Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of a New PL25 Family Ulvan Lyase from Marine Bacterium Alteromonas sp. A321
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
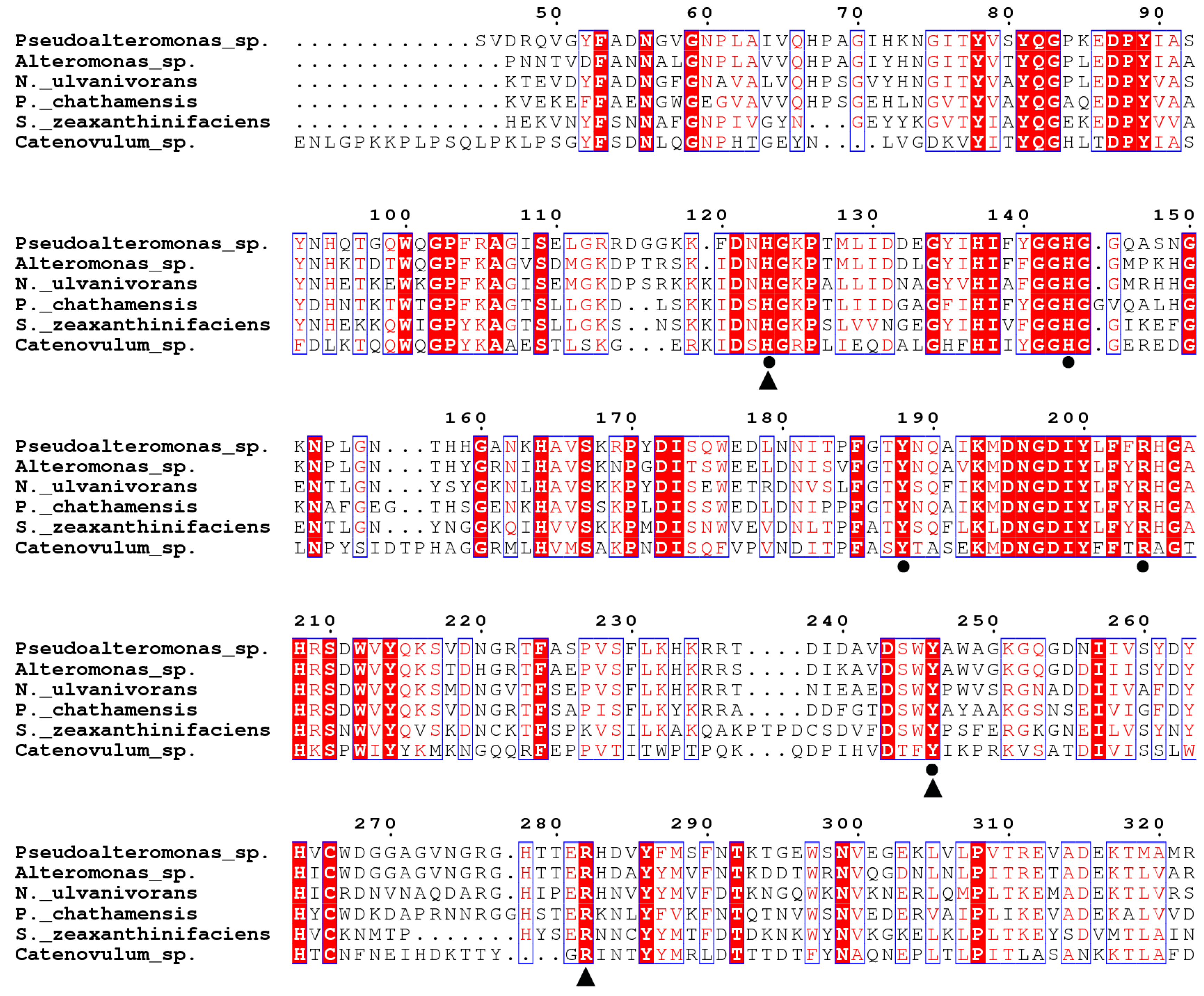
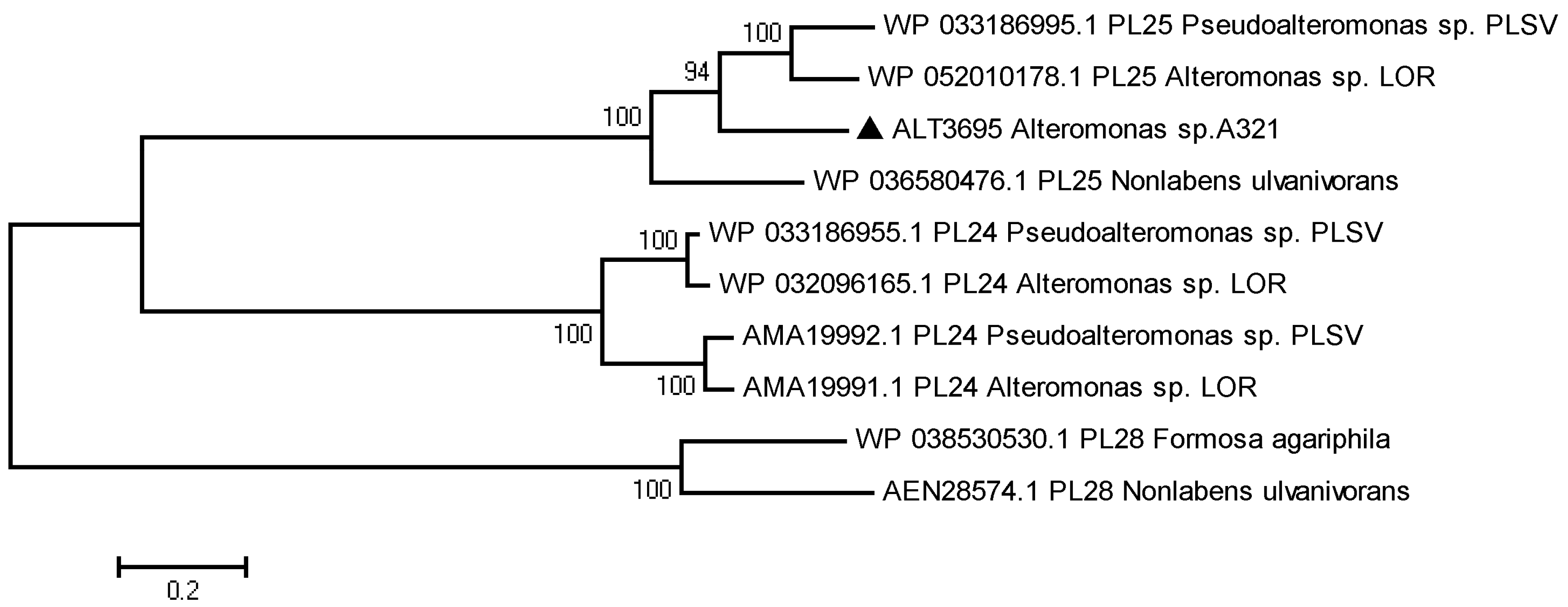
2.1. Sequence Analysis
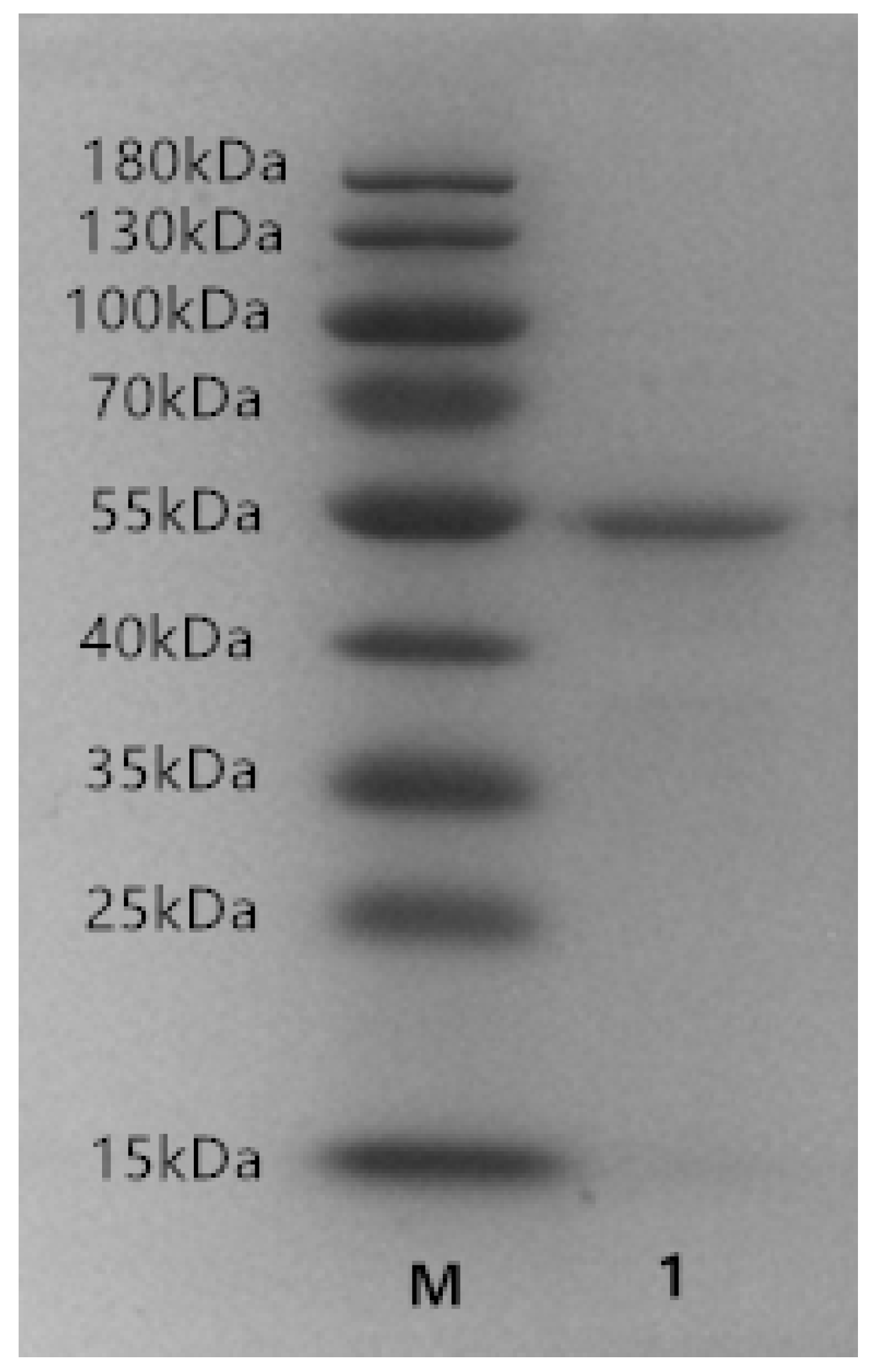
2.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant ALT3695
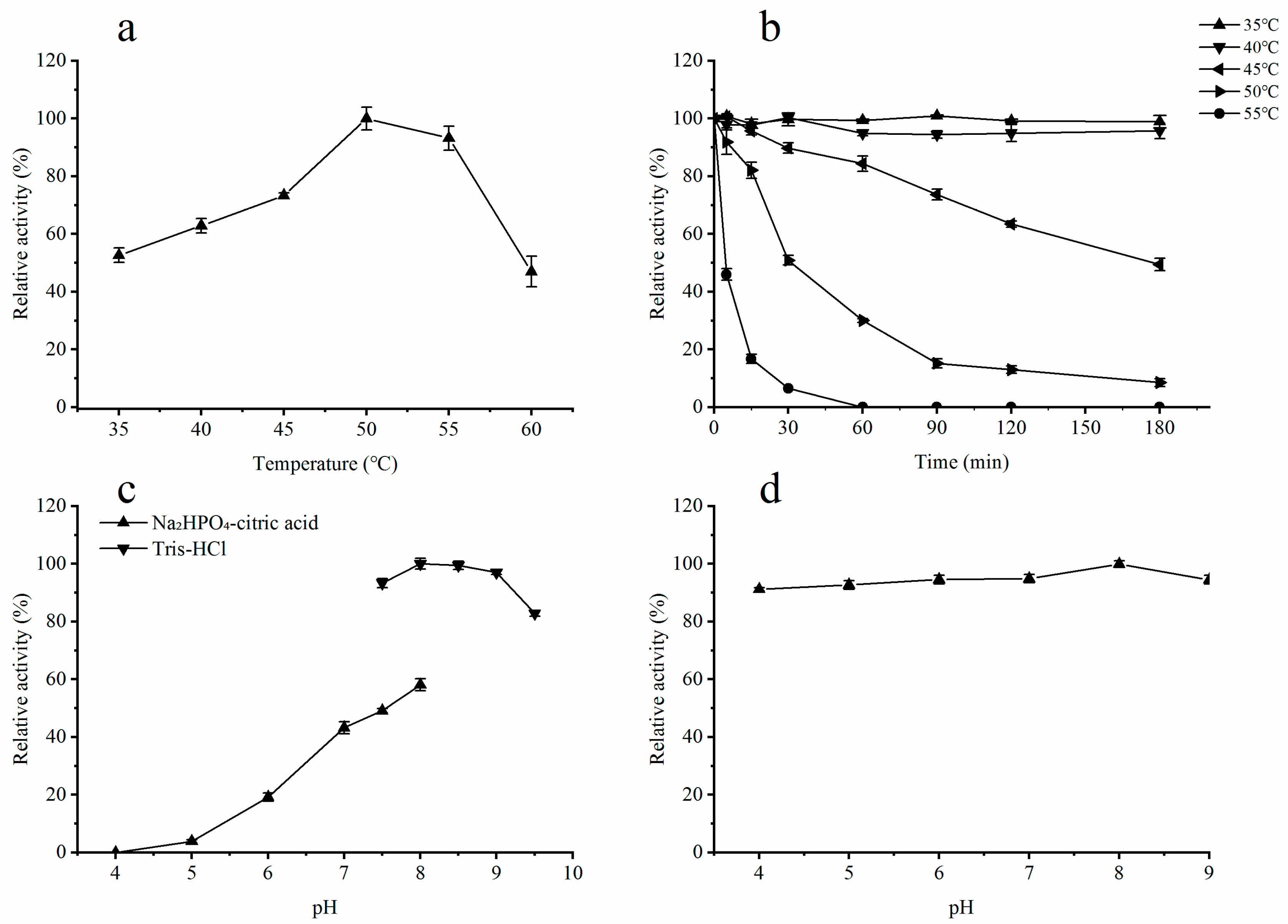
2.3. Influence of Temperature on the Activity of Recombinant ALT3695
2.4. Influence of pH on the Activity of Recombinant ALT3695
2.5. Influences of Surfactants, Metal Ions, and Metal Chelators on the Activity of Recombinant ALT3695
2.6. Kinetic Parameters of Recombinant ALT3695
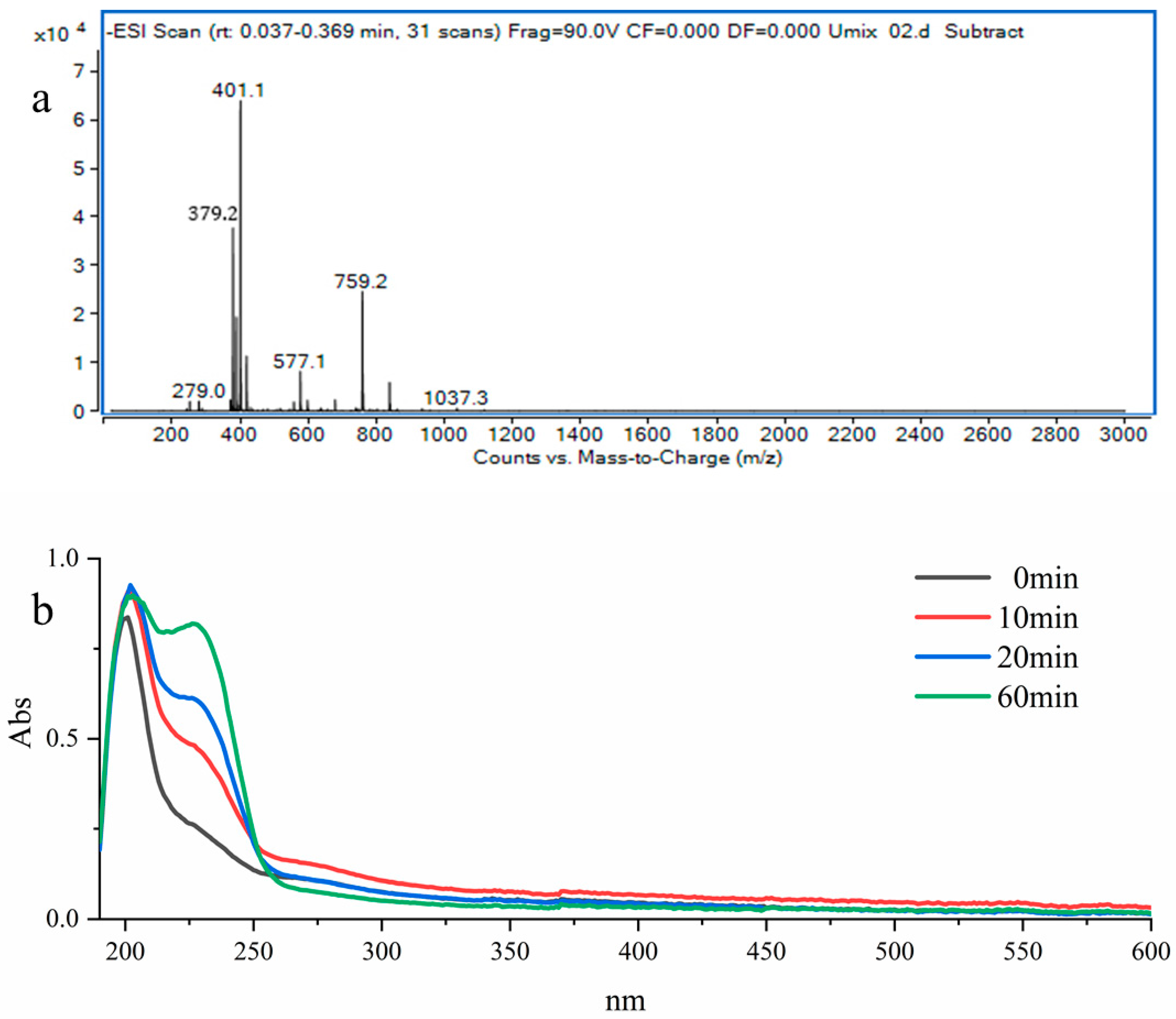
2.7. Analysis of Enzymatic Products
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Medium
3.2. Sequence Analysis
3.3. Construction of the Recombinant ALT3695-Expressing Strain
3.4. Expression of Recombinant ALT3695
3.5. Enzyme Purification
3.6. Enzyme Activity Assay
3.7. Characterization of Recombinant ALT3695
3.8. Kinetic Measurements
3.9. Analysis of Enzymatic Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lahaye, M.; Robic, A. Structure and functional properties of ulvan, a polysaccharide from green seaweeds. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.; Jiang, N.; Liu, X.; Wan, M.; Chang, X.; Liu, D.; Qi, H.; Liu, S. Antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic activities of purified polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Chi, Y.; Hwang, H.; Wang, P. Directional preparation of anticoagulant-active sulfated polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera using artificial neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.T.; Quach, T.M.; Nguyen, T.N.; Vu Luong, D.; Bui, M.L.; Tran, T.T. Structure and cytotoxic activity of ulvan extracted from green seaweed Ulva lactuca. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S. Antihyperlipidemic activity of high sulfate content derivative of polysaccharide extracted from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Briseño, J.A.; Cruz-Suarez, L.E.; Sassi, J.F.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Zapata-Benavides, P.; Mendoza-Gamboa, E.; Rodríguez-Padilla, C.; Trejo-Avila, L.M. Sulphated polysaccharides from Ulva clathrata and Cladosiphon okamuranus seaweeds both inhibit viral attachment/entry and cell-cell fusion, in NDV infection. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, R. Antioxidant activity of different molecular weight sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa Kjellm (Chlorophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2005, 17, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Li, N.; Liu, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Antihyperlipidemic effects of different molecular weight sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 48, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Hwang, H.; Wang, P. Production of enzymes by Alteromonas sp. A321 to degrade polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhan, Q.; Wang, J.; Chi, Y.; Wang, P. A novel low molecular weight Enteromorpha polysaccharide-iron (III) complex and its effect on rats with iron deficiency anemia (IDA). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Qiao, L.; Gao, Y.; Guan, H.; Hwang, H.; Aker, W.G.; Wang, P. Purification and characterization of a novel enzyme produced by Catenovulum sp. LP and its application in the pre-treatment to Ulva prolifera for bio-ethanol production. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahaye, M.; Brunel, M.; Bonnin, E. Fine chemical structure analysis of oligosaccharides produced by an ulvan-lyase degradation of the water-soluble cell-wall polysaccharides from Ulva sp. (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Carbohydr. Res. 1997, 304, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konasani, V.R.; Jin, C.; Karlsson, N.G.; Albers, E. Ulvan lyase from Formosa agariphila and its applicability in depolymerisation of ulvan extracted from three different Ulva species. Algal Res. 2018, 36, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collén, P.N.; Sassi, J.F.; Rogniaux, H.; Marfaing, H.; Helbert, W. Ulvan lyases isolated from the Flavobacteria Persicivirga ulvanivorans are the first members of a new polysaccharide lyase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42063–42071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopel, M.; Helbert, W.; Belnik, Y.; Buravenkov, V.; Herman, A.; Banin, E. New family of ulvan lyases identified in three isolates from the alteromonadales order. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5871–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foran, E.; Buravenkov, V.; Kopel, M.; Mizrahi, N.; Shoshani, S.; Helbert, W.; Banin, E. Functional characterization of a novel “ulvan utilization loci” found in Alteromonas sp. LOR genome. Algal Res. 2017, 25, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaganathan, T.; Helbert, W.; Kopel, M.; Banin, E.; Cygler, M. Structure–function analyses of a PL24 family ulvan lyase reveal key features and suggest its catalytic mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 4026–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaganathan, T.; Boniecki, M.T.; Foran, E.; Buravenkov, V.; Mizrachi, N.; Banin, E.; Helbert, W.; Cygler, M. New ulvan-degrading polysaccharide lyase family: structure and catalytic mechanism suggests convergent evolution of active site architecture. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaganathan, T.; Banin, E.; Helbert, W.; Cygler, M. Structural and functional characterization of PL28 family ulvan lyase NLR48 from Nonlabens ulvanivorans. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 11564–11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydahl, M.G.; Kračun, S.K.; Fangel, J.U.; Michel, G.; Guillouzo, A.; Génicot, S.; Mravec, J.; Harholt, J.; Wilkens, C.; Motawia, M.S.; et al. Development of novel monoclonal antibodies against starch and ulvan-implications for antibody production against polysaccharides with limited immunogenicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, G.; Lü, X.; Hwang, H.; Aker, W.G.; Wang, P. Purification and characterization of polysaccharides degradases produced by Alteromonas sp. A321. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.M.; Xu, P.; Guo, Q.; Cheng, X.; Gao, D.; Sun, D.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, F. Biochemical characterization of a novel ulvan lyase from Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain PLSV. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2610–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisky, L.; Stanetty, C.; Mihovilovic, M.D.; Schweder, T.; Hehemann, J.H.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Biochemical characterization of an ulvan lyase from the marine flavobacterium Formosa agariphila KMM 3901T. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6987–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, A.G. The measurement of sea water pH. Mar. Chem. 1993, 44, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Shen, X.; Chen, K.; Jiang, H.; Liu, D. Dual role of Zn2+ in maintaining structural integrity and suppressing deacetylase activity of SIRT1. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, S.; Ikeo, M.; Ueno, Y.; Taneda, D. Effects of Tween 80 on cellulase stability under agitated conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, A.; Liu, B.; Li, W.; Xing, J. Improvement of cellulose conversion caused by the protection of Tween-80 on the adsorbed cellulase. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 56, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhu, L.; Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Su, J.; Shao, B. Immobilization of an enzyme from a Fusarium fungus WZ-I for chlorpyrifos degradation. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, Y.; Nakamichi, Y.; Itoh, T.; Mikami, B.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K. Substrate specificity of streptococcal unsaturated glucuronyl hydrolases for sulfated glycosaminoglycan. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 18059–18069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Mao, W.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Yan, M.; Lin, C.; et al. Chemical characteristic of an anticoagulant-active sulfated polysaccharide from Enteromorpha clathrate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Purification Steps | Total Protein (mg) | Total Activity (U) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Purification (fold) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude enzymes | 21.39 | 20.49 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 100.00 |
| BeaverBeads™ IDA-Nickel | 5.69 | 10.68 | 1.88 | 1.96 | 52.12 |
| (a) | ||||
| Metal Ions | Concentration (mM) | Relative Activity (%) | Concentration (mM) | Relative Activity (%) |
| Control | - | 100.01 ± 1.37 | - | 100.01 ± 1.37 |
| K+ | 10 | 101.85 ± 1.66 | 20 | 103.62 ± 1.92 |
| Ca2+ | 10 | 112.34 ± 0.48 | 20 | 142.51 ± 2.62 |
| Mg2+ | 10 | 106.13 ± 0.42 | 20 | 117.13 ± 2.12 |
| Zn2+ | 10 | ND | 20 | ND |
| Ba2+ | 10 | 105.49 ± 2.03 | 20 | 121.23 ± 2.39 |
| Cu2+ | 10 | 17.05 ± 0.68 | 20 | ND |
| Fe2+ | 10 | 19.65 ± 2.85 | 20 | ND |
| Co2+ | 10 | 29.88 ± 2.51 | 20 | ND |
| Cd2+ | 10 | ND | 20 | ND |
| Hg2+ | 10 | ND | 20 | ND |
| Fe3+ | 10 | ND | 20 | ND |
| (b) | ||||
| Reagents | Concentration (mM) | Relative Activity (%) | Concentration (mM) | Relative Activity (%) |
| Control | - | 100 ± 0.21 | - | 100 ± 0.21 |
| Tween-20 | 5 | 98.73 ± 2.22 | 10 | 84.17 ± 1.52 |
| Tween-80 | 5 | 103.29 ± 0.44 | 10 | 101.14 ± 1.67 |
| Triton X-100 | 5 | 104.01 ± 0.32 | 10 | 97.36 ± 1.85 |
| EDTA | 5 | 32.11 ± 1.23 | 10 | ND |
| 1,10-phenanthroline | 5 | 106.71 ± 0.79 | 10 | 117.08 ± 1.71 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Du, C.; Chi, Y.; Zuo, S.; Ye, H.; Wang, P. Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of a New PL25 Family Ulvan Lyase from Marine Bacterium Alteromonas sp. A321. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100568
Gao J, Du C, Chi Y, Zuo S, Ye H, Wang P. Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of a New PL25 Family Ulvan Lyase from Marine Bacterium Alteromonas sp. A321. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(10):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100568
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jian, Chunying Du, Yongzhou Chi, Siqi Zuo, Han Ye, and Peng Wang. 2019. "Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of a New PL25 Family Ulvan Lyase from Marine Bacterium Alteromonas sp. A321" Marine Drugs 17, no. 10: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100568
APA StyleGao, J., Du, C., Chi, Y., Zuo, S., Ye, H., & Wang, P. (2019). Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of a New PL25 Family Ulvan Lyase from Marine Bacterium Alteromonas sp. A321. Marine Drugs, 17(10), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100568




