The Bisindole Alkaloid Caulerpin, from Seaweeds of the Genus Caulerpa, Attenuated Colon Damage in Murine Colitis Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Caulerpin Decreases Cell Migration to Peritoneal Cavity in Model of Peritonitis Induced by Zymosan
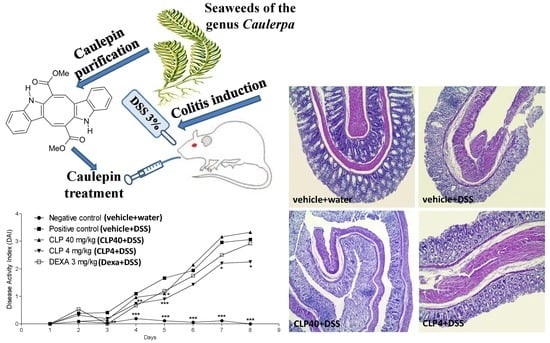
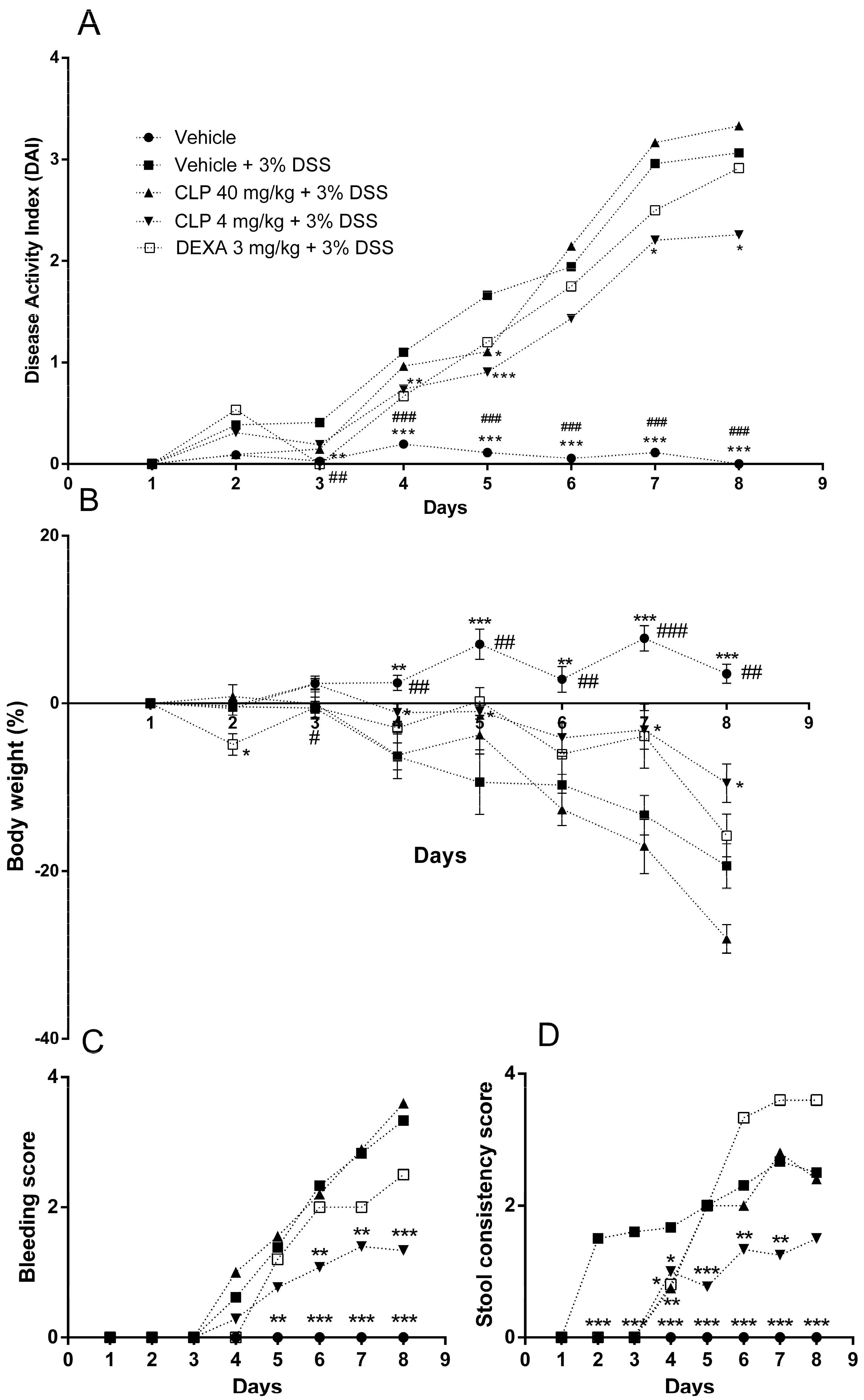
2.2. The Treatment of Mice with Caulerpin Ameliorates the Body Weight Loss and the Disease Activity Index Induced by DSS
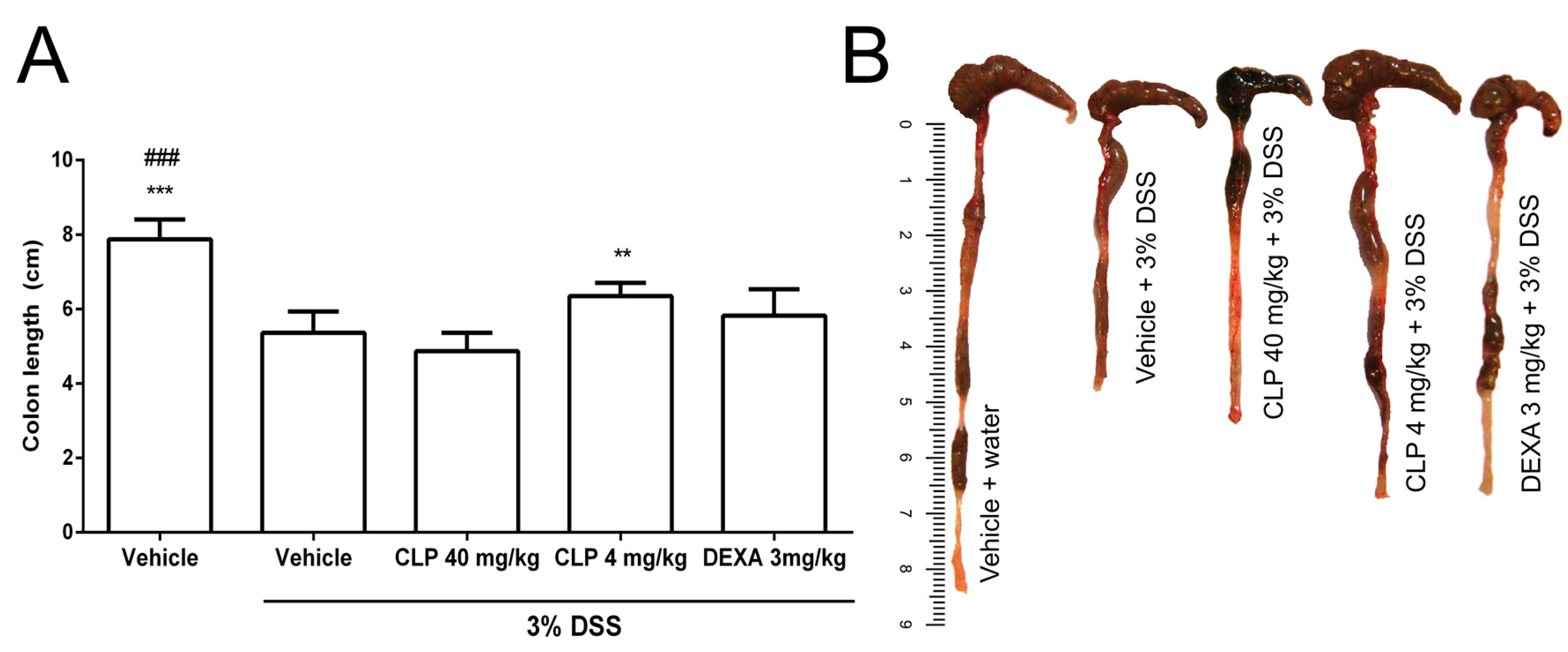
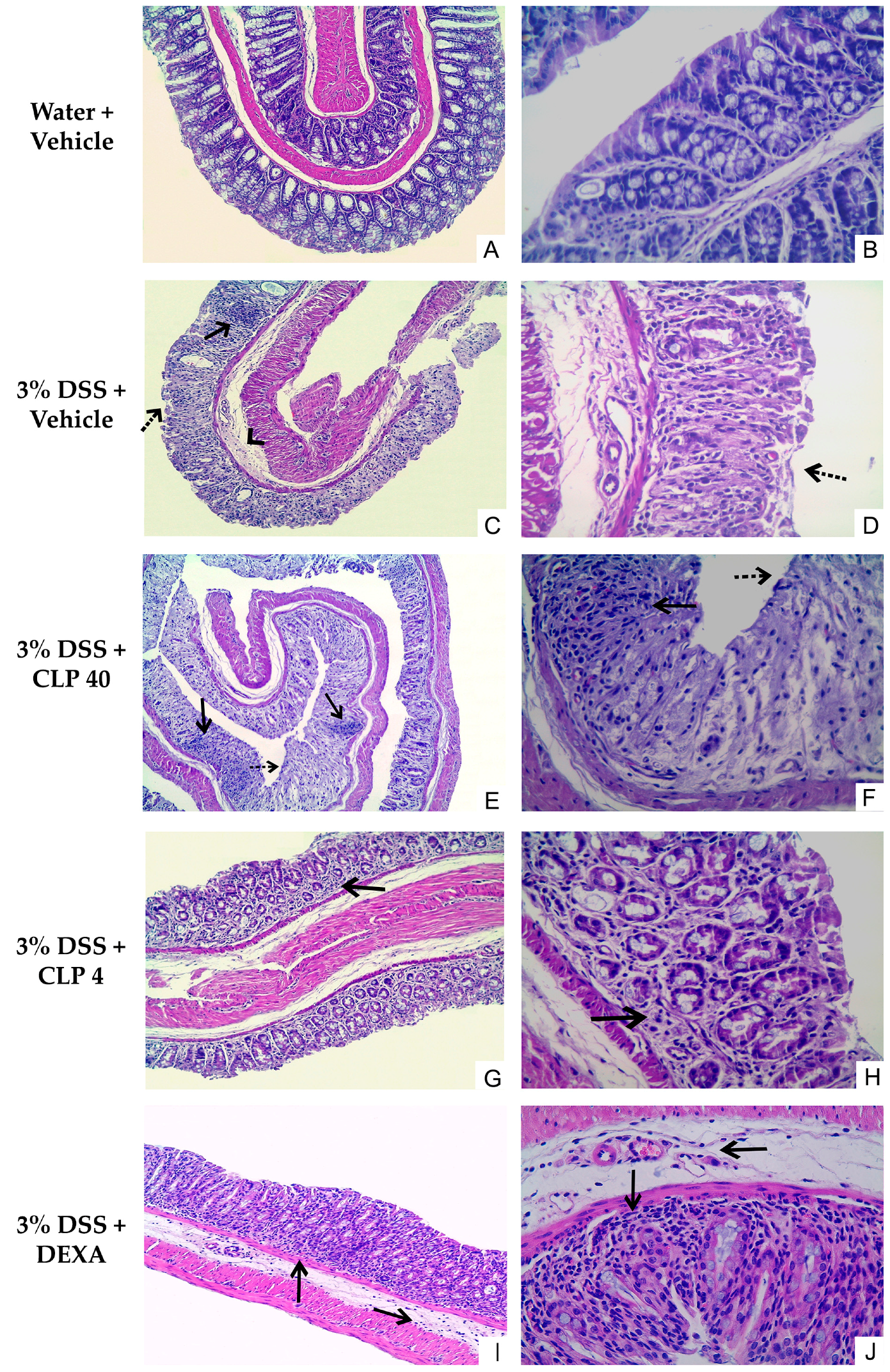
2.3. The Treatment of Mice with Caulerpin Attenuates the Colon Tissue Damage Induced by DSS
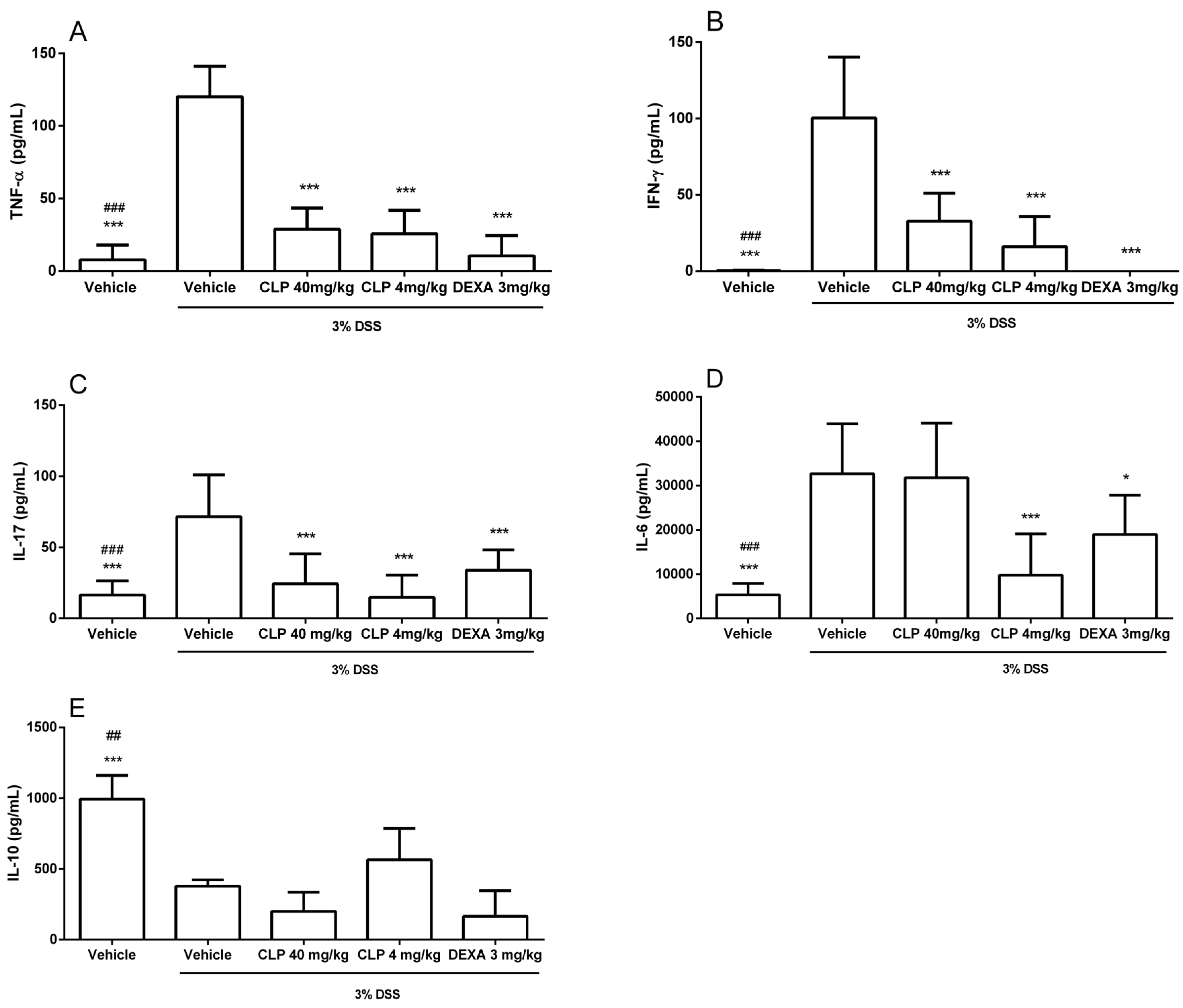
2.4. The Treatment of Mice with Caulerpin Decreases the Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in DSS Colitis Model
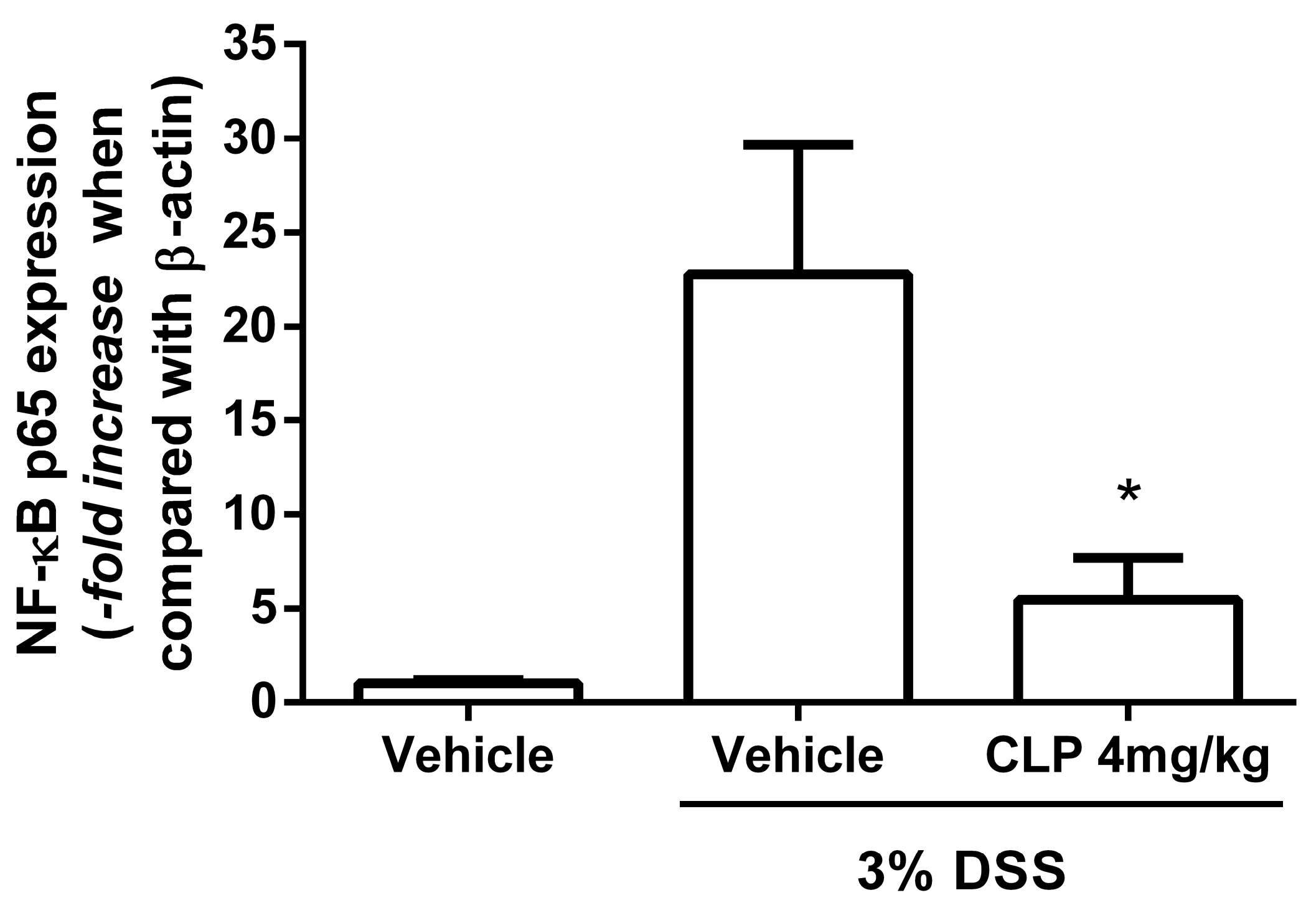
2.5. The Treatment of Mice with Caulerpin Decreases the Expression of NFkB p65 in DSS Colitis Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Extraction and Purification of Caulerpin (CLP)
4.2. NMR Spectra of Caulerpin
4.3. Animals
4.4. Treatments
4.5. Peritonitis Model
4.6. Colitis Model
4.7. Expression Analysis of NF-κB p65 Subunit
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallo, R.L.; Hooper, L.V. Epithelial Antimicrobial Defence of the Skin and Intestine. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, C.L.; Elson, C.O.; Hatton, R.D.; Weaver, C.T. Reciprocal interactions of the intestinal microbiota and immune system. Nature 2012, 489, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.M.; Emerick, A.P.; Soares, E.G. Aspectos epidemiológicos das doenças intestinais inflamatórias na macrorregião de saúde leste do Estado de Minas Gerais. Ciencia Saude Coletiva 2010, 15, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matricon, J.; Barnich, N.; Ardid, D. Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Self Nonself 2010, 1, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risques, R.A.; Lai, L.A.; Himmetoglu, C.; Ebaee, A.; Li, L.; Feng, Z.; Bronner, M.P.; Al-Lahham, B.; Kowdley, K.V.; Lindor, K.D.; et al. Ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer arises in a field of short telomeres, senescence, and inflammation. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halaweish, I.; Alam, H.B. Surgical Management of Severe Colitis in the Intensive Care Unit. J. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 30, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larmonier, C.B.; Midura-Kiela, M.T.; Ramalingam, R.; Laubitz, D.; Janikashvili, N.; Larmonier, N.; Ghishan, F.K.; Kiela, P.R. Modulation of neutrophil motility by curcumin: Implications for inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, A.; Zoccali, M.; Costa, S.; Troci, A.; Contessini-Avesani, E.; Fichera, A. Surgical treatment of ulcerative colitis in the biologic therapy era. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornbluth, A.; Sachar, D.B. Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults: American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneethan, U.; Shen, B. Pros and cons of medical management of ulcerative colitis. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2010, 23, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanò, V.; Attanzio, A.; Cascioferro, S.; Carbone, A.; Montalbano, A.; Barraja, P.; Tesoriere, L.; Cirrincione, G.; Diana, P.; Parrino, B. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of New Thiazole Nortopsentin Analogs. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.B.; Rudd, D.; Smith, J.; Kotiw, M.; Mouatt, P.; Seymour, L.M.; Liu, L.; Benkendorff, K. Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Structure-Activity Relationships of Brominated Indoles from a Marine Mollusc. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Matta, C.B.; de Souza, E.T.; de Queiroz, A.C.; de Lira, D.P.; de Araújo, M.V.; Cavalcante-Silva, L.H.; de Miranda, G.E.; de Araújo-Júnior, J.X.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Santos, B.V.O.; et al. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity from algae of the genus Caulerpa. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical structures and bioactivities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. Mar. Drug 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, P.; Quintana, S.E.; Reglero, G.; Fornari, T.; García-Risco, M.R. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) as an Innovative Green Technology for the Effective Enrichment of Galician Algae Extracts with High Quality Fatty Acids and Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, S.; Gholampour, H.; Farzadinia, P.; Daneshi, A.; Ramavandi, B.; Moazzeni, A.; Keshavarz, M.; Bargahi, A. Anti-diabetic effects of Sargassum oligocystum on Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornara, L.; Pastorino, G.; Borghesi, B.; Salis, A.; Clericuzio, M.; Marchetti, C.; Damonte, G.; Burlando, B. Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile Ethanolic Extract Modulates Cell Activities with Skin Health Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, V.P. Estudo Fitoquímico com fins Farmacológicos da alga Betônica Caulerpa Racemosa. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Paraíba, João Pessoa, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Guven, K.C.; Percot, A.; Sezik, E. Alkaloids in marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, E.T.; de Lira, D.P.; de Queiroz, A.C.; de Aquino, A.B.; Mella, E.A.; Lorenzo, V.P.; de Miranda, G.E.; de Araújo-Júnior, J.X.; Chaves, M.C.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; et al. The antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory actives of Caulerpin, a bisindole alkaloid, isoleted from seaweeds of the genus Caulerpa. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, N.R.P.V.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Villaça, R.C.; Ferreira, W.; Pinto, A.M.; Teixeira, V.L.; Cirne-Santos, C.; Paixão, I.C.N.P.; Giongo, V. Caulerpin as a potential antiviral drug against herpes simplex virus type 1. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2012, 22, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chay, C.I.C.; Cansino, R.G.; Pinzón, C.I.E.; Torres-Ochoa, R.O.; Martínez, R. Synthesis and Anti-Tuberculosis Activity of the Marine Natural Product Caulerpin and Its Analogues. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; Dong, M.; Wu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Kong, Z.; Dai, X.; Xu, B. Metabolic reprogramming and AMPKα1 pathway activation by caulerpin in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante-Silva, L.H.; Correia, A.C.C.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; da Silva, B.A.; Santos, B.V.O.; de Lira, D.P.; Sousa, J.C.; de Miranda, G.E.; Cavalcante, F.A.; Alexandre-Moreira, M.S. Spasmolytic Effect of Caulerpine Involves Blockade of Ca2+ Influx on Guinea Pig Ileum. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Mao, A.; Yu, Z.; He, K. Anti-endotoxin and anti-inflammatory effects of Chinese herbal medicinal alkaloid ingredients in vivo. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Koziol, A.; Plytycz, B.; Arnold, B. Inflammatory macrophages, and not only neutrophils, die by apoptosis during acute peritonitis. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitencourt, M.A.; Dantas, G.R.; Lira, D.P.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; de Miranda, G.E.; Santos, B.; Souto, J.T. Aqueous and methanolic extracts of Caulerpa mexicana suppress cell migration and ear edema induced by inflammatory agents. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vowinkel, T.; Kalogeris, T.J.; Mori, M.; Krieglstein, C.F.; Granger, D.N. Impact of dextran sulfate sodium load on the severity of inflammation in experimental colitis. Digest. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melgar, S.; Karlsson, A.; Michaelsson, E. Acute colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium progresses to chronicity in C57BL/6 but not in BALB/c mice: Correlation between symptoms and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G1328–G1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitencourt, M.A.O.; Silva, H.M.D.; Abílio, G.M.F.; Miranda, G.E.C.; Moura, A.M.A.; de Araújo-Júnior, J.X.; Silveira, E.J.D.; Santos, B.V.O.; Souto, J.T. Anti-inflammatory effects of methanolic extract of green algae Caulerpa mexicana in a murine model of ulcerative colitis. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2015, 25, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.; He, X.; Zeng, Y.J.; Dai, S.S. Sinomenine protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice via adenosineA(2A) receptor signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSharari, S.D.; Akbarali, H.I.; Abdullah, R.A.; Shahab, O.; Auttachoat, W.; Ferreira, G.A.; White, K.L.; Lichtman, A.H.; Cabral, G.A.; Damai, M.I. Novel Insights on the Effect of Nicotine in a Murine Colitis Model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 344, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredin, M.F.; Vidal, A.; Utkovic, H.; Götlind, Y.Y.; Willén, R.; Jansson, L.; Hultgren Hörnguist, E.; Melgar, S. The application and relevance of ex vivo culture systems for assessment of IBD treatment in murine models of colitis. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 58, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meeteren, M.E.; Meijssen, M.A.C.; Zulstra, F.J. The effect of dexamethasone treatment on murine colitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, C.; Qu, L.; Ding, X.; Cao, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, G. Therapeutic effects of triptolide via the inhibition of IL-1β expression in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.P.; Li, J.H.; He, S.Y.; Chen, O.; Shi, L. Effect of curcumin on p38MAPK expression in DSS-induced murine ulcerative colitis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 3450–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegmund, B.; Rieder, F.; Albrich, S.; Wolf, K.; Bidlingmaier, C.; Firestein, G.S.; Boyle, D.; Lehr, H.A.; Loher, F.; Hartmann, G.; et al. Adenosine kinase inhibitor GP515 improves experimental colitis in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 296, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Mathis, J.M.; Jennings, M.H.; Jordan, P.; Wang, Y.; Ando, T.; Joh, T.; Alexander, J.S. Reversal of experimental colitis disease activity in mice following administration of an adenoviral IL-10 vector. J. Inflamm. 2005, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocón, B.; Aranda, C.J.; Gámez-Belmonte, R.; Suárez, M.D.; Zarzuelo, A.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; Sánchez de Medina, F. The glucocorticoid budesonide has protective and deleterious effects in experimental colitis in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 116, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.C.; Song, L.J.; Deng, H.Z. Protective Effect of Total Alkaloids of Sophora Alopecuroides on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Chronic Colitis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2011, 17, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yin, R.; Cong, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, E.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, N. Oxymatrine lightened the inflammatory response of LPS-induced mastitis in mice through affecting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Inflammation 2014, 37, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müzes, G.; Molnár, B.; Tulassay, Z.; Sipos, F. Changes of the cytokine profile in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5848–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Gaboriau-Routhiau, V. The immune system and the gut microbiota: Friends or foes? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsianos, E.V.; Katsanos, K. Do we really understand what the immunological disturbances in inflammatory bowel disease mean? World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alex, P.; Zachos, N.C.; Nguyen, T.; Gonzales, L.; Chen, T.E.; Conklin, L.S.; Centola, M.; Li, X. Distinct cytokine patterns identified from multiplex profiles of murine DSS and TNBS-induced colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boismenu, R.; Chen, Y. Insights from mouse models of colitis. J. Leuk. Biol. 2000, 67, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Kolachala, V.; Dalmasso, G.; Nguyen, H.; Laroui, H.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Merlin, D. Temporal and spatial analysis of clinical and molecular parameters in dextran sodium sulfate induced colitis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennick, D.M.; Fort, M.M. Lessons from genetically engineered animal models. XII. IL-10-deficient (IL-10(-/-) mice and intestinal inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 278, G829–G833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Camarillo, G.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K. Immunoregulatory Pathways Involved in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2188–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raddatz, D.; Bockemuül, M.; Ramadori, G. Quantitative measurement of cytokine mRNA in inflammatory bowel disease: Relation to clinical and endoscopic activity and outcome. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 17, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, K.L.; Zheng, L.B.; Kanazawa, Y.; Shih, D.Q. Immunopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Shi, T.; Zhong, C.; Wang, Y.; Chang, M.; Liu, X. IL-10 and IL-10 Receptor Mutations in Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Res. 2017, 10, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.C.; He, S.H. IL-10 and its related cytokines for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.M. Iridoid glycosides fraction of Folium syringae leaves modulates NF-κB signal pathway and intestinal epithelial cells apoptosis in experimental colitis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, C.C.; Drygiannakis, I.; Naganuma, M.; Feldman, S.; Bekiaris, V.; Linden, J.; Ware, C.F.; Ernst, P.B. Extracellular adenosine regulates colitis through effects on lymphoid and nonlymphoid cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G338–G346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.C.; Bernstein, C.N.; Khan, K.J.; Abreu, M.T.; Marshall, J.K.; Talley, N.J.; Moayyedi, P. Glucocorticosteroid therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Seljelid, R.; Plytycz, B. Role of mast cells in zymosan-induced peritoneal inflammation in Balb/c and mast cell-deficient WBB6F1 mice. J. Leuk. Biol. 2001, 69, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuesco, D.; Comalada, M.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Nieto, A.; Lorente, M.D.; Concha, A.; Zarzuelo, A.; Gálvez, J. The intestinal anti-inflammatory effect of quercitrin is associated with an inhibition in iNOS expression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittem, C.G.; Williams, A.D.; Williams, C.S. Murine Colitis modeling using Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS). J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Score | Weight Loss (%) | Rectal Bleeding | Stool Consistency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0–2 | Absent | Well formed |
| 1 | >2–5 | - | - |
| 2 | >5–10 | Visible | Softened |
| 3 | >10–15 | - | - |
| 4 | >15–20 | Intense bleeding | Diarrheic |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucena, A.M.M.; Souza, C.R.M.; Jales, J.T.; Guedes, P.M.M.; De Miranda, G.E.C.; De Moura, A.M.A.; Araújo-Júnior, J.X.; Nascimento, G.J.; Scortecci, K.C.; Santos, B.V.O.; et al. The Bisindole Alkaloid Caulerpin, from Seaweeds of the Genus Caulerpa, Attenuated Colon Damage in Murine Colitis Model. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090318
Lucena AMM, Souza CRM, Jales JT, Guedes PMM, De Miranda GEC, De Moura AMA, Araújo-Júnior JX, Nascimento GJ, Scortecci KC, Santos BVO, et al. The Bisindole Alkaloid Caulerpin, from Seaweeds of the Genus Caulerpa, Attenuated Colon Damage in Murine Colitis Model. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(9):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090318
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucena, Alessandra M. M., Cássio R. M. Souza, Jéssica T. Jales, Paulo M. M. Guedes, George E. C. De Miranda, Adolpho M. A. De Moura, João X. Araújo-Júnior, George J. Nascimento, Kátia C. Scortecci, Barbara V. O. Santos, and et al. 2018. "The Bisindole Alkaloid Caulerpin, from Seaweeds of the Genus Caulerpa, Attenuated Colon Damage in Murine Colitis Model" Marine Drugs 16, no. 9: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090318
APA StyleLucena, A. M. M., Souza, C. R. M., Jales, J. T., Guedes, P. M. M., De Miranda, G. E. C., De Moura, A. M. A., Araújo-Júnior, J. X., Nascimento, G. J., Scortecci, K. C., Santos, B. V. O., & Souto, J. T. (2018). The Bisindole Alkaloid Caulerpin, from Seaweeds of the Genus Caulerpa, Attenuated Colon Damage in Murine Colitis Model. Marine Drugs, 16(9), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090318