Abstract
Three new polyoxygenated steroids, michosterols A–C (1–3), and four known compounds (4–7) were isolated from the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extract of the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae, collected off the coast of Taitung. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic analyses and comparison of the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data with related steroids. The cytotoxicity of compounds 1–3 against the proliferation of a limited panel of cancer cell lines was assayed. Compound 1 was found to display moderate cytotoxicity against adenocarcinomic human alveolar basal epithelial (A549) cancer cells. It also exhibited potent anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing superoxide anion generation and elastase release in N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB)-stimulated human neutrophils. Furthermore, 3 could effectively inhibit elastase release, as well.
1. Introduction
Previous chemical investigations on the octocorals of the genus Lobophytum have led to the isolation of structurally unique steroids [1,2,3,4,5,6], some of which have been shown to exhibit cytotoxic [2,3,5,6] and anti-inflammatory [2,5] activities. For the purpose of searching for bioactive compounds, we have previously investigated the chemical constituents of soft corals of the genus Lobophytum growing in Taiwanese waters, which resulted in the discovery of a series of bioactive natural products [6,7,8,9,10,11]. Previous investigations also have shown that the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae could produce bioactive cembranolides with cytotoxicity towards cancer cell lines [12,13,14]. With the aim of discovering more bioactive marine natural products for new drug development in the future, we again investigated the chemical constituents of a Formosan soft coral L. michaelae. From this study, we have isolated three new polyoxygenated steroids, michosterols A–C (1–3), together with four known compounds: brassicasterol (4) [15], 24S-methylcholesterol (5) [16], 23-demethylgorgosterol (23-demethylgorgost-5-en-3β-ol) (6) [17,18,19] and gorgosterol (7) [20]. Extensive spectroscopic analyses, including mass spectrometry, 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy (Supplementary Materials, Figures S1–S26), and comparison of spectroscopic data of the new compounds with those of the previously reported structurally-related compounds have allowed us to establish the structures of 1–3. Compound 1 possesses a double bond between C-16 and C-17 and an unusual side-chain with a hydroperoxyl group at C-20, whereas 2 has this group at C-16 and an uncommon olefinic structure at C-17 and C-20. The in vitro cytotoxicity of 1–3 against three cancer cell lines, adenocarcinomic human alveolar basal epithelial (A549), human colorectal adenocarcinoma (DLD-1) and human prostatic carcinoma (LNCap), was evaluated. The abilities of compounds 1–3 to inhibit superoxide anion generation and elastase release in N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB)-stimulated human neutrophils was also assayed.
2. Results and Discussion
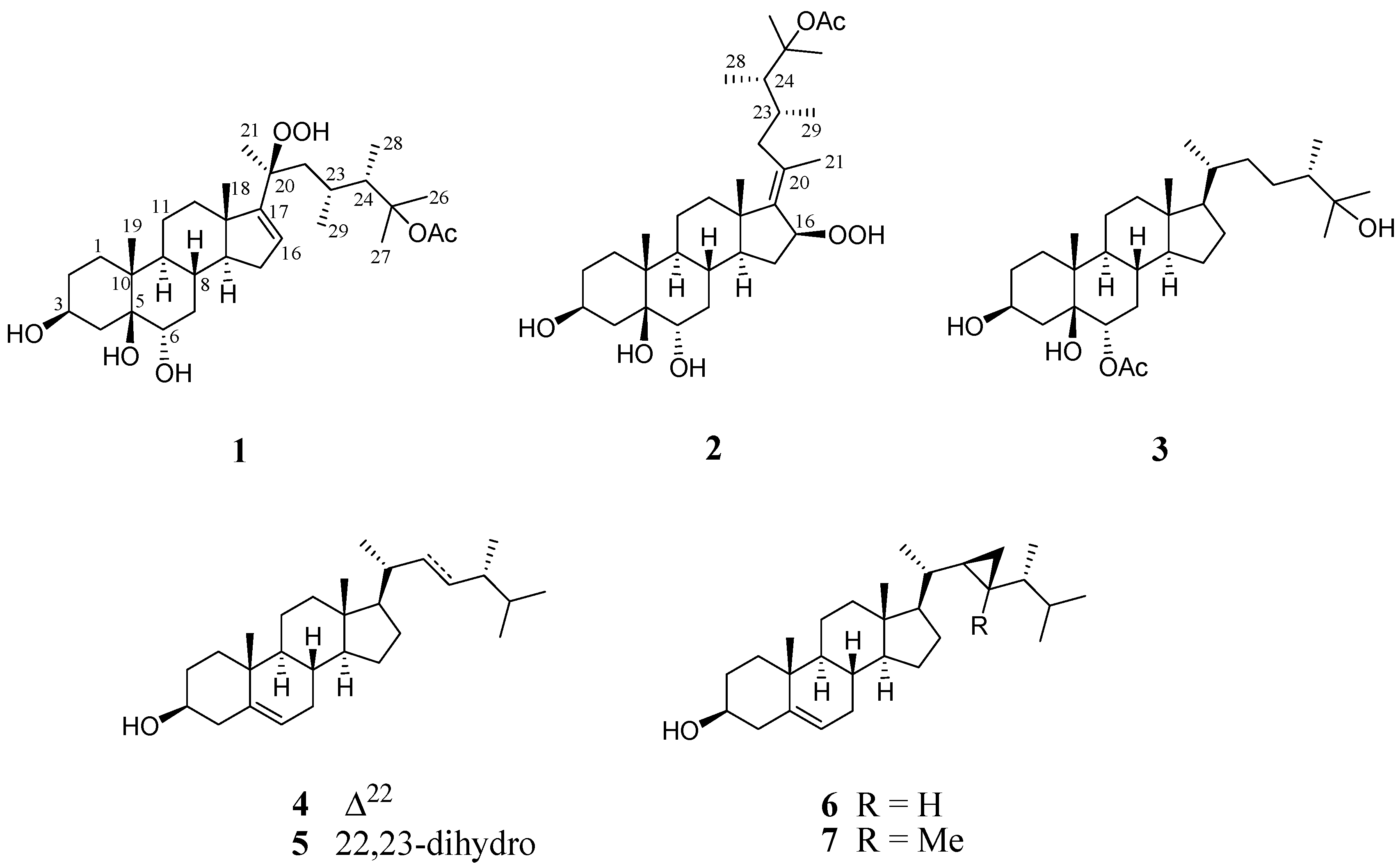
The frozen bodies of L. michaelae were sliced and exhaustively extracted with ethyl acetate (EtOAc). The EtOAc extract was separated by repeated gravity column chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to afford three new and four known triterpenoids steroids 1–7 (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1–7.
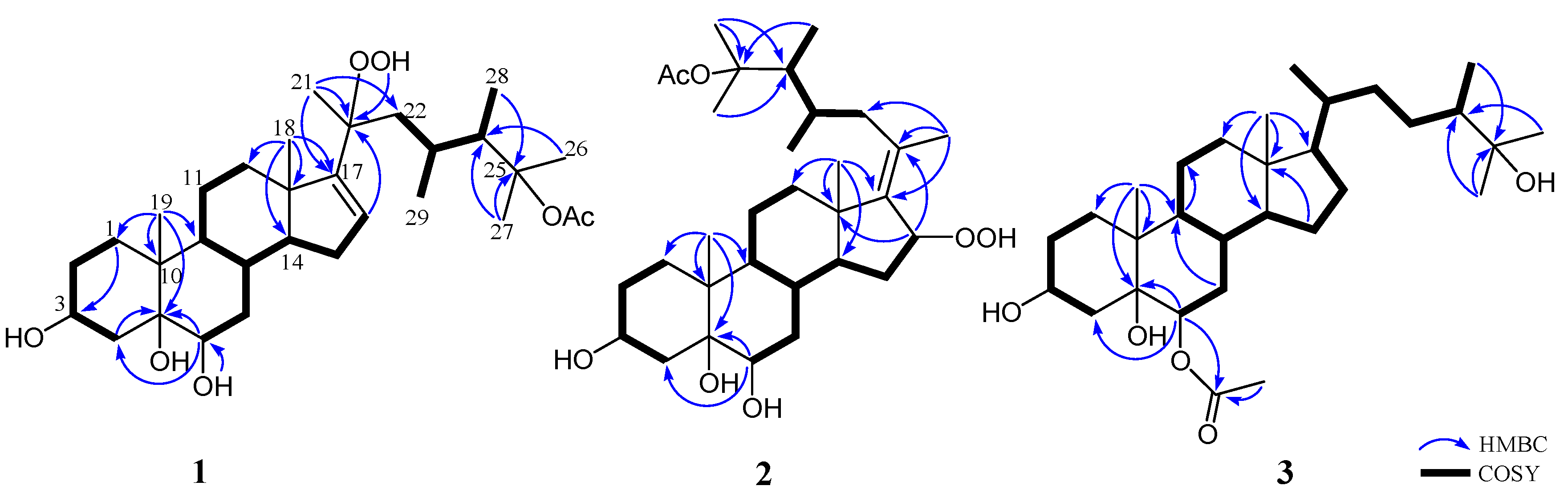
The molecular formula of 1, an amorphous solid, was determined as C31H52O7 based on the [M + Na]+ ion peak obtained by high-resolution electron spray ionisation mass spectrometry (HRESIMS), implying six degrees of unsaturation. The 13C NMR spectrum showed 31 carbon signals, including an ester carbonyl (δC 171.9, C), a double bond (δC 157.6, C and 127.0, CH), two oxymethines (δC 71.8 and 67.7, each CH) and three oxygenated sp3 quaternary carbons (δC 87.2, 85.6, and 78.1) (Table 1). The 1H NMR spectrum in conjunction with the heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) spectrum revealed the presence of eight methyl groups (δH 2.03 (3H, s), 1.50 (3H, s), 1.41 (3H, s), 1.31 (3H, s), 0.96 (6H, s), 0.93 (3H, d, J = 6.8 Hz) and 0.88 (3H, d, J = 7.2 Hz)), an olefinic methine proton (δH 5.70 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz)) and a hydroperoxy group signal at δH 8.06 (br s). Thus, the remaining four unsaturations of 1 corresponded to a tetracyclic skeleton. In the correlation spectroscopy (COSY) spectrum, it was possible to identify three different structural units extending from C-1 to C-4; C-6 to both C-12 and C-16 through C-8; and C-22 to both C-28 and C-29 through C-23 (Figure 2). From the heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation (HMBC) spectrum, the correlations of H3-19 to C-1, C-5, C-9 and C-10, H3-18 to C-12, C-13, C-14 and C-17, H-6 to C-4 and C-5, H-16 to C-20, H3-21 to C-17, C-20 and C-22, both H3-26 and H3-27 to C-24 and H3-28 to C-25 permitted the establishment of the carbon skeleton of a 23,24-dimethycholestane (Figure 2). The hydroperoxy group positioned at C-20 was confirmed from the HMBC correlation of the hydroperoxy proton δH 8.06 (br s) to the oxygenated carbon at δC 85.6; hence, the acetoxy group was positioned at C-25 (δC 87.2). The planar structure of 1 was thus established unambiguously.

Table 1.
13C and 1H NMR data of compounds 1–3 in CDCl3.
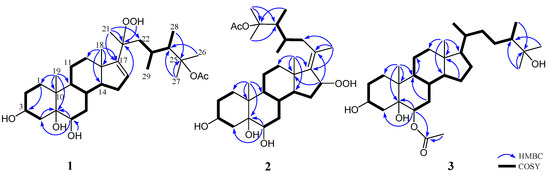
Figure 2.
Selected COSY and HMBC correlations of 1–3.
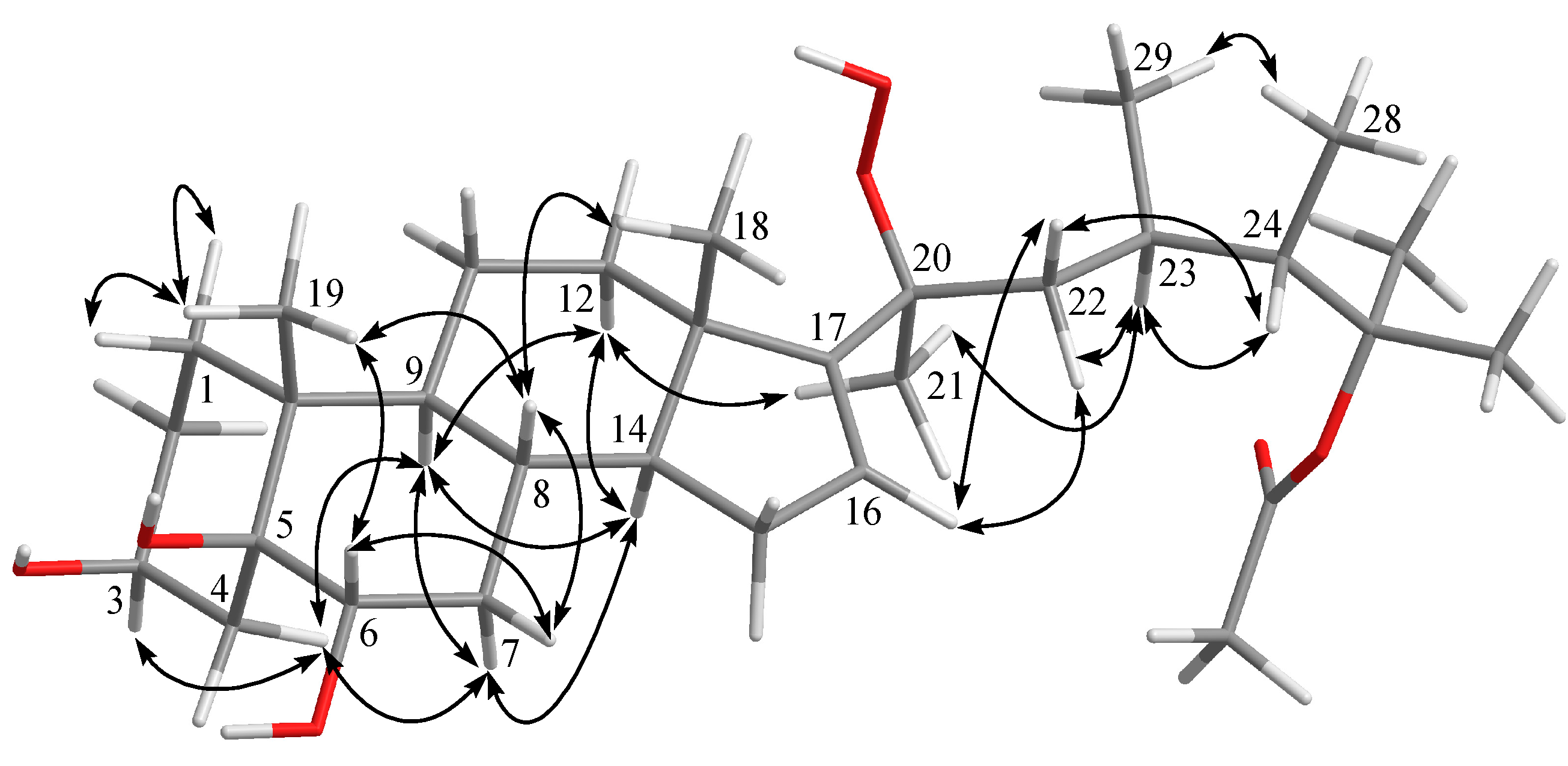
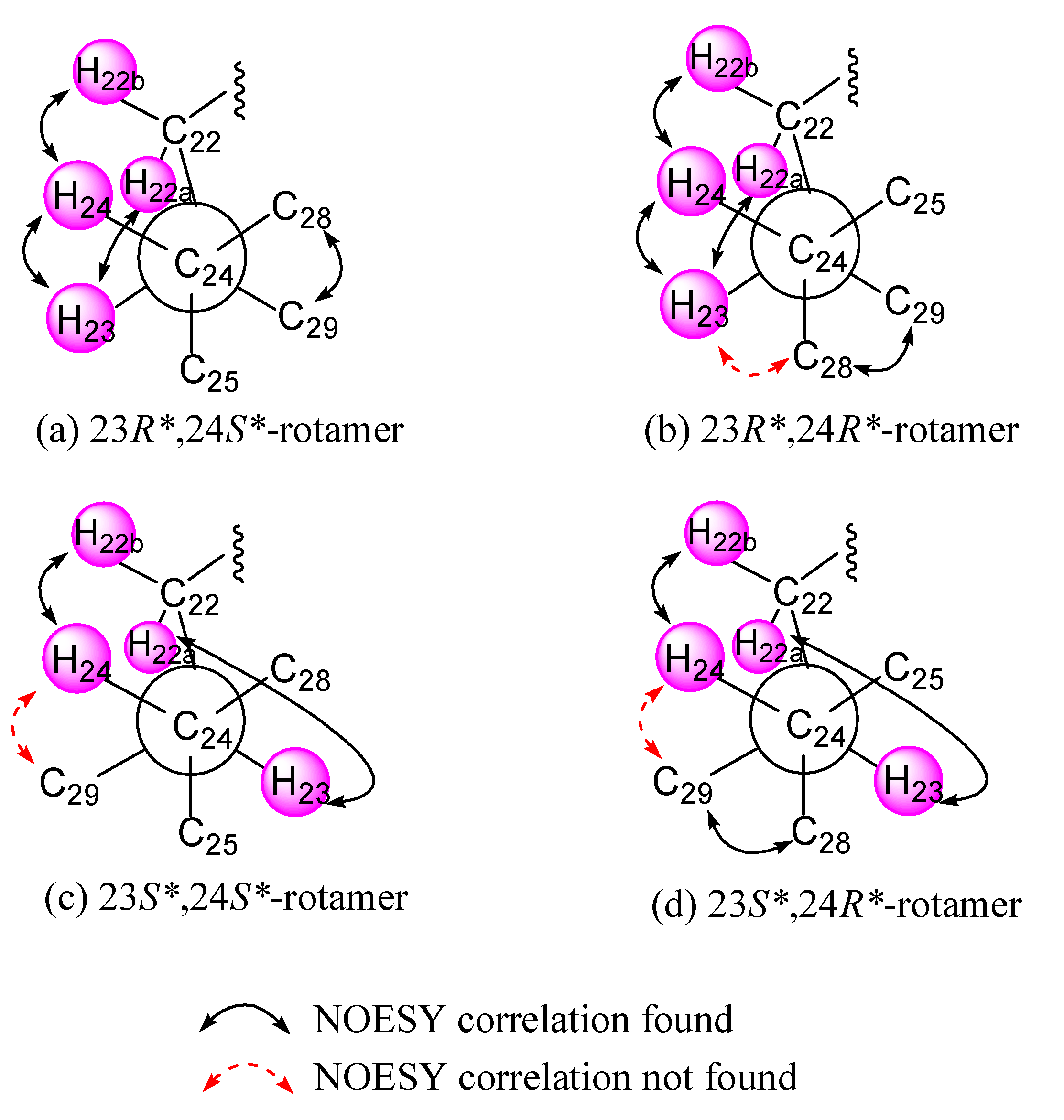
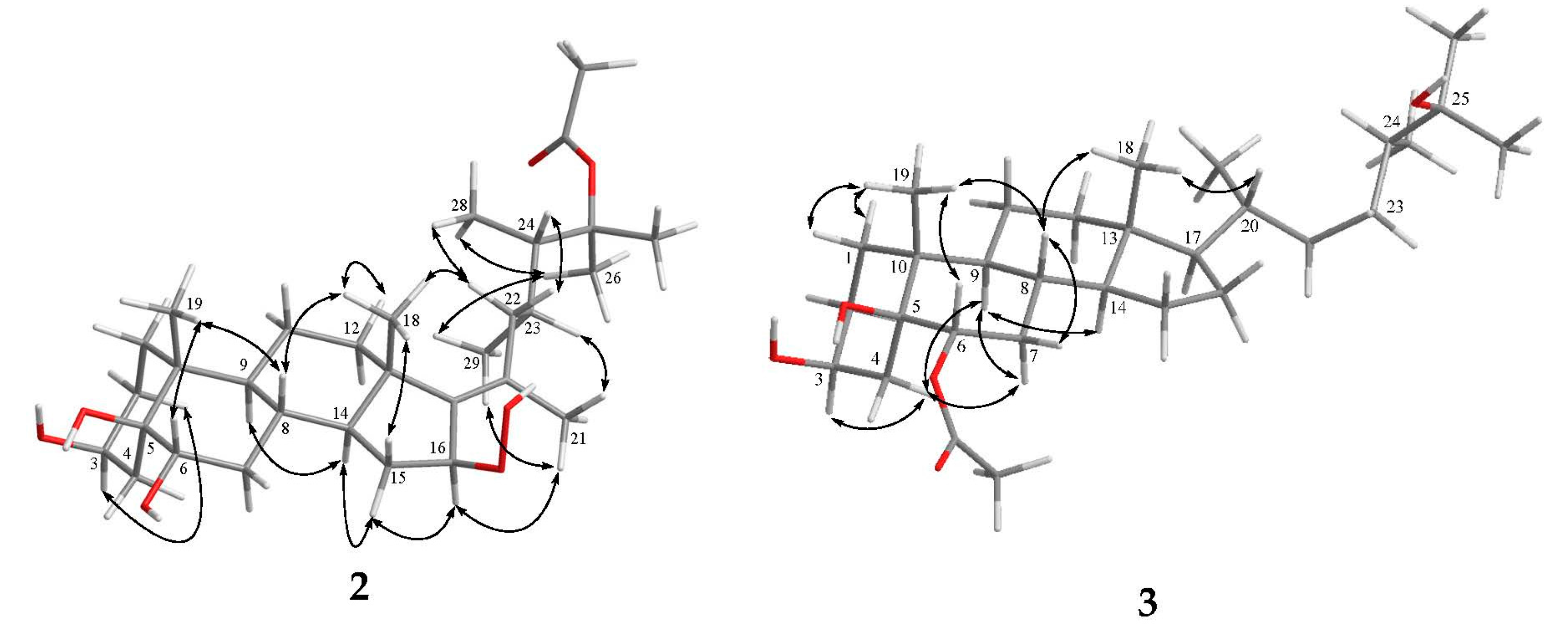
The relative configuration of 1 was deduced by interpretation of the nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) correlations (Figure 3), analysis of 3JH-H values and comparison of carbon chemical shifts. As depicted in Figure 3, it was found that the NOE interactions displayed by both H3-18 and H3-19 with H-8 and H3-19 with H-6, while one of the methylene protons at C-7 (δH 1.85, m), showed NOESY correlations with both of H-6 and H-8. Therefore, assuming the β-orientation of H3-19, H-6, H-7 at δH 1.85, H-8 and H3-18 should be positioned on the β-face, while the other H-7 (δH 1.09, q, J = 12.0 Hz) was assigned as H-7α. Moreover, H-14 showed NOESY correlations with H-7α, H-9 and one proton of H2-12 (δH 2.06, m); whereas the latter proton was NOE correlated with H3-21. This reflects theα-orientations of H-9, H-14 and H3-21 and, consequently, the β-orientation of the hydroperoxy group at C-20 of the side chain. Further, H3-21 exhibited NOESY correlation with H-23; and H-23 expressed NOE interaction with H-24 as did H3-28 with H3-29, respectively, while no NOE interaction was found for H-23 with H3-28 and for H-24 with H3-29. Thus, the 23R*, 24S* relative configurations were revealed (Figure 3) and further supported by the comparison of the NOE interactions in 1 with those anticipated in its other three 23,24-rotamers (Figure 4). Finally, the configurations of C-3, C-5 andC-6 were elucidated by comparison of the 1H NMR chemical shifts and coupling constants of H-3 and H-6 with those of related steroids (Table 2). The δ and J values of H-3 (δH 4.24, s) and H-6 (δH 3.74–3.81, dd, J = 12.0, 4.8 Hz) of known compound 5β-cholestane-3β,5,6α-triol [21,22] were found to be similar to the corresponding H-3 (δH 4.27, br s) and H-6 (δH 3.82, dd, J = 12.0, 4.8 Hz) of 1 (Table 2). Consequently, the relative configuration of 1 was determined unequivocally. Since it has been known for quite a long time that both H3-18 and H3-19 should be positioned on the β-face for natural steroids, thus the absolute configuration of 1 should be the same as shown in Structure 1.
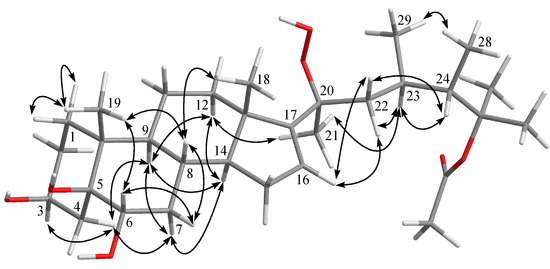
Figure 3.
Selected NOESY correlations of compound 1.
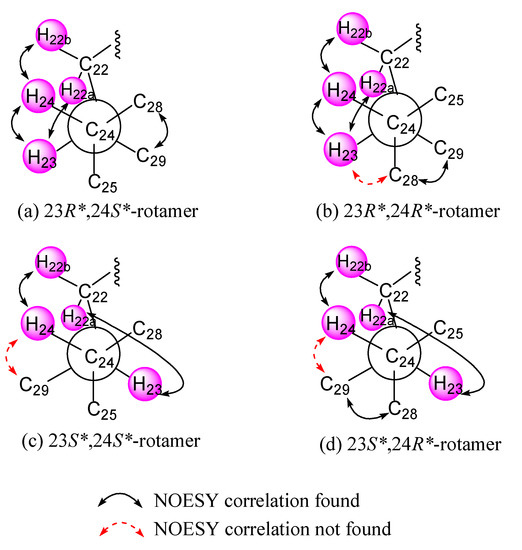
Figure 4.
(a–d) C-24/C-25 rotamers of compound 1.

Table 2.
The 1H NMR chemical shifts and coupling constants of the H-3 and H-6 of compound 1 and the related steroids [22].
Analysis of the 13C NMR and HRESIMS spectral data of 2 revealed that it has the same molecular formula as that of 1. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of 2 are similar to those of 1, and the molecular skeleton of 2 was further established by HMBC correlations from H3-21 to C-17 (δC 143.6, C), C-20 (δC 132.8, C) and C-22 (δC 41.2, CH2); H-16 (δH 4.96, dd, J = 7.5, 7.5 Hz) to C-13 (δC 44.1, C) and C-20; and the COSY correlation between H2-15 and H-16 (Figure 2). The above results showed that an olefinic proton signal (δH 5.70, d, J = 2.0 Hz) in 1 was replaced by an oxymethine proton (δH 4.96, dd, J = 7.5, 7.5 Hz), which also showed correlation with the signal of C-16 (δC 86.1) in the HSQC spectrum of 2. Further, a proton signal appearing at δH 8.91 (br s) was found not to be correlated with any carbon signal in the HSQC spectrum. Thus, this should be the signal of a hydroperoxy group substituted at C-16, as confirmed by the downfield shift of this carbon in 2 in comparison with the chemical shifts of the corresponding carbons of two 16-hydroxy analogues, δC 72.3 for faccisteroid B [23] and 71.8 for hippuristerone L [24]. The comparison of the 1H NMR chemical shifts and the analysis of NOESY correlations of 2 revealed the same configurations at C-3, C-5, C-6, C-8, C-9, C-10, C-13, C-14, C-23 and C-24 as those of 1. Further, NOESY correlations from H3-18 to H-8, H-15β (δH 1.69, m) and H-22β (δH 1.76 m) were observed, while H-15α (δH 2.08 m) was correlated with H-14 and H-16 and H-16 with H3-21, suggesting a β-orientation of hydroperoxy group at C-16 and the E geometry of Δ17(20) in 2. On the basis of the above findings and the careful analysis of NOESY correlations (Figure 5), the structure of 2 was determined as illustrated in Figure 1.
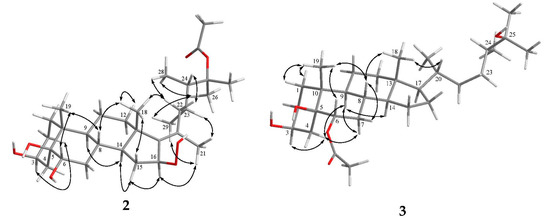
Figure 5.
Selected NOESY correlations of compounds 2 and 3.
Michosterol C (3) was isolated as a white powder and has a molecular formula of C30H52O5 by the analysis of HRESIMS. The IR spectrum of 3 also revealed the presence of hydroxy (3416 cm−1) and ester carbonyl (1718 cm−1) groups. Comparison of the 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 1) of compounds 2 and 3 pointed out that the A–C rings of 3 were similar to those of 2, with the exception of signals assigned to C-6, where the hydroxymethine (δH 3.80, dd, J = 12.0, 5.0 Hz; δC 71.7) in 2 was replaced by an acetoxymethine (δH 4.97, dd, J = 12.0, 4.8 Hz; δC 75.8) in 3. The acetoxy group substitution at C-6 was determined by the HMBC correlations of H-6 (δH 4.97) with C-4 (δC 31.1, CH2), C-5 (δC 77.4, C) and an acetoxy carbonyl carbon (δC 171.9, C), and further confirmed by the COSY spectrum (Figure 2). Furthermore, the signal of a hydroperoxy-bearing methine group at C-16 (δH 4.96, dd, J = 7.5, 7.5 Hz; δC 86.1) in 2 was replaced by signals of a methylene group (H2-16:δH 1.28 m and 1.84 m; δC 28.0). Comparison of the NMR data of 3, measured in CD3OD (see the Experimental Section) with those of (24S)-ergostane-6-acetate-3β,5α,6β,25-tetraol [21] indicated that the planar structure and the configurations of the side chain of both compounds are the same. Furthermore, the configurations of C-3, C-5 and C-6 were elucidated by comparison of the 1H NMR coupling constants with the related steroids (Table 1 and Table 2). The J values of H-3 (δH 4.11, br s) and H-6 (δH 4.97, dd, J = 12.0, 4.8 Hz) of compound 3 were identical to the corresponding H-3 (δH 4.27, br s) and H-6 (δH 3.82, dd, J = 12.0, 4.8 Hz) of 1. In addition, NOESY correlations of H3-19 with both H-6 and H-8, H-8 with H-7β (δH 1.81, m), H-7α (δH 1.07, m) with H-4α (δH 1.92, m) and H-9 and H-4α with H-3 confirmed the α-orientations of the H-3 and 6-OAc group and the β-orientation of the 5-OH group (Figure 5). Thus, the structure of 3 was established as shown in Figure 1.
The cytotoxicity of the isolates 1–3 against A549, DLD-1 and LNCap cancer cells was assayed. The results showed that only compound 1 exhibited a moderate cytotoxicity effect against the A549 cell line with an IC50 value of 14.9 ± 5.7 μg/mL. The other compounds were found not to be cytotoxic against the above cancer cell lines (IC50’s > 20 μg/mL).
The anti-inflammatory activities of the new compounds 1–3 on pro-inflammatory responses were evaluated by measuring their ability to suppress fMLP/CB-induced superoxide anion (O2−•) generation and elastase release in human neutrophils. From the results (Table 3), compound 1 showed significant inhibitory effects against superoxide anion generation and elastase release in fMLP/CB-stimulated cells at the 10 μM concentration tested, with the IC50 values being 7.1 ± 0.3 μM and 4.5 ± 0.9 μM, respectively. Further, compound 3 exhibited stronger inhibitory activities against elastase release, with the IC50 values of 0.9 ± 0.1 μM.

Table 3.
Inhibitory effects of compounds 1–3 on superoxide anion generation and elastase release in N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB)-induced human neutrophils at 10 μM.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
The specific optical rotation values and IR spectral absorptions were recorded on a JASCO P-1020 digital polarimeter (JASCO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and a JASCO J-815 spectrophotometer (JASCO Corporation), respectively. A Varian 400MR FT-NMR or Varian Unity INOVA-500 FT-NMR (Varian Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) was applied to record the 1H and 13C NMR spectra with the chemical shifts shown as ppm referenced to the solvent residue of CDCl3 (δH 7.26 ppm and δC 77.0 ppm) and CD3OD (δH 3.31 ppm and δC 49.0 ppm), respectively. A Bruker APEX II mass spectrometer equipped with an ESI ionization source (Bruker, Bremen, Germany) was used for acquiring high-resolution mass data. The HPLC system used in this study was composed of a Hitachi L-2455 instrument (Hitachi Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a reversed-phase (RP-18) column (ODS-3, 5 μm, 250 × 20 mm, Sciences Inc., Tokyo, Japan).
3.2. Animal Material
The collection of the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae Tixier-Durivault (1956) was performed off the coast of Jihui Fishing Port, Taitung County, Taiwan, in March 2013. The organism was stored in a freezer at −20 °C until extraction. Prof. C.-F. Dai performed the species identification. A voucher specimen (JiH-201314) of this soft coral has been deposited at National Sun Yat-sen University.
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The frozen bodies of L. michaelae (3.2 kg, wet wt) were sliced and exhaustively extracted with EtOAc (3 × 4 L). The EtOAc extract (5.95 g) was chromatographed over silica gel by column chromatography and eluting with EtOAc in n-hexane (0–100%, stepwise), followed by acetone in EtOAc (50–100%, stepwise) to yield 22 fractions. Fraction 9 was eluted with acetone/n-hexane (1:6) on silica gel to give twelve subfractions (SFr.9-1–SFr.9-12), and SFr.9-3 was separated on RP-18 gel, using MeOH/H2O (7:1) to give ten subfractions (SFr.9-3-1–SFr.9-3-10); SFr.9-3-2 was subjected to PR-HPLC with CH3CN/MeOH (1:10) to obtain compounds 4 (1.9 mg), 5 (3.6 mg), 6 (2.9 mg) and 7 (3.4 mg). Fraction 14, eluted with n-hexane/EtOAc (1:4), also was rechromatographed over a Sephadex LH-20 column, using acetone as the mobile phase. In turn, SFr. 14-2 was separated on silica gel, using acetone/n-hexane (1:4) to give two subfractions SFr. 14-2-1–SFr.14-2-2. SFr.14-2-2 was isolated on RP-HPLC using MeOH/H2O (10:1) to give 3 (32.3 mg). SFr.14-4 was further purified by reversed phase HPLC using methanol/H2O (4: 1) to obtain 1 (5.6 mg) and 2 (1.6 mg).
Michosterol A (1): amorphous solid; [α] −5 (c 1.25, CHCl3); IR (neat) vmax 3393, 2972, 2938, 1712, 1453, 1371, 1270, 1153, 1051 and 757 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data (400 MHz; CDCl3), see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 559 [M + Na]+; HRESIMS m/z 559.3601 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C31H52O7Na, 559.3605).
Michosterol B (2): amorphous solid; [α] −51 (c 0.25, CHCl3); IR (neat) vmax 3418, 2933, 1713, 1455, 1375, 1259, 1053 and 756 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data (500 MHz; CDCl3), see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 559 [M + Na]+; HRESIMS m/z 559.3603 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C31H52O7Na, 559.3605).
Michosterol C (3): white powder; [α] +34 (c 0.91, CHCl3); IR (neat) vmax 3416, 2942, 2870, 1718, 1454, 1375, 1260, 1049 and 756 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data (400 MHz; CDCl3), see Table 1; 1H NMR (CD3OD, 400 MHz): δH 4.94 (1H, dd, J = 12.0, 5.2 Hz, H-6), δH 4.14 (1H, br s, H-3), δH 2.07 (3H, s, H-6-OAc), δH 2.04 (1H, m, H-12a), δH 1.97 (2H, m, H2-4), δH 1.89 (1H, m, H-16a), δH 1.84 (1H, m, H-7a), δH 1.83 (1H, m, H-1a), δH 1.76 (1H, m, H-23a), δH 1.65 (1H, m, H-2a), δH 1.59 (2H, m, H-2b and H-8), δH 1.58 (1H, m, H-15a), δH 1.56 (1H, m, H-22a), δH 1.48 (1H, m, H-11a), δH 1.40 (1H, m, H-20), δH 1.36 (2H, m, H-1b and H-11b), δH 1.32 (1H, s, H-24), δH 1.31 (1H, m, H-16), δH 1.20 (1H, m, H-12b), δH 1.19 (1H, m, H-17), δH 1.14 (1H, m, H-14), δH 1.13 (3H, s, H3-27), δH 1.12 (1H, m, H-15), δH 1.11 (3H, s, H3-26), δH 1.07 (1H, m, H-7b), δH 0.97 (3H, s, H3-19), δH 0.96 (3H, d, J = 5.2 Hz, H3-21), δH 0.95 (1H, m, H-22b), δH 0.89 (3H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H3-28), δH 0.78 (1H, m, H-23), δH 0.71 (3H, s, H3-18); 13C NMR (CD3OD, 100 MHz): 173.0 (C, C-6-OAc), 78.1 (C, C-5), 76.3 (CH, C-6), 74.4 (C, C-25), 68.2 (CH, C-3), 57.7 (CH, C-14), 57.6 (CH, C-17), 46.6 (CH, C-24), 44.4 (CH, C-9), 44.1 (C, C-13), 43.2 (C, C-10), 41.4 (CH2, C-12), 38.0 (CH, C-20), 36.5 (CH2, C-22), 35.3 (CH, C-8), 34.8 (CH2, C-7), 32.1 (CH2, C-4), 29.5 (CH2, C-16), 29.4 (CH2, C-23), 28.5 (CH2, C-2), 27.4 (CH3, C-27), 26.7 (CH2, C-1), 26.0 (CH3, C-26), 25.5 (CH2, C-15), 23.0 (CH2, C-11), 21.6 (CH3, C-6-OAc), 19.8 (CH3, C-21), 17.9 (CH3, C-19), 15.5 (CH3, C-28), 12.8 (CH3, C-18); ESIMS m/z 515 [M + Na]+; HRESIMS m/z 515.3708 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C30H52O5Na, 515.3707).
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
A549, DLD-1 and LNCap cancer cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA). Evaluation of cytotoxicity for the isolated metabolites from L. michaelae was performed according to the Alamar Blue assay [25,26].
3.5. Human Neutrophil Superoxide Anion Generation and Elastase Release
Human neutrophils were isolated through dextran sedimentation and Ficoll centrifugation. By following the procedures described previously, the assay of superoxide anion generation was measured from the SOD-inhibitable reduction of ferricytochrome C. The elastase release experiment was performed according to methoxy-succinyl-alanyl-alanyl-prolyl-valine-p-nitroanilide (MeO-Suc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val-p-nitroanilide) as the enzyme substrate. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, and comparisons were made using Student’s t-test [27,28].
4. Conclusions
Our investigation demonstrated that a Taiwanese soft coral L. michaelae could be a good source of bioactive substances. Three new polyoxygenated steroids, michosterols A–C (1–3), were isolated. Compound 1 has an unusual side-chain, and 2 possesses a 17,20-double bound with rare substituents at both sp2 carbons. Compound 1 exhibited moderate anti-inflammatory activities in the inhibition of superoxide anion generation and elastase release in the fMLP/CB-stimulated human neutrophils, and 3 exhibited significant inhibitions toward elastase release, as well. Thus, compounds 1 and 3 can be considered as promising leads in the development of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Supplementary Materials
HRESIMS, 1H, 13C, HSQC, COSY, HMBC and NOESY NMR spectra of new compounds 1–3 are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/16/3/93/s1. Figure S1: HRESIMS spectrum of 1, Figure S2: 1H NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S3: 13C NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 at 100 MHz, Figure S4: HSQC NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S5: COSY NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S6: HMBC NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S7: NOESY NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S8: HRESIMS spectrum of 2, Figure S9: 1H NMR spectrum of 2 in CDCl3 at 500 MHz, Figure S10: 13C NMR spectrum of 2 in CDCl3 at 125 MHz, Figure S11: HSQC NMR spectrum of 2 in CDCl3 at 500 MHz, Figure S12: COSY NMR spectrum of 2 in CDCl3 at 500 MHz, Figure S13: HMBC NMR spectrum of 2 in CDCl3 at 500 MHz, Figure S14: NOESY NMR spectrum of 2 in CDCl3 at 500 MHz, Figure S15: HRESIMS spectrum of 3, Figure S16: 1H NMR spectrum of 3 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S17: 13C NMR spectrum of 3 in CDCl3 at 100 MHz, Figure S18: HSQC NMR spectrum of 3 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S19: COSY NMR spectrum of 3 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S20: HMBC NMR spectrum of 3 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S21: NOESY NMR spectrum of 3 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S22: 1H NMR spectrum of 3 in CD3OD at 400 MHz, Figure S23: 13C NMR spectrum of 3 in CD3OD at 100 MHz, Figure S24: HSQC NMR spectrum of 3 in CD3OD at 400 MHz, Figure S25: COSY NMR spectrum of 3 in CD3OD at 400 MHz, Figure S26: HMBC NMR spectrum of 3 in CD3OD at 400 MHz.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST104-2113-M-110-006 and 105-2113-M-110-002), and the National Sun Yat-sen University-Kaohsiung Medical University (NSYSU-KMU) Joint Research Projects (NSYSUKMU 105-I008, and 106-I007) awarded to J.-H.S.
Author Contributions
Jyh-Horng Sheu designed the whole experiment. Chiung-Yao Huang contributed to the structural elucidation and manuscript preparation. Wan-Ru Tseng performed the purification, structural elucidation, data acquisition and cytotoxicity assay. Chi-Jen Tai also performed data acquisition. Atallah F. Ahmed contributed to data analysis and manuscript preparation. Pei-Lun Chiang and Tsong-Long Hwang performed the anti-inflammatory assay. Chang-Feng Dai contributed to the collection of soft coral and species identification.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rama Rao, M.; Venkatesham, U.; Rami Reddy, M.V.; Venkateswarlu, Y. An unusual novel C29 steroid from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Wen, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Hsu, C.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chiang, M.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Steroid and cembranoids from the Dongsha atoll soft coral Lobophytum sarcophytoides. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 7129–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.A.; Christie, E.M.; Jaspars, M.; van Ofwegen, L.P. A bioactive secosterol with an unusual A- and B-ring oxygenation pattern isolated from an Indonesian soft coral Lobophytum sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.E.; Mohamed, T.A.; Elshamy, A.I.; Hassanien, A.A.; Abdel-Azim, N.S.; Shreadah, M.A.; Abdelgawad, I.I.; Elkady, E.M.; Pare, P.W. A new steroid from the Red Sea soft coral Lobophytum lobophytum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, T.H.; Ngan, N.T.T.; Van Kiem, P.; Van Minh, C.; Kim, Y.H. A new sterol from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 249. [Google Scholar]
- Sheu, J.H.; Veh, T.H. Isolation of a bioactive sterol from the soft coral Lobophytum mirabile. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 1991, 38, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Teng, W.T.; Huang, C.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Sheu, J.H. Anti-inflammatory lobane and prenyleudesmane diterpenoids from the soft coral Lobophytum varium. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, T.A.; Elshamy, A.I.; Hussien, T.A.; Su, J.H.; Sheu, J.H.; Hegazy, M.E.F. Lobophylins F–H: Three new cembrene diterpenoids from soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.E.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. Cembranoids with 3,14-ether linkage and a secocembrane with bistetrahydrofuran from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Lobophytum sp. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Yeh, H.C.; Sheu, J.H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.J.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive cembranoids from the Dongsha atoll soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.K.; Duh, C.Y. New cytotoxic cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.T.; Wang, S.K.; Soong, K.; Duh, C.Y. New cytotoxic cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae. Chem. Phar. Bull. 2007, 55, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.K.; Duh, C.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.C.; Soong, K.; Fang, L.S. Studies on Formosan soft corals. II. Cytotoxic cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinming, G.; Lin, H.; Jikai, L. A novel sterol from Chinese truffles Tuber indicum. Steroids 2001, 66, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahelivao, M.P.; Lubken, T.; Gruner, M.; Kataeva, O.; Ralambondrahety, R.; Andriamanantoanina, H.; Checinski, M.P.; Bauer, I.; Knolker, H.J. Isolation and structure elucidation of natural products of three soft corals and a sponge from the coast of Madagascar. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 2593–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Pattabhiraman, T. Chemistry of coelenterates. XXII. New marine sterol possessing a side chain cyclopropyl group: 23-demethylgorgosterol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 6073–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, A.; Teshima, S.I.; Ando, T. Sterols of coelenterates. Comp. Biochem./Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1977, 57, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.D.; Powers, T.J.; Djerassi, C.; Fayos, J.; Clardy, J. A stereoselective synthesis of two stereoisomers of demethylgorgosterol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, N.C.; Hale, R.L.; Djerassi, C. The structure and absolute configuration of the marine sterol gorgosterol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 5281–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Shao, C.L.; Qi, X.; Li, X.B.; Li, J.; Sun, L.L.; Wang, C.Y. Polyoxygenated sterols from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Y.; Han, L. 4,5-Epoxycholestane-3,6-diols: Templates for generating the full set of eight cholestane-3,5,6-triol stereoisomers in multigram scales, but not for a cholestane-3,4,6-triol. Steroids 2007, 72, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.R.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Shih, S.P.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Sheu, J.H. New bioactive steroids from the soft coral Klyxum flaccidum. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12546–12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.H.; Huang, L.F.; Wu, S.L.; Su, J.H.; Huang, H.C.; Sheu, J.H. Steroids from the gorgonian. Isis hippuris. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, G.R.; Caton, M.C.; Nova, M.P.; Parandoosh, Z. Assessment of the Alamar Blue assay for cellular growth and viability in vitro. J. Immunol. Methods 1997, 204, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Chung, P.J.; Ho, C.M.; Kuo, C.Y.; Hung, M.F.; Huang, Y.T.; Chang, W.Y.; Chang, Y.W.; Chan, K.H.; Hwang, T.L. Propofol inhibits superoxide production, elastase release, and chemotaxis in formyl peptide-activated human neutrophils by blocking formyl peptide receptor 1. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6511–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.P.; Hsieh, P.W.; Chang, Y.J.; Chung, P.J.; Kuo, L.M.; Hwang, T.L. 2-(2-Fluorobenzamido)benzoate ethyl ester (EFB-1) inhibits superoxide production by human neutrophils and attenuates hemorrhagic shock-induced organ dysfunction in rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).