Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from the Sea Discovered Using Bacterial N-acyl-homoserine Lactone-Based Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bacterial AHL-Based Biosensors
2.1. Pigment-Based Biosensors
2.2. Bioluminescence-Based Biosensor
2.3. gfp-Based Biosensors
2.4. β-Galactosidase-Based Biosensor
3. Marine Microorganisms
3.1. QSI from Marine Bacteria
3.2. QSI from Marine Fungi
3.3. QSI from Marine Cyanobacteria
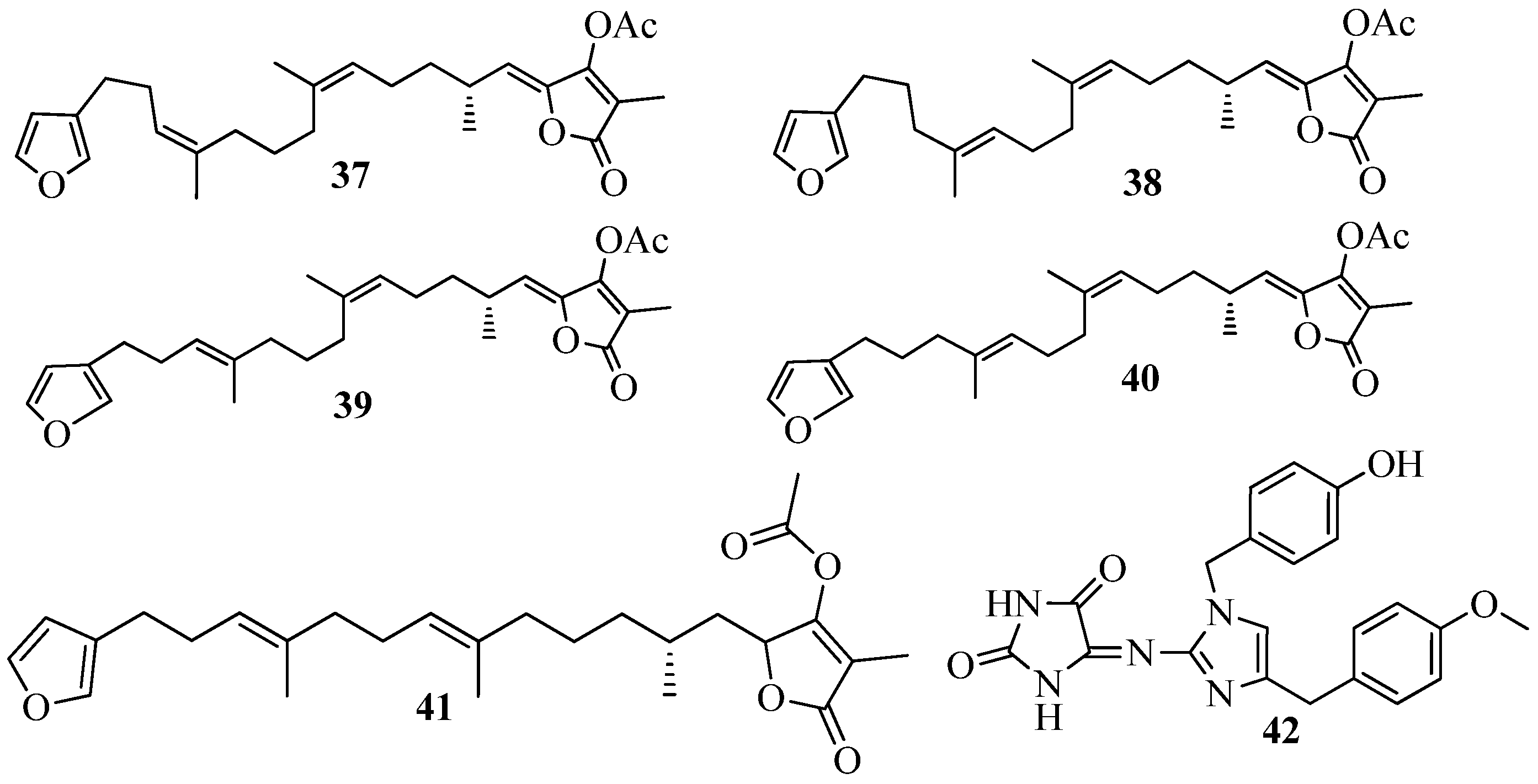
4. QSI from Marine Sponges
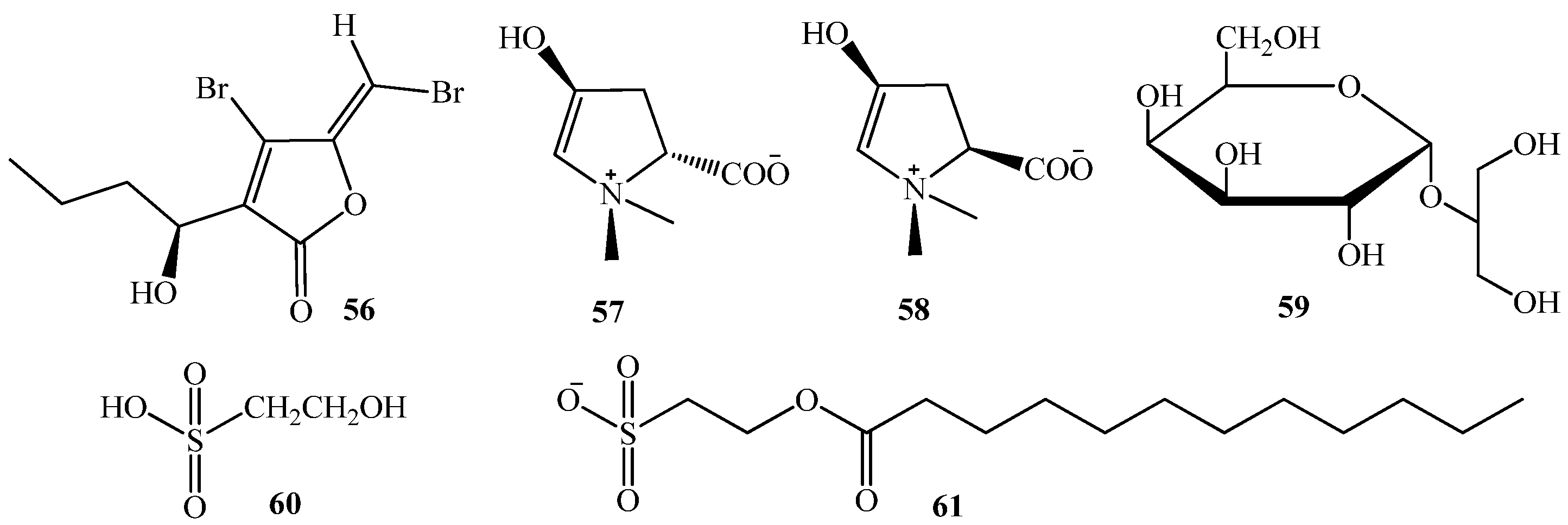
5. QSI from Marine Algae
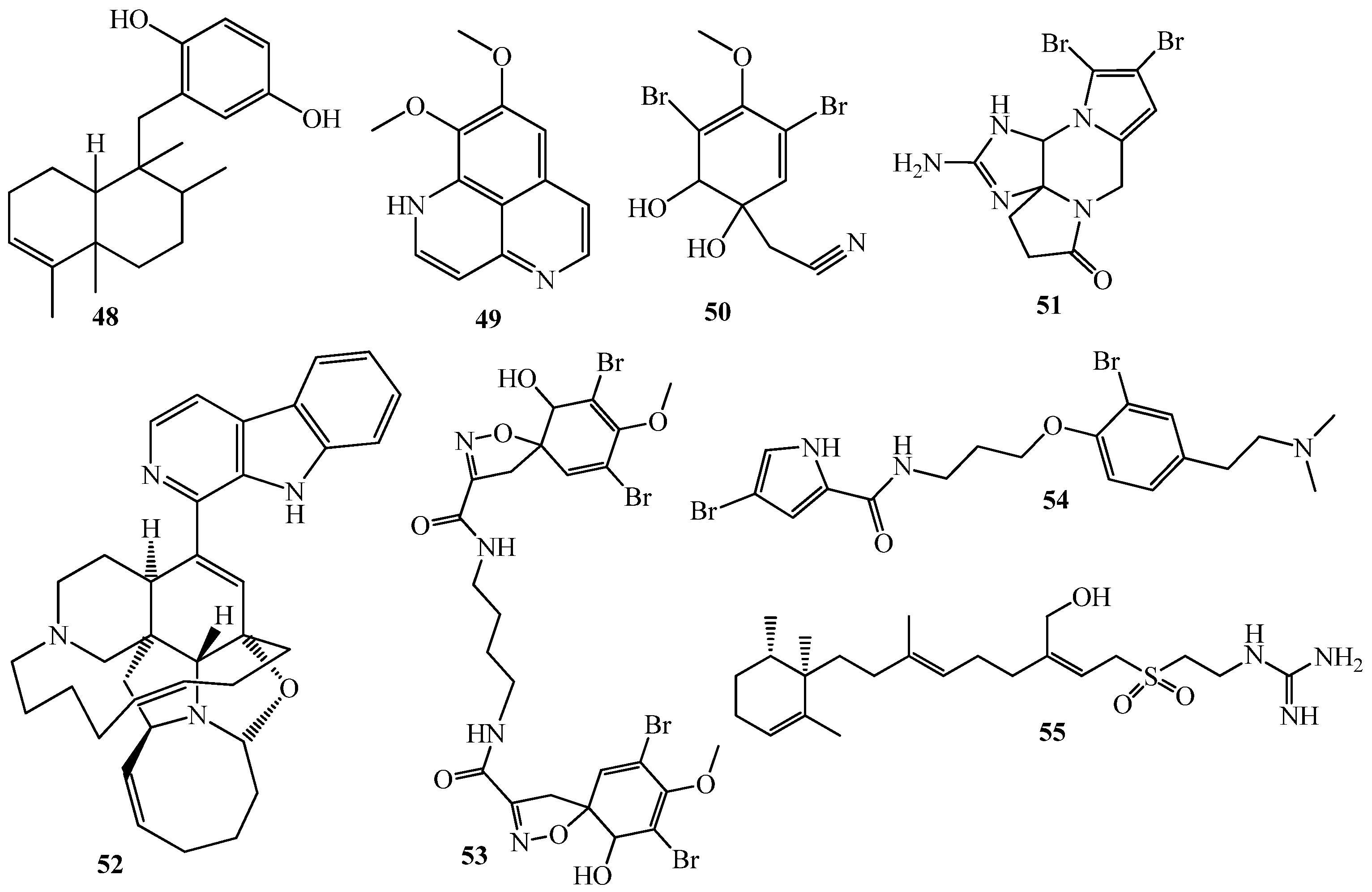
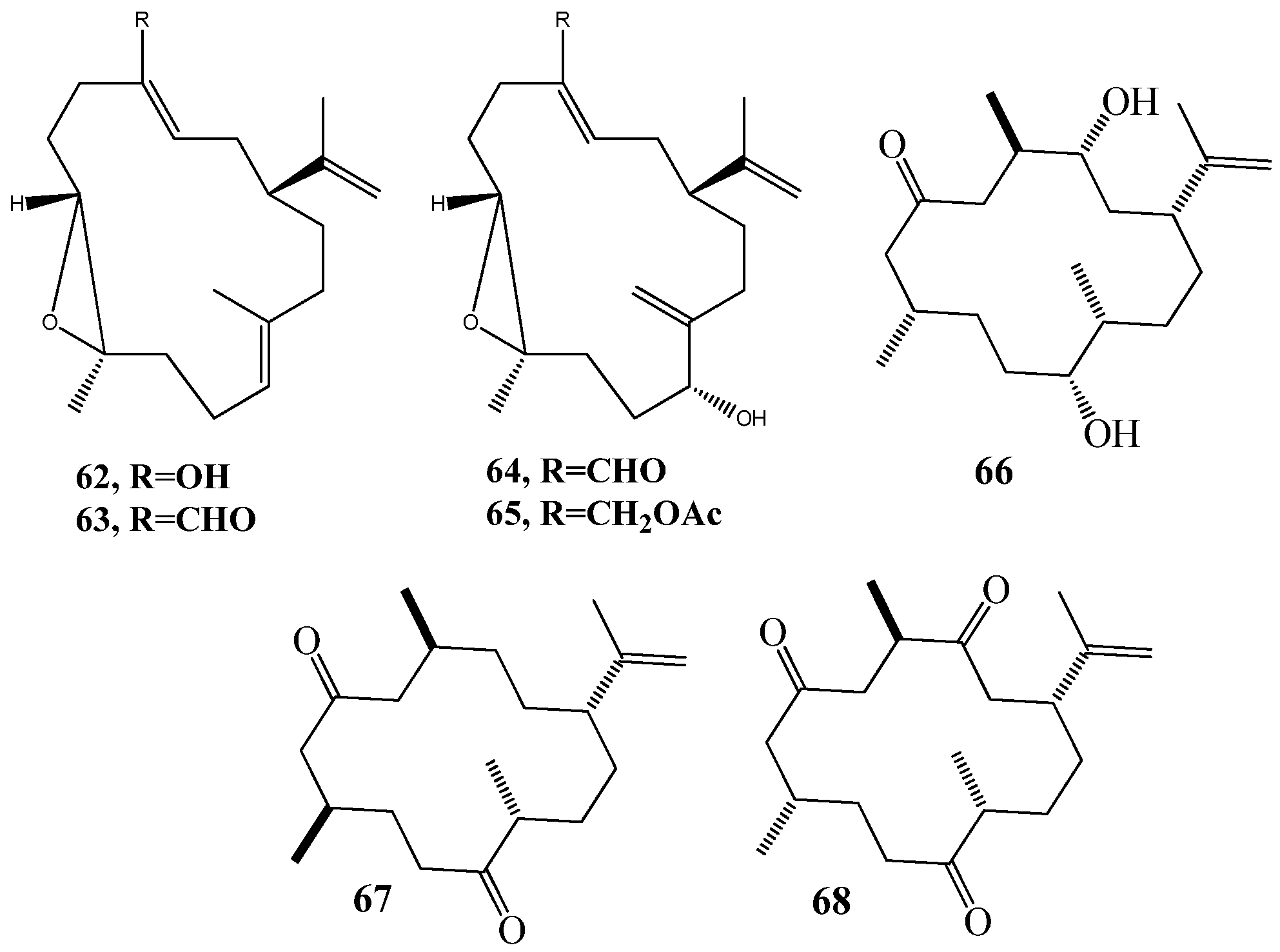
6. QSI from Cnidarians
7. QSI from Bryozoa
8. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arias, C.A.; Murray, B.E. Emergence and management of drug-resistant enterococcal infections. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2008, 6, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, D.; Toleman, M.A.; Giske, C.G.; Cho, H.S.; Sundman, K.; Lee, K.; Walsh, T.R. Characterization of a new metallo-beta-lactamase gene, bla(NDM-1), and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5046–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuya, E.Y.; Lowy, F.D. Antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in the community setting. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelbaum, P.C. 2012 and beyond: Potential for the start of a second pre-antibiotic era? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, C.A.; Murray, B.E. The rise of the Enterococcus: Beyond vancomycin resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The ‘accidental’ pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L.; Baquero, F. Interactions among strategies associated with bacterial infection: Pathogenicity, epidemicity, and antibiotic resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 647–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Nijnik, A.; Philpott, D.J. Modulating immunity as a therapy for bacterial infections. Nat. Rev. Microboil. 2012, 10, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winzer, K.; Hardie, K.R.; Williams, P. Bacterial cell-to-cell communication: Sorry, can’t talk now—Gone to lunch! Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial Quorum Sensing: Its Role in Virulence and Possibilities for Its Control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, A.K.; Vinothkumar, K.; Rajpara, N. Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors: Attractive alternatives for control of infectious pathogens showing multiple drug resistance. Recent Pat. Anti Infect. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqua, C.; Greenberg, E.P. Listening in on bacteria: Acyl-homoserine lactone signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, A.P.; Guttman, J.A.; Finlay, B.B. Manipulation of host-cell pathways by bacterial pathogens. Nature 2007, 449, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaSarre, B.; Federle, M.J. Exploiting Quorum Sensing To Confuse Bacterial Pathogens. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 73–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M.; Harper, D. Animal Signals; OUP Oxford: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.C.; Popat, R.; Diggle, S.P.; Brown, S.P. Targeting virulence: Can we make evolution-proof drugs? Nat. Rev. Microboil. 2014, 12, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Bossier, P. Can Bacteria Evolve Resistance to Quorum Sensing Disruption? PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, T.; Perron, G.G.; Buckling, A.; van Delden, C. Quorum sensing inhibition selects for virulence and cooperation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Schaefer, A.L.; Dandekar, A.A.; Greenberg, E.P. Quorum sensing and policing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa social cheaters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellbye, B.; Schuster, M. The sociomicrobiology of antivirulence drug resistance: A proof of concept. MBio 2011, 2, e00131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; Garcia-Contreras, R.; Pu, M.; Sheng, L.; Garcia, L.R.; Tomas, M.; Wood, T.K. Quorum quenching quandary: Resistance to antivirulence compounds. ISME J. 2012, 6, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.C.; Meickle, T.; Ladwa, D.; Teplitski, M.; Paul, V.; Luesch, H. Lyngbyoic acid, a “tagged” fatty acid from a marine cyanobacterium, disrupts quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skindersoe, M.E.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; de Nys, R.; Givskov, M. Quorum Sensing Antagonism from Marine Organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Y.M.; Yin, W.F.; Ho, C.Y.; Mustafa, M.R.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Awang, K.; Narrima, P.; Koh, C.-L.; Appleton, D.R.; Chan, K.-G. Malabaricone C from Myristica cinnamomea Exhibits Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.-L.; Sam, C.-K.; Yin, W.-F.; Tan, L.Y.; Krishnan, T.; Chong, Y.M.; Chan, K.-G. Plant-Derived Natural Products as Sources of Anti-Quorum Sensing Compounds. Sensors 2013, 13, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasdale, M.E.; Donovan, K.A.; Forschner-Dancause, S.R.; Rowley, D.C. Gram-Positive Marine Bacteria as a Potential Resource for the Discovery of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.H.; Gusti, A.R.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, L.H. Identification of quorum-quenching N-acyl homoserine lactonases from Bacillus species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, X. Quorum Quenching Enzymes and Their Application in Degrading Signal Molecules to Block Quorum Sensing-Dependent Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17477–17500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wang, L.-H.; Wang, J.; Dong, Y.-H.; Hu, J.Y.; Zhang, L.-H. Quorum quenching enzyme activity is widely conserved in the sera of mammalian species. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Givskov, M.; de Nys, R.; Manefield, M.; Gram, L.; Maximilien, R.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Steinberg, P.D.; Kjelleberg, S. Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signalling. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 6618–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nealson, K.H.; Platt, T.; Hastings, J.W. Cellular Control of the Synthesis and Activity of the Bacterial Luminescent System. J. Bacteriol. 1970, 104, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steindler, L.; Venturi, V. Detection of quorum-sensing N-acyl homoserine lactone signal molecules by bacterial biosensors. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 266, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasdale, M.E.; Liu, J.; Wallace, J.; Akhlaghi, F.; Rowley, D.C. Secondary Metabolites Produced by the Marine Bacterium Halobacillus salinus That Inhibit Quorum Sensing-Controlled Phenotypes in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.D.; Zhou, L.M.; Ma, Q.Y.; Huang, S.Z.; Wang, P.; Dai, H.F.; Zhao, Y.X. Metabolites with Gram-negative bacteria quorum sensing inhibitory activity from the marine animal endogenic fungus Penicillium sp. SCS-KFD08. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 40, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, B.; Kavita, K.; Westphal, J.; Hartmann, A.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Quorum Sensing Inhibition by Asparagopsis taxiformis, a Marine Macro Alga: Separation of the Compound that Interrupts Bacterial Communication. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natrah, F.M.I.; Kenmegne, M.M.; Wiyoto, W.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P.; Defoirdt, T. Effects of micro-algae commonly used in aquaculture on acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing. Aquaculture 2011, 317, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, R.M.M.; Dobretsov, S.; Al-Fori, M.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Sudesh, K.; Paul, V.J. Quorum-sensing inhibitory compounds from extremophilic microorganisms isolated from a hypersaline cyanobacterial mat. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobretsov, S.; Teplitski, M.; Bayer, M.; Gunasekera, S.; Proksch, P.; Paul, V.J. Inhibition of marine biofouling by bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors. Biofouling 2011, 27, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobretsov, S.; Teplitski, M.; Alagely, A.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Paul, V.J. Malyngolide from the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula interferes with quorum sensing circuitry. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, L.; König, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Pukall, R.; Stackebrandt, E.; Eberl, L.; Riedel, K. Secondary Metabolites of Flustra foliacea and Their Influence on Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3469–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, J.; Brango-Vanegas, J.; Costa, G.M.; Castellanos, L.; Arévalo, C.; Duque, C. Marine organisms as source of extracts to disrupt bacterial communication: Bioguided isolation and identification of quorum sensing inhibitors from Ircinia felix. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manefield, M.; Welch, M.; Givskov, M.; Salmond, G.P.; Kjelleberg, S. Halogenated furanones from the red alga, Delisea pulchra, inhibit carbapenem antibiotic synthesis and exoenzyme virulence factor production in the phytopathogen Erwinia carotovora. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 205, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tello, E.; Castellanos, L.; Arevalo-Ferro, C.; Duque, C. Cembranoid diterpenes from the Caribbean sea whip Eunicea knighti. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tello, E.; Castellanos, L.; Arévalo-Ferro, C.; Duque, C. Disruption in Quorum-Sensing Systems and Bacterial Biofilm Inhibition by Cembranoid Diterpenes Isolated from the Octocoral Eunicea knighti. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tello, E.; Castellanos, L.; Arevalo-Ferro, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C.; Duque, C. Absolute stereochemistry of antifouling cembranoid epimers at C-8 from the Caribbean octocoral Pseudoplexaura flagellosa. Revised structures of plexaurolones. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 9112–9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.L.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Scott, R.M.; Paul, V.J.; Teplitski, M. Microbiome shifts and the inhibition of quorum sensing by Black Band Disease cyanobacteria. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, T.; Tintillier, F.; Lucasson, A.; Moriou, C.; Bonno, E.; Petek, S.; Magré, K.; Al Mourabit, A.; Saulnier, D.; Debitus, C. Quorum sensing inhibitors from Leucetta chagosensis Dendy, 1863. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.B.; Koh, K.P.; Kim, J.S.; Seo, Y.; Park, S. The effects of betonicine, floridoside, and isethionic acid from the red alga Ahnfeltiopsis flabelliformis on quorum-sensing activity. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2008, 13, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Seo, Y.W.; Park, S. Quorum sensing inhibitors from the red alga, Ahnfeltiopsis flabelliformis. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2007, 12, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, L.; Kuo, A.; Dunlap, P.V. AinS and a new family of autoinducer synthesis proteins. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6946–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanzelka, B.L.; Parsek, M.R.; Val, D.L.; Dunlap, P.V.; Cronan, J.E.; Greenberg, E.P. Acylhomoserine Lactone Synthase Activity of the Vibrio fischeri AinS Protein. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 5766–5770. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143 Pt 12, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, D.; Grossmann, G.; Sequin, U.; Brandl, H.; Bachofen, R. Effects of natural and chemically synthesized furanones on quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum. BMC Microbiol. 2004, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, M.B.K.; Zhu, H.; Sankaridurg, P.R.; Willcox, M.D.P. Salicylic Acid Reduces the Production of Several Potential Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Associated with Microbial Keratitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4453–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernin, L.S.; Winson, M.K.; Thompson, J.M.; Haran, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; Chet, I.; Williams, P.; Stewart, G.S.A.B. Chitinolytic Activity in Chromobacterium violaceum: Substrate Analysis and Regulation by Quorum Sensing. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 4435–4441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winson, M.K.; Swift, S.; Fish, L.; Throup, J.P.; Jorgensen, F.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Williams, P.; Stewart, G.S. Construction and analysis of luxCDABE-based plasmid sensors for investigating N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 163, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meighen, E.A. Molecular biology of bacterial bioluminescence. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meighen, E.A.; Szittner, R.B. Multiple repetitive elements and organization of the lux operons of luminescent terrestrial bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 5371–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, S.; Karlyshev, A.V.; Fish, L.; Durant, E.L.; Winson, M.K.; Chhabra, S.R.; Williams, P.; Macintyre, S.; Stewart, G.S. Quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas salmonicida: Identification of the LuxRI homologs AhyRI and AsaRI and their cognate N-acylhomoserine lactone signal molecules. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5271–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Skindersoe, M.E.; Hentzer, M.; Kristoffersen, P.; Kote, M.; Nielsen, J.; Eberl, L.; Givskov, M. Screening for quorum-sensing inhibitors (QSI) by use of a novel genetic system, the QSI selector. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1799–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, J.M.; Bassler, B.L. Three parallel quorum-sensing systems regulate gene expression in Vibrio harveyi. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 6902–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsien, R.Y. The green fluorescent protein. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 509–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, K.; Hentzer, M.; Geisenberger, O.; Huber, B.; Steidle, A.; Wu, H.; Hoiby, N.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Eberl, L. N-acylhomoserine-lactone-mediated communication between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia in mixed biofilms. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3249–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, B.; Riedel, K.; Hentzer, M.; Heydorn, A.; Gotschlich, A.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Eberl, L. The cep quorum-sensing system of Burkholderia cepacia H111 controls biofilm formation and swarming motility. Microbiology 2001, 147, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.B.; Heydorn, A.; Hentzer, M.; Eberl, L.; Geisenberger, O.; Christensen, B.B.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M. gfp-based N-acyl homoserine-lactone sensor systems for detection of bacterial communication. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Heydorn, A.; Andersen, J.B.; Parsek, M.R.; Rice, S.A.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Hoiby, N.; et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 2002, 148, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, J.; Cook, J.L. Reporter genes: Application to the study of mammalian gene transcription. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 188, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrand, S.K.; Qin, Y.; Oger, P. Quorum-sensing system of Agrobacterium plasmids: Analysis and utility. Methods Enzymol. 2002, 358, 452–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.D.; Ping, G.; Daly, S.L.; Cha, C.; Cronan, J.E.; Rinehart, K.L.; Farrand, S.K. Detecting and characterizing N-acyl-homoserine lactone signal molecules by thin-layer chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6036–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, S.; Bie, X. Characterization and Identification of a Novel Marine Streptomyces sp. Produced Antibacterial Substance. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3670–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ashforth, E.; Ren, B.; Song, F.; Dai, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, L. Bioprospecting microbial natural product libraries from the marine environment for drug discovery. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 382–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurav, K.; Kannabiran, K. Diversity and Optimization of Process Parameters for the Growth of Streptomyces VITSVK9 spp İsoled From Bay of Bengal, İndia. J. Nat. Environ. Sci. 2010, 1, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Huiru, Z.; Biting, D.; Yun, J.; Wei, J.; Kunming, D. Study on the anti-quorum sensing activity of a marine bacterium Staphylococcus saprophyticus 108. BioTechnology Indian J. 2013, 7, 480–487. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Matamoros, D.; Fonseca, M.L.; Duque, C.; Ramos, F.A.; Castellanos, L. Screening of marine bacterial strains as source of quorum sensing inhibitors (QSI): First chemical study of Oceanobacillus profundus (RKHC-62B). VITAE 2016, 23, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Ansari, M.I.; Ahmad, A.; Mishra, M. Major bioactive metabolites from marine fungi: A Review. Bioinformation 2015, 11, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, K.T.; Rho, J.R.; Choi, H.D.; Kang, J.S.; Son, B.W. Gamma-pyrone derivatives, kojic acid methyl ethers from a marine-derived fungus Alternaria [correction of Altenaria] sp. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.J.; Sohn, M.-J.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.-G. Meleagrin, a New FabI Inhibitor from Penicillium chryosogenum with at Least One Additional Mode of Action. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.; Friedman, A.J.; Choi, H.; Hogan, J.; McCammon, J.A.; Hook, V.; Gerwick, W.H. The marine cyanobacterial metabolite gallinamide A is a potent and selective inhibitor of human cathepsin L. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleigrewe, K.; Almaliti, J.; Tian, I.Y.; Kinnel, R.B.; Korobeynikov, A.; Monroe, E.A.; Duggan, M.; Di Marzo, V.; Sherman, D.H.; Dorrestein, P.C.; et al. Combining Mass Spectrometric Metabolic Profiling with Genomic Analysis: A Powerful Approach for Discovering Natural Products from Cyanobacteria. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, B.R.; Engene, N.; Teasdale, M.E.; Rowley, D.C.; Matainaho, T.; Valeriote, F.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Natural products chemistry and taxonomy of the marine cyanobacterium Blennothrix cantharidosmum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.C.; Teplitski, M.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Isolation and biological evaluation of 8-epi-malyngamide C from the Floridian marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Mascuch, S.J.; Villa, F.A.; Byrum, T.; Teasdale, M.E.; Smith, J.E.; Preskitt, L.B.; Rowley, D.C.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H. Honaucins A–C, Potent Inhibitors of Eukaryotic Inflammation and Bacterial Quorum Sensing: Synthetic Derivatives and Structure-Activity Relationships. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaser, R.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Modular Strategies for Structure and Function Employed by Marine Cyanobacteria: Characterization and Synthesis of Pitinoic Acids. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 4050–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine Sponge Derived Natural Products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and Opportunities for Discovery of Bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Perinu, C.; Cirino, G.; De Gruttola, L.; Roviezzo, F. Tedanol: A potent anti-inflammatory ent-pimarane diterpene from the Caribbean Sponge Tedania ignis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7542–7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teta, R.; Irollo, E.; Della Sala, G.; Pirozzi, G.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Smenamides A and B, chlorinated peptide/polyketide hybrids containing a dolapyrrolidinone unit from the Caribbean sponge Smenospongia aurea. Evaluation of their role as leads in antitumor drug research. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4451–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Teta, R.; Miceli, R.; Ceccarelli, L.S.; Della Sala, G.; Camerlingo, R.; Irollo, E.; Mangoni, A.; Pirozzi, G.; Costantino, V. Isolation and Assessment of the in Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity of Smenothiazole A and B, Chlorinated Thiazole-Containing Peptide/Polyketides from the Caribbean Sponge, Smenospongia aurea. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A. Glycolipids from sponges. 20. J-Coupling analysis for stereochemical assignments in furanosides: Structure elucidation of vesparioside B, a glycosphingolipid from the marine sponge Spheciospongia vesparia. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 6158–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A. Ectyoceramide, the First Natural Hexofuranosylceramide from the Marine Sponge Ectyoplasia ferox. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 2003, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Duque, C.; Hara, N.; Fujimoto, Y. Variabilin 11-Methyloctadecanoate, A Branched-Chain Fatty Acid Ester of Furanosesterterpene Tetronic Acid, from the Sponge Ircinia Felix. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1995, 6, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Duque, C.; Sato, N.; Fujimoto, Y. (8Z,13Z,20Z)-Strobilinin and (7Z,13Z,20Z)-Felixinin: New Furanosesterterpene Tetronic Acids from Marine Sponges of the Genus Ircinia. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurav, K.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Haber, M.; Burgsdorf, I.; Oliviero, G.; Costantino, V.; Morgenstern, D.; Steindler, L. In Search of Alternative Antibiotic Drugs: Quorum-Quenching Activity in Sponges and their Bacterial Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardoim, C.C.; Costa, R. Microbial Communities and Bioactive Compounds in Marine Sponges of the Family Irciniidae—A Review. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5089–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supriyono, A.; Schwarz, B.; Wray, V.; Witte, L.; Muller, W.E.; van Soest, R.; Sumaryono, W.; Proksch, P. Bioactive alkaloids from the tropical marine sponge Axinella carteri. Z. Naturforsch. C 1995, 50, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hertiani, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ortlepp, S.; van Soest, R.W.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Hentschel, U.; Kozytska, S.; Muller, W.E.; Proksch, P. From anti-fouling to biofilm inhibition: New cytotoxic secondary metabolites from two Indonesian Agelas sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertiani, T. New hope on drug leads development from deep ocean: Halogenated alkaloids of Agelas sponge. Indones. J. Pharm. 2014, 25, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, R.; Brenzinger, M.; Kunze, A.; Gross, H.J.; Proksch, P. Wound Activation of Protoxins in Marine Sponge Aplysina aerophoba. J. Chem. Ecol. 1997, 23, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loïc, G.C.; Leonel, P. Review of Marine Algae as Source of Bioactive Metabolites: A Marine Biotechnology Approach. In Marine Algae; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 195–227. [Google Scholar]
- El Gamal, A.A. Biological importance of marine algae. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, M.J.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. Antimicrobial Action of Compounds from Marine Seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, I.; Chojnacka, K. Algae as production systems of bioactive compounds. Eng. Life Sci. 2015, 15, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-C.; Hou, M.-F.; Huang, H.-W.; Chang, F.-R.; Yeh, C.-C.; Tang, J.-Y.; Chang, H.-W. Marine algal natural products with anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, H.; Barreira, L.; Figueiredo, F.; Custódio, L.; Vizetto-Duarte, C.; Polo, C.; Rešek, E.; Engelen, A.; Varela, J. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids of Marine Macroalgae: Potential for Nutritional and Pharmaceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1920–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janczyk, W.; Socha, P.; Lebensztejn, D.; Wierzbicka, A.; Mazur, A.; Neuhoff-Murawska, J.; Matusik, P. Omega-3 fatty acids for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Design and rationale of randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworjanyn, A.S.; De Nys, R.; Steinberg, D.P. Localisation and surface quantification of secondary metabolites in the red alga Delisea pulchra. Mar. Biol. 1999, 133, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delago, A.; Mandabi, A.; Meijler, M.M. Natural Quorum Sensing Inhibitors—Small Molecules, Big Messages. Isr. J. Chem. 2016, 56, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.; Liljefors, T.; Persson, T.; Nielsen, J.; Kjelleberg, S.; Givskov, M. The LuxR receptor: The sites of interaction with quorum-sensing signals and inhibitors. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3589–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, J.; Peixe, L.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Calado, R. Cnidarians as a Source of New Marine Bioactive Compounds—An Overview of the Last Decade and Future Steps for Bioprospecting. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1860–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, M.; Brugler, M.R.; Cartwright, P.; Collins, A.G.; Dawson, M.N.; Fautin, D.G.; France, S.C.; McFadden, C.S.; Opresko, D.M.; Rodriguez, E.; et al. The phylum Cnidaria: A review of phylogenetic patterns and diversity 300 years after Linnaeus. Zootaxa 2007, 1668, 127–182. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, T.; Kem, W.R. The phylum Cnidaria and investigations of its toxins and venoms until 1990. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, J.H.; Winson, M.K.; Porter, J.S. Bryozoan metabolites: An ecological perspective. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, Y.; Shiroiwa, T.; Murayama, S.; Matsunaga, S.; Goto, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Fusetani, N. Identification of Renieramycin A as an Antileishmanial Substance in a Marine Sponge Neopetrosia sp. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Leone, P.; Carroll, A.R.; Towerzey, L.; King, G.; McArdle, B.M.; Kern, G.; Fisher, S.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Quinn, R.J. Exiguaquinol: A Novel Pentacyclic Hydroquinone from Neopetrosia exigua that Inhibits Helicobacter pylori MurI. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2585–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thale, Z.; Johnson, T.; Tenney, K.; Wenzel, P.J.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J.; Media, J.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Structures and Cytotoxic Properties of Sponge-Derived Bisannulated Acridines. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 9384–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
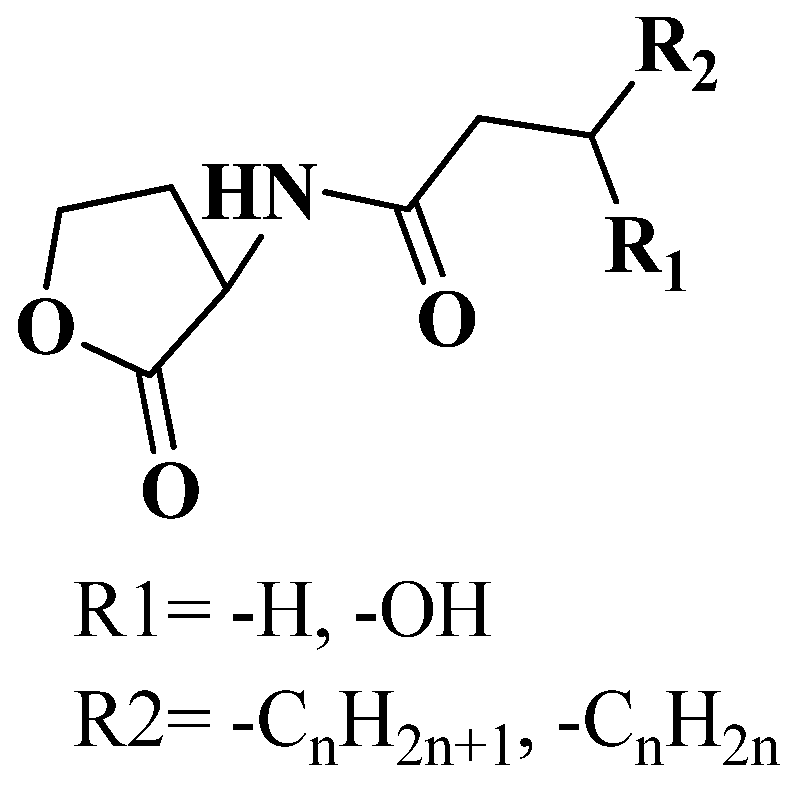

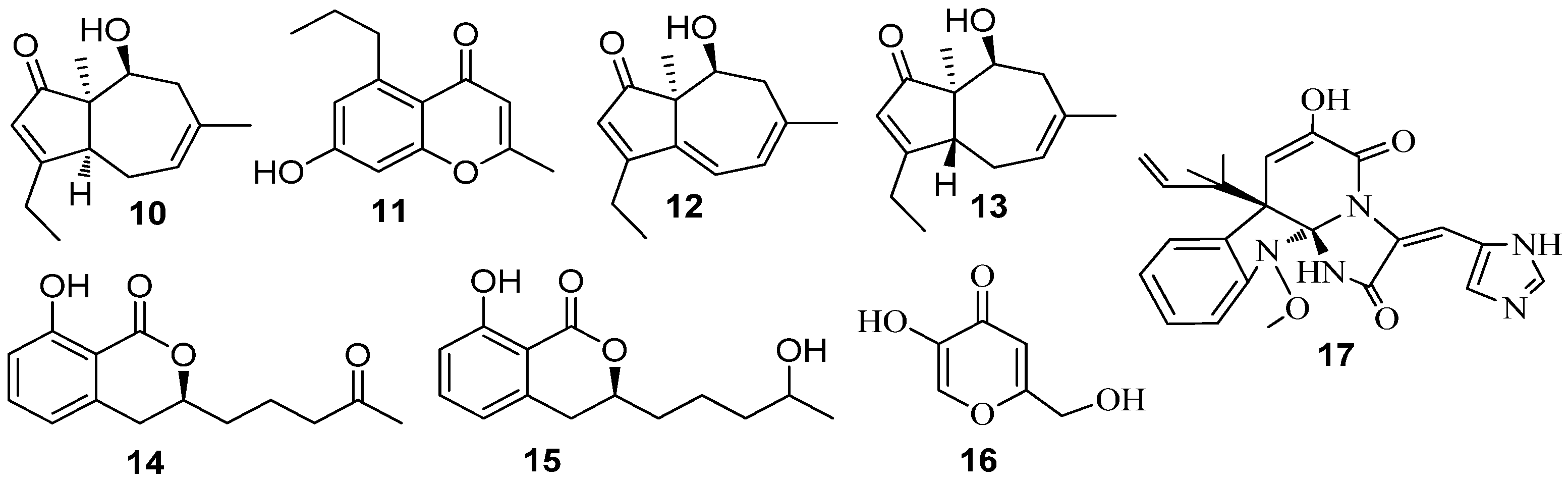
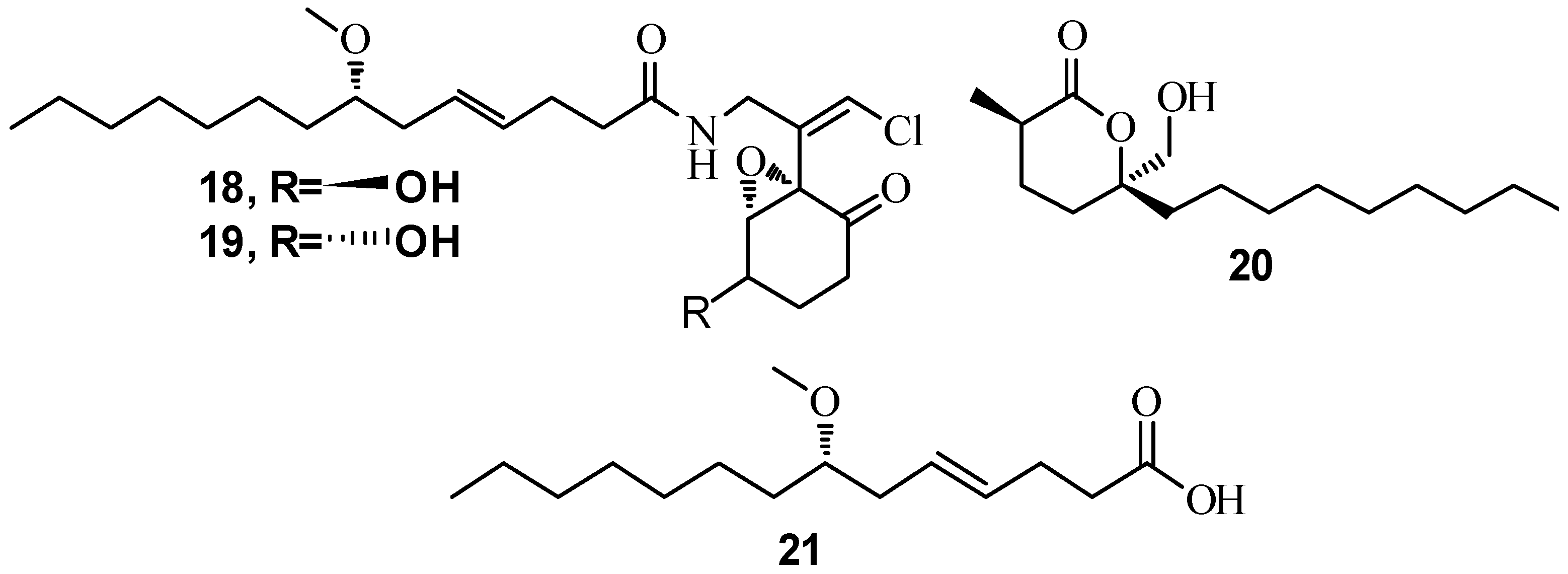
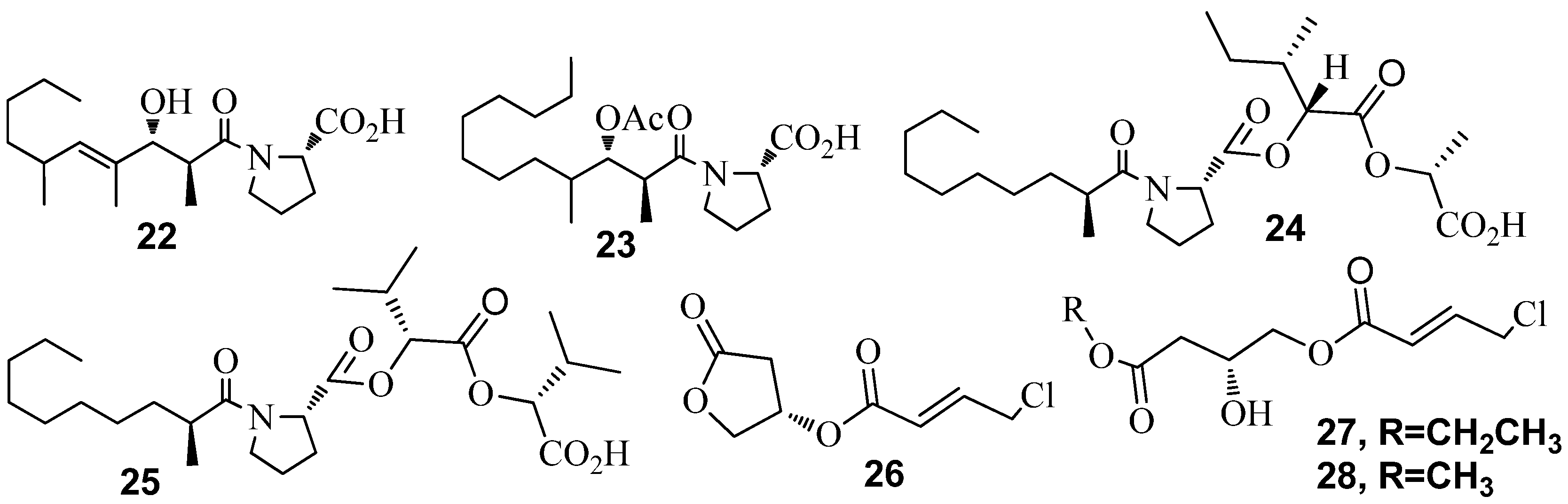



| Strain/Plasmid | QS System | Reporter System | Detection Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 | CviI/R | Violacein pigment | C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL | [35,36,37,38] |
| Chromobacterium violaceum CV017 | CviI/R | Violacein pigment | 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL | [39,40,41] |
| Escherichia coli pSB403 | LuxI/R (V. fisheri) | luxCDABE | 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL | [37,42] |
| Escherichia coli pSB536 | AhyI/R (A. hydrophyla) | luxCDABE | C4-HSL | [24] |
| Escherichia coli pSB401 | LuxI/R (V. fisheri) | luxCDABE | 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL | [39,40,43,44,45,46,47] |
| Escherichia coli pSB1075 | LasI/R (P. aeruginosa) | luxCDABE | 3-oxo-C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, C12-HSL | [39,40,41] |
| QSIS2 | LasI/R (P. aeruginosa) | luxCDABE | 3-oxo-C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, C12-HSL | [25] |
| Vibrio harveyi JMH 612 | LuxPQ (Vibrio harveyi) | luxQ | 3-OH-C4-HSL | [48,49] |
| Agrobacterium tumifaciencens pZLR4 | TraI/R (A. tumefaciens) | β-galactosidase | All 3-oxo-HSLs | [41,50,51] |
| Escherichia coli pKDT17 | LasI/R (P. aeruginosa) | β-galactosidase | 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C12-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL | |
| QSIS1 | LuxI/R (V. fisheri) | β-galactosidase | 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL | [25] |
| pAS-C8 | CepI/R (B. cepacia) | gfp | C8-HSL | [42] |
| pKR-C12 | LasI/R (P. aeruginosa) | gfp | 3-oxo-C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL | [42] |
| Escherichia coli JB525 | LuxI/R (V. fisheri) | gfp | 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL | [35] |
| QSIS3 | LuxI/R (V. fisheri) | gfp | 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL | [25] |
| Tn5-Las | LasI/R (P. aeruginosa) | gfp | 3-oxo-C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL | [25] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saurav, K.; Costantino, V.; Venturi, V.; Steindler, L. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from the Sea Discovered Using Bacterial N-acyl-homoserine Lactone-Based Biosensors. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030053
Saurav K, Costantino V, Venturi V, Steindler L. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from the Sea Discovered Using Bacterial N-acyl-homoserine Lactone-Based Biosensors. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaurav, Kumar, Valeria Costantino, Vittorio Venturi, and Laura Steindler. 2017. "Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from the Sea Discovered Using Bacterial N-acyl-homoserine Lactone-Based Biosensors" Marine Drugs 15, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030053
APA StyleSaurav, K., Costantino, V., Venturi, V., & Steindler, L. (2017). Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from the Sea Discovered Using Bacterial N-acyl-homoserine Lactone-Based Biosensors. Marine Drugs, 15(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030053








