Monoraphidium convolutum var. pseudosabulosum | − *** | − *** | − *** |
| Chlorella fusca | − *** | − *** | − *** |
| Kirchneriella obesa | 0 | + ** | − ** |
| Monoraphidium sp. | − *** | − *** | − *** |
| Chlorella sp. | − *** | − *** | − *** |
| Oocystis cf. submarina | + *** | + *** | + *** |
| Diatoms | |||
| Cyclotella meneghiniana | − * | − ** | − * |
| Amphora coffeaeformis | − ** | 0 | − *** |
| Navicula perminuta | − *** | 0 | 0 |
| Nitzschia fonticola | − *** | 0 | − *** |
| Fistulifera saprophila | − ** | 0 | − *** |
| Skeletonema marinoi | 0 | 0 | − *** |
| Target Species | Effect on Phenotypes of Synechococcus sp. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3a | ||||
| Photosynthetic Pigments | ||||||
| Chl a | Car | Chl a | Car | Chl a | Car | |
| Cyanobacteria | ||||||
| Planktolyngbya sp. | + ** | 0 | + * | − * | + ** | 0 |
| Aphanizomenon sp. | + * | 0 | 0 | 0 | + ** | 0 |
| Nostoc sp. | − * | − ** | − * | − * | − * | − ** |
| Synechocystis sp. | − * | 0 | − * | 0 | − * | 0 |
| Phormidium sp. | − *** | − *** | − *** | − *** | − *** | − * |
| Pseudanabaena sp. | − * | − *** | − * | 0 | − *** | − *** |
| Green algae | ||||||
| Monoraphidium convolutum var. pseudosabulosum | − * | − ** | − * | − ** | − ** | − *** |
| Chlorella fusca | − * | − * | 0 | 0 | − * | 0 |
| Kirchneriella obesa | − *** | − ** | − *** | − ** | − *** | − ** |
| Monoraphidium sp. | − *** | − ** | − *** | − ** | − *** | − *** |
| Chlorella sp. | − *** | 0 | − *** | 0 | − *** | 0 |
| Oocystis cf. submarina | − *** | − ** | − ** | − ** | − ** | − ** |
| Diatoms | ||||||
| Cyclotella meneghiniana | − * | 0 | 0 | 0 | − *** | − ** |
| Amphora coffeaeformis | − *** | − *** | − *** | − *** | − ** | − *** |
| Navicula perminuta | − * | − * | 0 | 0 | − * | − * |
| Nitzschia fonticola | − *** | − ** | − *** | − ** | − *** | − *** |
| Fistulifera saprophila | − *** | − *** | − *** | − *** | − *** | − *** |
| Skeletonema marinoi | 0 | − ** | 0 | 0 | − *** | − *** |
| Name of Compound | RT | Molecular | MW | Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Area % | SI | Peak Area % | SI | Peak Area % | SI | ||||
| Silanediol, dimethyl- | 4.301 | C2H8O2Si | 92 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 13.03 | 97 |
| Oxime-, methoxy-phenyl- | 8.444 | C8H9NO2 | 151 | 0.79 | 83 | 12.91 | 83 | 4.51 | 83 |
| Eicosane, 10-methyl- | 15.060 | C21H44 | 296 | 64.98 | 96 | 6.73 | 94 | ND | ND |
| Target Species | Identification in CCBA Collection |
|---|---|
| Cyanobacteria | |
| Planktolyngbya sp. | BA-50 |
| Aphanizomenon sp. | BA-69 |
| Nostoc sp. | BA-81 |
| Synechocystis sp. | BA-121 |
| Phormidium sp. | BA-141 |
| Pseudanabaena sp. | BA-142 |
| Chlorophyta | |
| Monoraphidium convolutum var. pseudosabulosum | BA-17 |
| Chlorella fusca | BA-18 |
| Kirchneriella obesa | BA-51 |
| Monoraphidium sp. | BA-165 |
| Chlorella sp. | BA-167 |
| Oocystis cf. submarina | BA-172 |
| Bacilariophyta | |
| Cyclotella meneghiniana | BA-10 |
| Amphora coffeaeformis | BA-16 |
| Navicula perminuta | BA-30 |
| Nitzschia fonticola | BA-34 |
| Fistulifera saprophila | BA-56 |
| Skeletonema marinoi | BA-98 |
| Studied Strain | Linear Regression | Correlation Coefficient (r) |
|---|---|---|
| BA-120 | N = 4242096·OD − 35834 | 0.97 |
| BA-124 | N = 93029379·OD − 98415 | 0.99 |
| BA-132 | N = 139120177·OD − 44353 | 0.99 |
| BA-50 | N = 74916153·OD + 46981 | 0.92 |
| BA-69 | N = 6716526·OD − 86633 | 0.96 |
| BA-81 | N = 39891877·OD − 11899 | 0.95 |
| BA-121 | N = 163917381·OD − 246275 | 0.98 |
| BA-141 | N = 86779699·OD − 44781 | 0.98 |
| BA-142 | N = 126415680·OD + 100972 | 0.98 |
| BA-17 | N = 24943668·OD − 263873 | 0.99 |
| BA-18 | N = 14395782·OD + 100101 | 0.97 |
| BA-51 | N = 12365968·OD − 246229 | 0.99 |
| BA-165 | N = 13120468·OD + 10489 | 0.99 |
| BA-167 | N = 3678299·OD + 274144 | 0.93 |
| BA-172 | N = 3363550·OD + 91273 | 0.98 |
| BA-10 | N = 8775538·OD − 1251 | 0.98 |
| BA-16 | N = 4385135·OD + 15527 | 0.98 |
| BA-30 | N = 6412449·OD − 8836 | 0.97 |
| BA-34 | N = 8050792·OD + 17824 | 0.98 |
| BA-56 | N = 7326981·OD − 57789 | 0.99 |
| BA-98 | N = 38103552·OD + 75013 | 0.97 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konarzewska, Z.; Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S.; Felpeto, A.B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Latała, A. Assessment of the Allelochemical Activity and Biochemical Profile of Different Phenotypes of Picocyanobacteria from the Genus Synechococcus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040179
Konarzewska Z, Śliwińska-Wilczewska S, Felpeto AB, Vasconcelos V, Latała A. Assessment of the Allelochemical Activity and Biochemical Profile of Different Phenotypes of Picocyanobacteria from the Genus Synechococcus. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(4):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040179
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonarzewska, Zofia, Sylwia Śliwińska-Wilczewska, Aldo Barreiro Felpeto, Vitor Vasconcelos, and Adam Latała. 2020. "Assessment of the Allelochemical Activity and Biochemical Profile of Different Phenotypes of Picocyanobacteria from the Genus Synechococcus" Marine Drugs 18, no. 4: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040179
APA StyleKonarzewska, Z., Śliwińska-Wilczewska, S., Felpeto, A. B., Vasconcelos, V., & Latała, A. (2020). Assessment of the Allelochemical Activity and Biochemical Profile of Different Phenotypes of Picocyanobacteria from the Genus Synechococcus. Marine Drugs, 18(4), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040179







