AbeTx1 Is a Novel Sea Anemone Toxin with a Dual Mechanism of Action on Shaker-Type K+ Channels Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
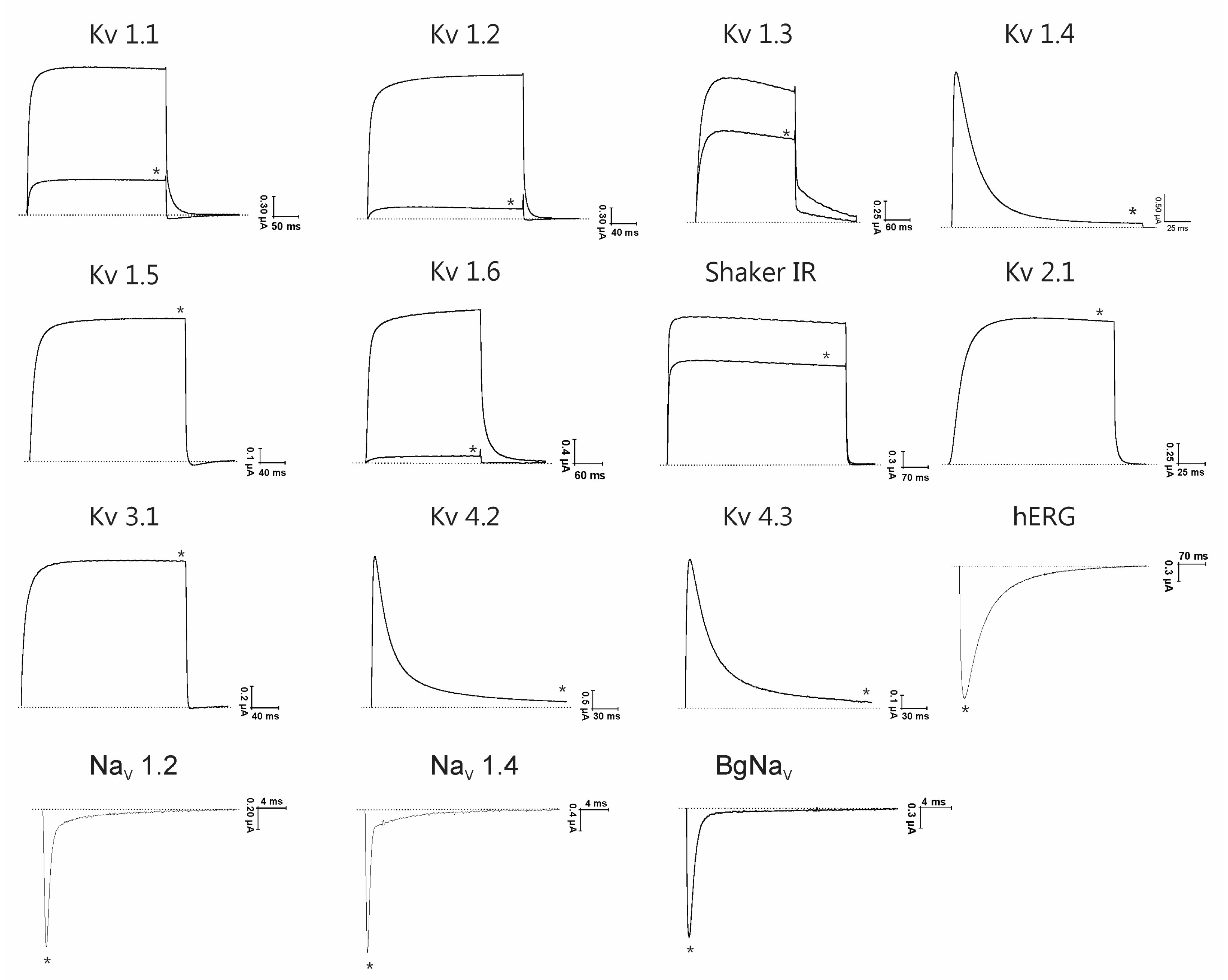
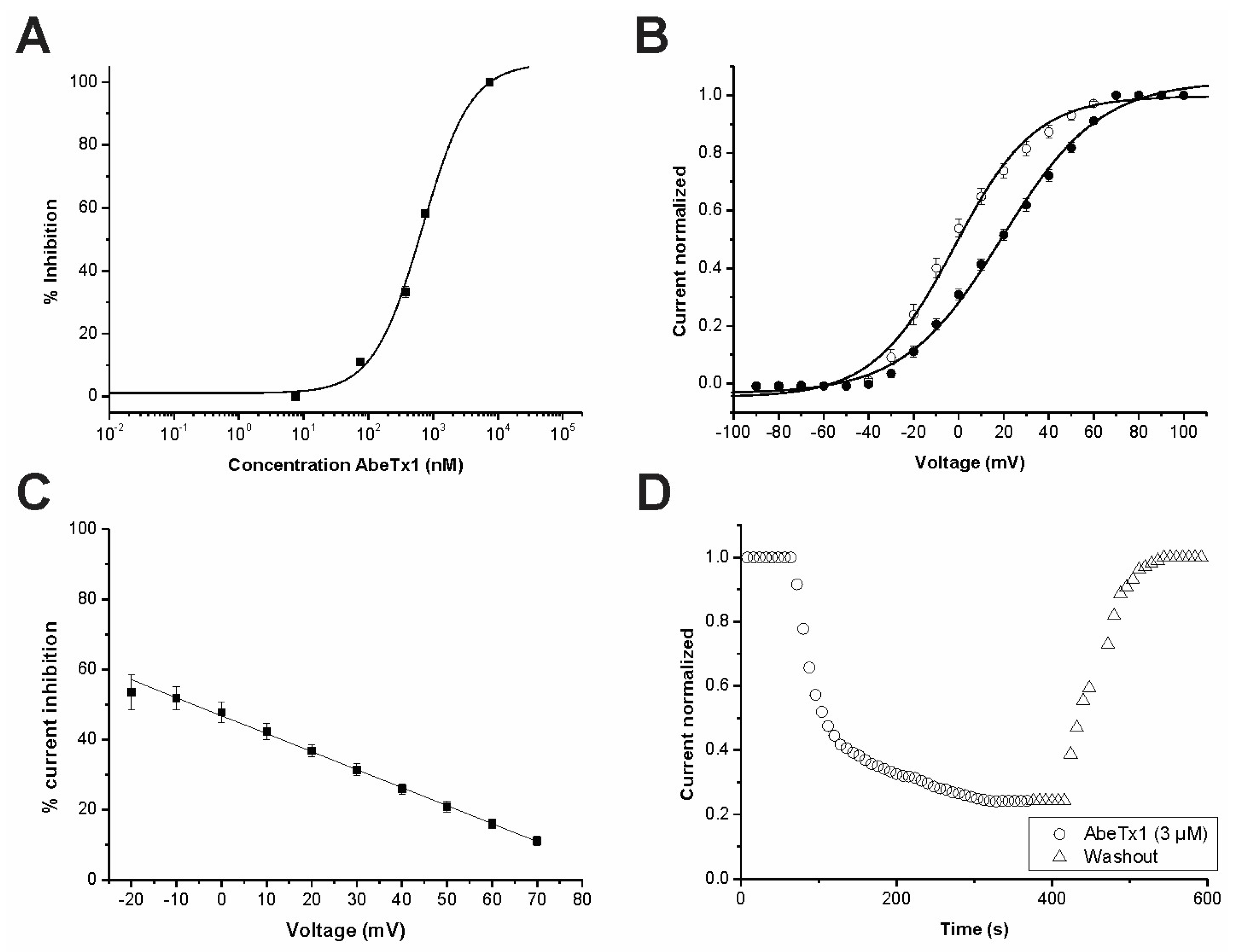
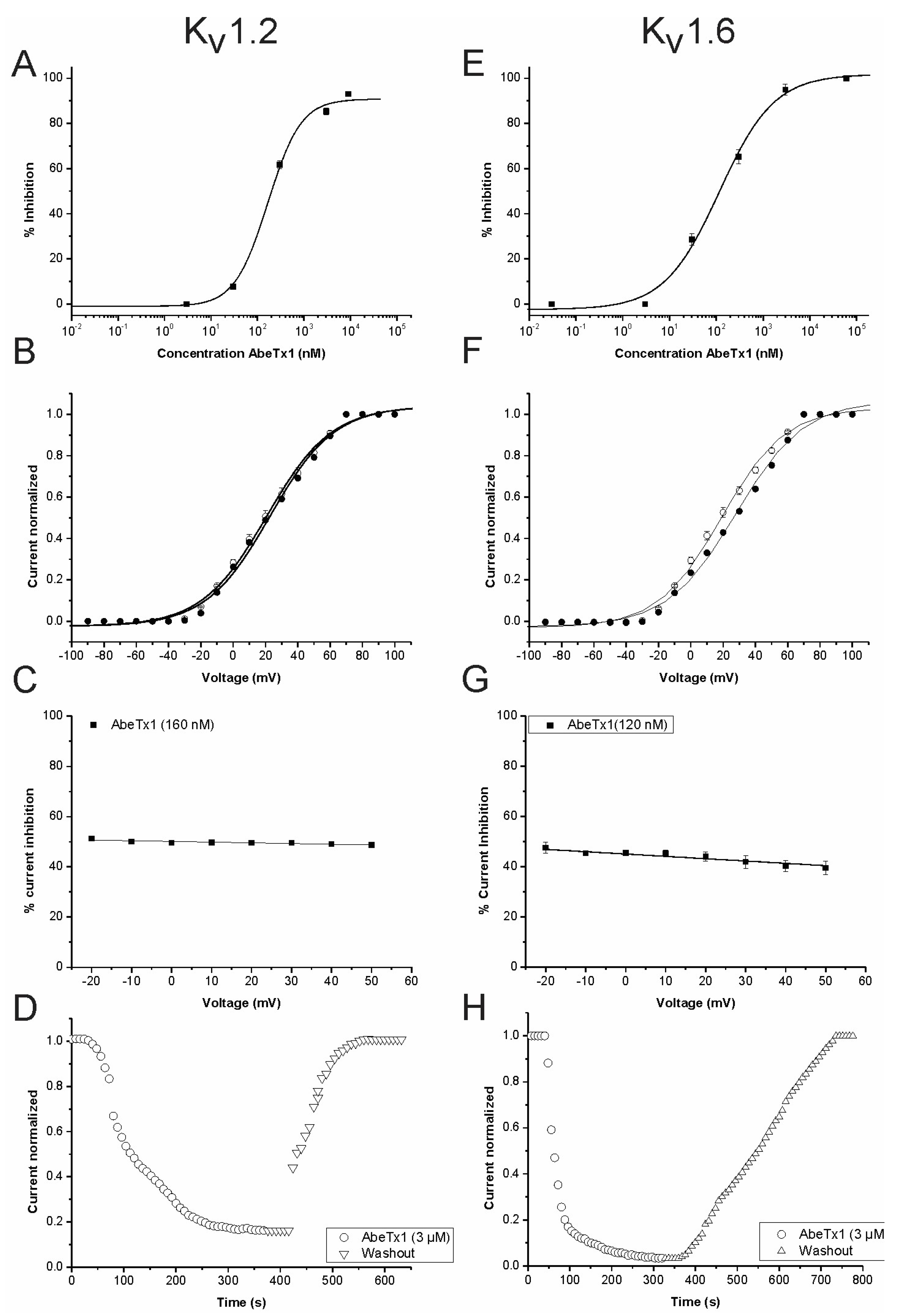
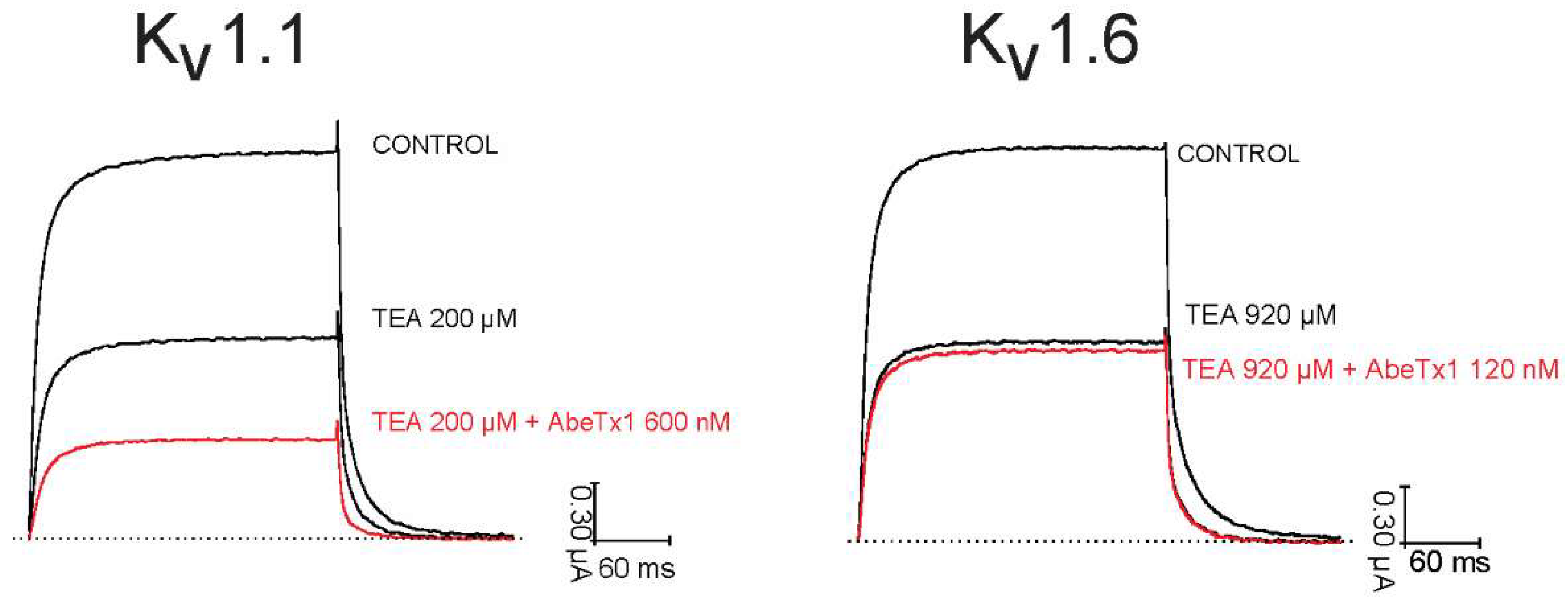
2. Results
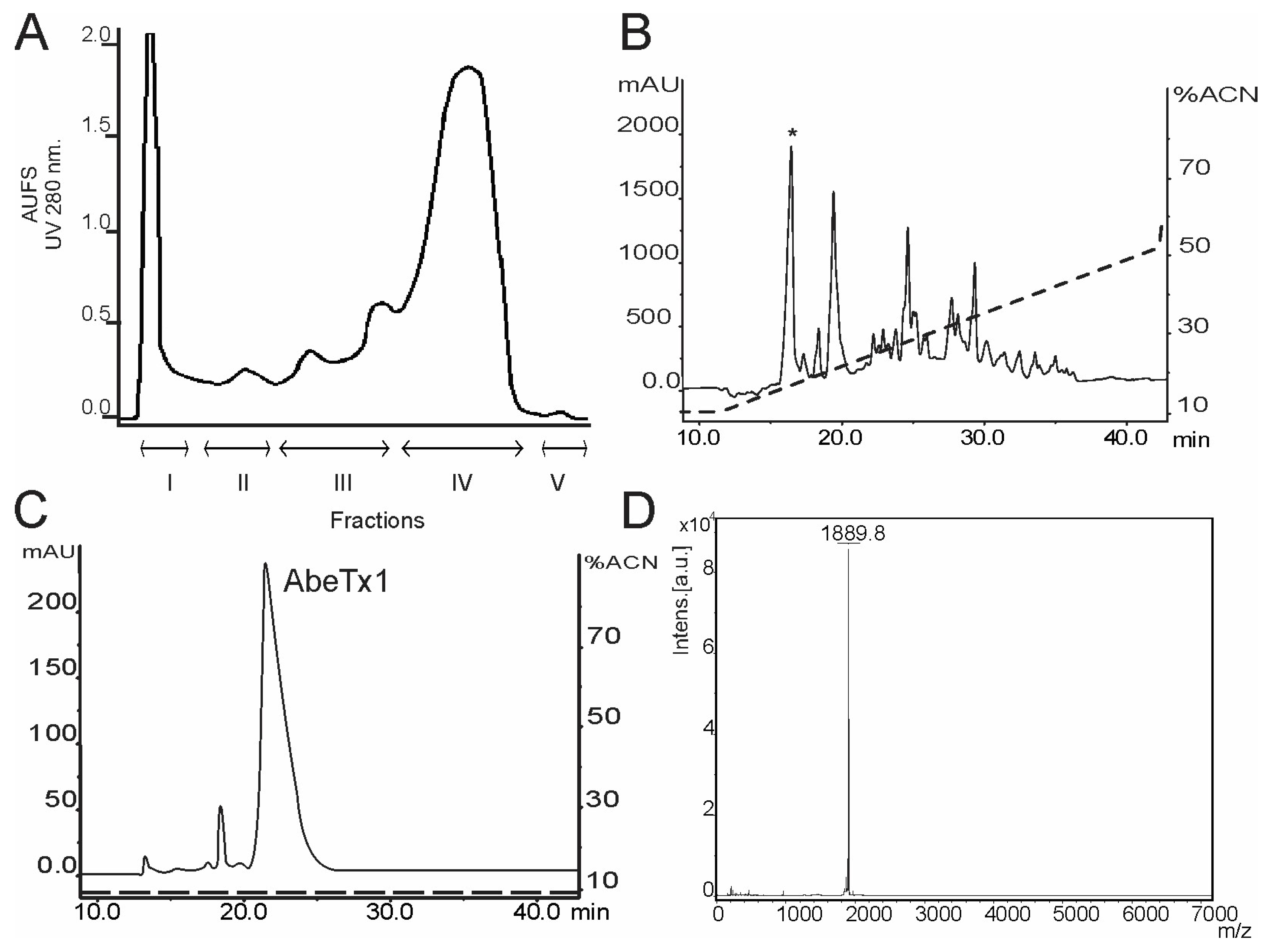
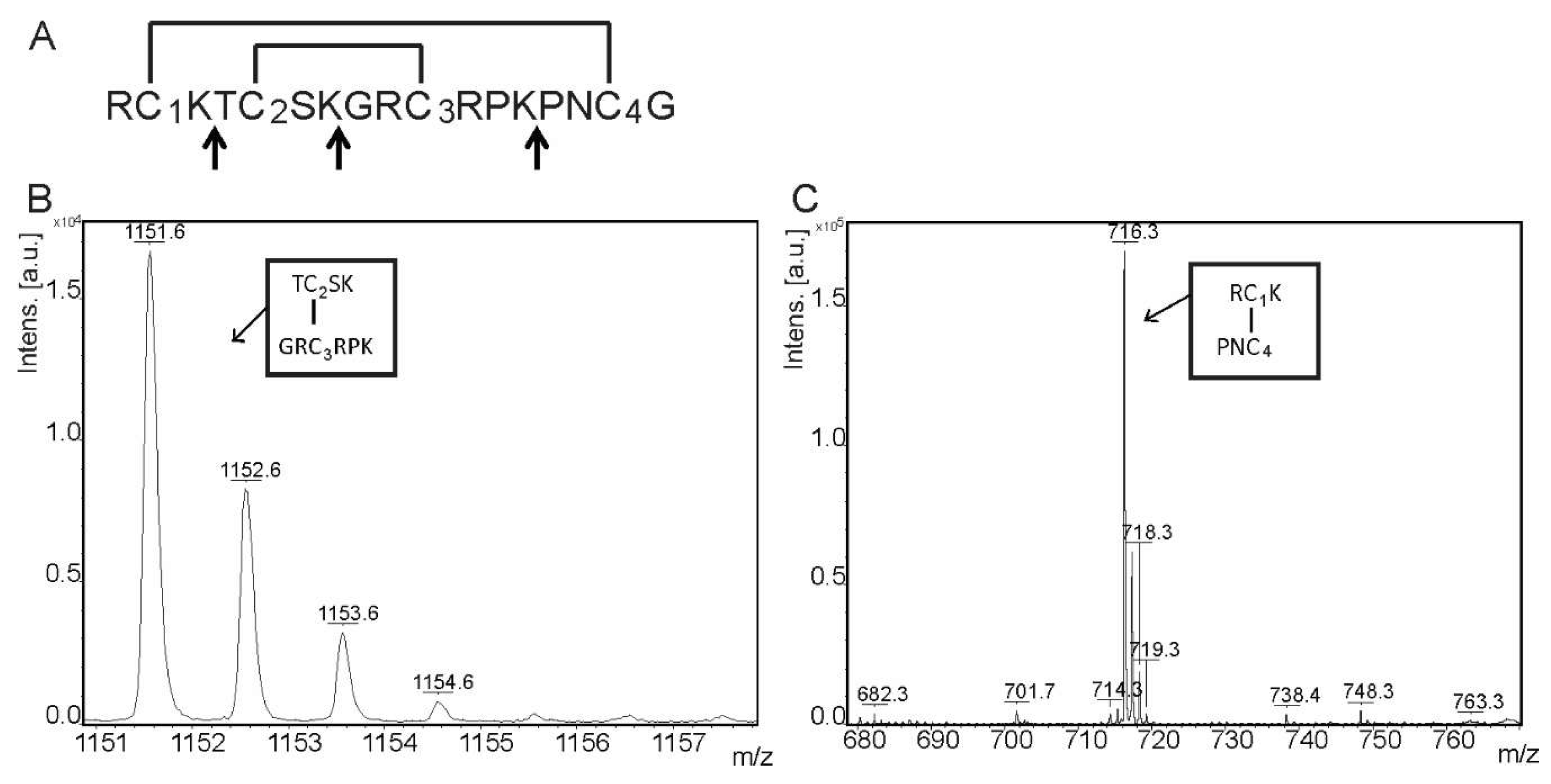
2.1. Biochemical Properties
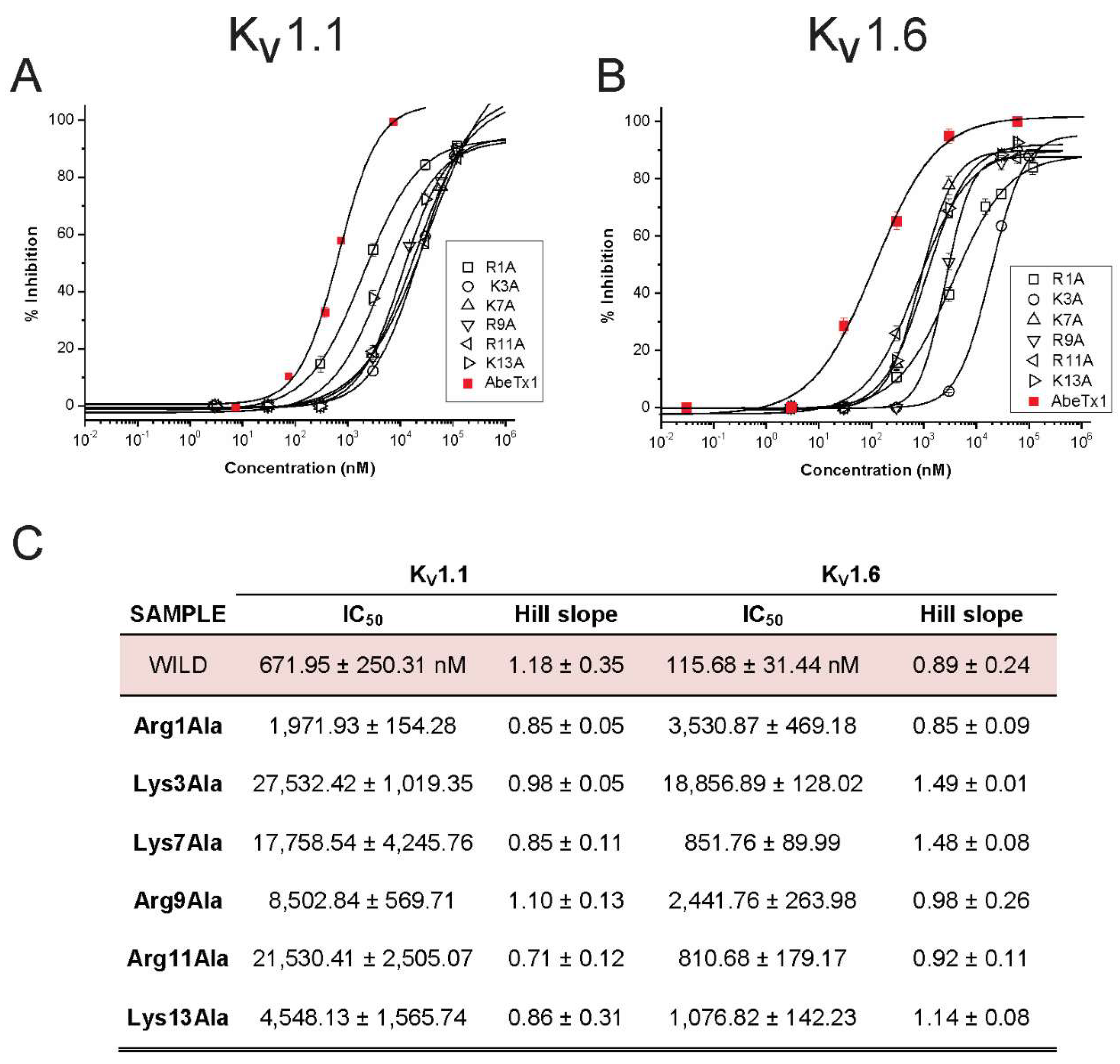
2.2. Pharmacological Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venom Extraction and Purification of AbeTx1
4.2. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.3. AbeTx1 Disulfide Bonds Pattern Determination
4.4. Amino Acid Sequence Determination
4.5. Large Unilamellar Vesicles (LUVs) Preparation
4.6. Circular Dichroism
4.7. AbeTx1 Analogs Synthesis–Alanine Substitution
4.8. Heterologous Expression of Ion Channels in Xenopus Laevis Oocytes
4.9. Electrophysiological Recordings
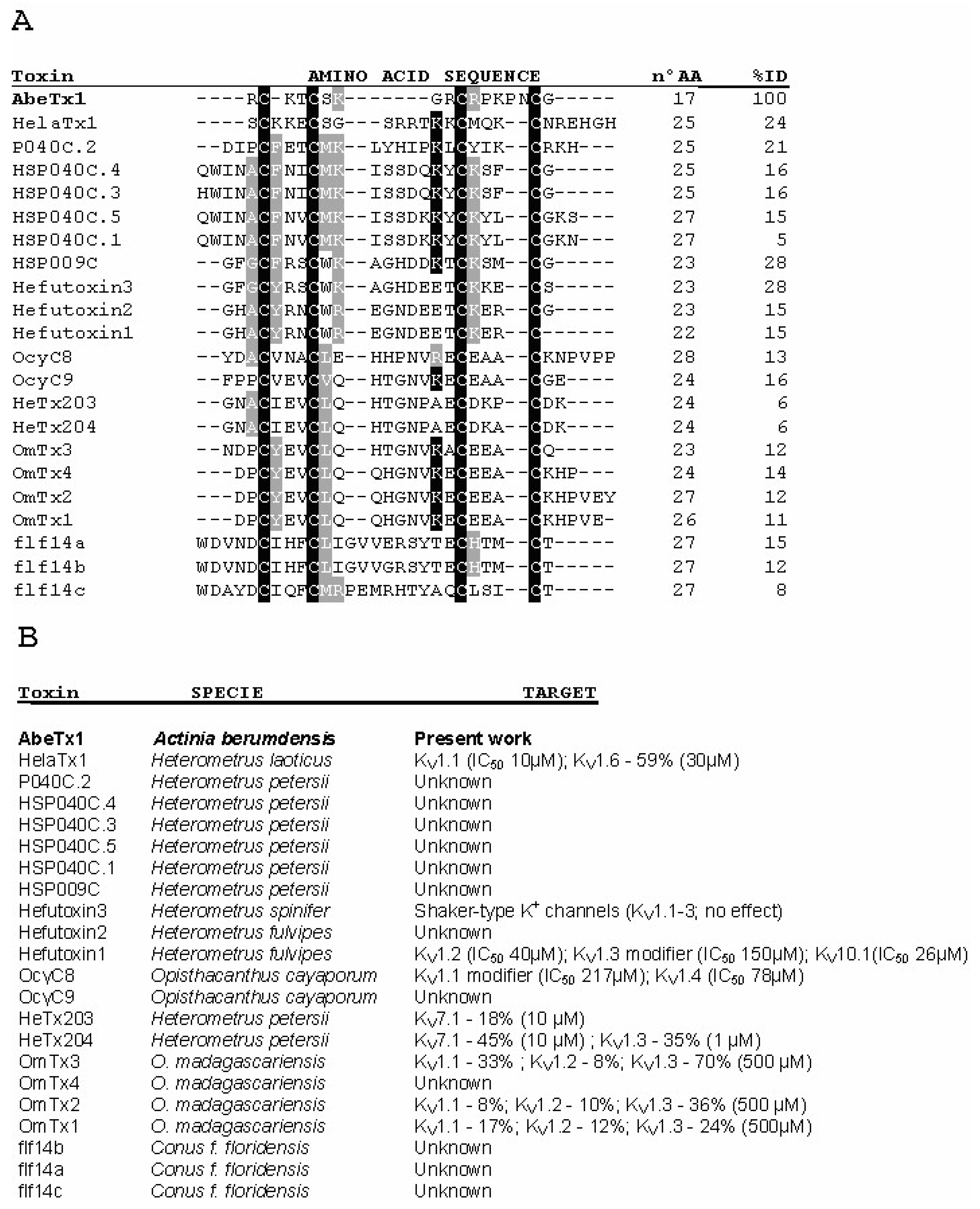
4.10. Bioinformatics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutman, G.A.; Chandy, K.G.; Adelman, J.P.; Aiyar, J.; Bayliss, D.A.; Clapham, D.E.; Covarriubias, M.; Desir, G.V.; Furuichi, K.; Ganetzky, B.; et al. International union of pharmacology. XLI. compendium of voltage-gated ion channels: Potassium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguinetti, M.C.; Spector, P.S. Potassium channelopathies. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanilla, F. Ion channels: From conductance to structure. Neuron 2008, 60, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Garcia, M.L. Therapeutic potential of venom peptides. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.; Chan, A.H.; Koludarov, I.; Munoz-Gomez, S.A.; Antunes, A.; Fry, B.G. Evolution stings: The origin and diversification of scorpion toxin peptide scaffolds. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 5, 2456–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytgat, J.; Chandy, K.G.; Garcia, M.L.; Gutman, G.A.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; van der Walt, J.J.; Possani, L.D. A unified nomenclature for short-chain peptides isolated from scorpion venoms: Alpha-KTx molecular subfamilies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.N.; Sivaraja, V.; Huys, I.; Sasaki, T.; Cheng, B.; Kumar, T.K.; Sato, K.; Tytgat, J.; Yu, C.; San, B.C.; et al. kappa-Hefutoxin1, a novel toxin from the scorpion Heterometrus fulvipes with unique structure and function. Importance of the functional diad in potassium channel selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30040–30047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremonez, C.M.; Maiti, M.; Peigneur, S.; Cassoli, J.S.; Dutra, A.A.; Waelkens, E.; Lescrinier, E.; Herdewijn, P.; de Lima, M.E.; Pimenta, A.M.; et al. Structural and functional elucidation of peptide Ts11 shows evidence of a novel subfamily of scorpion venom toxins. Toxins (Basel) 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandendriessche, T.; Kopljar, I.; Jenkins, D.P.; Diego-Garcia, E.; Abdel-Mottaleb, Y.; Vermassen, E.; Clynen, E.; Schoofs, L.; Wulff, H.; Snyders, D.; et al. Purification, molecular cloning and functional characterization of HelaTx1 (Heterometrus laoticus): The first member of a new kappa-KTX subfamily. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagot, B.; Pimentel, C.; Dai, L.; Pil, J.; Tytgat, J.; Nakajima, T.; Corzo, G.; Darbon, H.; Ferrat, G. An unusual fold for potassium channel blockers: NMR structure of three toxins from the scorpion Opisthacanthus madagascariensis. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirthanan, S.; Pil, J.; Abdel-Mottaleb, Y.; Sugahara, Y.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Joseph, J.S.; Sato, K.; Tytgat, J. Assignment of voltage-gated potassium channel blocking activity to kappa-KTx1.3, a non-toxic homologue of kappa-hefutoxin-1, from Heterometrus spinifer venom. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargos, T.S.; Restano-Cassulini, R.; Possani, L.D.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Schwartz, C.A.; Alves, E.M.; de Freitas, S.M.; Schwartz, E.F. The new kappa-KTx 2.5 from the scorpion Opisthacanthus cayaporum. Peptides 2011, 32, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Zeng, D.Y.; Hu, Y.T.; He, Y.W.; Pan, N.; Ding, J.P.; Cao, Z.J.; Liu, M.L.; Li, W.X.; Yi, H.; et al. Structural and functional diversity of acidic scorpion potassium channel toxins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreels, L.; Peigneur, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Vriens, K.; Waelkens, E.; Zhu, S.; Thevissen, K.; Cammue, B.P.; Sato, K.; Tytgat, J. Expanding the pharmacological profile of kappa-hefutoxin 1 and analogues: A focus on the inhibitory effect on the oncogenic channel Kv10.1. Peptides 2016, 98, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazao, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Sea anemone (cnidaria, anthozoa, actiniaria) toxins: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1812–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orts, D.J.; Moran, Y.; Cologna, C.T.; Peigneur, S.; Madio, B.; Praher, D.; Quinton, L.; De Pauw, E.; Bicudo, J.E.; Tytgat, J.; et al. BcsTx3 is a founder of a novel sea anemone toxin family of potassium channel blocker. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4839–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, W.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Guo, L.; Li, W. Molecular diversity of toxic components from the scorpion Heterometrus petersii venom revealed by proteomic and transcriptome analysis. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2471–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, C.; Rahmankhah, S.; Lauer-Fields, J.; Bubis, J.; Fields, G.B.; Mari, F. A novel conotoxin framework with a helix-loop-helix (Cs alpha/alpha) fold. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 15986–15996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.A.; Standker, L.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Garateix, A.G.; Forssmann, W.G.; Beress, L.; Valdes, O.; Hernandez, Y.; Laguna, A. Combining multidimensional liquid chromatography and MALDI-TOF-MS for the fingerprint analysis of secreted peptides from the unexplored sea anemone species Phymanthus crucifer. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 903, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassoli, J.S.; Verano-Braga, T.; Oliveira, J.S.; Montandon, G.G.; Cologna, C.T.; Peigneur, S.; Pimenta, A.M.; Kjeldsen, F.; Roepstorff, P.; Tytgat, J.; et al. The proteomic profile of Stichodactyla duerdeni secretion reveals the presence of a novel O-linked glycopeptide. J. Proteom. 2013, 87, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madio, B.; Undheim, E.A.B.; King, G.F. Revisiting venom of the sea anemone Stichodactyla haddoni: Omics techniques reveal the complete toxin arsenal of a well-studied sea anemone genus. J. Proteom. 2017, 166, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orts, D.J.; Peigneur, S.; Madio, B.; Cassoli, J.S.; Montandon, G.G.; Pimenta, A.M.; Bicudo, J.E.; Freitas, J.C.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Tytgat, J. Biochemical and electrophysiological characterization of two sea anemone type 1 potassium toxins from a geographically distant population of Bunodosoma caissarum. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 655–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, T.; Kawahata, S.; Ishida, M.; Nagai, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Novel peptide toxins from the sea anemone Stichodactyla haddoni. Peptides 2008, 29, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaharenko, A.J.; Ferreira, W.A., Jr.; Oliveira, J.S.; Richardson, M.; Pimenta, D.C.; Konno, K.; Portaro, F.C.; de Freitas, J.C. Proteomics of the neurotoxic fraction from the sea anemone Bunodosoma cangicum venom: Novel peptides belonging to new classes of toxins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2008, 3, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Kozlov, S.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Sanamyan, N.P.; Sanamyan, K.E.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Bondarenko, D.A.; Murashev, A.N.; Mineev, K.S.; et al. Sea anemone peptide with uncommon beta-hairpin structure inhibits acid-sensing ion channel 3 (ASIC3) and reveals analgesic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23116–23127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Randall, A.Z.; Sweredoski, M.J.; Baldi, P. SCRATCH: A protein structure and structural feature prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Macarthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. Procheck—A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; Andreotti, N.; Jouirou, B.; Sabatier, J.M. Animal toxins acting on voltage-gated potassium channels. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2503–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatier, J.M.; Mouhat, S.; De Waard, M. Contribution of the functional dyad of animal toxins acting on voltage-gated Kv1-type channels. J. Pept. Sci. 2005, 11, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.R.; Robertson, B.; Fedida, D. Gating currents from a Kv3 subfamily potassium channel: Charge movement and modification by BDS-II toxin. J. Physiol. 2007, 584, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.S.; Diochot, S.; Lazdunski, M.; Tseng, G.N. APETx1 from sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima is a gating modifier peptide toxin of the human Ether-a-go-go-related potassium channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heginbotham, L.; MacKinnon, R. The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels. Neuron 1992, 8, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaeus, M.J.; Vamvouka, M.; Focia, P.J.; Gross, A. Structural basis of TEA blockade in a model potassium channel. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Merino, E.; Becerril, B.; Possani, L.D. Novel interactions between K+ channels and scorpion toxins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 24, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Q.; Zhu, S.Y.; Chi, C.W.; Tytgat, J. Turret and pore block of K+ channels: What is the difference? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 24, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, C.; Goodchild, S.J.; Weatherall, K.L.; Jane, D.E.; Liegeois, J.F.; Seutin, V.; Marrion, N.V. Allosteric block of KCa2 channels by apamin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27067–27077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilly, S.; Lamy, C.; Marrion, N.V.; Liegeois, J.F.; Seutin, V. Ion-channel modulators: More diversity than previously thought. Chembiochem 2011, 12, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, M.W.; Kem, W.R.; Mahnir, V.M.; Byrnes, M.E.; Zaydenberg, I.; Khaytin, I.; Krafte, D.S.; Hill, R. Identification of essential residues in the potassium channel inhibitor ShK toxin: Analysis of monosubstituted analogs. In Peptides: Chemistry, Structure and Biology; Kaumaya, P.T.P., Hodges, R.S., Eds.; Escom: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Sun, C.; Song, D.; Shen, J.; Xu, N.; Gunasekera, A.; Hajduk, P.J.; Olejniczak, E.T. Nuclear magnetic resonance structural studies of a potassium channel-charybdotoxin complex. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 15834–15841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouirou, B.; Mouhat, S.; Andreotti, N.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M. Toxin determinants required for interaction with voltage-gated K+ channels. Toxicon 2004, 43, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’Barek, S.; Mosbah, A.; Sandoz, G.; Fajloun, Z.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Rochat, H.; Sampieri, F.; Guijarro, J.I.; Mansuelle, P.; Delepierre, M.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of Pi4, a scorpion toxin from Pandinus imperator that acts on K+ channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 3583–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, S.A.; Pheasant, D.J.; Miller, C. The charybdotoxin receptor of a Shaker K+ channel: Peptide and channel residues mediating molecular recognition. Neuron 1994, 12, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, S.; Mosbah, A.; Visan, V.; Wulff, H.; Delepierre, M.; Darbon, H.; Grissmer, S.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M. The ‘functional’ dyad of scorpion toxin Pi1 is not itself a prerequisite for toxin binding to the voltage-gated Kv1.2 potassium channels. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.D.; Garcia, M.L. Interaction of agitoxin2, charybdotoxin, and iberiotoxin with potassium channels: Selectivity between voltage-gated and Maxi-K channels. Proteins 2003, 52, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peigneur, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kawano, C.; Nose, T.; Nirthanan, S.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Tytgat, J.; Sato, K. Active sites of spinoxin, a potassium channel scorpion toxin, elucidated by systematic alanine scanning. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 2927–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandri-Haber, N.; Lecoq, A.; Gasparini, S.; Grangier-Macmath, G.; Jacquet, G.; Harvey, A.L.; de Medeiros, C.; Rowan, E.G.; Gola, M.; Menez, A.; et al. Mapping the functional anatomy of BgK on Kv1.1, Kv1.2, and Kv1.3—Clues to design analogs with enhanced selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 35653–35661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouser, G.; Fleische, S.; Yamamoto, A. Two dimensional thin layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids 1970, 5, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
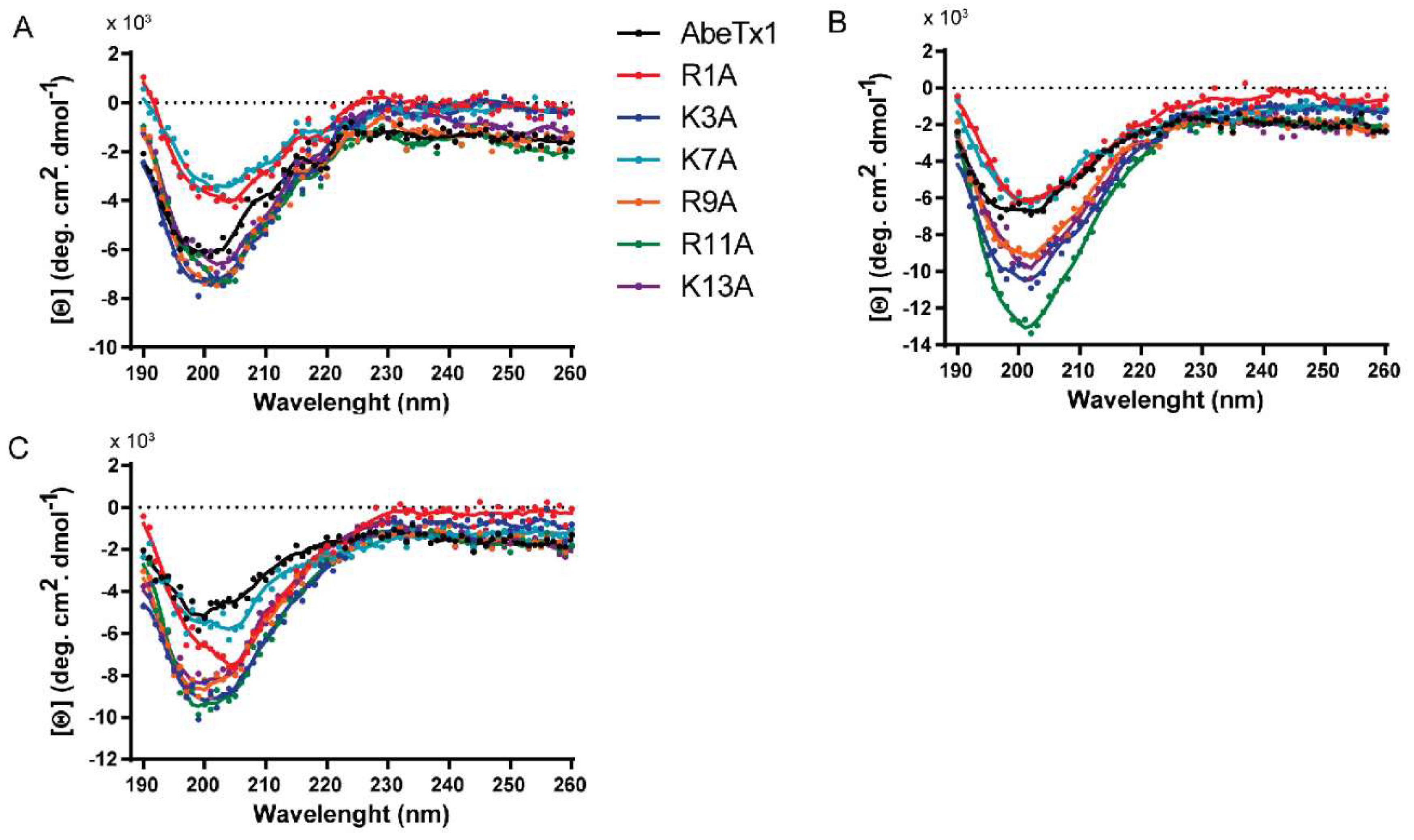
| WT | Arg1Ala | Lys3Ala | Lys7Ala | Arg9Ala | Arg11Ala | Lys13Ala | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tris Buffer | Helix | 14.54 | 13.38 | 13.84 | 14.12 | 13.08 | 13.48 | 13.73 |
| Beta | 34.75 | 34.96 | 35.83 | 34.6 | 35.67 | 36.03 | 36.18 | |
| Turn | 17.54 | 17.11 | 17.46 | 17.26 | 17.19 | 17.4 | 17.52 | |
| Random Coil | 33.17 | 34.55 | 32.87 | 34.1 | 34.06 | 33.09 | 32.65 | |
| POPC | Helix | 14.7 | 13.11 | 14.03 | 13.71 | 13.5 | 13.54 | 13.46 |
| Beta | 34.09 | 34.92 | 34.98 | 34.29 | 34.88 | 35.4 | 35.97 | |
| Turn | 17.38 | 16.98 | 17.41 | 17.06 | 17.15 | 17.29 | 17.37 | |
| Random Coil | 33.92 | 34.92 | 33.58 | 34.94 | 34.47 | 33.77 | 33.20 | |
| POPC:POPS (80:20) | Helix | 13.03 | 13.16 | 13.63 | 12.4 | 13.61 | 13.71 | 13.55 |
| Beta | 35.32 | 35.27 | 36.37 | 35.39 | 35.98 | 35.88 | 36.62 | |
| Turn | 17.06 | 17.11 | 17.57 | 16.82 | 17.46 | 17.49 | 17.57 | |
| Random Coil | 34.59 | 34.46 | 32.43 | 35.39 | 32.87 | 32.92 | 32.27 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
B. Orts, D.J.; Peigneur, S.; Silva-Gonçalves, L.C.; Arcisio-Miranda, M.; P. W. Bicudo, J.E.; Tytgat, J. AbeTx1 Is a Novel Sea Anemone Toxin with a Dual Mechanism of Action on Shaker-Type K+ Channels Activation. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100360
B. Orts DJ, Peigneur S, Silva-Gonçalves LC, Arcisio-Miranda M, P. W. Bicudo JE, Tytgat J. AbeTx1 Is a Novel Sea Anemone Toxin with a Dual Mechanism of Action on Shaker-Type K+ Channels Activation. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(10):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100360
Chicago/Turabian StyleB. Orts, Diego J., Steve Peigneur, Laíz Costa Silva-Gonçalves, Manoel Arcisio-Miranda, José Eduardo P. W. Bicudo, and Jan Tytgat. 2018. "AbeTx1 Is a Novel Sea Anemone Toxin with a Dual Mechanism of Action on Shaker-Type K+ Channels Activation" Marine Drugs 16, no. 10: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100360
APA StyleB. Orts, D. J., Peigneur, S., Silva-Gonçalves, L. C., Arcisio-Miranda, M., P. W. Bicudo, J. E., & Tytgat, J. (2018). AbeTx1 Is a Novel Sea Anemone Toxin with a Dual Mechanism of Action on Shaker-Type K+ Channels Activation. Marine Drugs, 16(10), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100360






