Abstract
Natural products are primal and have been a driver in the evolution of organic chemistry and ultimately in science. The chemical structures obtained from marine organisms are diverse, reflecting biodiversity of genes, species and ecosystems. Biodiversity is an extraordinary feature of life and provides benefits to humanity while promoting the importance of environment conservation. This review covers the literature on marine natural products (MNPs) discovered in Indonesian waters published from January 1970 to December 2017, and includes 732 original MNPs, 4 structures isolated for the first time but known to be synthetic entities, 34 structural revisions, 9 artifacts, and 4 proposed MNPs. Indonesian MNPs were found in 270 papers from 94 species, 106 genera, 64 families, 32 orders, 14 classes, 10 phyla, and 5 kingdoms. The emphasis is placed on the structures of organic molecules (original and revised), relevant biological activities, structure elucidation, chemical ecology aspects, biosynthesis, and bioorganic studies. Through the synthesis of past and future data, huge and partly undescribed biodiversity of marine tropical invertebrates and their importance for crucial societal benefits should greatly be appreciated.
1. Introduction
Natural products have been the core of the evolution of organic chemistry. About 40 molecules have been detected that have had revolutionary effects and become indispensable for human society [1]. In particular, three MNPs, (+)-palytoxin, (+)-brevetoxin B, and (–)-ecteinascidin 743, are engines for its development. The beautiful and challenging structures of MNPs have been disclosed by several methods, including classic and modern structure elucidation, even though they are often available only in invisibly small amounts and have unprecedented properties in nature. This is becoming the predominant task of organic chemistry [2].
MNPs are defined as secondary metabolites produced by marine organisms, both macro- and microorganisms, as responses that are part of their defense strategies, responses to the food chain, or as communication signals with their environment. Moreover, these functions are related to biodiversity, which is considered an important key for obtaining diverse metabolites, the structures of which are responsible for the characteristics of a vast range of chemical reactions, both in living and non-living systems.
Biodiversity generally refers to the number of species living in a particular ecosystem. The accepted number of species on land is 0.45–1.9 million [3,4], while the species richness in the oceans is estimated to be 0.30–10 million [5]. Some of the highest concentrations of species are located in the tropical region [6]. Due to high diversity of species, and hence the high competition for survival, MNPs exhibit chemical structures and biological activities that are different from those of traditionally investigated terrestrial natural products. The uniqueness of skeletons, functional groups (FGs) and remote chiral centers are some features of MNPs that are presented in this review.
To date, eight marine-derived natural products [7,8,9,10] have been recorded as approved drugs, of which seven molecules have been used to date. (–)-Ecteinascidin 743 (Yondelis®) was derived directly from the Caribbean ascidian Ecteinascidia turbinata (the true producer was recently established as γ-proteobacterial endosymbiont Candidatus endoecteinascidia frumentensis [11]). The molecule is used for treatment of advanced soft tissue sarcoma and for treatment of recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer when combined with liposomal doxorubicin. The peptide ω-conotoxin MVIIa (Prialt®) from the venom of the cone snail Conus magus is used for analgesic treatment. The anticancer agent (–)-eribulin mesylate (Halaven®) is a synthetic truncated derivative of the polyketide halichondrin B, a super-carbon chain compound isolated from the Japanese sponge Halichondria okadai. The last approved anticancer drug related to MNPs is the antibody−drug conjugate (ADC) brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris®). It consists of a tumor-specific antibody and the pentapeptide auristatin E, a derivative of dolastatin 10 derived from the Indian sea hare Dolabella auricularia. The molecule is used for the treatment of primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (pcALCL) or CD30-expressing mycosis fungoides (MF) in those who have received prior systemic therapy. In addition, the ADC is used to treat untreated stage III or IV classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) in combination with chemotherapy. A mixture of two ethyl esters of fish-derived ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentanaenoic acid (EPA) was approved under the trade name Lovaza® and is used for reducing serum triglycerides. Iota-carrageenan (Carragelose®), isolated from red algae Eucheuma/ Cnondrus, works as an anti-viral barrier in the nasal cavity. Two nucleosides, the anticancer agent (+)-cytarabine (Cytosar®) and the antiviral drug against herpes simplex virus (–)-vidarabine (Vira-A®) are derivatives of spongothymidine and spongouridine from the Caribbean sponge Tethya crypta, respectively. (–)-Vidarabine (Vira-A®) has been discontinued in the US and in Europe.
The structural diversities of natural products affording unique pharmacological or physiological activities and intricate structures have contributed to breakthroughs in basic (i.e., organic) chemistry and applied sciences (e.g., marine biotechnology), and have even led to a few Nobel Prizes [12]. Ultimately, the diversity of chemicals and biological activities can provide excellent tools for other scientific fields, including biology, agriculture, medicine, materials, energy, and the environment. These facts have made marine organisms attractive targets for research endeavors.
Indonesia is located at one of the centers of biodiversity hotspots [13], endowed with a coral reef triangle, and is an epicenter of marine biodiversity covering 10.36 million km2 of ocean and coastal waters surrounding Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, Timor Leste, and Australia [14]. The country consists of 34 provinces (Figure 1) [15] and surrounding water areas encompassing 5.79 million km2, of which 1.08% or 62,600 km2 is protected as national parks [16]. The features of this area include not only species richness, endemism and habitat diversity, but its relatively pristine condition. An understanding of the fundamental biodiversity [17,18] gained through investigation of bioactive molecules is required by having skills to do individual chemical investigations with small specimens to reduce costs and to minimize environmental impact. Another way is to use fermentation and culture of marine microbes. Although permission to collect and export specimens has been given, researchers must be aware and respectful of indigenous knowledge and cultural sensitivities [19]. Chemists are not yet adept at easily creating molecules with high potency for use as medicines, whereas nature has an enormous, almost incomprehensible, capacity for diversity and adaptation [20,21]. Perhaps the most important way of solving biodiversity problems is through the synthesis of past and future data not only on the basis of taxonomic and spatial distribution, but also through chemical and biological—including ecological and genetic, as well as medicinal—perspectives. This would be in tandem with national and international collaborative research programs [22,23]. The wise use of cutting-edge technology and access to biodiversity through benefit-sharing agreements are believed to conserve our global ecosystems while advancing science.
Figure 1.
Map of Indonesia and its 34 provinces [15]: SRA (Special Region of Aceh), NST (North Sumatra), RAU (Riau), RUI (Riau Islands), WST (West Sumatra), JMI (Jambi), BKU (Bengkulu), SST (South Sumatra), BBI (Bangka–Belitung Islands), LPG (Lampung), BTN (Banten), JSCR (Jakarta Special Capital Region), WJV (West Java), CJV (Central Java), SRY (Special Region of Yogyakarta), EJV (East Java), BLI (Bali), WNT (West Nusa Tenggara), ENT (East Nusa Tenggara), WKM (West Kalimantan), CKM (Central Kalimantan), EKM (East Kalimantan), SKM (South Kalimantan), NKM (North Kalimantan), NSW (North Sulawesi), GTO (Gorontalo), WSW (West Sulawesi), CSW (Central Sulawesi), SSW (South Sulawesi), SES (Southeast Sulawesi), NMU (North Maluku), MLU (Maluku), SRWP (Special Region of West Papua), and PUA (Papua).
Although Indonesian MNPs have been reviewed [24,25,26], there is no comprehensive review from the earliest research of Indonesian MNPs to the present. The earliest observation of marine products was realized by poisoning with clupeoid fish [27], while the first MNP discovered in Indonesian waters was (−)-25-hydroxy-24ξ-methylcholesterol 1 [28], isolated in 1972 (Figure 2).
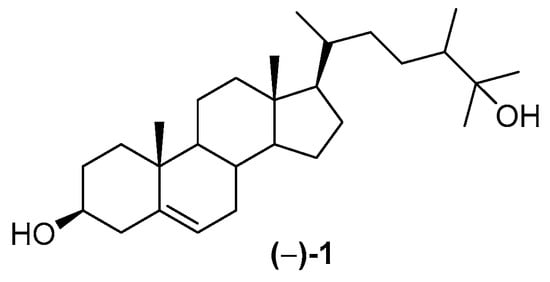
Figure 2.
Structure of (–)-25-hydroxy-24ξ-methylcholesterol 1.
To provide a current status of Indonesian MNPs, we performed a literature review of new chemical structures found in Indonesian waters, including their chemistry, biological activities, spatio-temporal dimensions, taxonomy, and dissemination of information from marine macro- and microorganisms published during the period January 1970–December 2017. An estimated 15,500 new MNPs were discovered worldwide between 1970 and 2010 [29], among which about 486 new molecules (3.1%) were found in Indonesia. In the period 1990–2009, the number of new MNPs worldwide was 9812 [30], while that from Indonesian waters was 406 (4.1%). The present work covered a total of 732 original MNPs, with 4 known to be synthetic compounds, 34 revised, and 9 unnatural MNPs, from January 1970 to December 2017 (Figure 3A). In addition, 43 MNPs were isolated as mixtures, while 130 MNPs were reported with incomplete stereochemistry. Of 732 MNPs, none of them has been approved or is under clinical trial.
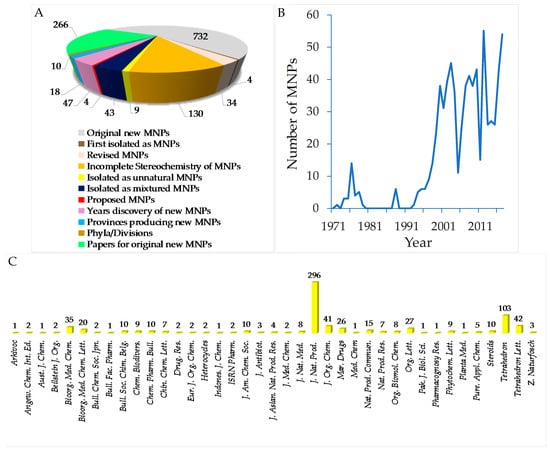
Figure 3.
Statistics of new Indonesian MNPs from January 1970 to December 2017 (A). Distribution of new MNPs on the basis of their publication per year (B) and journal titles (C).
Before 1990, the exploration trend of Indonesian MNPs was relatively steady; however, after 1990 the discovery of new molecules has increased significantly (Figure 3B). More specifically, in the period of 1970–1979, 31 terpenoids were the only MNPs reported. In the next decade, 1980–1989, the structural types of Indonesian MNPs were alkaloids (4 molecules) and polyketides (2 molecules). From 1990 to 1999, the numbers of Indonesian MNPs were: 27 terpenoids, 19 alkaloids, 11 polyketides, 5 peptides, 1 fatty acid, and 1 carbohydrate. The discovery of new Indonesian MNPs was at its highest in the period 2000–2009, with 139 terpenoids, 121 alkaloids, 44 polyketides, 30 peptides, and 8 fatty acids. In the current decade, 2010–2017, the structural types of Indonesian MNPs were 116 alkaloids, 79 terpenoids, 64 polyketides, 25 peptides, 4 fatty acids, and 1 carbohydrate. Alongside improvement of techniques for structure elucidation, separation, and synthesis, the increased number of bioactive Indonesian MNPs in the last two decades may be due to logistical ease, as many Indonesian biodiversity hotspots are in remote areas.
The original Indonesian MNPs were reported in 266 papers in 39 different journals. Among them, J. Nat. Prod. is placed for top tier dissemination (296 molecules, 40.4%) followed by Tetrahedron (103 molecules, 14.1%), Tetrahedron Lett. (42 molecules, 5.7%), and J. Org. Chem. (41 molecules, 5.6%) (Figure 3C). Of 266 papers, 117 papers (44.0%) were written by local researchers who are affiliated with Indonesian research centers/universities.
The chemical diversity of Indonesian MNPs has been analyzed with respect to carbon skeleton, functional group, rare motif, and atomic diversity. New carbon skeletons were observed in 28 molecules, while rare FGs and motifs were found in 18 and 44 molecules, respectively (Figure 4). A few examples of new carbon skeletons can be seen in vannusal A (198), halioxepine (281), manadomanzamine A (318), and phormidolide (702), while rare FGs and motifs can be seen in sinulasulfone (44), polycarpaurine C (487), siladenoserinol A (505), lanesoic acid (541), and petroquinone A (734), to name a few. In this review, the MNPs are organized into their structural types, consisting of 276 terpenoids (37.7%), 260 alkaloids (35.5%), 60 peptides (8.2%), 13 fatty acids and linear molecules (1.8%), 121 polyketides (16.5%), and 2 carbohydrates (0.3%) (Figure 4B). Among 97 chemical types of Indonesian MNPs, piperidine alkaloids (48 molecules), tyrosine alkaloids (38 molecules), indole alkaloids (37 molecules), aromatic polyketides (34 molecules), and quinones (33 molecules) are listed as the top five chemical types (Figure 4C).
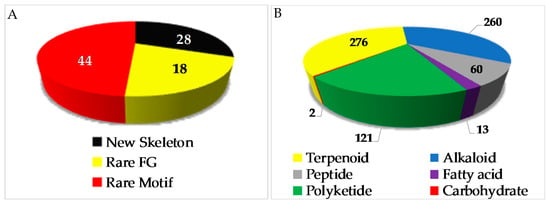
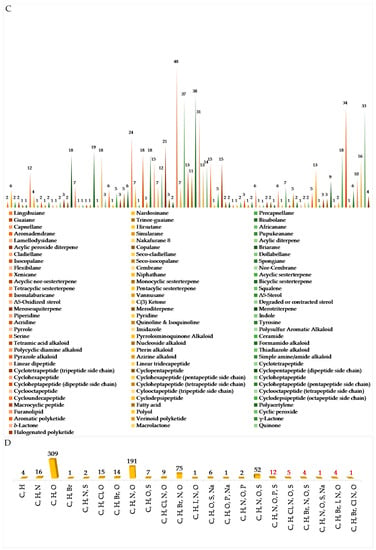
Figure 4.
Distribution of new Indonesian MNPs on the basis of chemical skeletons (A), classes (B), chemical types (C), and atomic diversities (D).
The evaluation of atomic diversity within Indonesian MNPs (Figure 4D) shows that 27 molecules (written in red numbers) contain 6 different atoms in 1 molecule, while the majority (326 molecules) contain 3 different atoms in 1 molecule. Most of them contain C, H, O, N, with the addition of Br and I (4 molecules), as in enisorine E (438), agelanesins B (464) and D (466), 1-O-methylhemibastadinol 4 (440); Br and Cl (1 molecule), as in diazonamide E (611); Br and S, as in mauritamides D (462), B (467) and C (468); Cl and S (4 molecules), as in dysithiazolamide (552), biakamides A–D (742–745); P and S (12 molecules), as in siladenoserinols A–L (505–516); Na and S (1 molecule), as in cupolamide A (564). Of 732 molecules, 373 (51.0%) are nitrogenous molecules. Further inspection of the atomic diversity indicated that 122 molecules (16.7%) possess a ratio of H/C < 1, which is often challenging with respect to structure elucidation [31]. The smallest H/C was found in cadiolide B (679) (H/C = 0.4). In terms of molecular weight, the biggest MNP is kakelokelose (747), with an estimated molecular weight of between 3 and 500 kDa, while the smallest MNP was plakofuranolactone (683), at 172 Da. The biggest unsaturation number (Un) 43 of petroquinones A (734) and B (735) is composed of 16 rings and 27 double bonds, while the smallest is 1 in strepsiamides A–C (518–520).
The chemical diversity of Indonesian MNPs can also be reflected by the use of several orthogonal-tactic-classic and modern structure elucidations describing the nature of Indonesian MNPs, such as molecular size, complexity, and type and distribution of functional groups. Having a single crystal molecule, the structure elucidation task is more straightforward and secured to perform by employing X-ray crystallography to reveal the 2D and 3D molecular structure, including absolute configuration and conformation. Of 732 original MNPs, 30 MNPs were determined by X-ray crystallography in combination with other spectroscopic data. In addition, three revised MNPs, vannusal B (199b), trans, trans-[D-allo-ile] ceratospongamide (566b) and 659b, were securely determined with the aid of X-ray diffraction.
The presence and position of nitrogen atoms and their correlations to hydrogen or carbon atoms within the molecules can be detected by 15N NMR and NH-HMBC as in manadomanzamine A (318), neo-kauluamine (321), lanesoic acid (541), polycarpathiamine A (544), sintokamide A (553), and cis, cis-ceratospongamide (565), while P-containing molecules can be evaluated by the use of 31P NMR as in siladenoserinol A (505). The planar structure of the 10-membered polysulfur ring, as in lissoclibadin 1 (498), could be elucidated by applying NOEs with a combination of other tactics such as quantum chemical calculation (QCC). The presence of a sulfate group can be detected by infrared (IR) and confirmed by mass spectrometry (MS)/MS fragmentation, as in polycarpaurines B and C (497–498).
For cyclic molecules with rigid three- to six-membered rings, their relative stereochemistry can be elucidated by analyzing 1H–1H spin coupling constants (3JHH), chemical shifts and NOEs. For geometrically flexible molecules such as multiple stereocenters of acyclic chains or macrocycles, it cannot be concluded with NOEs. To handle such molecules, NMR-based approaches including J-based configuration analysis (JBCA), universal NMR database (UDB), theoretical calculation of NMR parameters and residual dipolar couplings (RDCs) [32] were applied as tools to determine the relative configuration of natural products. Of 732 molecules, relative stereochemistry of at least four molecules 541, 552, 702, and 708 were elucidated with the aid of JBCA method, while the relative configuration of one molecule as in 595 was elucidated by JBCA-QCC tactics.
The absolute configurations (ACs) of MNPs can be elucidated by NMR in two approaches: (a) substrate analysis without derivatization (i.e., by the addition of a chiral solvating agent (CSA)) and (b) analysis of the diastereomeric derivatives prepared with a chiral derivatizing agent (CDA) [33]. The ACs of 31 Indonesian MNPs were determined by applying CDA. If chiral molecules possess appropriate chromophore(s), electronic circular dichroism (ECD) can be applied, as in 56 MNPs. Comparison of the ECD calculated by the time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) with the experimental ECD spectra was performed for the ACs of as-exemplified lamellodysidine A (41), niphatheolide A (128), sulawesin A (133), and nakamuric acid (448a). However, nakamuric acid (448a) was first revised to 448b1 by synthesis [34], and later to 448b2 based on the comparison of experimental and calculated ECD spectra [35]. Molecular modelling, total synthesis, and QCC were used to determine the structure of vannusals A (198) and B (199) [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Combination of NMR and chemical degradation helped to determine the long carbon chain molecules, karatungiols A (655) and B (626) [44]. For small heterocyclic molecules with the ratio of H/C < 1, total synthesis is helpful for confirming unusual rings, as in latonduine A (450) [45] and polycarpathiamine A (544) [46].
With respect to phylogeny, new MNPs have been discovered from 5 kingdoms, 10 phyla, 14 classes, 32 orders, 64 families, 106 genera, and 94 species (Figure 5A,B) in Indonesian waters over the past 47 years. Three phyla (Porifera, Cnidaria, and Chordata) are found to be the major sources (498 molecules, 68.0%; 116 molecules, 15.8%; and 60 molecules, 8.2%, respectively) of novel metabolites. The remaining 8.0% were discovered from the following phyla: Mollusca (3 molecules, 0.4%), Rhodophyta (3 molecules, 0.4%), Ciliophora (2 molecules, 0.3%), Dinoflagellate (2 molecules, 0.3%), Ascomycota (45 molecules, 6.1%), Cyanobacteria (1 molecule, 0.1%), and Actinobacteria (2 molecules, 0.3%). The phylum Porifera, the largest source of Indonesian MNPs, consists of three classes: Demospongiae (91.8%), Homoscleromorpha (6.6%) and Calcarea (1.6%). Among these, Demospongiae is comprised of 11 orders and 32 families. The Cnidaria is comprised of 1 class (Anthozoa), 3 orders (Alcyonacea, Pennatulacea, Actinaria), and 9 families (Alcyoniidae, Nephtheidae, Xeniidae, Briareidae, Ellisellidae, Isididae, Veretillidae, Pennatulidae, and Stichodactylidae).
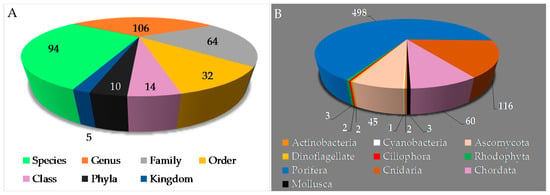
Figure 5.
Distribution of new Indonesian MNPs on the basis of biological sources (A,B).
The top 10 genera reported for new MNPs are Achantostrongylophora (4.4%), Xestospongia (3.6%), Sinularia (3.4%), Apysinella, Theonella and Strepsichordaia (each 2.9%), Plakortis, Petrosia, Spongia, Melophlus (each 2.6%), Agelas, Rhabdastrella, and Lissoclinum (each 2.5%). Unknown genera were the sources of 6.2% of new MNPs. Symbiotic relationships are generally found between sponges and fungi, algae and fungi, and dinoflagellates and acoel flatworms. The list of Indonesian marine organisms producing new MNPs is described in Figure 6.
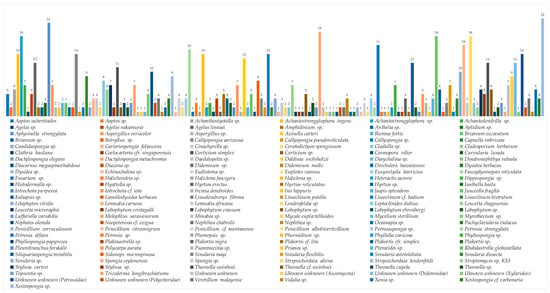
Figure 6.
Distribution of new Indonesian MNPs on the basis of biological sources and a list of species of Indonesian marine organisms reported to contain new MNPs. Unknown unknown is an unidentified species from certain phyla.
The most frequently evaluated biological activities of Indonesian MNPs is cytotoxicity (122 molecules, 16.7%) (Figure 7). Results are generally expressed in the terms of the dose or concentration that inhibits cell growth to 50% of the control (ED50, EC50, ID50, IC50, LD50, LC50 in μg/mL or μM), and the criterion for a cytotoxic compound is ED50 < 4 μg/mL [47]. Cytotoxic evalution has been performed on cell-based (120 human, 26 murine, and 1 monkey Cercopithecus aethiops cell lines), enzyme-based (mainly protease and kinase), and brine shrimp (Artemia salina) assays. Of 122 molecules, four molecules—60, 619, 652, and 702—showed significant toxicity against A. salina. Antibacterial activity has been the second most frequently used bioassay for Indonesian MNPs, with 43 molecules (5.9%) showing significant results followed by anticancer (4.0%), cytostatic (3.0%), antifungal (2.7%), and antiparasitic activity (2.6%). Of 4.0% anticancer molecules, only 2.3% showed anticancer activity without cytotoxicity. It is noteworthy that at least 86 out of 260 alkaloids have been isolated and tested as salt forms against various targets of assays. In addition, about 609 molecules have been used for in vitro assay, while 10 molecules had been used for in vivo evaluation.
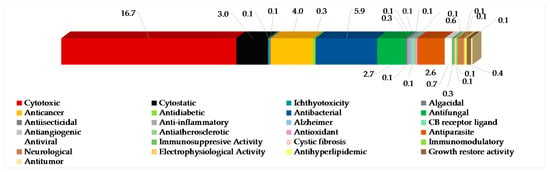
Figure 7.
Distribution of new Indonesian MNPs on the basis of their significant biological activity.
Biogeography of Indonesian MNPs shows that 18 (NST, WST, BTN, JSCR, WJV, CJV, BLI, ENT, EKM, NSW, GTO, CSW, SSW, SES, NMU, MLU, SRWP, and PUA) of 34 provinces are sources of new MNPs. Among the 18 provinces, more than 70% of the total new MNPs are supplied by five provinces: NSW (33.0%), SSW (12.7%), MLU (10.4%), BLI (7.8%), and EKM (6.6%) (Figure 8A,B). The frequent discovery of Indonesian MNPs in the Eastern part of Indonesia may be due to it being closer to the center of Coral Triangle.
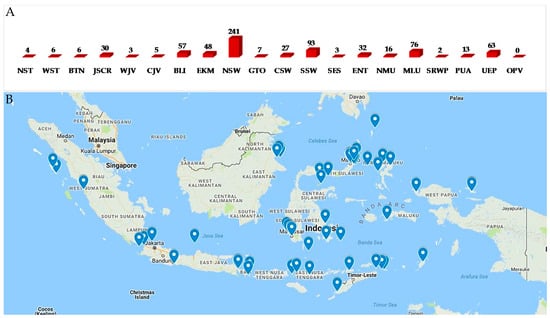
Figure 8.
Distribution of new Indonesian MNPs on the basis of their biogeography hotspots (A,B) (OPV other provinces).
From the above results, it can be seen that Indonesian marine macro- and micro-organisms are still largely underexplored and may provide viable sources and inspiration for a large number of new chemical entities. Modern structure elucidation and other strategies are keys to providing new therapeutic agents and/or new tools for life science studies.
Data presented in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19, Figure 20, Figure 21, Figure 22, Figure 23, Figure 24, Figure 25, Figure 26, Figure 27, Figure 28, Figure 29, Figure 30, Figure 31, Figure 32, Figure 33, Figure 34, Figure 35, Figure 36 and Figure 37, Figures S1–S22 and Tables S1–S22 were assembled from the SciFinder®, Scopus®, and MarinLit databases and through manual curation of all published articles from an extensive panel of journals in chemistry and chemical biology fields. We emphasized new structures and structural revisions as elucidated through a variety of modern methods. Biological activities, origins of organisms, bioorganic studies on the MNPs, and syntheses that led to revision of structures or stereochemical assignments were also highlighted. We hope this comprehensive review will provide a useful overview and will help direct future efforts in Indonesian scientific development, governance, resource management, and conservation regarding the value of marine biodiversity.
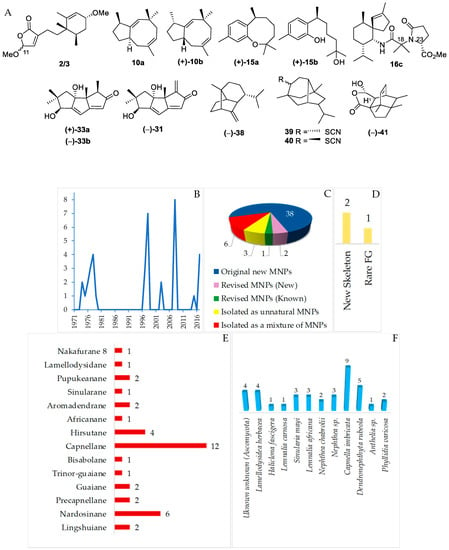
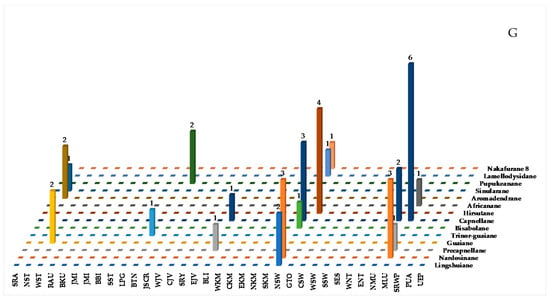
Figure 9.
Structures of marine sesquiterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017 (A): representative. Distribution of new marine sesquiterpenoids by year (B). Statistics of new marine sesquiterpenoids (C). Distribution of new marine sesquiterpenoids on the basis of their skeletons (D,E), biological sources (F), and biogeography (G).
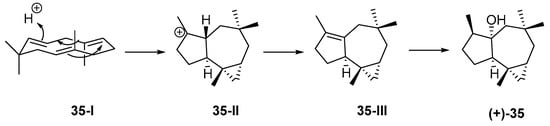
Figure 10.
Plausible biosynthetic pathway of (+)-africanol 35.
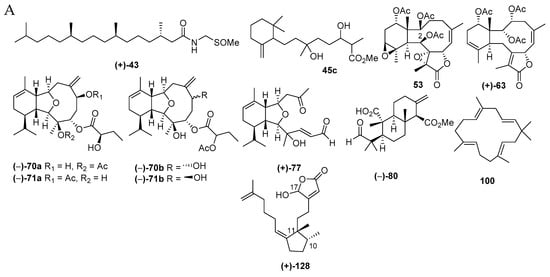
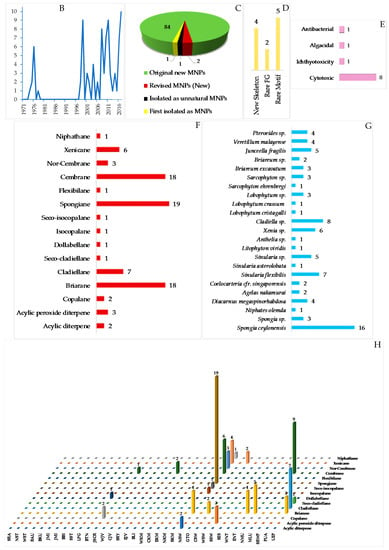
Figure 11.
Structures of marine diterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017 (A): representative. Distribution of new marine diterpenoids by year (B). Statistics of new marine diterpenoids (C). Distribution of new marine diterpenoids on the basis of their skeletons (D,F), significant biological activity (E), biological sources (G), and biogeography (H).
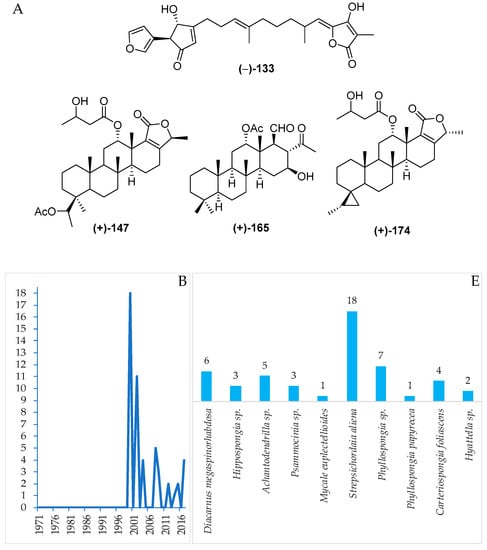
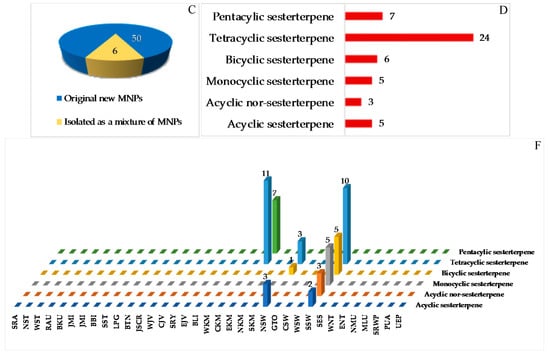
Figure 12.
Structures of marine sesterterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of new marine sesterterpenoids by year (B). Statistics of new marine sesterterpenoids (C). Distribution of new marine sesterterpenoids on the basis of their skeletons (D), biological sources (E), and biogeography (F).
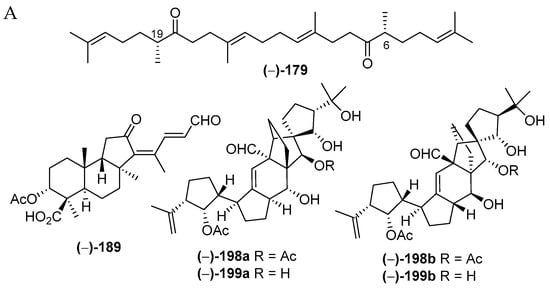
Figure 13.
Structures of marine triterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of new marine triterpenoids by year (B). Statistics of new marine triterpenoids (C). Distribution of new marine triterpenoids on the basis of their skeletons (D), biological sources (E), and biogeography (F).
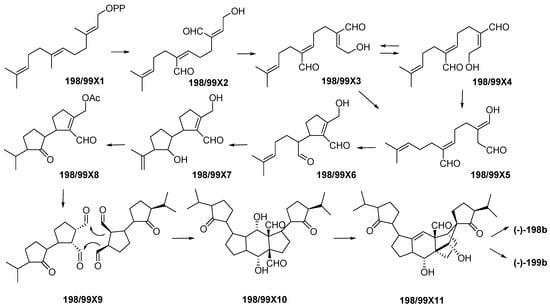
Figure 14.
Plausible biosynthetic pathway of (–)-vannusals A 198b and B 199b.
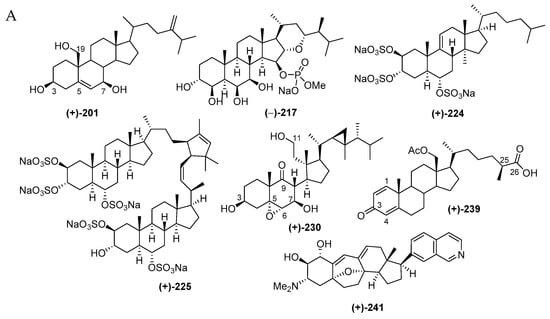
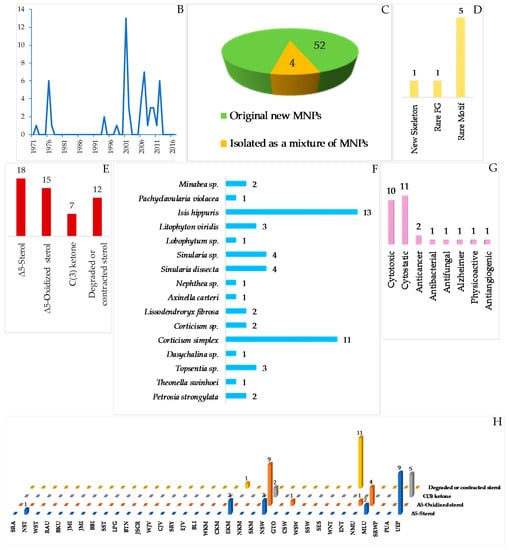
Figure 15.
Structures of marine steroids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of new marine steroids by year (B). Statistics of new marine steroids (C). Distribution of new marine steroids on the basis of their skeletons (D,E), biological sources (F), significant biological activity (G), and biogeography (H).
Figure 16.
Structures of marine saponins from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative.
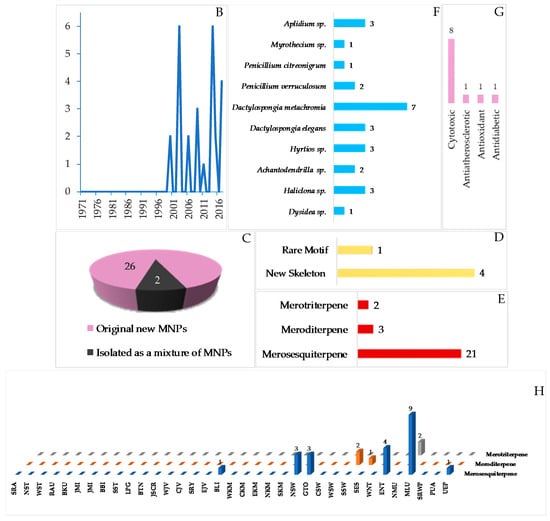
Figure 17.
Structures of marine meroterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of new marine meroterpenoids by year (B). Statistics of new marine meroterpenoids (C). Distribution of new marine meroterpenoids on the basis of their skeletons (D,E), biological sources (F), significant biological activity (G), and biogeography (H).
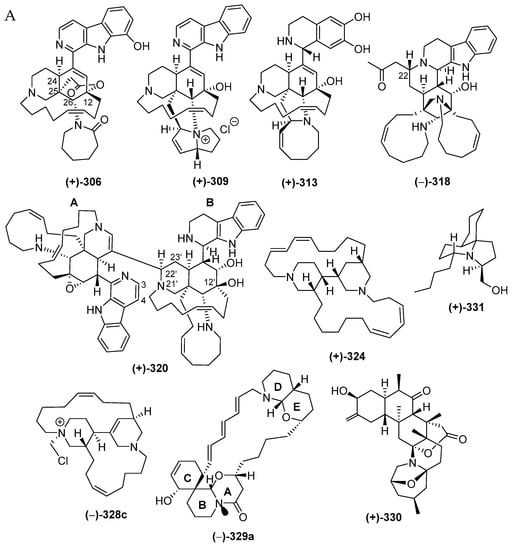
Figure 18.
Structures of marine piperidine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of new marine piperidines by year (B). Statistics of new marine piperidines (C). Distribution of new marine piperidine molecules on the basis of their skeletons (D), significant biological activity (E), biological sources (F), and biogeography (G).
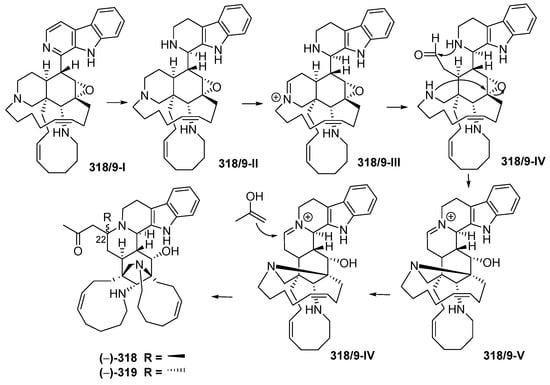
Figure 19.
Plausible biosynthetic pathway of (–)-manadomanzamines A 318, B 319.
Figure 20.
Structures of marine pyridine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of new alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of new marine pyridine molecules (C). Distribution of new marine pyridine molecules on the basis of biological sources (D), and biogeography (E).
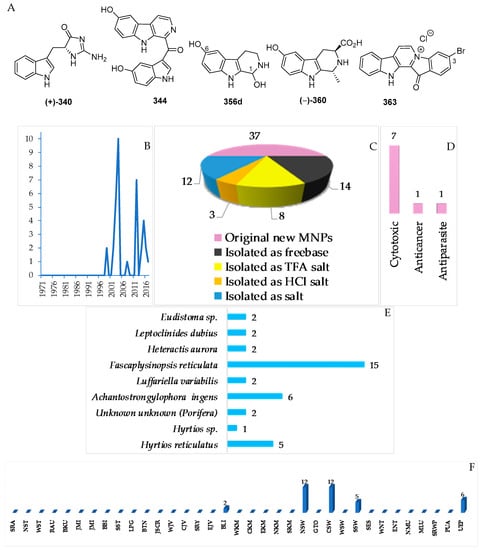
Figure 21.
Structures of marine indole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of new marine indole alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of new marine indole alkaloids (C). Distribution of new marine indole alkaloids, biological activity (D), biological sources (E), and biogeography (F).
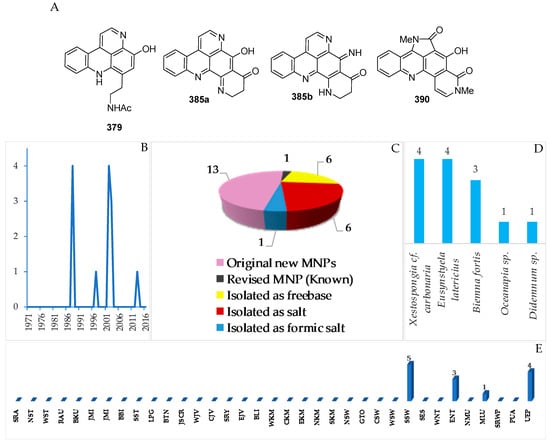
Figure 22.
Structures of marine acridine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of new marine acridine alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of new marine acridine molecules (C). Distribution of new marine acridine-containing molecules on the basis of their biological sources (D), and biogeography (E).
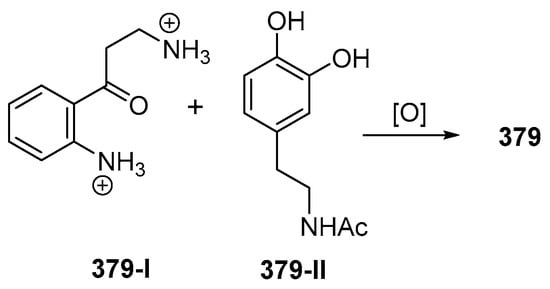
Figure 23.
Biomimetic synthesis of styelsamine B (379) from kynuramine (379-I) and N-acetyl dopamine (379-II).
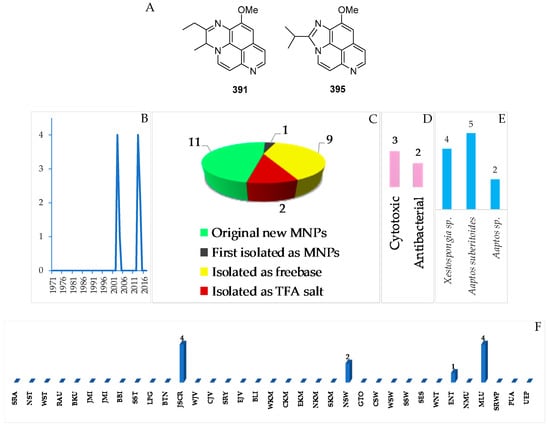
Figure 24.
Structures of marine quinoline or isoquinoline alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of the alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of new marine quinoline or isoquinoline alkaloids (C). Distribution of new marine quinoline and isoquinoline alkaloids on the basis of their biological activity (D), biological sources (E), and biogeography (F).
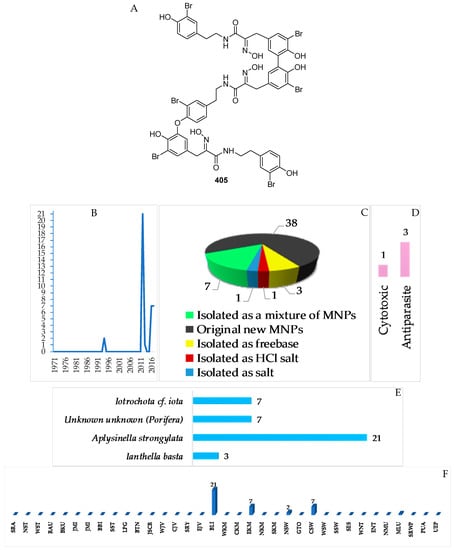
Figure 25.
Structures of marine tyrosine alkaloids from Indonesian waters in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of the alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of new tyrosine alkaloids (C). Distribution of new marine tyrosine-containing alkaloids on the basis of their, biological activity (D), biological sources (E), and biogeography (F).
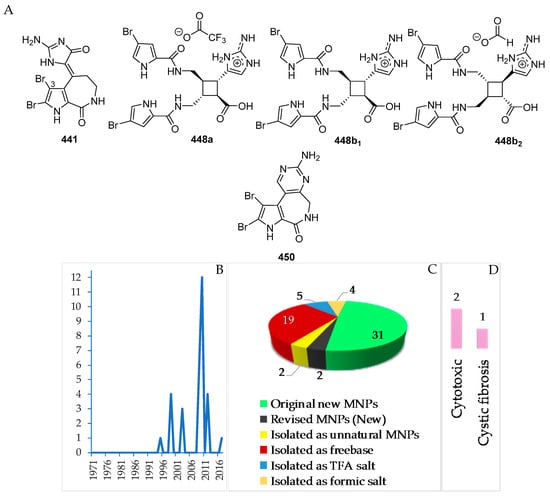
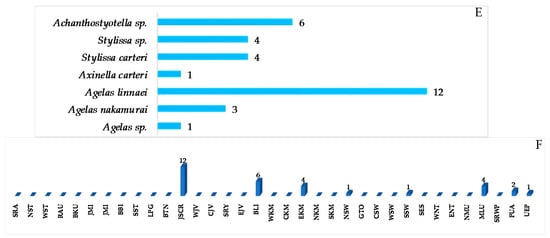
Figure 26.
Structures of marine pyrrole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of the alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of new pyrrole alkaloids (C). Distribution of new marine pyrrole-containing alkaloids on the basis of their, biological activity (D), biological sources (E), and biogeography (F).
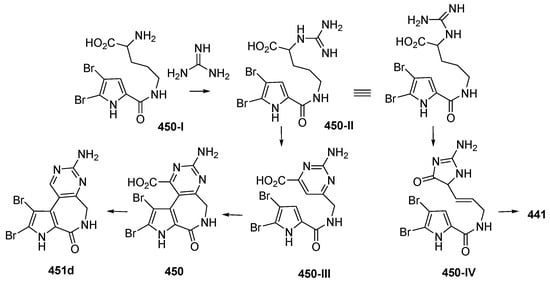
Figure 27.
The plausible biosynthetic pathway of latonduines A 450, B 451d, and (Z)-3-bromohymenialdisine 441.
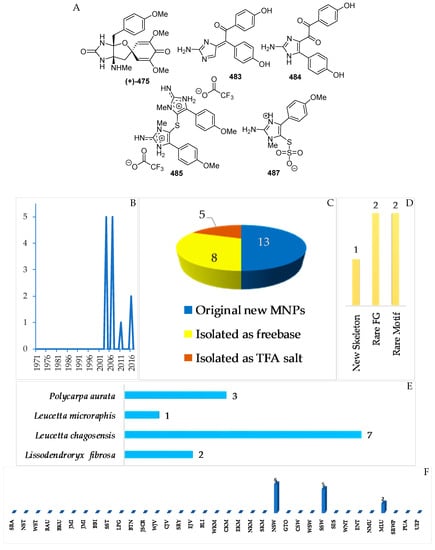
Figure 28.
Structures of marine imidazole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of the alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of imidazole alkaloids (C). Distribution of new marine imidazole alkaloids on the basis of their chemical skeletons (D), biological sources (E), and biogeography (F).
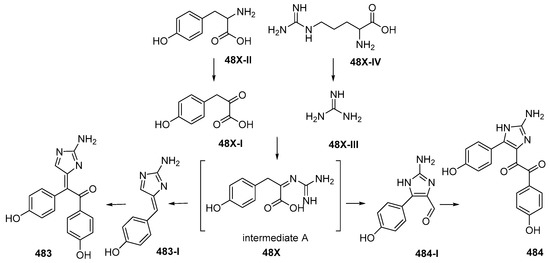
Figure 29.
The plausible biosynthetic pathway of lissodendrins A 483 and B 484.
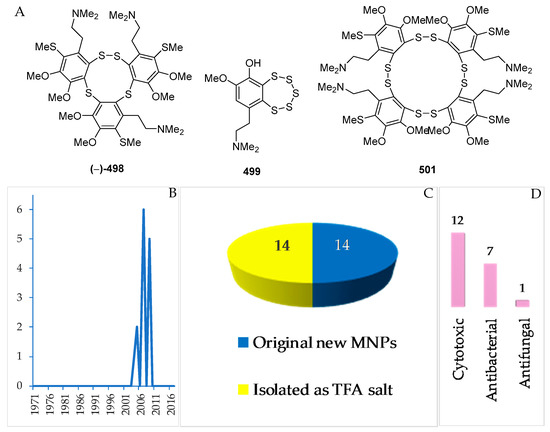
Figure 30.
Structures of marine polysulfur aromatic alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of the alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of polysulfur aromatic alkaloids (C). Distribution of new marine polysulfur aromatic-containing alkaloids on the basis of their biological activity (D).
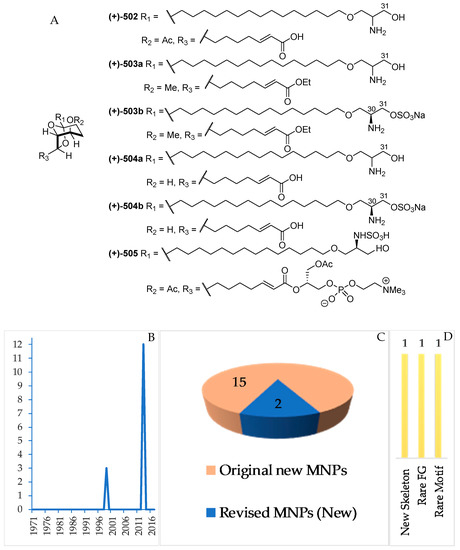
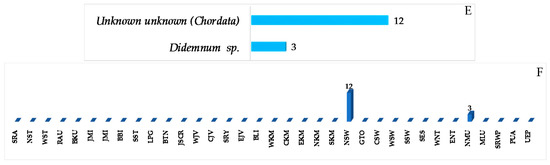
Figure 31.
Structures of marine serine-containing alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of the alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of the alkaloids (C). Distribution of marine serine-containing alkaloids on the basis of their chemical skeleton (D), biological source (E), and biogeography (F).
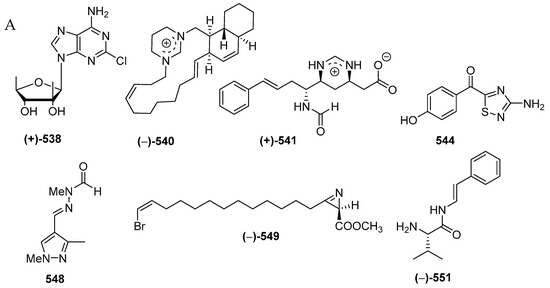
Figure 32.
Structures of other marine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of other marine alkaloids by year (B). Statistics of other marine alkaloids (C). Distribution of other marine alkaloids on the basis of biological activity (D), biological source (E), and biogeography (F).
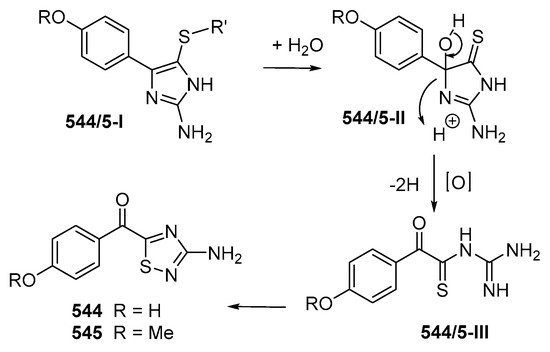
Figure 33.
Plausible biosynthetic relation of polycarpathiamines A 544 and B 545.
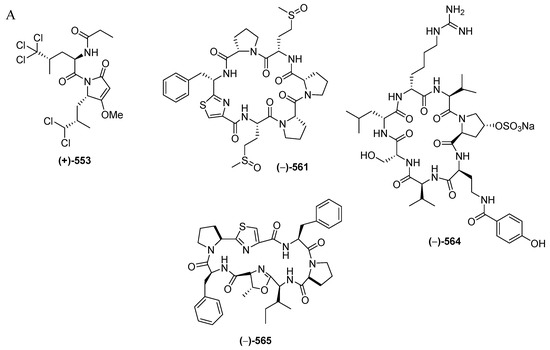
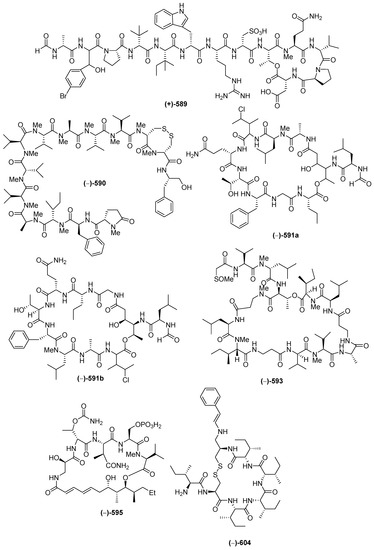
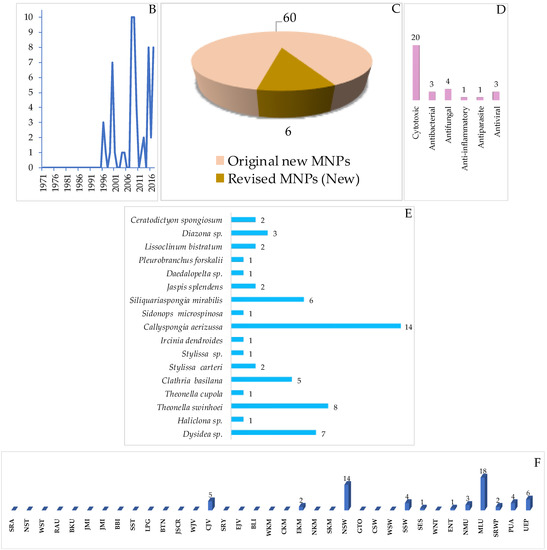
Figure 34.
Structures of marine peptides from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of marine peptides by year (B). Statistics of marine peptides (C). Distribution of marine peptides on the basis of biological activity (D), biological source (E), and biogeography (F).
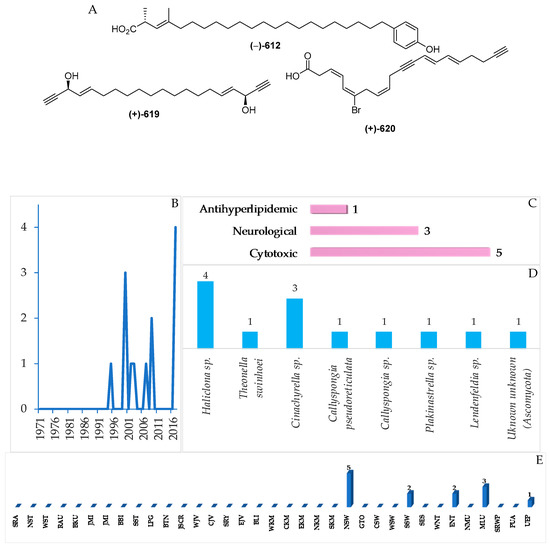
Figure 35.
Structures of fatty acids and linear molecules from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of this group of metabolites by year (B). Distribution of marine fatty acid on the basis of their biological activity (C), biological source (D), and biogeography (E).
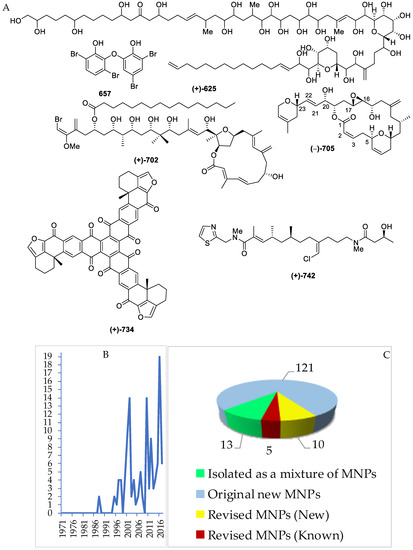
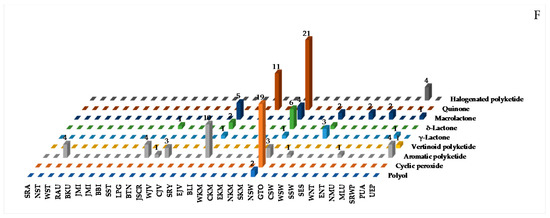
Figure 36.
Structures of marine polyketides from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017: (A) representative. Distribution of marine polyketides by year (B). Statistics of marine polyketides (C). Distribution of marine polyketide on the basis of their biological activity (D), biological source (E), and biogeography (F).
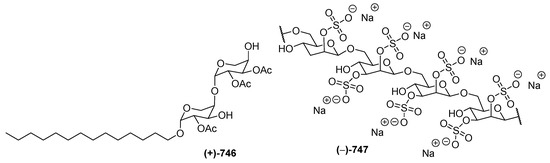
Figure 37.
Structures of marine carbohydrates from Indonesian waters in 1970–2017.
2. New MNPs Discovered from Indonesian Waters in the Period 1970–2017
2.1. General
There are five important components in MNP research programs: (1) collection and identification of marine organisms or culture of microorganisms, (2) screening of crude extracts for bioactivity or chemical structures, (3) isolation and structure elucidation of MNPs, (4) pharmacological evaluation of isolated compounds, and (5) further development of MNPs for science and technolgy. Self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) diving is generally used to collect shallow-water marine biota. SCUBA is also used to take photographs for characterization of specimens and to record ecological information on marine biota. The specimens are sorted and stored either frozen in aqueous ethanol or as dried material. Voucher specimens are prepared for taxonomic studies. At greater depths, specimens are collected by rebreather diving, dredging, trawling, and submersibles.
Many challenges must be overcome for this work. The presence of inorganic salt may become a problem if the sample amount is minuscule and the compounds are water-soluble, making them more difficult to handle than lipophilic compounds. When the bioassay is based on the behavior of marine organisms, it is difficult to mimic the marine environment. A routine procedure for isolation work is to group molecules by the level of their polarity, followed by separation and purification of target fractions using a variety of chromatographic methods. Bioassay or a signature of functional groups (substructures) or even molecular weight can be used as a guide for isolation or identification of MNPs. As a rule, in vitro bioassays require very little material, and take a shorter time to perform. It is normal to screen crude extracts with in vitro assays and reserve in vivo assays for pure compounds. Thin layer chromatography (TLC), NMR, and MS spectra can be used to identify characteristic extracts or fractions as guides for isolation work.
Modern structure elucidation requires a variety of spectroscopic methods (NMR, MS, IR, ultraviolet (UV), ECD, X-ray diffraction, vibrational circular dichroism (VCD), and others), chemical transformations (derivatives or selective degradation or total synthesis), molecular modeling or computational calculations, information technology with molecular networking, and biosynthetic consideration in order to reveal the planar and stereostructure of target molecules. In general, the chemical structure of molecules with low H/C ratios (<1) is challenging to elucidate [31]. To find a new molecule, one should consider a strategy of dereplication using NMR, LC-MS, MS/MS, or DNA sequence [48], in addition to exploring new groups of marine organisms and geographical selection of collection sites [30]. On the other hand, known molecules can be screened with a set of new assays in order to find new function of molecules.
2.2. Terpenoids
A total of 276 marine terpenoids were discovered within the period, consisting of 38 sesquiterpenoids, 84 diterpenoids, 50 sesterterpenoids, 21 triterpenoids, 52 steroids, 5 saponins, and 26 meroterpenoids. Among them, six molecules 10a, 33a, 70a, 71a, 198a, and 199a have been revised. One molecule, 53, was isolated as a natural product, while it had been synthesized previously. Five molecules, 16c, 17c, 18c, 45c, 200c, and 252c, were isolated as derivatives. Of 276 terpenoids, ACs of 18 molecules were determined by X-ray crystallography. In addition, ACs can also be revealed by the use of ECD as in 21 terpenoids. Modified Mosher’s method was applied for 14 chiral terpenoids, while total syntheses proved the ACs of 3 terpenoids. Since the biological activity of true natural products is preferable, one should consider replacing the FG with the original one. Alternatively, the chromatography system can be modified so that the original molecule can be obtained. Indonesian marine terpenoids were found to show cytotoxic (37 molecules), cytostatic (18 molecules), anticancer without cytotoxicity (4 molecules), antifungal (5 molecules), antibacterial (3 molecules), antidiabetic (2 molecules), ichthyotoxic, algicidal, antiinsecticidal, anti-inflammatory, anti-Alzheimer, physicoactive (CB receptor ligand), antiangiogenic, antiatherosclerotic, and antioxidant activity (each 1 molecule).
2.2.1. Sesquiterpenoids
Sesquiterpenoids isolated from Indonesian waters from January 1970 to December 2017 are summarized in Figure 9A, Figure S1 and Table S1 of the Supplementary Materials. As shown in Figure 9B, some sesquiterpenoids had been discovered in an earlier period (1970–1980). The marine sesquiterpenoids are comprised of 38 new natural products, 3 revised molecules (2 new and 1 known), 3 derivatives 16c, 17c and 18c, and 6 mixtures (Figure 9C). Two molecules, 2/3 and 41, have been reported to have new skeletons, and 1 molecule, 39/40, contains a rare functional group (Figure 9D). Fourteen different types of carbon skeletons (Figure 9E) are observed. Among them, capnellane (12 molecules), nardosinane (6 molecules), and hirsutane (4 molecules) are top three. Two molecules remain to be determined with respect to their stereochemistry (2/3 and 39/40). The ACs of six sesquiterpenoids, 4, 7, 22, 31, 35, and 38, and one derivative, 16c, have been determined by X-ray crystallography. In addition, ECD was applied to 6 molecules, 2/3, 12, 38, 41, and 42. The modified Mosher’s method was applied to 31. Of 38 molecules, one molecule, 10a, was revised to 10b by total synthesis [49,50,51,52]. The structure of 15a was corrected to 15b after total synthesis [53,54,55,56,57]. Hirsutanol C (33a) was revised to 33b by the work of a fungal metabolite [58]. Four phyla, Ascomycota (4 molecules), Porifera (5 molecules), Cnidaria (27 molecules), and Mollusca (2 molecules), were recorded to be sources of new sesquiterpenoids (Figure 9F). The new molecules are mainly found in NSW and MLU (Figure 9G).
The first sesquitepenoid found in Indonesian waters was africanol (35) from Lemnalia africana and Lemnalia nitida, collected off Tanimbar, MLU. Its structure, including AC, was established by X-ray analysis [59] and confirmed by total synthesis [60,61]. It was proposed that 35 was derived from a humulene through its CT (cross and parallel rearrangements of two double bonds) conformer 35-I, which undergoes acid-catalyzed closure to the 9-africyl cation 35-II, followed by proton loss and hydration to provide 35 (Figure 10). Africanol (35) showed toxicity against guppy Lebistes reticulatus and unicellular algae Chaetoceros septentrionalis, Astrionella japonica, Thallasioscira excentricus, Protocentrum micans, and Amphidinium carterae [62].
2.2.2. Diterpenoids
Diterpenoids are molecules more frequently found from Cnidarian (56 molecules, 66.7%), particularly Alcyonacea (57.1%), than from Porifera (28 molecules, 33.3%). The diterpenoids found in Indonesian waters from January 1970 to December 2017 are compiled in Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials, Figure 11A and Figure S2. As for sesquiterpenoids, initial studies on diterpenoids were performed in 1970s, and publication increased after 1996 (Figure 11B). All of these efforts resulted in 84 new, 2 revised, 1 derivative, and 1 known but first from marine (Figure 11C). Among the new molecules, 4 have new skeletons, 80, 100, 117, and 128 (Figure 11D), 2 molecules contain rare FGs, sulfoxide or sulfone, and 5 molecules are listed to possess a rare structural motif, 77, 79, 113, 119, and 124 (Figure 11D). The chemical diversity of Indonesian marine diterpenoids (84 molecules) was proved, as there were 15 different skeletons: 19 spongianes, 18 each of briaranes and cembranes, 7 cladiellanes, 6 xenicanes, 3 each of nor-cembranes and acyclic peroxide diterpenes, 2 each of copalanes and acyclic diterpenes, and 1 each of niphatane, flexibilane, seco-cladiellane, dollabelane, isocopalane, and seco-isocopalane (Figure 11F). Four molecules, 101, 108, 110, and 112, were determined by X-ray analysis. ECD was used to reveal the ACs of 8 molecules, 43, 44, 79, 82, 88, 89, 90, and 128. In particular, 5 molecules, 82, 88–90 and 128, were elucidated by comparing actual spectra and calculated ECD. The modified Mosher’s method was applied for 8 molecules, 54–57, 63, 70a, 113, and 124. Two molecules, 70a and 71a, were revised to 70b and 71b. NSW is the most favored place for finding new marine diterpenes (41 molecules, 48.8%), followed by MLU (10 molecules, 11.9%) (Figure 11H). One molecule, 45c, was isolated as a derivative, while molecule 53 was isolated as a natural product for the first time, but was previously known as a semisynthetic.
The AC of niphateolide A (128), an inhibitor of p53-Hdm2 interaction [63] from the sponge Niphates olemda, was established as 10R,11R by ECD measurements in the vacuum-ultraviolet region based on theoretical calculation. The remaining stereocenter at C17 remains unsolved.
2.2.3. Sesterterpenoids
The sestertepenoids found in Indonesian waters from January 1970 to December 2017 are shown in Table S3 and Figure 12A, Figure S3. The first sesterterpenoids were 147–152 and 173–178, isolated from Strepsichordaia aliena in 2000. Of the 56 sesterterpenoids reported, 50 were new and 6 were isolated as mixtures (Figure 12C). The molecules are comprised of 24 tetracylic followed by 7 pentacyclic, 6 bicyclic, 5 each of monocyclic and acyclic sesterterpenoids, and 5 acyclic norsesterterpenoids (Figure 12D). Three molecules, 148, 165 and 174, including their ACs, were revealed by X-ray crystallography, while the ACs of 2 molecules, 160 and 161, were disclosed by comparing calculated and experimental ECD. The AC of 165 was determined by the modified Mosher’s method. The biological sources of Indonesian sesterterpenoids are exclusively from the phylum Porifera, class Demospongiae with 6, 9, and 10 differrent families, genera, and species, respectively (Figure 12E). In regard to biological activities, significant cytotoxicity was observed for 9 molecules, while others were recorded as exhibiting anticancer activity without cytotoxic (2 molecules), cytostatic, antidiabetic, and antifungal activities (1 molecule each) (Figure 12D). Marine sesterterpenoids were mainly found in specimens in SSW (25 molecules) and EKM (18 molecules) (Figure 12G).
2.2.4. Triterpenoids
Indonesian marine triterpenoids (Table S4 and Figure 13A, Figure S4) are comprised of 21 new, 7 mixtures, 1 derivative, and 2 revised molecules (Figure 13C). The triterpenes are grouped into three structural classes: squalane (1), isomalabaricanes (18) and vannusanes (2 molecules). Of 21, only vannusals A (198) and B (199) were found to have a new skeleton. The 3 skeletons were obtained from 3 species, Euplotes vannus for 198a and 199a, Rhabdastrella globostellata for 180–197, and Hyrtios erectus for 179 (Figure 13C,D). The AC of 1 molecule, 199b, was solved by X-ray analysis. Of the triterpenoids, six were found to show significant cytostatic activity. The metabolites were mainly isolated from specimens collected in SSW (12 molecules) (Figure 13F). Two molecules, 198a and 199a, were revised to 198b and 199b [36,37,38,39,40,41]. The stereochemistry of vannusal B (199b) was also examined by density functional theory (DFT) calculation [42]. A plausible biosynthetic pathway of vannusals A (198b) and B (199b) was proposed (Figure 14) [43].
2.2.5. Steroids
Indonesian marine steroids found in the period of 1970–2017 are comprised of 52 pure molecules and 4 mixtures (Figure 15C) and are shown in Table S5 in Supplementary Materials and Figure 15A, Figure S5. The discovery trend increased in the first 5 years and also in the years after 1990 (Figure 15B). The ratio among new skeletons, rare functional groups, and rare motifs is 1:1:5 (Figure 15D). Four different skeletons are observed in 52 steroids (Figure 15E). Among them, Δ5-sterols constitute the majority (18 molecules). Sulfated steroids were reported as 203, 206 and 224–226, while a phosphated steroid was observed in 217. From 1970–2017, Indonesian marine sulfated steroids have contributed 3.3% of the total marine sulfated steroids worldwide, while Indonesian marine phosphated steroids are expected to contribute 20% of total marine phosphated steroids. The ACs of three steroids, 201, 204 and 241, were disclosed by X-ray analysis, while that of 241 was determined by ECD spectrum. For two molecules, 224 and 239, their absolute configurations were determined by MTPA esters and PGME methods, respectively. With regard to the biological sources, the steroids were mainly obtained from the phyla Cnidaria (29 molecules) and Porifera (23 molecules), as listed in Figure 15F. In regard to biological activities, 10 molecules showed significant cytotoxicity, while 11 molecules were cytostastic (Figure 15G). The molecules were isolated mainly from specimens from NSW (14 molecules) and ENT (11 molecules) (Figure 15H).
The unique molecules in the steroids are cortistatins isolated from the sponge Corticium simplex collected off Flores, ENT, with a new skeleton comprised of a 9(10-19)-abeo-androstane and isoquinoline [64]. The structure of cortistatin A (241) was determined by X-ray analysis and the ECD excition chirality method. Molecules 241–244 showed selective antiproliferative properties against human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). The most potent member, cortistatin A (241), showed a selectivity index of more than 3000 against HUVECs in comparison with human fibroblast (NHDF) and several other tumor cells KB31, K562 and Neuro 2A. Additional members, cortistatins E (250), F (251), G (248), and H (249) with N-methyl piperidine or 3-methylpyridine unit isolated from the same source, also showed antiproliferative activity against HUVECs [65]. Three additional cortistatins J (245), K (246) and L (247) were isolated from the same source [66]. The first synthesis of 241 verified its 3D structure, featuring an inexpensive terrestrial steroid prednisone as the starting material [67]. The second total synthesis of 241 was achieved by using intra-molecular oxa-Michael addition/aldol/dehydration cascade reaction, Sonogashira, and Suzuki-Miyaura couplings [68].
Molecules 241 and 245 were confirmed to show an antiproliferative effect on additional cancer cell lines: MCF7, NCI-H460, SF268, IA9, PTX22, and A8, including drug-resistant ones [69]. Structure–activity relationships with natural cortistatins and synthetic analogues suggested that substitution at position 7’ of isoquinoline is a key determinant of the phenotypic effects of cortistatins [69,70,71]. It is hypothesized that the biological activity of 241 is due to inhibition of one or more protein kinases. Molecule 241 inhibits the function of several different kinases in vitro. It is proposed that 241 may occupy the ATP-binding site of at least one of the following enzymes: Rho associated, protein kinase (ROCK), or cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 8 and 11 [72]. The X-ray crystallographic analysis of the ligand-protein complex disclosed that the isoquinoline binds to the kinase hinge, that the steroid region of the molecule is complementary to the shape of the ATP-binding cleft, that the terminal polar A ring is exposed to solvent, and that a salt bridge exists between an aspartate side chain (ROCK I only) and dimethylamino group of 241 [72].
2.2.6. Saponins
Only five saponins 253–257 with 1 derivative 252c were discovered in Indonesian waters in the period 1970–2017 (Table S6 and Figure 16A, Figure S6). All the saponins retain a lanostane skeleton with five sugar moieties. ECD spectrum has been used to reveal the stereochemistry of 252c. Four molecules, 253–256, were found in a specimen of the sponge Melophlus sarassinorum from SSW, while 257 was from a Petrosia sp. of NSW. Significant antifungal activity was observed for sarasinoside J (253).
2.2.7. Meroterpenoids
Marine meroterpenoids, comprised of 26 pure compounds and 2 mixtures, have been discovered since 2000 (Table S7 and Figure 17A–C, Figure S7). Marine meroterpenoids are composed of various skeletons, as shown in 264–265, 281 and 282, while a rare motif is exhibited by 276. The majority of marine meroterpenoids found in Indonesian waters are the 21 merosesquiterpenoids, followed by the 3 meroditerpenoids and the 2 merotriterpenoids (Figure 17E). X-ray crystallography was used for two molecules, 264–265, to determine their ACs, while ECD spectra were used to elucidate the ACs of 261–262. The marine meroterpenoids were isolated from the phyla Ascomycta (4 molecules), Porifera (19 molecules), and Chordata (3 molecules). More specifically, 19 molecules from Porifera were found in 3 families: Dysideidae (2 molecules), Chalinidae (3 molecules), and Dictyodendrillidae (2 molecules). With regard to their biological activities, 8 molecules showed significant cytotoxicity, followed by 1 molecule as antiatherosclerotic and 1 molecule as antioxidant and antidiabetic (Figure 17G). The marine merosesquiterpeoids were isolated from specimens from MLU (9 molecules), while meroditerpenoids (2 molecules) and merotriterpenoids (2 molecules) were found from SSW and NMU, respectively (Figure 17H).
2.3. Alkaloids
The alkaloids from Indonesian marine sources are comprised of 260 new molecules, 5 revised molecules (332a, 333a, 348a, 403a, and 404a), 3 derivatives (328c, 452c and 453c), and 3 molecules that were known, but had been isolated for the first time as natural products (397 and 546–547). Of these, 102 and 91 molecules were isolated as freebases and salt forms, respectively, and 7 as mixtures. The total of 260 Indonesian marine alkaloids can be grouped into 48 piperidines, 7 pyridines, 37 indoles, 13 acridines, 11 quinolines or isoquinolines, 38 tyrosines, 31 pyrroles, 13 imidazoles, 14 polysulfur aromatics, 15 serines, and 33 others. The last group is comprised of a pyrroloimino-quinone, 5 ceramides, 15 tetramic acids, 2 nucleosides, 2 formamides, a polycyclic diamine, a pterin alkaloid, 2 thiadiazoles, a pyrazole, an azirine, and 2 simple amines/amides. Purification of alkaloids is often challenging due to the presence of nitrogen atoms and their behavior as a base. To tackle this problem, researchers often adjust the pH of mobile phases of chromatography by adding formic acid or trifluoroacetic acid, or modify the stationary phase into a suitable one. Because of their basic nature, many alkaloids are tested as salt forms. Significant activity was observed for 118 molecules consisting of cytotoxic (49), antibacterial (29), anticancer without cytotoxicity (1), antiparasitic (9), antifungal (8), immunosuppresive (2 molecules), antiviral, anti-cystic fibrosis, immunomodulatory, anti-neurodisease, and electrophysiological activity (each 1 molecule).
2.3.1. Piperidine Alkaloids
The majority of piperidine alkaloids are manzamine-related molecules characterized by the presence of a unique polycyclic ring system. The molecules are compiled in Table S8 in Supplementary Materials and are drawn as in Figure 18A, Figure S8. The first piperidine alkaloid found in Indonesian waters was halicyclamine A (322), from a Haliclona sponge, in 1994, followed by more alkaloids after 2001 (Figure 18B). As mentioned earlier in Figure 4C, piperidine alkaloids constitute one of the dominant groups of Indonesian MNPs, with 48 molecules, which were classified into 33 manzamines, 284–286, 297–302, 309–312, and 318–321, 2 degraded β-carbolines, 313 and 314, 3 ircinal-related molecules, 315–317, 6 molecules with two piperidines, 322–327, one fused piperidine-pyran, 329a, one zoanthamine, 330, and 2 molecules with a piperidine in a tricyclic system, 331–332. Inspection of the chemical structures allowed us to identify new skeletons in 313 and 318, rare functional groups in 309 and 329a, and 6 molecules with rare structural motifs in 306–308, 311 and 320–321 (Figure 18D). X-ray analysis was used to reveal ACs of molecules 289, 324 and 327. ACs of three 306, 313 and 328c were determined by comparing experimental and calculated ECD spectra, while three others, 290, 293 and 330, were elucidated with modified Mosher’s method. In terms of their biological activities, significant antibacterial (14), cytotoxic (11), anticancer without cytotoxicity (1), antiparasitic (5), antifungal (5), antiviral and immunosuppresive activity (each 1 molecule) were observed (Figure 18E). The sources of piperidine alkaloids are Porifera (45), Cnidaria (1), and Chordata (2 molecules). In total, 48 molecules were isolated from specimens of NSW (31), JSCR (7), ENT, BLI (3), and SES, NMU, PUA (1 molecule each) (Figure 18G).
Manadomanzamines A (318) and B (319) (Figure 18A, Figure S8), obtained from a sponge Acanthostrongylophora sp. collected off Manado, have a novel skeleton [73]. Their ACs and conformation were determined by ECD, NOESY and molecular modelling analysis. Molecules 318 and 319 showed growth inhibition against HIV-1 and against fungi causing opportunistic infection with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Biosynthesis of 318 and 319 is proposed, as shown (Figure 19).
2.3.2. Pyridine Alkaloids
Only 7 molecules were classified as pyridine alkaloids, as shown in Table S9 and in Figure 20A–C, Figure S9. The molecules were reported recently, in 2016–2017 (Figure 20B). One molecule, 333a, was revised to the known 333b after comparing NMR data of total synthesis work [74]. The incorrect structure of 333a was due to the misinterpretation of HMBC signals.
2.3.3. Indole Alkaloids
There have been 37 new and 1 proposed 356d indole alkaloids in the Indonesian MNPs (Table S10, Figure 21A–C, Figure S10). ECD was used to determine ACs of (–)-360. In addition, the ACs of two indoles, 340 and 341, were determined by total synthesis. Cytotoxicity was the dominant biological activitiy reported for indole alkaloids (7), followed by antiparasitic and anticancer activity (1 molecule each). The alkaloids were found to be from Porifera (31), Cnidarian (2) and Chordata (4 molecules).
2.3.4. Acridine Alkaloids
In total, 13 new and 1 revised acridine alkaloids were reported from Indonesian waters (Figure 22A–C, Figure S11 and Table S11). Of 13 molecules, six were isolated as free bases, while the remaining seven were obtained as salts. One molecule, 385a, has been revised to 385b. A new skeleton was proposed for 390. Research on marine acridines began with the discovery of styelsamines A–D (378–381) in 1988 (Figure 22B). The structure of the alkaloid 390 was determined by X-ray analysis. Six molecules showed significant cytotoxicity. The acridine alkaloids were isolated from Porifera (8) and Chordata (5 molecules).
The ascidian Eusynstyla latericius, collected off Makassar, SSW, was found to contain styelsamines A–D (378–381, Figure 23A, Figure S11) which showed cytotoxic effect against HCT116 cells [75]. A biomimetic synthesis of styelsamine B (379) was conducted from kynuramine (379-I) and N-acetyl dopamine (379-II) (Figure 23) featuring a CeCl3-catalyzed oxidative coupling of 379-I and 379-II in the presence of silver oxide [76]. The structure of styelsamine C (380) was also confirmed by a total synthesis utilizing biaryl Suzuki cross-coupling [77]. The preparation of 379 and 381 was also achieved by using a simple biomimetic synthetic method [78]. Styelsamine D (381) could be a biosynthetic intermediate for a large subset of pyridoacridine alkaloids [79]. Styelsamines B (379) and D (381) showed high affinity to calf thymus DNA [78].
2.3.5. Quinoline and Isoquinoline Alkaloids
In total, 11 natural quinoline or isoquinoline alkaloids were discovered in Indonesian waters (Figure 24A–C, Figure S12, Table S12). The very first member of this group is an aaptamine derivative obtained off Jakarta, JSCR (Figure 24B). Of 11 molecules, nine were isolated as free bases, while two were obtained as salts. Two molecules, 391 and 395, of the class contained a rare motif. With respect to biological activity, 3 molecules showed significant cytotoxicity, while 2 molecules were antibacterial (Figure 24D). All the compounds were found from the marine sponges Aaptos suberitoides (5), Aaptos sp. (2) and Xestospongia sp. (4 molecules) (Figure 24E). JSCR (4 molecules) and MLU (4 molecules) were the major source areas of the group (Figure 24F).
2.3.6. Tyrosine Alkaloids
A total of 38 tyrosine alkaloids were found in Indonesian waters. Of 38 molecules, 7 molecules were isolated as mixtures (Figure 25A–C, Figure S13, Table S13). The first member of this class was bastadin reported in 1994. The chemical structures of this class contained 1 new skeleton 405. With respect to biological activity, antiparasitic activity was seen for 3 molecules followed by one cytotoxic molecule (Figure 25E). The sources of tyrosine alkaloids are Porifera consisting of 3 species and 1 undescribed species (Figure 25F). Most molecules were found from specimens of BLI (21), EKM (7), CSW (7), and NSW (2 molecules) (Figure 25G).
2.3.7. Pyrrole Alkaloids
A total of 31 pyrrole alkaloids have been discovered from the Indonesian waters in addition to 2 revised and 2 derivatives (Figure 26A–C, Figure S14 and Table S14). Nineteen molecules out of 31 were isolated as free bases, while 9 were isolated as salts. The first member, 441, was discovered in 1995, and 12 molecules were reported in 2010 (Figure 26B). This class of alkaloids contains 1 new skeleton in 450 and 1 rare motif in 448. The ACs of two molecules, 443 and 448b2, of this class were determined by ECD spectra, while 1 molecule, 450, was confirmed by total synthesis. Cytotoxicity (2 molecules) and anti-cystic fibrosis (1 molecule) are the signature of significant biological activity of the pyrrole alkaloids (Figure 26E). The sources of pyrrole alkaloids are exclusively Porifera, consisting of 3 families (Agelasidae 22 molecules, Axinellidae 1 molecule, and Scopalinidae 8 molecules).
Two dimeric bromopyrrole alkaloids, nakamuric acid (448a) and its methyl ester, 449, showing antibiotic activity against B. subtilis, were isolated from the sponge Agelas nakamurai, collected in MLU [80]. A total synthesis of (9R,10S,9′R,10′S)-nakamuric acid (449a) was accomplished by the minimal use of protective groups with exploration of 2-aminoimidazole [34]. The AC of 448a was established to be (9S,10R,9′S,10′R) by comparison of the experimental and calculated ECD spectra [35]. Thus, 448a was proved to be an enantiomer of the synthetic one. The sponge Stylissa carteri from SSW was found to contain two unprecedented molecules, latonduines A (450) and B (451d) [45]. Their structures were elucidated by analysis of spectroscopic data and confirmed by total synthesis of 450. It is proposed that ornithine is the biogenetic precursor to the aminopyrimidine fragment, as shown in Figure 27.
2.3.8. Imidazole Alkaloids
The marine sponges Lissodendroryx fibrosa, Leucetta chagosensis, and Leucetta microraphis, as well as the ascidian Polycarpa aurata (Figure 28E), are the sources of 13 imidazole alkaloids, which were isolated as free bases (8) and salts (5 molecules) (Figure 28A–C, S 15, Table S15). Compound 483 retains 1 new skeleton, while four compounds, 475, 484, 485, and 487, have rare structural motifs (Figure 28D). With regard to biological activity, significant antifungal (1) and cytotoxic activity (3 molecules) was found (Figure 28E). The sources of imidazole alkaloids were collected at 3 regions (NSW, 6; SSW, 5; MLU, 2 molecules).
Lissodendrins A (483) and B (484) (Figure 28A, Figure S15), 2-amino imidazole alkaloids, were isolated from the sponge Lissodendoryx (Acanthodoryx) fibrosa collected off Ambon, MLU [81]. The latter compound contains a (p-hydroxyphenyl)glyoxal moiety as an unprecedented skeleton. A plausible biosynthetic scheme for these compounds was proposed, as in Figure 29 [81].
2.3.9. Polysulfur Aromatic Alkaloids
Polysulfur aromatic alkaloids are an unusual class of MNPs. To date, there have been 14 MNPs isolated as salts (Figure 30A–C, Figure S16, and Table S16). The polysulfur aromatic alkaloids were reported in 2005 (3), 2007 (6), and 2009 (5 molecules) (Figure 30B). The first discovery of this group was lissoclibadin 1 (498) [82]. Three molecules, 498, 499 and 501, of polysulfur aromatic alkaloids retain new skeletons. With respect to biological activity, significant cytotoxic (12), antibacterial (7), and antifungal activity (1 molecule) was reported (Figure 30D). All the molecules were found from Lissoclinum cf. badium collected in NSW.
2.3.10. Serine-Derived Alkaloids
A total of 15 serine-derived alkaloids have been discovered (Figure 31A–C, Figure S17, Table S17). Among them, 2 molecules, 503a and 504a, were revised to 503b and 504b. All the alkaloids share a common structural feature: 6,8-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane (6,8-DOBCOs). One of them, 502, possesses a new skeleton. The first discovery in this group was reported in 1999 (3 molecules), which was followed by another 12 molecules before 2013 (Figure 31B). The ACs were determined for 505 by ECD and for 503b, 504b and 505 by total synthesis. With regard to biological activities, significant anticancer activity without cytotoxicity was reported for 4 molecules. Tunicates were proved as the sole source of this class of MNPs. The majority of the molecules were isolated from specimens collected in NSW (12) and NMU (3 molecules).
2.3.11. Other Marine Alkaloids
A total of 33 alkaloids do not belong to the above structural classes. They are comprised of a pyrroloimino-quinone, five ceramides, 15 tetramic acids, two nucleosides, two formamides, one polycyclic diamine, one pterin, two thiadiazoles, one pyrazole, one azirine, two simple amine/amide alkaloids (2 molecules) (Figure 32A–C, Figure S18, Table S18). Of 33 molecules, seven, 538, 540, 541, 544, 548, 549, and 551, contain rare structural motifs. ACs of three molecules, 524, 525 and 538, were determined by ECD. With regard to biological activities, cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity were seen in 4 and 3 molecules, respectively, whereas antifungal, immunosuppresive, immunomodulatory, neurological, and electrophysiological activity were shown in one molecule each (Figure 32D). The sources of the molecules are 10 sponge species and 2 tunicates (Figure 32E). The majority of the alkaloids were found from specimens from SSW (19), MLU (4), NSW (2), EKM (2), and BLI (1 molecule) (Figure 32F).
Bioorganic studies of melophlin A (523) to dynamins II and I-like proteins in cells, thereby modulating signal transduction through the Ras network, was conducted by using a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) [83]. Furthermore, Mg or Zn complexes of 523 are antiproliferative in various cancer cells, while they are less toxic to normal fibroblasts. The complexes dissolve more in water than Ca analogue [84]. Melophlin A (523) also exhibited anti-dormant mycobacterial activity [85] and cytotoxicity against L1210 cells [86]. The influence of 523 on the colony formation of Chinese hamster V79 lung cells and of the production of interleukin (IL)-8 in phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)-stimulated HL60 cells were examined [87].
Two alkaloids containing an uncommon 1,2,4-thiadiazole ring named polycarpathiamines A (544) and B (545) (Figure 32B) were isolated from the ascidian Polycarpa aurata collected in MLU [46]. The structures of 544 and 545 were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and by synthesis. Polycarpathiamine A (544) showed cytotoxicity to L5178Y cells. The biosynthetic relation of 544 and 545 was proposed as shown in Figure 33.
2.4. Peptides
Marine peptides have emerged as a very important class of bioactive compound in Indonesian MNPs. The class is comprised of 60 natural and 6 revised MNPs (Figure 34A–C, Figure S19, Table S19). The natural peptides can be grouped into: linear dipeptides, 552–557, a linear tridecapeptide, 590, a cyclotetrapeptide, 608, two cyclopentapeptides, 604–605, cyclohexapeptides, 558–563, cyclohepta-peptides, 564–570, a cyclooctapeptide, 571, cycloundecapeptides, 572a–575, cyclopeptides with a linear peptidic chain, 576a, 577–579, 580a, 581, 582b, 583–588, and 606–607, and cyclodepsipeptide, 591a–603, cyclodepsipeptide with a side chain, 589, and macrocyclic peptides, 609–611. Nine molecules, 553, 561, 564, 589, 590, 591a, 593, 595, and 602, are categorized as having rare FG and structural motifs. After their first discovery in 1996, the number of Indonesian marine peptides has kept increasing until now. The ACs of peptides (41 molecules) have generally been determined by Marfey analysis. Only 3 peptides, 553, 565 and 566b, were solved by X-ray crystallography. With respect to biological activity, 20 peptides were reported to be cytotoxic, followed by 4 with antifungal, 3 each with antibacterial and antiviral, and one each with anti-inflammatory and antiparasitic activities (Figure 34E). Indonesian marine peptides have been found from 4 phyla (Rhodophyta, Porifera, Chordata, and Mollusca). On the biogeography, MLU (18 molecules) and NSW (14 molecules) are the top places for the discovery of Indonesian marine peptides (Figure 34F).
2.5. Fatty Acids and Linear Molecules
A total of 13 (or 12) Indonesian marine fatty acids or linear molecules, probably biosynthesized through acetate pathways, have been reported, and they were characterized by the presence of double or triple bonds or their combination, ranging from 1 to 7 (Figure 35A, Figure S20, Table S20). After the first discovery of (–)-elenic acid (612) in 1995, this group of metabolites has been reported continuously (Figure 35B). Of 13 molecules, one showed cytotoxicity, three showed neurological, and five showed antihyperlipidemic activity (Figure 35D). The ACs of the metabolites were determined by modified Mosher’s method for 615–619, and by total synthesis for 613 and 615–617. With respect to biological sources, 12 molecules were found from Porifera and 1 from Ascomycota (Figure 35E). All the molecules were isolated from specimens collected in NSW (5), MLU (3), SSW and ENT (2 each), and UEP (1 molecule).
2.6. Polyketides
Several polyketides have been discovered in Indonesian waters, particularly since 1995. The molecules can be grouped into 121 natural, 13 mixtures, and 10 revised molecules (Figure 36A–C, Figure S21 and Table S21). Of 121 polyketides, significant biological activities were observed, with 11 cytotoxic, 9 antiparasitic, 8 antibacterial, 7 anticancer without cytotoxicity, 4 cytostatic, and 3 each of antifungal and growth restoring activity (Figure 36D). Polyketides can be classified into 9 different structural groups, consisting of 2 polyols, 18 cyclic peroxides, 34 aromatic polyketides, 1 vertinoid polyketide, 6 γ-lactones, 10 δ-lactones, 16 macrolides, 33 quinones, and 4 halogenated polyketides. Stereo or regiochemistry of four molecules 659b, 687–688 and 705 were determined by X-ray crystallography, while the ACs of 21 molecules were determined by ECD. Seven structures, 659a, 663a, 664a, 689a, 692a, 693a, and 701a, were revised to 659b, 663b, 664b, 689b, 692b, 693b, and 701b. In addition, four molecules, 661a, 662a, 665a, 666a, were revised twice as 661b1 to 661b2, 662b1 to 662b2, 665b1 to 665b2, and 666b1 to 666b2. The revision was made by reisolation work, total synthesis, and X-ray analysis. For large molecules, such as 625 and 626, structure elucidation was aided by chemical degradation. The polyketides were isolated from specimens of 5 phyla: Ascomycota (35 molecules), Ciliophora (2 molecules), Rhodophyta (1 molecule), Porifera (78 molecules), and Chordata (2 molecules).
2.7. Carbohydrates
One each of carbohydrates 746 and 747 (Figure 37) was isolated from a soft coral Sinularia sp. and from the tunicate Didemnum molle collected in NSW. Sinularioside (746), a triacetylated glycolipid, contains two α-D-arabinopyranoses and a myristyl alcohol [88]. The structure of 747 was solved by interpretation of MS and NMR data, along with ECD analysis of degradation products. Molecule 746 was proved to inhibit LPS-induced nitric oxide (NO) release. A polysaccharide, kakelokelose (747), inhibited the proliferation of HIV. Analysis of 1H and 13C NMR data of the polysaccharide and its desulfated derivative revealed that it consisted of a sequence of 2,3-disulfated mannose units joined through β-1,6 glycosidic linkages.
3. Conclusions
Over the past 47 years (from January 1970 to December 2017), 732 new natural products, 4 compounds isolated for the first time as natural products but known previously as synthetic entities, 34 compounds with structural revision, and 9 derivative compounds have appeared in 270 papers. Currently, have been over 29,000 MNPs [89] discovered since the first report of spongothymidine in 1950 [90,91]. Original Indonesian MNPs have largely been found in Porifera, Cnidaria and Chordata, while the global trends are Porifera, Cnidaria, and Ascomycota [89]. In addition to the three phyla, Indonesian MNPs have been found in 94 species, 106 genera, 64 families, 32 orders, and 14 classes. The chemical diversity of Indonesian MNPs has been substantiated on the basis of 28 compounds with new skeletons and 62 molecules with rare structural motifs and FGs, while atomic diversity is manifested in 27 molecules with 6 different atoms in 1 molecule. Of 732 molecules, 373 (51.0%) are nitrogenous. In addition, 122 molecules (16.7%) possessed a ratio of H/C < 1. Of 34 defined provinces, 18 (NST, WST, BTN, JSCR, WJV, CJV, BLI, ENT, EKM, NSW, GTO, CSW, SSW, SES, NMU, MLU, SRWP, and PUA) have been reported as collection sites for new MNPs. Among these, NSW, MLU, SSW, BLI, and EKM were the major regions for specimens, while there still remain underexplored regions with vast areas, like MLU, even though a certain number of MNPs have already been discovered. A large number of Indonesian marine macro- and microorganisms are still underexplored, and they may provide inspiration for many chemical entities. The significant biological activity of Indonesian MNPs is dominated by cytotoxicity (16.7%), followed by antibacterial activity (5.9%). By exploring untapped novel groups of organisms and by proposing newer biological targets, MNP researchers may be able to enhance the search for new marine drugs to treat human diseases. Moreover, careful and innovative techniques for the MNPs isolation are required for identification of new structures and activities including unstable intermediates [92]. The establishment of the Nagoya Protocols on the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) in 2010 has had a positive impact on global biodiversity especially in Indonesia by encouraging productive interaction between biodiversity-rich source countries and the more science and technology-advanced countries. International natural product researchers are strongly urged to be guided by the CBD principles in a fair and equitable framework that includes access and benefit-sharing [93]. These interactions will be crucial for conserving our global biodiversity [94] and providing valuable new MNPs for humankind. Therefore, the current primary issues in marine conservation, such as the loss of biodiversity through over-exploitation and habitat degradation, can be overcome. Additional information can be found in the Supplementary Materials [95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170,171,172,173,174,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204,205,206,207,208,209,210,211,212,213,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225,226,227,228,229,230,231,232,233,234,235,236,237,238,239,240,241,242,243,244,245,246,247,248,249,250,251,252,253,254,255,256,257,258,259,260,261,262,263,264,265,266,267,268,269,270,271,272,273,274,275,276,277,278,279,280,281,282,283,284,285,286,287,288,289,290,291,292,293,294,295,296,297,298,299,300,301,302,303,304,305,306,307,308,309,310,311,312,313,314,315,316,317,318,319,320,321,322,323,324,325,326,327,328,329,330,331,332,333,334,335,336,337,338,339,340,341,342,343,344,345,346,347,348,349,350,351,352,353,354,355,356,357,358,359,360,361,362,363,364,365,366,367,368,369,370,371,372,373,374,375,376,377,378,379,380,381,382,383,384,385,386,387,388,389,390,391,392,393,394,395,396,397,398,399,400,401,402,403,404,405,406,407,408,409,410,411,412,413,414,415,416,417,418,419,420,421,422,423,424,425,426,427,428,429,430,431,432,433,434,435,436,437,438,439,440,441,442,443,444,445,446,447,448,449,450,451,452,453,454,455,456,457,458,459,460,461,462,463,464,465,466,467,468,469,470,471,472,473,474,475,476,477,478,479,480,481,482,483,484,485,486,487,488].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/17/6/364/s1, Figure S1: Structures of marine sesquiterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S1: Marine sesquiterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S2: Structures of marine diterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S2: Marine diterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S3: Structures of marine sesterterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S3: Marine sesterterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S4: Structures of marine triterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S4: Marine triterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S5: Structures of marine steroids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S5: Marine steroids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S6: Structures of marine saponins from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S6: Marine saponins from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S7: Structures of marine meroterpenoids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S7: Marine meroterpe-noids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S8: Structures of marine piperidine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S8: Marine piperidine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S9: Structures of marine pyridine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S9: Marine pyridine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S10: Structures of marine indole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S10: Marine indole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S11: Structures of marine acridine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S11: Marine acridine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S12: Structures of marine quinoline and isoquinoline alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017,Table S12: Marine quinoline and isoquinoline alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S13: Structures of marine tyrosine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S13: Marine tyrosine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S14: Structures of marine pyrrole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S14: Marine pyrrole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S15: Structures of marine imidazole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S15: Marine imidazole alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S16: Structures of marine polysulfur aromatic alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S16: Marine polysulfur aromatic alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S17: Structures of marine serine-derived alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S17: Marine serine-derived alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S18: Structures of other marine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S18: Other marine alkaloids from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S19: Structures of marine peptides from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S19: Marine peptides from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S20: Structures of marine fatty acids and linear molecules from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S20: Marine fatty acids and linear molecules from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S21: Structures of polyketides from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S21: Marine polyketides from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Figure S22: Structures of carbohydrates from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017, Table S22: Marine carbohydrates from Indonesian waters found in 1970–2017.
Funding
This research was funded by Indonesian Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher Education, Indonesia awarded to N.H.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation, Indonesian Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher Education, Indonesia under its excellence basic research university program (1769/IT3.11/PN/2018 and 4175/IT3.L1/PN/2019) awarded to N.H.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nicolau, K.C.; Montagnon, T. Molecules that Changed the World; Willey-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 9–319. ISBN 978-3-527-30983-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, R.W. Classical Methods in Structure Elucidation of Natural Products; Willey-VCHA: Zürich, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–259. ISBN 978-3-906390-79-6. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.; Buckingham, J.; Munro, M. Taxonomy and Marine Natural Products Research. In Handbook of Marine Natural Products; Fattorusso, E., Gerwick, W.H., Tagliatela-Scafati, O., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 3–54. ISBN 978-90-481-3833-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pimm, S.L.; Jenkins, C.N.; Abell, R.; Brooks, T.M.; Gittleman, J.L.; Joppa, L.N.; Raven, P.H.; Roberts, C.M.; Sexton, J.O. The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science 2014, 344, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appeltans, W.; Ahyong, A.T.; Anderson, G.; Angel, M.V.; Artois, T.; Baily, N.; Bamber, R.; Barber, A.; Bartsch, I.; Berta, A.; et al. The magnitude of global marine species diversity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H. Why are there so many species in the tropics? J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinski, T.F. All natural: The renaissance of natural product chemistry. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3849–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, J.-Y.; Orlikova, B.; Diederich, M. Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) regulatory networks in marine organisms: From physiological observations toward marine drug discovery. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4967–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.; Vieira, H.; Gaspar, H.; Santos, S. Marketed marine natural products in the pharmaceutical and cosmeceutical industries: Tips for success. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1066–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, C. Marine natural products in medicinal chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, M.M.; Jain, S.; Porat, D.; Dick, G.J.; Sherman, D.H. Identification and analysis of the bacterial endosymbiont specialized for production of the chemotherapeutic natural product ET-743. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3964–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2008 and 2010. Available online: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/chemistry/ (accessed on 26 February 2019).
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, R.; Cruz-Trinidad, A.; Geronimo, R.; Aliño, P. Opportunities and challenges in the coral triangle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7930–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provinces of Indonesia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ Provinces_of_Indonesia (accessed on 10 July 2017).
- Glaser, M.; Baitoningsih, W.; Ferse, S.C.A.; Neil, M.; Deswandi, R. Whose sustainability? Top-down participation and emergent rule in marine protected area management in Indonesia. Mar. Policy. 2010, 34, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, E.; Gonzales, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Perrings, C.; Venail, P.; Narwani, A.; Mace, G.M.; Tilman, D.; Wardle, D.A.; et al. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 2012, 486, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visbeck, M. Ocean science research is key for a sutainable future. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J. Marine natural product chemistry: Past, present, and future. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, D. Chemistry of biologically and physiologically intriguing phenomena. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, C.R.; Bertin, M.J.; Lokey, R.S.; Gerwick, W.H.; Linington, R.G. Retrospective analysis of natural products provide insights for future discovery trends. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5601–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, J. Collaborations: The rise of research networks. Nature 2012, 490, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Bonn, A.; Guerra, C.A. Recognizing the quiet extinction of invertebrates. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, A.S.; Tarman, K.; Uria, A.R. Marine natural products: Prospects and impacts on the sustainable development in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the Indonesian Students’ Scientific Meeting, Delft, The Netherlands, 13–15 May 2008; pp. 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chasanah, E. Marine biodiscovery research in Indonesia: Challenges and rewards. J. Coastal Dev. 2008, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Putra, M.Y.; Muniarsih, T. Distribution and diversity of marine natural products from Indonesian marine organisms. J. Coastal Life Med. 2016, 4, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuer, P.J. Toxins from fish and other marine organisms. Adv. Food Res. 1970, 18, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbrecht, J.P.; Tursch, B.; Djerassi, C. A new sterol from an alcyonarian. Steroids 1972, 20, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge derived natural products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and opportunities for discovery of bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, M.C.; Puga, J.; Serôdio, J.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Calado, R. Trends in the discovery of new marine natural products from invertebrates over the last two decades−where and what are we bioprospecting? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.N.; Amagata, T.; Oliver, A.G.; Tenney, K.; Wenzel, P.J.; Crews, P. Structure revision of spiroleucettadine, a sponge alkaloid with a bicylic core meager in H-atoms. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 8719–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumori, N.; Murata, M. NMR studies on natural product: Stereochemical determination and conformational analysis in solution and in membrane. In Experimental Approaches of NMR Spectroscopy; Naito, A., Asakura, T., Shimada, I., Takegoshi, K., Yamamoto, Y., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2018; pp. 383–414. ISBN 978-981-10-5966-7. [Google Scholar]
- Seco, J.M.; Quiñoá, E.; Riguera, R. Assignment of the absolute configuration of polyfunctional compounds by NMR using chiral derivatizing agents. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4603–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, D.P.; Li, K.; Maue, M.; Zografos, A.L.; Baran, P.S. Total synthesis of dimeric pyrolle-imidazole alkaloids; sceptrin, ageliferin, nagelamide E, oxysceptrin, nakamuric acid, and the axinellamine carbon skeleton. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4762–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-T.; Lin, B.; Li, S.-G.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Xu, Y.; Hua, H.-M.; Lin, H.-W. New bromopyrrole alkaloids from the marine sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guella, G.; Dini, F.; Pietra, F. Metabolites with a novel C30 backbone from marine ciliates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1134–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, K.C.; Zhang, H.; Ortiz, A.; Dagneau, P. Total synthesis of the originally assigned structure of vannusal B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8605–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, K.C.; Zhang, H.; Ortiz, A. The true structure of the vannusals, part 1: Initial forays into suspected and intelegence gathering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5642–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, K.C.; Ortiz, A.; Zhang, H. The true structures of the vannusals, part 2: Total synthesis and revised structure of vannusal B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolau, K.C.; Ortiz, A.; Zhang, H.; Dagneau, P.; Lanver, A.; Jennings, M.P.; Arseniyadis, S.; Faraoni, R.; Lizos, D.E. Total synthesis and structural revision of vannusals A and B: Synthesis of the originally assigned structure of vannusal B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7138–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolau, K.C.; Ortiz, A.; Zhang, H.; Guella, G. Total synthesis and structural revision of vannusals A and B: Synthesis of the true structures of vannusals A and B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7153–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saielli, G.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Ortiz, A.; Zhang, H.; Bagno, A. Addressing the stereochemistry of complex organic molecules by density functional theory-NMR: Vannusal B in retrospective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6072–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guella, G.; Skropeta, D.; Di Giuseppe, G.; Dini, F. Structures, biological activities and phylogenetic relationships of terpenoids from marine ciliates of the genus Euplotes. Mar. Drugs 2010, 87, 2080–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washida, K.; Koyama, T.; Yamada, K.; Kita, M.; Uemura, D. Karatungiols A and B, two novel antimicrobial polyol compounds, from the symbiotic marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 2521–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnington, R.G.; Williams, D.E.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Latonduines A and B, new alkaloids isolated from the marine sponge Stylissa carteri: Structure elucidation, synthesis, and biogenetic implications. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2735–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, C.-D.; Weber, H.; Hartmann, R.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.; Lai, D.; Proksch, P. New cytotoxic 1,2,4-thiadiazole alkaloids from the ascidian Polycarpa aurata. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2230–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Bowden, B.F.; Toth, S.I. Antitumor and cytotoxic compound from marine organisms. In Marine Biotechnology: Pharmaceutical and Bioactive Natural Products; Attaway, D.H., Zaborsky, O.R., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 197–308. ISBN 0-306-44174-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gerwick, W.H. The face of a molecule. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2583–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, A.M.; Pattenden, G. Capnellane sesquiterpenes. Total synthesis of epiprecapnelladiene and Δ8(9)-capnellane. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I. 1983, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, Y.; Shirai, M.; Michino, T.; Kakisawa, H. Preparation of an 8-membered ring via intramolecular [2+2] photocycloadduct: Formal total synthesis of (±)-precapnelladiene. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1993, 66, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Inouye, Y. Preparation of (R)-(2-cyclopentyl)methanol and the first total synthesis of (8R, 11R)-precapnelladiene. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 67, 2880–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Ito, H.; Iguchi, K. Enantioselective formal synthesis of (+)-precapnelladiene by chiral copper-catalyzed asymmetric [2+2]-cycloaddition reaction. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefinovic, M.; Snieckus, V. Connecting directed ortho metalation and olefin metathesis strategies. Benzene-fused multiring-sized oxygen heterocyles. First synthesis of radulanin A and helianane. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 2808–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabui, S.K.; Venkateswaran, R.V. Synthesis of helianane, an unusual marine sesquiterpene employing ring-expansion by flash vacuum thermolysis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 9653–9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, K.; Kanematsu, M.; Yoshida, M.; Shishido, K. Efficient enantioselective total synthesis of (+)-helianane. Synlett 2011, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartieri, F.; Mesiano, L.E.; Borghi, D.; Desperati, V.; Gennari, C.; Papeo, G. Total synthesis of (+)-7, 11-helianane and (+)-5-chloro-7,11-helianane through stereoselective aromatic Claisen rearrangement. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 6794–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.; Jiménez-Alonso, S.; Brown, E.R.; Pettus, T.R.R. Total synthesis and repudiation of the helianane family. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5500–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, R.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Shigetomi, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Ubukata, M. Absolute configurations of (–)-hirsutanol A and (–)-hirsutanol C produced by Gloestereum incarnatum. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, R. Measurement of Bijvoet differences. Structure and absolute configuration of africanol, a sesquiterpene. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 1976, B32, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, L.A.; Ham, W.H. Total synthesis of africanol. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 2341–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, L.A.; Ham, W.H. Total synthesis of the marine sesquiterpenes dactylol and africanol. De novo construction of a cyclooctanoid natural product from cycloheptane precursors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursch, B. Some recent developments in the chemistry of alcyonaceans. Pure Appl. Chem. 1976, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Matsuo, K.; Kawabata, T.; Kobashigawa, Y.; Morioka, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; et al. Niphateolide A: Isolation from the marine sponge Niphates olemda and determination of its absolute configuration by an ECD analysis. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 6956–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Sanagawa, M.; Setiawan, A.; Kotoku, N.; Kobayashi, M. Cortistatins A, B, C, and D, anti-angiogenic steroidal alkaloids, from the marine sponge, Corticium simplex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3148–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Aoki, S.; Tanabe, D.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Cortistatins E, F, G, and H, four novel steroidal alkaloids from marine sponge Corticium simplex. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 4074–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Tanabe, D.; Setiawan, A.; Arai, M.; Kobayashi, M. Cortistatins J, K, L, novel abeo-9(10-19)-androstane-type steroidal alkaloids with isoquinoline unit, from marine sponge Corticium simplex. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 4485–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenvi, R.A.; Guerrero, C.A.; Shi, J.; Li, C.-C.; Baran, P.S. Synthesis of (+)-cortistatin A. J. Am Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7241–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nicolau, K.C.; Sun, Y.-P.; Peng, X.-P.; Polet, D.; Chen, D.Y.K. Total synthesis of (+)-cortistatin A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7310–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, K.C.; Peng, X.-S.; Sun, Y.-P.; Polet, D.; Zhou, B.; Lim, C.S.; Chen, D.Y.-K. Total synthesis and biological evaluation of cortistatins A and J and analogues thereof. J. Am Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10587–10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Tanabe, D.; Arai, M.; Suna, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Tsujibo, H.; Tsujikawa, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kobayashi, M. Structure-activity relationship and biological property of cortistatins, anti-angiogenic spongean steroidal alkaloids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6758–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czako, B.; Kurti, L.; Mammoto, A.; Ingber, D.E.; Corey, E.J. Discovery of potent and practical antiangiogenic agents inspired by cortistatin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9014–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cee, V.J.; Chen, D.Y.-K.; Lee, M.R.; Nicolau, K.C. Cortistatin A is a high-affinity ligand of protein kinase ROCK, CDK8, CDK11. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8952–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Hu, J.-F.; Kazi, A.B.; Li, Z.; Avery, M.; Peraud, O.; Hill, R.; Franzblau, F.; Zhang, F.; Schinazi, R.F.; et al. Manadomanzamines A and B: A novel alkaloid ring system with potent activity against Mycobacteria and HIV-1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13382–13386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, S.O.; Larghi, E.L.; Bracca, A.B.J.; Kaufman, T.S. Synthesis of the unique angular tricyclic chromone structure proposed fro aspergillitine, and its relationship with alkaloid TMC-120B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 4124–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copp, B.R.; Jompa, J.; Tahir, A.; Ireland, C.M. Styelsamines A–D: New tetracyclic pyridoacridine alkaloids from the Indonesian ascidian Eusynstyela latericius. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 63, 8024–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyler, D.; Heathcock, C.H. A simple biomimetic synthesis of styelsamine B. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 4323–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, S.; Kubo, A. Total synthesis of styelsamine C, a cytotoxic fused tetracyclic aromatic alkaloid. Heterocyles 2003, 60, 2017–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.K.H.; Copp, B.R. Synthesis, DNA binding and antitumor evaluation of styelsamine and cystodytin analgues. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 274–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyler, D.; Heathcock, C.H. The pyridoacridine family tree: A useful scheme for designing synthesis and predicting undiscovered natural products. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, C.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Ferdinandus, E.; Pattisina, L.A.; Sudarsono. New bromopyrrole alkaloids from the Indopacific sponge Agelas nakamurai. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1295–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhlesi, A.; Hartman, R.; Achten, E.; Chaidir; Hartmann, T.; Lin, W.; Daletos, G.; Proksch, P. Lissodendrins A and B: 2-Aminoimidazole alkaloids from the marine sponge Lissodendroryx (Acanthodoryx) fibrosa. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pratasik, S.B.; Nishikawa, T.; Shida, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Nagai, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Namikoshi, M. Lissoclibadin 1, a novel trimeric sulfur-bridged dopamine derivative, from the tropical ascidian Lissoclinum cf. badium. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7015–7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoth, T.; Warburg, K.; Katzka, C.; Rai, A.; Wolf, A.; Brockmeyer, A.; Janning, P.; Reubold, T.F.; Eschenburg, S.; Manstein, D.J.; et al. The ras pathway modulator melophlin A target dynamins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7240–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biersack, B.; Diestel, R.; Jagusch, C.; Sasse, F.; Schobert, R. Metal complexes of natural melophlins and their cytotoxic and antibiotic activities. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Yamano, Y.; Kamiya, K.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Anti-dormant mycobacterial activity and target molecule of melophlins, tetramic acid derivatives isolated from a marine sponge of Melophlus sp. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 70, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Hasegawa, M.; Harada, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Nagai, H.; Namikoshi, M. Melophlins P, Q, R, and S: Four new tetramic acid derivatives, from two Palauan marine sponges of the genus Melophlus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Fujita, A.; Xu, J.; Mochizuki, M.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Effects of melophlins on colony formation of Chinese hamster V79 cells and IL-8 production in PMA-stimulated HL-60 cells. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, M.Y.; Ianaro, A.; Panza, E.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Tagliatela-Scafati, O. Sinularioside, a triacetylated glycolipid from the Indonesian soft coral Sinularia sp., is an inhibitor of NO release. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2723–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, W.; Feeney, R.J. The isolation of a new thymine pentoside from sponges. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 70, 2809–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, W.; Feeney, R.J. Contributions to the study of marine products. XXXII. The nucleosides of sponges. I.1. J. Org. Chem. 1951, 16, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakimoto, T.; Abe, I. Labile natural products. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012, 3, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallier, L.E.; McMeel, O.; Greiber, T.; Vanagt, T.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Jaspars, M. Access to and use of marine genetic resources: Understanding the legal framework. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Katz, F.; Newman, D.J.; Rosenthal, J. Legal and ethical issues involving marine biodiscovery and development. In Handbook of Marine Natural Products; Fattorusso, E., Gerwick, W.H., Tagliatela-Scafati, O., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 1315–1342. ISBN 978-90-481-3833-3. [Google Scholar]
- Torii, M.; Kato, H.; Hitora, Y.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Lamellodysidines A and B, sesquiterpenes isolated from the marine sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2536–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursch, B.; Colin, M.; Daloze, D.; Losman, D.; Karlsson, R. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XII. Lemnacarnol, a novel sesquiterpene from the soft coral Lemnalia carnosa. Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1975, 84, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, R.; Losman, D. Structure and absolute configuration of the sesquiterpene lemnacarnol. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 1977, B33, 1614–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, B.F.; Coll, J.C.; Mitchell, S.J.; Nemorin, J.L.E.; Sternhell, S. Studies of Australian soft corals. XXIII The co-occurence of bicyclogermacrene and lemnacarnol derivatives in Parerythropodium fulvum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 3105–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursch, B.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Kaisin, M. Terpenoids from coelenterates. In Marine Natural Products: Chemical and Biological Perspectives; Scheuer, P.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 2, pp. 247–296. ISBN 978-0-12-624002-3. [Google Scholar]
- Daloze, D.; Braekman, J.C.; Georget, P.; Tursch. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XXII. Two novel sesquiterpenes from soft corals of of the genera Lemnalia and Paralemnalia (Coelenterate, Octocorallia, Alcyonacea). Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1977, 86, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapojos, M.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Nakazawa, T.; Oda, T.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Three new nardosinane type sesquiterpenes from an Indonesian soft coral Nephthea sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanoglu, E.; Gebreyesus, T.; Beechan, C.M.; Djerassi, C. Terpenoids LXXVI. Precapnelladiene, a possible biosynthetic precursor of the capnellane skeleton. Tetrahedron. 1979, 35, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, D.; Hänel, F.; Dahse, H.-M.; Seifert, K. Capnellenes from the soft coral Dendronephthyta rubeola. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handayani, D.; Edrada, R.A.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; Witte, L.; van Ofwegen, L.; Kunzmann, A. New oxygenated sesquiterpenes from the Indonesian soft coral Nephthea chabrolii. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, N.; Murni, A.; Yamauchi, M.; Higashi, M.; Tanaka, J. A new trinor-guaiane sesquiterpene from an Indonesian soft coral Anthelia sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1907–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, B.; Crews, P. The structure and probable biogenesis of helianane, a heterocyclic sesquiterpene, from the Indo-Pacific Sponge Haliclona? fascigera. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 2646–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.E.; Patrick, B.O.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Roberge, M.; Andersen, R.J. Boneratamides A–C, new sesquiterpenoids isolated from the marine sponge Axinyssa aplysinoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1752–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanoglu, E.; Gebreyesus, T.; Beechan, C.M.; Djerassi, C. Terpenoids LXXV. Δ9(12)-capnellane, a new sesquiterpene hydrocarbon from the softcoral Capnella imbricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 1671–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.A.; Jaspars, M.; Adamson, K.; Woods, S.; Wallace, H.M. The capnellenes revisited: New structures and new biological activity. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 12953–12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wang, S.-K.; Duh, C.-Y. Capnellenes from the Formosan soft coral Capnella imbricata. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Y.M.; Singy, G.; Kaisin, M.; Eggert, H.; Djerassi, C.; Tursch, B.; Daloze, D.; Braekman, J.C. Terpenoids-LXXI: Chemical studies of marine invertebrates-XIV. Four representatives of a novel sesquiterpene class-the capnellane skeleton. Tetrahedron 1976, 32, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, Y.-H.; Chen, W.-F.; Sung, C.-S.; Duh, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-S.; Tai, M.-H.; Tzeng, S.-F.; Wen, Z.-H. Capnellene, a natural marine compound derived soft coral, attenuates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaisin, M.; Sheikh, Y.M.; Durham, D.J.; Djerassi, C.; Tursch, B.; Daloze, D.; Braekman, J.C.; Losman, D.; Karlsson, R. Capnellane-a new tricyclic sesquiterpene skeleton. Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 15, 2239–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Y.M.; Djerassi, C.; Braeekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Kaisin, M.; Tursch, B.; Karlsson, R. Terpenoids-LXXII. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates-XXVI-Δ9(12)-capnellene-3β,8β,10α,14-tetrol, a novel polyoxygenated sesquiterpene from the Alyconarian Capnella imbricata. Tetrahedron 1977, 33, 2115–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.S.; Abrell, L.M.; Avelar, A.; Borgeson, B.M.; Crews, P. New hirsutane based sesquiterpenes from salt water cultures of a marine sponge-derived fungus and the terrestrial fungus Coriulus consors. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 7335–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-J.; Lan, W.-J.; Lam, C.-K.; Yang, F.; Zhu, X.-F. Hirsutane sesquiterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Chondrostereum sp. Chem. Biodiversity. 2011, 8, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, W.-D.; Deng, R.; Li, D.-D.; Wu, K.-W.; Feng, G.-K.; Li, H.-J.; Zhu, X.-F. Hirsutanol A induces apoptosis and autophagy via reactive oxygen species accumulation in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 119, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursch, B.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Fritz, P.; Kelecom, A.; Karlsson, R.; Losman, D. Chemical studies of marine invertebrate. VIII. Africanol, an unusual sesquiterpene from Lemnalia africana (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alcyonacea). Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 15, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beechan, C.M.; Djerassi, C.; Eggert, H. Terpenoids-LXXIV. The sesquiterpenes from the soft coral Sinularia mayi. Tetrahedron 1978, 34, 2503–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beechan, C.M.; Djerassi, C.; Finer, J.S.; Clardy, J. Terpenoids LXXIII. Sinularene, a sesquiterpene hydrocarbon based on a novel skeleton from the soft coral, Sinularia mayi. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 2395–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasman; Edrada, R.A.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. New 9-thiocyanatopupukeanane sesquiterpenes from the nudibranch Phyllidia varicosa and its sponge-prey Axinyssa aculeata. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1512–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, M.Y.; Ianaro, A.; Panza, E.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Sinulasulfoxide and sinulasulfone, sulfur-containing alkaloids from the Indonesian soft coral Sinularia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 3937–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmoun, M.; Braekman, J.C.; Dewelle, J.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R.; de Voogd, N.J.; van Soest, R.W.M. New terpenoids from two Indonesian marine sponges. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Müller, W.E.G.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A.; Proksch, P. Diacarperoxides, norterpene cyclic peroxides from the sponge Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertiani, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ortlepp, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Hentschel, U.; Kozytska, S.; Muller, W.E.G.; Proksch, P. From anti-fouling to biofilm inhibition: new cytotoxic secondary metabolites from two Indonesian Agelas sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.; Nieto, R.M.; Jiménez, C. New briarane stecholide diterpenes from the Indonesian gorgonian Briareum sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Huang, L.-H.; Lee, S.-F.; Wu, T.; Chang, B.-Y.; Duh, C.-Y.; Fang, L.-S.; Soong, K.; Lee, T.-J. New cytotoxic briarane diterpenes from the Formosan gorgonian Briareum sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C. Absolute structures of new briarane diterpenoids from Junceella fragilis. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J.; Williams, G.C. Malayenolides A–D, novel diterpenes from the Indonesian sea pen Veretillum malayense. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Okano, M.; Matsui, K.; Itoh, T.; Satari, R.; Akiyama, S.; Kobayashi, M. Brianthein A, a novel briarane-type diterpene reversing multidrug resistance in human carcinoma cell line, from the gorgonian Briareum excavatum. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 8951–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, C.; Yamamoto, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Tanaka, J.; Ichiba, T.; Marriot, G.; Rachmat, R.; Higa, T. Briarane diterpenes from two species of octocorals, Ellisella sp. and Pteroeides sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Tai, C.-Y.; Hwang, T.-L.; Weng, C.-F.; Li, J.-J.; Fang, L.-S.; Wang, W.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. Cladielloides A and B: New eunicellin-type diterpenoid from an Indonesian octocoral Cladiella sp. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Tai, C.-Y.; Su, Y.-D.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lu, M.-C.; Weng, C.-F.; Su, J.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. Discovery of new eunicellins from an Indonesian octocoral Cladiella sp. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Fang, L.-S.; Wang, W.-H.; Liu, M.-C.; Su, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. Cladielloides C and D: Novel eunicellin-based diterpenoids from an Indonesian Octocoral Cladiella sp. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Su, Y.-D.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hong, P.-H.; Hu, L.-C.; Yen, W.-H.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Huang, S.-J.; et al. New 6-hydroxyeunicellins from a soft coral Cladiella sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murni, A.; Hanif, N.; Tanaka, J. A new cytotoxic dolabellane from the Indonesian soft coral Anthelia sp. Indones. J. Chem. 2013, 13, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fattorusso, E.; Romano, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Bavestrello, G.; Bonelli, P.; Calcinai, B. Coelodiol and coeloic acid, ent-isocopalane diterpenes from the Indonesian sponge Coelocarteria cfr. singaporensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 2197–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Ceylonamides A–F, nitrogenous spongian diterpenes that inhibit RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis, from the marine sponge Spongia ceylonensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Kagiyama, I.; Hitora, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Ceylonins A–F, spongian diterpene derivatives that inhibit RANKL-induced formation of multinuclear osteoclasts, from the marine sponge Spongia ceylonensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Tsukamoto, S. Ceylonins G-I: Spongian diterpenes from the marine sponge Spongia ceylonensis. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, S.M.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Park, E.-J.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Kelly, M.; Williams, P.G. Spongiapyridine and related spongians isolated from an Indonesian Spongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hérin, M.; Tursch, B. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XXV. Flexibilene, an unprecedented fifteen-membered ring diterpene hydrocarbon from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata, Octocorallia). Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1976, 85, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, J.; Matz, J.R.; Kees, K.L.; Bock, P.A. Synthesis of flexibilene, a naturally occuring 15-membered-ring diterpene. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 1777–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursch, B.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Hérin, M.; Karlsson, R. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. X. Lobophytholide, a new cembranolide diterpene from the soft coral Lobophytum cristagalli (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alyconacea). Tetrahedron Lett. 1974, 15, 3769–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursch, B.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Dedeuerwaerder, H.; Karlsson, R. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XXXI. Crassolide, a highly oxygenated diterpene from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alcynoacea). Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1978, 87, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-K.; Duh, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.-C.; Soong, K.; Fang, L.-S. Studies on Formosan soft corals, II. Cytotoxic cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-T.; Wang, S.-K.; Soong, K.; Duh, C.-Y. New cytotoxic cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum michaele. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesando, D.; Graillet, C.; Braekman, J.-C.; Dubreuil, A.; Girard, J.-P.; Puiseux-Dao, S. The use of sea urchin eggs as a model to investigate the effects of diterpene isolated from a soft coral. Toxicol. In Vitro 1991, 5, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januar, H.I.; Zamani, N.P.; Soedharma, D.; Chasanah, E. New cytotoxic cembranoid from Indonesian soft coral Sarcophyton sp. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017, 9, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursch, B.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates-XIII. 2-Hydroxynepthenol, a novel cembrane diterpene from the soft coral Lithophyton viridis (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alconacea). Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1975, 84, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-K.; Weng, Y.-L.; Chiang, M.Y.; Dai, C.-F. Cytotoxic terpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Nephthea brassica. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Shimada, A.; Kato, T. Cyclization of polyenes xxx1 synthesis of 2-hydroxy-and 1,2-dehydro-7,8-oxido-nephthenols and and cembrenol. Chem. Lett. 1978, 7, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hérin, M.; Tursch, B. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XXIV. Minor cembrane diterpenes from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata, Octocorallia). Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1976, 85, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, K.H.; Müller, M.; Ghani, M.A.; Dahse, H.-M.; Seifert, K. Terpenes from the soft corals Litophyton arboreum and Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Chem. Biodiversity 2010, 7, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januar, H.I.; Chasanah, E.; Motti, C.A.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Liptrot, C.H.; Wright, A.D. Cytotoxic cembranes from Indonesian specimens of the soft coral Nephthea sp. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursch, B.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Hérin, M.; Karlsson, H.; Losman, D. Chemical Studies of marine invertebrates-XI. Sinulariolide, a new cembranolide diterpene from the softcoral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alyconacea). Tetrahedron 1975, 31, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, R. The structure and absolute configuration of sinulariolide, a cembranolide diterpene. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 1977, B33, 2027–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.-W.; Chang, F.-R.; McPhail, A.T.; Lee, K.-H.; Wu, Y.-C. New cembranolide analogues from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia flexibilis and their cytotoxicity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2003, 17, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-H.; Lin, Y.-F.; Yeh, H.-C.; Wang, W.-H.; Fan, T.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H. Oxygenated cembranoids from the cultured and wild-type soft corals Sinularia flexibilis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, H.-J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Sheu, J.-H.; Su, J.-H. Anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia discrepans. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, P.; Gu, Q.; Li, W.D.; Guo, J.L.; Qiao, W.; Feng, D.Q.; Tang, S.A. Antifouling activity against bryozoan and barnacle by cembrane diterpenes from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 120, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Sheu, J.-H.; Chiang, M.-Y.; Wen, Z.-H.; Dai, C.-F.; Su, J.-H. Structural elucidation and structure−anti-inflammatory activity relationships of cembranoids from cultured soft corals Sinularia sandensis and Sinularia flexibilis. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2015, 63, 7211–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceret, T.L.; Coll, J.C.; Uchio, Y.; Sammarco, P.W. Antimicrobial actvity of the diterpenes flexibilide and sinulariolide derived from Sinularia flexibilis Quoy and Gaimard 1833 (Coelenterata, Octocorallia). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endrocrinol. 1998, 120, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceret, T.L.; Sammarco, P.W.; Coll, J.C.; Uchio, Y. Discrimination between several diterpenoid compounds in feeding by Gambusia affinis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Comp. Pharmacol. 2001, 128, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, K.; Bowden, B.F. A natural algacide from soft coral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alcyonacea). J. Chem. Ecol. 1997, 23, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceret, T.L.; Brown, L.; Meiiler, J.; Coll, J.C.; Sammarco, P.W. Cardiac and vascular responses of isolated rat tissues with diterpenes from Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata: Octocorallia). Toxicon 1996, 34, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neoh, C.-A.; Wang, R.Y.-L.; Din, Z.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-K.; Tsai, F.-J.; Weng, S.-H.; Wu, Y.-J. Induction of apoptosis by sinulariolide from soft coral through mitochondrial-related and p38MAPK pathways on human bladder carcinoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2893–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-H.; Su, J.-S.; Chiu, C.-C.; Lin, J.-J.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Hwang, W.-I.; Chen, Y.-K.; Lo, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-J. Proteomic investigation of the sinulariolide-treated melanoma cells A375: Effects on the cell apoptosis through mitochondrial-related pathway and activation of cascapase cascade. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2625–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Su, J.-H.; Tsao, C.-Y.; Hung, C.-T.; Chao, H.-H.; Lin, J.-J.; Liao, M.-H.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Huang, H.H.; Tsai, F.-J.; et al. Sinulariolide induced hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis through activation of mitochondrial-related apoptotic and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP pathway. Molecules 2013, 18, 10146–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-J.; Neoh, C.-A.; Tsao, C.-Y.; Su, J.-H.; Li, H.-H. Sinulariolide suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 through MAPKs and P13K/Akt signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16469–16482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.-C.; Din, Z.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-J.; Liu, C.-I. Sinulariolide suppresses cell migration and invasion by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 and urokinase through the PI3K/ AKT/mTOR signalling pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.Y.; Wu, Y.-J.; Liu, Z.N.; Chuang, C.W.; Huang, H.H.; Kuo, S.M. Anticancer effects of sinulariolide-conjugated hyaluronan nanoparticles on lung adenocarcinoma cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.-W.; Li, Y.-R.; Huang, W.Y.; Su, J.-H.; Chan, H.-L.; Lin, S.-H.; Liu, C.-S.; Lin, S.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Sinulariolide suppresses LPS-induced phenotypic and functional maturation of dendritic cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6992–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maida, M.; Carroll, A.R.; Coll, J.C. Variability of terpene content in the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata: Octocorallia), and its ecological implications. J. Chem. Ecol. 1993, 19, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceret, T.L.; Sammarco, P.W.; Coll, J.C. Effects of diterpenes derived from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis on the eggs, sperm, and embryos of the scleractinian corals Montipora digitata and Acropora tenuis. Mar. Biol. 1995, 122, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek-Wagner, K.; Bowden, B.F. Effects of bleaching on secondary metabolite chemistry of alcyonacean soft corals. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 1543–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-H.; Liaw, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Shen, Y.-C. Cembrane diterpenoids from the Taiwanese soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 9157–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-R.; Tsai, F.-J.; Lin, J.-J.; Huang, H.H.; Chiu, C.-C.; Su, J.-H.; Yang, Y.-T.; Chen, J.Y.-F.; Wong, B.-S.; Wu, Y.-J. Induction of apoptosis by 11-dehydrosinulariolide via mitochondrial dysregulation and ER stress pathways in human melanoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1883–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-F.; Chakraborty, C.; Sung, C.-S.; Feng, C.-W.; Jean, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Hung, H.-C.; Huang, T.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Su, T.-M.; et al. Neuroprotection by marine-derived compound, 11-dehydrosinulariolide, in an in vitro Parkinson’s disease. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-I.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, J.-C.; Su, J.-H.; Huang, H.H.; Chen, J.Y.-F.; Wu, Y.-J. Proteomic analysis of anti-tumor effects of 11-dehydrosinulariolide on CAL-27 cells. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1254–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.-C.; Yen, W.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Chiang, M.Y.-N.; Wen, Z.-H.; Chen, W.-F.; Lu, T.-J.; Chang, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; et al. Cembrane derivatives from the soft corals, Sinularia gaweli and Sinularia flexibilis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2154–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Chen, N.-F.; Feng, C.-W.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Hung, H.-C.; Tsui, K.-H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Sung, P.-J.; Chen, W.-F.; Wen, Z.-H. A coral-derived compound improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury through its antiapoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-Y.; Jean, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-P.; Chen, W.-F.; Sun, Y.-M.; Su, J.-H.; Lu, Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Hung, H.-C.; Sung, P.-J.; et al. A soft coral-derived compound, 11-epi-sinulariolide acetate suppresses inflammatory response and bone destruction in adjuvant-induced arthritis. PLoS ONE 2013, e62926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-J.; Su, J.-H.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Liao, M.-H.; Wu, Y.-J. 11-epi-Sinulariolide acetate reduces cell migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing the activation of ERK1/2, p38MAPK and FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4783–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-J.; Wang, R.Y.L.; Chen, J.-C.; Chiu, C.-C.; Liao, M.-H.; Wu, Y.-J. Cytotoxicity of 11-epi-sinulariolide acetate isolated from cultured soft corals on HA22T cells through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway and mitochondrial dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanduja, R.; Sanduja, S.K.; Weinheimer, A.J.; Alam, M.; Martin, G.E. Isolation of the cembranolide diterpenes dihydrosinularin and 11-epi-sinulariolide from the marine mollusk Planaxis sulcatus. J. Nat. Prod. 1986, 49, 718–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Romano, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Irace, C.; Maffettone, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C. Oxygenated cembranoids of the decaryiol type from the Indonesian soft coral Lobophytum sp. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 2898–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, D.; Dahse, H.-M.; Seifert, K. Furanocembranoids from the soft corals Sinularia asterolobata and Litophyton arboreum. Chem. Biodiversity. 2008, 5, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapojos, M.M.; Lee, J.-S.; Oda, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Takahashi, O.; Ukai, K.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Tsukamoto, S.; et al. Two unprecedented cembrene-type terpenes from an Indonesian soft coral Sarcophyton sp. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Luciano, P.; Putra, M.Y.; Tagliatela-Scafati, O.; Lanaro, A.; Pana, E.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C. Chloroscabrolides, chlorinated norcembranoids from the Indonesian soft coral Sinularia sp. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 7983–7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anta, C.; González, N.; Santafé, G.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C. New xenia diterpenoids from the Indonesian soft coral Xenia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Romano, A.; Tagliatela-Scafati, O.; Achmad, M.J.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C. Xenimanadins A–D, a family of xenicane diterpenoids from the Indonesian soft coral Xenia sp. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 3141–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, K.S.; Williams, D.E.; Hollander, I.; Frommer, E.; Mallon, R.; Collins, K.; Wojciechowicz, D.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Novel sesterterpenoid and norsesterterpenoid RCE-protease inhibitors isolated from the marine sponge Hippospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 4801–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhayat, E.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; van Soest, R.; Wiryowidagdo, W.; Mohamed, M.H.; Müller, W.E.G.; Proksch, P. New luffarielloide derivatives from the Indonesian sponge Acanthodendrilla sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, A.H.; Kagiyama, I.; El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Ammar, N.M.; Hifnawy, M.S.; Tsukamoto, S. Sulawesins A–C, furanosesterterpene tetronic acids that inhibit USP7 from a Psammocinia sp. marine sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2045–20150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R. Diacarperoxide S, new norterpene cyclic peroxide from the sponge Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Al Haidari, R.A.; Mohamed, G.A. Megaspinoxide A: New norterpene cyclic peroxide from the sponge Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa. Nat. Prod. J. 2014, 4, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.I.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J.; Kelly, M. Honulactones: New bishomoscalarane sesterterpenes from the Indonesian sponge Strepsichordaia aliena. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 6837–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, J.I.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly, M. Scalarane-based sesterterpenes from an Indonesian sponge Strepsichordaia aliena. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Crews, P.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A. Cytotoxic phyllactone analogs from the marine sponge Phyllospongia papyrecea. Med. Chem. (Sharjah, United Arab Emirates). 2017, 13, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Hollander, I.; Feldberg, L.; Frommer, E.; Mallon, R.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Scalarane-base sesterterpenoid RCE-protease inhibitors isolated from the Indonesian Carteriospongia foliascens. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Namikoshi, M. Two new protein tyrosinase phosphatase 1B inhibitors, hyattellactones A and B, from the Indonesian marine sponge Hyattella sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.C.; Tanaka, J.; de Voogd, N.J.; Higa, T. New scalarane class sesterterpenes from an Indonesian sponge, Phyllospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.E.; Tahir, A.; Andersen, R.J. A new acyclic diketotriterpenoid isolated from the Indonesian marine sponge Hyrtios erectus. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enders, D.; Schüßeler, T. First highly efficient asymmetric synthesis of the Hyrtios erectus diketotriterpenoid. Synthesis 2002, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, M.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Müller, W.E.G.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Cytotoxic isomalabaricane triterpenes from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Sanagawa, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Setiawan, A.; Arai, M.; Kobayashi, M. Novel isomarabarican triterpenes, exhibiting selective anti-proliferative activity against vascular endothelial cells, from marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 4818–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, V.; Sala, G.D.; Mangoni, A.; Perinu, C.; Teta, R. Blurring the boundary between bio- and geohopanoids: Plakohopanoid, a C32 biohopanoid ester from Plakortis cf. lita. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5171–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, M.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Losman, D.; Tursch, B. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XXIII. A novel polyhydroxylated sterol from the soft coral Lithophyton viridis (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alycynoacea). Steroids 1976, 28, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Naka, Y.; Itoh, T.; Furukawa, T.; Rachmat, R.; Akiyama, S.; Kobayashi, M. Lembehsterols A and B, novel sulfated sterols inhibiting thymidine phosphorylase, from the marine sponge Petrosia strongylata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, M.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Losman, D.; Tursch, B. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XXIX. 4α-Methyl-3β, 8β-dihydroxy-5α-ergost-24(28)-en-23-one, a novel polyoxygenated sterol from the softcoral Litophyton viridis (Coelenterata, Octocroallia, Alycyonacea). Steroids 1977, 30, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angawi, R.F.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Dien, H.A.; Fattorusso, E.; Scala, F.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Dehydroconicasterol and aurantoic acid, a chlorinated polyene derivative, from the Indonesian sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, N.; Barral, M.A.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C. New cytotoxic steroids from the gorgonian Isis hippuris. Structure-activity studies. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 3487–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Sorribas, A.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kelly, M.; Williams, P.G. Topsentinols, 24-isopropyl steroids from the marine sponge Topsentia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, G.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Bavestrello, G.; Calcinai, B.; Dien, H.A.; Ligresti, A.; Marzo, V.D. Desulfohaplosamate, a new phosphate-containing steroid from Dasychalina sp., is a selective cannabinoid CB 2 receptor ligand. Steroids 2011, 76, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurek, J.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Two steroidal alkaloids from a sponge, Corticium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotto, M.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Tursch, B. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XVIII. Four novel polyhydroxylated steroids from Sinularia dissecta. Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1976, 85, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushiyama, S.; Umaoka, H.; Kato, H.; Suwa, Y.; Morioka, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; et al. Manadosterols A and B, sulfonated sterol dimers inhibiting the ubc13-uev1A interaction, isolated from the marine sponge Lissodendryx fibrosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, M.Y.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Polyhydroxylated sterols from the Indonesian soft coral Sinularia sp. and their effect on farnesoid X-activated receptor. Steroids 2012, 77, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, L.A.; Christie, E.M.; Jaspars, M.; van Ofwegen, L.P. A bioactive secosterol with an unusual A- and B-ring oxygenation pattern isolated from an Indonesian soft coral Lobophytum sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anta, C.; González, N.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C. A new secosterol from the Indonesian octocoral Pachyclavularia violacea. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1357–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lee, J.-S.; Nakazawa, T.; Ukai, K.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Wewengkang, D.; Rotinsulu, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Tsukamoto, S.; Namikoshi, M. (25S)-Cholesten-26-oic acid derivatives from an Indonesian soft coral Minabea sp. Steroids 2009, 74, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallimore, W.A.; Cabral, C.; Kelly, M.; Scheuer, P.J. A novel D-ring unsaturated A-nor sterol from the Indonesian sponge, Axinella carteri Dendy. Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 22, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flyer, A.N.; Si, C.; Myers, A.G. Synthesis of cortistatins A, J, K, and L. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothberg, I.; Tursch, B.M.; Djerassi, C. Terpenoids. LXVIII. 23ξ-acetoxy-17-deoxy-7,8-dihydroholothurinogenin, a new triterpenoid sapogenin from a sea cucumber. J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.-F.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Nimtz, M.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. Norlanostane triterpenoidal saponins from the marine sponge Melophlus sarassinorum. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Jeon, J.-e.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, K.-B. Nortriterpene gylcosides of the sarasinoside class from the sponge Lipastrotethya sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarisit, W.; Yamazaki, H.; Kanno, S.-I.; Tomizawa, A.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Ukai, K.; Kapojos, M.M.; Namikoshi, M. A tetramic acid derivative with protein tyrosinase phospahatase 1B inhibitory activity and a new nortriterpene glycoside from the Indonesian marine sponge Petrosia sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piña, I.C.; Sanders, M.L.; Crews, P. Puupehenone congeners from an Indo-Pacific Hyrtios sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, H.A.; Pham, N.B.; Muhammad, T.S.T.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Quinn, R.J. Merosesquiterpene congeners from the Australian sponge Hyrtios digitatus as potential drug leads for atherosclerosis disease. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Nakayama, W.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Izumikawa, Y.; Iwasaki, K.; Toraiwa, K.; Ukai, K.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; et al. Verruculides A and B, two new protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors from an Indonesian ascidian-derived Penicillium verruculosum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3087–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Takasaki, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Oda, T.; Yamada, J.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Ukai, K.; Nagai, H.; Namikoshi, M. Four new macrocyclic trichothecenes from two strains of marine-derived fungi of the genus Myrothecium. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebel, R.; Rusman, Y.; Brauers, G.; Proksch, P.; Frank, W.; Wray, V. Novel oxygenated meroterpenoids from the sponge-derived fungus Penicillium citreonigrum. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 961–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusman, Y. Isolation of New Secondary Metabolites from Sponge-Associated and Plant-Derived Endophytic Fungi. Ph.D. Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, H.H.; Tanaka, J.; Rachmat, R.; Higa, T. Floresolides, new metacyclophane hydroquinone lactones froman ascidian, Aplidium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 1243–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, K.C.; Xu, H. Total synthesis of floresolide B and Δ6,7-Z-floresolide B. Chem. Commun. 2006, 6, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebada, S.S.; de Voogd, N.; Kalscheuer, R.; Müller, W.E.G.; Chaidir; Proksch, P. Cytotoxic drimane meroterpenoids from the Indonesian marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 22, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Kong, D.; Matsui, K.; Rachmat, R.; Kobayashi, M. Sesquiterpene aminoquinones, from a marine sponge, induce erythroid differentiation in human chronic myelogenous leukemia, K562 cells. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daletos, G.; de Voogd, N.J.; Muller, W.E.G.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.; Feger, D.; Kubbutat, M.; Aly, A.H.; Proksch. Cytotoxic and protein kinase inhibiting nakijiquinones and nakijiquinols from the sponge Dactylospongia metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suna, H.; Arai, M.; Tsubotani, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Dysideamine, a new sesquiterpene aminoquinone, protects hippocampal neuronal cells against iodoacetic acid-induced cell death. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3968–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Telliez, J.-B.; Liu, J.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Meroterpenoid MAPKAP (MK2) inhibitors isolated from the Indonesian marine sponge Acanthodendrilla sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2127–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basabe, P.; Martín, M.; Bodero, O.; Blanco, A.; Marcos, I.S.; Díez, D.; Urones, J.G. Synthesis of (+)-makassaric acid, a protein kinase MK2 inhibitor. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 6008–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trianto, A.; Hermawan, I.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tanaka, J. Halioxepine, a new meroditerpene from an Indonesian sponge Haliclona sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 1311–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, P.; Harrison, B. New triterpene-ketides (merotriterpenes), haliclotriols A and B, from an Indo-Pacific Haliclona sp. sponge. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 9039–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Kelly, M.; Kara, U.A.K.; Ang, K.K.H.; Katsuyama, I.; Dunbar, D.C.; Khan, A.A.; Hamann, M.T. New manzamine alkaloids with potent activity against infectious diseases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousaf, M.; El Sayed, K.; Rao, K.V.; Lim, C.W.; Hu, J.-F.; Kelly, M.; Franzblau, S.G.; Zhang, F.; Peraud, O.; Hill, R.T.; et al. 12,34-Oxamanzamines, novel biocatalytic and natural products from manzamine producing Indo-Pacific sponges. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 7397–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.H.; Holmes, M.J.; Higa, T.; Hamann, M.T.; Kara, U.A.K. In vivo antimalarial activity of the beta-carboline alkaloid manzamine A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1645–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Shen, X.; El Sayed, K.A.; Dunbar, D.C.; Perry, T.L.; Wilkins, S.P.; Hamann, M.T.; Bobzin, S.; Huesing, J.; Camp, R.; et al. Marine natural products as prototype agrochemical agents. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2003, 51, 2246–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.; Kasanah, N.; Wahyuono, S.; Tekwani, B.L.; Schinazi, R.F.; Hamann, M.T. Three new manzamine alkaloids from a common Indonesian sponge and their activity against infectious and tropical parasitic diseases. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.; Donia, M.S.; Peng, J.; Garcia-Palomero, E.; Alonso, D.; Martinez, A.; Medina, M.; Franzblau, S.G.; Tekwani, B.L.; Khan, S.I.; et al. Manzamine B and E and ircinal A related alkaloids from an Indonesian Acanthostrongylophora sponge and their activity againstinfectious, tropical parasitic, and Alzheimer’s diseases. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-K.; Riswanto, R.; Won, T.-H.; Kim, H.; Elya, B.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, D.-C.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Manzamine alkaloids from an Acanthostrongylophora sp. sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.; Santarsiero, B.D.; Mesecar, A.D.; Schinazi, R.F.; Tekwani, B.L.; Hamann, M.T. New manzamine alkaloids with activity against infectious and tropical parasitic diseases from an Indonesian sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.; Hammond, N.L.; Peng, J.; Wahyuono, S.; McIntosh, K.A.; Charman, W.N.; Mayer, A.M.S.; Hamann, M.T. New manzamine alkaloids from an Indo-Pacific sponge. Pharmacokinetics, oral availability, and the significant activity of several manzamines against HIV-I, AIDS opportunistic infections, and inflammatory disease. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3512–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahba, A.E.; Fromentin, Y.; Zou, Y.; Hamann, M.T. Acantholactone, a new manzamine related alkaloid with an unprecedented δ-lactone and ε-lactam ring system. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 6329–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-desoky, A.; Kato, H.; Eguchi, K.; Kawabata, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Takeya, M.; Yokosawa, H.; et al. Acantholactam and pre-neo-kauluamine, manzamine-related alkaloids from the Indonesia Acanthostrongylophora ingens. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusato, A.; Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Eguchi, K.; Kawabata, T.; Fujiawara, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Takeya, M.; et al. Acanthomanzamines A−E with new manzamine frameworks from the marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3888–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlTarabeen, M.; Daletos, G.; Ebrahim, W.; Müller, W.G.; Hartmann, R.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Ircinal E, a new manzamine derivative from the Indonesian marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1951–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, I.I.; Ichiba, T.; Isobe, M.; Kelly-Borges, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Kauluamine: An unprecedented manzamine dimer from an Indonesian marine sponge, Prianos sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 10743–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspars, M.; Pasupathy, V.; Crews, P. A tetracyclic diamine alkaloid, halicyclamine A, from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 3253–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, S.; Miyata, Y.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Tetrahydrohalicylamine A and 22-hydrocylamine A, new cytotoxic bis-piperidine alkaloids from a marine sponge Amphimedon sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1758–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Sobou, M.; Vilchéze, C.; Baughn, A.; Hashizume, H.; Prusakorn, P.; Ishida, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Jacobs, W.R., Jr.; Kobayashi, M. Halicylcamine A, a marine spongean alkaloid as a lead for anti-tubercolosis agent. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 6732–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Liu, L.; Fujimoto, T.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. DedA protein relates to action-mechanism of halicylamine A, a marine spongean macrocyclic alkaloid, as an anti-dorman mycobacterial substance. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Ishida, S.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Haliclonacyclamines, tetracyclic alkylpiperidine alkaloids, as anti-dormant Mycobacterial substances from a marine sponge of Haliclona sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudianta, I.W.; Katavic, P.L.; Lambert, L.K.; Hayes, P.Y.; Banwell, M.G.; Munro, M.H.G.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Garson, M.J. Structure and absolute configuration of 3-alkylpiperidine alkaloids from an Indonesian sponge of the genus Halichondria. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 2752–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, A.S.; Hadi, T.A.; Fajarningsih, N.D.; Blanchfield, J.T.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Garson, M.J. Acanthocyclamine A from the Indonesian marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Aust. J. Chem. 2014, 67, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; Mai, L.H.; Longeon, A.; Teta, R.; Meijer, L.; van Soest, R.; Mangoni, A.; Constantino, V. Chloromethylhalicyclamine B, a marine-derived protein kinase CK1δ/ε Inhibitor. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, J.I.; Goetz, G.; Mau, C.M.S.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Williamson, R.T.; Kelly, M. ‘Upenamide: An unprecedented macrocyclic alkaloid from the Indonesian sponge Echinochalina sp. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 8465–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsworth, W.P.; Gallagher, K.A.; Jean, M.; Schmidt, J.P.; Diorazio, L.J.; Taylor, R.J.K. Direct imine acylation: Synthesis of the proposed structures of upenamide. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, E.; Romano, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Achmad, M.J.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C. Lobozoanthamine, a new zoanthamine-type alkaloid from the Indonesian soft coral Lobophytum sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 2189–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, H.H.; Tanaka, J.; Rachmat, R.; Setiawan, A.; Trianto, A.; Higa, T. Polycitorols A and B, new tricyclic alkaloids from an ascidian. Mar. Drugs 2005, 3, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.H.; Fu, H.Z.; Li, J.; Proksch, P. Novel chromone derivatives from marine fungus Aspergillus versicolor isolated from the sponge Xestospongia exigua. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2001, 12, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Brauers, G.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Berg, A.; Sudarsono; Proksch, P. Novel chromone derivatives from the fungus Aspergillus versicolor isolated from the marine sponge Xestospongia exigua. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, S.; Crews, P. A novel alkaloid from the Indo-Pacific sponge Clathria basilana. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 2389–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Kamiya, K.; Shin, D.; Matsumoto, H.; Hisa, T.; Setiawan, A.; Kotoku, N.; Kobayashi, M. N-Methylniphatyne A, a new 3-alkylpyridine alkaloid as an inhibitor of the cancer cells adapted to nutrient starvation, from an Indonesian marine sponge of Xestospongia sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Loveridge, S.T.; Tenney, K.; Crews, P. A new 3-alkylpyridine alkaloid from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. and its cytotoxic activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarisit, W.; Abdjul, D.; Yamazaki, H.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Kapojos, M.M.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Anti-mycobacterial alkaloids, cyclic 3-alkyl pyridinium dimers, fron the Indonesian marine sponge Haliclona sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3503–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, K.H.; Göhl, M.; Müller, T.; Seifert, K. Indole alkaloids from the sea anemone Heteractis aurora and homarine from Octopus syanea. Chem. Biodiversity. 2015, 12, 1746–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Wewengkang, D.; Nishikawa, T.; Rotinsulu, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Namikoshi, M. Two new tryptamine derivatives, leptoclinidamide and (–)-leptoclinidamine B, from an Indonesian ascidian Leptoclinides dubius. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmoun, M.; Devijer, C.; Daloze, D.; Braekman, J.-C.; van Soest, R.W.M. 5-Hydroxytryptamine-derived alkaloids from two marine sponges of the genus Hyrtios. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Wan, S.B.; Ren, S.M.; Jiang, T. First total synthesis of marine alkaloid hyrtiosulwesine. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2010, 21, 1307–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauleau, P.; Martin, M.-T.; Dau, M.-E.T.H.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L. Hyrtiazepine, an azepino-indole-type alkaloid from the red sea marine sponge Hyrtios erectus. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Zayed, M.F.; Sayed, H.M. Ingenines A and B, two new alkaloids from the sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Drug Res. 2015, 65, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A. Ingenines C and D, new cytotoxic pyrimidine-β-carboline alkaloids from the Indonesian sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 18, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A. Ingenine E, a new cytotoxic β-carboline alkaloid from the Indonesian sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Ebel, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Proksch, P. Achantomine A, a new pyrimidine-β-carboline from the sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, E.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; Tsukamoto, S. Variabines A and B: New β-carboline alkaloids from the marine sponge Luffariella variabilis. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Jompa, J.; Tahir, A.; Ireland, C.M. Trypargine alkaloids from a previously undescribed Eudistoma Ascidian. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanokuchi, R.; Imada, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Kato, H.; Watanabe, T.; Fujimuro, M.; Saeki, Y.; Yoshinaga, S.; Terasawa, H.; Iwasaki, N.; et al. Hyrtioreticulins A–E, indole alkaloids inhibiting the ubiquitin-activating enzyme, from the marine sponge Hyrtios reticulatus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4437–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segraves, N.L.; Lopez, S.; Johnson, T.A.; Said, S.A.; Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J.; Pietraszkiewicz; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Structures and cytotoxicities of fascaplysin and related alkaloids from two marine phyla—Fascaplysinopsis sponges and Didemnum tunicates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 3471–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhidkov, M.E.; Baranova, O.V.; Balaneva, N.N.; Fedorov, S.N.; Radchenko, O.S.; Dubovitskii, S.V. The first syntheses of 3-bromofascaplysin-marine alkaloids from Fascaplysinopsis reticulata and Didemnum sp. by application of a simple and effective approach to the pyrido [1,2-a:3,4-b’]diindole system. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 7998–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmich, A.S.; Fedorov, S.N.; Shastina, V.V.; Shubina, L.K.; Radchenko, O.S.; Balaneva, N.N.; Zhidkov, M.; Park, J.-I.; Kwak, J.Y.; Stonik, V.A. The anticancer activity of 3- and 10-bromofascaplysins is mediated by caspase -8, -9, -3-dependent apoptosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3834–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segraves, N.L.; Robinson, S.J.; Garcia, D.; Said, S.A.; Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Comparison of fascaplysin and related alkaloids: A study of structures, cytotoxicities, and sources. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bry, D.; Banaigs, B.; Long, C.; Bontemps, N. New pyridoacridine alkaloids from the purple morphof the ascidian Cystodytes dellechiajei. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 3041–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thale, Z.; Johnson, T.; Tenney, K.; Wenzel, P.J.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J.; Media, J.; Pietraszkiewics, H.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Structures and cytotoxic properties of sponge-derived bisannulated acridines. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 9384–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Wei, Ho.; Matsui, K.; Rachmat, R.; Kobayashi, M. Pyridoacridine alkaloids inducing neuronal differentiation in a neuroblastoma cell line, from marine sponge Biemna fortis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D.A.P.; Takada, K.; Ise, Y.; Bontemps, N.; Davis, R.A.; Furihata, K.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Two cell differentiation inducing pyridoacridines from a marine sponge Biemna sp. and their chemical conversions. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 5013–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.C.; Said, N.A.B.M.; Williams, E.D.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Davis, R.A. Ecionines A and B, two new cytotoxic pyridoacridine alkaloids from the Australian marine sponge, Ecionemia geodides. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Elkhayat, E.S.; Fouad, M.; Proksch, P. Sagitol C, a new cytotoxic pyridoacridine alkaloid from the sponge Oceanapia sp. Bull. Fac. Pharm. (Cairo Univ.) 2013, 51, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Venables, D.A.; Hopmann, C.; Salomon, C.E.; Jompa, J.; Tahir, A.; Faulkner, D.J.; Ireland, C.M. Plakinidine D, a new pyrroloacridine alkaloid from two ascidians of the genus Didemnum. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 1048–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcul, L.; Longeon, A.; Al Mourabit, A.; Guyot, M.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L. Novel alkaloids of the aaptamine class from an Indonesian marine sponge of the genus Xestospongia. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 6539–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.-D.; Hartmann, R.; Müller, W.E.G.; de Voogd, N.; Lai, D.; Proksch, P. Aaptamine derivatives from the Indonesian sponge Aaptos suberitoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Han, C.; Yamano, Y.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Aaptamines, marine spongean alkaloids, as anti-dormant mycobacterial substances. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlt, A.; Mander, L.; Rombang, W.; Rumampuk, R.; Soemitro, S.; Steglich, W.; Tarigan, P.; von Nussbaum, F. Alkaloids from marine organisms. Part 8: Isolation of bisdemethylaaptamine and bisdemethylaaptamine-9-O-sulfate from an Indonesian Aaptos sp. marine sponge. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 6101–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larghi, E.L.; Bohn, M.L.; Kaufman, T.S. Aaptamine and related products. Their isolation, chemical syntheses, and biological activity. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 4257–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Aaptoline A, a new quinoline alklaoid from the marine sponge Aaptos suberitoides. Heterocycles 2014, 88, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Jurek, J.; Carney, J.R.; Scheuer, P.J. Two more bastadins, 16 and 17, from an Indonesian sponge Ianthella basta. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couladourus, E.A.; Pitsinos, E.N.; Moutsos, V.I.; Sarakinos, G. A general method for the synthesis of bastarenes and isobastarenes: First total synthesis of bastadins 5, 10, 12, 16, 20, and 21. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, V.; Wauthoz, N.; Lefranc, F.; Niemann, H.; Amighi, K.; Kiss, R.; Proksch, P. Cyclic versus hemi-bastadins. Pleiotropic anti-cancer effects: From apoptosis to anti-angiogenic and anti-migratory effects. Molecules 2013, 18, 3543–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortlepp, S.; Sjögren, M.; Dahlström, M.; Weber, H.; Ebel, R.; Edrada, R.; Thoms, C.; Schupp, P.; Bohlin, L.; Proksch, P. Antifouling activity of bromotyrosine-derived sponge metabolites and synthetic analogues. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.V.; Ravinder, K.; Narasimhulu, M.; Sridevi, A.; Satyanarayana, N.; Kondapi, A.K.; Venkateswarlu, Y. New anticancer bastadin alkaloids from the sponge Dendrilla cactos. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 4452–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, H.; Lin, W.; Müller, W.E.G.; Kubbutat, M.; Lai, D.; Proksch, P. Trimeric hemibastadin congener from the marine sponge Ianthella basta. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudianta, I.W.; Skinner-Adams, T.; Andrews, K.T.; Davis, R.; Hadi, T.A.; Hayes, P.Y.; Garson, M.J. Psammaplysin derivatives from the Balinese marine sponge Aplysinella strongylata. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 2132–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Parrish, S.M.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Yip, M.L.; Turkson, J.; Kelly, M.; Williams, P. Bromotyrosine-derived metabolites from an Indonesian marine sponge in the family Aplysinellidae (order Verongiida). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCauley, E.P.; Lam, H.; Lorig-Roach, N.; Luu, J.; Lloyd, C.; Tenney, K.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Diaz, C.; Valeriote, F.; Auerbuch, V.; et al. Investigation of the physical and bioactive properties of bromo-and iodo-containing sponge-derived compounds possessing an oxyphenylethanime core. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 3225–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supriyono, A.; Schwarz, B.; Wray, V.; Witte, L.; Müller, W.E.G.; van Soest, R.; Sumaryono, W.; Proksch, P. Bioactive alkaloids from the tropical marine sponge Axinella carteri. Z. Naturforsch. 1995, 50c, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.N.E.; Schmitz, R.; Bergermann, A.; Totzke, F.; Kubbutat, M.; Müller, W.E.G.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Bishr, M.M.; Kamel, M.S.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A.; et al. Bioactive pyrrole alkaloids isolated from the Red sea: Marine sponge Stylissa carteri. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2018, 73, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, C.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; Steube, K.l.; Bringmann, G.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Sudarsono; Ferdinandus, E.; Pattisina, L.A.; Wiryowidagdo, S.; et al. New alkaloids from the Indopacific sponge Stylissa carteri. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, M.; Debbab, A.; Wray, V.; Müller, W.E.G.; Proksch, P. New bioactive alkaloids from the marine sponge Stylissa sp. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 10176–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Kanno, S.; Tomizama, A.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Ukai, K.; Kapojos, M.M.; Namikoshi, M. An anti-mycobacterial bisfunctionalized spingolipid and new bromopyrrole alkaloid from the Indonesian marine sponge Agelas sp. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlile, G.W.; Keyzers, R.A.; Teske, K.A.; Robert, R.; Williams, D.E.; Linington, R.G.; Gray, C.A.; Centko, R.M.; Yan, L.; Anjos, S.; et al. Correction of F508del-CFTR trafficking by the sponge alkaloid latonduine is modulated by interaction with PARP. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebada, S.S.; Linh, M.H.; Longeon, A.; de Voogd, N.J.; Durieu, E.; Meijer, L.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; Singab, A.N.B.; Müller, W.E.G.; Proksch, P. Dispacamide E and other bioactive bromopyrrole alkaloids from two Indonesian marine sponges of the genus Stylissa. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebada, S.S.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. Dibromopyrrole alkaloids from the marine sponge Acanthostylotella sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Spironaamidine, a new spiroquinone-containing alkaloid from the marine sponge Leucetta microraphis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 5342–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Berg, A.; van Soest, R.; Wiryowidagdo, S.; Proksch, P. New imidazole alkaloids from the Indonesian sponge Leucetta chagosensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koswatta, P.B.; Lovely, C.J. Concise total synthesis of naamine G and naamidine H. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2148–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Koswatta, P.B.; Jones, J.D.; Yousufuddin, M.; Lovely, C.J. Total syntheses of kealiinines A–C. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 6210–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, J.B.; Gligorich, K.M.; Welm, B.E.; Looper, R.E. Synthesis of the reported structures for kealiinines B and C. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4734–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Kawabata, T.; Kato, H.; Ohta, T.; Rotinsulu, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Ukai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Namikoshi, M. Naamidines H and I, cytotoxic imidazole alkaloids from the Indonesian marine sponge Leucetta chaogosensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1658–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Oda, T.; Fujita, A.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Nakazawa, T.; Ukai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Namikoshi, M. Three new sulfur-containing alkaloids, polycarpaurines A, B, and C, from an Indonesian ascidian Polycarpa aurata. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Q. First discovery of polycarpine, polycarpaurines A and C, and their derivatives as novel antiviral and antiphytopathogenic fungus agents. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2016, 64, 4264–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fujiawara, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Mishima, Y.; Nagai, H.; Shida, T.; Tachibana, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Namikoshi, M. Lissoclibadins 1–3, three new polysulfur alkaloids, from the ascidian Lissoclinum cf. badium. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 8611–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Kamoshita, K.; Maruyama, S.; Masuda, K.; Nishimoto, M.; Xu, J.; Ukai, K.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Namikoshi, M. Cytotoxicity of lissoclibadins and lissoclinotoxins, isolated from a tropical ascidian Lissoclinum cf. badium, against human soild-tumor-derived cell lines. Bio. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tatsuta, T.; Hosono, M.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Namikoshi, M.; Yamazaki, H. Lissoclibadin 1, a polysulfur aromatic alkaloid from the Indonesian ascidian Lissoclinum cf. badium, induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and suppresses tumor growth in nude mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, T.; Fujiawara, T.; Liu, H.; Ukai, K.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Mochizuki, M.; Namikoshi, M. Effect of lissoclibadins and lissoclinotoxins, isolated from a tropical ascidian Lissoclinum cf. badium, on IL-8 production in a PMA-stimulated promyelocytic leukemia cell line. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T.; Xu, J.; Nishikawa, T.; Oda, T.; Fujita, A.; Ukai, K.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Rotinsulu, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Namikoshi, M. Lissoclibadins 4–7, polysulfur aromatic alkaloids from the indonesian Ascidian Lissoclinum cf. badium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Takahashi, O.; Oda, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Ukai, K.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Kobayashi, H.; Tsukamoto, S.; et al. Lissoclibadins 8–14, polysulfur dopamine-derived alkaloids from the colonial ascidian Lissoclinum cf. badium. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 9598–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C. Didemniserinolipids A–C, unprecedented serinolipids from the tunicate Didemnum sp. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 5705–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyota, H.; Dixon, D.J.; Luscombe, C.K.; Hettsedt, S.; Ley, S.V. Synthesis, structure revision, and absolute configuration of (+)-didemniserinolipid B, a serinol marine natural product from a tunicate Didemnum sp. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3223–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Tong, R. Asymmetric total synthesis of (+)-didemniserinolipid B via Achmatowicz rearrangement/ bicycloketalization. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 6987–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Kato, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Iwasaki, N.; Suwa, Y.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Maarisit, W.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Morioka, H.; et al. Siladenoserinols A–L: New sulfonated serinol derivatives from a tunicate as inhibitors of p53-Hdm2 interaction. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Saito, K.; Kato, H.; Tsukamoto, S.; Doi, T. Total synthesis and biological evaluation of siladenoserinol A and its analogue. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5147–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, J.R.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Makaluvamine G, a cytotoxic pigment from an Indonesian sponge Histodermella sp. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 8483–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtsev, D.; Makarieva, T.; Utkina, N.; Santalova, E.; Kryukova, E.; Methfessel, C.; Tsetlin, V.; Stonik, V.; Kasheverov, I. Marine natural products acting on the acetylcholine-protein and nicotinic receptors: From computer modelling to binding studies and electrophysiology. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimov, M.M.; Chaikina, E.L.; Utkina, N.K. Alkaloids from marine sponges as stimulators of initial stages of development of agricultural plants. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; El-Khayat, E.S.; Gouda, Y.G.; Proksch, P. Strepsiamides A–C, new ceramides from the marine sponge Strepsichordaia lendenfeldi. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Fouad, M.A.; El-Khayat, E.S.; Proksch, P. Iotrochotamides I and II: New ceramides from the Indonesian sponge Iotrochota purpurea. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Higuchi, K.; Ye, Y.; Satari, R.; Kobayashi, M. Melophlins A and B, novel tetramic acids reversing the phenotype of ras-transformed cells, from the marine sponge, Melophlus sarassinorum. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 1833–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, B.-G.; Wiryowidagdo, S.; Wray, V.; van Soest, R.; Steube, K.G.; Guan, H.-S.; Proksch, P.; Ebel, R. Melophlins C–O, thirteen novel tetramic acids from the marine sponge Melophlus sarassinorum. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiba, T.; Nakao, Y.; Scheuer, P.J. Kumusine, a chloroadenine riboside from a sponge, Theonella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 3977–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Trachycladines A and B: 2’-C-Methyl-5’-deoxyribofuranosyl nucleosides from the marine sponge Trachycladus laevispirulifer. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 4296–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyowati, E.P.; Jenie, U.A.; Sudarsono; Kardono, L.B.S.; Rahmat, R. Identification of cytotoxic constituent of Indonesian sponge Kaliapsis sp. Pak. J. Biol. Sci 2008, 11, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Sulzmaier, F.J.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kelly, M.; Ramos, J.W. Neopetrocyclamines A and B, polycyclic diamine alkaloids from the sponge Neopetrosia cf. exigua. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Jimenez, C.; Blanco, M.; Tarazona, G.; Fernandez, R.; Cuevas, C. Lanesoic acid: A cytotoxic zwitterion from Theonella sp. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5832–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wagoner, R.M.; Jompa, J.; Tahir, A.; Ireland, C.M. A novel modified pterin from a Eudistoma species Ascidian. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1100–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhlesi, A.; Hartmann, R.; Kurtán, T.; Weber, H.; Lin, W.; Chaidir, C.; Müller, W.E.G.; Daletos, G.; Proksch, P. New 2-methoxy acetylenic acids and pyrazole alkaloids from the marine sponge Cinachyrella sp. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trianto, A.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tanaka, J. Two new compounds from an Indonesian sponge Dysidea sp. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhlesi, A.; Stuhldreier, F.; Wex, K.W.; Berscheid, A.; Hartmannn, R.; Rehberg, N.; Sureechatchaiyan, P.; Chaidir, C.; Kassack, M.U.; Kalscheuer, R.; et al. Cyclic cysteine-bridged peptides from the marine sponge Clathria basilana induce apoptosis in tumor cells and depolarize the bacterial cystoplasmic membrane. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2941–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardá, A.; Rodríguez, J.; Nieto, R.M.; Bassarello, C.; Gomez-Paloma, L.; Bifulco, G.; Jiménez, C. NMR J-based analysis of nitrogen-containing moieties and application to dysithiazolamide, a new polychlorinated dipeptide from Dysidea sp. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 10093–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardá, A.; Soengas, R.G.; Nieto, M.I.; Jiménez, C.; Rodríguez, J. Total synthesis of (–)-dysithiazolamide. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2175–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadar, M.D.; Williams, D.E.; Mawji, N.R.; Patrick, B.O.; Wikanta, T.; Chasanah, E.; Irianto, H.E.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Sintokamides A to E, chlorinated peptides from the sponge Dysidea sp. that inhibit transactivation of the N-terminus of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4947–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Zakarian, A. Concise total synthesis of sintokamides A, B, and E by a unified, protecting- group-free strategy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9702–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banuelos, C.A.; Travakoli, I.; Tien, A.H.; Caley, D.P.; Mawji, N.R.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.C.; Imamura, Y.; Yan, L.; et al. Sintokamide A is a novel antagonist of adrogen receptor that uniquely binds activation function-1 in its amino-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22231–22242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kwong, S.; Xu, Z.; Ye, T. Total synthesis of sintokamide C. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeson, K.J.; Hamann, M.T. Keenamide A, a bioactive cyclic peptide from the marine mollusk Pleurobranchus forskalii. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donia, M.S.; Wang, B.; Dunbar, D.C.; Desai, P.V.; Patny, A.; Avery, M.; Hamann, M.T. Mollamides B and C, cyclic hexapeptides from the Indonesian tunicate Didemnum molle. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mau, C.M.S.; Nakao, Y.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borger, M. Waiakeamide, a cyclic hexapeptide from the sponge Ircinia dendroides. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 6302–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urda, C.; Fernández, R.; Rodríguez, J.; Pérez, M.; Jiménez, C.; Cuevas, C. Bistramides M and N, oxazole-thiazole containing cyclic hexapeptides isolated from Lissoclinum bistratum interaction of zinc (II) with bistramide K. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnington, L.S.; Tanaka, J.; Higa, T.; Kimura, J.; Yoshimura, Y.; Nakao, Y.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J. Cupolamide A: A cytotoxic cylcic heptapeptide from two samples of the sponge Theonella cupola. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7765–7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.T.; Williamson, R.T.; Gerwick, W.H.; Watts, K.S.; McGough, K.; Jacobs, R. Cis,cis-and trans, trans-ceratospongamide, new bioactive cyclic heptapeptides from the Indonesian red alga Ceratodicyton spongiosum and symbiotic sponge Sigmadocia symbiotica. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokokawa, F.; Sameshima, H.; Shiori, T. Total synthesis of cis,cis-ceratospongamide, a bioactive thiazole-containing cyclic peptide from marine origin. Synlett 2001, SI, 968–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deng, S.; Taunton, J. Kinetic control of proline amide rotamers: Total synthesis of trans, trans- and cis, cis- ceratospongamide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 916–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsumura, N.; Sata, N.U.; Nishiyama, S. Synthetic studies on ceratospongamides, cyclic heptapeptides containing thiazole and oxazoline units: Total synthesis of cis, cis-ceratospongamide. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 75, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokokawa, F.; Sameshima, H.; In, Y.; Minoura, K.; Ishida, T.; Shiori, T. Total synthesis and conformational studies of ceratospongamide, a bioactive cyclic heptapeptide from marine origin. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 8127–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.A.; van den Bosch, J.J.K.; Versluis, K.; Thompson, G.S.; Jaspars, M. Structure determination and MSn analysis of two new lissoclinamides isolated from the Indo-Pacific ascidian Lissoclinum patella: NOE restrained molecular dynamics confirms the absolute stereochemistry derived by degradative methods. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 8345–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.A.; Milne, B.F.; Jaspars, M.; Kettenes-van den Bosch, J.J.; Versluis, K.; Heck, A.J.R.; Kelly, S.M.; Price, N.C. Metal binding of Lissoclinum patella metabolites. Part 2: Lissoclinamides 9 and 10. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 3199–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, A.H.; El-Desoky, A.; Kato, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Ammar, N.M.; Hifnawy, M.S.; Tsukamoto, S. Carteritins A and B, cyclic heptapeptides from the marine sponge Stylissa carteri. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Yamano, M.; Fujita, M.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Stylissamide X, a new proline-rich cyclic octapeptide as an inhibitor of cell migration, from an Indonesian marine sponge of Stylissa sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1818–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.C.; Ohtani, I.I.; Tanaka, J.; Higa, T.; Satari, R. Barangamide A, a new cyclic peptide from the Indonesian sponge Theonella swinhoei. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 5373–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.C.; Ohtani, I.I.; Ichiba, T.; Tanaka, J.; Satari, R.; Higa, T. New cyclic peptides from the Indonesian Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 9079–9092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. Callyaerin G, a new cytotoxic cyclic peptide from the marine sponge Callyspongia aerizusa. ARKIVOC 2008, xii, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.; Min, C.C.; Teuscher, F.; Ebel, R.; Kakoscheke, C.; Lin, W.; Wray, V.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Proksch, P. Callyaerins A–F and H, new cytotoxic cyclic peptides from the Indonesian marine sponge Callyspongia aerizusa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 4947–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daletos, G.; Kalscheuer, R.; Koliwer-Brandl, H.; Hartmann, R.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Callyaerins from the marine sponge Callyspongia aerizusa: cyclic peptides with antitubercular activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1910–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; de Leon Rodriguez, L.M.; Leung, I.K.H.; Cook, G.M.; Harris, P.W.R.; Brimble, M.A. Total synthesis and conformational study of callyaerin A: Anti tubercular cylic peptide bearing a rare rigidifying (Z)-2,3-diaminoacrylamide moiety. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 130, 3693–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.A.; Gustafson, K.R.; Cartner, L.K.; Shigematsu, N.; Pannel, L.K.; Boyd, M.R. Microspinosamide, a new HIV-inhibitory cyclic depsipeptide from the marine sponge Sidonops microspinosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Cao, L.; Matsui, K.; Rachmat, R.; Akiyama, S.; Kobayashi, M. Kendarimide A, a novel peptide reversing P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in tumor cells, from a marine sponge of Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 7053–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoku, N.; Cao, L.; Aoki, S.; Kobayashi, M. Absolute stereo-structure of kendarimide A, a novel MDR modulator, from a marine sponge. Heterocylces 2005, 65, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.P.; Carrol, J.; Naylor, S.; Crews, P. An antifungal cyclodepsipeptide, cyclolithistide A, from the sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 8757–8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, H.; Wakimoto, T.; Takada, K.; Ise, Y.; Abe, I. Revised structure of cylclolithistide A, a cyclic depsipeptide from the marine sponge Discodermia japonica. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinisi, A.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Dien, H.A.; Zampella, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. New tridecapeptides of the theonellapeptolide family from the Indonesian sponge Theonella swinhoei. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, A.; Bifulco, G.; Keffer, J.L.; Lloyd, J.R.; Baker, H.L.; Bewley, C.A. Celebesides A–C and theopapuamides B–D, depsipeptides from an Indonesian sponge that inhibit HIV-1 entry. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Wray, V.; de Voogd, N.J.; Deng, Z.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Two new jaspamide derivatives from the marine sponge Jaspis splendens. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urda, C.; Fenández, R.; Rodríguez, J.; Pérez, M.; Jiménez, C.; Cuevas, C. Daedophamide, a cytotoxic cyclodepsipeptide from a Daedalopelta sp. collected in Indonesia. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 3054–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Martín, M.J.; Rodríguez-Acebes, R.; Reyes, F.; Franscesh, A.; Cuevas, C. Diazonamides C–E, new cytotoxic metabolites from the ascidian Diazona sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juagdan, E.G.; Kalidindi, R.S.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Elenic acid, an inhibitor of topoisomerase II, from a sponge, Plakinastrella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 2905–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahanashi, S.; Takagi, M.; Takikawa, H.; Mori, K. Synthesis of elenic acid, an inhibitor of topoisomerase II from the sponge Plakinastrella sp. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans 1 1998, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoye, R.C.; Baigorria, A.S.; Danielson, M.E.; Pragman, A.A.; Rajapakse, H.A. Synthesis of elenic acid, an inhibitor of topoisomerase II. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 2450–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Abbanat, D.; Bernan, V.S.; Maiese, W.M.; Greenstein, M.; Jompa, J.; Tahir, A.; Ireland, C.M. Novel polyketide metabolites from a species of marine fungi. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, C.R.; Rao, N.N.; Sujitha, P.; Kumar, C.G. Protecting group-free syntheses of (4S,5S,11R)- and (4S,5S,11S)-iso-cladospolide B and their biological evaluation. Synthesis 2012, 44, 1663–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Gao, H.; Wu, C.; Zhu, T.; Che, Q.; Gu, Q.; Guo, P.; Li, D. Lipid-lowering polyketides from a soft coral-derived fungus Cladosporium sp. TZP29. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3606–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Matsui, K.; Tanaka, K.; Satari, R.; Kobayashi, M. Lembehyne A, a novel neuritogenic polyacetylene, from a marine sponge of Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 9945–9948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, N.; Nakajima, T.; Kobayashi, M. Total synthesis of lembehyne A, a neuritogenic spongean polyacetylene. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 1941–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Matsui, K.; Takata, T.; Kobayashi, M. In situ photoaffinity labeling of the target protein for a neuronal differentiation inducer. FEBS Lett. 2003, 544, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Matsui, K.; Takata, T.; Wei, H.; Kobayashi, M. Lembehyne A, a spongean polyacetylene, induces neuronal differentiation in neuroblastoma cell. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Matsui, K.; Wei, H.; Murakami, N.; Kobayashi, M. Structure-activity relationship of neuritogenic spongean acetylene alcohols, lembehynes. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 5417–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhemileva, L.U.; D’yakonov, V.A.; Makarov, A.A.; Andreev, E.N.; Yunusbaeva, M.M.; Dzhemilev, U.M. The first total synthesis of the marine acetylenic alcohol, lembehyne B-a selective inducer of early apoptosis in leukemia cancer cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’yakonov, V.A.; Makrov, A.A.; Dzemileva, L.U.; Andreev, E.N.; Dzhemilev, U.M. The first total synthesis of lembehyne B. Mendeleev Commun. 2017, 27, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’yakonov, V.A.; Dzhemileva, L.U.; Makarov, A.A.; Andreev, E.N.; Dzhemilev, U.M. Short and efficient synthetic route to lembehyne B possesing neuritogenic activity. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 52, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balansa, W.; Trianto, A.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tanaka, J. A new cytotoxic polyacetylenic alcohol from a sponge Callyspongia sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 1909–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Devijver, C.; Dubut, D.; van Soest, R.W.M. A new C-20 polyacetylene from the sponge Callyspongia pseudoreticulata. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 871–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratake, S.; Trianto, A.; Hanif, N.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tanaka, J. A new polyunsaturated brominated fatty acid from a Haliclona sponge. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.-D.; Nagle, D. Cytotoxic metabolites from an Indonesian Sponge Lendenfeldia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1824–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiba, T.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Two cytotoxic 3,6-epidioxy fatty acids from an Indonesian sponge, Plakortis sp. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 12195–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Nogawa, T.; Knight, J.C.; Doubek, D.L.; Hooper, J.N.A. Antineoplastic agents. 535. Isolation and structure of plakorstatins 1 and 2 from the Indo-Pacific sponge Plakortis nigra. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1611–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, C.; Persico, M.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Novellino, E.; Romano, A.; Scala, F.; Fattorusso, E.; et al. Manadoperoxides A–D from the Indonesian sponge Plakortis cfr. simplex. Further insights on the structure-activity relationships of simple 1,2-dioxane antimalarials. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, G.; Fattorusso, E.; Scala, F.; Teta, R.; Calcinai, B.; Bavestrello, G.; Dien, H.A.; Kaiser, M.; Tasdemir, D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Manadoperoxides, a new class of potent antitrypanosomal agents of marine origin. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 7197–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrell, L.M.; Borgeson, B.; Crews, P. A new polyketide secocurvularin from the salt water culture of a sponge derived fungus. Tetrahedon Lett. 1996, 37, 8983–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.-D.; Ketchum, S.O.; France, D.; Bair, K.; Gerwick, W. Vidalenolone, a novel phenolic metabolite from the tropical red alga Vidalia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, S.; Sheng-Ding, Z.; Hua-Jie, Z. Absolute configuration determination for natural products (1)-absolute configuration determination for ketone, lactone, and alcohol by comparing computed optical rotations and 13C NMR with the experimental results. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2011, 32, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Shiono, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; Murayama, T.; Koseki, T.; Katja, H.D.G.; Supratman, U.; Nakata, J.; Kakihara, Y.; Saeki, M.; Yoshida, J.; et al. GSK-3β inhibitory activities of novel dichroloresorcinol derivatives from Cosmospora vilior isolated from a mangrove plant. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 18, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadulco, R.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; Sudarsono; Berg, A.; Gräfe, U. New macrolides and furan carboxylic acid derivative from the sponge-derived fungus Cladosporium herbarum. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarman, K.; Lindequist, U.; Wende, K.; Porzel, A.; Arnold, N.; Wessjohann, L.A. Isolation of a new natural product and cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities of extracts from fungi of Indonesian marine habitats. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, D.; Edrada, R.A.; Proksch, P.; Wray, V.; Witte, L.; van Soest, R.W.; Kunzmann, A.; Soedarsono. Four new bioactive polybrominated diphenyl ethers of the sponge Dysidea herbacea from West Sumatra, Indonesia. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, N.; Tanaka, J.; Setiawan, A.; Trianto, A.; de Voogd, N.J.; Murni, A.; Tanaka, C.; Higa, T. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the Indonesian sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcul, L.; Chow, R.; Oliver, A.G.; Tenney, K.; White, K.N.; Wood, A.W.; Fiorilla, C.; Crews, P. NMR strategy for unravelling structures of bioactive sponge-derived oxy-polyhalogenated diphenyl ethers. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumilat, D.A.; Yamazaki, H.; Endo, K.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. A new biphenyl ether derivative produced by Indonesian ascidian-derived Penicilium albobiverticillium. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Miao, C.; Liu, P.; Hong, K.; Zhu, W. Sesquiterpenoids and benzofuranoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus ustus 094102. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, K.; Saito, F.; Nakazaki, A.; Takeuchi, T.; Tsubaki, K.; Sugawara, F.; Kobayashi, S. Synthesis of pseudodeflectusin and ustusorane C: Structural revision of aspergiones A and B. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 1635–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, F.; Kuramochi, K.; Nakazaki, A.; Mizushina, Y.; Sugawara, F.; Kobayashi, S. Synthesis and absolute configuration of (+)-pseudodeflectusin: Structural revision of aspergione B. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 4796–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, K.; Tsubaki, K. Synthesis and structural characterization of natural benzofuranoids. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadulco, R.; Brauers, G.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Sudarsono; Proksch, P. New metabolites from sponge-derived fungi Curvularia lunata and Cladosporium herbarum. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nakazawa, T.; Ukai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Rotinsulu, H.; Namikoshi, M. Tetrahydrobostrycin and 1-deoxytetrahydrobostrycin, two new hexahydroanthrone derivatives, from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiono, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Shibuya, F.; Yasuda, Y.; Koseki, T.; Supratman, U. Isolation of a phomoxanthone A derivative, a new metabolite of tetrahydroxanthone, from a Phomopsis sp. isolated from mangrove, Rhizhopora mucronata. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1735–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönsberg, D.; Debbab, A.; Mándi, A.; Vasylyeva, V.; Böhler, P.; Stork, B.; Engelke, L.; Hamacher, A.; Sawadogo, R.; Diedrich, M.; et al. Pro-apoptotic and immunostimulatory tetrahydroxanthone dimers from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis longicolla. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 12409–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Aoki, S.; Kobayashi, M. Komodoquinone A, a novel neuritogenic anthracycline, from marine Streptomyces sp. KS3. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Wei, H.; Kobayashi, M. Stereostrcuture of komodoquinone A, a neuritogenic anthracyline, from marine Streptomyces sp. KS3. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 1402–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotoku, N.; Higashimoto, K.; Kurioka, M.; Arai, M.; Sumii, Y.; Sowa, Y.; Sakai, T.; Kobayashi, M. Xylarianaphthol-1, a novel dinaphthofuran derivative, activates p21 promoter in a p53-independent manner. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3389–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edrada, R.A.; Wray, V.; Berg, A.; Gräfe, U.; Sudarsono; Brauers, G.; Proksch, P. Novel spiciferone derivatives from the fungus Drechslera hawaiiensis isolated from the marine sponge Callyspongia aerizusa. Z. Naturforsch. 2000, 55c, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spery, S.; Samuels, G.J.; Crews, P. Vertinoid polyketides from the salt culture of the fungus Tricoderma longibrachiatum separated from a Haliclona sponge. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 10011–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Jompa, J.; Tahir, A.; Buchanan, M.V.; Ireland, C.M. Cadiolides A and B, new metabolites from an ascidian of the genus Botryllus. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 4147–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, X.; Vaz Araujo, M.E.; Jullian, J.C.; Hocquemiller, R.; Figadère, B. Synthesis and structure determination of iso-cladospolide B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 2801–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, B.M.; Aponick, A. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic alkylation of meso- and dl-1,2-divinylethylene carbonate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3931–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, P.J.; Sperry, J.; Brimble, M.A. Heteroatom-directed reverse Wacker oxidations. Synthesis of the reported structure of (–)-herbaric acid. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 7388–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Sala, G.D.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Mangoni, A.; Steindler, L. Plakofuranolactone as a quorum quenching agent from the Indonesian sponge Plakortis cf. lita. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiono, Y.; Shibuya, F.; Koseki, T.; Harizon; Supratman, U.; Uesugi, S.; Kimura, K. A new α-pyrone metabolite from a mangrove plant endophytic fungus Fusarium sp. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 17, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarman, K.; Palm, G.J.; Porzel, A.; Merzweiler, K.; Arnold, N.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Unterseher, M.; Lindequist, U. Helicascolide C, a new lactone from an Indonesian marine algicolous strain of Daldinia eschscholzii (Xylariaceae, Ascomycota). Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.S.; Reddy, A.B.; Shankar, K.S. Concise total synthesis of helicascolides A, B, and C. Synthesis 2013, 45, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydal, A.M.; Berthold, D.; Spreider, P.A.; Breit, B. Stereodivergent and protecting-group-free synthesis of the helicascolide family: A rhodium-catalyzed atom-economical lactonization strategy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5765–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirirath, S.; Tanaka, J.; Ohtani, I.I.; Ichiba, T.; Rachmat, R.; Ueda, K.; Osada, H.; Higa, T. Bitungolides A–F, new polyketides from the Indonesian sponge Theonella cf. swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1820–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.M.; Shashidar, J.; Ghosh, S. A concise approach for the synthesis of bitungolides: Total syntheses of (–)-bitungolides B & E. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 4002–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashidar, J.; Reddy, K.M.; Ghosh, S. The first total synthesis of (–)-bitungolide E. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 3106–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Kumar, S.U.; Shashidhar, J. Total synthesis of (–)-bitungolide F and determination of its absolute stereochemistry. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 1582–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edrada, R.A.; Heubes, M.; Brauers, G.; Wray, V.; Berg, A.; Gräfe, U.; Wohlfarth, M.; Mühlbacher, J.; Schaumann, K.; Sudarsono; et al. Online analysis of xestodecalactones A–C, novel bioactive metabolites from the fungus Penicillium cf. montanense and their subsequent isolation from the sponge Xestospongia exigua. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, G.; Lang, G.; Michel, M.; Heubes, M. Stereochemical assignment of the fungal metabolite xestodecalactone A by total synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 2829–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Ng, F.; Danishefsky, S.J. A total synthesis of xestodecalactone A and proof of its absolute stereochemistry: Interesting observations on dienophilic control with 1,3-disubtituted nonequivalent allenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14185–14191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Quan, W.; Sun, Y.; She, X.; Pan, X. The first asymmetric total syntheses and determination of absolute configurations of xestodecalactones B and C. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 2694–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.S.; Thrimurtulu, N.; Gayathri, K.U.; Reddy, B.V.S.; Prasad, A.R. The stereoselective total synthesis of xestodecalactone C and epi-sporostatin via the prins cylisation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 6617–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, K.; Suresh, V.; Selvan, J.J.P.; Rao, C.B.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Stereoselective total synthesis of xestodecalactone C. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2009, 92, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.S.; Rao, Y.G.; Ravindar, K.; Reddy, B.V.S.; Narsaiah, A.V. Total synthesis of xestodecalactone C from L-malic acid. Synthesis 2009, 3157–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesner, S.; Cohen, N.; Ilan, M.; Yarden, O.; Carmeli, S. Pandangolide 1a, a metabolite of the sponge-associated fungus Cladosporium sp., and the absolute stereochemistry of pandangolide 1 and iso-cladospolide B. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, C.-D.; Hartmann, R.; Böhler, P.; Störk, B.; Wesselborg, S.; Lin, W.; Lai, D.; Proksch, P. Callyspongiolide, a cytotoxic macrolide from the marine sponge Callyspongia sp. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Kassekert, L.A.; Bungard, J.D. Enantioselective total synthesis and structural assignment of callyspongiolide. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 11357–11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, B.; Xu, Z.; Ye, T. Total synthesis and stereochemical assignment of callyspongiolide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6948–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, R.T.; Boulanger, A.; Vulpanovici, A.; Roberts, M.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Structure and absolute stereochemistry of phormidolide, a new toxic metabolite from the marine cyanobacterium Phormidium sp. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 7927–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trianto, A.; Hermawan, I.; Suzuka, T.; Tanaka, J. Two new cytotoxic candidaspongiolides from an Indonesian sponge. ISRN Pharm. 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corley, D.G.; Herb, R.; Moore, R.E.; Scheuer, P.J.; Paul, V.J. Laulimalides: New potent cytotoxic macrolides from a marine sponge and a nudibranch predator. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 3644–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñoà, E.; Kakou, Y.; Crews, P. Fijianolide, polyketide heterocycles from a marine sponge. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 3642–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefford, C.W.; Bernardinelli, G.; Tanaka, J.; Higa, T. Structures and absolute configurations of the marine toxins, latrunculin A and laulimalide. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, I.; Menche, D.; Britton, R.; Håkanson, A.E.; Silva-Martínez, M.A. Conformational studies and solution structure of laulimalide and simplified analogues using NMR spectroscopy and molecular modelling. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 3677–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepchatri, P.; Cicero, D.O.; Monteagudo, E.; Ghosh, A.K.; Cornett, B.; Weeks, E.R.; Snyder, J.P. Conformations of laulimalide in DMSO-d6. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12838–12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prota, A.E.; Bargsten, K.; Northcote, P.T.; Marsh, M.; Altmann, K.-H.; Miller, J.H.; Díaz, J.F.; Steinmatez, M.O. Structural basis of microtubule stabilization by laulimalide and peloruside A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, J.; Higa, T.; Bernardinelli, G.; Jefford, C.W. New cytotoxic macrolides from the sponge Fasciospongia rimosa. Chem. Lett. 1996, 25, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moobery, S.L.; Tien, G.; Hernandez, A.H.; Plubrukarn, A.; Davidson, B.S. Laulimalide and isolaulimalide, new paclitaxel-like microtubule-stabilizing agents. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Wang, Y. Total synthesis of (–)-laulimalide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11027–11028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Hoegenauer, E.K.; Enev, V.S.; Hanbauer, M.; Kaehlig, H.; Öhler, E.; Mulzer, J. Total synthesis of the microtubule stabilizing antitumor agent laulimalide and some nonnatural analogues: The power of Sharpless’ asymmetric epoxidation. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 3026–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, B.M., Jr.; Fang, F.G.; Johannes, C.W.; Pesant, M.; Tremblay, M.R.; Zhao, H.; Akasaka, K.; Li, X.-Y.; Liu, J.; Littlefield, B.A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of (–)-laulimalide analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollner, A.; Altmann, K.-H.; Gertsch, J.; Mulzer, J. The laulimalide family: Total synthesis and biological evaluation of neolaulimalide, isolaulimalide, laulimalide and a nonatural analogue. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 5979–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryor, D.E.; O’Brate, A.; Bilcer, G.; Diaz, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Kabaki, M.; Jung, M.K.; Andreu, J.M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Giannakakou, P.; et al. The microtubule stabilizing agent laulimalide does not bind in the taxoid site, kill cells resistant to paclitaxel and epothilones and may not require its epoxide moeity for activity. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 9109–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooberry, S.L.; Randall-Hlubek, D.A.; Leal, R.M.; Hedge, S.G.; Hubbard, R.D.; Zhang, L.; Wender, P.A. Microtubule-stabilizing agents based on designed laulimalide analogues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8803–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollner, A.; Mulzer, J. Total synthesis of neolaulimalide and isolaulimalide. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4701–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinisi, A.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Dien, H.A.; Zampella, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Isoswinholide B and swinholide K, potently cytotoxic dimeric macrolides from Theonella swinhoei. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 21, 5332–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Sorribas, A.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kelly, M.; Williams, P.G. Xestosaprols from the Indonesian Marine Sponge Xestospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán-Aguiñaga, N.; Soria-Mercado, I.E.; Williams, P. Xestosaprols D and E from the Indonesian marine sponge Xestospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Mai, L.H.; Longeon, A.; Copp, B.R.; Loaëc, N.; Bescond, A.; Meijer, L.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L. Novel adociaquinone derivatives from the Indonesian sponge Xestospongia sp. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2617–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanokashira, N.; Kukita, S.; Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Petroquinones: Trimeric xestoquinone derivatives isolated from the marine sponge Petrosia alfiani. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 5530–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kelly-Borges, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Noelaquinone, a new hexacyclic triazine quinone from an Indonesian Xestospongia sp. Heterocylces 1998, 49, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Foster, C.; Brisson, M.; Lazo, J.S.; Kinston, D.G.I. Halenaquinone and xestoquinone derivatives, inhibitors of Cdc25B phosphatase from a Xestospongia sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotoku, N.; Ishida, R.; Matsumoto, H.; Arai, M.; Toda, K.; Setiawan, A.; Muraoka, O.; Kobayashi, M. Biakamides A–D, unique polyketides from a marine sponge, act as selective growth inhibitors of tumor cells adapted to nutrient starvation. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, R.; Kinnel, R.B.; Bifulco, G.; Scheuer, P.J. Kakelokelose, a sulfated mannose polysaccharide with anti-HIV activity from the Pacific tunicate Didemnum molle. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 1979–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).