Use of Natural Antimicrobial Peptides and Bacterial Biopolymers for Cultured Pearl Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
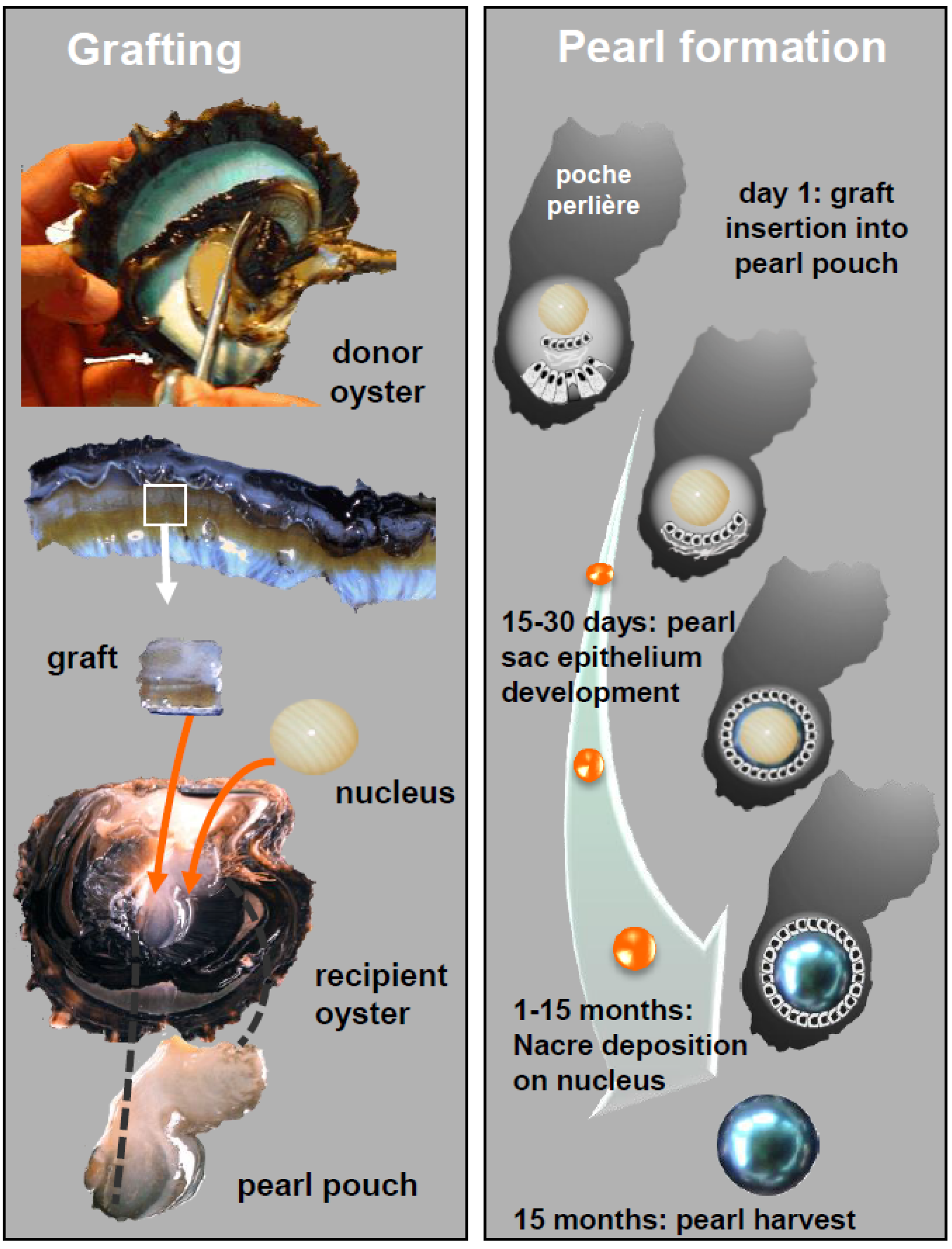
2. Results and Discussion
| Genus | Ref. | Proteins | Neutral Sugars | Uronic Acids | Hexosamines | Substituants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vibrio | Mo 245 | <1 | 2 (Gal) | 40 | 40 | Acetate |
| Nd | GG | <1 | 90 (Glc) | Tr (<5) | - | - |
2.1. SEM Analysis
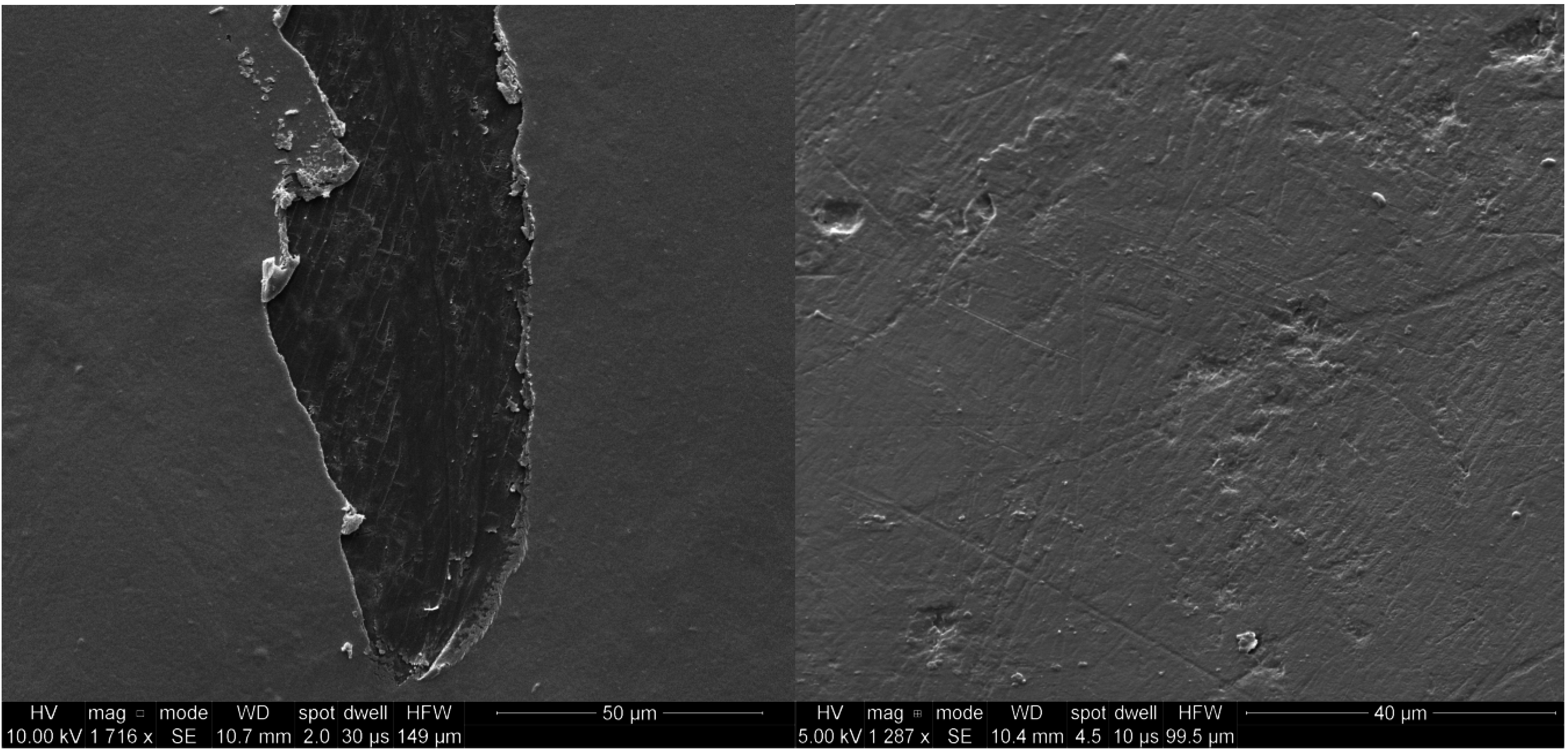
2.2. Biopolymer Antibacterial Activity
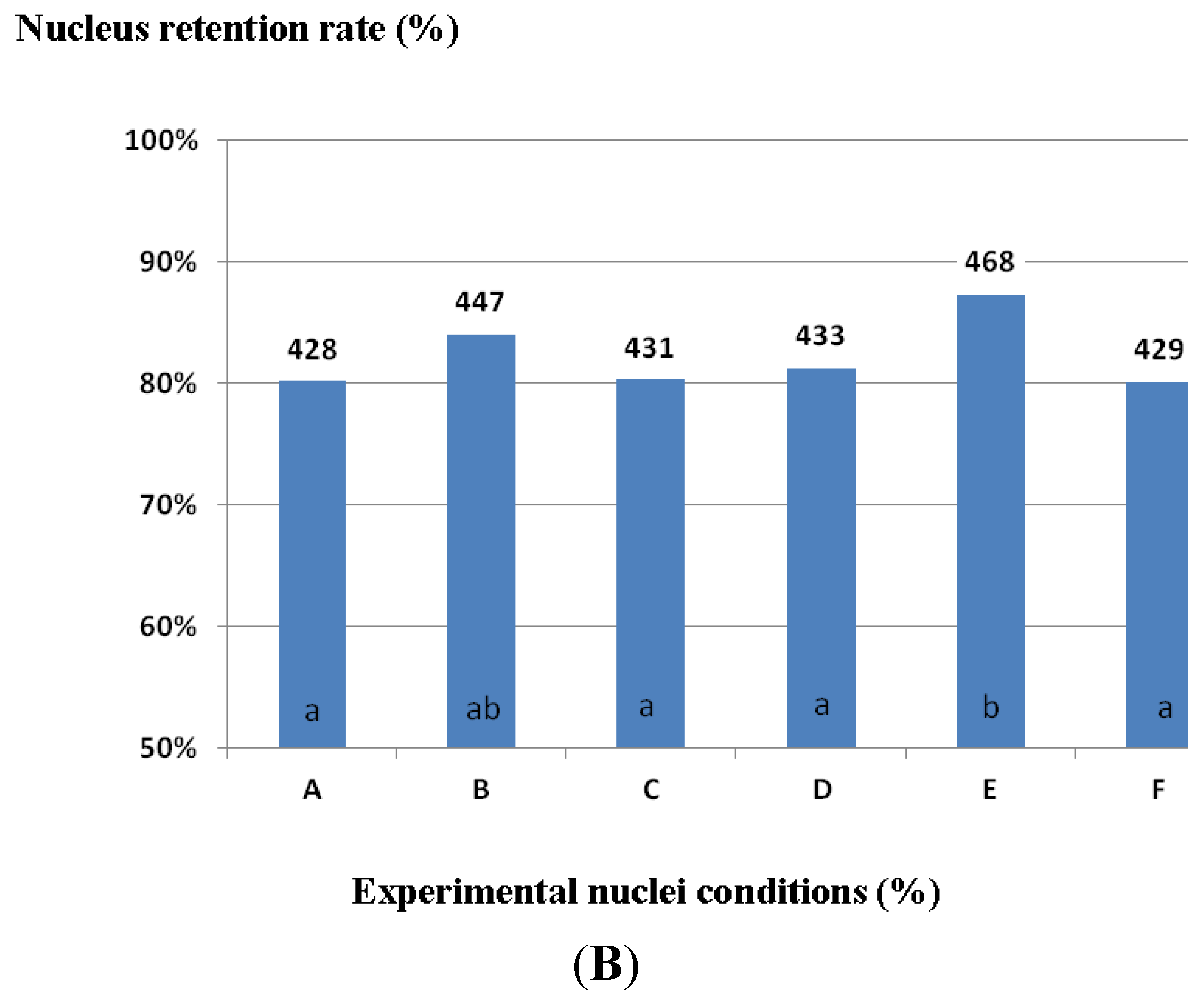
2.3. Laboratory Experiments

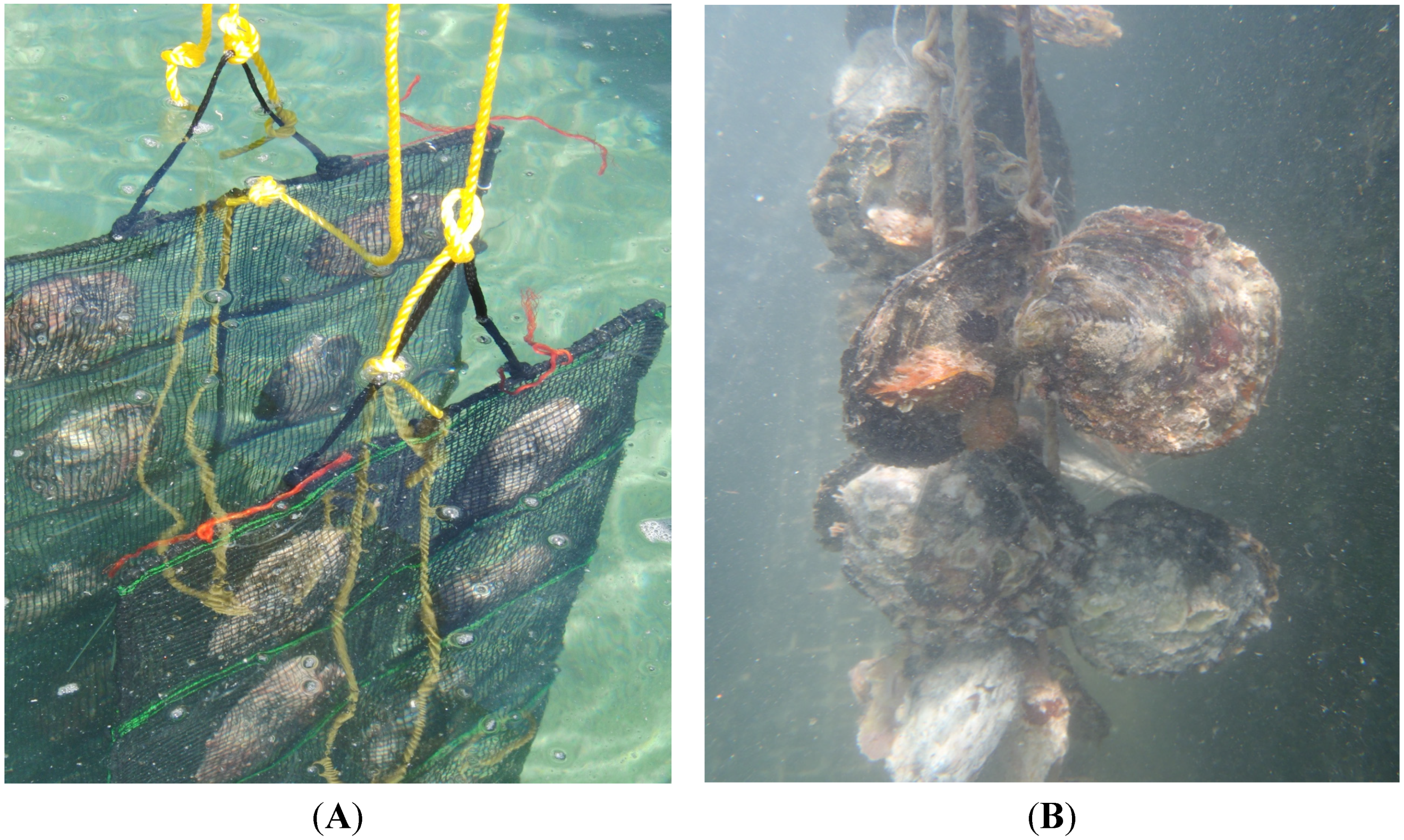
2.4. In Situ Experiments
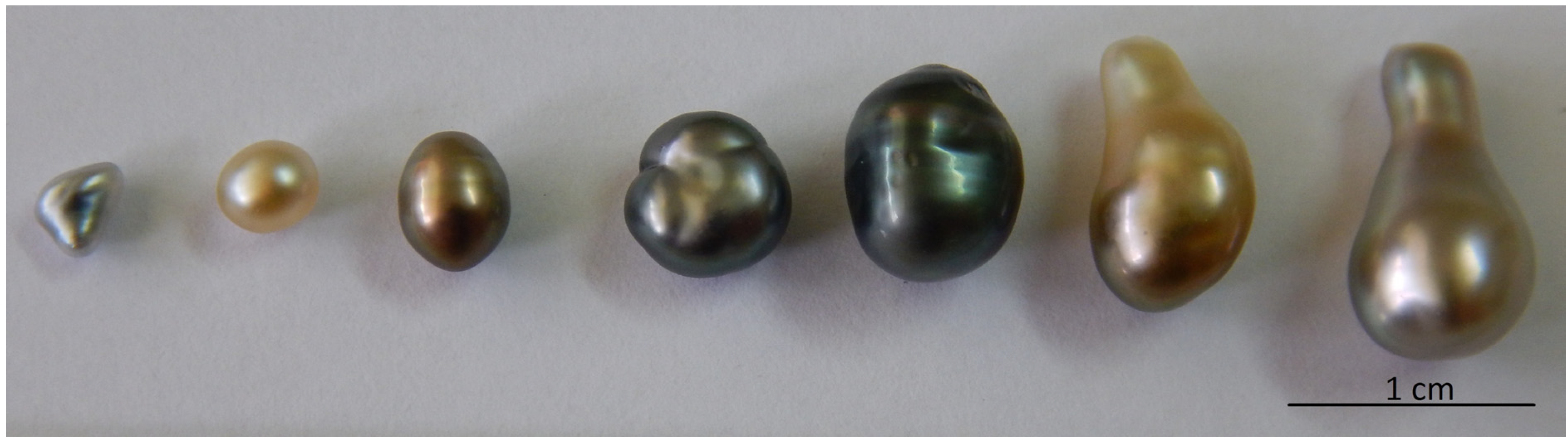


3. Material and Methods
3.1. Microbial Biopolymers
3.2. Antimicrobial Peptide
3.3. Nuclei
3.4. Coated Nuclei Preparation
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.6. Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity of the Molecules
3.7. Antimicrobial Property of Coated Nuclei
3.8. In Situ Experiments
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cochennec-Laureau, N.; Montagnani, C.; Saulnier, D.; Fougerouse, A.; Levy, P.; Lo, C. A histological examination of grafting success in pearl oyster Pinctada margaritifera in French Polynesia. Aquat. Living Resour. 2010, 23, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueguen, Y.; Montagnani, C.; Joubert, B.; Marie, C.; Belliard, A.; Tayale, J.; Fievet, P.; Levy, D.; Piquemal, F.; Marin, G.; et al. Characterization of Molecular Processes Involved in the Pearl Formation in Pinctada margaritifera for the Sustainable Development of Pearl Farming Industry in French Polynesia. In Recent Advances in Pearl Research—Proceedings of the International Symposium on Pearl Research 2011; Watabe, S., Maeyama, K., Nagasawa, H., Eds.; Terrapub: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; pp. 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Comps, M.; Fougerouse, A.; Bustles, D. A prokaryote infecting the black-lipped pearl oyster Pinctada margaritifica. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1998, 72, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, J.H.; Lucas, J.S.; Turner, I.; Mayer, R.J.; Newnham, R. Approaches to improve cultured pearl formation in Pinctada margaritifera through use of relaxation, antiseptic application and incision closure during bead insertion. Aquaculture 2000, 184, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southgate, P.; Lucas, J. The Pearl Oyster; Southgate, P., Lucas, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008; p. 544. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 196–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossi, A.; Sandri, L. Molecular diversity in gene-encoded, cationic antimicrobial polypeptides. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2002, 8, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial peptides: Pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmachary, M.; Krishnan, S.T.P.; Koh, J.L.Y.; Khan, A.M.; Seah, S.H.; Tan, T.W.; Brusic, V.; Bajic, V.B. ANTIMIC: A database of antimicrobial sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D586–D589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rougeaux, H.; Kervarec, N.; Pichon, R.; Raguenes, G.; Guezennec, J. Novel bacterial exopolysaccharides from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Carbohydr. Polym. 1996, 31, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I. A sticky business: Microbial polysaccharides; Current products and future trends. Microbiol. Today 2002, 29, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Mody, K.; Jha, B. Bacterial exopolysaccharides—A perception. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2007, 47, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, B.H.A. (Ed.) Microbial Production of Biopolymers and Polymer Precursors: Applications and Perspectives; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2009.
- Ullrich, M. (Ed.) Bacterial Polysaccharides: Current Innovations and Future Trends; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2009.
- Guezennec, J. Deep-sea hydrothermal vents: A new source of innovative bacterial exopolysaccharides of biotechnological interest? J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 29, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, C.A.; Guezennec, J.; Bowman, J.P. Bacterial exopolysaccharides from extreme marine environments with special consideration of the southern ocean, sea ice, and deep-sea hydrothermal vents: A review. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaus, B.; Kambourova, M.; Toksoy Oner, E. Exopolysaccharides from extremophiles: From fundamental to biotechnology. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guezennec, J.; Moppert, X.; Raguenes, G.; Richert, L.; Costa, B.; Simon Colin, C. Microbial mats in French Polynesia and their biotechnological applications. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliec-Jouault, S.; Zanchetta, P.; Helley, D.; Ratiskol, J.; Sinquin, C.; Fischer, A.M.; Guézennec, J. Exopolysaccharides produced by bacteria isolated from deep-sea hydrothermal vents: New agents with therapeutic potential. Pathol. Biol. 2004, 52, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guezennec, J.; Herry, J.M.; Kouzayha, A.; Bachere, E.; Mittelman, M.W.; Bellon Fontaine, M.-N. Exopolysaccharides from unusual marine environments inhibit early stages of biofouling. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 66, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körstgens, V.; Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J.; Borchard, W. Influence of calcium ions on the mechanical properties of a model biofilm of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, M.J. Alteromonas rubra sp. nov a new marine antibiotic-producing bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1979, 26, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstrøm, C.; Egan, S.; Franks, A.; McCLoy, S.; Kjelleberg, S. Antifouling activities expressed by marine surface associated Pseudoalteromonas species. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 41, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, M.J.; Flatau, G.N. Antibacterial activity of marine violet-pigmented Alteromonas with special reference to the production of brominated compounds. Can. J. Microbiol. 1976, 22, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, J.P. Bioactive compound synthetic capacity and ecological significance of marine bacterial genus Pseudoalteromonas. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 220–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onbasli, D.; Aslim, B. Determination of antimicrobial activity and production of some metabolites by Pseudomonas aeruginosa B1 and B2 in sugar beet molasses. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 4614–4619. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Naik, M.; Dubey, S.K. Hemolysin, protease, and EPS producing pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila strain An4 shows antibacterial activity against marine bacterial fish pathogens. J. Mar. Biol. 2010, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Jeba Malar, A.; Punitha, S.M.J. Antimicrobial activity of marine bacteria associated with polychaetes. Biores. Bull. 2010, 1, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Moppert, X.; le Costaouec, T.; Raguénès, G.; Simon-Colin, C.; Crassous, P.; Costa, B.; Guezennec, J. Investigation into the uptake of copper, iron and selenium by a highly sulphated bacterial exopolysaccharide isolated from microbial mats. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschatre, M.; Ghillebaert, F.; Guezennec, J.; Simon-Colin, C. Sorption of copper(II) and silver(I) by four bacterial exopolysaccharides. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2013, 171, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guezennec, J.; Simon-Colin, C.; Kouzayha, A.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachere, E. Nucleus Coated with a Film-Forming Coating Having Antibacterial and Cicatrizing Properties and the Method for Obtaining Same. U.S. Patent 20130152865, 20 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guezennec, J.; Pignet, P.; Raguenes, G.; Deslandes, E.; Lijour, Y.; Gentric, E. Preliminary chemical characterization of unusual eubacterial exopolysaccharides of deep-sea origin. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 24, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguénès, G.; Peres, A.; Ruimy, R.; Pignet, P.; Christen, R.; Loaec, M.; Rougeaux, H.; Barbier, G.; Guezennec, J. Alteromonas infernus sp. nov, a new polysaccharide producing bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1997, 82, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperstad, S.V.; Haug, T.; Blenck, H.-M.; Styrvold, O.B.; Li, C.; Stensvag, K. Antimicrobial peptides from marine invertebrates: Challenges and perspectives in marine antimicrobial peptide discovery. Biotech. Adv. 2011, 29, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Furunaka, H.; Miyata, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Muta, T.; Iwanaga, S.; Niwa, M.; Takao, T.; Shimonishi, Y. Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). Isolation and chemical structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 263, 16709–16713. [Google Scholar]
- Muta, T.; Iwanaga, S. Tachyplesin and anti-lipopolysaccharide factor. Methods Mol. Biol. 1997, 78, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morvan, A.; Iwanaga, S.; Comps, M.; Bachere, E. In vitro activity of the limulus antimicrobial peptide Tachyplesin I on marine bivalve pathogens. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1997, 69, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destoumieux, D.; Bulet, P.; Loew, D.; van Dorsselaer, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Bachère, E. Penaeidins: A new family of antimicrobial peptides isolated from the shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Decapoda). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28398–28406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niidome, T.; Tsuiki, M.; Tokunaga, Y.; Hatakeyama, T.; Aoyagi, H. Antibacterial activity of Arg/Pro-rich bactenecin 5 model peptides and their interaction with phospholipid membranes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 73, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guezennec, J.; Simon-Colin, C.; Kouzayha, A.; Bachere, E. Nucleus Covered with PHA. U.S. Patent 20130263793, 10 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simon-Colin, C.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachere, E.; Kouzayha, A.; Saulnier, D.; Gayet, N.; Guezennec, J. Use of Natural Antimicrobial Peptides and Bacterial Biopolymers for Cultured Pearl Production. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3732-3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063732
Simon-Colin C, Gueguen Y, Bachere E, Kouzayha A, Saulnier D, Gayet N, Guezennec J. Use of Natural Antimicrobial Peptides and Bacterial Biopolymers for Cultured Pearl Production. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(6):3732-3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063732
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimon-Colin, Christelle, Yannick Gueguen, Evelyne Bachere, Achraf Kouzayha, Denis Saulnier, Nicolas Gayet, and Jean Guezennec. 2015. "Use of Natural Antimicrobial Peptides and Bacterial Biopolymers for Cultured Pearl Production" Marine Drugs 13, no. 6: 3732-3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063732
APA StyleSimon-Colin, C., Gueguen, Y., Bachere, E., Kouzayha, A., Saulnier, D., Gayet, N., & Guezennec, J. (2015). Use of Natural Antimicrobial Peptides and Bacterial Biopolymers for Cultured Pearl Production. Marine Drugs, 13(6), 3732-3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13063732





