Investigating the Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Proteobacteria: A Survey of Molecules and Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Alphaproteobacteria
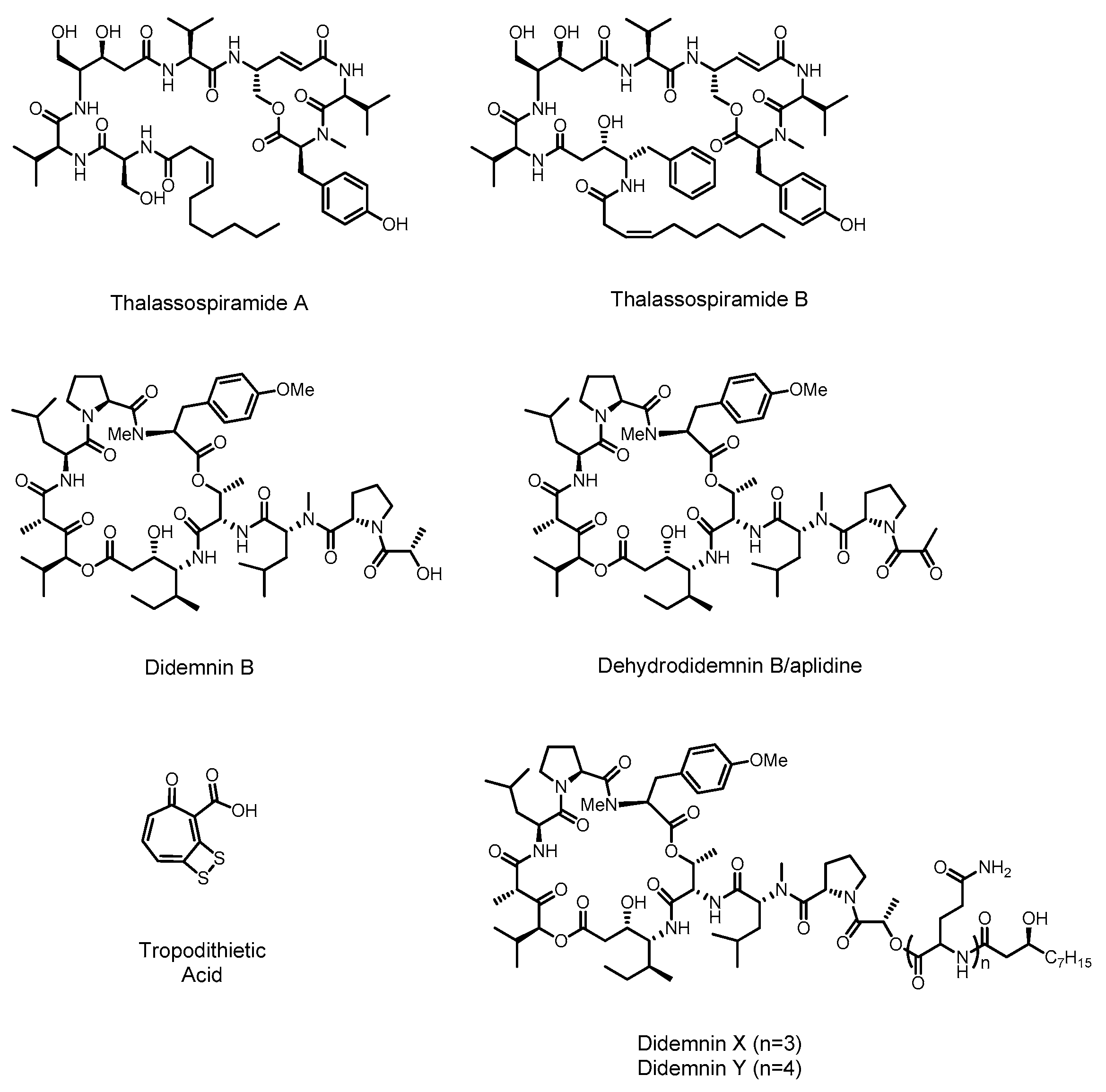
2.1. Didemnin
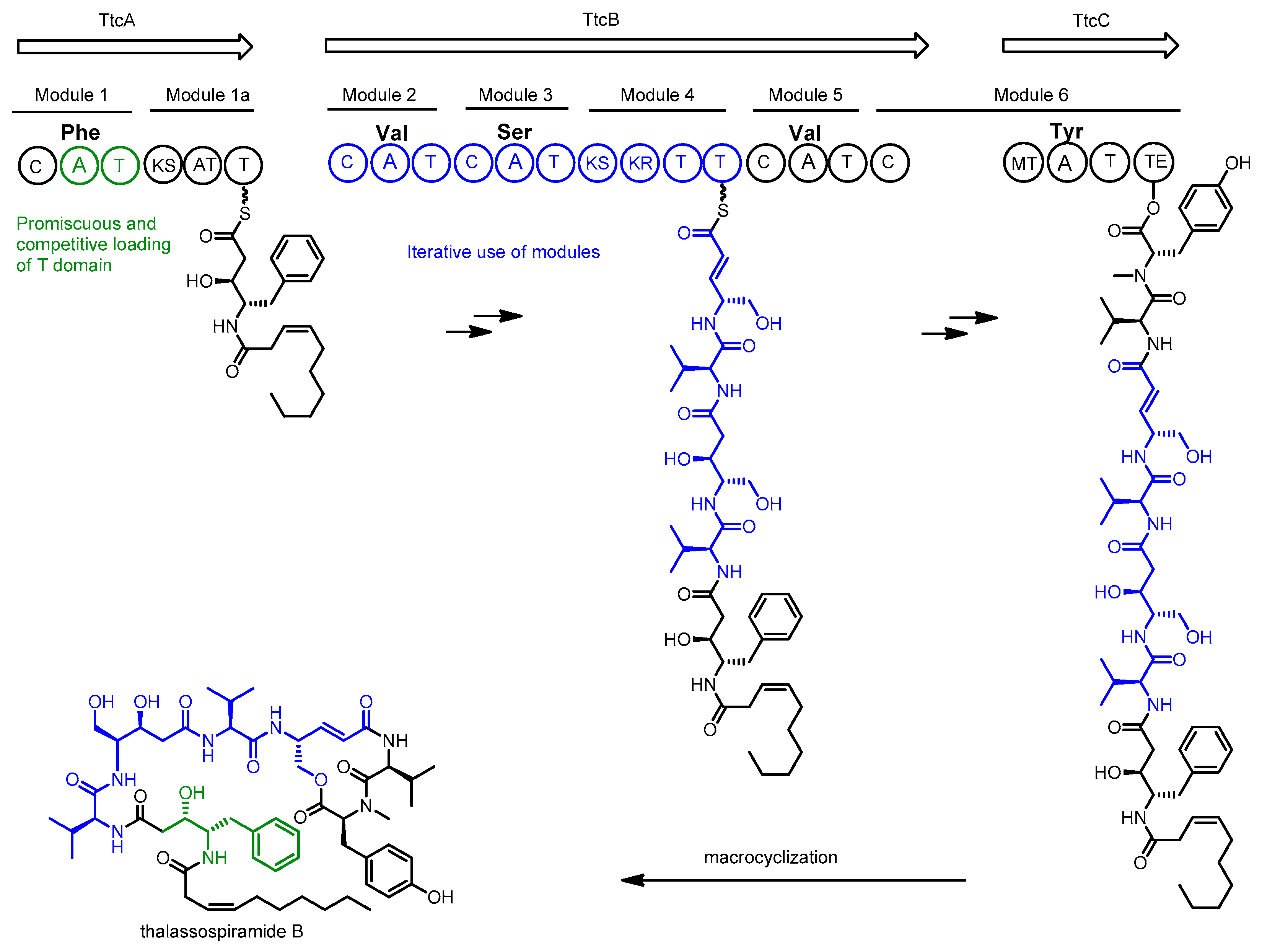
2.2. Thalassospiramide
2.3. Tropodithietic Acid
3. Gammaproteobacteria
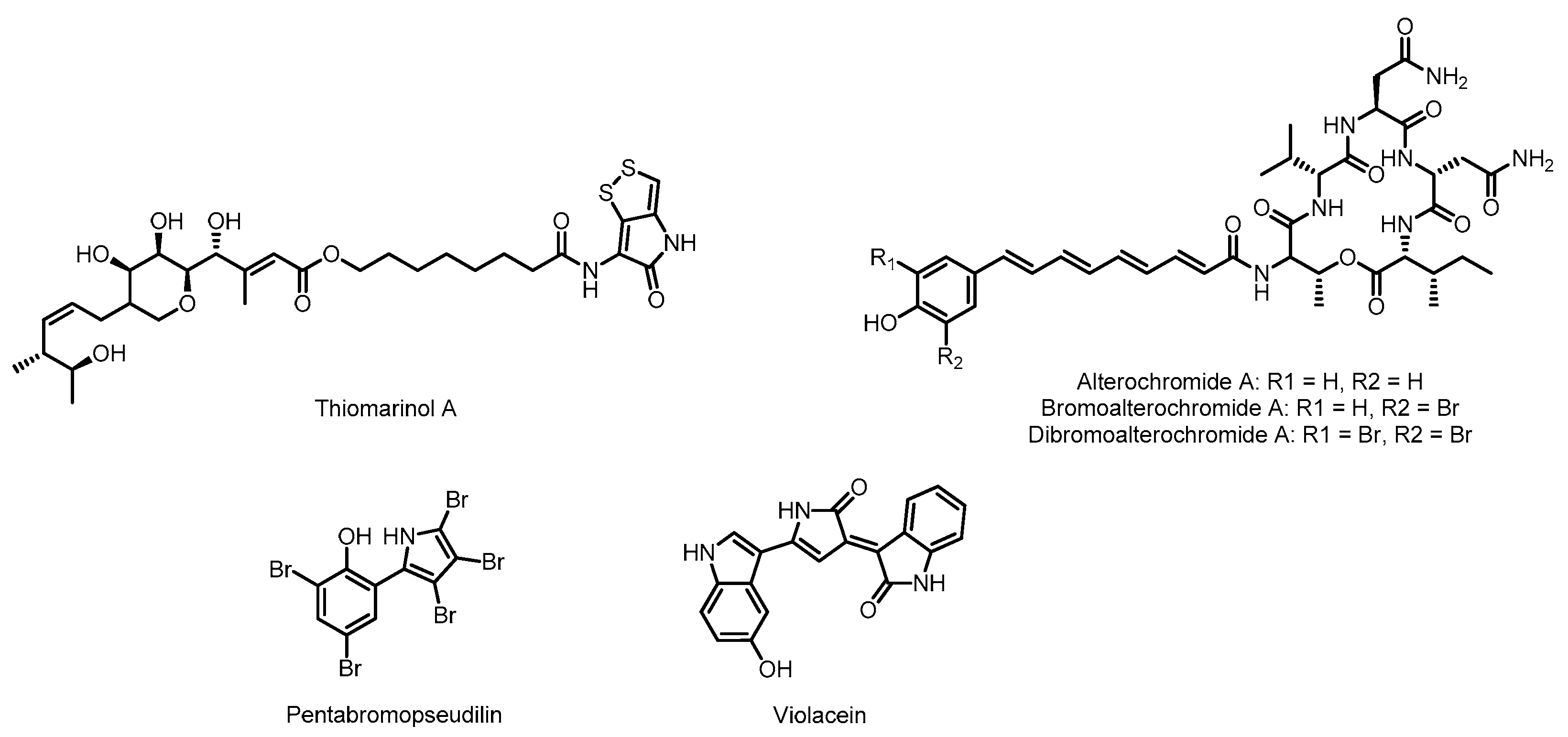
3.1. Thiomarinol
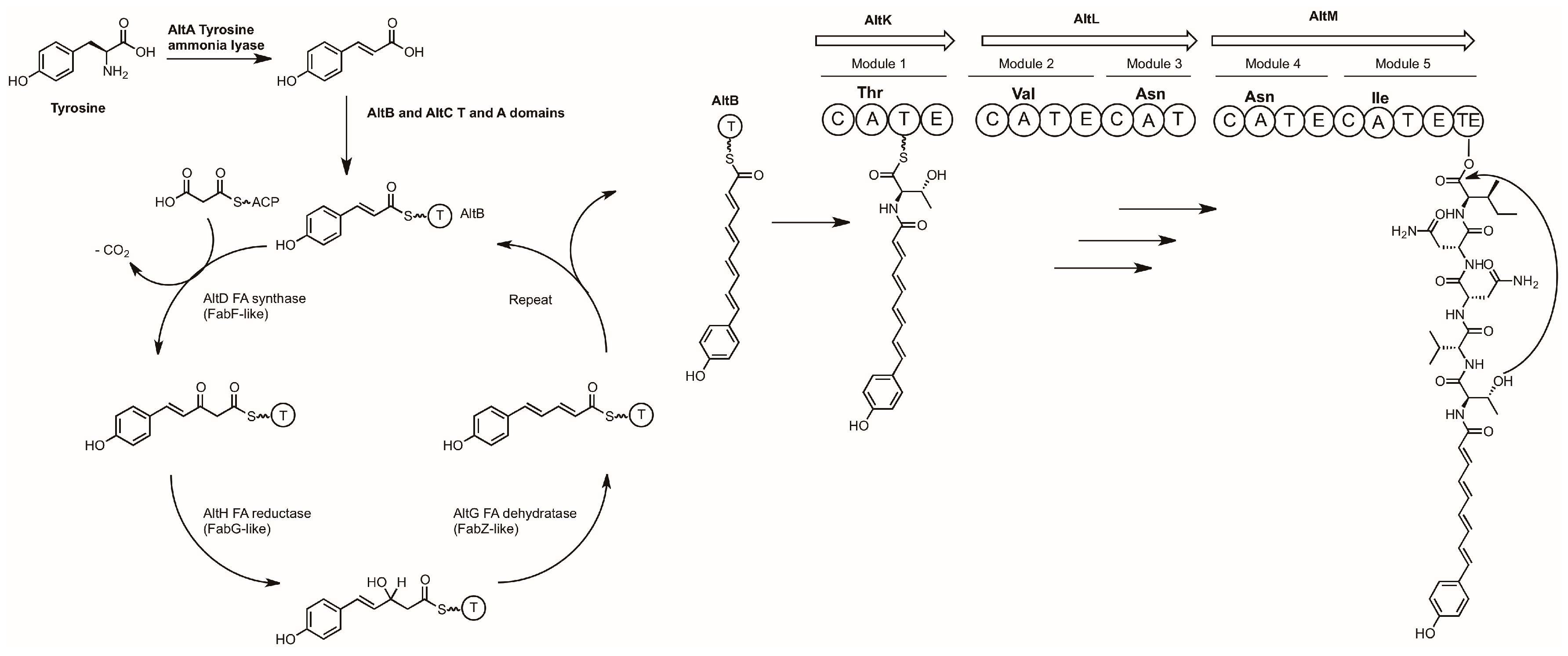
3.2. Alterochromides
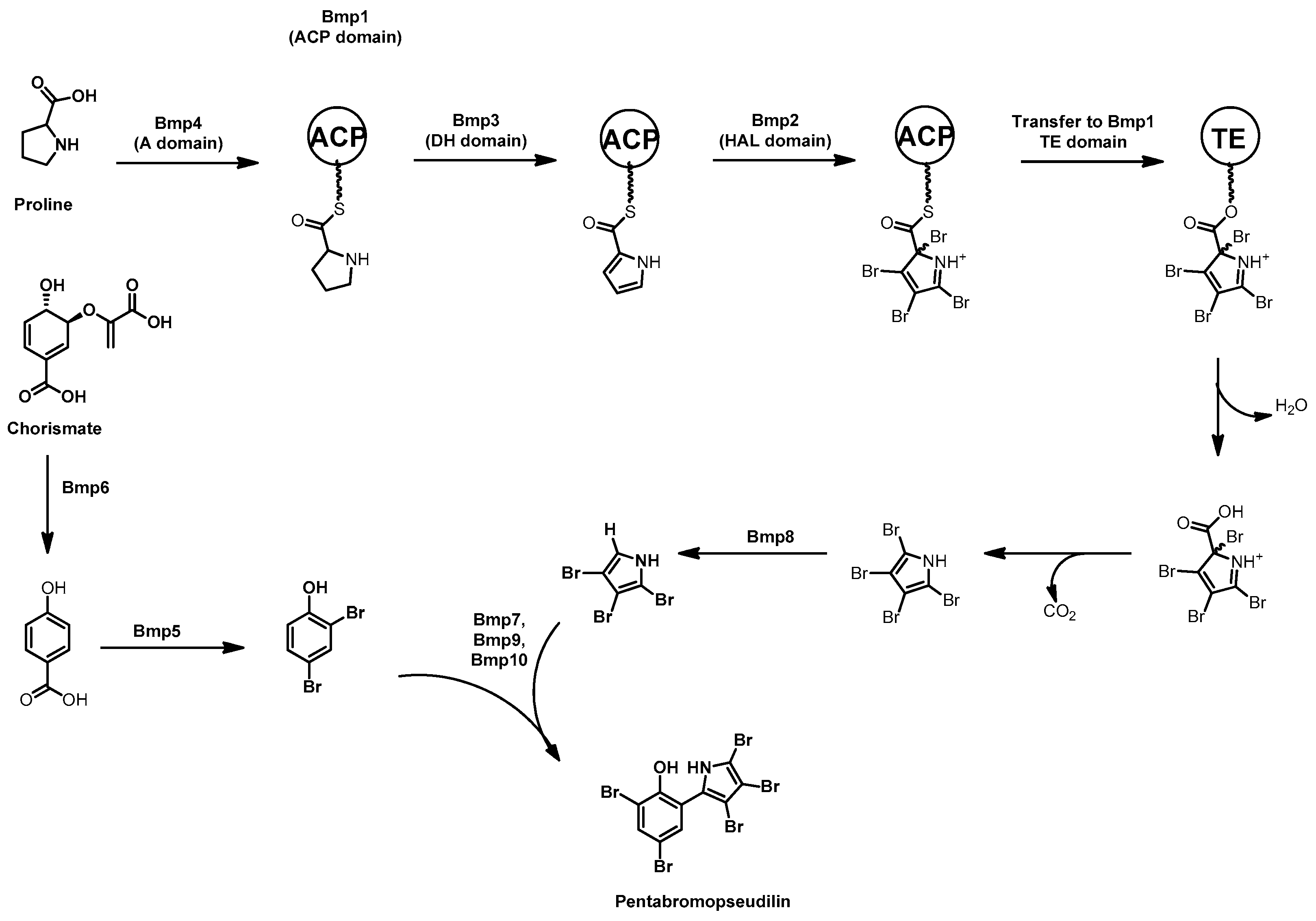
3.3. Pentabromopseudilin
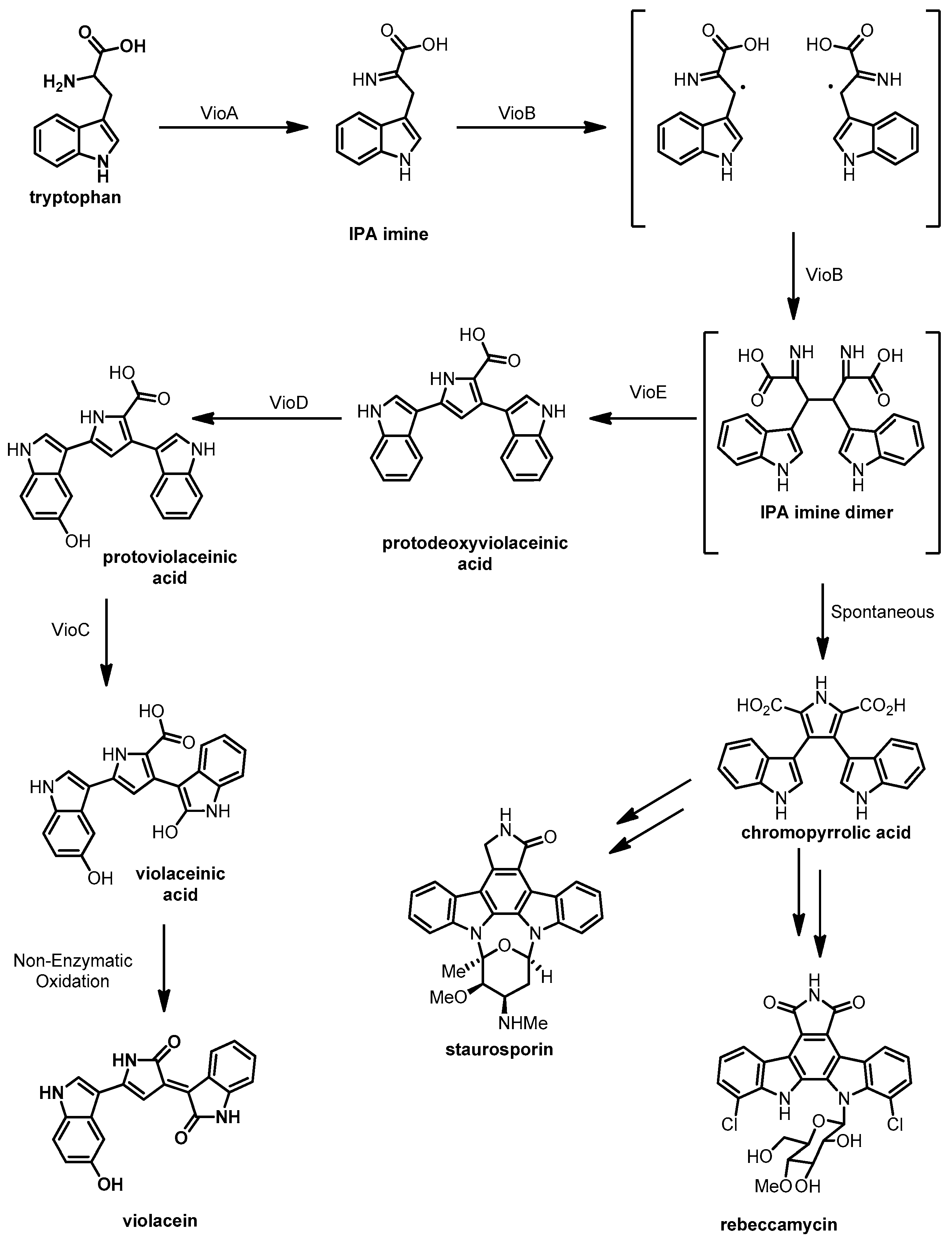
3.4. Violacein
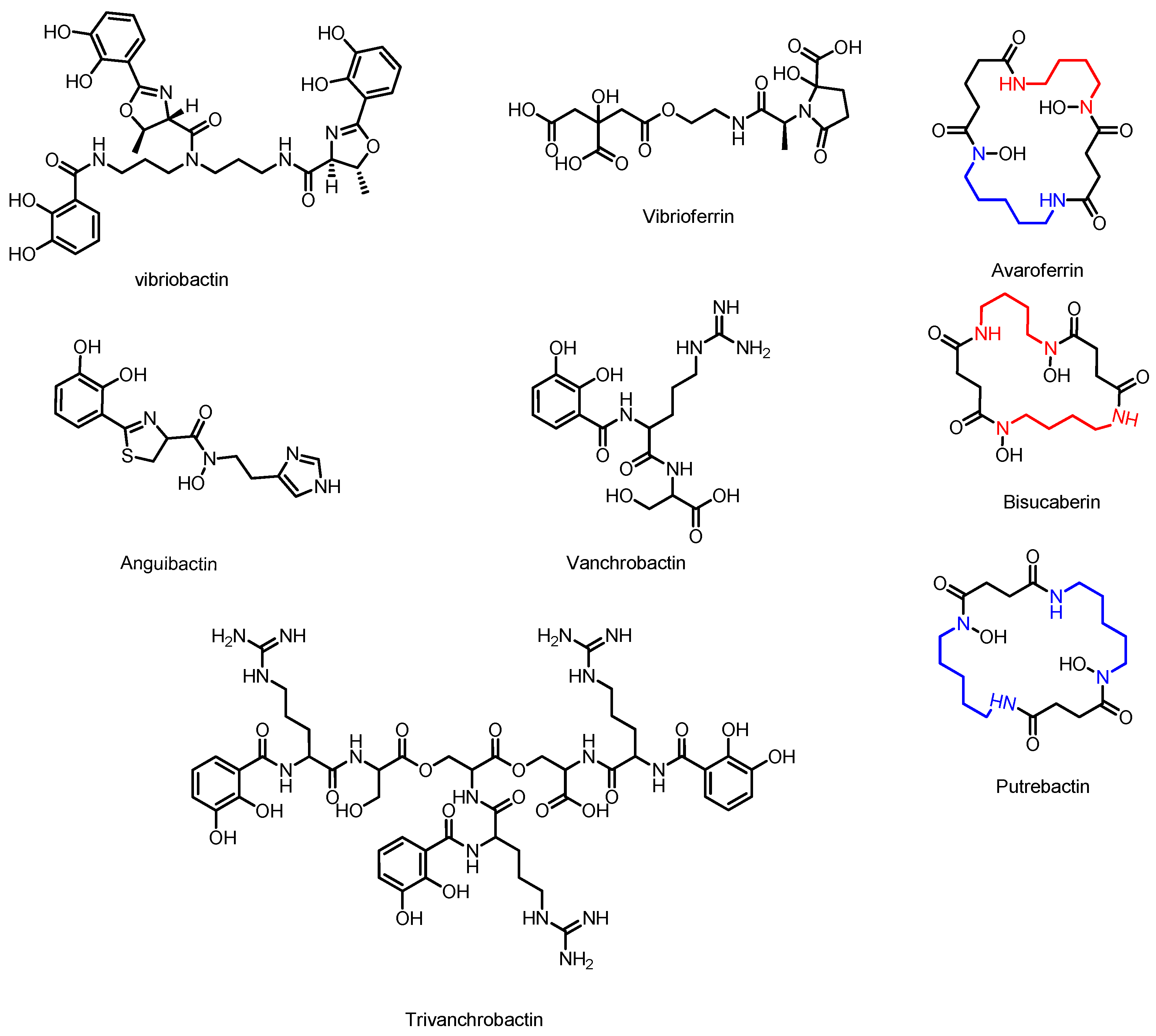
3.5. Avaroferrin, Putrebactin, and Bisucaberin
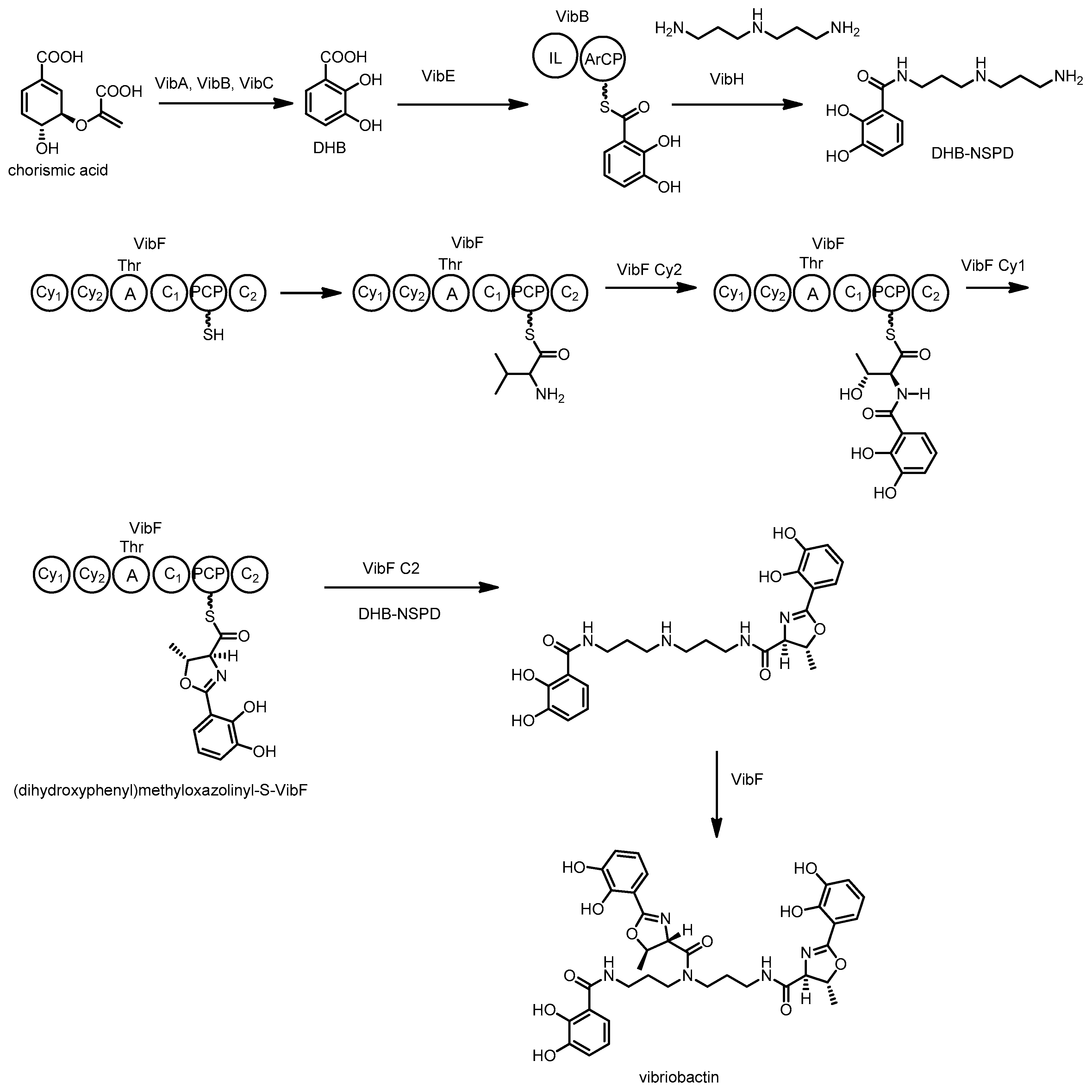
3.6. Vibriobactin
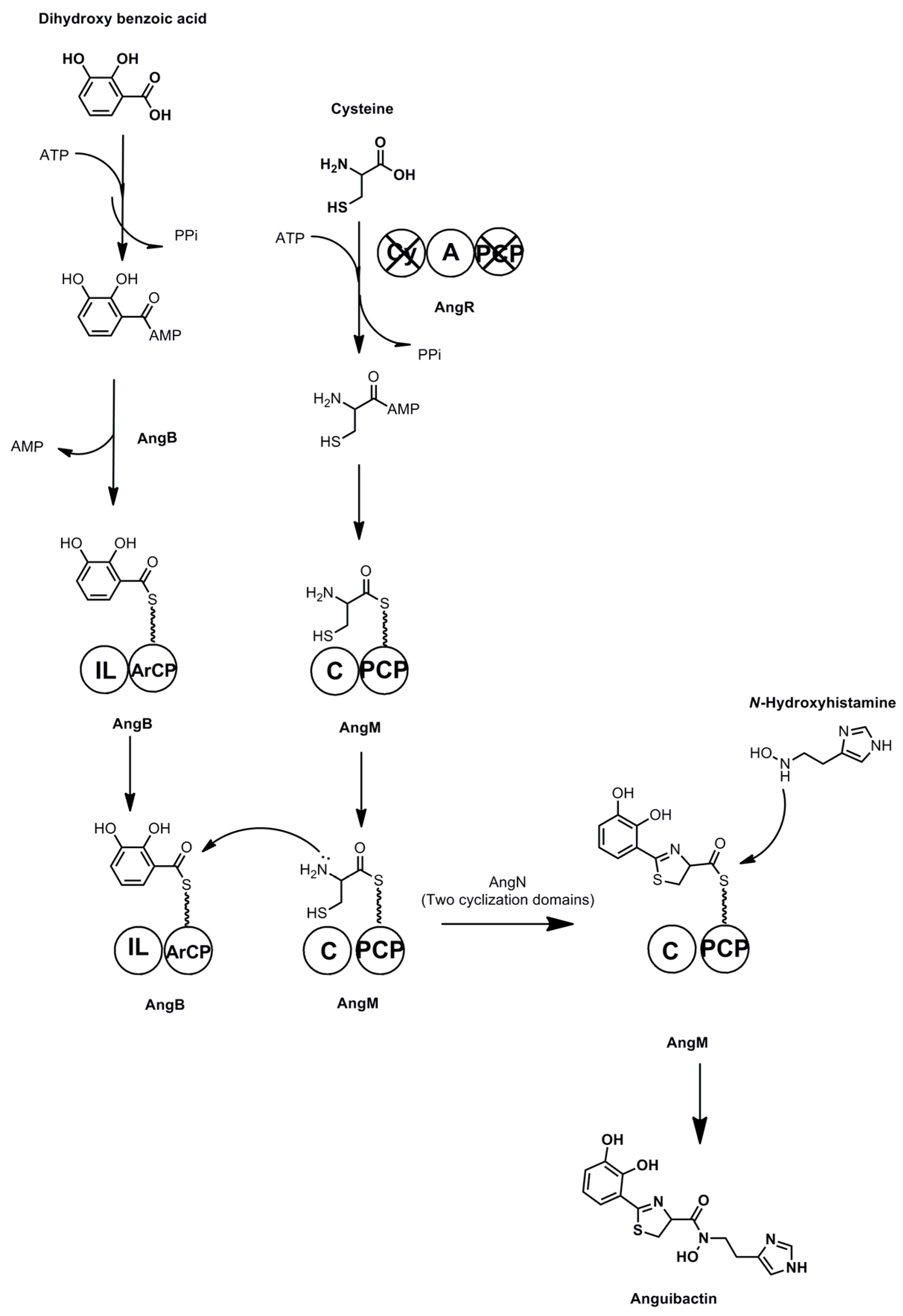
3.7. Anguibactin and Vanchrobactin
3.8. Vibrioferrin
4. Deltaproteobacteria
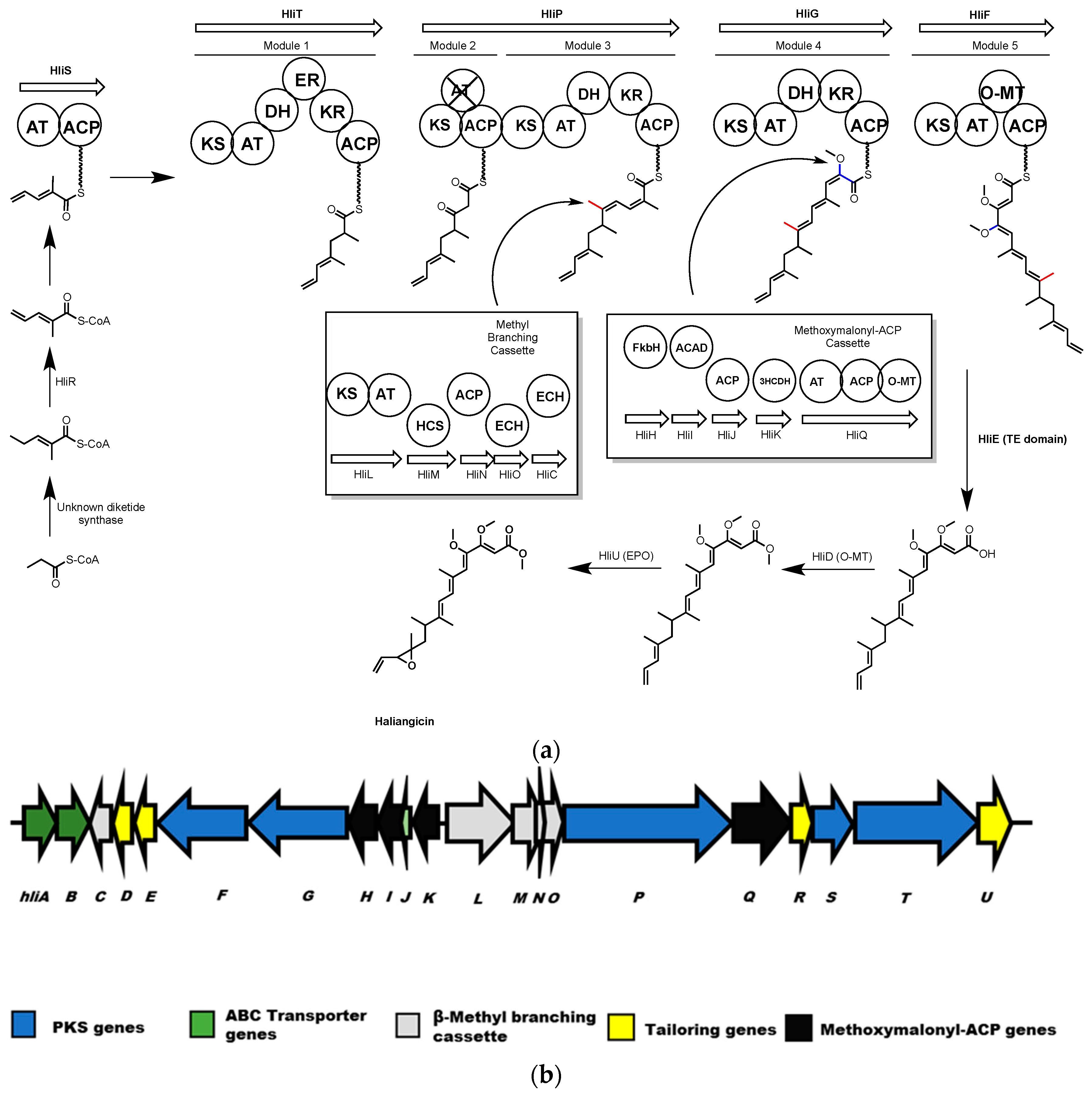
4.1. Haliangicin
4.2. Phenylnannolones
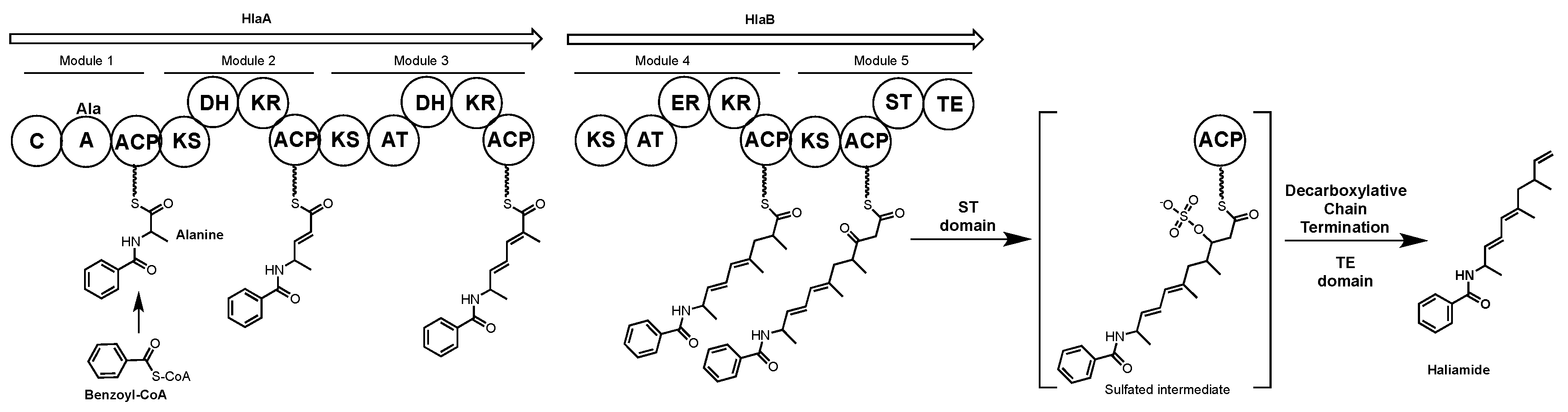
4.3. Haliamide
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dias, D.A.; Urban, S.; Roessner, U. A historical overview of natural products in drug discovery. Metabolites 2012, 2, 303–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lister, P.D.; Wolter, D.J.; Hanson, N.D. Antibacterial-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Clinical impact and complex regulation of chromosomally encoded resistance mechanisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 582–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniesa, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Hertwig, S.; Appel, B.; Brussow, H. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O104:H4: A new challenge for microbiology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4065–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.C.; Alton, E.W.; Bush, A. Cystic fibrosis. Br. Med. J. 2007, 335, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujie, A. The path to producing pharmaceuticals from natural products uncovered by academia-from the perspective of a science coordinator. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine natural products: A new wave of drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, M.H.; Fischbach, M.A. Computational approaches to natural product discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Klenk, H.P.; Clement, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, Physiology, and Natural Products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strieker, M.; Tanovic, A.; Marahiel, M.A. Nonribosomal peptide synthetases: Structures and dynamics. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felnagle, E.A.; Jackson, E.E.; Chan, Y.A.; Podevels, A.M.; Berti, A.D.; McMahon, M.D.; Thomas, M.G. Nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in the production of medically relevant natural products. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertweck, C. The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 4688–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 144–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 237–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 160–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 116–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 382–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Still, P.C.; Johnson, T.A.; Theodore, C.M.; Loveridge, S.T.; Crews, P. Scrutinizing the scaffolds of marine biosynthetics from different source organisms: Gram-negative cultured bacterial products enter center stage. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambadou, F.; Lanneluc, I.; Sable, S.; Klein, G.L.; Doghri, I.; Sopena, V.; Didelot, S.; Barthelemy, C.; Thiery, V.; Chevrot, R. Novel nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) genes sequenced from intertidal mudflat bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 357, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lane, A.L.; Moore, B.S. A sea of biosynthesis: Marine natural products meet the molecular age. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleigrewe, K.; Gerwick, L.; Sherman, D.H.; Gerwick, W.H. Unique marine derived cyanobacterial biosynthetic genes for chemical diversity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Miles, Z.D.; Winter, J.M.; Eustaquio, A.S.; El Gamal, A.A.; Moore, B.S. Enzymatic Halogenation and Dehalogenation Reactions: Pervasive and Mechanistically Diverse. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 5619–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.S. The phylogeny of proteobacteria: Relationships to other eubacterial phyla and eukaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 367–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.P.; Gillespie, J.J.; Sobral, B.W.; Nordberg, E.K.; Snyder, E.E.; Shallom, J.M.; Dickerman, A.W. Phylogeny of gammaproteobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferla, M.P.; Thrash, J.C.; Giovannoni, S.J.; Patrick, W.M. New rRNA gene-based phylogenies of the Alphaproteobacteria provide perspective on major groups, mitochondrial ancestry and phylogenetic instability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.P.; Sobral, B.W.; Dickerman, A.W. A robust species tree for the alphaproteobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 4578–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannoni, S.J.; Tripp, J.H.; Givan, S.; Podar, M.; Vergin, K.L.; Baptista, D.; Bibbs, L.; Eads, J.; Richardson, T.H.; Noordewier, M.; et al. Genome streamlining in a cosmopolitan oceanic bacterium. Science 2005, 309, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Medema, M.H.; Kazempour, D.; Fischbach, M.A.; Breitling, R.; Takano, E.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 2.0—A versatile platform for genome mining of secondary metabolite producers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W204–W212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Medema, M.H.; Kottmann, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Weber, T. The antiSMASH database, a comprehensive database of microbial secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D555–D559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, M.H.; Blin, K.; Cimermancic, P.; de Jager, V.; Zakrzewski, P.; Fischbach, M.A.; Weber, T.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. antiSMASH: Rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W339–W346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, T.; Blin, K.; Duddela, S.; Krug, D.; Kim, H.U.; Bruccoleri, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; Muller, R.; Wohlleben, W.; et al. antiSMASH 3.0-a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W237–W243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukimoto, M.; Nagaoka, M.; Shishido, Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Nishisaka, F.; Matsumoto, S.; Harunari, E.; Imada, C.; Matsuzaki, T. Bacterial production of the tunicate-derived antitumor cyclic depsipeptide didemnin B. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2329–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Kersten, R.D.; Nam, S.-J.; Lu, L.; Al-Suwailem, A.M.; Zheng, H.; Fenical, W.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Moore, B.S.; Qian, P.-Y. Bacterial biosynthesis and maturation of the didemnin anti-cancer agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8625–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinehart, K.L.J.; Gloer, J.B.; Hughes, R.G.J.; Renis, H.E.; McGovren, J.P.; Swynenberg, E.B.; Stringfellow, D.A.; Kuentzel, S.L.; Li, L.H. Didemnins: Antiviral and antitumor depsipeptides from a caribbean tunicate. Science 1981, 212, 933–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Currano, J.N.; Carroll, P.J.; Joullié, M.M. Didemnins, tamandarins and related natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 404–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.M.; Holoye, P.Y.; Murphy, W.K.; Forman, A.; Papasozomenos, S.C.; Hong, W.K.; Raber, M. Phase I/II clinincal trial of didemnin B in non-small-cell luncg cancer: Neuromuscular toxicity is dose-limiting. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1991, 29, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, S.K.; Wolf, M.K.; Eisenberger, M.A.; O'Rourke, M.; Brannon, W.; Crawford, E.D. Phase II evaluation of didemnin B in hormonally refractory metastatic prostate cancer. Investig. New Drugs 1995, 13, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinehart, K.L.; Lithgow-Bertelloni, A.M. Dehydrodidemnin B. U.S. Patent 5,834,586, 10 November 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wesener, S.R.; Potharla, V.Y.; Cheng, Y.-Q. Reconstitution of the FK228 biosynthetic pathway reveals cross talk between modular polyketide synthases and fatty acid synthase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, R.; Stroh, J.G.; Sullins, D.W.; Rinehart, K.L. Seven new didemnins from the marine tunicate Trididemnum solidum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 3734–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, D.; Pos, K.M.; Thines, M.; Grün, P.; Bode, H.B. A natural prodrug activation mechanism in nonribosomal peptide synthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 888–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, M.B.; McMillan, E.A.; Rosales, T.I.; Kim, H.S.; Ou, Y.-H.; Toombs, J.E.; Brekken, R.A.; Minden, M.D.; Macmillan, J.B.; White, M.A. Mode of action and pharmacogenomic biomarkers for exceptional responders to didemnin B. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.C.; Xu, Y.; Lu, L.; Kersten, R.D.; Shao, Z.; Al-Suwailem, A.M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Qian, P.-Y.; Moore, B.S. Biosynthetic Multitasking Facilitates Thalassospiramide Structural Diversity in Marine Bacteria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Meehan, M.J.; Gu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Xu, Y.; et al. Mechanism of action of thalassospiramides, a new class of calpain inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, L.; Lai, Q.; Zhu, B.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Herrup, K.; Moore, B.S.; Ross, A.C.; et al. Family-wide structural characterization and genomic comparisons decode diversity-oriented biosynthesis of thalassospiramides by marine proteobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 27228–27238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.-C.; Strangman, W.K.; Kauffman, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Thalassospiramides A and B, immunosuppressive peptides from the marine bacterium Thalassospira sp. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, S.; Pyee, Y.; Kim, E.-H.; Lee, S.K.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.-C. Thalassospiramide G, a New γ-Amino-Acid-Bearing Peptide from the Marine Bacterium Thalassospira sp. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.C.; Gulland, L.E.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Moore, B.S. Targeted capture and heterologous expression of the Pseudoalteromonas alterochromide gene cluster in Escherichia coli represents a promising natural product exploratory platform. ACS Synth. Biol. 2015, 4, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Liu, J.-H.; Zhang, X.-X.; Chen, Y.-G.; Wang, Z.-G.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.-Y.; Peng, Q.; Cui, X.-L. Fodinicurvata sediminas gen. nov., sp. nov. and Fodinicurvata fenggangensis sp. nov., poly-β-hydroxybutyrate-producing bacteria in the family Rhodospirillaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2575–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkhoff, T.; Bach, G.; Heidorn, T.; Liang, L.; Schlingloff, A.; Simon, M. Antibiotic production by a Roseobacter clade-affiliated species from the German Wadden Sea and its antagonistic effects on indigenous isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alvise, P.W.; Lillebø, S.; Wergeland, H.I.; Gram, L.; Bergh, Ø. Protection of cod larvae from vibriosis by Phaeobacter spp.: A comparison of strains and introduction times. Aquaculture 2013, 384–387, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.Z.; Wang, R.; Gitai, Z.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. Mode of action and resistance studies unveil new roles for tropodithietic acid as an anticancer agent and the gamma-glutamyl cycle as a proton sink. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, J.M.; Simo, R.; Massana, R.; Covert, J.S.; Casamayor, E.O.; Pedros-Alio, C.; Moran, M.A. Bacterial community structure associated with a dimethylsulfoniopropionate-producing North Atlantic algal bloom. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4237–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Curson, A.R.J.; Todd, J.D.; Johnston, A.W.B. Diversity of DMSP transport in marine bacteria, revealed by genetic analyses. Biogeochemistry 2012, 110, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, R.; Gantert, C.; Voss, M.; Eisenreich, W.; Haehnel, W.; Fuchs, G. Studies on the mechanism of ring hydrolysis in phenylacetate degradation: A metabolic branching point. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 11021–11034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, E.; Begly, T.P. Mechanistic studies on phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6449–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Brock, N.L.; Liesegang, H.; Dogs, M.; Preuth, I.; Simon, M.; Dickschat, J.S.; Brinkhoff, T. Genetic analysis of the upper phenylacetate catabolic pathway in the production of tropodithietic acid by Phaeobacter gallaeciensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3539–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, N.L.; Nikolay, A.; Dickschat, J.S. Biosynthesis of the antibiotic tropodithietic acid by the marine bacterium Phaeobacter inhibens. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5487–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offret, C.; Desriac, F.; Le Chevalier, P.; Mounier, J.; Jegou, C.; Fleury, Y. Spotlight on Antimicrobial Metabolites from the Marine Bacteria Pseudoalteromonas: Chemodiversity and Ecological Significance. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.L.; Alkhalaf, L.M.; Ryan, K.S. In vitro reconstitution of indolmycin biosynthesis reveals the molecular basis of oxazolinone assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2717–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.L.; Singh, R.; Alkhalaf, L.M.; Kuatsjah, E.; He, H.Y.; Eltis, L.D.; Ryan, K.S. A pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme that oxidizes an unactivated carbon-carbon bond. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magarvey, N.A.; Fortin, P.D.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Walsh, C.T. Gatekeeping versus promiscuity in the early stages of the andrimid biosynthetic assembly line. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Fischbach, M.A.; Clardy, J. A biosynthetic cluster for the acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor andrimid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10660–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Needham, J.; Kelly, M.T.; Ishige, M.; Andersen, R.H. Andrimid and moiramides A-C, metabolites produced in culture by a marine isolate of the bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens: Strucuter elucidation and biosynthesis. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 2058–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizawa, H.; Kagasaki, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Hideyuki, H.; Domon, H.; Utsui, Y.; Kodama, K.; Takahashi, S. Thiomarinol, a New Hybrid Antimicrobial Antibiotic Produced by a Marine Bacterium: Fermentation, Isolation, Structure, and Antimicrobial Activity. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, D.; Haines, A.S.; Song, Z.; Murphy, A.C.; Hothersall, J.; Stephens, E.R.; Gurney, R.; Cox, R.J.; Crosby, J.; Willis, C.L.; et al. A natural plasmid uniquely encodes two biosynthetic pathways creating a potent anti-MRSA antibiotic. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, K.; Soga, K.; Shimauchi, Y.; Ishikura, T. Holomycin and N-propionylholothin, antibiotics produced by a cephamycin C producer. J. Antibiot. 1977, 30, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celmer, W.D.; Solomons, I.A. The structures of thiolutin and aureothricin, antibiotics containing a unique pyrrolonodithiole nucleus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 2861–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Walsh, C.T. Identification of the gene cluster for the dithiolopyrrolone antibiotic holomycin in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19731–19735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, A.K.; Hothersall, J.; Cooper, S.M.; Stephens, E.; Simpson, T.J.; Thomas, C.M. Characterization of the Mupirocin Biosynthesis Gene Cluster from Pseudomonas fluorescens NCIMB 10586. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, R.; Thomas, C.M. Mupirocin: Biosynthesis, special features and applications of an antibiotic from a Gram-negative bacterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, A.K.; Hothersall, J.; Thomas, C.M. Quorum-sensing-dependent regulation of biosynthesis of the polyketide antibiotic mupirocin in Pseudomonas fluorescens NCIMB 10586. Microbiology 2001, 147, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hothersall, J.; Mazzetti, C.; O’Connell, Y.; Shields, J.A.; Rahman, A.S.; Cox, R.J.; Crosby, J.; Simpson, T.J.; Thomas, C.M.; et al. In vivo mutational analysis of the mupirocin gene cluster reveals labile points in the biosynthetic pathway: The “leaky hosepipe” mechanism. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.C.; Gao, S.-S.; Han, L.-C.; Carobene, S.; Fukuda, D.; Song, Z.; Hothersall, J.; Cox, R.J.; Crosby, J.; Crump, M.P.; et al. Biosynthesis of thiomarinol A and related metabolites of Pseudoalteromonas sp. SANK 73390. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.C.; Fukuda, D.; Song, Z.; Hothersall, J.; Cox, R.J.; Willis, C.L.; Thomas, C.M.; Simpson, T.J. Engineered thiomarinol antibiotics active against MRSA are generated by mutagenesis and mutasynthesis of Pseudoalteromonas SANK 73390. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 3271–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, Z.D.; Wever, W.J.; Economou, N.J.; Bowers, A.A.; Li, B. Enzymatic basis of “hybridity” in thiomarinol biosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 5137–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.; Mellows, G. Inhibition of isoleucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase in Echerichia coli by pseudomonic acid. Biochem. J. 1978, 176, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, B.; O’Neill, A.; Wilson, J.M.; O’Hanlon, P.J.; Chopra, I. Antimicrobial properties and mode of action of the pyrrothine holomycin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speitling, M.; Smetanina, O.F.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Laatsch, H. Bromoalterochromides A and A′, unprecedented chromopeptides from a marine Pseudoalteromonas maricaloris strain KMM 636. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolevskaya, M.P.; Smetanina, O.F.; Speitling, M.; Shevchenko, L.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Laatsch, H.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Ivanova, E.P.; Elyakov, G.B. Controlling production of brominated cyclic depsipeptides by Pseudoalteromonas maricaloris KMM 636T. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 40, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Wu, C.H.; Moree, W.J.; Lamsa, A.; Medema, M.H.; Zhao, X.; Gavilan, R.G.; Aparicio, M.; Atencio, L.; Jackson, C.; et al. MS/MS networking guided analysis of molecule and gene cluster families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2611–E2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkholder, P.; Pfister, R.; Leitz, F. Production of a pyrrole antibiotic by a marine bacterium. Appl. Microbiol. 1966, 14, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lovell, F.M. The Structure of a Bromine-Rich Marine Antibiotic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 4510–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Raimondi, M.V.; Cusimano, M.G.; Raffa, D.; Maggio, B.; Daidone, G.; Schillaci, D. Pharmaceutical Potential of Synthetic and Natural Pyrrolomycins. Molecules 2015, 20, 21658–21671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laatsch, H.; Renneberg, B.; Hanefeld, U.; Kellner, M.; Pudleiner, H.; Hamprecht, G.; Kraemer, H.-P.; Anke, H. Structure-activity relationships of phenyl- and benzoylpyrroles. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 43, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschke, J.D.; Hanefeld, U.; Laatsch, H. Biosynthesis of the marine antibiotic pentabromopseudilin. 2. The pyrrole ring. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanefeld, U.; Floss, H.G.; Laatsch, H. Biosynthesis of the marine antibiotic pentabromopseudilin. Part 1. The benzene ring. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 3604–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Thompson, B.; Chaney, N.; Wing, J.S.; Gould, S.J.; Loper, J.E. Characterization of the pyoluteorin biosynthetic gene cluster of Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, H. DNA assembler, an in vivo genetic method for rapid construction of biochemical pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouprina, N.; Larionov, V. Selective isolation of genomic loci from complex genomes by transformation-associated recombination cloning in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; El Gamal, A.A.; Yamanaka, K.; Poth, D.; Kersten, R.D.; Schorn, M.; Allen, E.E.; Moore, B.S. Biosynthesis of polybrominated aromatic organic compounds by marine bacteria. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Moore, B.S. Enzymatic synthesis of polybrominated dioxins from the marine environment. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1980–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Gamal, A.; Agarwal, V.; Diethelm, S.; Rahman, I.; Schorn, M.A.; Sneed, J.M.; Louie, G.V.; Whalen, K.E.; Mincer, T.J.; Noel, J.P.; et al. Biosynthesis of coral settlement cue tetrabromopyrrole in marine bacteria by a uniquely adapted brominase-thioesterase enzyme pair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3797–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, K.; Ryan, K.S.; Gulder, T.A.; Hughes, C.C.; Moore, B.S. Flavoenzyme-catalyzed atropo-selective N,C-bipyrrole homocoupling in marinopyrrole biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12434–12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Gamal, A.; Agarwal, V.; Rahman, I.; Moore, B.S. Enzymatic Reductive Dehalogenation Controls the Biosynthesis of Marine Bacterial Pyrroles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13167–13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, N.; Menck, C.F. Chromobacterium violaceum: A review of pharmacological and industiral perspectives. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 27, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtstein, H.C.; Van De Sand, V.F. Violacein, an antibiotic pigment produced by Chromobacterium violaceum. J. Infect. Dis. 1945, 76, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantanella, F.; Berlutti, F.; Passariello, C.; Sarli, S.; Morea, C.; Schippa, S. Violacein and biofilm production in Janthinobacterium lividum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranda, S.; Montes-Borrego, M.; Landa, B.B. Purple-pigmented violacein-producing Duganella spp. inhabit the rhizosphere of wild and cultivated olives in southern Spain. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.X.; Wang, H.S.; Zhang, C.; Lou, K.; Xing, X.H. Reconstruction of the violacein biosynthetic pathway from Duganella sp. B2 in different heterologous hosts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.H.; Xiong, H.; Lee, O.O.; Qi, S.H.; Qian, P.Y. Effect of agitation on violacein production in Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea isolated from a marine sponge. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 44, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Enomoto, K. Characterization of a gene cluster and its putative promoter region for violacein biosynthesis in Pseudoalteromonas sp. 520P1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, N.; Justo, G.Z.; Ferreira, C.V.; Melo, P.S.; Cordi, L.; Martins, D. Violacein: Properties and biological activities. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2007, 48 Pt 3, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Momen, A.Z.; Hoshino, T. Biosynthesis of violacein: Intact incorporation of the tryptophan molecule on the oxindole side, with intramolecular rearrangement of the indole ring on the 5-hydroxyindole side. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, T. Violacein and related tryptophan metabolites produced by Chromobacterium violaceum: Biosynthetic mechanism and pathway for construction of violacein core. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balibar, C.J.; Walsh, C.T. In vitro biosynthesis of violacein from L-tryptophan by the enzymes VioA-E from Chromobacterium violaceum. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 15444–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asamizu, S.; Hirano, S.; Onaka, H.; Koshino, H.; Shiro, Y.; Nagano, S. Coupling reaction of indolepyruvic acid by StaD and its product: Implications for biosynthesis of indolocarbazole and violacein. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, S.; Asamizu, S.; Onaka, H.; Shiro, Y.; Nagano, S. Crystal structure of VioE, a key player in the construction of the molecular skeleton of violacein. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 6459–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.S.; Balibar, C.J.; Turo, K.E.; Walsh, C.T.; Drennan, C.L. The violacein biosynthetic enzyme VioE shares a fold with lipoprotein transporter proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 6467–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhalaf, L.M.; Ryan, K.S. Biosynthetic manipulation of tryptophan in bacteria: Pathways and mechanisms. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.-C.; Zou, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Walsh, C.T.; Tang, Y. Oxidative Cyclization in Natural Product Biosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 117, 5226–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Sato, H.; Shinozaki, M.; Kuramoto, H.; Takamiya, Y.; Sato, T.; Nikaidou, N.; Watanabe, T.; Hoshino, T. Biosynthesis of violacein: A genuine intermediate, protoviolaceinic acid, produced by VioABDE, and insight into VioC function. Chem. Commun. 2007, 40, 4140–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ikawa, A.; Okaue, S.; Taniguchi, S.; Osaka, I.; Yoshimoto, A.; Kishida, Y.; Arakawa, R.; Enomoto, K. Quorum sensing signaling molecules involved in the production of violacein by Pseudoalteromonas. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1958–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mireille Aye, A.; Bonnin-Jusserand, M.; Brian-Jaisson, F.; Ortalo-Magne, A.; Culioli, G.; Koffi Nevry, R.; Rabah, N.; Blache, Y.; Molmeret, M. Modulation of violacein production and phenotypes associated with biofilm by exogenous quorum sensing N-acylhomoserine lactones in the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas ulvae TC14. Microbiology 2015, 161, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilands, J.B. Siderophores: Structure and Function of Microbial Iron Transport Compounds. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26723–26726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandy, M.; Butler, A. Microbial iron acquisition: Marine and terrestrial siderophores. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4580–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, M.L.; Price, N.M.; Bruland, K. Iron chemistry in seawater and its relationship to phytoplankton: A workshop report. Mar. Chem. 1995, 48, 157–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottcher, T.; Clardy, J. A chimeric siderophore halts swarming Vibrio. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 3510–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadi, N.; Oves-Costales, D.; Barona-Gomez, F.; Challis, G.L. A new family of ATP-dependent oligomerization-macrocyclization biocatalysts. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schupp, T.; Toupet, C.; Divers, M. Cloning and expression of two genes of Streptomyces pilosus involved in the biosynthesis of the siderophore desferrioxamine B. Gene 1988, 64, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, T.; Walkdmeir, U.; Divers, M. Biosynthesis of desferrioxamine B in Streptomyces pilosus: Evidence for the involvement of lysine decarboxylase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1987, 42, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barona-Gomez, F.; Wong, U.; Giannakopulos, A.E.; Derrick, P.J.; Challis, G.L. Identification of a cluster of genes that directs desferrioxamine biosynthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor M145. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 16282–16283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadi, N.; Arbache, S.; Song, L.; Oves-Costales, D.; Challis, G.L. Identification of a Gene Cluster That Directs Putrebactin Biosynthesis in Shewanella Species: PubC Catalyzes Cyclodimerization of N-Hydroxy-N-succinylputrescine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. Comm 2008, 130, 10458–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadi, N.; Song, L.; Challis, G.L. Bisucaberin biosynthesis: An adenylating domain of the BibC multi-enzyme catalyzes cyclodimerization of N-hydroxy-N-succinylcadaverine. Chem. Commun. 2008, 41, 5119–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soe, C.Z.; Telfer, T.J.; Levina, A.; Lay, P.A.; Codd, R. Simultaneous biosynthesis of putrebactin, avaroferrin and bisucaberin by Shewanella putrefaciens and characterization of complexes with iron(III), molybdenum(VI) or chromium(V). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 162, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.J.; Kimura, N.; Yokose, H.; Otsuka, M. Heterologous production of bisucaberin using a biosynthetic gene cluster cloned from a deep sea metagenome. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.J.; Sakai, R. Heterologous production of desferrioxamines with a fusion biosynthetic gene cluster. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, G.L.; Sigel, S.P.; Payne, S.M.; Neilands, J.B. Vibriobactin, a siderophore from Vibrio cholerae. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butterton, J.R.; Choi, M.H.; Watnick, P.I.; Carroll, P.A.; Calderwood, S.B. Vibrio cholerae VibF Is Required for Vibriobactin Synthesis and Is a Member of the Family of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trucksis, M.; Michalski, J.; Deng, Y.K.; Kaper, J.B. The Vibrio cholerae genome contains two unique circular chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14464–14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyckoff, E.E.; Smith, S.L.; Payne, S.M. VibD and VibH are required for late steps in vibriobactin biosynthesis in Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyckoff, E.E.; Stoebner, J.A.; Reed, K.E.; Payne, S.M. Cloning of a Vibrio cholerae vibriobactin gene cluster: Identification of genes required for early steps in siderophore biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 7055–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyckoff, E.E.; Valle, A.-M.; Smith, S.L.; Payne, S.M. A multifunctional ATP-binding cassette transporter system from Vibrio cholerae transports vibriobactin and enterobactin. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 7588–7596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keating, T.A.; Marshall, G.C.; Walsh, C.T. Vibriobactin Biosynthesis in Vibrio cholerae: VibH Is an Amide Synthase Homologous to Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Condensation Domains. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 15513–15521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, T.A.; Marshall, G.C.; Walsh, C.T. Reconstitution and Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae Vibriobactin Synthetase from VibB, VibE, VibF, and VibH. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 15522–15530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, T.A.; Marshall, C.G.; Walsh, C.T.; Keating, A.E. The structure of VibH represents nonribosomal peptide synthetase condensation, cyclization and epimerization domains. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2002, 9, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, A.M.; Mori, I.; Perry, R.D.; Walsh, C.T. The nonribosomal peptide synthetase HMWP2 forms a thiazoline ring during biogenesis of yersiniabactin, an iron-chelating virulence factor of Yersinia pestis. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 11637–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, I.; Schupp, T.; Ono, M.; Zirkle, R.; Molnamow, M.; Nowak-Thompson, B.; Englel, N.; Toupet, C.; Stratmann, A.; Cyr, D.; et al. The biosynthetic gene cluster for the microtubule-stabilizing agents epothilones A and B from Sorangium cellulosum So ce90. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, L.E.; Sello, J.; Keating, T.A.; Weinreb, P.H.; Walsh, C.T. Identification of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene cluster encoding the biosynthetic enzymes for assembly of the virulence-conferring siderophore mycobactin. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, C.G.; Hillson, N.J.; Walsh, C.T. Catalytic Mapping of the Vibriobactin Biosynthetic Enzyme VibF. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillson, N.J.; Balibar, C.J.; Walsh, C.T. Catalytically Inactive Condensation Domain C1 Is Responsible for the Dimerization of the VibF Subunit of Vibriobactin Synthetase. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11344–11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillson, N.J.; Walsh, C.T. Dimeric Structure of the Six-Domain VibF Subunit of Vibriobactin Synthetase: Mutant Domain Activity Regain and Ultracentrifugation Studies. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, M.A.F.; Hossain, M.B.; van der Helm, D.; Sanders-Loehr, J.; Actis, L.A.; Crosa, J.H. Structure of anguibactin, a unique plasmid-related bacterial siderophore from the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soengas, R.G.; Anta, C.; Espada, A.; Paz, V.; Ares, I.R.; Balado, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Lemos, M.L.; Jimenez, C. Structural characterization of vanchrobactin, a new catechol siderophore produced by the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum serotype O2. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 7113–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, A.; Montaos, M.A.; Balado, M.; Osorio, C.R.; Rodriguez, J.; Lemos, M.L.; Jimenez, C. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of conjugates between norfloxacin and analogues of the siderophore vanchrobactin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.B.; Jalal, M.A.F.; Van der Helm, D. Gallium-complex of anguibactin, a siderophore from fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 1998, 28, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmasky, M.E.; Salinas, P.C.; Actis, L.A.; Crosa, J.H. Increased production of the siderophore anguibactin mediated by pJM1-like plasmids in Vibrio anguillarum. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naka, H.; Liu, M.; Actis, L.A.; Crosa, J.H. Plasmid- and chromosome-encoded siderophore anguibactin systems found in marine Vibrios: Biosynthesis, transport and evolution. Biometals 2013, 26, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandy, M.; Han, A.; Blunt, J.; Munro, M.; Haygood, M.; Butler, A. Vanchrobactin and anguibactin siderophores produced by Vibrio sp. DS40M4. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, T.J.; Chai, S.; Crosa, J.H. The Overlapping angB and angG Genes Are Encoded within the trans-Acting Factor Region of the Virulence Plasmid in Vibrio anguillarum: Essential Role in Siderophore Biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 6762–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheimer, A.; Verweij, W.; Chen, Q.; Crosa, L.M.; Nagasawa, M.; Tolmasky, M.E.; Actis, L.A.; Crosa, J.H. Characterization of the angR Gene of Vibrio anguillarum: Essential Role in Virulence. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 6496–6509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balado, M.; Osorio, C.R.; Lemos, M.L. A gene cluster involved in the biosynthesis of vanchrobactin, a chromosome-encoded siderophore produced by Vibrio anguillarum. Microbiology 2006, 152 Pt 12, 3517–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Okujo, N.; Yoshida, T.; Matsuura, S.; Shinoda, S. Structure and iron transport activity of Vibrioferrin, a new siderophore of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Biochem. 1994, 115, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, T.; Funahashi, T.; Nakao, H.; Miyoshi, S.I.; Shinoda, S.; Yamamoto, S. Identification and Characterization of Genes Required for Biosynthesis and Transport of the Siderophore Vibrioferrin in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 6938–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.J.; Kimura, N.; Sakai, A.; Ichikawa, Y.; Hanyu, T.; Otsuka, M. Cloning and heterologous expression of the vibrioferrin biosynthetic gene cluster from a marine metagenomic library. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 2283–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaki, H.; Fudou, R.; Iizuka, T.; Nakajima, D.; Okazaki, K.; Shibata, D.; Ojika, M.; Harayama, S. PCR detection of type I polyketide synthase genes in myxobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5571–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fudou, R.; Iizuka, T.; Yamanaka, S. Haliangicin, a novel antifungal metabolite produced by a marine myxobacterium. 1. Fermentation and biological characteristics. J. Antibiot. 2001, 54, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Feng, Z.; Tomura, T.; Suzuki, A.; Miyano, S.; Tsuge, T.; Mori, H.; Suh, J.W.; Iizuka, T.; Fudou, R.; et al. Heterologous Production of the Marine Myxobacterial Antibiotic Haliangicin and Its Unnatural Analogues Generated by Engineering of the Biochemical Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderone, C.T. Isoprenoid-like alkylations in polyketide biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, B.J.; Moss, S.J.; Bai, L.; Kato, Y.; Toelzer, S.; Yu, T.W.; Floss, H.G. Identification of a set of genes involved in the formation of the substrate for the incorporation of the unusual “glycolate” chain extension unit in ansamitocin biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4176–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.C.; Williamson, R.M.; Grunanger, C.; Xu, J.; Gerth, K.; Martinez, R.A.; Moss, S.J.; Carroll, B.J.; Grond, S.; Unkefer, C.J.; et al. On the biosynthetic origin of methoxymalonyl-acyl carrier protein, the substrate for incorporation of “glycolate” units into ansamitocin and soraphen A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14325–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chooi, Y.H.; Fang, J.; Liu, H.; Filler, S.G.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y. Genome mining of a prenylated and immunosuppressive polyketide from pathogenic fungi. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chooi, Y.H.; Sheng, Y.; Valentine, J.S.; Tang, Y. Comparative characterization of fungal anthracenone and naphthacenedione biosynthetic pathways reveals an alpha-hydroxylation-dependent Claisen-like cyclization catalyzed by a dimanganese thioesterase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15773–15785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlendorf, B.; Leyers, S.; Krick, A.; Kehraus, S.; Wiese, M.; Konig, G.M. Phenylnannolones A-C: Biosynthesis of new secondary metabolites from the myxobacterium Nannocystis exedens. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 2997–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhired, S.M.; Crusemann, M.; Almeida, C.; Weber, T.; Piel, J.; Schaberle, T.F.; Konig, G.M. Biosynthesis of phenylnannolone A, a multidrug resistance reversal agent from the halotolerant myxobacterium Nannocystis pusilla B150. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, K.J.; Leadlay, P.F. Combinatorial biosynthesis of reduced polyketides. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Tomura, T.; Sato, J.; Iizuka, T.; Fudou, R.; Ojika, M. Isolation and Biosynthetic Analysis of Haliamide, a New PKS-NRPS Hybrid Metabolite from the Marine Myxobacterium Haliangium ochraceum. Molecules 2016, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, N.; Daum, C.; Lang, E.; Abt, B.; Kopitz, M.; Saunders, E.; Lapidus, A.; Lucas, S.; Glavina Del Rio, T.; Nolan, M.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Haliangium ochraceum type strain (SMP-2). Stand. Genom. Sci. 2010, 2, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, L.; Plaza, A.; Dubiella, C.; Groll, M.; Kaiser, M.; Muller, R. Macyranones: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Binding Mode of an Unprecedented Epoxyketone that Targets the 20S Proteasome. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8121–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Sitachitta, N.; Rossi, J.V.; Roberts, M.A.; Flatt, P.M.; Jia, J.; Sherman, D.H.; Gerwick, W.H. Biosynthetic pathway and gene cluster analysis of curacin A, an antitubulin natural product from the tropical marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1356–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Wang, B.; Kulkarni, A.; Gehret, J.J.; Lloyd, K.R.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H.; Wipf, P.; Hakansson, K.; Smith, J.L.; et al. Polyketide decarboxylative chain termination preceded by o-sulfonation in curacin a biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16033–16035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.R.; Shin, J.H.; Cho, J.S.; Yang, D.; Lee, S.Y. Systems Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, K.; Reynolds, K.A.; Kersten, R.D.; Ryan, K.S.; Gonzalez, D.J.; Nizet, V.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Moore, B.S. Direct cloning and refactoring of a silent lipopeptide biosynthetic gene cluster yields the antibiotic taromycin A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.C.; Larionov, V.; Kouprina, N. Highly efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated TAR cloning of genes and chromosomal loci from complex genomes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcken, R.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Lange, A.; Joerger, A.C.; Boeckler, F.M. Principles and applications of halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1363–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Timmermans, M.L.; Paudel, Y.P.; Ross, A.C. Investigating the Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Proteobacteria: A Survey of Molecules and Strategies. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15080235
Timmermans ML, Paudel YP, Ross AC. Investigating the Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Proteobacteria: A Survey of Molecules and Strategies. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(8):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15080235
Chicago/Turabian StyleTimmermans, Marshall L., Yagya P. Paudel, and Avena C. Ross. 2017. "Investigating the Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Proteobacteria: A Survey of Molecules and Strategies" Marine Drugs 15, no. 8: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15080235
APA StyleTimmermans, M. L., Paudel, Y. P., & Ross, A. C. (2017). Investigating the Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Proteobacteria: A Survey of Molecules and Strategies. Marine Drugs, 15(8), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15080235



