Jellyfish Bioactive Compounds: Methods for Wet-Lab Work
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proteomics in Jellyfish
2.1. Nematocyst Extraction
2.1.1. Autolysis
2.1.2. Alternative to Autolysis
2.2. Venom Extraction
2.2.1. Sonication
2.2.2. Nematocyst Mechanical Disruption
Glass Beads
Other Processes
Concentration of Venom Proteins
2.3. Toxin Purification, Detection and Identification
2.3.1. Electrophoresis
2.3.2. Gel Extraction
2.3.3. Gel Filtration and Columns
2.3.4. Fast Flow Anion-Exchange Chromatography
2.3.5. HPLC
2.3.6. Mass Spectrometry
2.3.7. Glycoproteins, Phosphoproteins and Antioxidant Protein Detection
2.3.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Toxicity Assays and Others
2.4.1. Venom Proteolytic Activity
2.4.2. Hemolytic Assay
2.4.3. Antimicrobial Assay
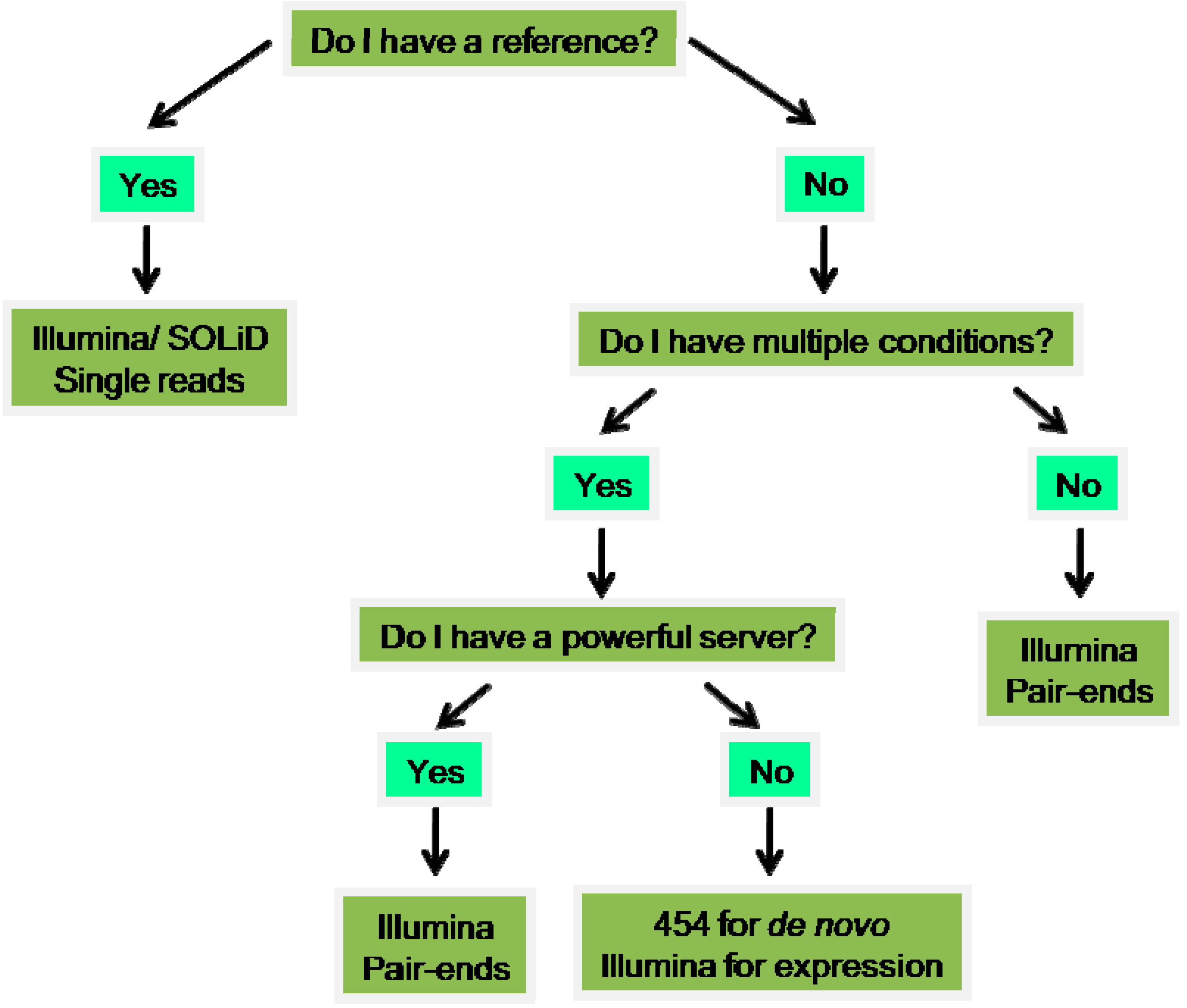
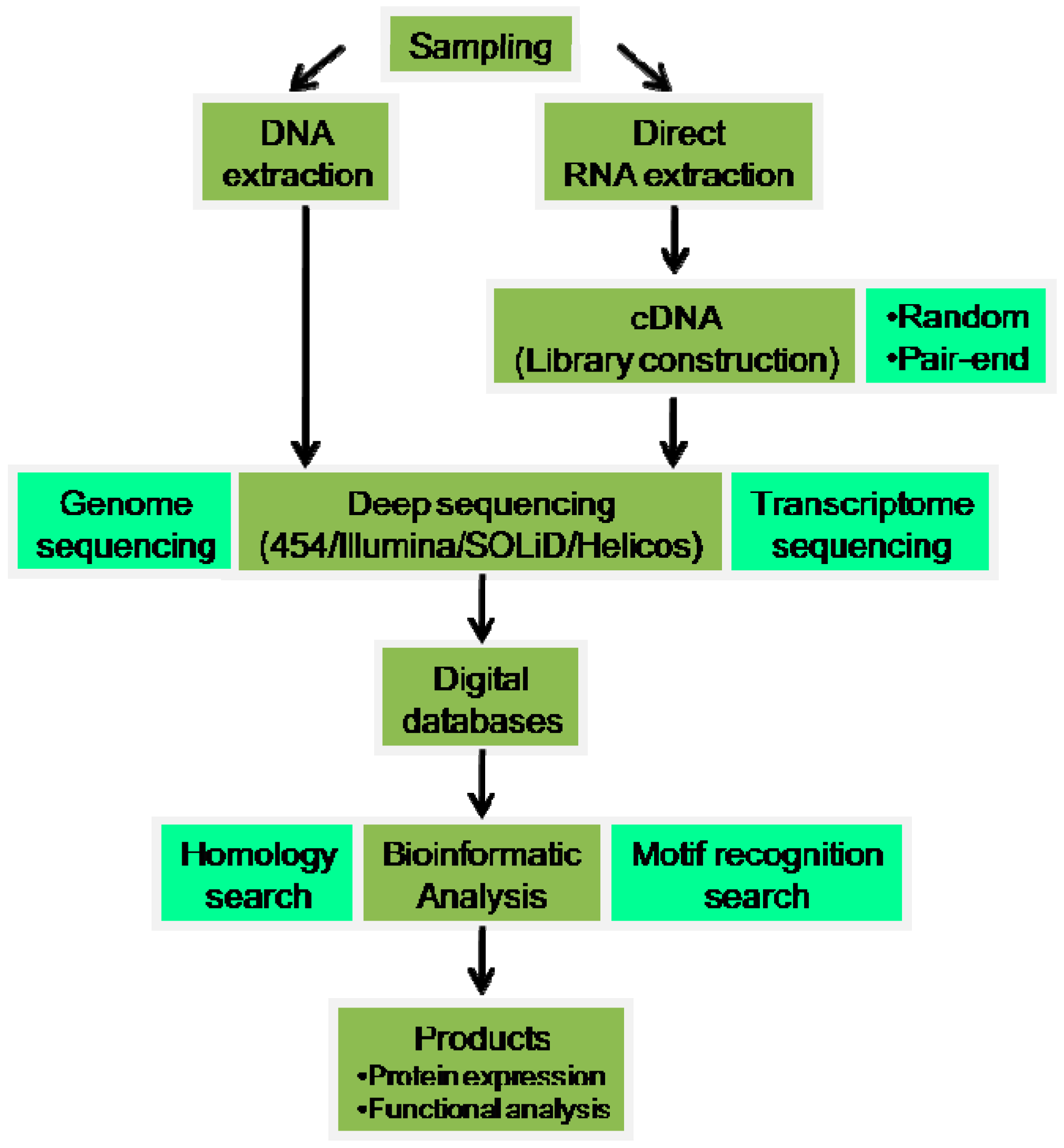
3. Genomics/Transcriptomics
3.1. Wet-Lab Genomics for Toxin-Coding Gene Discovery
3.2. Deep Sequencing Platforms
3.3. RNA Procedures
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urbarova, I.; Karlsen, B.; Okkenhaug, S.; Seternes, O.; Johansen, S.; Emblem, A. Digital marine bioprospecting: Mining new neurotoxin drug candidates from the transcriptomes of cold-water sea anemones. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.C.; Sung, P.; Duh, C.; Chen, B.; Sheu, J.; Yang, N.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of natural products isolated from soft corals of Taiwan between 2008 and 2012. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4083–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, S.D.; Emblem, A.; Karlsen, B.O.; Okkenhaug, S.; Hansen, H.; Moum, T.; Coucheron, D.H.; Seternes, O.M. Approaching marine bioprospecting in hexacorals by RNA deep sequencing. New Biotechnol. 2010, 27, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, Y.; Genikhovich, G.; Gordon, D.; Wienkoop, S.; Zenkert, C.; Ozbek, S.; Technau, U.; Gurevitz, M. Neurotoxin localization to ectodermal gland cells uncovers an alternative mechanism of venom delivery in sea anemones. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, M.C.; Puga, J.; Serodio, J.; Gomes, N.C.; Calado, R. Trends in the discovery of new marine natural products from invertebrates over the last two decades-where and what are we bioprospecting? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazão, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Sea anemone (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Actiniaria) toxins: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1812–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrette, T.; Seymour, J. A rapid and repeatable method for venom extraction from Cubozoan nematocysts. Toxicon 2004, 44, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Balandin, S.V.; Aleshina, G.M.; Tagaev, A.A.; Leonova, Y.F.; Krasnodembsky, E.D.; Men’shenin, A.V.; Kokryakov, V.N. Aurelin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from jellyfish Aurelia aurita with structural features of defensins and channel-blocking toxins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 348, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, D.; López-Vera, E.; Aguilar, M.B.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J. Preliminary results of the in vivo and in vitro characterization of a tentacle venom fraction from the jellyfish Aurelia aurita. Toxins 2013, 5, 2420–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, A.; Biswas, S.; Sarkar, A.; Chakrabarty, D. Anticoagulant activity of Moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) tentacle extract. Toxicon 2012, 60, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Jung, E.S.; Kang, C.; Yoon, W.D.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, E. Scyphozoan jellyfish venom metalloproteinases and their role in the cytotoxicity. Toxicon 2011, 58, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa, K.; Nakao, M.; Sakamoto, B.; Crow, G.L.; Nakajima, T. Isolation and characterization of a novel protein toxin from the Hawaiian box jellyfish (sea wasp) Carybdea alata. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa, K.; Nakao, M.; Ito, E.; Miyake, M.; Noda, M.; Nakajima, T. Novel proteinaceous toxins from the box jellyfish (sea wasp) Carybdea rastoni. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintner, A.H.; Seymour, J.E.; Edwards, S.L. Variation in lethality and effects of two Australian chirodropid jellyfish venoms in fish. Toxicon 2005, 46, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, D.; Burnell, J. Identification, cloning and sequencing of two major venom proteins from the box jellyfish, Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 2007, 50, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Aziz, A.; Loukas, A.; Potriquet, J.; Seymour, J.; Mulvenna, J. Venom proteome of the box jellyfish Chironex fleckeri. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, K.L.; Fernando, R.; Ramasamy, S.; Seymour, J.E.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. The in vitro vascular effects of two chirodropid (Chironex fleckeri and Chiropsella bronzie) venoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, K.L.; Isbister, G.K.; McGowan, S.; Konstantakopoulos, N.; Seymour, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. A pharmacological and biochemical examination of the geographical variation of Chironex fleckeri venom. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 192, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaousis, S.; Smout, M.; Wilson, D.; Loukas, A.; Mulvenna, J.; Seymour, J. Rapid short term and gradual permanent cardiotoxic effects of vertebrate toxins from Chironex fleckeri (Australian box jellyfish) venom. Toxicon 2014, 80, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa-Kuroda, K.; Nakao, M.; Oshiro, N.; Iwanaga, S.; Nakajima, T. A novel protein toxin from the deadly box jellyfish (Sea Wasp, Habu-kurage) Chiropsalmus quadrigatus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, S.; He, Q.; Wang, Q.; Ye, X.; Liu, G.; Nie, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. The acute toxicity and hematological characterization of the effects of tentacle-only extract from the jellyfish Cyanea capillata. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; He, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nie, F.; Li, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L. Cyanea capillata tentacle-only extract as a potential alternative of nematocyst venom: Its cardiovascular toxicity and tolerance to isolation and purification procedures. Toxicon 2009, 53, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, S.; Li, P. Isolation and characterization of lethal proteins in nematocyst venom of the jellyfish Cyanea nozakii Kishinouye. Toxicon 2010, 55, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Feng, J.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Qin, Y.; Li, K.; Li, P. Two-step purification and in vitro characterization of a hemolysin from the venom of jellyfish Cyanea nozakii Kishinouye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Han, D.Y.; Park, K.I.; Pyo, M.J.; Heo, Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, E. Characterization and neutralization of Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) jellyfish venom using polyclonal antibody. Toxicon 2014, 86, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, W.D.; Lim, D.; Hart, A.J.; Hodgson, W.C. Cardiovascular effects of Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) jellyfish venom in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 167, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisano, M.; Trapani, M.R.; Parrino, V.; Parisi, M.G.; Cappello, T.; D’Agata, A.; Benenati, G.; Natalotto, A.; Mauceri, A.; Cammarata, M. Haemolytic activity and characterization of nematocyst venom from Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Ital. J. Zool. 2013, 80, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Morabito, R.; Pizzata, T.; La Spada, G. Effect of various factors on Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) crude venom-induced haemolysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Pphysiol. 2008, 151, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, R.; Condello, S.; Curro, M.; Marino, A.; Ientile, R.; La Spada, G. Oxidative stress induced by crude venom from the jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca in neuronal-like differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol. Vitro 2012, 26, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, R.; La Spada, G.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Marino, A. Crude venom from nematocysts of the jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca as a tool to study cell physiology. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayed, Y.; Bousabbeh, M.; Mabrouk, H.B.; Morjen, M.; Marrakchi, N.; Bacha, H. Impairment of the cell-to-matrix adhesion and cytotoxicity induced by the Mediterranean jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca venom and its fractions in cultured glioblastoma cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruschetta, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; Morabito, R.; Marino, A.; Ahmad, A.; Spano, N.; Spada, G.L.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Pelagia noctiluca (Scyphozoa) crude venom injection elicits oxidative stress and inflammatory response in rats. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2182–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, J.; Lucio-Martínez, N. Isolation and prepurification of active compounds in venom from Pelagia noctiluca (Scyphozoa: Pelagiidae). Cienc. Mar. 2011, 37, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiar, S.; Andersson, M.M.; Gessesse, A.; Mattiasson, B.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Stability characteristics of a calcium-independent alkaline protease from Nesterenkonia sp. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 32, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Factors influencing hemolytic activity of venom from the jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusmani, L.; Avian, M.; Galil, B.; Patriarca, P.; Rottini, G. Biologically active polypeptides in the venom of the jellyfish Rhopilema nomadica. Toxicon 1997, 35, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xue, W.; Yue, Y.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Jellyfish venomics and venom gland transcriptomics analysis of Stomolophus meleagris to reveal the toxins associated with sting. J. Proteomics 2014, 106, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Qing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Cui, J.; Li, P. Application of nanoLC-MS/MS to the shotgun proteomic analysis of the nematocyst proteins from jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 899, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Qing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Cui, J.; Li, P. Isolation, identification and characterization of a novel antioxidant protein from the nematocyst of the jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yu, H.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Guo, Z.; Li, P. Factors affecting the protease activity of venom from jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 5370–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Qing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Cui, J.; Li, P. Isolation and in vitro partial characterization of hemolytic proteins from the nematocyst venom of the jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris. Toxicol. Vitro 2013, 27, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, T.; Lindsay, D.; Kitamura, M.; Konishi, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Nishida, S.; Kamio, M.; Nagai, H. Evaluation of the bioactivities of water-soluble extracts from twelve deep-sea jellyfish species. Fish. Sci. 2013, 79, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.G.; Schuchert, P.; Marques, A.C.; Jankowski, T.; Medina, M.; Schierwater, B. Medusozoan phylogeny and character evolution clarified by new large and small subunit rDNA data and an assessment of the utility of phylogenetic mixture models. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, A.J.; Chung, R.; Dunlap, W.; Morandini, A.; Marques, A.; Moura-da-Silva, A.; Ward, M.; Padilla, G.; da Silva, L.; Andreakis, N.; et al. Proteomic characterisation of toxins isolated from nematocysts of the South Atlantic jellyfish Olindias sambaquiensis. Toxicon 2013, 71, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, V.H.; Zara, F.; Marangoni, S.; Toyama Dde, O.; de Souza, A.J.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Toyama, M.H. Identification of two novel cytolysins from the hydrozoan Olindias sambaquiensis (Cnidaria). J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Garcia, C.M.; Fuentes-Silva, D.; Sanchez-Soto, C.; Dominguez-Perez, D.; Garcia-Delgado, N.; Varela, C.; Mendoza-Hernandez, G.; Rodriguez-Romero, A.; Castaneda, O.; Hiriart, M. Toxins from Physalia physalis (Cnidaria) raise the intracellular Ca2+ of beta-cells and promote insulin secretion. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5414–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, F.F.; Burnett, J.W.; Bloom, D.A.; Coliano, T.; Eldefrawi, M.E.; Erderly, H.; Aurelian, L.; Torres, M.; Heimer-de la Cotera, E.P. A comparison of the toxinological characteristics of two Cassiopea and Aurelia species. Toxicon 2001, 39, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, D.A.; Burnett, J.W.; Alderslade, P. Partial purification of box jellyfish (Chironex fleckeri) nematocyst venom isolated at the beachside. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.W.; Long, K.; Rubinstein, H.M. Beachside preparation of jellyfish nematocyst tentacles. Toxicon 1992, 30, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleo, A.; La Spada, G.; Falzea, G.; Denaro, M.G. Discharging effectiveness of lyotropic anions on nematocysts of Pelagia noctiluca. Mol. Physiol. 1983, 6, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.; Jin, Y.B.; Kwak, J.; Jung, H.; Yoon, W.D.; Yoon, T.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, E. Protective effect of tetracycline against dermal toxicity induced by Jellyfish venom. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.; Klug, M.; Tardent, P. Some physical and chemical properties of purified nematocysts of Hydra attenuata Pall. (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1987, 88, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calton, G.J.; Burnett, J.W. The purification of Portuguese man-of-war nematocyst toxins by gel diffusion. Comp. Gen. Pharmacol. 1973, 4, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badré, S. Bioactive toxins from stinging jellyfish. Toxicon 2014, 91, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, W.J. A simple ultraviolet spectrophotometric method for the determination of protein. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1956, 48, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nat. Methods 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, R.C., 3rd; Merril, C.R.; Shifrin, S. A highly sensitive silver stain for detecting proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 98, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, R.O.; Yamagata, S.; Miura, Y.; Harada, T.; Yamagata, T. Analysis of glycosaminoglycan-degrading enzymes by substrate gel electrophoresis (zymography). Anal. Biochem. 1995, 225, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottini, G.; Gusmani, L.; Parovel, E.; Avian, M.; Patriarca, P. Purification and properties of a cytolytic toxin in venom of the jellyfish Carybdea marsupialis. Toxicon 1995, 33, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, R.I.; Rosenman, M.; Harwig, S.S.; Jackson, R.; Eisenhauer, P. Ultrasensitive assays for endogenous antimicrobial polypeptides. J. Immunol. Methods 1991, 137, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, Y.; Galliot, B. RNAseq versus genome-predicted transcriptomes: A large population of novel transcripts identified in an Illumina-454 Hydra transcriptome. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanik, D.; Lubinski, T.; Granger, B.; Byrd, A.; Reitzel, A.; DeFilippo, L.; Lorenc, A.; Finnerty, J.R. Production of a reference transcriptome and transcriptomic database (EdwardsiellaBase) for the lined sea anemone, Edwardsiella lineata, a parasitic cnidarian. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.A.; Cassoli, J.S.; Sa, F.; Dong, Z.Q.; de Freitas, J.C.; Pimenta, A.M.; de Lima, M.E.; Konno, K.; Lee, S.M.; Garateix, A.; et al. Peptide fingerprinting of the neurotoxic fractions isolated from the secretions of sea anemones Stichodactyla helianthus and Bunodosoma granulifera. New members of the APETx-like family identified by a 454 pyrosequencing approach. Peptides 2012, 34, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Tsementzi, D.; Kyrpides, N.; Read, T.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Direct Comparisons of Illumina vs. Roche 454 Sequencing Technologies on the Same Microbial Community DNA Sample. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallapalli, G.; Kemen, E.; Robert-Seilaniantz, A.; Segonzac, C.; Etherington, G.; Sohn, K.; MacLean, D.; Jones, J.D. EXPRSS: An Illumina based high-throughput expression-profiling method to reveal transcriptional dynamics. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helm, R.; Siebert, S.; Tulin, S.; Smith, J.; Dunn, C. Characterization of differential transcript abundance through time during Nematostella vectensis development. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, F.; He, L.; Li, Z. Pyrosequencing reveals diverse microbial community associated with the zoanthid Palythoa autraliae from the South China Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alex, A.; Antunes, A. Pyrosequencing characterization of the microbiota from Atlantic intertidal marine sponges reveals high microbial diversity and the lack of co-occurrence patterns. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshlack, A.; Wakefield, M.J. Transcript length bias in RNA-seq data confounds systems biology. Biol. Direct. 2009, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingolia, N.T.; Brar, G.; Rouskin, S.; McGeachy, A.; Weissman, J.S. The ribosome profiling strategy for monitoring translation in vivo by deep sequencing of ribosome-protected mRNA fragments. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1534–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, C.A.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Cao, X.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Han, B.; Jing, X.; Sam, L.; Barrette, T.; Palanisamy, N.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Transcriptome sequencing to detect gene fusions in cancer. Nature 2009, 458, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, S.; Helmholz, H.; Ruhnau, C.; Prange, A. A novel proteinaceous cytotoxin from the northern Scyphozoa Cyanea capillata (L.) with structural homology to cubozoan haemolysins. Toxicon 2011, 57, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillewaert, H. Aurelia aurita . Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Aurelia_aurita#/media/File:Aurelia_aurita_1.jpg (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Seymour, J. Toxic Shock from Stinger Family. Available online: http://www.abc.net.au/science/news/health/HealthRepublish_700864.htm (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Ávila-Soria, G. Molecular characterization of Carukia barnesi and Malo kingi, Cnidaria; Cubozoa; Carybdeidae. Ph.D. Thesis, James Cook University, Townsville, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara, J. Alatina Alata, San Salvador, Bahamas. Available online: http://www.snipview.com/q/Alatina_alata (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Norman, M. Carybdea rastoni . Available online: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Carybdea_rastoni.jpeg#mediaviewer/File:Carybdea_rastoni.jpeg (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Gautsch, G. Avispa marina . Available online: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AAvispa_marina.jpg (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Brinkman, D.; Burnell, J. Partial purification of cytolytic venom proteins from the box jellyfish, Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 2008, 51, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Konstantakopoulos, N.; McInerney, B.; Mulvenna, J.; Seymour, J.; Isbister, G.; Hodgson, W.C. Chironex fleckeri (box jellyfish) venom proteins: Expansion of a cnidarian toxin family that elicits variable cytolytic and cardiovascular effects. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4798–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenCage, Chironex yamaguchii. Available online: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chiropsalmus_quadrigatus.jpg#mediaviewer/File:Chiropsalmus_quadrigatus.jpg (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Hershman, D. A Lion’s Mane Jelly. Available online: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Largelionsmanejellyfish.jpg#mediaviewer/File:Largelionsmanejellyfish.jpg (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Lassen, S.; Wiebring, A.; Helmholz, H.; Ruhnau, C.; Prange, A. Isolation of a Nav channel blocking polypeptide from Cyanea capillata medusae- a neurotoxin contained in fishing tentacle isorhizas. Toxicon 2012, 59, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Key, R. Bluefire Jellyfish Cyanea lamarckii. Available online: https://www.flickr.com/photos/roger_key/3607569672/ (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Helmholz, H.; Naatz, S.; Lassen, S.; Prange, A. Isolation of a cytotoxic glycoprotein from the Scyphozoa Cyanea lamarckii by lectin-affinity chromatography and characterization of molecule interactions by surface plasmon resonance. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 871, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershwin, L. Box Jellyfish No Bigger Than Your Fingernail Can Kill You in The Blink of an Eye. Available online: http://featuredcreature.com/box-jellyfish-no-bigger-than-your-fingernail-can-kill-you-in-the-blink-of-an-eye/ (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Endlessblue’s Blog, Nemopilema nomurai. Available online: http://endlessblue.jp/blog/2009/10/-nemopilema-nomurai.html (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Migotto, A.E. Hidromedusa. Available online: http://cifonauta.cebimar.usp.br/photo/2002/ (accessed on 5 March 2016).
- Hobgood, N. White-Spotted Jellyfish off The North Coast of Haiti. Available online: https:// commons. wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Phyllorhiza_punctata_%28White-spotted_jellyfish%29.jpg#mediaviewer/File:Phyllorhiza_punctata_%28White-spotted_jellyfish%29.jpg (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Carneiro, R.F.; Nascimento, N.; Costa, P.; Gomes, V.; de Souza, A.; de Oliveira, S.; Dos Santos Diz Filho, E.; Zara, F.; Fonteles, M.; de Oliveira Toyama, D.; et al. The extract of the jellyfish Phyllorhiza punctata promotes neurotoxic effects. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C. The Dunn Lab. Available online: http://dunnlab.org/ (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Tamkun, M.; Hessinger, D.A. Isolation and partial characterization of a hemolytic and toxic protein from the nematocyst venom of the Portuguese Man-of-War, Physalia physalis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 667, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, R.; Mas, R.; Garateix, A.; Garcia, M.; Chavez, M. Effects of a high molecular weight polypeptidic toxin from Physalia physalis (Portuguese man-of-war) on cholinergic responses. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 1990, 95, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, R.; Menendez, R.; Garateix, A.; Garcia, M.; Chavez, M. Effects of a high molecular weight toxin from Physalia physalis on glutamate responses. Neuroscience 1989, 33, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFall, G. Stomolophus meleagris Gray’s Reef. Available online: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AStomolophus_meleagris_Gray's_Reef.jpg (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Fischer, A.H.; Mozzherin, D.; Eren, A.M.; Lans, K.D.; Wilson, N.; Cosentino, C.; Smith, J. SeaBase: A multispecies transcriptomic resource and platform for gene network inference. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2014, 54, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, Y.; Gurevitz, M. When positive selection of neurotoxin genes is missing. The riddle of the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 3886–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, Y.; Weinberger, H.; Lazarus, N.; Gur, M.; Kahn, R.; Gordon, D.; Gurevitz, M. Fusion and retrotransposition events in the evolution of the sea anemone Anemonia viridis neurotoxin genes. J. Mol. Evol. 2009, 69, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, Y.; Weinberger, H.; Sullivan, J.C.; Reitzel, A.M.; Finnerty, J.R.; Gurevitz, M. Concerted evolution of sea anemone neurotoxin genes is revealed through analysis of the Nematostella vectensis genome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothberg, J.M.; Leamon, J.H. The development and impact of 454 sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J. The next-generation sequencing technology: A technology review and future perspective. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 53, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipson, D.; Raz, T.; Kieu, A.; Jones, D.R.; Giladi, E.; Thayer, E.; Thompson, J.F.; Letovsky, S.; Milos, P.; Causey, M. Quantification of the yeast transcriptome by single-molecule sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, S.; Robinson, M.; Tintori, S.; Goetz, F.; Helm, R.; Smith, S.; Shaner, N.; Haddock, S.; Dunn, C. Differential gene expression in the siphonophore Nanomia bijuga (Cnidaria) assessed with multiple next-generation sequencing workflows. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velculescu, V.E.; Zhang, L.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Serial analysis of gene expression. Science 1995, 270, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Polyak, K. Serial analysis of gene expression. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1743–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bombarely, A. Brief Guide for NGS Transcriptomics: From Gene Expression to Genetics. Available online: http://www.slideshare.net/aubombarely/rnaseq-analysis-19910448 (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Tulin, S.; Aguiar, D.; Istrail, S.; Smith, J. A quantitative reference transcriptome for Nematostella vectensis early embryonic development: A pipeline for de novo assembly in emerging model systems. EvoDevo 2013, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illumina®. Available online: http://www.illumina.com/ (accessed on 15 February 2015).
- Smith, D.R.; Kayal, E.; Yanagihara, A.A.; Collins, A.G.; Pirro, S.; Keeling, P.J. First complete mitochondrial genome sequence from a box jellyfish reveals a highly fragmented linear architecture and insights into telomere evolution. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emblem, A.; Karlsen, B.; Evertsen, J.; Miller, D.; Moum, T.; Johansen, S.D. Mitogenome polymorphism in a single branch sample revealed by SOLiD deep sequencing of the Lophelia pertusa coral genome. Gene 2012, 506, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayal, E.; Bentlage, B.; Collins, A.; Kayal, M.; Pirro, S.; Lavrov, D.V. Evolution of linear mitochondrial genomes in medusozoan cnidarians. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, S.C. Aiptasia palliada . Available online: http://www.seaslugforum.net/showall/aiptasia (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Lehnert, E.; Burriesci, M.; Pringle, J. Developing the anemone Aiptasia as a tractable model for cnidarian-dinoflagellate symbiosis: The transcriptome of aposymbiotic A. pallida. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elran, R.; Raam, M.; Kraus, R.; Brekhman, V.; Sher, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Lotan, T. Early and late response of Nematostella vectensis transcriptome to heavy metals. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 4722–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, J.W. Acropora palmata, Juvenile. Available online: http://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20p?see=I_JWP2&res=640 (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Polato, N.R.; Vera, J.C.; Baums, I.B. Gene discovery in the threatened elkhorn coral: 454 sequencing of the Acropora palmata transcriptome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, A.; Huisman, L.; Ball, E.; Hayward, D.; Grasso, L.; Chua, C.; Woo, H.; Gattuso, J.; Foret, S.; Miller, D.J. Whole transcriptome analysis of the coral Acropora millepora reveals complex responses to CO2-driven acidification during the initiation of calcification. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.; Aglyamova, G.; Wang, S.; Buchanan-Carter, J.; Abrego, D.; Colbourne, J.; Willis, B.; Matz, M.V. Sequencing and de novo analysis of a coral larval transcriptome using 454 GSFlx. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooyaei Mehr, S.F.; DeSalle, R.; Kao, H.; Narechania, A.; Han, Z.; Tchernov, D.; Pieribone, V.; Gruber, D.F. Transcriptome deep-sequencing and clustering of expressed isoforms from Favia corals. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karako-Lampert, S.; Zoccola, D.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Katzenellenbogen, M.; Tambutté, S.; Bertucci, A.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Deleury, E.; Allemand, D.; Levy, O. Transcriptome analysis of the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traylor-Knowles, N.; Granger, B.R.; Lubinski, T.J.; Parikh, J.R.; Garamszegi, S.; Xia, Y.; Marto, J.A.; Kaufman, L.; Finnerty, J.R. Production of a reference transcriptome and transcriptomic database (PocilloporaBase) for the cauliflower coral, Pocillopora damicornis. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Chen, Q.; Lun, J.; Xu, J.; Qiu, J.W. PcarnBase: Development of a transcriptomic database for the brain coral Platygyra carnosus. Mar. Biotechnol. (N.Y.) 2013, 15, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, P.J.; Campbell, R.D. Common Brown Hydra. Available online: http://nathistoc.bio.uci.edu/Cnidaria/Hydra.htm (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- Sanders, S.M.; Shcheglovitova, M.; Cartwright, P. Differential gene expression between functionally specialized polyps of the colonial hydrozoan Hydractinia symbiolongicarpus (Phylum Cnidaria). BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escoubas, P.; Quinton, L.; Nicholson, G.M. Venomics: Unravelling the complexity of animal venoms with mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Image | Species | Toxin | Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 [75] [75] | Aurelia aurita | Aurelin | nt | [8] |
| Metalloprotease | - | [11] | ||
 [76] * [76] * | Carukia barnesi | CbTX-I | nt | [77] |
| CbTX-II | nt | |||
 [78] [78] | Carybdea alata | CaTX-A | nt | [12] |
| CaTX-B | nt | |||
 [79] [79] | Carybdea rastoni | CrTX-A | nt | [13] |
| CrTX-B | nt | |||
 [80] [80] | Chironex fleckeri | CfTX-1 CfTX-2 CfTX-A CfTX-B | nt nt nt nt | [15,81] [82] |
 [83] [83] | Chiropsalmus quadrigatus | CqTX-A | nt | [20] |
 [84] [84] | Cyanea capillata (Cyanea nozakii) | CcTX-1 CcNT Metalloprotease | aa - | [74] [85] [11] |
 [86] * [86] * | Cyanea lamarckii | ClGP-1 | - | [87] |
 [88] * [88] * | Malo kingi | MkTX-A MkTX-B | nt nt | [77] |
 [89] [89] | Nemopilema nomurai | Metalloprotease | - | [11] [25] |
 [90] [90] | Olindias sambaquiensis | Metalloprotease | - | [44] |
 [91] [91] | Phyllorhiza punctata | Saxitoxin Gonyautoxin-4 Tetrodotoxin Brevetoxin-2 | - - - - - | [92] |
 [93] [93] | Physalia physalis | Physalitoxin P1 P3 PpV9.4 | - - - - | [94] [95] [96] [46] |
 [83] [83] | Rhopilema esculenta | Metalloprotease | - | [11] |
 [97] [97] | Stomolophus meleagris | SmP90 C-type lectin, PLA2, Kv+ toxin, Hemolysin Metalloprotease | aa - - - | [39] [37] |
| Order | Species | Tissue | Sequencing Platfform | Raw Reads (Milions) | Read Lengh (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Actiniaria * [114] | Aiptasia palliada * | Adults growing under different conditions | illumina | 208 | - | [115] |
| Bunodosoma granulifera | Adult | 454 | - | - | [65] | |
| Edwardsiella lineata | five developmental stages | illumina | 376.2 PE | 40 | [64] | |
| Nematostella vectensis | six developmental stages Adult stress w/four heavy metals | illumina | 165 SE 200 PE 15.22 SE | 50 100 | [68] [109] [116] | |
Scleractinia * [117] a | Acropora palmata * | Larvae | 454 GS-FLX | 0.960 | 398 | [118] |
| Acropora millipora | Larvae w/CO2 stress Larvae | illumina 454 GS-FLX | 28 628 PE | 38 232 | [119] [120] | |
| Favia corals | Adult | illumina | 80 PE | 75 | [121] | |
| Stylophora pistillata | Adults growing under different conditions | 454 GS-FLX | 521 | - | [122] | |
| Pocillopora damicornis | Adult colonies subject to a battery of stressors | 454 | 0.955 | 379 | [123] | |
| Platygyra carnosus | Adult colonies | illumina | 83 PE | 90 | [124] | |
Hydrozoa * [125] a | Hydractinia symbiolongicarpus | Adult feeding, reproductive, and defensive polyps | illumina | 0.066 | 200 | [126] |
| Hydra vulgaris * | Regenerating polyps | illumina 454 Titanium | 53.6 1.2 | - | [63] | |
| Nanomia bijuca | Nectophores, gastrozooids | 454, illumina, SOLiD SAGE, Helicos DGE | 943 | - | [105] | |
Scyphozoa [97] | Stomolophus meleagris | Tentacles | illumina | 108 | 90 | [37] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frazão, B.; Antunes, A. Jellyfish Bioactive Compounds: Methods for Wet-Lab Work. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040075
Frazão B, Antunes A. Jellyfish Bioactive Compounds: Methods for Wet-Lab Work. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(4):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040075
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrazão, Bárbara, and Agostinho Antunes. 2016. "Jellyfish Bioactive Compounds: Methods for Wet-Lab Work" Marine Drugs 14, no. 4: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040075
APA StyleFrazão, B., & Antunes, A. (2016). Jellyfish Bioactive Compounds: Methods for Wet-Lab Work. Marine Drugs, 14(4), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040075








