Abstract
Fucoidan, the sulfated fucose-rich polysaccharide derived from brown macroalgae, was reported to display some anti-cancer effects in in vitro and in vivo models that included apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. The proposed mechanisms of action involve enhanced immune surveillance and direct pro-apoptotic effects via the activation of cell signaling pathways that remain largely uncharacterized. This study aimed to identify cellular pathways influenced by fucoidan using an unbiased genetic approach to generate additional insights into the anti-cancer effects of fucoidan. Drug–gene interactions of Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan were assessed by a systematic screen of the entire set of 4,733 halpoid Saccharomyces cerevsiae gene deletion strains. Some of the findings were confirmed using cell cycle analysis and DNA damage detection in non-immortalized human dermal fibroblasts and colon cancer cells. The yeast deletion library screen and subsequent pathway and interactome analysis identified global effects of fucoidan on a wide range of eukaryotic cellular processes, including RNA metabolism, protein synthesis, sorting, targeting and transport, carbohydrate metabolism, mitochondrial maintenance, cell cycle regulation, and DNA damage repair-related pathways. Fucoidan also reduced clonogenic survival, induced DNA damage and G1-arrest in colon cancer cells, while these effects were not observed in non-immortalized human fibroblasts. Our results demonstrate global effects of fucoidan in diverse cellular processes in eukaryotic cells and further our understanding about the inhibitory effect of Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan on the growth of human cancer cells.
1. Introduction
Fucoidans are a class of fucose rich sulfated polysaccharides derived from brown macroalgae that are associated with a large range of bioactivities [1,2]. As a naturally occurring part of edible seaweed, it is already part of the normal diet in many countries. Therefore, certain fucoidan extracts have obtained ‘generally recognized as safe’ (GRAS) status in the US and received novel foods approval in the EU. Fucoidans have long been noted as a selectin blocking compound that inhibits cell–cell interactions [3]. This ability to disrupt cell–cell interactions is likely at least in part, responsible for the potent anti-inflammatory activity of different fucoidan preparations [1]. Fucoidans can also inhibit the adhesion of proteins and organisms to non-biological surfaces, and may help to inhibit biofouling [4]. The anti-microbial activity of fucoidans is also largely based on its inhibition of bacteria-substrate binding [5]. However, in a C. elegans infection model, a fucoidan extract increased the immunity of the host organism and downregulated quorum sensing genes in the bacterial pathogen, which suggests that fucoidans also have the potential to impact gene expression and cellular signaling pathways [6]. While fucoidan-mediated effects on yeasts and fungi are largely unexplored, different fucoidan preparations have also been investigated for their anti-cancer activity in vitro and in vivo [7,8]. In vivo, the anti-cancer response appears to be a combination of enhanced immune function, regulation of checkpoint inhibitor levels [9,10], and a direct cytotoxic activity on cancer cells such as DU-145 human prostate cancer cells [11]. In pre-clinical colon cancer cell models, fucoidans induced both apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, while the exact mechanism for this effect remains unclear [12,13,14,15]. One suggested mode of action involves fucoidan-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress that induces apoptotic cancer cell death via the activation of unfolded protein response (UPR) pathways [14,16,17]. Fucoidan treatment of HCT-116 colon cancer cells resulted in downregulation of the ER protein 29 (ERp29), and activated the phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha (p-eIF2a)/CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) pro-apoptotic cascade [14]. Surprisingly, another fucoidan preparation was also described to protect against endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress [18]. Autophagy, necessary for the bulk degradation of cellular components is recognized as an important mechanism for cell survival under conditions of ER stress. In this context, fucoidans are described as antagonists of scavenger receptors and may even protect against or modulate autophagy in macrophages [18,19].
Despite a large degree of experimental consistency, the molecular differences in fucoidan preparations significantly complicate the comparison of reported results. To obtain an unbiased view of the multiple, sometimes conflicting, biological activities and signaling mechanisms that are affected by fucoidans in proliferating cells, this study initially examined the effects of a well-defined fucoidan extract from the edible macroalga Undaria pinnatifida by screening a S. cerevisiae gene deletion library. This eukaryotic model and type of analysis has been used widely in genome-wide phenotypic screens to understand cellular responses to environmental stressors and to deduce drug–gene interactions in higher organisms [20,21,22,23,24]. For this purpose, the present study employed a single-gene deletion library of S. cerevisiae strains and incubated the gene deletion strains in the absence and presence of fucoidan. By comparing the overall growth (population density) of the gene deletion strains in the absence and presence of fucoidan we were able to unearth genes, and hence potential genetic/functional pathways impacted by fucoidan. This experimental approach enables a global view of drug–gene interactions in the yeast system, which, due to a high degree of functional conservation, can also inform our understanding of fucoidan-gene interactions in the mammalian system. We used this experimental approach to address the question of how one type of edible fucoidan—from Undaria pinnatifida—exerts its reported anti-cancer effects, and what, if any, effects it might have on normal healthy cells. Using this approach for the first time, the present study identified a wide range of fucoidan-affected cellular processes in yeast, some of which were subsequently confirmed in studies involving mammalian cells.
2. Results
2.1. Yeast Gene Deletion Library Results
To gain an unbiased insight into gene-fucoidan interactions, the growth of the complete library of 4,733 haploid S. cerevisiae gene deletion strains was measured in the absence and presence of 500 g/mL Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan, UPF. Based on a cutoff value of 1.5-fold change in cell growth at least 115 deletion strains showed reduced proliferation in the presence of fucoidan compared to control (YPD alone grown) cultures (Table S1). Out of these, 82 genes (71%) were associated with known cellular processes, while 33 genes (29%) were of unknown function. In contrast, 177 deletion strains showed increased growth in the presence of UPF (Table S1). From these, 136 genes (77%) were associated with well described cellular processes and 41 genes (23%) were of unknown function.
Overall, the data indicated that UPF likely interacts with a wide range of genes whose protein are potentially involved in distinct cellular processes, including DNA replication, maintenance and repair, mRNA transcription and processing, ribosome biogenesis, amino acid biosynthesis, carbohydrate and nucleotide metabolism, protein transport and degradation, organelle (mitochondria and vacuole) transport and maintenance, general and oxidative stress responses, and a considerable number of pathways whose precise identities in the eukaryotic/mammalian system remain to be fully determined. To interrogate this dataset in more detail, pathway analysis using String software was employed (Figure 1). In a first iteration, only the 115 genes were assessed whose absence reduced the growth of S. cerevisiae in the presence of UPF by at least 1.5-fold (Figure 1A). Using a high confidence interaction score of 0.9 (“highest confidence”), the software identified seven major functional groups that included peroxisome biogenesis, amino acid biogenesis, cyclin-cAMP signaling, cell cycle control, DNA repair, RNA polymerase complex, and energy metabolism (Figure 1A).
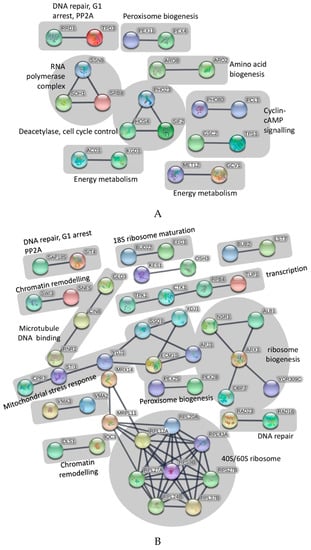
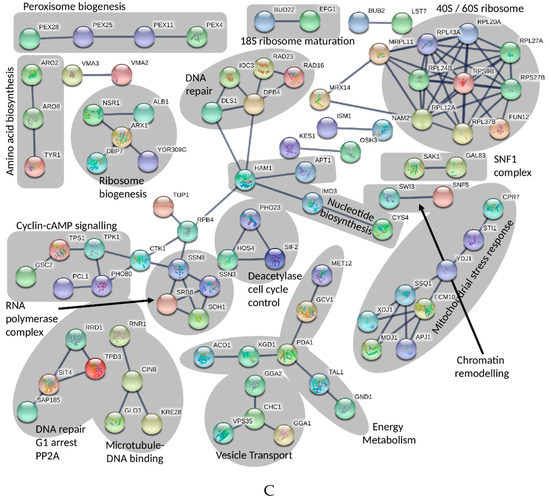
Figure 1.
(A) Pathway analysis of identified genes that resulted in reduced growth of S. cerevisiae in the presence of UPF. Pathway analysis was performed with String software (Version 10.5) using an interaction score of 0.9 (‘highest confidence’). The figure only shows connected genes with disconnected nodes hidden. (B) Pathway analysis of identified genes that resulted in increased growth of S. cerevisiae in the presence of UPF. Pathway analysis was performed with String software (Version 10.5) using an interaction score of 0.9 (‘highest confidence’). The figure only shows connected genes with disconnected nodes hidden. (C) Pathway analysis of all identified genes that interacted with UPF. Pathway analysis was performed with String software (Version 10.5) using an interaction score of 0.9 (‘highest confidence’). The figure only shows connected genes with disconnected nodes hidden.
As a second step, only those genes were interrogated, whose absence increased the growth of S. cerevisiae in the presence of UPF by at least 1.5-fold (Figure 1B). Using the same stringency settings of 0.9, the software strongly predicted the involvement of the ribosome function and biogenesis, chromatin remodeling and DNA repair, cell cycle checkpoints, mitochondrial stress response, transcription, peroxisome biogenesis, and microtubule-DNA dynamics (Figure 1B).
In a final analysis, all 292 genes identified as being important for the growth of S. cerevisiae (by at least 1.5-fold) in the presence of UPF were included together in the pathway analysis. This combined analysis revealed some genetic/functional pathways that were not identified in the initial analysis (Figure 1A,B), such as the effects of UPF on mitochondrial t-RNA synthase, nucleotide biosynthesis, transcription elongation and splicing, as well as protein transport mechanisms. In addition, this form of analysis strengthened previously identified pathway-UPF connections such as an effect on ribosome function, mitochondrial and energy metabolism and DNA repair by adding more genes to previously identified nodes (Figure 1C).
2.2. Mammalian Cell Studies
Based on the observed UPF-gene interactions in S. cerevisiae, a UPF-induced cellular stress response was postulated that included cell cycle checkpoints and DNA damage repair pathways. This study intended to translate the genetic pathways identified in yeast to a mammalian system. Since we did not aim to study anti-cancer activity of UPF in general, only one well characterized cell line was used exemplary instead of a range of cancer cell lines. To confirm the presence of UPF-induced cell cycle control and DNA damage in mammalian cells the general level of toxicity of UPF was assessed in HCT-116 colorectal cancer cells.
2.2.1. Viability Assessment Using WST-1
The WST-1 cell proliferation assay is frequently used as a measure of cell proliferation or cytotoxicity. It is based on the metabolic production of NAD(P)H, which is used as a surrogate marker for cell death, cytostatic activity or metabolic inhibition by test compounds [25]. To assess short-term effects of fucoidan treatment, log-phase HCT-116 colon cancer cells were exposed to UPF over 24 h before WST-1 conversion was measured (Figure 2). Surprisingly, the presence of UPF at concentrations of up to 100 µg/mL showed no signs of toxicity to the colon cancer cells in the WST-1 assay, regardless of serum concentration in the cell culture media. In fact, low UPF concentrations of up to 2.5 µM appeared to significantly increase WST-1 dye conversion (Figure 2). This effect likely represents an artefact of the redox-active nature of the UPF preparation as described for other compounds [26], which required us to assess cellular viability in the presence of UPF by other assays.
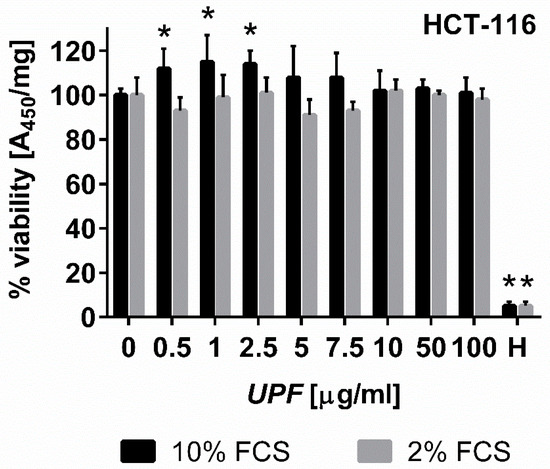
Figure 2.
Effect of UPF on metabolic activity/viability. Human colon carcinoma cells (HCT-116) were exposed to UPF concentrations of up to 100 µg/mL for 24 h before viability was assessed using WST-1 reagent. Data represent one typical experiment out of up to four independent experiments. WST-1 absorption data were standardized on protein content for each well, represent the mean of six individual wells per experiment and are expressed as % viability compared to the untreated control cells. Error bars represent SD with *: p < 0.05. Hydrogen peroxide (H, 100 µM) was used as a positive control for toxicity.
2.2.2. Colony Formation Assay
In contrast to the WST-1 assay that only detects acute toxicity of a compound based on metabolic activity, the colony formation assay was employed to also assess any long-term effects of UPF treatment. Consistent with the WST-1 data, UPF showed hardly any effects on the number of colonies after two weeks of continuous treatment. Only the highest UPF concentration (100 µM) showed a significant (p < 0.05) reduction in colony numbers by about 25% under optimal cell culture conditions (Figure 3A). To assess this effect in more detail, the experiment was repeated but the serum concentration of the cell culture media was reduced to 2%. Since the colony formation assay is essentially measuring ‘proliferative fitness’ of cells in culture, the reduction of growth factors is a commonly used approach to increase the stringency of this assay to detect mild, non-lethal toxicities. While this reduced FCS content did not change the overall cloning efficiency of the cells in the absence of UPF (similar numbers of colonies in the untreated cultures at 2% and 10% FCS; data not shown), it had a dramatic effect on the activity of UPF. Even at the lowest UPF concentration, a highly significant (p < 0.001) drop in colony numbers of about 70% was observed (Figure 3A). This toxicity increased further in a dose dependent manner, where only 7% residual colonies were observed at the highest UPF concentration (Figure 3A).
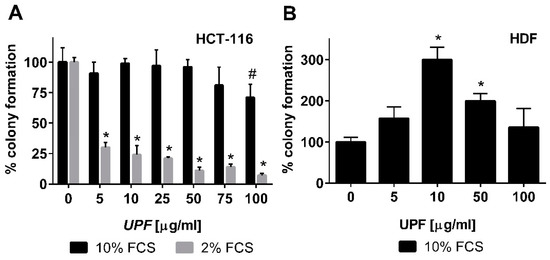
Figure 3.
Effect of UPF on colony formation. Human colon carcinoma cells (HCT-116, A) and human non-immortalized dermal fibroblasts (HDF, B) were exposed to UPF concentrations up to 100 µg/mL in a colony formation assay. Data represent one typical experiment out of up to four independent experiments. Data is expressed as the mean +/− SD of four plates and expressed as % colony formation compared to the untreated control cells. Error bars represent SD with #: p < 0.05 and * p < 0.001.
To assess if this toxicity was specific to immortalized cells or would also apply to other cell types, the effect of UPF was tested on the colony formation activity of non-immortalized primary human dermal fibroblasts (HDF). These cells are significantly more sensitive to their culture conditions and only form colonies with at least 10% fetal calf serum (FCS). Therefore, lower FCS concentrations could not be tested. In contrast to HCT-116 cells, UPF treatment of HDF cells led to a bell-shaped concentration curve with a significant increase in colony numbers between 10 and 50 µM. Even at the highest UPF concentration (100 µM), HDF still showed at least as many colonies as the untreated control cells (Figure 3B).
2.2.3. Assessment of UPF-induced DNA Damage
The specific toxicity observed in the colorectal cancer cell line was consistent with the yeast data that indicated an interaction between UPF and DNA repair pathways. The typical mode of action of most anti-cancer agents is the induction of DNA damage. Nuclear γH2AX staining is a marker of DNA damage-induced cellular repair activity and is frequently used as very sensitive marker for the presence of DNA damage, especially DNA double strand breaks [27]. To assess if UFP induces DNA damage, non-immortalized human skin fibroblasts (HDF) and colon cancer cells (HCT-116) were exposed to 100 µg/mL UPF over 24 h. In untreated HDF, only about 10% of cells showed any γH2AX foci at all and these cells displayed typically less than four foci. After exposure to UPF no increase in the number of positive cells was evident and the positive cells also did not show increased numbers of foci (Figure 4A,B) and those HDF with γH2AX foci had only very low numbers of foci (Figure 4B). In contrast to HDF, close to 40% of HCT-116 cells showed γH2AX foci in the absence of UPF, indicative of the genetic instability that is characteristic to many tumor cell lines. More importantly HCT-116 cells showed a very significant (p < 0.01) UPF-induced effect with nearly 90% of all cells positive for γH2AX foci after 24 h (Figure 4A). In contrast to HDF, HCT-116 cells also showed very high numbers of γH2AX foci per cell after exposure to UPF (Figure 4C).
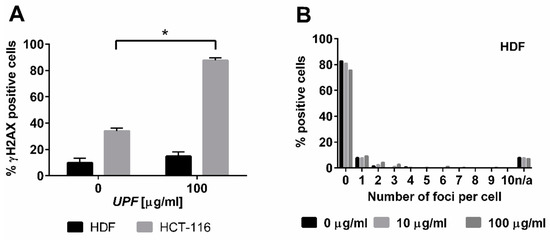
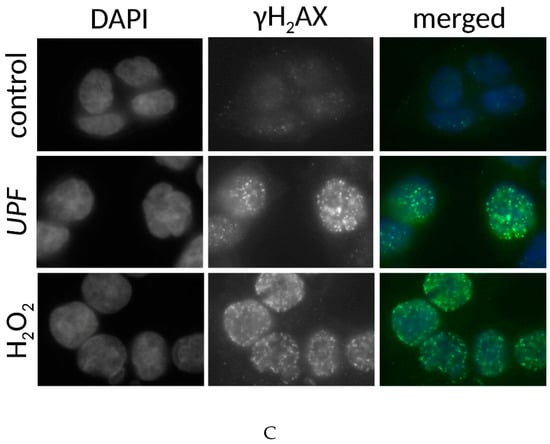
Figure 4.
DNA damage induction by UPF. Human colon carcinoma cells (HCT-116, A, C) and human non-immortalized dermal fibroblasts (HDF, A,B) were exposed to 100 µg/mL UPF before γH2AX immunostaining was performed (A) Data represents the mean of 3 experiments and expressed as % γH2AX-positive cells. Error bars represent SD with *: p < 0.001. (B) Data represent one typical experiment out of three experiments for HDF. n/a: cells excluded from analysis due to unquantifiable staining pattern. (C) Representative images for UPF-induced induction of nuclear γH2AX foci in HCT-116 cells. H2O2-treatment (100 µM, 30 min) was used as a positive control. Merged images represent software generated false color overlays of DAPI and γH2AX signals.
2.2.4. Cell Cycle Assay by Fluorescence-activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
To understand the long-term toxicity of UPF on HCT-116 cells in the colony formation assay, cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry was employed. UPF induced a significant (p < 0.01) G1 arrest at 72 h, while all prior time points remained non-significant. The corresponding reduction in S-phase cells approached significance (p = 0.052), while no effects were observed with regards to the number of cells in G2 phase (Figure 5).
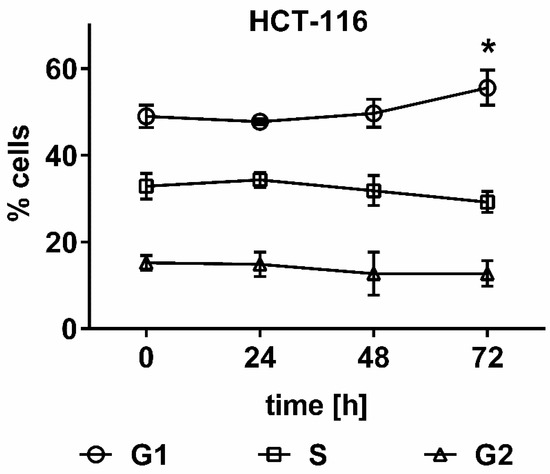
Figure 5.
Effect of UPF on cell cycle distribution. HCT 116 cells were treated with 100 µg/mL UPF for up to 72 h and cell cycle distribution was assessed by flow cytometry. Data represents the mean of four independent experiments performed over a two-month time period. Error bars represent SD with *: p < 0.01.
3. Discussion
This study initially examined the gene-drug interactions of Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan (UPF) by screening the complete S. cerevisiae gene deletion library to achieve an unbiased genome-wide assessment of the eukaryotic genetic/functional pathways potentially affected by this fucoidan. Especially in cases where (i) a test compound is associated with a multitude of biological effects, or (ii) nothing is known about the biological effects of a test compound, or (iii) a gene of interest, this approach has been used successfully [28]. The present study identified a large number of interacting pathways affected by UPF that broadly affected cellular energy metabolism, RNA synthesis, DNA synthesis and repair, cell cycle control, protein synthesis and transport. Our yeast data are in general agreement with a previous report that employed microarray gene expression analysis of Fucus vesiculosus extract treated pancreatic cells [29]. While that report also highlighted the effect of fucoidan on DNA damage repair and cell cycle regulation, it did not identify the additional pathways, such as ribosomal or mitochondrial involvement, that our analysis provided for UPF.
When the effects of UPF on cell cycle control predicted by the yeast results were subsequently tested in a mammalian cell culture system, our results largely confirmed previous reports of G1 arrest. Fucoidan isolated from Fucus vesiculosus was previously reported to induce a G1 arrest in the same cell line used in the present study [13], while polysaccharides from peony seeds also induced a G1 arrest in the same cell line [30]. However, in the present study UPF led to a much milder G1 arrest that only occurred after 72 hours and with lower magnitude compared to the previous report where a significant increase was already detected after 36 hours [13]. The extent of G1 arrest was much more comparable to the second report, which observed a G1-arrest already after 24 hours, so it remains unclear how many cells would have accumulated in G1 phase after 72 hours [30].
As a major difference to the previous studies [13,30], UPF did not induce any overt cytotoxicity or signs of cell death. Previous studies reported polysaccharide-induced loss of membrane integrity, reduced metabolism and apoptosis [13]. In the present study, a distinctive lack of UPF-induced cell death or cytotoxicity was evident in the WST-1 and the colony formation assays when the cells were grown under standard conditions. Only when cells were treated under conditions of reduced growth factor availability did UPF reduce cellular metabolism. This somewhat hidden sensitivity supports the yeast results that suggest that UPF interacts with cellular energy metabolism. Thus, the observed UPF hypersensitivity under reduced growth factor signaling indicates a synergistic mode of action. Surprisingly, UPF-induced cytotoxicity at the level of cell proliferation was only observed in the colon cancer cell line but not in non-immortalized human dermal fibroblasts (HDF). Although, it has to be acknowledged that toxicity in these cells could have been present at lower serum concentrations, these cells do not form colonies under these conditions and in contrast to signs of toxicity our results indicate a significant UPF-dependent increase in colony formation in HDF. This cell type specific difference was not entirely unexpected, as previous reports highlighted that fucoidans can induce proliferation in primary fibroblasts without inducing toxicity [31,32].
To explore the mild toxicity observed in the cancer cell line further, we investigated the possibility of fucoidan-induced DNA damage. Although molecular signatures indicative of fucoidan-induced DNA damage (such as Tunnel staining), have been reported earlier [14], low-molecular weight fucoidan was conversely reported to inhibit DNA-damage induced signaling (including γH2AX foci) in etoposide-treated HCT-116 cells [33]. Our results for the first time, indicate a direct and very potent DNA damaging activity by UPF by itself that appears to be very selective for the cancer cell line tested. In untreated HCT-116 cells, compared to fibroblasts, elevated basal levels of γH2AX foci were detected, which reflects the reported genetic instability and hypermutator phenotype of colorectal cancer cells [34]. Upon exposure to UPF, foci numbers in the cancer cell line increased dramatically, to 90 foci/nucleus, which is among the highest numbers reported, while foci numbers in the fibroblasts remained unaffected at a significantly lower level. This significant difference obviously poses the question: how can UPF elicit this cell type specific response and how exactly does UPF induce DNA damage?
Although, the majority of the literature reports anti-oxidant activity of fucoidan, our WST-1 results indicate that UPF has some redox activity that, together with the appropriate metabolic background could also act as a pro-oxidant. This double-edged redox activity has been reported for many common antioxidants from vitamins C and E to CoenzymeQ10 [35]. There is also evidence that the anti-cancer effects of fucoidans could be attributed to a pro-oxidant activity [36,37]. Whilst UPF-induced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) could well explain the rapid induction of DNA damage observed in the present study, it is striking that despite this toxicity, cell cycle effects only became evident after 72 hours. Even more surprising is the complete lack of detectable cell death in the presence of extensive DNA damage. A different Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan extract was previously reported to increase ROS production via a mitochondria-dependent mechanism in a hepatocarcinoma cell line [38]. In contrast to the present study, this was associated with cytotoxicity within 12–24 hours but with no effects on cell cycle within this time frame. However, previous reports of fucoidan-induced cell death in cancer cells typically used significantly higher concentrations of fucoidan compared to the present study [13,30,38]. We therefore cannot exclude that significantly higher UPF concentrations would have also induced cell death in our experimental setting. Given the uncertainty of achievable fucoidan concentrations in the cancer microenvironment in vivo, it is relatively futile to interpret these cytotoxic dose-differences with regards to any therapeutic usefulness. Nevertheless, a mitochondrial mode of action of UPF represents an intriguing possibility to explain the cell type specific differences observed in the present study. Given that cancer cells use their mitochondria in a manner very distinct to normal non-immortalized cells [39] future studies will have to delineate the detailed mechanisms of how fucoidans can specifically alter mitochondrial function in cancer cells to induce the cell type-specific effects observed in this and previous studies.
It has to be noted that one of the difficulties of comparative analysis is that fucoidan extracts from different source algae, prepared by using different methods may contain impurities such as polyphenolics, alginates, or other co-extracts. Since the concentrations used in many previous experiments have been relatively high, it cannot be excluded that minor co-extracts rather than the fucoidan itself could have affected the results. Therefore, the current study aimed to use fucoidan with a well-characterized molecular composition and at concentrations low enough to mimic potential physiologically achievable levels. This approach was chosen to enable comparative baseline data for future investigations. In addition, this study used an unbiased approach to identify Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan-gene interactions that were successfully translated to mammalian cell responses, which validates the use of S. cerevisiae as an initial screening tool. Therefore, this approach could be used in future studies to characterize and more importantly compare different fucoidan preparations that differ in their extraction methods, geographic sources, and species origins. This approach would enable cost effective and reliable comparisons of different extracts and their associated bioactivities.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
If not otherwise stated, all chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Castle Hill, NSW, Australia). Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan (UPF) was obtained from Marinova (Cambridge, TAS, Australia). This material was provided with a quoted fucoidan purity of 85.1% (dry weight). The calculation of fucoidan purity requires several inputs that are determined using spectrophotometric assays. The total carbohydrate content of a hydrolyzed sample was determined using the phenol-sulfuric method of Dubois [40,41], while the uronic acid content was determined by spectrophotometric analysis of the hydrolyzed compound in the presence of 3-phenylphenol, based on a method described by Filisetti-Cozzi and Carpita [41]. Sulfate content was analyzed spectrophotometrically using a BaSO4 precipitation method (BaCl2 in gelatin), based on the work of Dodgson [42], and found to be 24.6%. The molecular weight profile was determined via gel permeation chromatography using a size-exclusion column and reported relative to Dextran standards, with peak molecular weight found at 47.7 kDa.
4.2. Yeast Gene Deletion Library
Briefly, a stock concentration (5 mg/mL) of UPF was prepared in YPD liquid medium (10 g yeast extract, 20 g peptone, and 20 g dextrose / liter) and sterilized by filtration (cellulose acetate membrane, 0.45 mm pore size, Microscience, Taren Point NSW, Australia). Stock solutions were kept at 4 °C until required. The wild-type (parental) Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain BY4741 (MATa his3Δ1 leu2Δ0 met15Δ0 ura3Δ0), along with its mutant derivatives covering ~96% of the yeast genome, were obtained from GE Healthcare Dharmacon (Millennium Science, Mulgrave, VIC, Australia). The 4733 gene deletion strains (representing the entire set of nonessential genes for this organism) were supplied frozen in a 96-well microtitre plate format, with individual wells containing settled yeast cells in YPD liquid medium supplemented with 200 µg/mL G418 and 12.5% glycerol. Sub-master plates (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, North Ryde, NSW, Australia) were prepared by thawing the relevant master plate and transferring 10 µl aliquots of each well to 96-well plates containing 90 mL of YPD liquid medium supplemented with G418 (200 µg/mL). The plates were incubated for two days at 30 °C, before 12.5% glycerol was added to each well and the plates stored at minus 80 °C. To prepare experimental 96-well plates containing the deletion strains, the sub-master plates were thawed before a 10 µl aliquot of each well (containing ~1 × 106 cells) was transferred to 96-well plates containing either 90 mL YPD-alone, or 90 mL YPD+500 µg/mL UPF. The wild-type (parental) S. cerevisiae strain BY4741 was grown overnight at 30 °C in YPD liquid medium to a density of ~1 × 108, before a 10 µl aliquot was inoculated in wells of a 96-well plate containing either 90 mL YPD-alone, or else 90 mLYPD+500 µg/mL UPF. All plates were incubated at 30 °C, 5% CO2, for 24 h before the growth of the wild-type control and deletion strains was determined by optical density (OD) at 600 nm using a Spectramax M2 microplate spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA). The sensitivity of each strain to the fucoidan treatment was determined by comparing its growth (optical density) in the absence and presence of fucoidan. Gene deletion strains showing a growth deficit of at least ~1.5 fold were scored as sensitive.
4.3. Pathway Analysis
Pathway analysis was performed using String software 10.5 (https://string-db.org) using largely default settings with an interaction score of 0.9 and gene sets restricted to S. cerevisiae. Images were generated by hiding disconnected nodes and only showing connected genes. Line thickness was used to illustrate evidence. Settings for the maximum number of interactors to show were selected as first shell: none (only query genes); second shell: none (only query genes). Images were exported from String and pathways were annotated manually in PowerPoint.
4.4. Colony Formation Assay
UPF-containing media was filtered through 0.45 µm syringe top filters to generate stock solutions of 1 mg/mL. Human colorectal carcinoma cells (HCT-116, 91091055) or non-immortalized human dermal fibroblasts (HDF) (106-05A) were used. Single cell suspensions were seeded in culture media (HCT-116: McCoy’s 5A, M4892) with 2 or 10% FBS, HDF: DMEM (D5523)with 2 or 10% FBS. HCT-116 cells were seeded at 2000 cells per 10 cm culture dish in 2% FCS or 360 cells in 4cm culture dish in 10% while, HDF were seeded at 300 cells per 10 cm culture dish in 10% FCS. After overnight adhesion, the cells were exposed to fucoidan concentrations up to 100 µg/mL for two weeks without media change. The assay was terminated by fixation with 2% w/v paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10–15 min at RT. Colonies were then stained with 0.25% Coomassie Brilliant Blue in 50% (v/v) methanol, 10% (v/v) acetic acid for 5 min at RT. Colonies consisting of more than 50 cells were counted by eye (HCT-116) or under the microscope (HDF). Results are derived from at least four parallel replicates and presented as % colony formation (compared to the untreated control cells).
4.5. WST-1 Assay
This viability assay is based on the enzymatic cleavage of the tetrazolium salt WST-1 to formazan by cellular dehydrogenases present in viable cells. The dye cannot permeate the cell membrane and is reduced outside the cell via the plasma membrane electron transport system. HCT-116 cells were seeded at a density of 5000 cells per well in 96-well plates in 100 µl of 2 or 10% FBS containing McCoy’s media and allowed to adhere overnight. Cells were subsequently treated with various UPF concentrations for 24 h to assess acute toxicity. After this time-period the media was removed and 100 µl of fresh media containing 5 µl of WST-1 reagent (Cayman, Sapphire Biosciences Redfern, NSW, Australia) added in each well. Following a 2 h incubation at 37 °C the plate was read in a microplate reader at 450 nm. The WST-1 data for each well were standardized on protein content and the results expressed as % viability.
4.6. Detection of DNA Damage by γH2AX
To assess if UPF causes DNA damage, induction of nuclear γH2AX foci was quantified as described previously [43]. Briefly, 1 × 105 HCT-166 or HDF cells were seeded on sterile coverslips in 12 well plates. After adherence, cells were treated with 100 µg/mL fucoidan and incubated for 24 h. Cells were then fixed with 4% PFA in PBS for 15 min and lysed with 1 mL/well of B1 buffer (10% FBS, 0.5% Triton X-100 and PBS) for 1 h at RT on a plate shaker at 200 rpm, followed by two washes with 1 mL of the same buffer. Cells were then incubated with the anti-γH2AX antibody (anti-phospho-histone H2A.X(Ser139), (clone JBW301, Lot 2476967, Merck, Bayswater, VIC, Australia) in buffer B1 at 4 °C over night in a humidified chamber. Subsequently, the coverslips were washed 3 x 2 min with W1 buffer (5% FBS, 0.5% Triton X-100 and 0.5× PBS), followed by incubation with species-specific secondary antibody (Alexa Fluor 488 (ab’) 2 fragment of goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L), (ab150117, Abcam, Melbourne, VIC, Australia) for 1 h at RT in B1 buffer. After three washes with W1 buffer and one wash with 1 mL PBS/well, cells were incubated with DAPI (1:10,000) for 5 min to stain the nuclei. After three more washes with 0.5 × PBS, auto-fluorescence was quenched by incubating the cells with 1 mL of W2 buffer (5mM CuSO4 in 5 mM ammonium acetate buffer adjusted to pH 5) /well for 20 min at RT. Coverslips were then mounted on microscope slides using Slow Fade Gold anti-fade reagent (S36936, Thermo-Fisher Scientific, North Ryde, NSW, Australia) and stored in the dark until used. Slides were then assessed by counting 3 x 100 cells per condition. The number of cells that contained foci as well as how many foci per cell were present was assessed.
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
After incubation with 0.1 mg/mL UPF for up to 72h HCT-116 cells were harvested by trypsinization and washed with Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline (DPBS). 1.5 × 106 cells were resuspended in 750 µl of cold DPBS and left on ice for 10 min. 3 mL of 95% ethanol (−20 °C) were added steadily to the cells, while gently vortexing, before the cells were further fixed for 30 min at 4 °C on ice. Cells were then washed with DPBS twice by centrifuging for 5 min at 850 g. Supernatant was aspired carefully before cells being resuspended in 450 µl of cold DPBS and counted to adjust cell density to 1 × 106 cells/mL. Cells were additionally treated with 5 µl of ribonuclease A (10 mg/mL) before DNA was stained with 100 µl of propidium iodide (PI) (1 mg/ mL) and incubated light-protected at 37 °C for 15 min. Fluorescence was measured using an attune acoustic focusing cytometer (Applied Biosystems, Thermo-Fisher Scientific, North Ryde, NSW, Australia). 10,000 events per sample were collected using the accompanying attune acoustic focusing software. Changes in the percentage of cell distribution for each phase of the cell cycle were used to determine cell cycle effects of Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan compared to untreated control cells. Cell cycle data was analyzed using FLOWJO software (version 10, Treestar, Ashland, Oregon, USA).
5. Conclusions
Exposure of a S. cerevisiae deletion library to an Undaria pinnatifida fucoidan extract (UPF) identified a total of 292 genes, whose products are potentially involved in the cellular response to UPF. Pathway analysis grouped these genes into a large number of pathways and cellular functions that included ribosome function and biogenesis, cell cycle signaling and DNA repair, nucleotide and amino acid biosynthesis, peroxisomal biosynthesis, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, RNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and transport. Two exemplary pathways were confirmed in the human colon cancer cell line HCT-116. In this cell line UPF reduced colony formation, induced a slow G1 arrest and significant amounts of DNA damage, which was not observed in non-immortalized primary human dermal fibroblasts.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/17/1/54/s1, Table S1: Yeast screen data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.G. and J.H.F.; Methodology, N.G., M.A., R.E., and M.C.; Formal Analysis, M.A., J.P. and M.C.; Investigation, M.A., J.P. and M.C., Resources, D.S., S.K., and A.P.; Data Curation, N.G., M.A., J.P. and M.C.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, N.G. and J.H.F.; Visualization, N.G. and M.C.; Supervision, N.G., M.A., and R.E.; Project Administration, N.G. and D.S. Funding Acquisition, N.G., J.H.F., and D.S.
Funding
This research was funded by Marinova Pty. Ltd. and the Australian Department of Industry and Innovation (Innovations connections), grant number (RC49508).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Australian government Department of Industry and Innovation.
Conflicts of Interest
The current study was sponsored in part by Marinova Pty Ltd. J.Helen Fitton, Damien Stringer, Sam Karpiniec, and Ahyoung Park are employees of Marinova Pty Ltd.
References
- Lee, Y.E.; Kim, H.; Seo, C.; Park, T.; Lee, K.B.; Yoo, S.Y.; Hong, S.C.; Kim, J.T.; Lee, J. Marine polysaccharides: Therapeutic efficacy and biomedical applications. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitton, J.H.; Stringer, D.N.; Karpiniec, S.S. Therapies from fucoidan: An update. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5920–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Ding, Y.; Cai, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Shi, Z. Low molecular weight fucoidan attenuates experimental abdominal aortic aneurysm through interfering the leukocyte-endothelial cells interaction. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7089–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Thuy, L.T.; Ki, S.H.; Ko, S.; Kim, S.; Cho, W.K.; Choi, J.S.; Kang, S.M. Multipurpose Antifouling Coating of Solid Surfaces with the Marine-Derived Polymer Fucoidan. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1800137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, E.G.; Verbrugghe, P.; Perkins, T.T.; Tay, C.Y. Fucoidans Disrupt Adherence of Helicobacter pylori to AGS Cells In Vitro. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2015, 2015, 120981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, S.; Khan, W.; Kulshreshtha, G.; Evans, F.; Critchley, A.T.; Fitton, J.H.; Stringer, D.N.; Gardiner, V.A.; Prithiviraj, B. The fucose containing polymer (FCP) rich fraction of Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. protects Caenorhabditis elegans against Pseudomonas aeruginosa by triggering innate immune signaling pathways and suppression of pathogen virulence factors. Algae 2015, 30, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, L.; Burney, M.; Gaikwad, A.; Nyshadham, P.; Nugent, E.K.; Gonzalez, A.; Smith, J.A. Preclinical Evaluation of Safety of Fucoidan Extracts From Undaria pinnatifida and Fucus vesiculosus for Use in Cancer Treatment. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, M.; Mathew, L.; Gaikwad, A.; Nugent, E.K.; Gonzalez, A.O.; Smith, J.A. Evaluation Fucoidan Extracts from Undaria pinnatifida and Fucus vesiculosus in Combination With Anticancer Drugs in Human Cancer Orthotopic Mouse Models. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Liang, H.; Tang, Q.; Xue, C.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Bian, K.; Zhang, L.; et al. The Protective and Immunomodulatory Effects of Fucoidan Against 7,12-Dimethyl benz[a]anthracene-Induced Experimental Mammary Carcinogenesis Through the PD1/PDL1 Signaling Pathway in Rats. Nutr. Cancer 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.O.; Zhang, W.; Du, J.Y.; Wong, K.W.; Oda, T.; Yu, Q. Fucoidan can function as an adjuvant in vivo to enhance dendritic cell maturation and function and promote antigen-specific T cell immune responses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Pan, H.F.; Shao, S.L.; Xu, X.M. Anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects of Fucoidan on prostate cancer: Possible JAK-STAT3 pathway. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.H. Fucoidan present in brown algae induces apoptosis of human colon cancer cells. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Park, S.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Yoon, D.; Han, M.H.; Lee, D.S.; Choi, G.; Yim, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, D.H.; et al. Induction of p53-Independent Apoptosis and G1 Cell Cycle Arrest by Fucoidan in HCT116 Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Fucoidan induces cancer cell apoptosis by modulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress cascades. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, S.A.; Szegezdi, E.; Mulloy, B.; Samali, A.; Tuohy, M.G. An unfractionated fucoidan from Ascophyllum nodosum: Extraction, characterization, and apoptotic effects in vitro. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Lin, T.-Y.; Hu, C.-H.; Shu, D.T.F.; Lu, M.-K. Fucoidan upregulates TLR4/CHOP-mediated caspase-3 and PARP activation to enhance cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 432, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Lu, M.K.; Leng, P.J.; Tsao, S.M.; Wu, Y.C. Fucoidan induces Toll-like receptor 4-regulated reactive oxygen species and promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, N.; Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Ben, J.; Yang, Q.; Bai, H.; Chen, Q. Class A scavenger receptor activation inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagy in macrophage. J. Biomed. Res. 2014, 28, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seimon, T.A.; Obstfeld, A.; Moore, K.J.; Golenbock, D.T.; Tabas, I. Combinatorial pattern recognition receptor signaling alters the balance of life and death in macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19794–19799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, T.J.; Rosenbach, A.S.; Ideker, T.; Samson, L.D. Damage recovery pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae revealed by genomic phenotyping and interactome mapping. Mol. Cancer Res. 2002, 1, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Birrell, G.W.; Giaever, G.; Chu, A.M.; Davis, R.W.; Brown, J.M. A genome-wide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for genes affecting UV radiation sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12608–12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Game, J.C.; Birrell, G.W.; Brown, J.A.; Shibata, T.; Baccari, C.; Chu, A.M.; Williamson, M.S.; Brown, J.M. Use of a genome-wide approach to identify new genes that control resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res. 2003, 160, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, A.; Zhou, X.; Ellen, T.P.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Rooney, J.P.; Kurtz, A.; Klein, C.B.; Dai, W.; Begley, T.J.; et al. A genome-wide deletion mutant screen identifies pathways affected by nickel sulfate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Arita, A.; Ellen, T.P.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Rooney, J.P.; Kurtz, A.D.; Klein, C.B.; Dai, W.; Begley, T.J.; et al. A genome-wide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals pathways affected by arsenic toxicity. Genomics 2009, 94, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.V.; Herst, P.M.; Tan, A.S. Tetrazolium dyes as tools in cell biology: New insights into their cellular reduction. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2005, 11, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.S.; Berridge, M.V. Evidence for NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1)-mediated quinone-dependent redox cycling via plasma membrane electron transport: A sensitive cellular assay for NQO1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, S.; Takeiri, A.; Tanaka, K.; Harada, A.; Matsuzaki, K.; Taketo, J.; Matsuo, S.; Fujii, E.; Mishima, M. Advantages of evaluating gammaH2AX induction in non-clinical drug development. Genes Environ. 2018, 40, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.L.; Kumar, A. Mutant power: Using mutant allele collections for yeast functional genomics. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2016, 15, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, U.; Zenthoefer, M.; Peipp, M.; Kerber, J.; Plenge, J.; Managò, A.; Fuhrmann, M.; Geyer, R.; Hennig, S.; Adam, D.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms by Which a Fucus vesiculosus Extract Mediates Cell Cycle Inhibition and Cell Death in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4470–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, J.J.; Thakur, K.; Hu, F.; Zhang, J.G.; Wei, Z.J. Anti-Cancerous Potential of Polysaccharide Fractions Extracted from Peony Seed Dreg on Various Human Cancer Cell Lines Via Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, R.K.; Perumal, S.; Thangam, R.; Gopinath, A.; Ramadass, S.K.; Madhan, B.; Sivasubramanian, S. Collagen-fucoidan blend film with the potential to induce fibroblast proliferation for regenerative applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.S.; Li, H.; Balcos, M.C.; Yun, H.Y.; Baek, K.J.; Kwon, N.S.; Choi, H.R.; Park, K.C.; Kim, D.S. Fucoidan promotes the reconstruction of skin equivalents. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.M.; Liu, P.Y.; Chen, Y.A.; Tseng, H.Y.; Shen, P.C.; Hwang, P.A.; Hsu, H.L. Oligo-Fucoidan prevents IL-6 and CCL2 production and cooperates with p53 to suppress ATM signaling and tumor progression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, K.C.G.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Johannessen, B.; Bruun, J.; Danielsen, S.A.; Bjornslett, M.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Eknaes, M.; Lind, G.E.; et al. Multi-omics of 34 colorectal cancer cell lines—A resource for biomedical studies. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouayed, J.; Bohn, T. Exogenous antioxidants--Double-edged swords in cellular redox state: Health beneficial effects at physiologic doses versus deleterious effects at high doses. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.Y. Fucoidan as a marine anticancer agent in preclinical development. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.O.; Song, M.G.; Kim, Y.N.; Park, J.I.; Kwak, J.Y. The mechanism of fucoidan-induced apoptosis in leukemic cells: Involvement of ERK1/2, JNK, glutathione, and nitric oxide. Mol. Carcinog. 2010, 49, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Teng, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Hou, L.; Zou, X. Fucoidan derived from Undaria pinnatifida induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells via the ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y. Cancer Energy Metabolism: Shutting Power off Cancer Factory. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filisetti-Cozzi, T.M.C.C.; Carpita, N.C. Measurement of uronic acids without interference from neutral sugars. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 197, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogson, K.S. Determination of inorganic sulphate in studies on the enzymic and non-enzymic hydrolysis of carbohydrate and other sulphate esters. Biochem. J. 1961, 78, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becherel, O.J.; Jakob, B.; Cherry, A.L.; Gueven, N.; Fusser, M.; Kijas, A.W.; Peng, C.; Katyal, S.; McKinnon, P.J.; Chen, J.; et al. CK2 phosphorylation-dependent interaction between aprataxin and MDC1 in the DNA damage response. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).