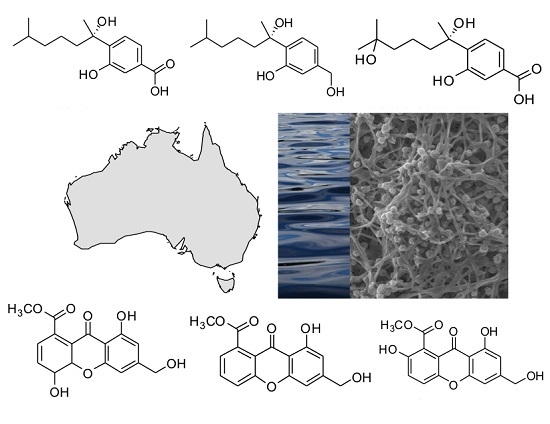
Aspergillus Sydowii Marine Fungal Bloom in Australian Coastal Waters, Its Metabolites and Potential Impact on Symbiodinium Dinoflagellates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1 Australian Terrestrial A. Sydowii Strains
2.2. Australian Marine A. Sydowii ASBS Strain
2.3. US Marine A. Sydowii FK1 Strain
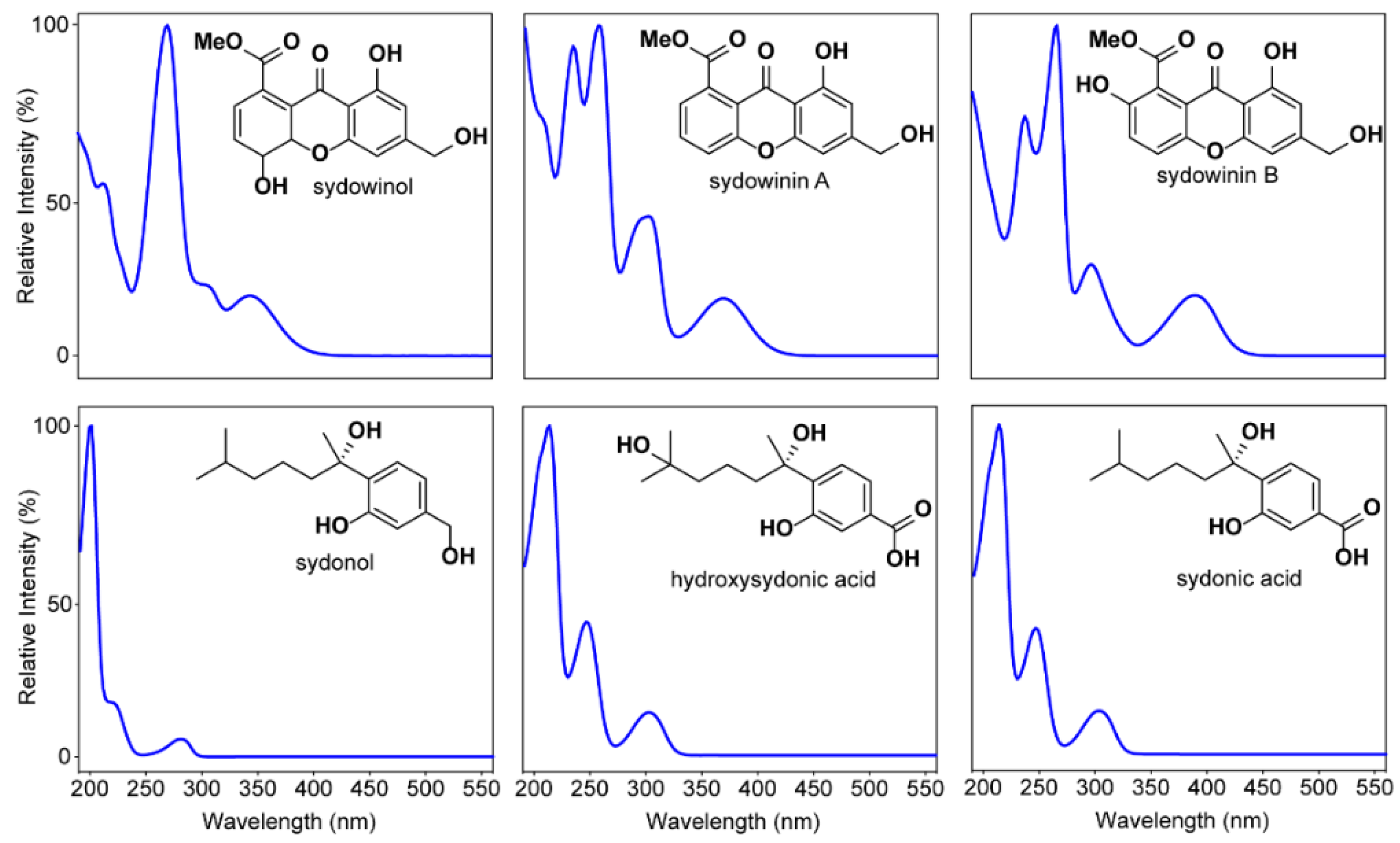
2.4. Fungal Strains from the 2009 CPR Silks, and Metabolites in CPR Silk Materials
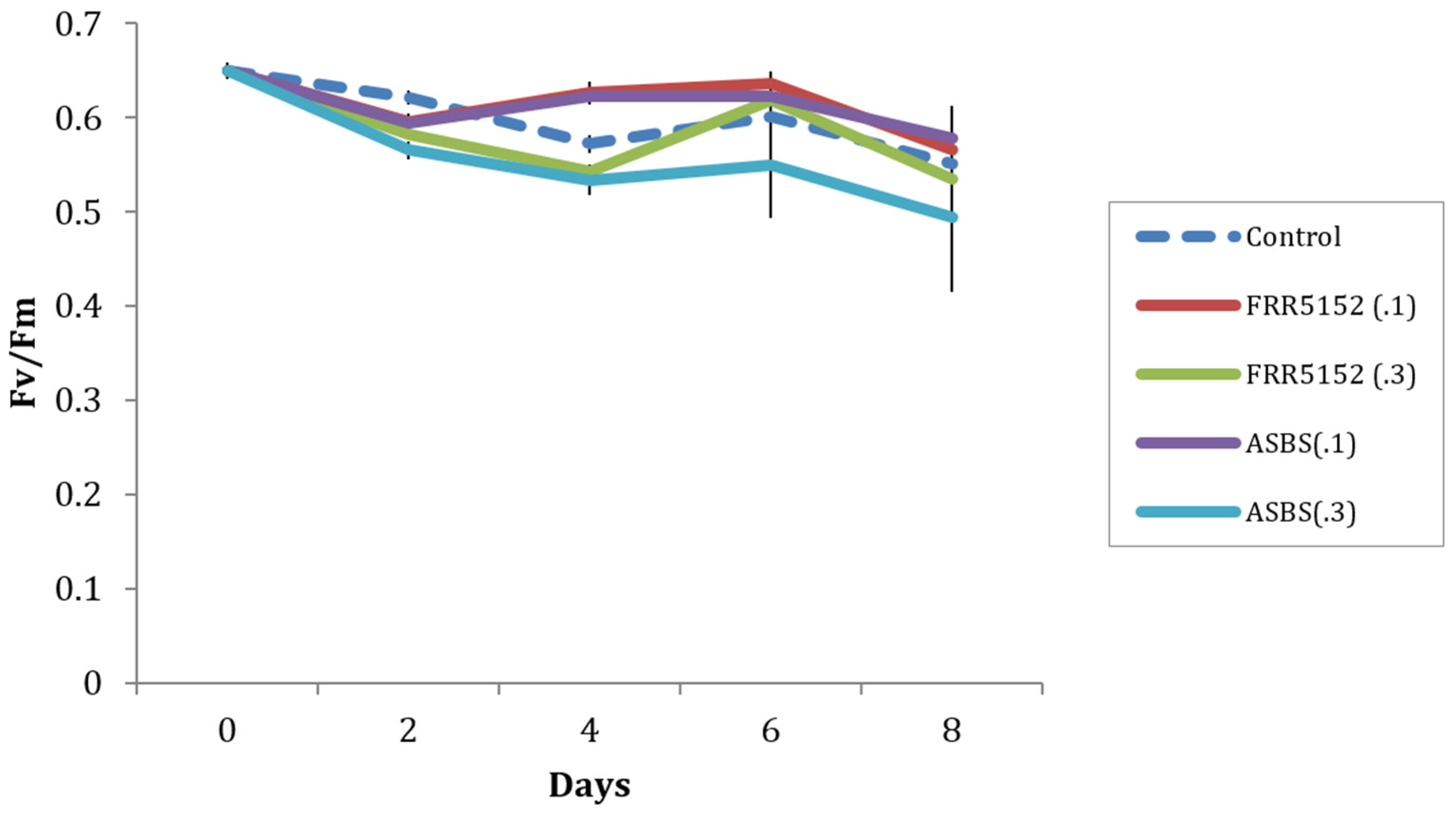
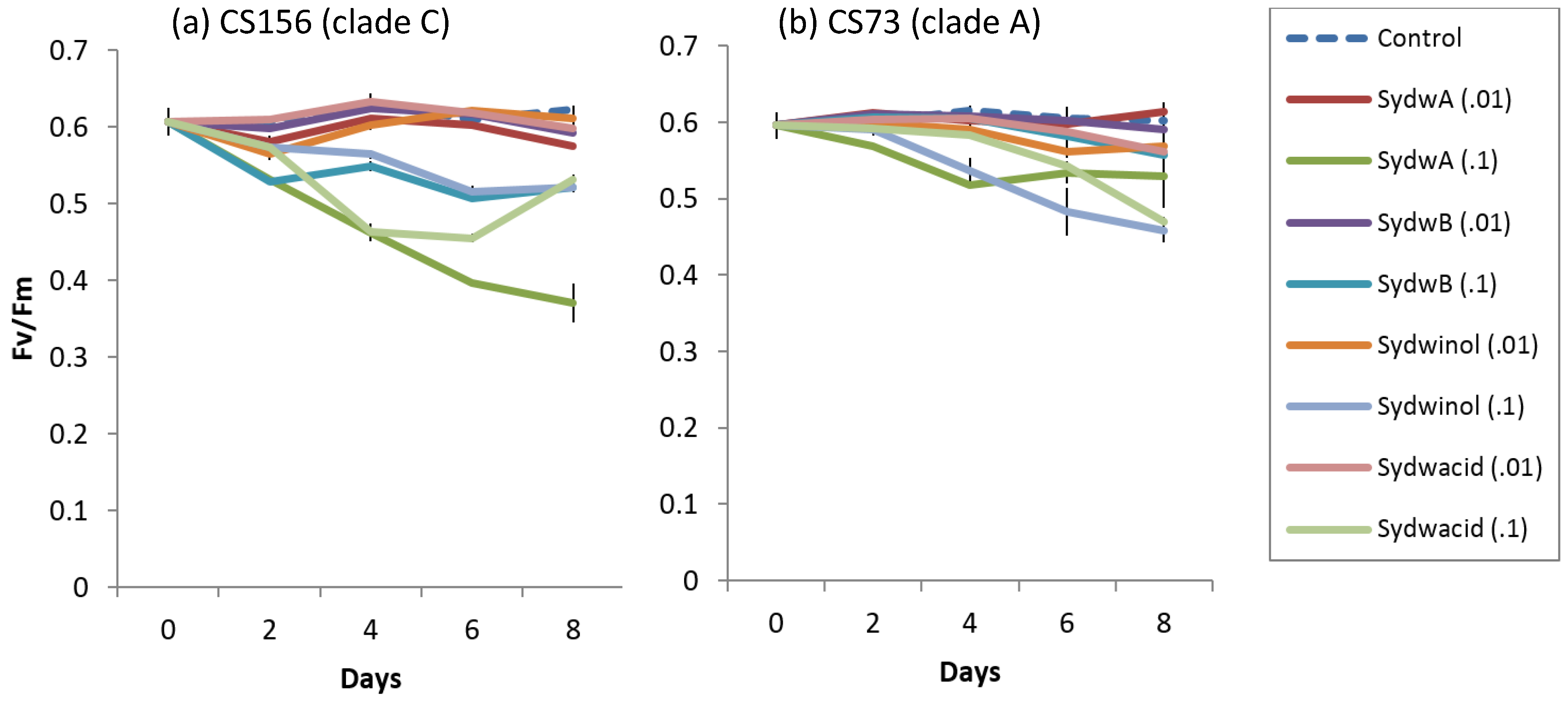
2.5. Effect of Terrestrial and Marine A. Sydowii Crude Extracts on Symbiodinium Photo-Physiological State
2.6. Effect of Known A. Sydowii Metabolites on Symbiodinium Photo-Physiological State
3. Discussion
3.1. Dust Generated Microbial Raft Ecosystem
3.2. Secondary Metabolites Associated with Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic Strains of A. Sydowii
3.3. Effect of Fungal Crude Extracts and A. Sydowii Typical Metabolites on Symbiodinium Photophysiology
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Fungal Isolation from the Continuous Plankton Recorder Silks and A. Sydowii Strains
4.2. HPLC Analysis on Fungal Secondary Metabolites
4.3. Symbiodinium Dinoflagellate Strains
4.4. Crude Extracts and Typical A. Sydowii Secondary Metabolites
4.5. Symbiodinium Photophysiology Assays
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Hallegraeff, G.; Coman, F.; Davies, C.; Hayashi, A.; McLeod, D.; Slotwinski, A.; Whittock, L.; Richardson, A.J. Australian dust storm associated with extensive Aspergillus sydowii fungal “bloom” in coastal waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3315–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, C.A.; Kim, C.J.S.; Lyles, J.M.; Harvell, C.D. Special issue oceans and humans health: The ecology of marine opportunists. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.W.; Ives, L.D.; Nagelkerken, I.A.; Richie, K.B. Caribbean sea-fan mortalities. Nature 1996, 383, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Harvell, C.D. The rise and fall of a six-year coral-fungal epizootic. Am. Nat. 2004, 164, S52–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.W.; Weil, E. Aspergillosis of Gorgonians. In Coral Health and Disease, 1st ed.; Rosenberg, E., Loya, Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, J.F.; Ellner, S.P.; Vu, I.; Kim, K.; Harvell, C.D. Impacts of aspergillosis on sea fan coral demography: Modeling a moving target. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, A.M.S.; Brandt, M.E.; Smith, T.B.; Thornhill, D.J.; Baker, A.C. Symbiodinium associations with diseased and healthy scleractinian corals. Coral Reefs 2009, 28, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, D.M.; Taylor, J.W.; Ritchie, K.B.; Smith, G.W. Cause of sea fan death in the West Indies. Nature 1998, 394, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypien, K.L.; Andras, J.P.; Harvell, C.D. Globally panmictic population structure in the opportunistic fungal pathogen Aspergillus sydowii. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 4068–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alker, A.P.; Smith, G.W.; Kim, K. Characterization of Aspergillus sydowii (Thom et Church), a fungal pathogen of Caribbean sea fan corals. Hydrobiologia 2001, 460, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, T.; Nagayama, K.; Hatsuda, Y. Two new metabolites, sydonic acid and hydroxysydonic acid, from Aspergillus sydowi. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1978, 42, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, T.; Sato, Y.; Hatsuda, Y. Isolation of new metabolites from Aspergillus sydowi and structure of sydowic acid. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1975, 39, 2337–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisuwan, K.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Kaewpet, M.; Phongpaichit, S.; Hutadilok-Towatana, N.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. Sesquiterpene and xanthone derivatives from the sea fan-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii PSU-F154. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.B.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhu, R.X.; Chang, W.Q.; Yuan, H.Q.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhao, Z.T.; Lou, H.X. Identification and biological evaluation of secondary metabolites from the endolichenic fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Song, F.; Ma, L.; Chen, C.; Xiao, X.; Ren, B.; Liu, X.; Dai, H.; Piggott, A.M.; Av-Gay, Y.; et al. Sydowiols A–C: Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors from an East China Sea marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sydowii. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 6081–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, J.; Polson, S.C.; Polson, S.W.; Smith, G.W.; Frisvad, J.C. Study of secondary metabolites associated with virulent and non-virulent strains of Aspergillus sydowii: Sea fan pathogen. In Proceedings of the 8th Symposium on the Natural Histroy of the Bahamas, Salvador, Bahamas, June 2001; pp. 48–52.
- Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N. Chlorophyll fluorescence—A practical guide. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, V.H.; Shinn, E.A.; Foreman, W.T.; Griffin, D.W.; Holmes, C.W.; Kellogg, C.A.; Majewski, M.S.; Richardson, L.L.; Ritchie, K.B.; Smith, G.W. African and Asian Dust: From Desert Soils to Coral Reefs. Bioscience 2003, 53, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Põlme, S.; Kõljalg, U.; Yorou, N.S.; Wijesundera, R.; Ruiz, L.V.; Vasco-Palacios, A.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Suija, A.; et al. Global diversity and geography of soil fungi. Science 2014, 346, 1256688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fremlin, L.J.; Piggott, A.M.; Lacey, E.; Capon, R.J. Cottoquinazoline A and cotteslosins A and B, metabolites from an australian marine-derived strain of Aspergillus versicolor. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.B.G. Fifty years of marine mycology. Fungal Divers. 2011, 50, 73–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison-Gardiner, S. Dominant fungi from Australian coral reefs. Fungal Divers. 2002, 9, 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Andreakis, N.; Høj, L.; Kearns, P.; Hall, M.R.; Ericson, G.; Cobb, R.E.; Gordon, B.R.; Evans-Illidge, E. Diversity of marine-derived fungal cultures exposed by DNA barcodes: The algorithm matters. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo-Hernández, C.; Zuluaga-Montero, A.; Bones-González, A.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Sabat, A.M.; Bayman, P. Fungi in healthy and diseased sea fans (Gorgonia ventalina): Is Aspergillus sydowii always the pathogen? Coral Reefs 2008, 27, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.H.R.; Gregg, T.M.; Takabayashi, M. Does coral disease affect symbiodinium? Investigating the impacts of growth anomaly on symbiont photophysiology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinsky, Z.; Berman-Frank, I. Uncoupling primary production from population growth in photosynthesizing organisms in aquatic ecosystems. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 63, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, J.M.; Hayes, R.; Goreau, T.J.; Smith, G.W. Zooxanthellae regulation in yellow blotch/band and other coral diseases contrasted with temperature related bleaching: In situ destruction vs. expulsion. Symbiosis 2004, 37, 63–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-haim, Y.; Zicherman-keren, M.; Rosenberg, E. Temperature-regulated bleaching and lysis of the coral Pocillopora damicornis by the novel pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4236–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, N.L.; Ward, J.R.; Coffroth, M.A. Stable Symbiodinium composition in the sea fan Gorgonia ventalina during temperature and disease stress. Biol. Bull. 2005, 209, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ein-Gil, N.; Ilan, M.; Carmeli, S.; Smith, G.W.; Pawlik, J.R.; Yarden, O. Presence of Aspergillus sydowii, a pathogen of gorgonian sea fans in the marine sponge Spongia obscura. ISME J. 2009, 3, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochon, X.; Montoya-Burgos, J.I.; Stadelmann, B.; Pawlowski, J. Molecular phylogeny, evolutionary rates, and divergence timing of the symbiotic dinoflagellate genus Symbiodinium. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 38, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Suzuki, G.; Hayashibara, T.; Koike, K. Do corals select zooxanthellae by alternative discharge? Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stat, M.; Morris, E.; Gates, R.D. Functional diversity in coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9256–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toller, W.W.; Rowan, R.; Knowlton, N. Repopulation of Zooxanthellae in the Caribbean Corals Montastraea annularis and M. faveolata following Experimental and Disease-Associated Bleaching. Biol. Bull. 2001, 201, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oppen, M.J.H.; Mieog, J.C.; Sanchez, C.A.; Fabricius, K.E. Diversity of algal endosymbionts (zooxanthellae) in octocorals: The roles of geography and host relationships. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2403–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, B.; James Cook Universiry, Queensland, Australia. Personal communication, 2015.
- Lacey, E.; Tennant, S. Secondary metabolites. The focus of biodiscovery and perhaps the key to unlocking new depths in taxonomy. Microbiol. Aust. 2003, 24, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, R.R.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]

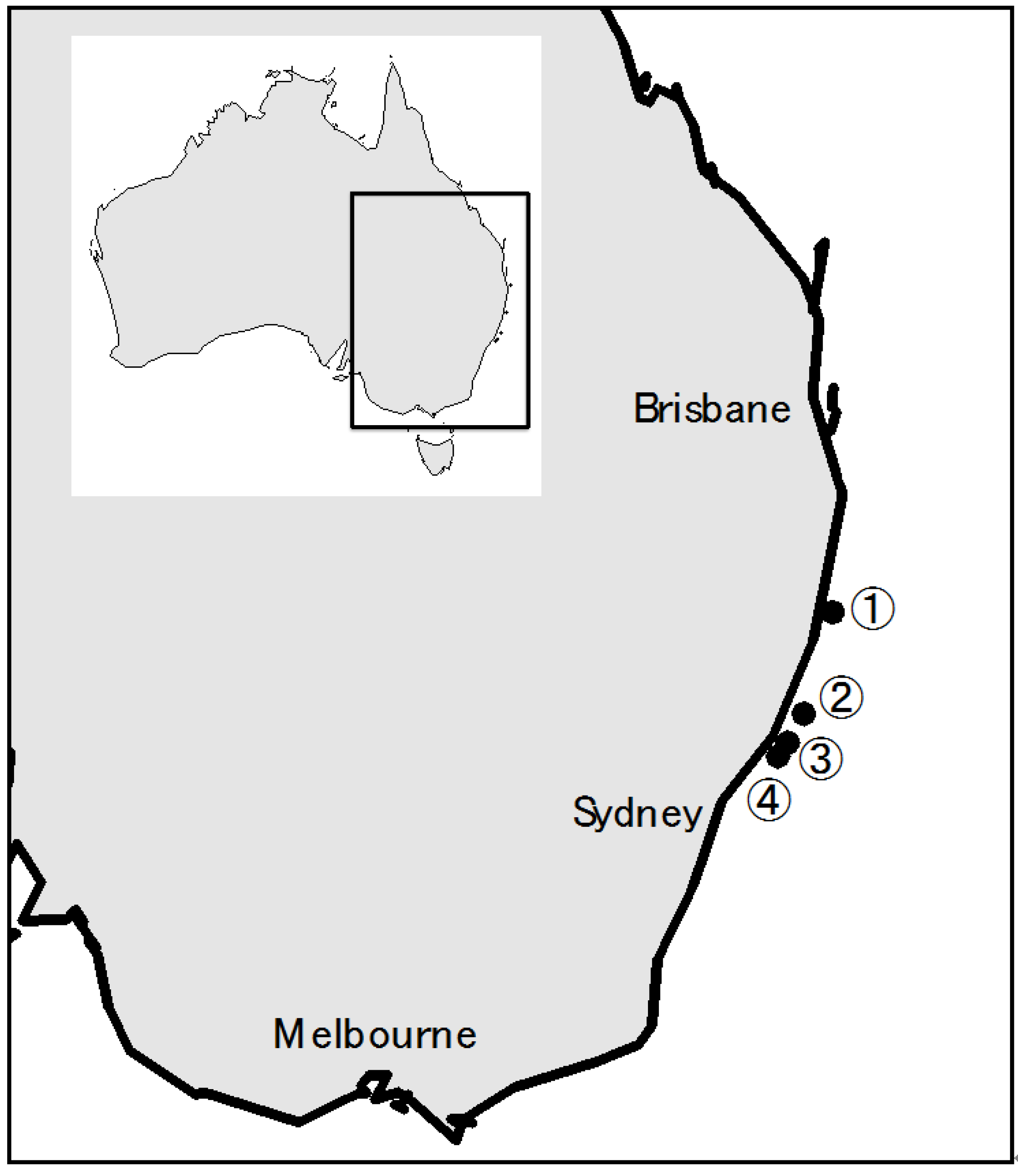
| Location | Species | Metabolite(s) | % Isolates |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A. sydowii | sydonic acid | 5.3 (2) |
| sydonic acid, sydonol | 15.8 (6) | ||
| sydonic acid, unknown metabolites1 | 7.9 (3) | ||
| Penicilllium sp. | rugulosin | 2.6 (1) | |
| Unknown 1 | no detectable metabolites | 5.3 (2) | |
| 2 | A. sydowii | sydonic acid | 7.9 (3) |
| sydonic acid, sydowinin B | 2.6 (1) | ||
| sydonic acid, unknown metabolites1 | 10.5 (4) | ||
| Aspergillus sp. | sterigmatocystin | 2.6 (1) | |
| 3 | Penicillium sp. | rugulosin | 2.6 (1) |
| 4 | A. sydowii | sydonic acid | 21.1 (8) |
| sydonic acid, sydonol | 2.6 (1) | ||
| Aspergillus sp. | sterigmatocystin | 5.3 (2) | |
| Cladosporium sp. | no detectable metabolites | 2.6 (1) | |
| Unknown 2 | unknown metabolite2 | 5.3 (2) | |
| Total 38 isolates |
| CS-No. | Clade | Source Location |
|---|---|---|
| CS-73 | Clade A | Heron Is., Great Barrier Reef, Queensland, Australia |
| CS-156 | Clade C | Hawaii, USA |
| CS-163 | Clade A1 | Palau |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayashi, A.; Crombie, A.; Lacey, E.; Richardson, A.J.; Vuong, D.; Piggott, A.M.; Hallegraeff, G. Aspergillus Sydowii Marine Fungal Bloom in Australian Coastal Waters, Its Metabolites and Potential Impact on Symbiodinium Dinoflagellates. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14030059
Hayashi A, Crombie A, Lacey E, Richardson AJ, Vuong D, Piggott AM, Hallegraeff G. Aspergillus Sydowii Marine Fungal Bloom in Australian Coastal Waters, Its Metabolites and Potential Impact on Symbiodinium Dinoflagellates. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayashi, Aiko, Andrew Crombie, Ernest Lacey, Anthony J. Richardson, Daniel Vuong, Andrew M. Piggott, and Gustaaf Hallegraeff. 2016. "Aspergillus Sydowii Marine Fungal Bloom in Australian Coastal Waters, Its Metabolites and Potential Impact on Symbiodinium Dinoflagellates" Marine Drugs 14, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14030059
APA StyleHayashi, A., Crombie, A., Lacey, E., Richardson, A. J., Vuong, D., Piggott, A. M., & Hallegraeff, G. (2016). Aspergillus Sydowii Marine Fungal Bloom in Australian Coastal Waters, Its Metabolites and Potential Impact on Symbiodinium Dinoflagellates. Marine Drugs, 14(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14030059