Abstract
Polar organisms have been found to develop unique defences against the extreme environment environment, leading to the biosynthesis of novel molecules with diverse bioactivities. This review covers the 219 novel natural products described since 2001, from the Arctic and the Antarctic microoganisms, lichen, moss and marine faunas. The structures of the new compounds and details of the source organism, along with any relevant biological activities are presented. Where reported, synthetic and biosynthetic studies on the polar metabolites have also been included.
1. Introduction
Organisms from special ecosystems such as the polar regions are a rich source of various chemical scaffolds and novel natural products with promising bioactivities. Polar regions, which refer to the Arctic, the Antarctic and their subregions, are remote and challenging areas on the earth. To survive under the constant influence of low temperatures, strong winds, low nutrient and high UV radiation or combinations of these factors [1], polar organisms require a diverse array of biochemical and physiological adaptations that are essential for survival. These adaptations are often accompanied by modifications to both gene regulation and metabolic pathways, increasing the possibility of finding unique functional metabolites of pharmaceutical importance.
Polar regions are complex ecosystems that harbor diverse groups of fauna and microorganisms including bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi. Physiological adaptations have enabled psychrophilic organisms to thrive in the polar regions, especially microorganisms which are high in number and usually uncharacterized [2,3,4,5]. However, when compared to the large number of polar microorganisms which have been reported, very few have been screened for the production of interesting secondary metabolites. The advent of modern techniques provides the opportunity to find novel metabolites.
From 2001 to 2016, a vast amount of new biological natural compounds with various activities, such as anti-bacteria, anti-tumor, anti-virus and so on, have been isolated from polar organisms including microorganisms, lichen, moss, bryozoans, cnidarians, echinoderms, molluscs, sponges and tunicates. Natural products from the Arctic or the Antarctic organisms have been the subject of several review articles. In 2007, Lebar et al. reviewed the studies on structure and bioactivity of cold-water marine natural products, including many polar examples [6]. In 2009, Wilson and Brimble reviewed molecules derived from the extremes of life, including some polar examples [7]. In 2011, advances in the chemistry and bioactivity of arctic sponge were reviewed by Hamann and his co-workers [8]. In 2013, Liu et al. reviewed a number of new secondary metabolites with various activities derived from both Antarcitc and Arctic organisms [9], while in 2014, Skropeta and Wei published a review on natural products isolated from deep-sea sources, which included some polar organisms [10]. Moreover, Blunt and his co-workers published periodical reviews on the characteristics of various marine natural products with some polar examples [11,12,13].
However, comprehensive reviews of natural products from polar regions were rare; therefore, we describe here the source, chemistry, and biology of the newly discovered biomolecules from the polar organisms. We also summarize the chemical synthesis and the biosynthetic relationship of metabolites. The Metabolites Name Index in combination with the Source Index, the Biological Activity Index and the References on isolation in the accompanying tables, will help understand the fascinating chemistry and biology of natural products derived from polar organisms.
2. Microorganisms
The microbial diversity of polar environments is a fertile ground for new bioactive compounds, genes, proteins, microorganisms and other products with potential for commercial use [14].
2.1. Unicellular Bacteria
The culture broth of the marine bacterium Bacillus sp., isolated from the sea mud near the Arctic pole, was found to yield three new cyclic acylpeptides named as mixirins A (1), B (2) and C (3) (Figure 1) [15]. All of the three compounds were found to display significant cytotoxicity against human colon tumor cells (HCT-116) with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 0.68, 1.6, 1.3 μg/mL, respectively.

Figure 1.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Arctic bacteria (compounds 1–14).
Four new aromatic nitro compounds (4–7) (Figure 1) along with fifteen known ones were reported from the Salegentibacter strain T436, isolated from a bottom section of a sea ice floe collected from the Arctic Ocean. The new natural products showed weak antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities [16]. Further study of the same bacterium isolate yielded another seven new aromatic nitro compounds (8–14) (Figure 1) [17].
A novel diketopiperazine, named cyclo-(d-pipecolinyl-l-isoleucine) (15) (Figure 2), and two new linear peptides (16, 17) (Figure 2), along with seven known diketopiperazines were isolated from the cell-free culture supernatant of the Antarctic psychrophilic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 [18]. Peptide 17 and a known phenyl-containing diketopiperazine showed free radical scavenging properties, with the phenyl group essential for activity.

Figure 2.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic bacteria (compounds 15–22).
From the Antarctic cyanobacterium Nostoc CCC 537, an antibacterial lead molecule (18) (Figure 2) was obtained. Compound 18 exhibited antibacterial activity against two Gram positive pathogenic strains and seven Gram negative strains including three multi-drug resistant strains of Escherichia coli, with minimal inhibition concentration (MIC) values in the range of 0.5–16.0 μg/mL [19].
Two pigments named violacein (19) and flexirubin (20) (Figure 2) were isolated from two Antarctic bacterial strains. The two compounds displayed antibacterial activities against some mycobacteria with low MIC values (ranging from 2.6 to 34.4 μg/mL), and might be valuable natural lead compounds for new antimycobacterial drugs used for tuberculosis chemotherapy [20].
Bioassay-guided purification of Antarctic strain Pseudomonas BNT1 extracts produced three rhamnolipids including two new ones (21, 22). Compound 21 was effective against the tested human pathogens strains Burkholderia cepacia, B. metallica, B. seminalis, B. latens and Staphylococcus aureus with low MIC and minimun bacteriocidal concentration (MBC) values, while compound 22 only had moderate antimicrobial effect against S. aureus with an MBC value of 100 μg/mL [21].
2.2. Actinomycetes
In this century, actinomyces derived from polar regions have yielded an array of interesting new metabolites. Three new pyrrolosesquiterpenes, glyciapyrroles A (23), B (24), and C (25) (Figure 3), along with three known ones, iketopiperazines cyclo(leucyl-prolyl), cyclo(isoleucyl-prolyl), and cyclo(phenylalanyl-prolyl), were isolated from the Streptomyces sp. NPS008187 originating from a marine sediment collected in Alaska near the Arctic [22].

Figure 3.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Arctic actinomyces (compounds 23–27, 30, 31).
The Arctic seaweed-associated actinomycete Nocardiopsis sp. 03N67 was found to produce a rare bioactive diketopiperazine, cyclo-(l-Pro-l-Met) (26) (Figure 3). It inhibited tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced tube formation and invasion at 10 μM, a concentration at which no cytotoxicity was observed. Anti-angiogenesis activity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) of compound 26 is an encouraging bioprobe to develop new anticancer therapeutics from such type of small molecules in near future [23].
The marine actinomycete Nocardia dassonvillei BM-17, obtained from a sediment sample collected in the Arctic Ocean, has furnished a new secondary metabolite, N-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-2-phenazinamine (27) (Figure 3), and six known antibiotics. The new compound showed weak antifungal activity against Candida albicans, with a MIC value of 64 μg/mL and low cancer cell cytotoxicity against HepG2, A549, HCT-116 and COC1 cells, with IC50 values of 40.33, 38.53, 27.82 and 28.11 μg/mL, respectively [24].
Chemical examination from the Arctic actinomycete Streptomyces nitrosporeus CQT14-24 resulted in the isolation of two new alkaloids, named as nitrosporeusines A (28) and B (29) (Scheme 1), with an unprecedented skeleton containing benzenecarbothioc cyclopenta[c]pyrrole-1,3-dione. Both 28 and 29 showed inhibitory activity against the influenza WSN virus (H1N1) in Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells with the dose of 50 μM. In an in vitro plaque reduction assay, 29 exhibited dose-dependent reduction of the production of the viral progeny which was produced by the infected MDCK cells with influenza A/WSN/33 virus. The half effective concentration (EC50) value of 29 for the inhibition of viral plaque formation was quite comparable to that of the positive control oseltamivir phosphate (Osv-P) [25]. Their biological activities have attracted interest to synthesize these compounds. Efficient stereoselective synthesis of the natural enantiomer of nitrosporeusines A and B was performed by Reddy’s groups. An overall five-step process starting from 5,6-dihydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrole-1,3(2H,4H)-dione and p-hydroxybenzoic acid is summarized in Scheme 1 [26].

Scheme 1.
Synthesis of natural products nitrosporeusines A (28) and B (29). Reagents and conditions: (a) SeO2, 1,4-dioxane, microwave, 110 °C, 61%; (b) Amano PS lipase, THF, CH2=CHOAc, 38%; (c) Amano PS lipase, phosphate buffer, 92%; (d) Lawesson's reagent, acetonitrile, microwave, 100 °C, 53%; (e) H2O, room temperature (rt), 65%.
Two new secondary metabolites, arcticoside (30) and C-1027 chromophore-V (31) (Figure 3), were isolated along with three kown compounds, C-1027 chromophore-III, fijiolides A and B from the culture of an Arctic marine actinomycete Streptomyces strain. Compounds 30 and 31 inhibited Candida albicans isocitrate lyase, an enzyme that plays an important role in the pathogenicity of C. albicans. Furthermore, 31 exhibited significant cytotoxicity against breast carcinoma MDA-MB231 cells and colorectal carcinoma HCT-116 cells, with IC50 values of 0.9 and 2.7 μM, respectively [27].
A Streptomyces griseus strain NTK 97, recovered from an Antarctic terrestrial sample, yielded a new angucyclinone antibiotic frigocyclinone (32) (Figure 4), consisting of a tetrangomycin moiety attached through a C-glycosidic linkage with the aminodeoxysugar ossamine. Frigocyclinone revealed good inhibitory activities against Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus [28]. Another Antarctic Streptomyces griseus strain NTK14 was shown to contain the novel-type angucyclinone gephyromycin (33) (Figure 4), and two known compounds, fridamycin E and dehydrorabelomycin. Gephyromycin, with an unprecedented intramolecular ether bridge, displayed glutaminergic activity (agonist) towards neuronal cells. In addition, 33 exhibited no acute cytostatic activities, and the lack of cytotoxicity made its neuroprotective properties even more valuable [29].
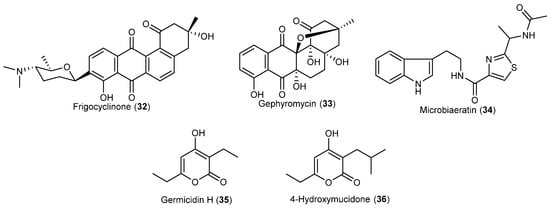
Figure 4.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic actinomyces (compounds 32–36).
A new sulphur-containing natural alkaloid named microbiaeratin (34) (Figure 4) was characterized, together with the known bacillamide from the culture of Microbispora aerata strain IMBAS-11A, isolated from the Antarctic Livingston Island. A low antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of 34 was determined with L-929 mouse fibroblast cells, K-562 human leukemia cells and HeLa human cervix carcinoma cells [30].
The Nocardiopsis sp. SCSIO KS107 was isolated from Antarctic seashore sediment. Fermentation and isolation of this strain provided two new α-pyrones germicidin H (35), 4-hydroxymucidone (36), and a known compound 7-hydroxymucidone. Only the known compound showed antibacterial activity against Micrococcus luteus with an MIC value of 16 μg/mL [31].
2.3. Fungi
The rapid growth and ability to metabolize a wide variety of substrates have enabled fungi to become the predominant components of the microorganisms in polar regions. The psychrotolerant fungus Penicillium algidum, collected from soil under a Ribes sp. in Greenland near the Arctic, yielded the new cyclic nitropeptide, psychrophilin D (37) (Figure 5), together with two known cyclic peptides, cycloaspeptide A and cycloaspeptide D. The compounds were tested in antimicrobial, antiviral, anticancer and antiplasmodial assays. Psychrophilin D exhibited a moderate activity with half infective dose (ID50) value of 10.1 μg/mL in the P388 murine leukaemia cell assay. Cycloaspeptide A and D exhibited moderate activity (IC50 = 3.5 and 4.7 μg/mL, respectively) against Plasmodium falciparum [32].

Figure 5.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Arctic fungi (compounds 37–48).
Three new cytochalasins Z24, Z25, Z26 (38–40) (Figure 5) and one known compound, scoparasin B, were isolated from the Arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. These compounds were evaluated for cytotoxic activities against several human tumor cell lines. Among them, compound 38 showed moderate cytotoxicity toward human breast cancer MCF-7 cell line with IC50 value of 9.33 mΜ [33]. Further investigation of Eutypella sp. D-1 led to the discovery of two new diterpenes, libertellenone G (41) and libertellenone H (42) (Figure 5), together with two known pimarane diterpenes. Compound 41 exhibited antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus. Compound 42 showed slight cytotoxicity toward most cell lines, with half-maximal inhibitory concentration values ranging from 3.31 to 44.1 μM. In addition, the cytotoxicity of 42 is most likely dependent on the presence of its cyclopropane ring as deduced from the inactivity of other similar compounds [34]. Recently, three pimarane diterpenoids, Eutypenoids A–C (43–45), were also isolated from the culture of Eutypella (E.) sp. D-1. Using a ConA-induced splenocyte proliferation model, compound 44 exhibited potent immunosuppressive activities [35].
An unusual polyketide with a new carbon skeleton, lindgomycin (46) (Figure 5) [36], and the recently described ascosetin (47) (Figure 5) [37] were extracted from different Lindgomycetaceae strains, which were isolated from an Arctic sponge. Both the compounds exhibited strong antibiotic activities against the clinically relevant Gram-positive bacteria (including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and human pathogenic yeast Candida albicans.
Trichoderma polysporum strain OPU1571, recovered from a moss, Sanionia uncinata, growing in the high arctic wetlands on Spitsbergen Island, Svalbard, Norway, yielded eleven compounds, including a new one (48) (Figure 5). The in vitro investigation suggested that compound 48 showed a concentration-dependent growth-inhibitory effect on snow rot pathogen Pythium iwayamai at 5 days [38].
Fermentation of the Antarctic ascomycete fungus Geomyces sp. yielded five new asterric acid derivatives, ethyl asterrate (49), n-butyl asterrate (50), and geomycins A–C (51–53) (Figure 6). The new metabolites were tested for their antibacterial and antifungal activities. Geomycin B (52) showed significant antifungal activity against Aspergillus fumigatus ATCC 10894, with IC50/MIC values of 0.86/29.5 μM (the positive control fluconazole showed IC50/MIC values of 7.35/163.4 μM). Geomycin C (53) displayed moderate antimicrobial activities against the Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 and Streptococcus pneumoniae CGMCC 1.1692) and Gram-negative bacterium (Escherichia coli CGMCC 1.2340) [39].

Figure 6.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic fungi (compounds 49–59).
Chemical investigation of the marine-derived fungus Trichoderma asperellum, collected from the sediment of the Antarctic Penguin Island, resulted in the isolation of six new peptaibols named asperelines A–F (54–59) (Figure 6), which are characterized by an acetylated N-terminus and a C-terminus containing an uncommon prolinol residue. The compounds were tested against fungi and bacteria, but they showed only weak inhibitory activity toward the early blight pathogen Alternaria solani, the rice blast Pyricularia oryzae, and the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli [40]. Further study on the same fungus strain determined thirty-eight short peptaibols, including thirty-two new compounds namely asperelines G–Z13 [41].
Two new epipolythiodioxopiperazines, named chetracins B (60) and C (61), and five new diketopiperazines, named chetracin D (62) and oidioperazines A–D (63–66) (Figure 7), were obtained from the Antarctic fungus Oidiodendron truncatum GW3-13. An in vitro 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl) 2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) cytotoxicity assay revealed potent biological activity for 60 in the nanomolar range against a panel of five human cancer lines, HCT-8, BEL-7402, BGC-823, A-549 and A-2780. New metabolites 61 and 62 displayed significant cytotoxicity at a micromolar concentration, whereas 63–66 showed no significant cytotoxicity at 10 μM. Comparison of the bioactivity data suggested that the sulfide bridge was a determinant factor for their cytotoxicity, while the number of sulfur atoms in the bridge did not seem to influence activity [42].

Figure 7.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic fungi (compounds 60–68).
In 2012, two highly oxygenated polyketides, penilactones A and B (67 and 68) (Figure 7) of related structure but opposite absolute stereochemistry, were isolated from the Antarctic deep-sea derived fungus Penicillium crustosum PRB-2. The nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) inhibitory activities of 67 and 68 were tested by means of transient transfection and reporter gene expression assay, and only 67 showed weak activity with an inhibitory rate of 40% at a concentration of 10 μM. A plausible biosynthetic pathway for 67 and 68 was proposed as shown in Scheme 2 [43]. The penilactones contain a new carbon skeleton formed from two 3,5-dimethyl-2,4-diol-acetophenone units and a γ-butyrolactone moiety, and have been prepared by a biomimetic synthesis reported the following year as shown in Scheme 3 [44].
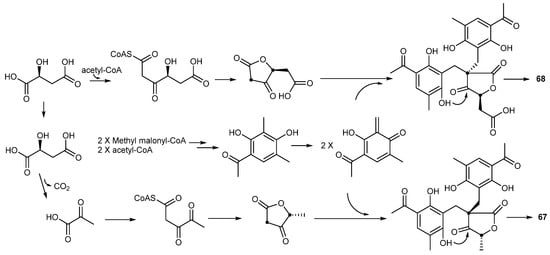
Scheme 2.
Proposed biosynthesis of penilactones A (67) and B (68).
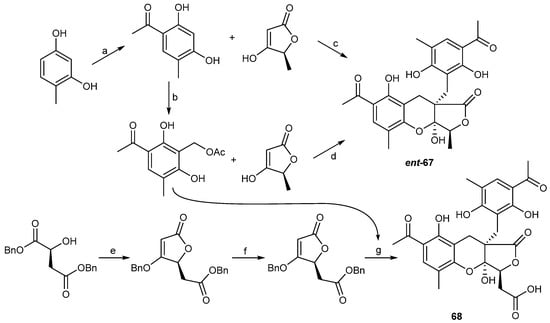
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of ent-penilactone A (ent-67) and penilactone B (68). Reagents and conditions: (a) AcOH, BF3.Et2O, 90 °C, 71%; (b) HCHO, NaOAc, AcOH, 80 °C, 75%; (c) HCHO, NaOAc, AcOH, 90 °C, then 110 °C, 46%; (d) toluene, 110 °C, 93%; (e) Ph3P=C=C=O, toluene, 110 °C, 52%; (f) H2, PD/C, MeOH, rt, 99%; (g) dioxane, 110 °C, 86%.
A new chloro-trinoreremophilane sesquiterpene (69) (Figure 8), three new chlorinated eremophilane sesquiterpenes (70–72) (Figure 8), together with a known compound, eremofortine C (73) (Scheme 4), were isolated from the Antarctic deep-sea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19N-1 in 2013. Compound 69 showed moderate cytotoxic activity against HL-60 and A549 cancer cell lines. In addition, the plausible metabolic network of these isolated products was proposed as demonstrated in Scheme 4 [45]. Further investigation of this strain yielded five new eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes (74–78) and a new rare lactam-type eremophilane (79) (Figure 8). Their cytotoxities against HL-60 and A-549 human cancer cell lines were valuated, and 78 was the most active one with IC50 value of 5.2 μM against the A-549 cells [46].

Figure 8.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic fungi (compounds 69–72, 74–85).
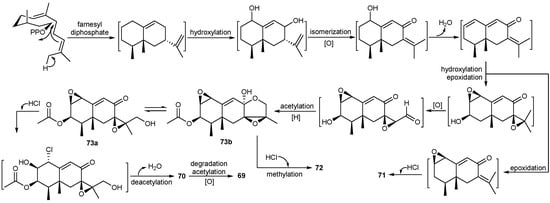
Scheme 4.
Proposed biogenetic network for compounds 69–73.
Two new meroterpenoids, named chrodrimanins I and J (80 and 81) (Figure 8), together with five known biosynthetically related chrodrimanins, were isolated from the culture of the Antarctic moss-derived fungus Penicillium funiculosum GWT2-24. Distinguished from all of the reported chrodrimanins, compounds 80 and 81 possess a unique cyclohexanone (E ring) instead of a δ-lactone ring. However, only the known compounds exhibited inhibitory activities against influenza virus A (H1N1) [47].
Fermentation of a Pseudogymnoascus sp. fungus isolated from an Antarctic marine sponge, yielded four new nitroasterric acid derivatives, pseudogymnoascins A–C (82–84) and 3-nitroasterric acid (85) (Figure 8), along with two known compounds questin and pyriculamide. These compounds are the first nitro derivatives of the known fungal metabolite asterric acid [48].
Five new highly oxygenated α-pyrone merosesquiterpenoids, ochraceopones A–E (86–90) (Scheme 5), together with one new double bond isomer of asteltoxin, isoasteltoxin (91) (Figure 9), and two known asteltoxin derivatives, asteltoxin and asteltoxin B, were isolated from the Antarctic soil-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702. Ochraceopones A–D (86–89) were the first examples of α-pyrone merosesquiterpenoids possessing a linear tetracyclic carbon skeleton. All the isolated compounds were tested for their antiviral, cytotoxic, antibacterial, and antitubercular activities. Among the new compounds, 86 and 91 exhibited promising antiviral activities against the H1N1 and H3N2 influenza viruses. In addition, a possible biosynthetic pathway for ochraceopones A–E was proposed in Scheme 5 [49].

Scheme 5.
Postulated biogenetic pathway for ochraceopones A–E (86–90).

Figure 9.
The structure of isoasteltoxin (91) derived from the Antarctic fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702.
3. Lichen
Lichens are symbiotic associations of fungi and algae and/or cyanobacteria that produce unique characteristic secondary metabolites by comparison to those of higher plants. Several species of lichens have been used for various remedies in folk medicine since ancient time and variety of biologically active lichen metabolites, including antimycobacterial, antiviral, antioxidant and antiherbivore properties, have been described [50,51]. Antarctic lichens may have evolved unique secondary metabolites to help in surviving the extreme environment in which they live [52,53,54].
Professor Oh’s group has made great efforts in discovery of new metabolites from the Antarctic lichens. From the MeOH extract of the Antarctic lichen Stereocaulon alpinum, a new cyclic depsipeptide stereocalpin A (92) (Figure 10) [55], together with three new usnic acid derivatives usimines A–C (93–95) (Figure 10) [56], were isolated by various chromatographic methods. Compound 92 incorporated an unprecedented 5-hydroxy-2,4-dimethyl-3-oxo-octanoic acid in the structure, and showed marginal levels of cytotoxicity against three human tumor cell lines, HT-29, B16/F10 and HepG2. In addition, compounds 92–95 moderately inhibited the activity of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) in a dose-dependent manner. Inhibition of PTP1B is predicted to be an excellent, novel therapy to target type 2 diabetes and obesity [57]. Furher investigation of this Antarctic lichen recovered seven phenolic lichen metabolites. Among the compounds, the depsidone-type compound, lobaric acid (96) (Figure 10) and two pseudodepsidone-type compounds, 97 and 98 (Figure 10), exhibited potent inhibitory activity against PTP1B with low IC50 values in a non-competitive manner [58]. In 2013, a new pseudodepsidone-type metabolite, lobastin (99) (Figure 10), with antioxidant and antibacterial activity was also reported from this strain [59].

Figure 10.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic lichen (compounds 92–104).
Four new diterpene furanoids, hueafuranoids A–D (100–103) (Figure 10) have been isolated from the MeOH extract of the Antarctic lichen Huea sp. Compound 100 showed inhibitory activity against therapeutically targeted protein, PTP1B with an IC50 value of 13.9 μM [60].
From the Antarctic lichen Ramalina terebrata, the novel compound ramalin (104) (Figure 10) was isolated. The experimental data showed that ramalin displayed potent antioxidant activity and can be a strong therapeutic candidate for controlling oxidative stress in cells [61].
4. Mosses
Mosses represent a relatively untapped natural source to be explored for new bioactive metabolites. Chemical studies of Antarctic moss Polytrichastrum alpinum led to the isolation of two new benzonaphthoxanthenones, ohioensins F and G (105 and 106) (Figure 11), along with two known compounds ohioensins A and C. All of the four compounds showed potent inhibitory activity against therapeutically targeted protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B). Kinetic analysis of PTP1B inhibition by ohioensin F (105) suggested that benzonaphthoxanthenones inhibited PTP1B activity in a non-competitive manner [62].
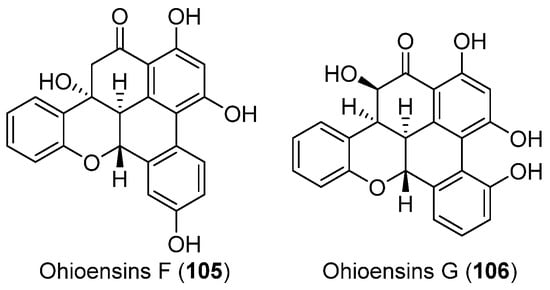
Figure 11.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic moss (compounds 105, 106).
5. Bryozoans
Bryozoans (moss animals and lace corals) have yielded a significant number of bioactive metabolites and have been reviewed elsewhere [63]. However, there is only a single report on secondary metabolites from a polar bryozoan. In 2011, an investigation into the chemistry of the Arctic bryozoan Tegella cf. spitzbergensis resulted in the isolation and structural determination of ent-eusynstyelamide B (107) and three new derivatives, eusynstyelamides D–F (108–110) (Figure 12) [64]. Ent-eusynstyelamide B (107) is the enantiomer of the known brominated tryptophan metabolite eusynstyelamide B [65]. Antimicrobial activities were reported for 107–110, with MIC values as low as 6.25 μg/mL for 107 and 110 against Staphylococcus aureus. Eusynstyelamides were generally more active against Gram-positive bacteria than Gram-negative bacteria [64].
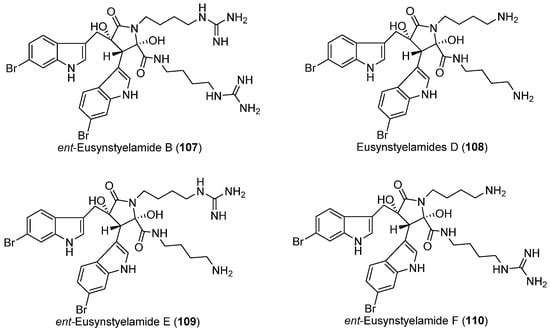
Figure 12.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Arctic bryozoan (compounds 107–110).
6. Cnidarians
Cnidarians are the second largest source (after sponges) of new marine natural products reported each year, with a predominance of terpenoids [11,12,13] and are also well represented in the polar regions. In 2003, fractionation of the bioactive extract from the chemically defended Antarctic gorgonian coral Ainigmaptilon antarcticus yielded two sesquiterpenes, ainigmaptilones A (111) and B (112) (Figure 13). Ainigmaptilone A has broad spectrum bioactivity toward sympatric predatory and fouling organisms, including antibiotic activity [66].

Figure 13.
Secondary metabolites derived from the polar cnidarians (compounds 111–137).
The ethereal extract of another Antarctic gorgonian Dasystenella acanthina was found to contain three main nonpolar and relatively transient sesquiterpene metabolites, including a new compound, furanoeudesmane (113) (Figure 13). Compound 113 was toxic at 46 μM in a Gambusia affinis ichthyotoxicity test. According to this result, an involvement of these molecules in the defensive mechanisms of the animal could be suggested [67].
Seven new steroids, compounds 114–120 (Figure 13), were isolated from the Antarctic octocoral Anthomastus bathyproctus. The in vitro cytotoxicity has been tested against three human tumor cell lines MDA-MB-231 (breast adenocarcinoma), A-549 (lung carcinoma), and HT-29 (colon adenocarcinoma). Compounds 115–118 displayed weak activity as inhibitors of cell growth [68].
Chemical investigation of the lipophilic extract of the Antarctic soft coral Alcyonium grandis led to the finding of nine unreported sesquiterpenoids, compounds 121–129 (Figure 13) [69]. These molecules are members of the illudalane class and in particular belong to the group of alcyopterosins. Similar illudalanes have been isolated from the sub-Antartic deep sea soft coral Alcyonium paessleri [70]. Repellency experiments conducted using the omnivorous Antarctic sea star Odontaster validus revealed a strong activity in the lipophilic extract of A. grandis against predation [69]. The total synthesis of some members of the alcyopterosin family has been reported already by many research groups [71,72,73,74,75].
More recently, the isolation and characterization of two new tricyclic sesquiterpenoids, shagenes A (130) and B (131) (Figure 13) were presented. The two compounds were isolated from an undescribed soft coral collected from the Scotia Arc in the Southern Ocean. Exploration of the bioactivity found that shagenes A was active against the visceral leishmaniasis causing parasite, Leishmania donovani (IC50 value = 5 μM), with no cytotoxicity against the mammalian host [76].
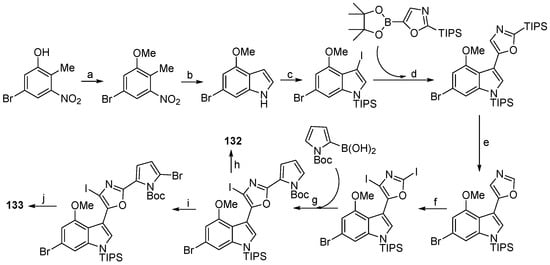
In 2012, two halogenated natural products breitfussin A (132) and breitfussin B (133) (Figure 13) were isolated from the Arctic hydrozoan Thuiria breitfussi collected at Bjørnøya (Bear Island) [77]. Recently, Hedberg and co-workers synthesized breitfussins A and B firstly using Suzuki coupling reactions to join the heteroaromatic rings, thus confirming the assigned structure of these natural products (Scheme 6) [78]. Soon after, a conceptually distinct synthesis of breitfussin B through late-stage bromination of the breitfussin core was reported by Khan and Chen [79].
Scheme 6.
Synthesis of Breitfussin A (132) and B (133). Reagents and conditions: (a) MeI, Cs2CO3, DMF, rt, 82%; (b) Dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal (DMFDMA), Pyrrolidine, DMF, then Zn, AcOH/H2O, 80 °C, 61%; (c) Iodine chloride, Pyridine (ICl, Py), CH2Cl2, then NaH, Three isopropyl silicon alkyl chloride (TIPSCl), THF, 81%; (d) 1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene]dichloropalladium (Pd(dppf)Cl2), K3PO4, Toluene/H2O, 80 °C; (e) 10% aq HCl, THF, 0 °C, 89%; (f) Lithium hexamethyldisilazide (LiHMDS), −78 °C, then I2, −78 °C, 15%; (g) Pd(dppf)Cl2, Cs2CO3, Dioxane/H2O, rt, 61%; (h) Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf), Et3N, CH2Cl2, 0 °C to rt, then Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF), THF, 0 °C, 64%; (i) N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS), THF, −78 °C to rt, 57%; (j) Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), CH2Cl2, 0 °C to rt, then TBAF, THF, 0 °C, 67%.
From the Arctic soft coral Gersemia fruticosa, three new diterpenes named gersemiols A–C (134–136) together with a new eunicellane diterpene, eunicellol A (137), have been obtained. All compounds were tested for their antimicrobial activity against several bacteria and fungi. Only eunicellol A was found to exhibit moderate anti-bacterial activity against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) with MIC value of 24–48 μg/mL [80].
7. Echinoderms
Echinoderms are well known producers of bioactive glycosylated metabolites [11,12,13], and many new natural products have been described from the polar examples. In 2001, two new trisulfated triterpene glycosides, liouvillosides A (138) and B (139) (Figure 14), were isolated from the Antarctic sea cucumber Staurocucumis liouvillei. Liouvillosides A and B are two new examples of a small number of trisulfated triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers belonging to the family Cucumariidae. Both glycosides were found to be virucidal against herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) at concentrations below 10 μg/mL [81]. A novel triterpene holostane disulfated tetrasaccharide olygoglycoside, turquetoside A (140) (Figure 14), having a rare terminal 3-O-methyl-d-quinovose, was isolated from the Antarctic sea cucumber Staurocucumis turqueti [82]. The occurrence of 3-O-methyl-d-quinovose in triterpene glycosides in S. turqueti and in the congeneric Antarctic sea cucumber S. liouvillei suggests that the presence of this sugar in carbohydrate chains of triterpene glycosides is a taxonomical character of the genus Staurocucumis [81,82].

Figure 14.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic sea cucumbers (compounds 138–143).
Subsequently, another three new triterpene glycosides, achlioniceosides A1 (141), A2 (142), and A3 (143) (Figure 14), were obtained from the Antarctic sea cucumber Achlionice violaecuspidata. Glycosides 141–143 are the first triterpene glycosides isolated from a sea cucumber belonging to the order Elasipodida [83].
8. Molluscs
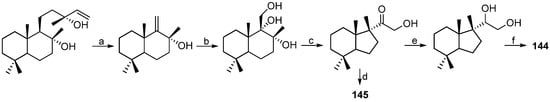
The nudibranch Austrodoris kerguelenensis is distributed widely around the Antarctic coast and continental shelves. In 2003, two unprecedented nor-sesquiterpenes, austrodoral (144) and its oxidised derivative austrodoric acid (145) (Figure 15), were isolated from the skin of the marine dorid A. kerguelenensis, collected in the Antarctic. A role of stress-metabolites could be suggested for these compounds [84]. A short and efficient synthesis of 144 and 145 was reported as shown in Scheme 7 [85]. Further chemical study of this Antarctic nudibranch yielded two novel 2-monoacylglycerols (146) and (147) (Figure 15), along with two known 1,2-diacyl glyceryl esters [86].

Figure 15.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic nudibranch Austrodoris kerguelenensis (compounds 144–147).
Scheme 7.
Synthesis of austrodoral (144) and austrodoric acid (145). Reagents and conditions: (a) four steps, 59% [87,88]; (b) OsO4, H2O, t-BuOH, trimethylamine N-oxide, pyridine, reflux, 24 h, 87%; (c) BF3·OEt2, CH2Cl2, 0 °C to rt, 20 min, 95%; (d) NaBH4, EtOH, rt, 15 min, 97%; (e) Pb(OAc)4, CH2Cl2, rt, 45 min, 92%; (f) NaIO4, t-BuOH–H2O, reflux, 12 h, 91%.
Investigation of the nudibranch A. kerguelenensis collected near the Antarctic Peninsula resulted in the isolation of three new diterpenes, palmadorins A–C (148–150) (Figure 16) [89]. Detailed investigation of this Antarctic nudibranch led to the discovery of a diverse suite of new diterpenoid glyceride esters, palmadorins D–S (151–166) (Figure 16), including one (palmadorin L) that is the first halogenated diterpene from this well-studied nudibranch. Palmadorin A (148), B (149), D (151), M (160), N (161), and O (162) inhibit human erythroleukemia (HEL) cells with low micromolar IC50, and palmadorin M inhibits Jak2, STAT5, and Erk1/2 activation in HEL cells and causes apoptosis at 5 mM [90].

Figure 16.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic nudibranch (compounds 148–167).
Recently, a new homosesterterpene named granuloside (167) (Figure 16), was characterized from the Antarctic nudibranch Charcotia granulosa. Granuloside was the first linear homosesterterpene skeleton ever reported and, despite the low molecular complexity, its chemical structure poses many questions about its biogenesis and origin in the nudibranch [91].
9. Sponges
Marine sponges are the largest source of new marine natural products reported annually [11,12,13] and have provided a rich array of biologically important compounds [92]. There are a large number of studies on sponges from warm or tropical waters, whereas little is known about the chemistry of sponges from the Arctic or Antarctic waters. Actually, polar species of marine sponges can also be a rich source of biologically and structurally interesting molecules.
Pyridinium alkaloids are widely distributed in marine sponges of different genera. In 2003, chemical investigation of the Arctic sponge Haliclona viscosa led to the isolation of a new trimeric 3-alkyl pyridinium alkaloid, viscosamine (168) (Figure 17) [93]. Further investigation of this sponge yielded one new 3-alkyl pyridinium alkaloid, viscosaline (169) (Figure 17) [94], and two new 3-alkyltetrahy-dropyridine alkaloids, haliclamines C (170) and D (171) (Figure 17) [95]. In 2009, new haliclamines E (172) and F (173) (Figure 17) were subsequently obtained from this Arctic sponge [96]. Compound 169 showed activity in the feeding deterrence assay against the amphipod Anonyx nugax and the starfish Asterias rubens from the North Sea [97]. Compounds 169 and 170 showed a strong inhibition against two bacterial strains isolated from the vicinity of the sponge [95,97]. The synthesis of the Arctic sponge alkaloids were also achieved by two groups [97,98].
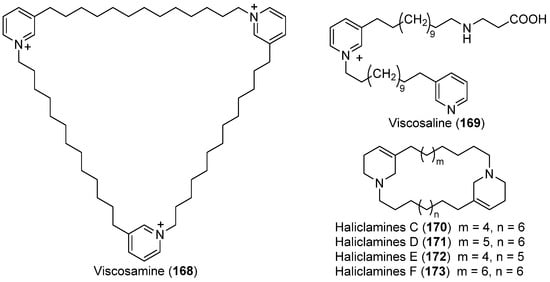
Figure 17.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Arctic sponge Haliclona viscosa (compounds 168–173).
A new sesterterpene, caminatal (174), and two novel sesterterpenes, oxaspirosuberitenone (175) and 19-episuberitenone (176) (Scheme 8) were obtained from the Antarctic sponge Suberites caminatus [99,100]. Their possible biogenesis were proposed as shown in Scheme 8.
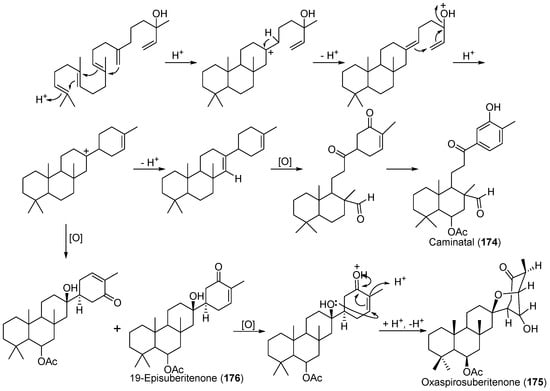
Scheme 8.
Possible biogenesis of caminatal (174), oxaspirosuberitenone (175) and 19-episuberitenone (176).
Four new diterpenoids, 177–180 (Figure 18) were isolated from the Antarctic sponge Dendrilla membranosa. Compound 177 was a nor-diterpene gracilane skeleton derivative, while 178–180 are C-20 aplysulphurane-type diterpenes [101].

Figure 18.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic sponges (compounds 177–189) and the Arctic sponge (compounds 190–193).
Three new sesterterpenes of the suberitane class, suberitenones C (181) and D (182) and suberiphenol (183) (Figure 18), were isolated from the sponge Suberites sp. collected from Antarctica. Unfortunately, the new compounds were neither cytotoxic against the human leukemia K562 cell-line nor antimicrobial against B. subtilis, C. albicans, E. coli and S. aureus [102].
Five new steroids, norselic acids A–E (184–188) (Figure 18), were isolated from the sponge Crella sp. collected in Antarctica. Norselic acid A displayed antibiotic activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-sensitive S. aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and Candida albicans, and reduced consumption of food pellets by sympatric mesograzers. Compounds 184–188 were also active against the Leishmania parasite with low micromolar activity [103].
Darwinolide (189), a novel spongian diterpene, was characterized from the Antarctic sponge Dendrilla membranosa. Darwinolide displayed antibiofilm activity against MRSA with no mammalian cytotoxicity, and may present a suitable scaffold for the development of novel antibiofilm agents to treat drug resistant bacterial infections [104].
Barettin (190), 8,9-dihydrobarettin (191), bromoconicamin (192) and a novel brominated marine indole (193) (Figure 18) were isolated from the sponge Geodia barretti collected off the Norwegian coast. The compounds were evaluated as inhibitors of electric eel acetylcholinesterase. Compounds 190 and 191 displayed significant inhibition of the enzyme, 192 was less potent against acetylcholinesterase, and 193 was inactive. Based on the inhibitory activity, a library of 22 simplified synthetic analogs was designed and prepared to probe the role of the brominated indole. From the structure–activity investigation, it was shown that the brominated indole motif is not sufficient to generate a high acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity, even when combined with natural cationic ligands for the acetylcholinesterase active site. The four natural compounds were also analysed for butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activity and shown to display comparable activities [105].
10. Tunicates
Tunicates comprise >2800 species and have yielded a diverse array of bioactive metabolites [10,106], including anticancer agents such as didemnin B from Trididemnum solidum, diazonamide from Diazona angulata, and the approved anticancer drug Ecteinascidin 743 (Yondelis™) from Ecteinascidia turbinata [107,108].
Bioassay-guided fractionation of CH2Cl2/MeOH extracts of the tunicate Aplidium cyaneum collected in Antarctica led to the isolation of aplicyanins A–F (194–199) (Figure 19), a group of alkaloids containing a bromoindole nucleus and a 6-tetra-hydropyrimidine substituent at C-3. Cytotoxic activity in the submicromolar range as well as antimitotic properties were found for compounds 195, 197, and 199, whereas compounds 194 and 196 proved to be inactive at the highest concentrations tested and compound 198 displayed only mild cytotoxic properties. The results clearly suggested a key role for the presence of the acetyl group at N-16 in the biological activity of this family of compounds [109].

Figure 19.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic tunicates (compounds 194–209).
Five new ecdysteroids, hyousterones A–D (200–203) and abeohyousterone (204) (Figure 19), were isolated from the Antarctic tunicate Synoicum adareanum by Baker and co-workers. Abeohyousterone (204) has moderate cytotoxicity toward several cancer cell lines. Hyousterones bearing the 14β-hydroxy group (200 and 202) were weakly cytotoxic, while the 14α-hydroxy hyousterones (201 and 203) were devoid of cytotoxicity [110]. Further chemical investigation of the same Antarctic tunicate S. adareanum yielded five new bioactive macrolides, palmerolide A (205) and D–G (206–209) (Figure 19). Most of these palmerolides were potent V-ATPase inhibitors and had sub-micromolar activity against melanoma [111,112]. Especially, palmerolide A remained the most potent of this series of natural products against melanoma cells. In the National Cancer Institute (NCI) sixty-cell panel, palmerolide A did not display cytotoxicity below 1 μM against any non-melanoma cell lines. In vivo activity of palmerolide A in mice has been confirmed in the NCI’s hollow fiber assay [113]. Structural features of palmerolide A such as the carbamate and the vinyl amide moieties led the Baker group to hypothesize a bacterial origin for this polyketide. One finding that supported the possibility was the identification of polyketide synthase (PKS) genes, similar to bryostatin biosynthetic genes [114]. Due to promising biological activity and limited access to natural supplies, as well as their challenging structures, palmerolide A and congeneric structures are important targets for chemical synthesis. Recent advances in the synthesis of the palmerolides have been reviewed by Lisboa and Dudley [115]. To date, three total syntheses [116,117,118,119,120] of palmerolide A have been reported. Four groups disclosed formal syntheses [121,122,123,124,125,126], and various synthetic approaches have also been described [127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135]. The synthesis of the reported structure of palmerolide C has also been achieved, and a structural revision has been proposed [136].
In 2009, bioassay-guided fractionation of the Antarctic ascidian Aplidium species, led to the characterization of two new biologically active meroterpene derivatives, rossinones A (210) and B (211) (Figure 20). The rossinones exhibited antiinflammatory, antiviral and antiproliferative activities [137]. In additon, rossinone B (211) was proven to take part in the whole-colony chemical defense of Aplidium falklandicum, repelling both sea stars and amphipods [138]. The following year, a biomimetic total synthesis of (±)-rossinone B was achieved through a highly efficient strategy as shown in Scheme 9 [139]. Two years later, three novel rossinone-related meroterpenes (212–214) (Figure 20) were obtained from the Antarctic ascidian Aplidium fuegiense. The new compounds were found to be selectively localized in the viscera of the ascidian [140].
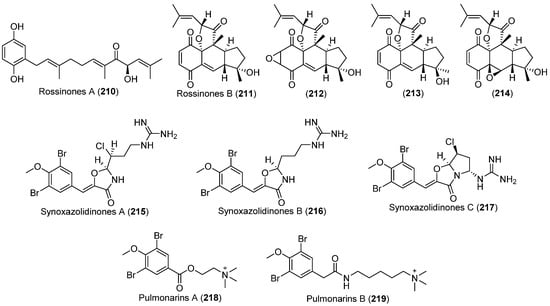
Figure 20.
Secondary metabolites derived from the Antarctic tunicates (compounds 210–214) and the Arctic tunicate (compounds 215–219).
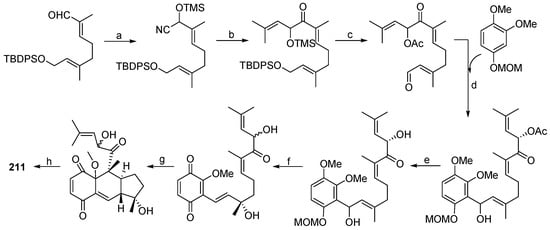
Scheme 9.
Synthesis of rossinone B (211). Reagents and conditions: (a) Trimethylsilyl cyanide (TMSCN), NEt3, CH3CN, 99%; (b) LiHMDS, THF, −78 °C, then 3-methyl-2-butenal, TMS migration, 75%; (c) 1 N HCl, THF, then Ac2O/py, then HF, CH3CN, then 2,2-Dimethoxypropane (DMP), 4-(Dicyanomethylene)-2-methyl-6-(4-dimethylaminostyryl)-4H-pyran (DCM), 51%; (d) nBuLi, −78 °C, 88%; (e) K2CO3/MeOH, 79%; (f) 6 N HNO3, then AgO, 90%; (g) toluene, sealed tube, 150 °C; (h) CH3OH/H2O, TsOH, 80 °C, 31%.
From the sub-Arctic ascidian Synoicum pulmonaria collected off the Norwegian coast, three new brominated guanidinium oxazolidinones were isolated, named synoxazolidinones A–C (215–217) (Figure 20) [141,142,143]. The backbone of the compounds contains a 4-oxazolidinone ring rarely seen in natural products. Synoxazolidinones A (215) and B (216) exhibited antibacterial and antifungal activities, and 215 displayed higher activity than 216 because of the chlorine atom in its structure [141]. Synoxazolidinone C could inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus at a concentration of 10 μg/mL [142]. In addition, 215 and 217 displayed a broad and high activity toward the adhesion and growth of 16 known biofouling species of marine bacteria, microalgae, and crustaceans. Compound 217 was the most active compound and was comparable to the commercial antifouling product Sea-Nine-211 [144]. Pulmonarins A (218) and B (219) (Figure 20) were two new dibrominated marine acetylcholinesterase inhibitors that were also isolated from this sub-Arctic ascidian. Both 218 and 219 displayed reversible, noncompetitive acetylcholinesterase inhibition comparable to several known natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitiors [145]. In addition, the pulmonarins were generally active against the adhesion and growth of several bacteria [144].
11. Conclusions
As demonstrated by this review, polar organisms have yielded an impressive array of novel compounds (Table 1) with complex structures and potent biological activities including the cytotoxic cyclic acylpeptides, mixirins A–C (1–3), from the Arctic marine bacterium Bacillus sp. [15]; the unusual antibacterial polyketide, lindgomycin (46) from the culture broth of a Lindgomycetaceae strain [36]; the antioxidant compound ramalin (104) from the Antarctic lichen Ramalina terebrata [61]; the new antiparasitic tricyclic sesquiterpenoids, shagenes A (130) and B (131) from an undescribed Antarctic soft coral [76]; and the new macrolides, palmerolide A (205) and D–G (206–209) with potent V-ATPase inhibitory and sub-micromolar activity against melanoma from the Antarctic tunicate Synoicum adareanum [111,112].

Table 1.
Novel natural products isolated from polar organisms.
The natural products derived from polar regions appear to have a high hit rate regarding biological activity, varying from cytotoxic, enzyme inhibitory, antioxidant, antiparasitic, antiviral to antibacterial and so on. Secondary metabolism in polar habitats is largely driven by ecological requirements of the producing organism. Successful organisms will often have specific metabolic pathways that produce unique functional natural products that bestow ecological advantage, increasing the possibility of finding pharmaceutical lead molecules.
However, when compared to the large number of polar microorganisms which have been reported, very few have been screened for the production of interesting secondary metabolites. This situation may be attributed to the difficulties in cultivating polar microorganisms, some of which cannot survive under normal laboratory conditions and therefore cannot be cultured using traditional techniques. As yet, the potential of this area remains virtually untapped. Nowadays, advances in laboratory techniques have led to cultivation of some previously inaccessible extremophiles. Moreover, new tools developed recently in the fields of bioinformatics [146], analytics [147], and molecular biology [148], in combination with rapid improvement in sequencing technology, might herald a new era of research into this specific source.
Acknowledgments
The authors express thanks to the people who helped with this work. This work was financed by NSFC grant (21602152, 81403036), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2016BB01, ZR2014HM048), Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development Program (2016GSF202002), Shandong Provincial Medical Science and Technology Development Project (2013WS0321), Taian Science and Technology Development Project (2016NS1214), Shandong Provincial Education Department Project (J15LM56), National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (201610439263) and Taishan Medical University High-level Development Project (2015GCC15).
Author Contributions
Yuan Tian and Yan-Ling Li contributed equally in the writing of this manuscript. Feng-Chun Zhao collected all the references.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Santiago, I.F.; Soares, M.A.; Rosa, C.A.; Rosa, L.H. Lichensphere: A protected natural microhabitat of the non-lichenised fungal communities living in extreme environments of Antarctica. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tian, X.P.; Zhu, T.J.; Yang, L.L.; Li, W.J. Streptomyces fildesensis sp. nov., a novel streptomycete isolated from Antarctic soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2011, 100, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Moon, E.Y.; Cho, J.C.; Lee, H.K.; Hong, S.G. Actimicrobium antarcticum gen. nov., sp. nov., of the family Oxalobacteraceae, isolated from Antarctic coastal seawater. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snauwaert, I.; Peeters, K.; Willems, A.; Vandamme, P.; Vuyst, L.D.; Hoste, B.; Bruyne, K.D. Carnobacterium iners sp. nov., a psychrophilic, lactic acid-producing bacterium from the littoral zone of an Antarctic pond. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ruan, C.; Peng, F.; Deng, Z.; Hong, K. Streptomyces arcticus sp. nov., isolated from the Arctic. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebar, M.D.; Heimbegner, J.L.; Baker, B. Cold-water marine natural products. J. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, Z.E.; Brimble, M.A. Molecules derived from the extremes of life. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 44–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.; Kelly, M.; Bowling, J.; Sims, J.; Waters, A.; Hamann, M. Advancement into the Arctic region for bioactive sponge secondary metabolites. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2423–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.T.; Lu, X.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, B.; Jiao, B.H.; Zheng, H. Bioactive natural products from the antarctic and arctic organisms. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skropeta, D.; Wei, L. Recent advances in deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 31, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 160–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 116–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 382–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pascale, D.; De Santi, C.; Fu, J.; Landfald, B. The microbial diversity of Polar environments is a fertile ground for bioprospecting. Mar. Genom. 2012, 8, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.L.; Hua, H.M.; Pei, Y.H.; Yao, X.S. Three new cytotoxic cyclic acylpeptides from marine Bacillus sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1029–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zereini, W.; Schuhmann, I.; Laatsch, H.; Helmke, E.; Anke, H. New aromatic nitro compounds from Salegentibacter sp. T436, an Arctic Sea ice bacterium: Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological activities. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhmann, I.; Yao, C.B.F.; Al-Zereini, W.; Anke, H.; Helmke, E.; Laatsch, H. Nitro derivatives from the Arctic ice bacterium Salegentibacter sp. isolate T436. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitova, M.; Tutino, M.L.; Infusini, G.; Marino, G.; De Rosa, S. Exocellular peptides from Antarctic psychrophile Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asthana, R.K.; Deepali; Tripathi, M.K.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, S.P.; Nath, G.; Srivastava, R.; Srivastava, B.S. Isolation and identification of a new antibacterial entity from the Antarctic cyanobacterium Nostoc CCC 537. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojib, N.; Philpott, R.; Huang, J.P.; Niederweis, M.; Bej, A.K. Antimycobacterial activity in vitro of pigments isolated from Antarctic bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2010, 98, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedesco, P.; Maida, I.; Esposito, F.P.; Tortorella, E.; Subko, K.; Ezeofor, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Tabudravu, J.; Jaspars, M.; Fani, R.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of monoramnholipids produced by bacterial strains isolated from the Ross Sea (Antarctica). Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macherla, V.R.; Liu, J.; Bellows, C.; Teisan, S.; Nicholson, B.; Lam, K.S.; Potts, B.C.M. Glaciapyrroles A, B, and C, pyrrolosesquiterpenes from a Streptomyces sp. isolated from an Alaskan marine sediment. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Mondol, M.A.M.; Yu, T.K.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, H.J. An angiogenesis inhibitor isolated from a marine-derived actinomycete, Nocardiopsis sp. 03N67. Phytochem. Lett. 2010, 3, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, J.; Bao, W.; Wang, Y.; Xi, T. A novel anticancer and antifungus phenazine derivative from a marine actinomycete BM-17. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Si, L.; Shi, Z.; Tian, L.; Liu, D.; Zhou, D.; Prokch, P.; Lin, W. Nitrosporeusines A and B, unprecedented thioester-bearing alkaloids from the Arctic Streptomyces nitrosporeus. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5366–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philkhana, S.C.; Jachak, G.R.; Gunjal, V.B.; Dhage, N.M.; Bansode, A.H.; Reddy, D.S. First synthesis of nitrosporeusines, alkaloids with multiple biological activities. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1252–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.; Ahn, C.H.; Shin, Y.; Won, T.H.; Ko, K.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J.; Nam, S.I.; Oh, D.C. New benzoxazine secondary metabolites from an Arctic Actinomycete. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2526–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruntner, C.; Binder, T.; Pathom-aree, W.; Goodfellow, M.; Bull, A.T.; Potterat, O.; Puder, C.; Hörer, S.; Schmid, A.; Bolek, W.; et al. Frigocyclinone, a novel angucyclinone antibiotic produced by a Streptomyces griseus strain from Antarctica. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, G.; Lang, G.; Maksimenka, K.; Hamm, A.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Dieter, A.; Bull, A.T.; Stach, J.E.M.; Kocher, N.; Müller, W.E.G.; Fiedler, H.P. Gephyromycin, the first bridged angucyclinone, from Streptomyces griseus strain NTK 14. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, V.; Kolarova, M.; Aleksieva, K.; Gräfe, U.; Dahse, H.M.; Laatsch, H. Microbiaeratin, a new natural indole alkaloid from a Microbispora aerata strain, isolated from Livingston Island, Antarctica. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 37, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Saurav, K.; Yu, Z.; Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T.; Li, J.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C. α-Pyrones with diverse hydroxy substitutions from three marine-derived Nocardiopsis Strains. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalsgaard, P.W.; Larsen, T.O.; Christophersen, C. Bioactive cyclic peptides from the psychrotolerant fungus Penicillium algidum. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.T.; Hu, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Jiao, B.H.; Lu, X.L.; Liu, X.Y. Bioactive tyrosine-derived cytochalasins from fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.L.; Liu, J.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, B.H.; Zheng, H. Pimarane diterpenes from the Arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Chen, X.C.; Chen, Z.Q.; Wang, G.M.; Zhu, S.G.; Yan, Y.F.; Chen, K.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, Y.M. Eutypenoids A–C: Novel pimarane diterpenoids from the Arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Wiese, J.; Labes, A.; Kramer, A.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Lindgomycin, an unusual antibiotic polyketide from a marine fungus of the Lindgomycetaceae. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4617–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondeyka, J.G.; Smith, S.K.; Zink, D.L.; Vicente, F.; Basilio, A.; Bills, G.F.; Polishook, J.D.; Garlisi, C.; Mcguinness, D.; Smith, E.; et al. Isolation, structure elucidation and antibacterial activity of a new tetramic acid, ascosetin. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamo, M.; Tojo, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Itabashi, T.; Takeda, H.; Wakana, D.; Hosoe, T. Isolation of growth inhibitors of the snow rot pathogen Pythium iwayamai from an arctic strain of Trichoderma polysporum. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Che, Y. Bioactive asterric acid derivatives from the Antarctic ascomycete fungus Geomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Xue, C.; Tian, L.; Xu, M.; Chen, J.; Deng, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Asperelines A–F, peptaibols from the marine-derived fungus Trichoderma asperellum. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, W.; Proksch, P.; Shao, B.; Lin, W. Sequential determination of new peptaibols asperelines G-Z12 produced by marine-derived fungus Trichoderma asperellum using ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography combined with electrospray-ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1309, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, D.; Luan, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T. Cytotoxic metabolites from the antarctic psychrophilic fungus Oidiodendron truncatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Ma, H.; Zhu, T.; Li, J.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Penilactones A and B, two novel polyketides from Antarctic deep-sea derived fungus Penicillium crustosum PRB-2. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9745–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.T.J.; George, J.H. Total synthesis of ent-penilactone A and penilactone B. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3891–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Lin, A.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Four new chloro-eremophilane sesquiterpenes from an Antarctic deep-sea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19N-1. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Wu, G.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. New eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from an Antarctic deepsea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19N-1. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Che, Q.; Li, D.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T. Chrodrimanins I and J from the Antarctic moss-derived fungus Penicillium funiculosum GWT2-24. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, L.; Jiménez, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Areche, C.; Chávez, R.; Henríquez, M.; de la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; Segade, Y.; Vaca, I. 3-Nitroasterric acid derivatives from an Antarctic sponge-derived Pseudogymnoascus sp. fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Qin, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; et al. Antiviral merosesquiterpenoids produced by the Antarctic fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingόlfsdόttir, K. Usnic acid. Phytochemistry 2002, 61, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.C.S.; Müller, K. Lichen metabolites. 1. Inhibitory action against leukotriene B4 biosynthesis by a non-redox mechanism. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, B.; Bhattarai, H.D.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.G.; Shin, H.W.; Yim, J.H. Antibacterial potential of Antarctic lichens against human pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, B.; Bhattarai, H.D.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.G.; Shin, H.W.; Yim, J.H. Antioxidant activity of polar lichens from King George Island (Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2008, 31, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, V.; Kolarova, M.; Aleksieva, K. Diphenylether and macrotriolides occurring in a fungal isolate from the antarctic lichen Neuropogon. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 37, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Park, S.M.; Sohn, J.H.; Oh, H. Stereocalpin A, a bioactive cyclic depsipeptide from the Antarctic lichen Stereocaulon alpinum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.; Sohn, J.H.; Park, S.M.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Oh, H. Usimines A-C, bioactive usnic acid derivatives from the Antarctic lichen Stereocaulon alpinum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, S.; Fantus, I.G. Inhibition of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B: Potential therapy for obesity, insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes mellitus. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 21, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.; Sohn, J.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Oh, H. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory effects of depsidone and pseudodepsidone metabolites from the Antarctic lichen Stereocaulon alpinum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2801–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, H.D.; Kim, T.; Oh, H.; Yim, J.H. A new pseudodepsidone from the Antarctic lichen Stereocaulon alpinum and its antioxidant, antibacterial activity. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, H. New diterpene furanoids from the Antarctic lichen Huea sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 7393–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, B.; Bhattarai, H.D.; Koh, H.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Han, S.J.; Lee, H.K.; Oh, H.; Shin, H.W.; Yim, J.H. Ramalin, a novel nontoxic antioxidant compound from the Antarctic lichen Ramalina terebrata. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.; Choi, Y.H.; Sohn, J.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Oh, H. Ohioensins F and G: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory benzonaphthoxanthenones from the Antarctic moss Polytrichastrum alpinum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, J.H.; Winson, M.K.; Porter, J.S. Bryozoan metabolites: An ecological perspective. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, M.; Tabudravu, J.N.; Jaspars, M.; Strøm, M.B.; Hansen, E.; Andersen, J.H.; Kristiansen, P.E.; Haug, T. The antibacterial ent-eusynstyelamide B and eusynstyelamides D, E, and F from the Arctic bryozoan Tegella cf. spitzbergensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapiolas, D.M.; Bowden, B.F.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Willis, R.H.; Doyle, J.R.; Muirhead, A.N.; Liptrot, C.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Wolff, C.W.W.; Wright, A.D.; et al. Eusynstyelamides A, B, and C, nNOS inhibitors, from the ascidian Eusynstyela latericius. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iken, K.B.; Baker, B.J. Ainigmaptilones, sesquiterpenes from the Antarctic gorgonian coral Ainigmaptilon antarcticus. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 888–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavagnin, M.; Mollo, E.; Castelluccio, F.; Crispino, A.; Cimino, G. Sesquiterpene metabolites of the antarctic gorgonian Dasystenella acanthina. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellado, G.G.; Zubía, E.; Ortega, M.J.; Lόpez-González, P.J. Steroids from the Antarctic octocoral Anthomastus bathyproctus. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Nunez-Pons, L.; Castelluccio, F.; Avila, C.; Gavagnin, M. Illudalane sesquiterpenoids of the alcyopterosin series from the Antarctic marine soft coral Alcyonium grandis. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, J.A.; Rodriguez Brasco, M.F.; Spagnuolo, C.; Seldes, A.M. Illudalane sesquiterpenoids from the soft coral Alcyonium paessleri: The first natural nitrate esters. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 4482–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkielsztein, L.M.; Bruno, A.M.; Renou, S.G.; Moltrasio de Iglesias, G.Y. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of alcyopterosin A and illudalane derivatives as anticancer agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Nakano, Y.; Suzuki, D.; Urabe, H.; Sato, F.J. Selective preparation of benzyltitanium compounds by the metalative Reppe reaction. Its Application to the first synthesis of alcyopterosin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9682–9683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Oda, S.; Yukawa, T.; Shirakawa, E.; Hiyama, T. Stannylative cycloaddition of enynes catalyzed by palladium-iminophosphine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15650–15651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.L.; Snyder, J.K. Intramolecular rhodium-catalyzed [2+2+2] cyclizations of diynes with enones. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 2907–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, T.; Tran, H.A.; Witulski, B. Total syntheses of the marine illudalanes alcyopterosin I, L, M, N, and C. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 5644–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Salm, J.L.; Wilson, N.G.; Vesely, B.A.; Kyle, D.E.; Cuce, J.; Baker, B.J. Shagenes A and B, new tricyclic sesquiterpenes produced by an undescribed Antarctic octocoral. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 2630–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, K.Ø.; Schuler, B.; Williams, A.J.; Demissie, T.B.; Hansen, E.; Andersen, J.H.; Svenson, J.; Blinov, K.; Repisky, M.; Mohn, F.; et al. A combined atomic force microscopy and computational approach for the structural elucidation of breitfussin A and B: Highly modified halogenated dipeptides from Thuiaria breitfussi. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12238–12241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.K.; Guttormsen, Y.; Haug, B.E.; Hedberg, C.; Bayer, A. A concise total synthesis of breitfussin A and B. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.H.; Chen, J.S. Synthesis of breitfussin B by late-stage bromination. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 3718–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo-Preckler, C.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Mahajan, N.; de la Cruz, M.; de Pedro, N.; Reyes, F.; Iken, K.; Avila, C.; Thomas, O.P. Gersemiols A-C and eunicellol A, diterpenoids from the Arctic soft coral Gersemia fruticosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, M.S.; Roccatagliata, A.J.; Kuriss, A.; Chludil, H.; Seldes, A.M.; Pujol, C.A.; Damonte, E.B. Two new cytotoxic and virucidal trisulfated triterpene glycosides from the Antarctic sea cucumber Staurocucumis liouvillei. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjashchenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kalinin, V.I.; Taboada, S.; Avila, C. Triterpene glycosides from Antarctic sea cucumbers IV. Turquetoside A, a 3-O-methylquinovose containing disulfated tetraoside from the sea cucumber Staurocucumis turqueti (Vaney, 1906) (=Cucumaria spatha). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2013, 51, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kalinin, V.I.; Taboada, S.; Bosh, A.; Avila, C.; Stonik, V.A. Triterpene glycosides from Antarctic sea cucumbers. 2. Structure of Achlioniceosides A(1), A(2), and A(3) from the sea cucumber Achlionice violaecuspidata (=Rhipidothuria racowitzai). J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavagnin, M.; Carbone, M.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G. Austrodoral and austrodoric acid: Nor-sesquiterpenes with a new carbon skeleton from the Antarctic nudibranch Austrodoris kerguelenensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.J.; Chahboun, R.; Barranco, I.; Torres, E.C.; Alvarez, E.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, R. First enantiospecific synthesis of marine nor-sesquiterpene (+)-austrodoral from (–)-sclareol. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 5321–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavagnin, M.; Carbone, M.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G. Further chemical studies on the Antarctic nudibranch Austrodoris kerguelenensis: New terpenoid acylglycerols and revision of the previous stereochemistry. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 5579–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.J.; Chahboun, R.; Barranco, I.; Torres, E.C.; Alvarez, E.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, R. First enantiospecific synthesis of the antitumor marine sponge metabolite (–)-15-oxopuupehenol from (–)-sclareol. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrero, A.F.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.J.; Chahboun, R.; González Díaz, C. New routes toward drimanes and nor-drimanes from (–)-Sclareol. Synlett 2000, 11, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Diyabalanage, T.; Iken, K.B.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Baker, B.J. Palmadorins A–C, diterpene glycerides from the antarctic nudibranch Austrodoris kerguelenensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschek, J.A.; Mevers, E.; Diyabalanage, T.; Chen, L.; Ren, Y.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Wu, J.; Baker, B.J. Palmadorin chemodiversity from the Antarctic nudibranch Austrodoris kerguelenensis and inhibition of Jak2/STAT5-dependent HEL leukemia cells. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9095–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutignano, A.; Moles, J.; Avila, C.; Fontana, A. Granuloside, a unique linear homosesterterpene from the Antarctic nudibranch Charcotia granulosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1761–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skropeta, D.; Pastro, N.; Zivanovic, A. Kinase inhibitors from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2131–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, C.A.; Köck, M. Viscosamine: The first naturally occurring trimeric 3-alkyl pyridinium alkaloid. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 3567–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, C.A.; Köck, M. Viscosaline: New 3-alkyl pyridinium alkaloid from the Arctic sponge Haliclona viscosa. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, C.A.; Lippert, H.; Lichte, E.; Köck, M. Two new haliclamines from the Arctic sponge Haliclona viscosa. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 3154–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.; Timm, C.; Köck, M. New haliclamines E and F from the Arctic sponge Haliclona viscosa. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 3061–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, C.; Mordhorst, T.; Köck, M. Synthesis of 3-alkyl pyridinium alkaloids from the arctic sponge Haliclona viscosa. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorey, B.J.; Lee, V.; Baldwin, J.E. Synthesis of the Arctic sponge alkaloid viscosaline and the marine sponge alkaloid theonelladin C. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 5587–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Brito, I.; Dorta, E.; Cueto, M.; San-Martín, A.; Darias, J. Synthesis of the Arctic sponge alkaloid viscosaline and the marine sponge alkaloid theonelladin C. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 5939–5942. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Brito, I.; Cueto, M.; San-Martín, A.; Darias, J. Suberitane network, a taxonomical marker for Antarctic sponges of the genus Suberites? Novel sesterterpenes from Suberites caminatus. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 4707–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Marrero, A.R.; Dorta, E.; Cueto, M.; San-Martín, A.; Darias, J. Conformational analysis and absolute stereochemistry of ‘spongian’-related metabolites. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Ahn, J.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Rho, J.R.; Shin, J. New sesterterpenes from the Antarctic sponge Suberites sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.S.; Mutka, T.; Vesley, B.; Amsler, M.O.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Perman, J.A.; Singh, M.P.; Maiese, W.M.; Zaworotko, M.J.; et al. Norselic acids A–E, highly oxidized anti-infective steroids that deter mesograzer predation, from the Antarctic sponge Crella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1842–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Salm, J.L.; Witowski, C.G.; Fleeman, R.M.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Shaw, L.N.; Baker, B.J. Darwinolide, a new diterpene scaffold that inhibits methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm from the Antarctic sponge Dendrilla membranosa. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, E.K.; Hansen, E.; Moodie, L.W.K.; Isaksson, J.; Sepčić, K.; Cergolj, M.; Svenson, J.; Andersen, J.H. Marine AChE inhibitors isolated from Geodia barretti: Natural compounds and their synthetic analogs. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.F.; Namikoshi, M. Bioactive nitrogenous metabolites from ascidians. Heterocycles 2007, 74, 53–88. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1216–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, B.S. Ascidians: Producers of amino acid derived metabolites. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1771–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, F.; Fernández, R.; Rodríguez, A.; Francesch, A.; Taboada, S.; Ávila, C.; Cuevas, C. Aplicyanins A–F, new cytotoxic bromoindole derivatives from the marine tunicate Aplidium cyaneum. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 5119–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Diyabalanage, T.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; Valeriote, F.A.; Baker, B.J. Ecdysteroids from the Antarctic tunicate Synoicum adareanum. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diyabalanage, T.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Palmerolide A, a cytotoxic macrolide from the Antarctic tunicate Synoicum adareanum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5630–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguez, J.H.; Diyabalanage, T.K.K.; Miyata, Y.; Xie, X.S.; Valeriote, F.A.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Palmerolide macrolides from the Antarctic tunicate Synoicum adareanum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6608–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Q.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Wani, M.C.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Swanson, S.M. Use of the in vivo hollow fiber assay in natural products anticancer drug discovery. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riesenfeld, C.S.; Murray, A.E.; Baker, B.J. Characterization of the microbial community and polyketide biosynthetic potential in the palmerolide-producing tunicate Synoicum adareanum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisboa, M.P.; Dudley, G.B. Synthesis of cytotoxic palmerolides. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 16146–16168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Lebreton, S.; De Brabander, J.K. Total synthesis and structure revision of the marine metabolite palmerolide A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6386–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Guduru, R.; Sun, Y.P.; Banerji, B.; Chen, D.Y.K. Total synthesis of the originally proposed and revised structures of palmerolide A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5896–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Sun, Y.P.; Guduru, R.; Banerji, B.; Chen, D.Y.K. Total synthesis of the originally proposed and revised structures of palmerolide A and isomers thereof. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3633–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravu, V.R.; Leung, G.Y.C.; Lim, C.S.; Ng, S.Y.; Sum, R.J.; Chen, D.Y.K. Chemical synthesis and biological evaluation of second-generation palmerolide A analogues. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2011, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, M.; Rauniyar, V.; Kaspar, L.T.; Hall, D.G. Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of palmerolide A via organoboron methodology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14216–14217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jägel, J.; Maier, M.E. Formal total synthesis of palmerolide A. Synthesis 2009, 17, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Gowrisankar, P.; Pujari, S.A.; Kaliappan, K.P. A formal total synthesis of palmerolide A. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 5858–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujari, S.A.; Gowrisankar, P.; Kaliappan, K.P. A Shimizu non-aldol approach to the formal total synthesis of palmerolide A. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 3137–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.R.; Pawar, A.B. Enantioselective formal synthesis of palmerolide A. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 4252–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, A.B.; Prasad, K.R. Formal total synthesis of palmerolide A. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 15202–15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisboa, M.P.; Jones, D.M.; Dudley, G.B. Formal synthesis of palmerolide A, featuring alkynogenic fragmentation and syn-selective vinylogous aldol chemistry. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliappan, K.P.; Gowrisankar, P. Synthetic studies on a marine natural product, palmerolide A: Synthesis of C1-C9 and C15-C21 fragments. Synlett 2007, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägel, J.; Schmauder, A.; Binanzer, M.; Maier, M.E. A concise route to the C3–C23 fragment of the macrolide palmerolide A. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 13006–13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantagrel, G.; Meyer, C.; Cossy, J. Synthetic studies towards the marine natural product palmerolide A: Synthesis of the C3-C15 and C16-C23 fragments. Synlett 2007, 19, 2983–2986. [Google Scholar]
- Lebar, M.D.; Baker, B.J. Synthesis of the C3–14 fragment of palmerolide A using a chiral pool based strategy. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.R.; Pawar, A.B. Stereoselective synthesis of C1–C18 region of palmerolide A from tartaric acid. Synlett 2010, 7, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.K.; Xu, Y.H.; Loh, T.P. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling of unactivated alkenes with acrylates: Application to the synthesis of the C13–C21 fragment of palmerolide A. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 13284–13287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.M.; Dudley, G.B. Synthesis of the C1–C15 region of palmerolide A using refined Claisen-type addition-bond cleavage methodology. Synlett 2010, 2, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Lisboa, M.P.; Jeong-Im, J.H.; Jones, D.M.; Dudley, G.B. Toward a new palmerolide assembly strategy: Synthesis of C16–C24. Synlett 2012, 23, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Jena, B.K.; Mohapatra, D.K. Synthesis of the C1–C15 fragment of palmerolide A via protecting group dependent RCM reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 3415–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florence, G.J.; Wlochal, J. Synthesis of the originally proposed structure of palmerolide C. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 14250–14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleton, D.R.; Chuen, C.S.; Berridge, M.V.; Webb, V.L.; Copp, B.R. Rossinones A and B, biologically active meroterpenoids from the Antarctic ascidian, Aplidium species. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 9195–9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Pons, L.; Carbone, M.; Vázquez, J.; Rodríguez, J.; Nieto, R.M.; Varela, M.M.; Gavagnin, M.; Avila, C. Natural products from Antarctic colonial Ascidians of the genera Aplidium and Synoicum: Variability and defensive role. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1741–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y. Rapid biomimetic total synthesis of (±)-rossinone B. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 5554–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Núñez-Pons, L.; Paone, M.; Castelluccio, F.; Avila, C.; Gavagnin, M. Rossinone-related meroterpenes from the Antarctic ascidian Aplidium fuegiense. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 3541–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M.; Strøm, M.B.; Svenson, J.; Jaspars, M.; Milne, B.F.; Tørfoss, V.; Andersen, J.H.; Hansen, E.; Stensvåg, K.; Haug, T. Synoxazolidinones A and B: Novel bioactive alkaloids from the ascidian Synoicum pulmonaria. Org. Lett. 2010, 21, 4752–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, M.; Svenson, J.; Jaspars, M.; Strøm, M.B.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Andersen, J.H.; Hansen, E.; Kristiansen, P.E.; Stensvåg, K.; Haug, T. Synoxazolidinone C; a bicyclic member of the synoxazolidinone family with antibacterial and anticancer activities. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 1804–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmann, K.H.; Šebestík, J.; Novotná, J.; Stensen, W.; Urbanová́, M.; Svenson, J.; Svendsen, J.S.; Bouř, P.; Ruud, K. Determining the absolute configuration of two marine compounds using vibrational chiroptical spectroscopy. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 858–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepos, R.; Cervin, G.; Hellio, C.; Pavia, H.; Stensen, W.; Stensvåg, K.; Svendsen, J.S.; Haug, T.; Svenson, J. Antifouling compounds from the sub-Arctic ascidian Synoicum pulmonaria: Synoxazolidinones A and C, pulmonarins A and B, and synthetic analogues. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2105–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, M.; Svenson, J.; Sepčić, K.; Trembleau, L.; Engqvist, M.; Andersen, J.H.; Jaspars, M.; Stensvåg, K.; Haug, T. Isolation and synthesis of pulmonarins A and B, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from the colonial ascidian Synoicum pulmonaria. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouslimani, A.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Dorrestein, P.C. Mass spectrometry of natural products: Current, emerging and future technologies. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, K.J. The structural biology of biosynthetic megaenzymes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).