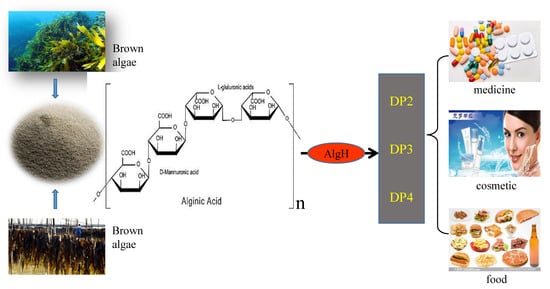
The Characterization and Modification of a Novel Bifunctional and Robust Alginate Lyase Derived from Marinimicrobium sp. H1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Sequence Analysis of AlgH
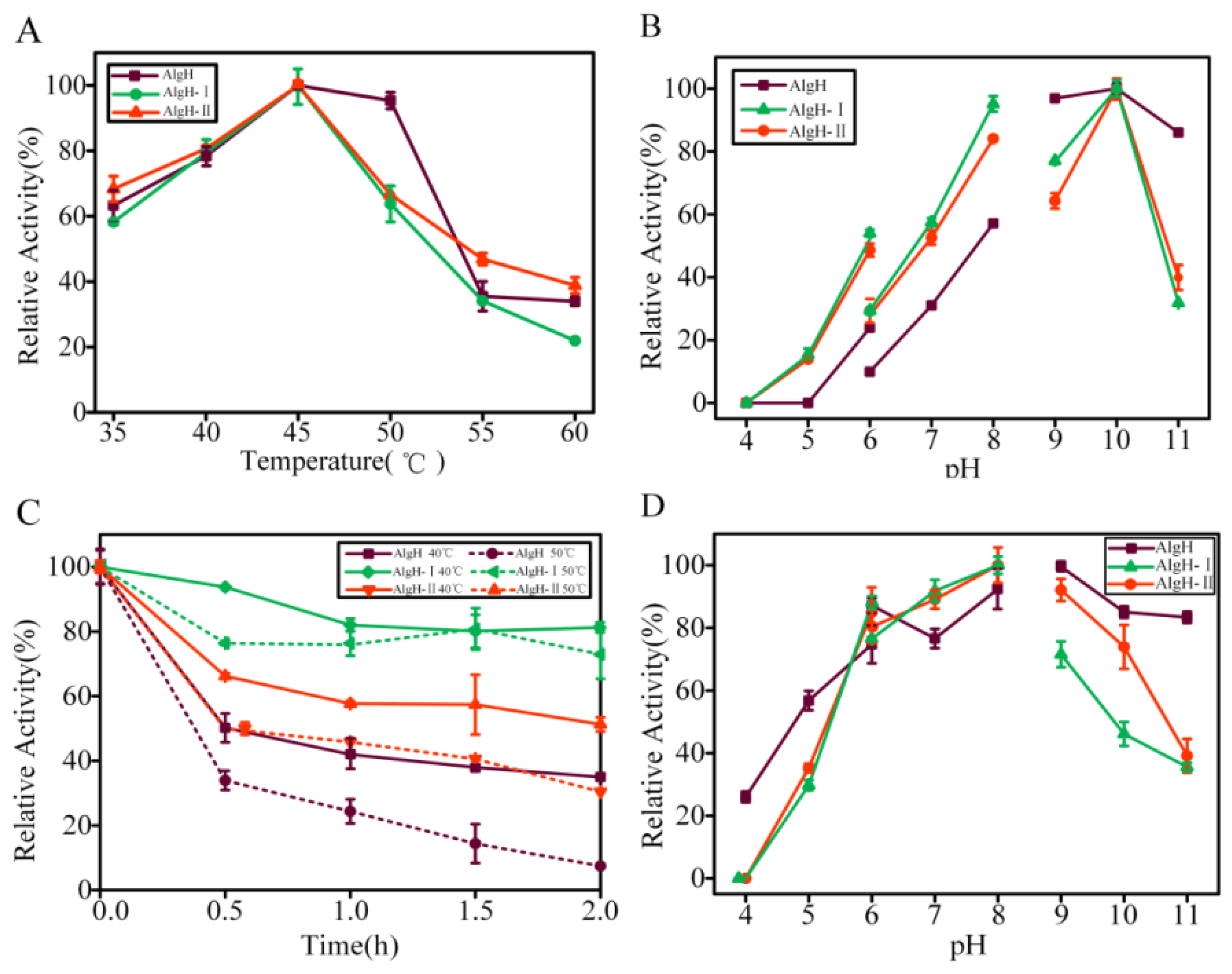
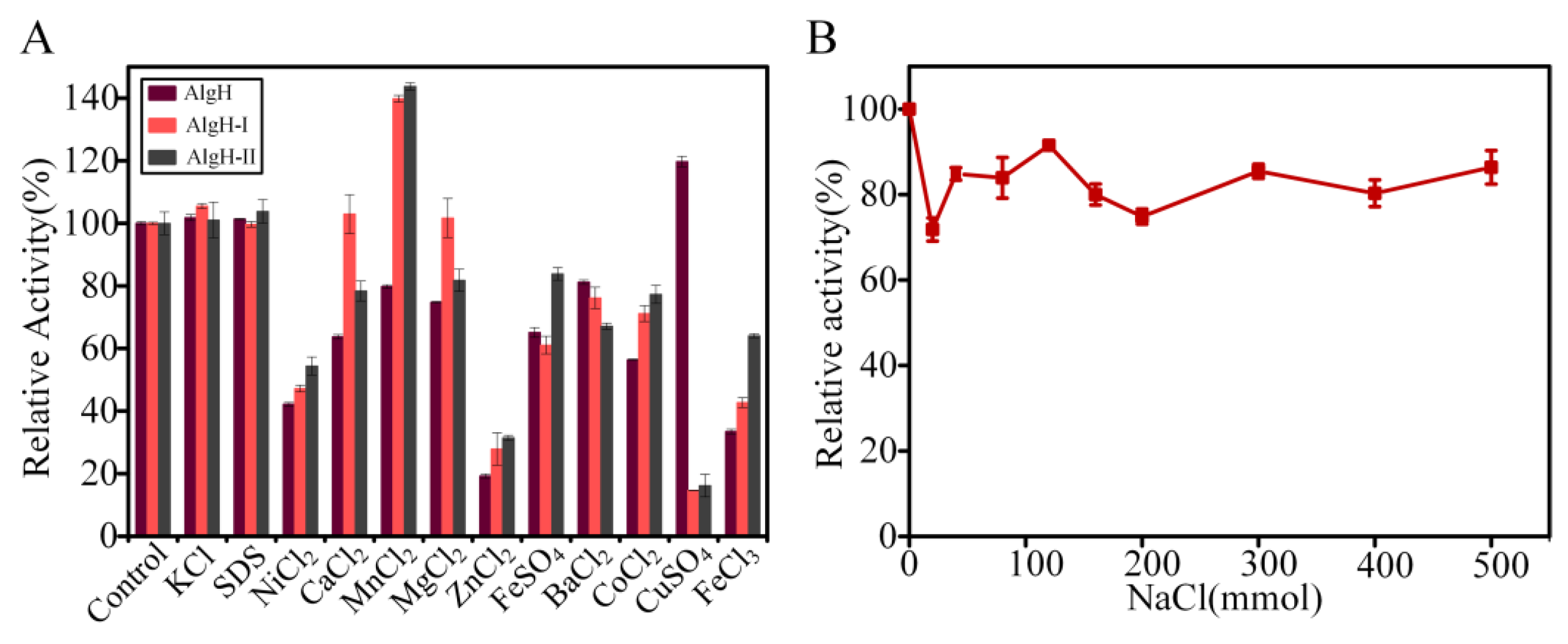
2.2. Biochemical Characteristics of AlgH
2.3. The Effect of the Non-Catalytic Domain of AlgH
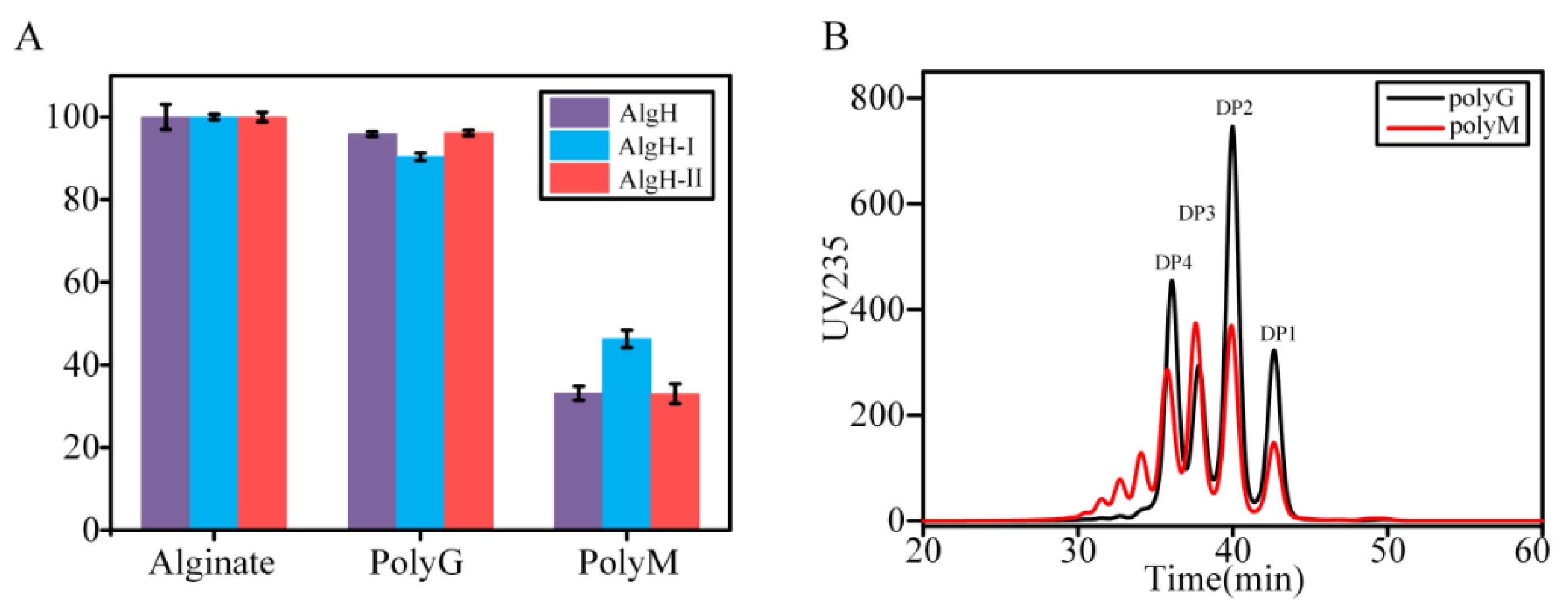
2.4. Substrate Specificity and Enzymatic Kinetics of the Recombinant Alginate Lyases
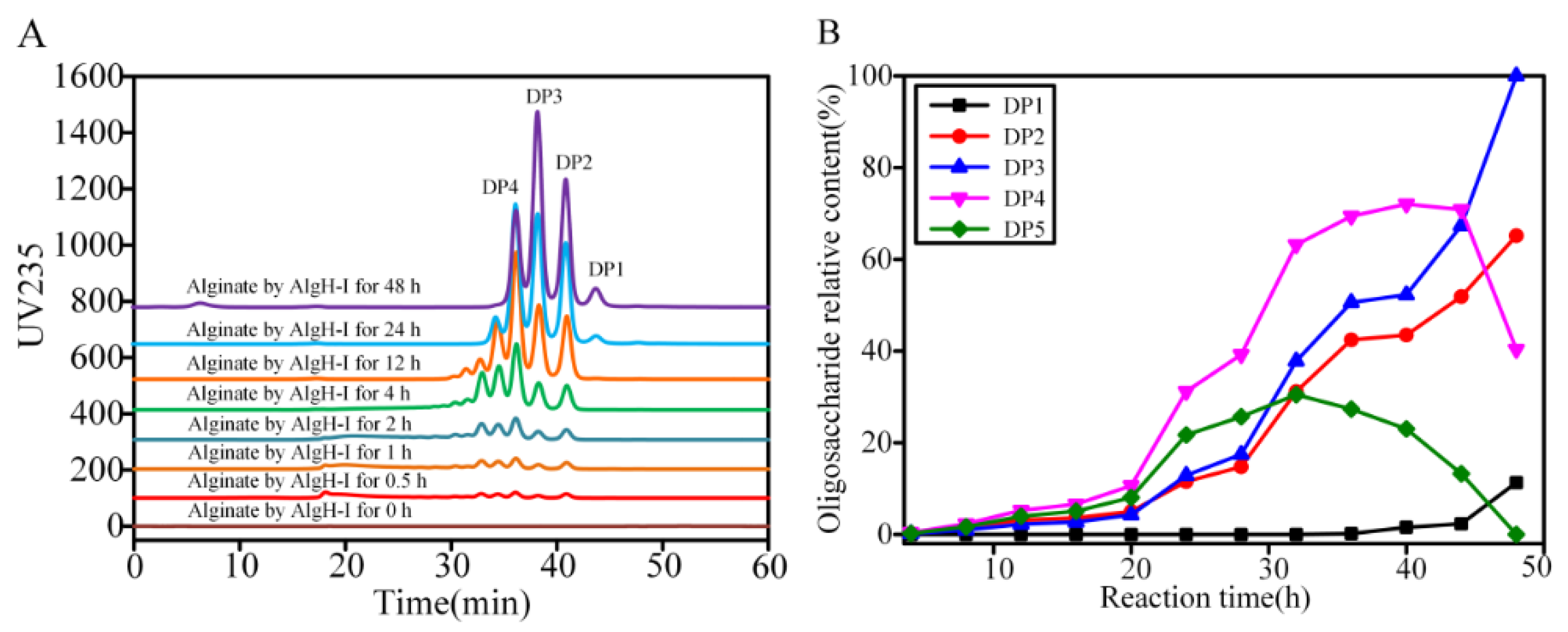
2.5. Degradation Mode and Product Analysis of the Alginate Lyase
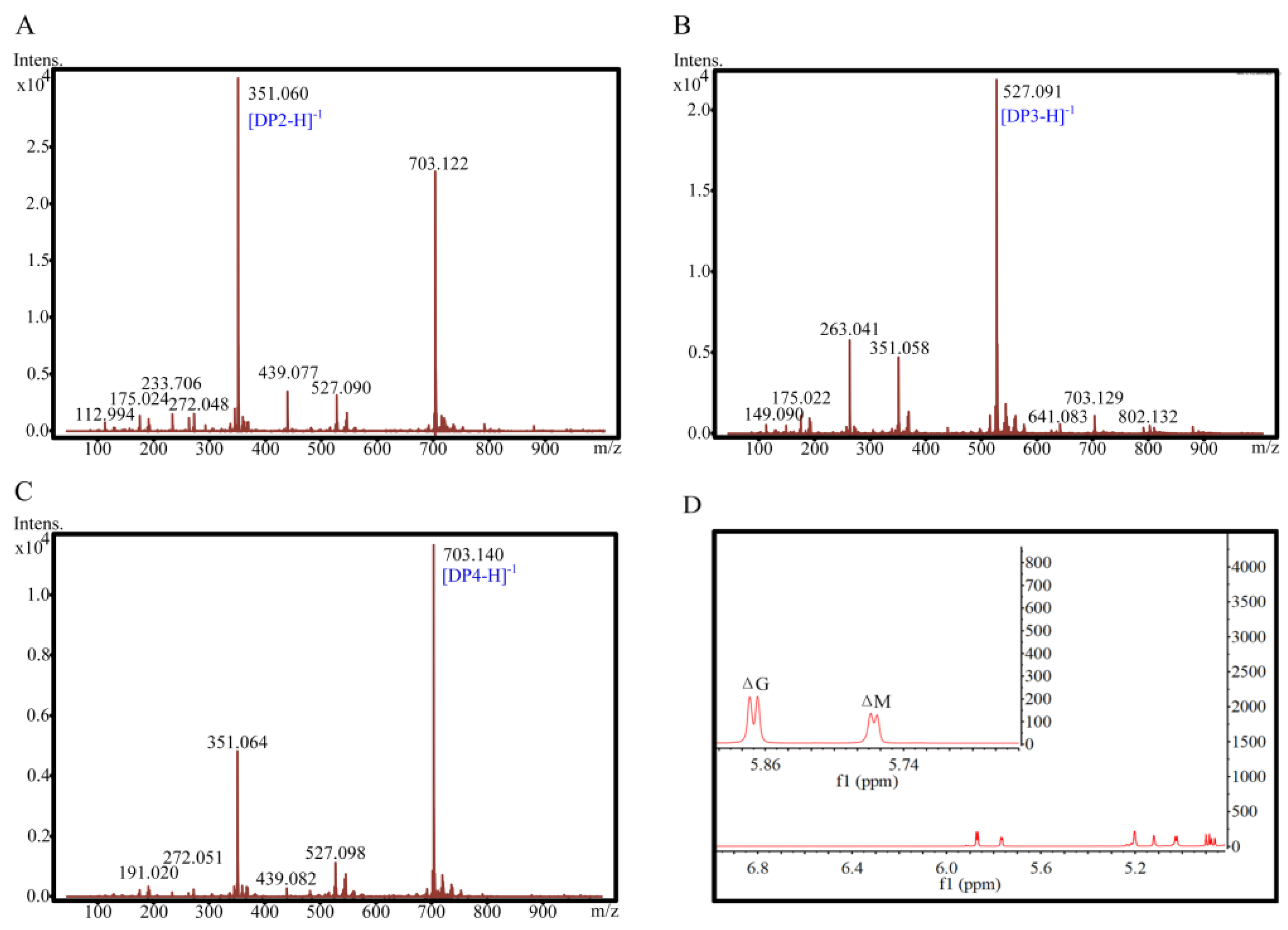
2.6. ESI-MS and 1H-NMR Spectral Analyses of Degradation Products
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cloning and Expression of Recombinant Alginate Lyases
3.2. The Purification of Recombinant Alginate Lyases
3.3. Enzymatic Activity Assay
3.4. Determination of the Substrate Specificities and Enzymatic Kinetics of Recombinant Alginate Lyases
3.5. The Biochemical Characterization of Recombinant Alginate Lyases
3.6. HPLC Analysis of Degradation Products
3.7. ESI-MS and 1H-NMR Spectral Analysis of Degradation Products
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, P.; Zhu, Y.M.; Men, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, Y.X. Purification and characterization of a novel alginate lyase from the marine Bacterium bacillus sp. Alg07. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.J.; Zhang, K.K.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, W.Z.; Lyu, Q.Q.; Ji, A.G. Characterization of a Novel PolyM-Preferred Alginate Lyase from Marine Vibrio splendidus OU02. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.E.; Wang, Q.B.; Lu, D.R.; Han, W.J.; Li, F.C. A Novel Bifunctional Endolytic Alginate Lyase with Variable Alginate-Degrading Modes and Versatile Monosaccharide-Producing Properties. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.W.; Ni, F.; Ning, L.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Z. Cloning and Characterization of a New pH -Stable Alginate Lyase with High Salt Tolerance from Marine Vibrio sp NJ-04. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A. Characterization of PL-7 Family Alginate Lyases from Marine Organisms. Methods Enzymol. 2018, 605, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, R.; Danno, H.; Uchida, M.; Ishihara, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kaneniwa, M.; Ohtsubo, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Tsuda, M. Analysis of extracellular alginate lyase and its gene from a marine bacterial strain, Pseudoalteromonas atlantica AR06. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Preston, L.A.; Schiller, N.L. Alginate lyase: Review of Major Sources and Enzyme Characteristics, Structure-Function Analysis, Biological Roles, and Applications. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 289–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Y.; Wang, Q.Z.; Lu, M.Q.; Xu, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, R.C.; Liao, W.; Huang, S.S. AlgM4: A New Salt-Activated Alginate Lyase of the PL7 Family with Endolytic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, K.; Yamasaki, M.; Mikimi, B.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K. Substrate recognition by family 7 alginate lyase from Sphingomonas sp. A1. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 380, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, C.G.; Lee, E.Y. Alginate lyase: Structure, property, and application. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2011, 16, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, R.; Inoue, A.; Ojima, T. Identification of 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-Gluconate Kinase and 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-Phosphogluconate Aldolase in an Alginate-Assimilating Bacterium, Flavobacterium sp. Strain UMI-01. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.T.; Lin, H.; Kim, S.M. Purification and characterization of a Na+/K+ dependent alginate lyase from turban shell gut Vibrio sp. YKW-34. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.J.; Chang, Y.G.; Shen, J.J. Cloning, expression and characterization of an endo-acting bifunctional alginate lyase of marine bacterium Wenyingzhuangia fucanilytica. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 154, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, M.; Moriwaki, S.; Miyake, O.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K.; MIkami, B. Structure and functionof a hypothetical Pseudomonas aeruginosa protein PA1167 classified into amily PL-7: A novel alginate lyase with a beta-sandwich fold. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31863–31872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavagnat, F.; Duez, C.; Guinand, M.; Potin, P.; Barbevron, T.; Henrissat, B.; Wallach, J.; Ghuysen, J.M. Cloning, sequencing and overexpression in Escherichia coli of the alginatelyase-encoding aly gene of Pseudomonas alginovora: Identification of three classes of alginate lyases. Biochem. J. 1996, 319, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.M.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, K.K.; Yan, J.P.; Irbis, C. Purification and characterization of alginate lyase from Sphingomonas sp. ZH0. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 126, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.W.; Yin, H. Alginate lyase: Review of major sources and classification, properties, structure-function analysis and applications. Bioengineered 2015, 3, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.J.; Preston, J.F.; Ingram, L.O. Cloning of Alginate Lyase Gene (alxM) and Expression in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 1870–1872. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.J.; Gu, J.Y.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Liu, H.H.; Li, Y.Z.; Li, F.C. Novel Alginate Lyase (Aly5) from a Polysaccharide-Degrading Marine Bacterium, Flammeovirga sp. Strain MY04: Effects of Module Truncation on Biochemical Characteristics, Alginate Degradation Patterns, and Oligosaccharide-Yielding Properties. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 82, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.W.; Ni, F.; Sun, Y.; Ning, L.M.; Yao, Z. Elucidation of degrading pattern and substrate recognition of a novel bifunctional alginate lyase from Flammeovirga sp. NJ-04 and its use for preparation alginate oligosaccharides. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuoristo, K.S.; Fredriksen, L.; Oftebro, M.; Arntzen, M.O.; Aarstad, O.A.; Stokke, R.; Steen, I.H.; Hansen, L.D.; Schuller, R.B.; Aachmann, F.L.; et al. Production, characterization and application of an alginate lyase, AMOR_PL7A, from hot vents in the Arctic Mid-Ocean Ridge. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badur, A.H.; Jagtap, S.S.; Yalamanchili, G.; Lee, J.K.; Zhao, H.; Rao, C.V. Alginate Lyases from Alginate-Degrading Vibrio splendidus 12B01 Are Endolytic. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.W.; Chen, M.J.; Yin, H.; Du, Y.G.; Ning, L.M. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Alginate to Produce Oligosaccharides by a New Purified Endo-Type Alginate Lyase. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, S.; Henrissat, B.; Labre, F.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.; Helbert, W. Functional Exploration of the Polysaccharide. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawabe, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ezura, Y.; Gacesa, P. Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of Pseudoalteromonas elyako_ii IAM 14594 gene (alyPEEC) encoding the extracellular alginate lyase. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 335, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.Y.; Wang, D.D.; Gu, J.Y.; Li, J.G.; Liu, H.H.; Li, F.C.; Han, W.J. Biochemical Characteristics and Variable Alginate-Degrading Modes of a Novel Bifunctional Endolytic Alginate Lyase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01608–e01617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.W.; Ning, L.M.; Jiang, Y.C.; Ge, L. Biochemical Characterization and Degradation Pattern of a Novel Endo-Type Bifunctional Alginate Lyase AlyA from Marine Bacterium Isoptericola halotolerans. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.F.; Han, F.; Yu, W.G. Cloning, sequence analysis, and expression of gene alyPI encoding an alginate lyase from marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. CY24. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, W.G.; Han, F. Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of a Cold-Adapted and Surfactant-Stable Alginate Lyase from Marine Bacterium Agarivorans sp. L11. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.W.; Sun, Y.; Ni, F.; Ning, L.M.; Yao, Z. Characterization of a new endo-type alginate lyase from Vibrio sp.NJU-03. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Uchimura, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Nogi, Y.; Horikoshi, K. A new high-alkaline alginate lyase from a deep-sea bacterium Agarivorans sp. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, K.; Tanji, Y.; Hori, K.; Unno, H. Evidence for a novel Chlorella virus-encoded alginate lyase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 180, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Bao, M.M.; Wu, Y.; Yu, W.G.; Han, F. Family 13 carbohydrate-binding module of alginate lyase from Agarivorans sp. L11 enhances its catalytic efficiency and thermostability, and alters its substrate preference and product distribution. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.I.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, E.Y.; Kim, H.S. Molecular cloning, purification, and characterization of a novel polyMG-specific alginate lyase responsible for alginate MG block degradation in Stenotrophomas maltophilia KJ-2. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 95, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.A.; Chen, X.H.; Bi, X.L.; Ren, Y.N.; Han, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Y.T.; Yao, R.Y.; Li, S.Y. Characterization of an Alkaline Alginate Lyase with pH-Stable and Thermo-Tolerance Property. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Shi, H.; Zhou, J.; Tan, Z.B.; Yuan, M.D.; Yao, P.; Liu, X.Y. Characterization of a Novel Alginate Lyase from Marine Bacterium Vibrio furnissii H1. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, S.M.; Hudgens, J.W.; Heselpoth, R.D.; Bales, P.M.; Nelson, D.C. Characterization of AlgMsp, an Alginate Lyase from Microbulbifer sp. 6532A. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, O.; Ochiai, A.; Hashimoto, W.; Murata, K. Origin and Diversity of Alginate Lyases of Families PL-5 and -7 in Sphingomonas sp. Strain A1. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Gong, Q.H.; Song, K.; Li, J.B.; Yu, W.G. Cloning, Sequence Analysis and Expression of Gene alyVI Encoding Alginate Lyase from Marine Bacterium Vibrio sp. QY101. DNA Seq. 2004, 15, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, W.; Miyake, O.; Ochiai, A.; Murata, K. Molecular Identification of Sphingomonas sp. A1 Alginate Lyase (A1-IV_) as a Member of Novel Polysaccharide Lyase Family 15 and Implications in Alginate Lyase Evolution. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Jagtap, S.; Nair, S.K. Structure of a PL17 Family Alginate Lyase Demonstrates Functional Similarities Among Exotype Depolymerases. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 8645–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhu, B.; Wang, W.; Tan, H.; Yin, H. Characterization of a new oligoalginate lyase from marine bacterium Vibrio sp. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.H.; Kam, N.; Lee, E.Y.; Kim, H.S. Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Oligoalginate Lyase from a Newly Isolated Bacterium Sphingomonas sp. MJ-3. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Wei, T.D.; Chen, X.L.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, P.; Xie, B.B.; Qin, Q.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Pang, X.H.; Zhou, B.C.; et al. Molecular Insight into the Role of the N-terminal Extension in the Maturation, Substrate Recognition, and Catalysis of a Bacterial Alginate Lyase from Polysaccharide Lyase Family 18. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 29558–29569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


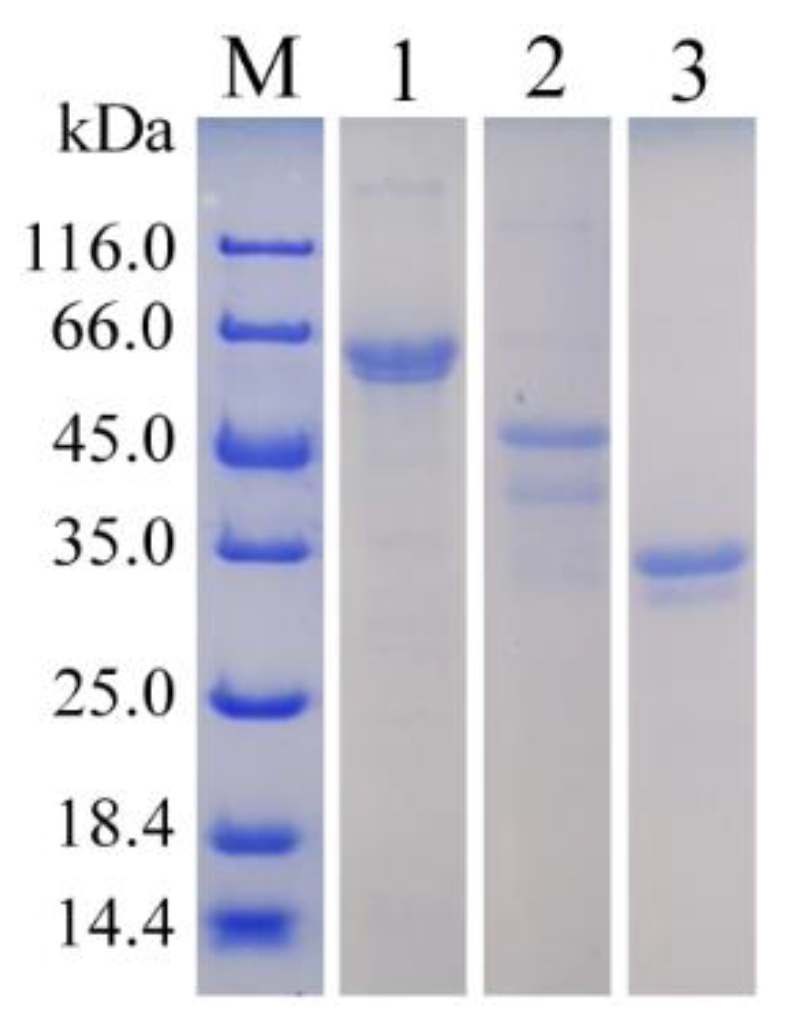
| Enzyme | Organism | Optimal pH | Optimal Temperature (°C) | Activity (U/mg) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL6 | KJ-2 | Stenotrophomas Maltophilia | 8.0 | 40 | N.D | [34] |
| PL7 | AlgH-I | Marinimicrobium koreense H1 | 10.0 | 45 | 5510 | This study |
| Aly7B_Wf | FucanilyticaVibrio | 8.5 | 40 | 23.24* | [13] | |
| AlgM4 | Vibrio weizhoudaoensis M0101 | 8.5 | 30 | 4638# | [8] | |
| rAlgSV1-PL7 | Shewanella Species YH1 | 8.0 | 45 | N.D | [35] | |
| AlyA | Isoptericola Halotolerans NJ-05 | 7.5 | 55 | 7984 # | [27] | |
| AlgNJU-03 | Vibrio sp. NJU-03 | 7.0 | 30 | 6468.9 | [30] | |
| AlgNJ-04 | Vibrio sp. NJ-04 | 7.0 | 40 | 2416 | [4] | |
| AlyH1 | Vibrio furnissii H1 | 7.5 | 40 | 2.40 * | [36] | |
| AlgMsp | Microbulbifer sp. 6532A | 8.0 | 50 | N.D | [37] | |
| AlyL1 | Agarivorans sp. L11 | 8.6 | 40 | 1370 | [29] | |
| AlyPI | Pseudoalteromonas sp. CY24 | 7.0 | 40 | N.D | [28] | |
| A1-II’ | Sphingomonas sp. Strain A1 | 7.5 | 40 | 2.89 | [38] | |
| AlyVI | Vibrio sp. QY101 | 7.5 | 40 | N.D | [39] | |
| PL15 | A1-IV’ | Sphingomonas sp. A1 | 8.5 | 50 | 12.1 | [40] |
| PL17 | Alg17c | Saccharophagus Degredans | 7.5 | 30 | N.D | [41] |
| Oal17A | Vibrio sp. W13 | 7.0 | 30 | 2.11 | [42] | |
| AlgL | Sphingomonas sp. MJ-3 | 6.5 | 50 | N.D | [43] | |
| PL18 | Aly-SJ02 | Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM0524 | N.D | N.D | N.D | [44] |
| Substrate | Enzyme | Vmax (U∙mg of protein−1) | Km (mg∙mL−1) | kcat (s−1) | kcat/Km (mg−1∙mL∙s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Alginate | AlgH | 224.6 ± 33.6 | 6.6 ± 2.2 | 260.6 ± 36.2 | 39.5 ± 5.2 |
| AlgH-I | 450.5 ± 82.1 | 6.9 ± 2.6 | 262.6 ± 41.5 | 38.1 ± 4.9 | |
| AlgH-II | 340.2 ± 70.3 | 7.7 ± 3.3 | 255.5 ± 32.9 | 33.2 ± 4.1 | |
| PloyG | AlgH | 146.6 ± 15.6 | 7.6 ± 1.6 | 155.7 ± 17.1 | 20.5 ± 2.6 |
| AlgH-I | 277.8 ± 21.3 | 7.3 ± 1.5 | 162.1 ± 16.8 | 22.2 ± 2.4 | |
| AlgH-II | 199.7 ± 18.5 | 7.5 ± 1.2 | 149.8 ± 13.5 | 19.9 ± 1.8 | |
| PloyM | AlgH | 62.6 ± 8.8 | 9.1 ± 2.4 | 66.8 ± 6.7 | 7.3 ± 0.5 |
| AlgH-I | 106.8 ± 17.1 | 8.1 ± 2.5 | 62.3 ± 5.6 | 7.6 ± 0.3 | |
| AlgH-II | 78.4 ± 9.8 | 7.9 ± 1.9 | 58.8 ± 4.9 | 7.4 ± 0.2 |
| Primer Name | Nucleotide Sequence (5′to 3′) |
|---|---|
| AlgHf | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGAAAATCAACAGGTTACTTCCTTTC |
| AlgHr | TGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGATCGTGGGTGTGCTCAAGGG |
| AlgH-If | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGCAGGTGGGTTGCGGCGATTTTGCCG |
| AlgH-Ir | AGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGATCGTGGGTGTGCTCAAGGG |
| AlgH-IIf | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGAGCTTGACCAACCCGGGCTTTG |
| AlgH-IIr | AGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGATCGTGGGTGTGCTCAAGGG |
| FU-F | CGCGAGCAGCGGCGAGGTGTTCGCACAGGTGGGTTGCGGCGATTT |
| FU-R | CGGCAAAATCGCCGCAACCCACCTGTGCGAACACCTCGCCGCTGCT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, J.; Chen, P.; Zeng, Y.; Men, Y.; Mu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y. The Characterization and Modification of a Novel Bifunctional and Robust Alginate Lyase Derived from Marinimicrobium sp. H1. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100545
Yan J, Chen P, Zeng Y, Men Y, Mu S, Zhu Y, Chen Y, Sun Y. The Characterization and Modification of a Novel Bifunctional and Robust Alginate Lyase Derived from Marinimicrobium sp. H1. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(10):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100545
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Junjun, Peng Chen, Yan Zeng, Yan Men, Shicheng Mu, Yueming Zhu, Yefu Chen, and Yuanxia Sun. 2019. "The Characterization and Modification of a Novel Bifunctional and Robust Alginate Lyase Derived from Marinimicrobium sp. H1" Marine Drugs 17, no. 10: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100545
APA StyleYan, J., Chen, P., Zeng, Y., Men, Y., Mu, S., Zhu, Y., Chen, Y., & Sun, Y. (2019). The Characterization and Modification of a Novel Bifunctional and Robust Alginate Lyase Derived from Marinimicrobium sp. H1. Marine Drugs, 17(10), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100545