Tumor Protein (TP)-p53 Members as Regulators of Autophagy in Tumor Cells upon Marine Drug Exposure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
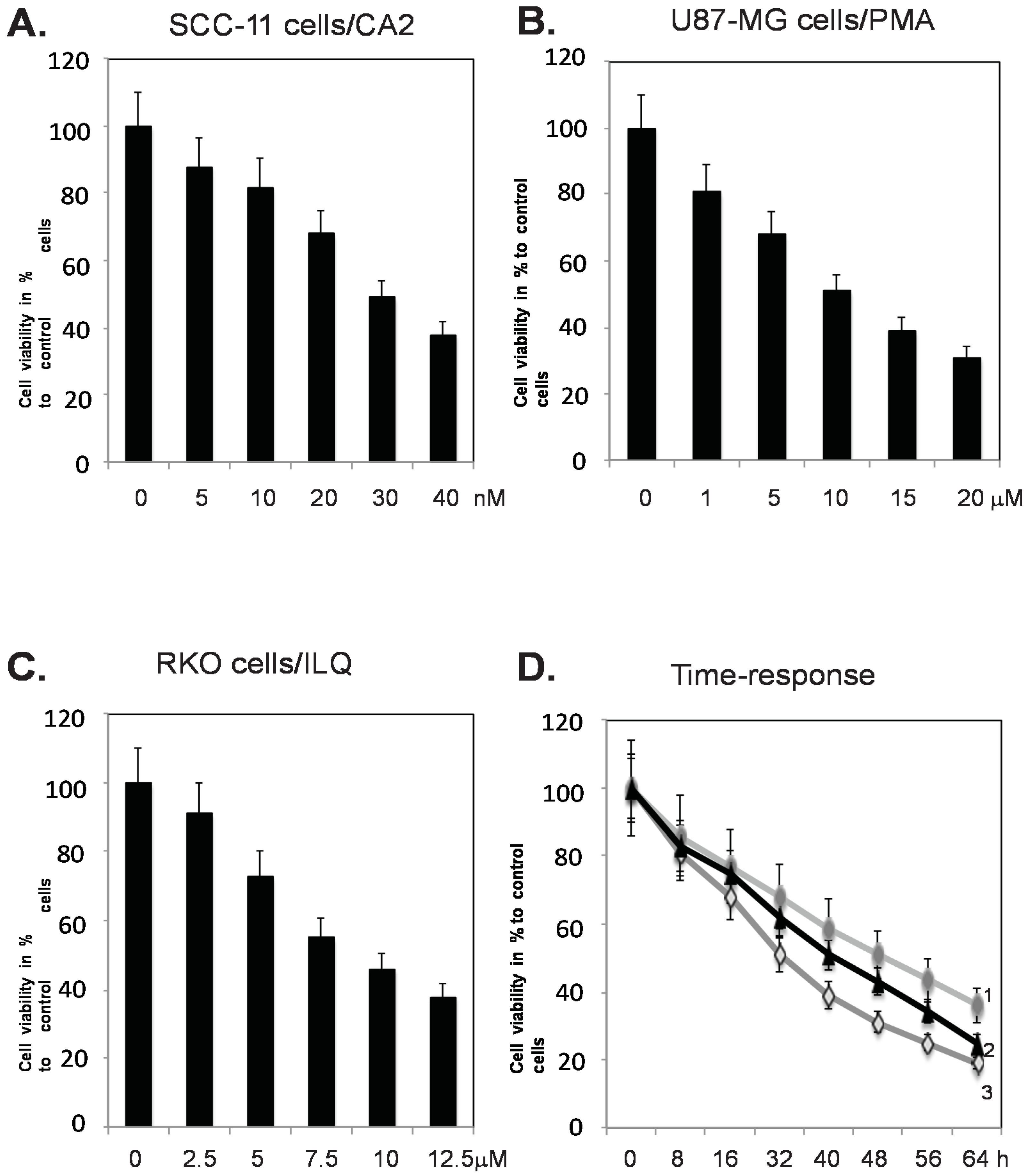
2.1. Marine Compounds Decrease Tumor Cell Viability in a Dose- and Time Dependent Manner
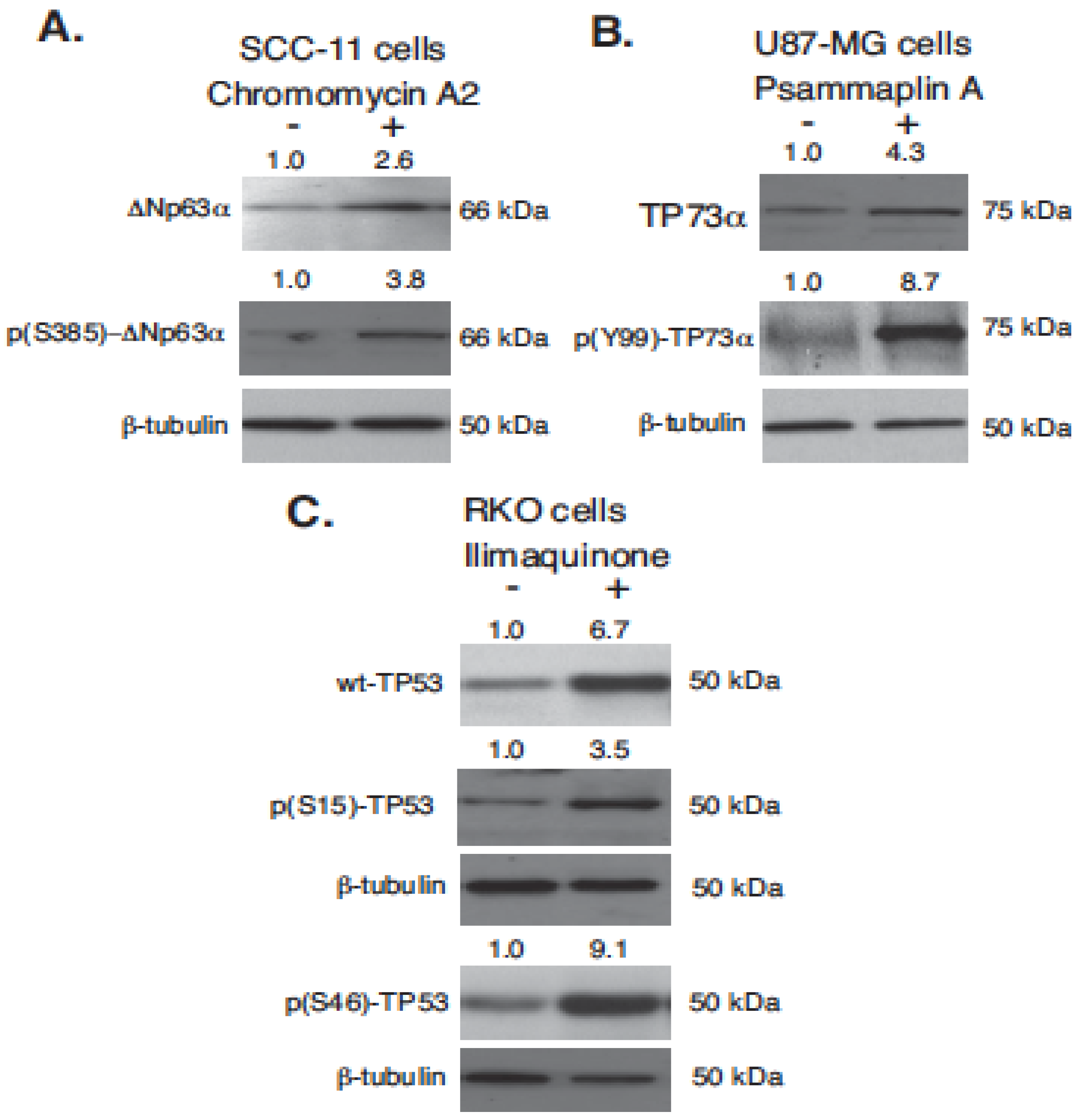
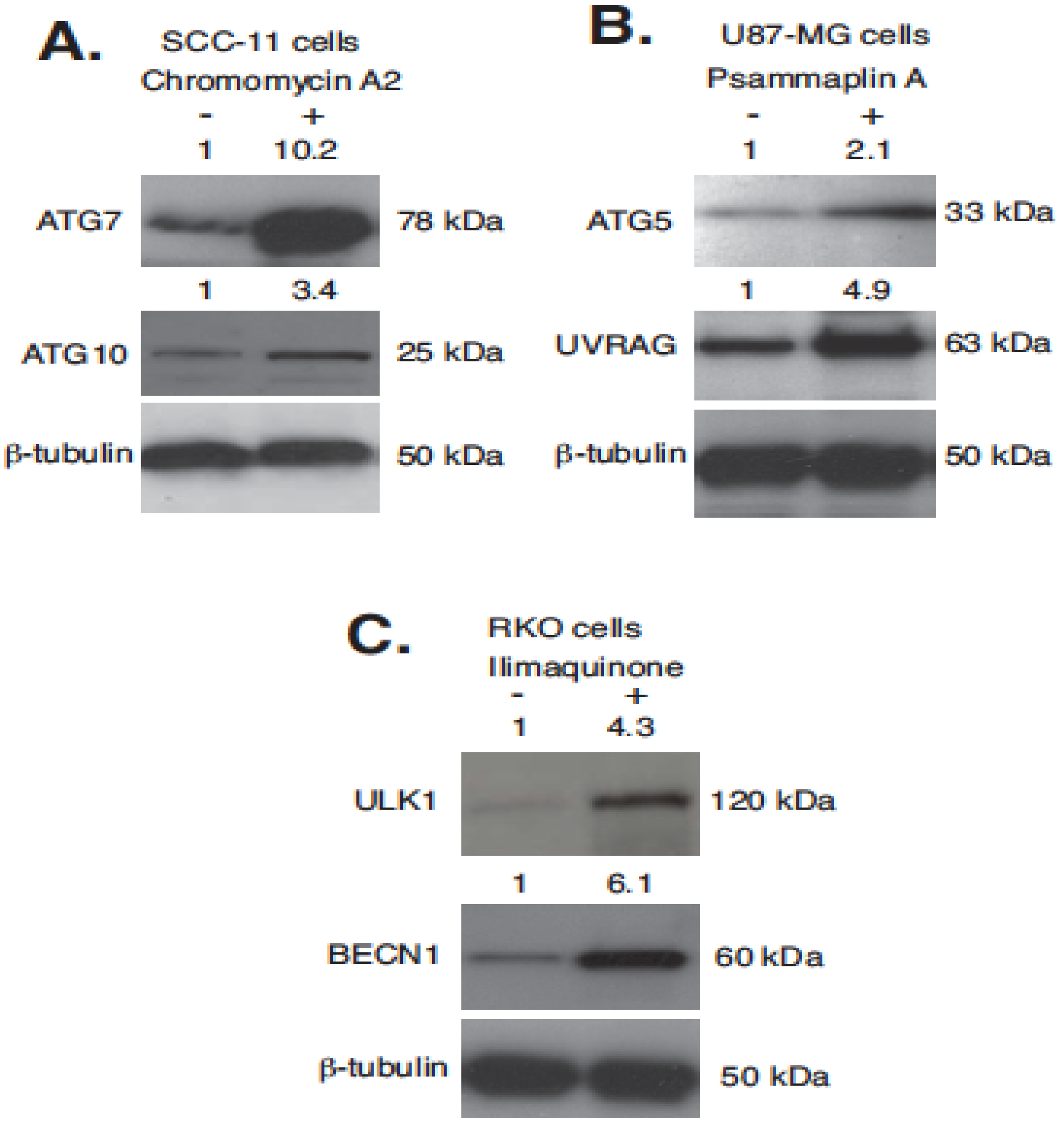
2.2. Marine Compounds Induce Expression and Phosphorylation of TP53 Family Members in Human Tumor Cells
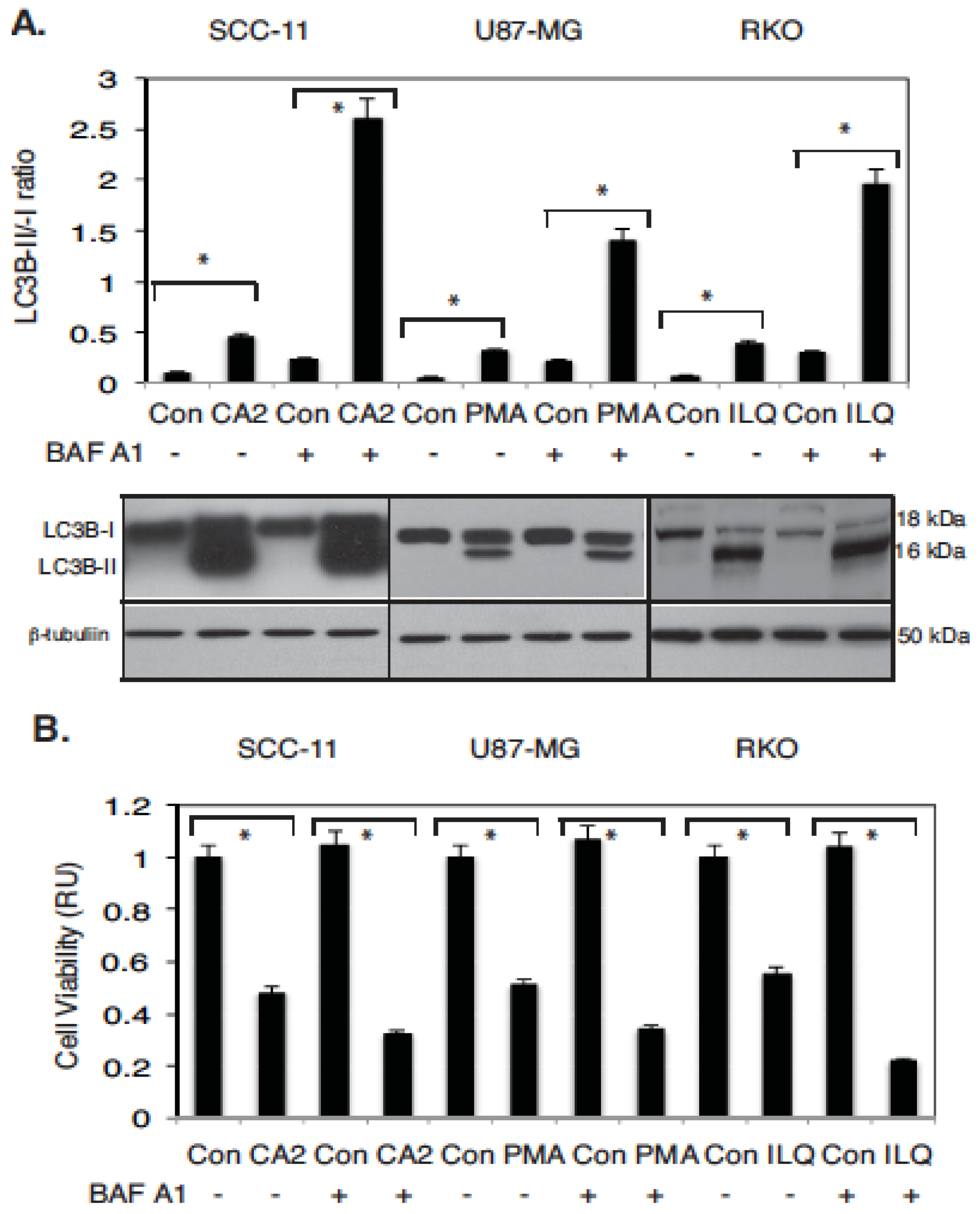
2.3. Marine Compounds Induce Autophagic Flux in Human Tumor Cells
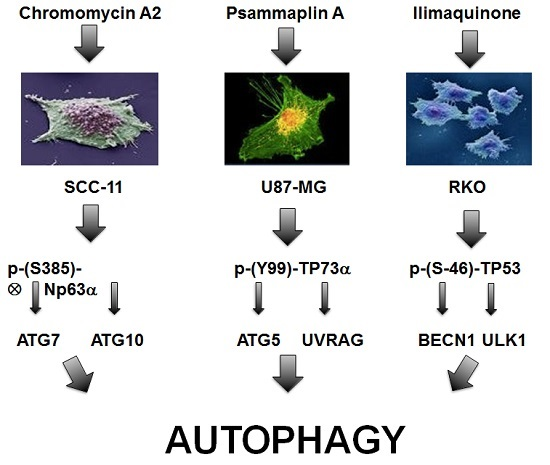
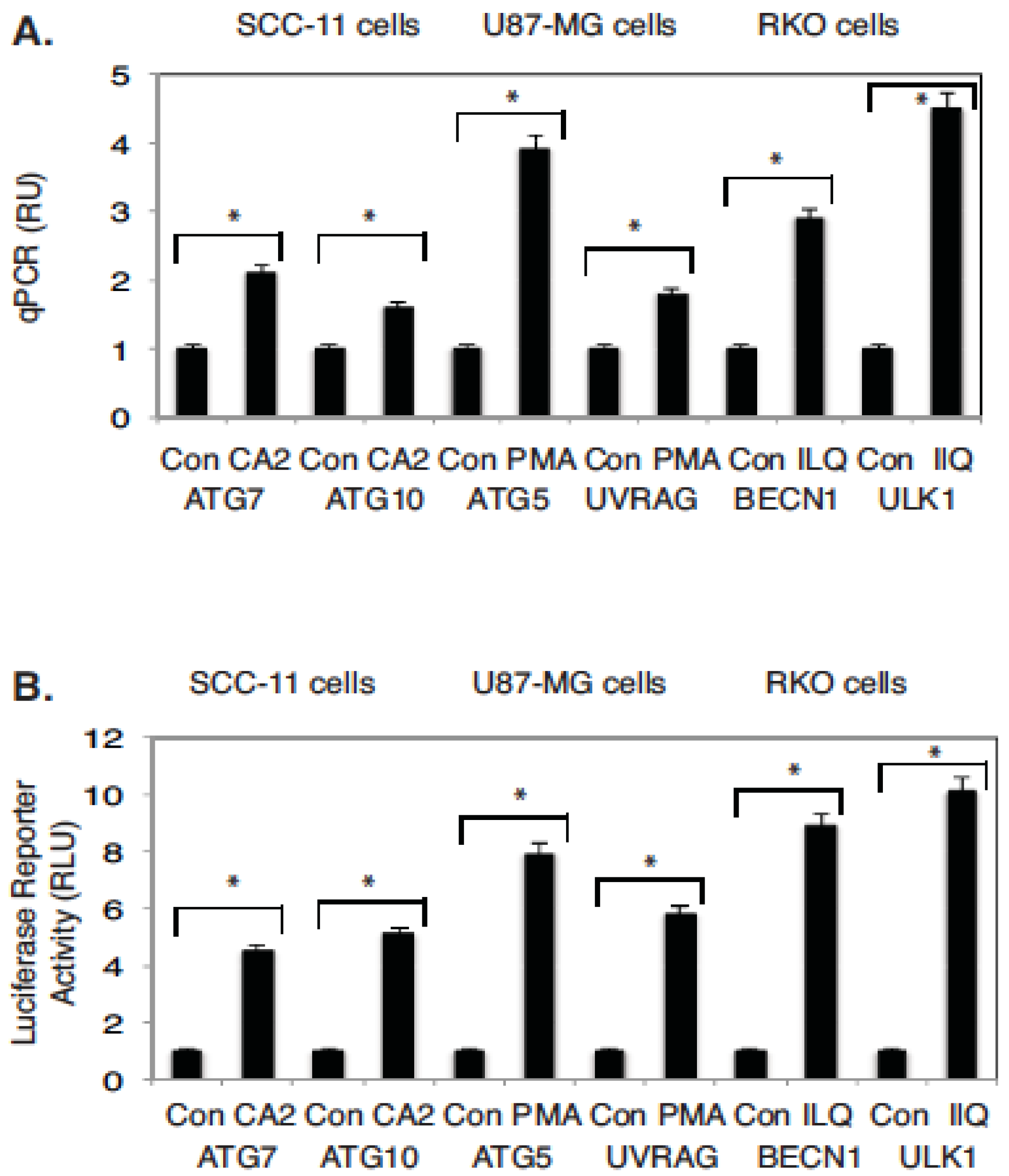
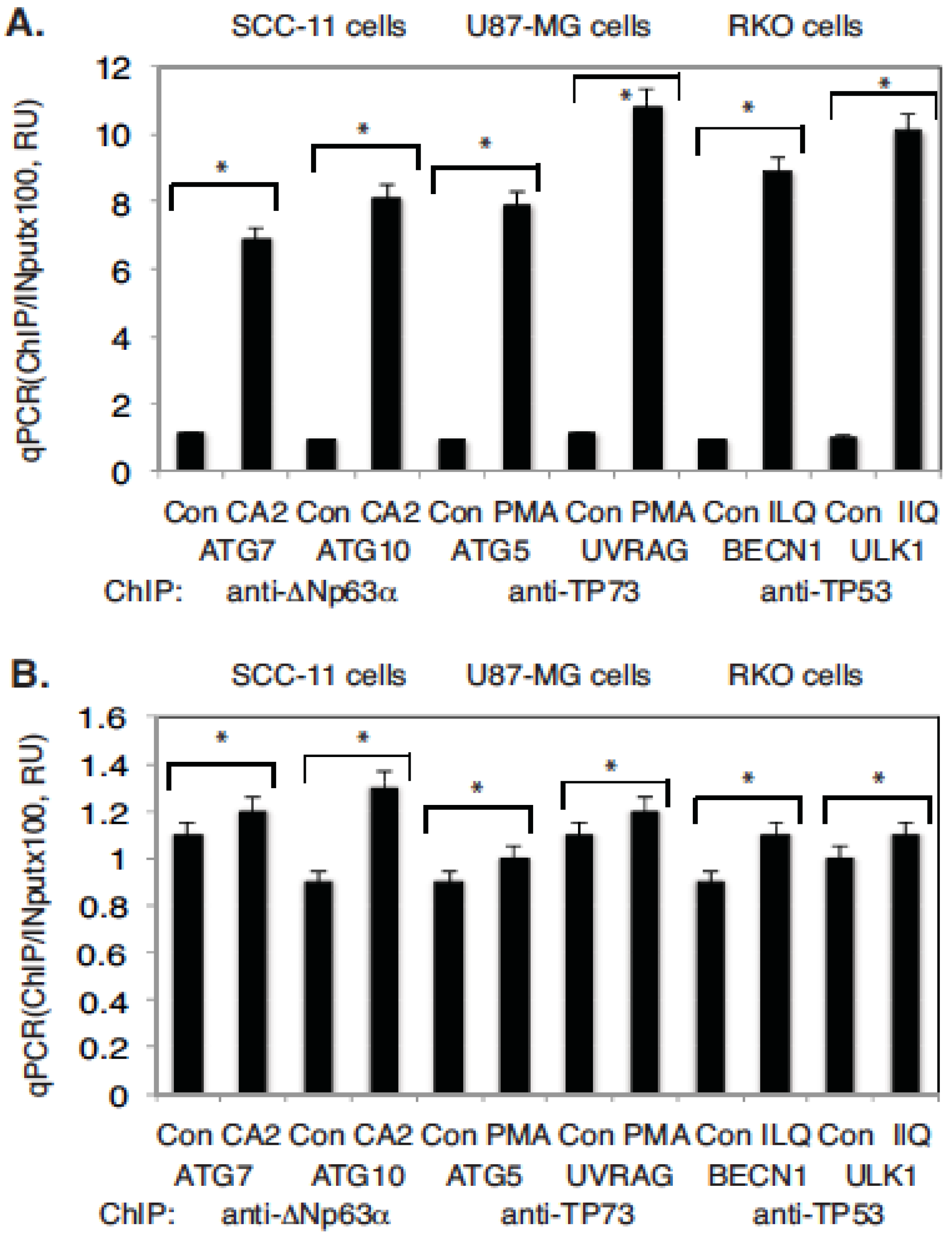
2.4. Marine Compounds Activate Transcription of Autophagic Genes through TP53 Family Member’s Transcriptional Function
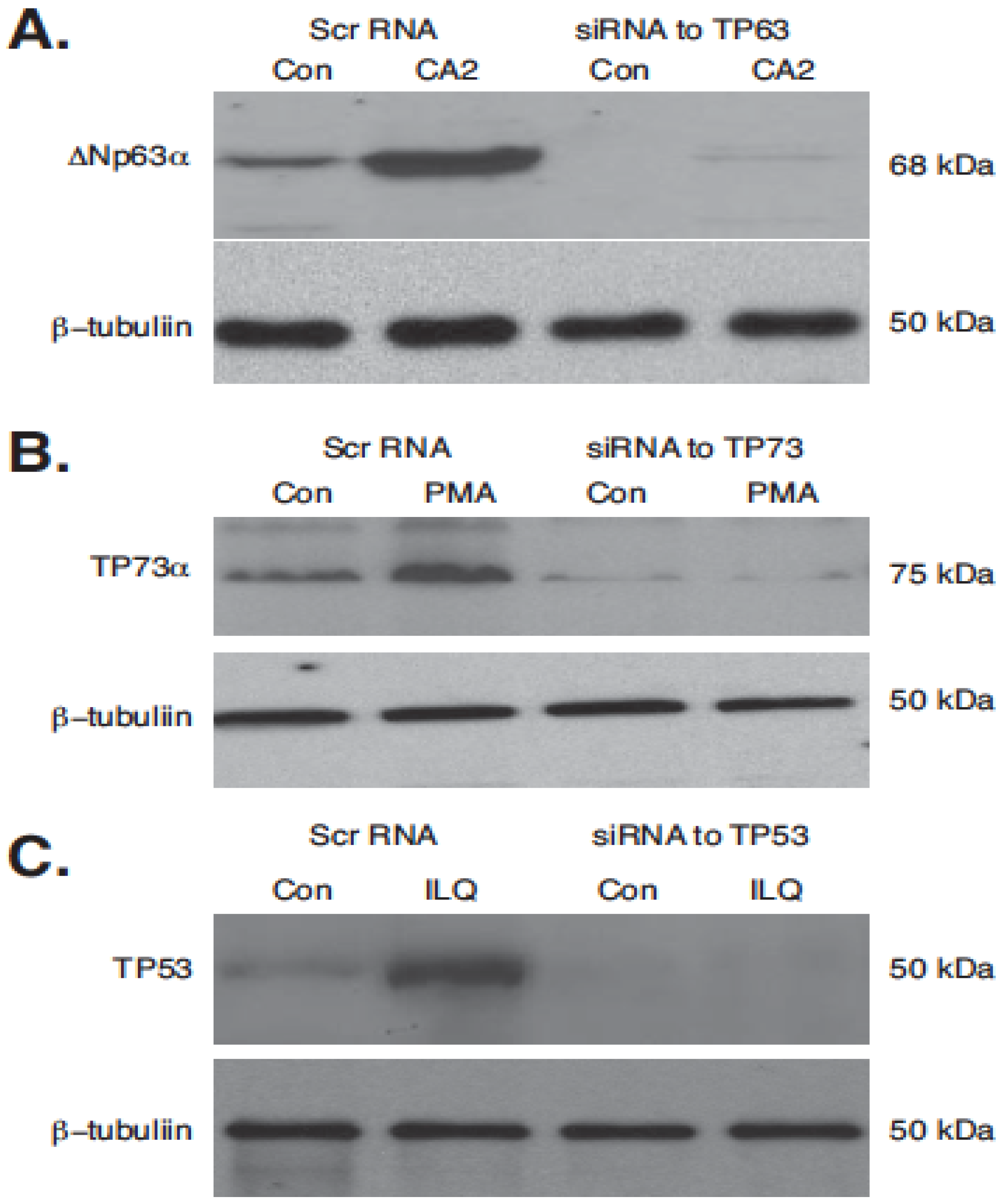
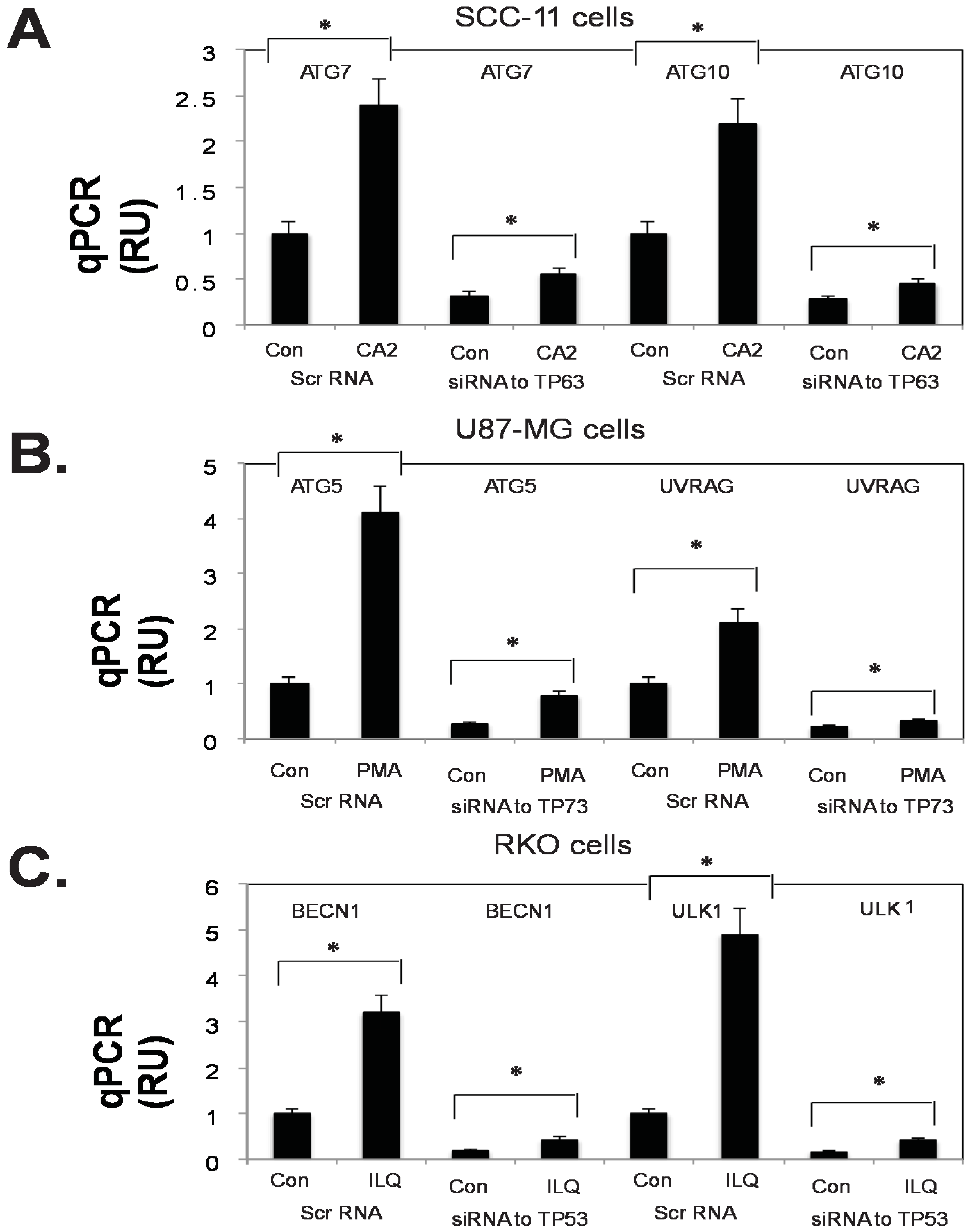
2.5. Silencing of TP53 Family Members Modulated the Expression of Autophagic Genes in Tumor Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines, Reagents, and Antibodies
4.2. Real-Time Quantitative (q) PCR Assay
4.3. Transfections and Luciferase Reporter Assays
4.4. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
4.5. Small Interfering (si) RNA and Transfection
4.6. Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Debnath, J. The Evolving, Multifaceted Roles of Autophagy in Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2016, 130, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosway, B.; Lovat, P. The role of autophagy in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 2016, 54, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, W.P.; Thomas, A.D.; Kaina, B. DNA damage and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Rehman, S.K.; Zhang, W.; Wen, A.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J. Autophagy is a therapeutic target in anticancer drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1806, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belaid, A.; Ndiaye, P.D.; Filippakis, H.; Roux, J.; Röttinger, É.; Graba, Y.; Brest, P.; Hofman, P.; Mograbi, B. Autophagy: Moving Benchside Promises to Patient Bedsides. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2015, 15, 684–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S. p53, Autophagy and tumor suppression. Autophagy 2005, 1, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morselli, E.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Mariño, G.; Michaud, M.; Vitale, I.; Maiuri, M.C.; Kroemer, G. Oncosuppressive functions of autophagy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 2251–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflaum, J.; Schlosser, S.; Müller, M. p53 Family and Cellular Stress Responses in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Tasdemir, E.; Criollo, A.; Morselli, E.; Vicencio, J.M.; Carnuccio, R.; Kroemer, G. Control of autophagy by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitomsky, N.; Hofmann, T.G. Apoptosis and autophagy: Regulation of apoptosis by DNA damage signalling—Roles of p53, p73 and HIPK2. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6074–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Galluzzi, L.; Morselli, E.; Kepp, O.; Malik, S.A.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy regulation by p53. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasdemir, E.; Chiara Maiuri, M.; Morselli, E.; Criollo, A.; D’Amelio, M.; Djavaheri-Mergny, M.; Cecconi, F.; Tavernarakis, N.; Kroemer, G. A dual role of p53 in the control of autophagy. Autophagy 2008, 4, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E. Autophagy and p53. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenzelmann Broz, D.; Spano Mello, S.; Bieging, K.T.; Jiang, D.; Dusek, R.L.; Brady, C.A.; Sidow, A.; Attardi, L.D. Global genomic profiling reveals an extensive p53-regulated autophagy program contributing to key p53 responses. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 1016–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.M. p53 and autophagy in cancer: Guardian of the genome meets guardian of the proteome. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Jin, L.; Huang, X.; Geng, S.; He, C.; Hu, X. p53 signaling and autophagy in cancer: A revolutionary strategy could be developed for cancer treatment. Autophagy 2011, 7, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbluth, J.M.; Pietenpol, J.A. mTOR regulates autophagy-associated genes downstream of p73. Autophagy 2009, 5, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crighton, D.; Wilkinson, S.; O’Prey, J.; Syed, N.; Smith, P.; Harrison, P.R.; Gasco, M.; Garrone, O.; Crook, T.; Ryan, K.M. DRAM, a p53-induced modulator of autophagy, is critical for apoptosis. Cell 2006, 126, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crighton, D.; O’Prey, J.; Bell, H.S.; Ryan, K.M. p73 regulates DRAM-independent autophagy that does not contribute to programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crighton, D.; Wilkinson, S.; Ryan, K.M. DRAM links autophagy to p53 and programmed cell death. Autophagy 2007, 3, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, L.Y.; O’Prey, J.; Baudot, A.D.; Hoekstra, A.; Ryan, K.M. DRAM-1 encodes multiple isoforms that regulate autophagy. Autophagy 2012, 8, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Malik, S.A.; Morselli, E.; Kepp, O.; Criollo, A.; Mouchel, P.L.; Carnuccio, R.; Kroemer, G. Stimulation of autophagy by the p53 target gene Sestrin2. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eby, K.G.; Rosenbluth, J.M.; Mays, D.J.; Marshall, C.B.; Barton, C.E.; Sinha, S.; Johnson, K.N.; Tang, L.; Pietenpol, J.A. ISG20L1 is a p53 family target gene that modulates genotoxic stress-induced autophagy. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, K.S.; Wilkinson, S.; James, J.; Ryan, K.M.; Vousden, K.H. PUMA- and Bax-induced autophagy contributes to apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Liu, H.; Agostini, M.; Yousefi, S.; Perren, A.; Tschan, M.P.; Mak, T.W.; Melino, G.; Simon, H.U. p73 regulates autophagy and hepatocellular lipid metabolism through a transcriptional activation of the ATG5 gene. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratovitski, E.A. Tumor Protein p63/microRNA Network in Epithelial Cancer Cells. Curr. Genom. 2013, 14, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibi, K.; Trink, B.; Patturajan, M.; Westra, W.H.; Caballero, O.L.; Hill, D.E.; Ratovitski, E.A.; Jen, J.; Sidransky, D. AIS is an oncogene amplified in squamous cell carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5462–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.L.; Holcakova, J.; Finlan, L.E.; Nekulova, M.; Hrstka, R.; Gueven, N.; DiRenzo, J.; Smith, G.; Hupp, T.R.; Vojtesek, B. ΔNp63 transcriptionally regulates ATM to control p53 Serine-15 phosphorylation. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ratovitski, E.A. Phospho-ΔNp63α/Rpn13-dependent regulation of LKB1 degradation modulates autophagy in cancer cells. Aging 2010, 2, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Guerrero-Preston, R.; Ratovitski, E.A. Phospho-ΔNp63α-dependent regulation of autophagic signaling through transcription and micro-RNA modulation. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Elaborating the role of natural products-induced autophagy in cancer treatment: Achievements and artifacts in the state of the art. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.F.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Chen, N. Autophagy-associated targeting pathways of natural products during cancer treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 10557–10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Yakisich, J.S. Natural products targeting autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/ mTOR pathway as anticancer agents. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.X.; Ouyang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, B. Plant natural compounds: Targeting pathways of autophagy as anti-cancer therapeutic agents. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayarathna, S.; Jothy, S.L.; Chen, Y.; Kanwar, J.R.; Sasidharan, S. Anti-Cancer Natural Products Inducing Cross-talk between Apoptosis and Autophagy Mutual Proteins to Regulate Cancer Cell Death: Design of Future Green Anticancer Therapies. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 6175–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Pan, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, M.; Hao, X.; Liang, G.; Feng, Y. Fangchinoline induces autophagic cell death via p53/sestrin2/AMPK signalling in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussavou, G.; Kwak, D.H.; Obiang-Obonou, B.W.; Maranguy, C.A.; Dinzouna-Boutamba, S.D.; Lee, D.H.; Pissibanganga, O.G.; Ko, K.; Seo, J.I.; Choo, Y.K. Anticancer effects of different seaweeds on human colon and breast cancers. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4898–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, P.; Wu, T.; Zeng, W. Microtubule-targeting anticancer agents from marine natural substance. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine-sourced anti-cancer and cancer pain control agents in clinical and late preclinical development. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akl, M.R.; Ayoub, N.M.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Orabi, K.Y.; Foudah, A.I.; El Sayed, K.A. Araguspongine C induces autophagic death in breast cancer cells through suppression of c-MET and HER2 receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 288–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, L.A.; Jimenez, P.C.; Sousa Tda, S.; Freitas, H.P.; Rocha, D.D.; Wilke, D.V.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F.; Deusdênia Loiola Pessoa, O.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Chromomycin A2 induces autophagy in melanoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5839–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, Y.J.; Yoon, S.; Lee, J.; Choi, W.S.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Psammaplin A induces Sirtuin 1-dependent autophagic cell death in doxorubicin-resistant MCF-7/adr human breast cancer cells and xenografts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chung, K.J.; Hwang, I.H.; Gwak, J.; Park, S.; Ju, B.G.; Yun, E.; Kim, D.E.; Chung, Y.H.; Na, M.; et al. Activation of p53 with ilimaquinone and ethylsmenoquinone, marine sponge metabolites, induces apoptosis and autophagy in colon cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kang, K.S.; Choi, K.C.; Ko, H. Cardamonin induces autophagy and an antiproliferative effect through JNK activation in human colorectal carcinoma HCT116 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2559–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.; Hauschild, J.; Amann, K.; Tabakmakher, K.M.; Venz, S.; Walther, R.; Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Shubina, L.K.; Fedorov, S.N.; et al. Marine alkaloid Monanchocidin a overcomes drug resistance by induction of autophagy and lysosomal membrane permeabilization. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17328–17341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailon-Moscoso, N.; González-Arévalo, G.; Velásquez-Rojas, G.; Malagon, O.; Vidari, G.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Ratovitski, E.A.; Ostrosky-Wegman, P. Phytometabolite Dehydroleucodine Induces Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, and DNA Damage in Human Astrocytoma Cells through p73/p53 Regulation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136527. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Q.; Carrier, F.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Induction of cellular p53 activity by DNA-damaging agents and growth arrest. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 4242–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughery, J.; Cox, M.; Smith, L.M.; Meek, D.W. Critical role for p53-serine 15 phosphorylation in stimulating transactivation at p53-responsive promoters. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7666–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Preston, R.; Ratovitski, E.A. Cisplatin Exposure of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells leads to the Modulation of Autophagic pathway. In Autophagy: Cancer, Other Pathologies, Inflammation, Immunity, and Infection; Hayat, M.A., Ed.; Elsevier Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Chapter 17; Volume 1, pp. 251–267. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, C.B.; Fu, P.Y.; Ky, N.; Zhu, H.S.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Srinivasan, K.G.; Hamza, M.S.; Zhao, Y. NF-κB p65 repression by the sesquiterpene lactone, Helenalin, contributes to the induction of autophagy cell death. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, G.L.; Russo, M.; Castellano, I.; Napolitano, A.; Palumbo, A. Ovothiol isolated from sea urchin oocytes induces autophagy in the Hep-G2 cell line. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4069–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Shin, H.S.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Viriditoxin regulates apoptosis and autophagy via mitotic catastrophe and microtubule formation in human prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.L.; Fang, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y. Tephrosin-induced autophagic cell death in A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Yang, G.; Sun, X.; Geng, C.; Li, Q.; Yao, X.; Chen, M. Citreoviridin Induces Autophagy-Dependent Apoptosis through Lysosomal-Mitochondrial Axis in Human Liver HepG2 Cells. Toxins 2015, 7, 3030–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Q.; Tou, F.; Su, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Z. The natural product peiminine represses colorectal carcinoma tumor growth by inducing autophagic cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 462, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ratovitski, E.A. Tumor Protein (TP)-p53 Members as Regulators of Autophagy in Tumor Cells upon Marine Drug Exposure. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14080154
Ratovitski EA. Tumor Protein (TP)-p53 Members as Regulators of Autophagy in Tumor Cells upon Marine Drug Exposure. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(8):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14080154
Chicago/Turabian StyleRatovitski, Edward A. 2016. "Tumor Protein (TP)-p53 Members as Regulators of Autophagy in Tumor Cells upon Marine Drug Exposure" Marine Drugs 14, no. 8: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14080154
APA StyleRatovitski, E. A. (2016). Tumor Protein (TP)-p53 Members as Regulators of Autophagy in Tumor Cells upon Marine Drug Exposure. Marine Drugs, 14(8), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14080154