Bioactive Capnosanes and Cembranes from the Soft Coral Klyxum flaccidum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.5. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Fekry, M.I.; Al-Hammady, M.A.; Khalil, M.N.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Meyer, A.; Porzel, A.; Westphal, H.; Wessjohann, L.A. Cytotoxic Effects of Sarcophyton sp. Soft Corals-Is there a correlation to their NMR fingerprints? Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Chokkalingam, U.; Hwang, T.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive Isoprenoid-Derived Natural Products from a Dongsha Atoll Soft Coral Sinularia Erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Sung, P.J.; Uvarani, C.; Su, J.H.; Lu, M.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, S.L.; Sheu, J.H. Glaucumolides A and B biscembranoids with new structural type from a cultured soft coral Sarcophyton Glaucum. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltahawy, N.A.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Radwan, M.M.; ElSohly, M.A.; Hassanean, H.A.; Ahmed, S.A. Cytotoxic cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton Auritum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3984–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.F.; Kurtan, T.; Mandi, A.; Yao, L.G.; Li, J.; Lan, L.F.; Guo, Y.W. Structural, stereochemical and bioactive studies of cembranoids from Chinese soft coral Sarcophyton Trocheliophorum. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Chiou, S.F.; Hsu, C.H.; Wang, S.K.; Dai, C.F.; Chiang, M.Y.; Duh, C.Y. Durumolides A−E, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum durum. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 9698–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, A.; Rudi, A.; Benayahu, Y.; Kashman, Y. Three biscembranoids and their monomeric counterpart cembranoid, a biogenetic Diels-Alder precursor, from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1951–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Lin, C.C.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Isolation and structure elucidation of cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton stellatum. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Sheu, J.H.; Chiang, M.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Su, J.H. Structural elucidation and structure-anti-inflammatory activity relationships of cembranoids from cultured soft corals Sinularia sandensis and Sinularia flexibilis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7211–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.P.; Luyen, B.T.; Ngan, N.T.; Song, S.B.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Kiem, P.V.; Kim, Y.H.; Minh, C.V. New anti-inflammatory cembranoid diterpenoids from the Vietnamese soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.F.; Tang, X.L.; Sun, Y.T.; Luo, X.C.; Zhang, J.; van Ofwegen, L.; Sung, P.J.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Terpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia sp. Collected in Yongxing Island. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Duh, C.Y. Secocrassumol, a seco-cembranoid from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6028–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Lin, S.T.; Wang, S.K.; Duh, C.Y. α-Tocopherols from the Formosan soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhu, Z.D.; Gu, Y.C.; Li, J.; Zhu, W.L.; Guo, Y.W. Further new diterpenoids as PTP1B inhibitors from the Xisha soft coral Sinularia polydactyla. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Bie, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, D.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Sarcophyolides B-E, new cembranoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3186–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Liu, D.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Capnosane-type cembranoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum with antibacterial effects. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 8703–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roethle, P.A.; Trauner, D. The chemistry of marine furanocembranoids, pseudopteranes, gersolanes and related natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 298–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.H.; Wang, G.H.; Liaw, C.C.; Lee, M.F.; Wang, S.H.; Cheng, D.L.; Chou, T.H. Extracts from Cladiella australis, Clavularia viridis and Klyxum simplex (soft corals) are capable of inhibiting the growth of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 95–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.; Wu, Y.C.; Chiang, M.Y.; Su, J.H.; Wang, W.H.; Fan, T.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 7016–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, B.W.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Simplexins A-I, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Klyxum simplex. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.; Chao, C.H.; Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. Anti-inflammatory eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2363–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.; Chao, C.H.; Su, J.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Wang, W.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Sung, P.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Klysimplexins I-T, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Wang, W.H.; Sung, P.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Klysimplexins U-X, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.J.; Chen, B.W.; Wen, Z.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Su, J.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Klymollins A-H, bioactive eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the formosan soft coral Klyxum molle. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2467–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Su, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Chen, B.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Simplexins J-O, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from a Dongsha Atoll soft coral Klyxum simplex. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.C.; Chen, B.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Sheu, J.H. Eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Klyxum molle with inhibitory activity on superoxide generation and elastase release by neutrophils. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.Y.; Hsu, F.J.; Tai, C.J.; Wei, W.C.; Yang, N.S.; Sheu, J.H. Klymollins T-X, bioactive eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Klyxum molle. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3060–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.R.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Shih, S.P.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Sheu, J.H. New bioactive steroids from the soft coral Klyxum flaccidum. Rsc. Adv. 2015, 5, 12546–12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.Y.; Chokkalingam, U.; Tai, C.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Wei, W.C.; Yang, N.S.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. New eunicellin-derived diterpenoids from a Taiwanese soft coral Klyxum molle. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, W.R.; Huang, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Hwang, T.L.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. New cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory steroids from the soft coral Klyxum flaccidum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3253–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Tsai, C.R.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Klyflaccicembranols A-I, new cmbranoids from thes soft coral Klyxum flaccidum. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, W.R.; Chiang, P.L.; Hwang, T.L.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Klyflaccisteroids K-M, bioactive steroidal derivatives from a soft coral Klyxum flaccidum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, G.M.; Wright, A.D. New cembranoid Diterpenes from the Soft Coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.A.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Schleyer, M.H. Cembrane diterpenes from the southern African soft coral Cladiella kashmani. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1551–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, K.; Shimura, H.; Yamada, Y. New Cembrane-type diterpenoids from the Okinawan soft coral Sinularia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1779–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhu, H.; Chen, D.; Liu, D.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Pavidolides A−E, new cembranoids from the soft coral Sinularia pavida. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 5759–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Yao, L.G.; Li, X.W.; Guo, Y.W. Sarcophytrols A–C, new capnosane diterpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.E.; Gamal Eldeen, A.M.; Shahat, A.A.; Abdel-Latif, F.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Whittlesey, B.R.; Pare, P.W. Bioactive hydroperoxyl cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Ahmed, A.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. New Cembranoids and a biscembranoid peroxide from the soft coral Sarcophyton cherbonnieri. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.H.; Ahmed, A.F.; Sung, P.J.; Chao, C.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Manaarenolides A-I, diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia manaarensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, H.O.; Berger, S.; Braun, S. Carbon13 NMR Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Wen, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Wu, Y.C.; Hu, W.P.; Sheu, J.H. Oxygenated cembranoids from a Formosan soft coral Sinularia gibberosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. FEBS 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, G.R.; Caton, M.C.; Nova, M.P.; Parandoosh, Z. Assessment of the Alamar Blue assay for cellular growth and viability in vitro. J. Immunol. Methods 1997, 204, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.L.; Li, G.L.; Lan, Y.H.; Chia, Y.C.; Hsieh, P.W.; Wu, Y.H.; Wu, Y.C. Potent inhibition of superoxide anion production in activated human neutrophils by isopedicin, a bioactive component of the Chinese medicinal herb Fissistigma oldhamii. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Chung, P.J.; Ho, C.M.; Kuo, C.Y.; Hung, M.F.; Huang, Y.T.; Chang, W.Y.; Chang, Y.W.; Chan, K.H.; Hwang, T.L. Propofol inhibits superoxide production, elastase release, and chemotaxis in formyl peptide-activated human neutrophils by blocking formyl peptide receptor 1. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6511–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

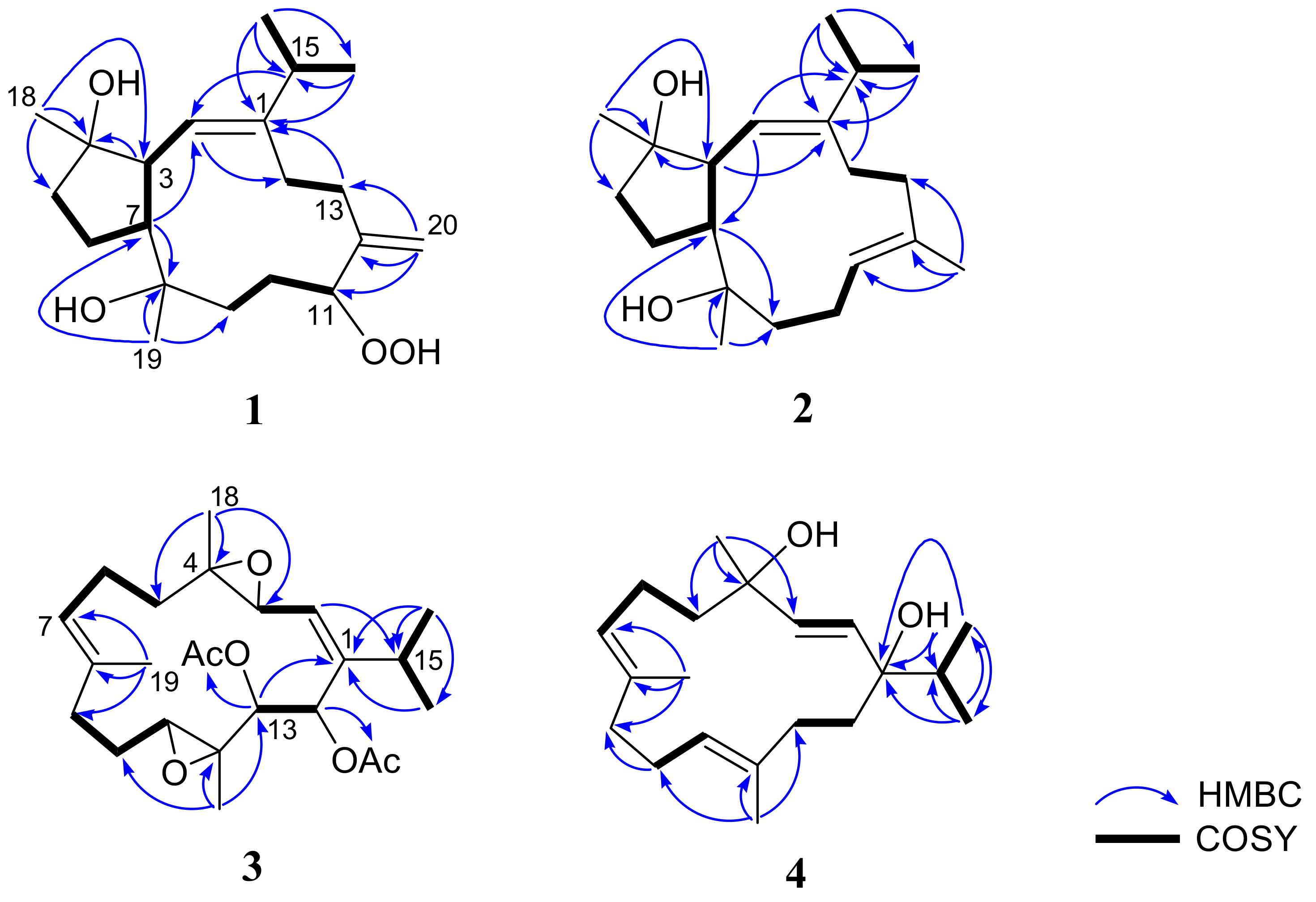
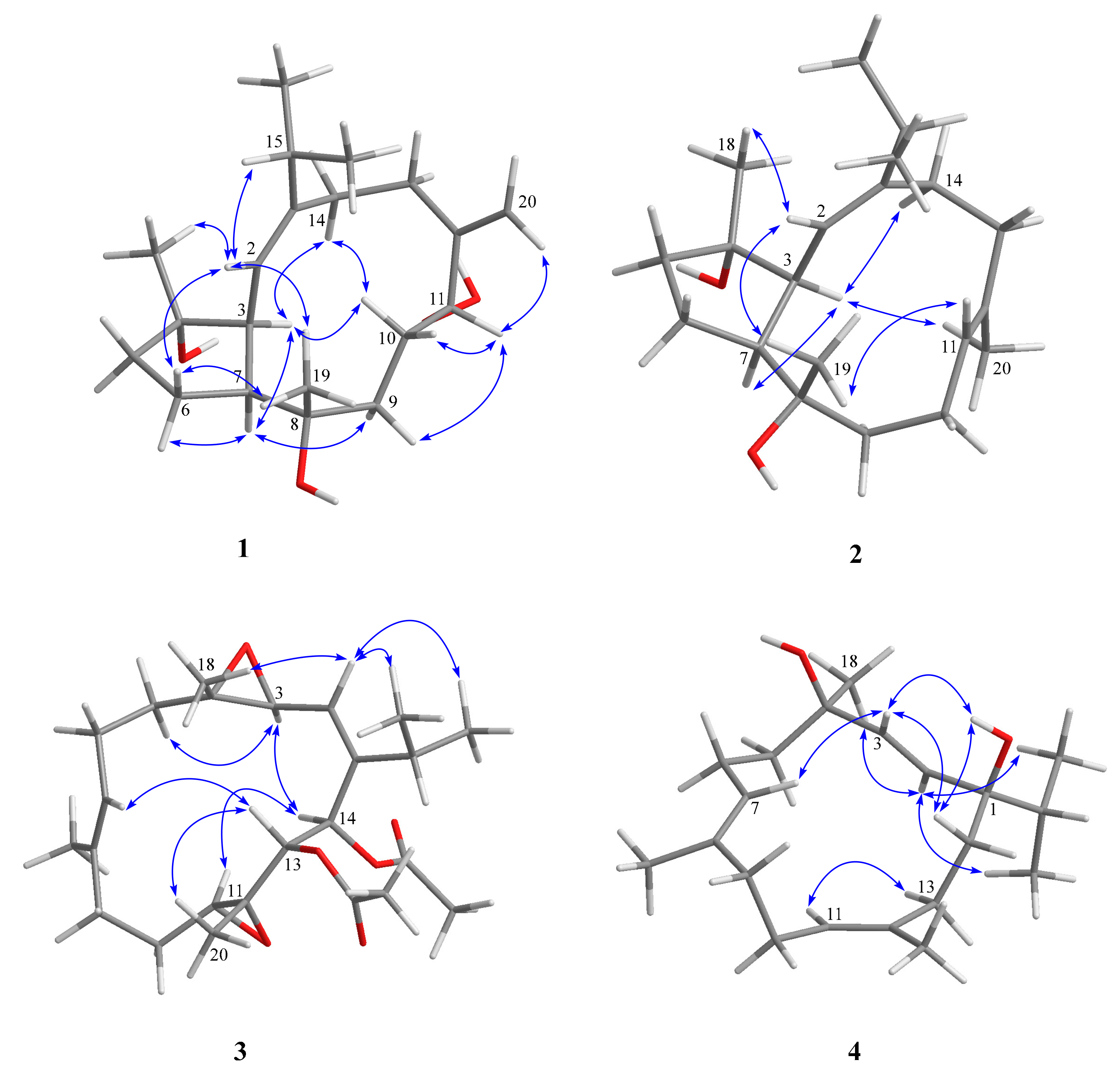
| Position | 1 a | 2 b | 3 b | 4 c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 146.6, C | 144.4, C | 149.6, C | 78.6, C |
| 2 | 122.3, CH d | 121.8, CH | 124.8, CH | 131.5, CH |
| 3 | 51.0, CH | 51.1, CH | 58.1, CH | 136.5, CH |
| 4 | 82.8, C | 82.8, C | 62.1, C | 72.3, C |
| 5 | 40.3, CH2 | 37.7, CH2 | 37.8, CH2 | 43.9, CH2 |
| 6 | 25.5, CH2 | 23.0, CH2 | 23.5, CH2 | 22.3, CH2 |
| 7 | 50.5, CH | 54.3, CH | 126.4, CH | 128.4, CH |
| 8 | 74.5, C | 75.2, C | 133.7, C | 132.8, C |
| 9 | 37.9, CH2 | 44.1, CH2 | 35.9, CH2 | 39.0, CH2 |
| 10 | 25.4, CH2 | 23.1, CH2 | 24.0, CH2 | 23.9, CH2 |
| 11 | 90.7, CH | 127.1, CH | 59.1, CH | 126.5, CH |
| 12 | 148.1, C | 132.3, C | 60.4, C | 136.3, C |
| 13 | 30.3, CH2 | 36.0, CH2 | 73.2, CH | 36.2, CH2 |
| 14 | 28.6, CH2 | 28.3, CH2 | 67.8, CH | 32.7, CH2 |
| 15 | 32.7, CH | 32.9, CH | 28.9, CH | 38.7, CH |
| 16 | 21.1, CH3 | 21.2, CH3 | 24.2, CH3 | 16.7, CH3 |
| 17 | 23.7, CH3 | 23.8, CH3 | 24.0, CH3 | 17.6, CH3 |
| 18 | 25.8, CH3 | 25.2, CH3 | 17.5, CH3 | 27.8, CH3 |
| 19 | 27.1, CH3 | 22.1, CH3 | 15.9, CH3 | 14.8, CH3 |
| 20 | 117.4, CH2 | 17.3, CH3 | 16.2, CH3 | 14.7, CH3 |
| 13-OAc | 20.7, CH3 | |||
| 170.4, C | ||||
| 14-OAc | 20.7, CH3 | |||
| 169.0, C |
| Position | 1 a | 2 b | 3 b | 4 c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4.96 d (9.5) d | 5.05 d (10.8) | 5.25 m | 5.59 d (16.0) |
| 3 | 2.89 dd (10.0, 10.0) | 2.37 dd (7.8, 9.6) | 3.56 d (9.6) | 6.05 d (16.0) |
| 5 | 1.52 2H, m | 1.72 m; 1.65 m | 1.48 m; 2.11 m | 1.52 m; 1.99 m |
| 6 | 1.94 m; 1.64 m | 1.88 m; 1.76 m | 2.13 m; 2.23 m | 2.22 m; 2.35 m |
| 7 | 2.63 m | 2.65 ddd (6.6, 7.8, 9.6) | 5.22 m | 5.34 dd (7.5, 7.5) |
| 9 | 1.85 ddd (13.0, 13.0, 3.0); 1.20 ddd (13.0, 13.0, 4.5) | 1.88 m; 2.00 m | 2.14 m; 2.24 m | 1.96 m; 2.18 m |
| 10 | 1.94 m; 1.68 ddd (13.0, 10.5, 3.0) | 2.14 m | 1.09 m; 1.61 m | 2.04 m; 2.23 m |
| 11 | 4.27 dd (11.0, 4.5) | 4.99 dd (7.6, 7.6) | 3.12 dd (5.6, 5.6) | 5.18 dd (9.0, 3.5) |
| 13 | 2.66 m; 2.20 dd (11.5, 5) | 2.03 m; 1.92 m | 5.49 d (7.6) | 2.10 m; 2.15 d (3.0) |
| 14 | 2.79 ddd (11.5, 11.5, 4.5); 2.00 m | 2.40 dd (14.4, 7.2); 1.94 ddd (14.4, 12.0, 3.0) | 5.89 d (7.6) | 1.86 td (12.5, 3.5); 1.60 m |
| 15 | 2.22 sept (7.0) | |||
| 16 | 0.97 3 H, d (7.0) | 1.06 3H, d (7.2) | 1.02 3H, d (6.4) | 0.87 3H, d (7.0) |
| 17 | 0.90 3 H, d (7.0) | 1.02 3H, d (6.8) | 1.02 3H, d (6.4) | 0.87 3H, d (7.0) |
| 18 | 0.99 3 H, s | 1.14 3H, s | 1.33 3H, s | 1.40 3H, s |
| 19 | 1.05 3 H, s | 1.25 3H, s | 1.64 3H, s | 1.60 3H, s |
| 20 | 4.93 s; 4.97 s | 1.67 3H, s | 1.26 3H, s | 1.67 3H, s |
| 13-OAc | 2.14 3H, s | |||
| 14-OAc | 2.01 3H, s | |||
| 1-OH | 2.39 s | |||
| 11-OOH | 7.64 br s |
| Compound | Cell Lines IC50 (μg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A549 a | DLD-1 b | P388D1 c | |
| 1 | 9.7 ± 1.2 | 6.0 ± 0.4 | 7.2 ± 1.8 |
| 2 | 28.6 ± 3.8 | 31.6 ± 3.7 | 30.4 ± 4.8 |
| 3 | − d | − | 19.6 ± 8.3 |
| 4 | − | − | − |
| 5 | − | − | − |
| 6 | − | − | − |
| 7 | 10.8 ± 4.9 | 11.7 ± 4.8 | 8.9 ± 2.2 |
| Doxorubicin e | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 |
| Compounds | Superoxide Anion | Elastase Release | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) a | Inh % b | IC50 (μM) a | Inh % b | |||
| 2 | >10 | 24.46 ± 6.99 | * | >10 | 29.96 ± 6.14 | ** |
| 3 | >10 | 8.88 ± 3.33 | >10 | 27.18 ± 4.05 | ** | |
| 4 | >10 | 3.29 ± 0.88 | * | >10 | 14.43 ± 3.75 | * |
| 5 | >10 | 8.89 ± 4.28 | >10 | 14.89 ± 3.62 | * | |
| 6 | >10 | 4.73 ± 1.53 | * | >10 | 3.09 ± 3.88 | |
| 7 | >10 | 11.95 ± 2.53 | ** | 7.22 ± 0.85 | 59.66 ± 0.83 | *** |
| Idelalisib | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 102.8 ± 2.2 | *** | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 99.6 ± 4.2 | *** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, W.-R.; Ahmed, A.F.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-Y.; Tai, C.-J.; Orfali, R.S.; Hwang, T.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Sheu, J.-H. Bioactive Capnosanes and Cembranes from the Soft Coral Klyxum flaccidum. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080461
Tseng W-R, Ahmed AF, Huang C-Y, Tsai Y-Y, Tai C-J, Orfali RS, Hwang T-L, Wang Y-H, Dai C-F, Sheu J-H. Bioactive Capnosanes and Cembranes from the Soft Coral Klyxum flaccidum. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080461
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Wan-Ru, Atallah F. Ahmed, Chiung-Yao Huang, Yi-Ying Tsai, Chi-Jen Tai, Raha S. Orfali, Tsong-Long Hwang, Yi-Hsuan Wang, Chang-Feng Dai, and Jyh-Horng Sheu. 2019. "Bioactive Capnosanes and Cembranes from the Soft Coral Klyxum flaccidum" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080461
APA StyleTseng, W.-R., Ahmed, A. F., Huang, C.-Y., Tsai, Y.-Y., Tai, C.-J., Orfali, R. S., Hwang, T.-L., Wang, Y.-H., Dai, C.-F., & Sheu, J.-H. (2019). Bioactive Capnosanes and Cembranes from the Soft Coral Klyxum flaccidum. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080461







