Potential Threats Posed by New or Emerging Marine Biotoxins in UK Waters and Examination of Detection Methodologies Used for Their Control: Cyclic Imines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
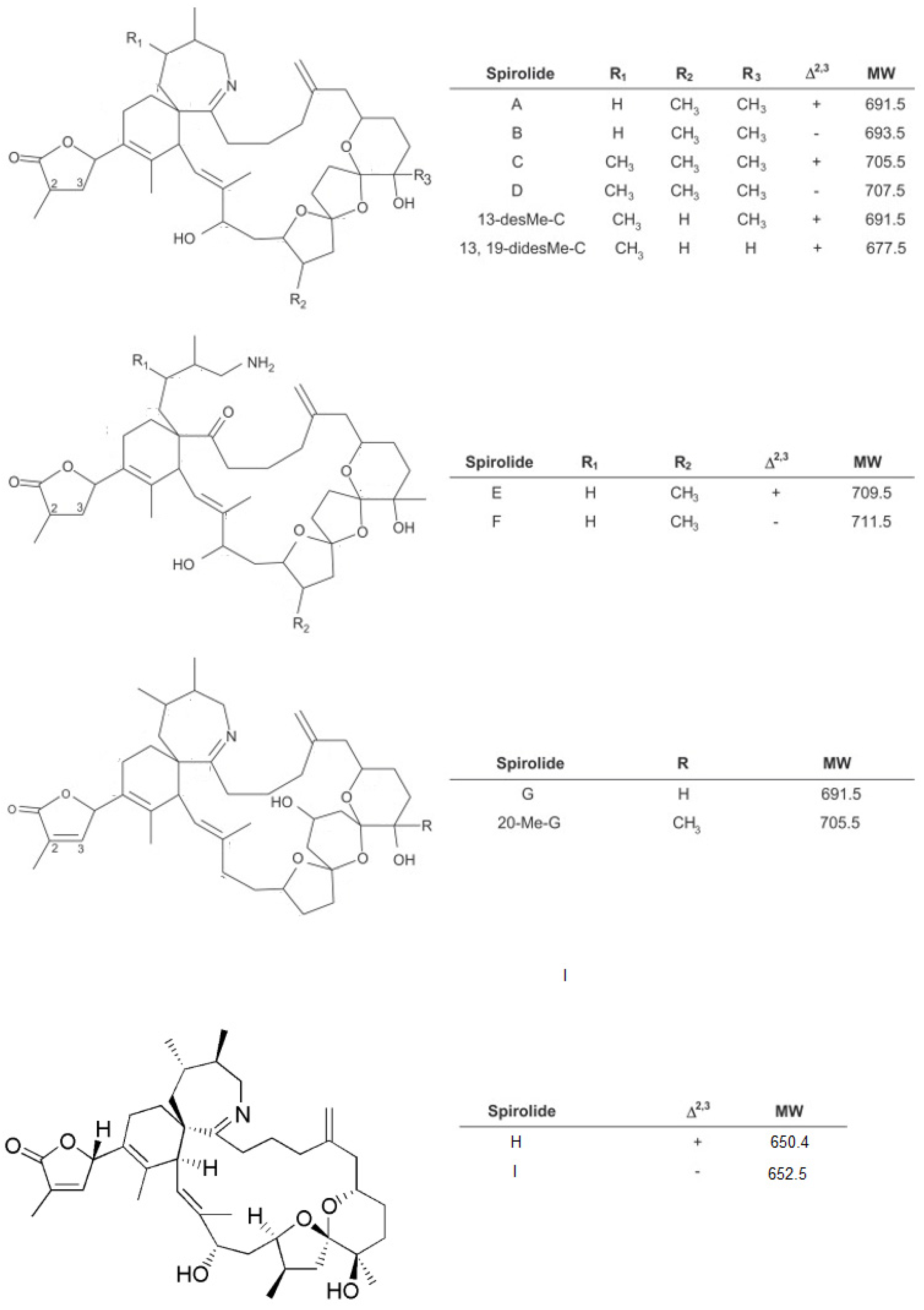
1.1. Spirolides
1.2. Gymnodimines
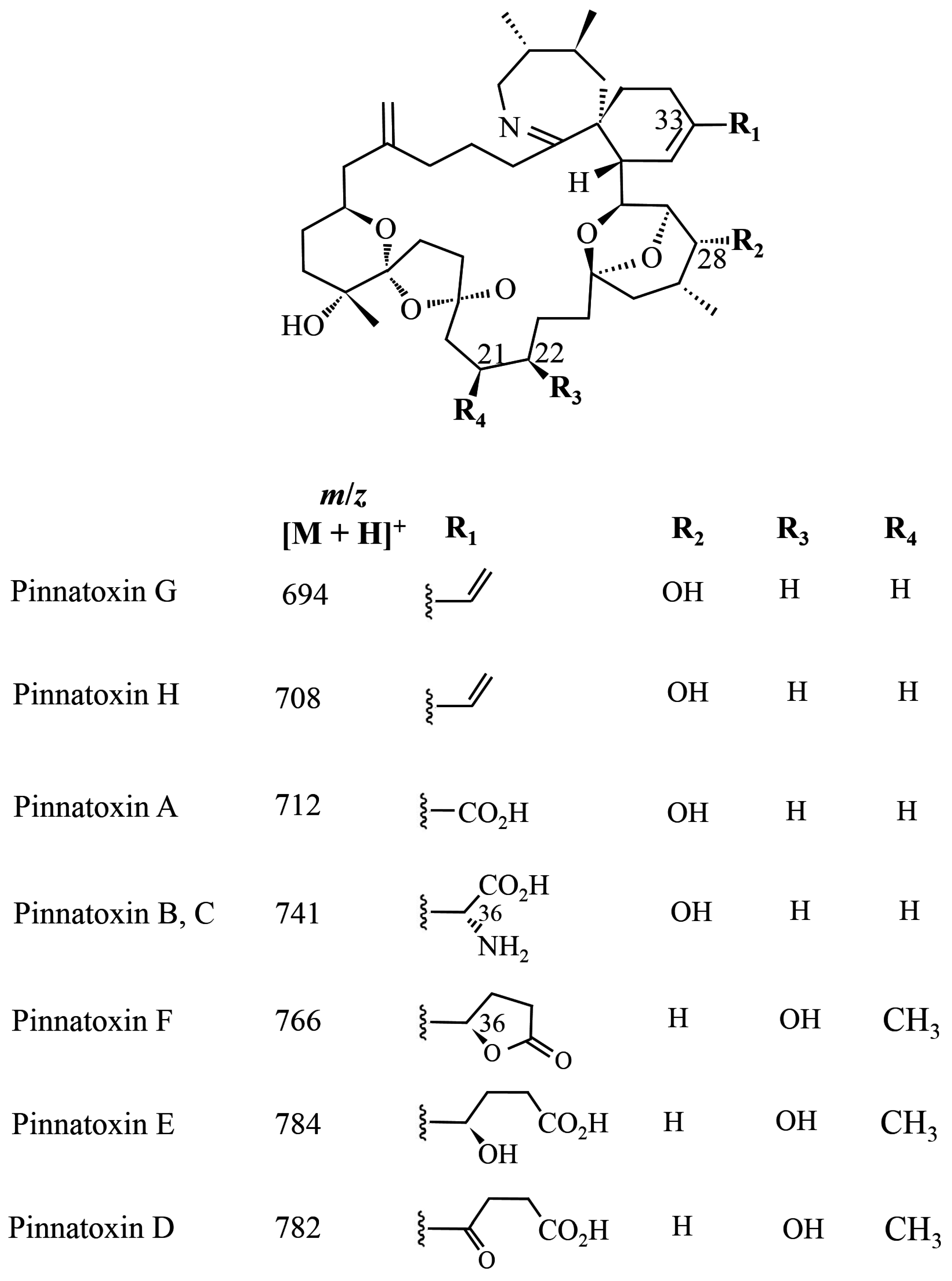
1.3. Pinnatoxins
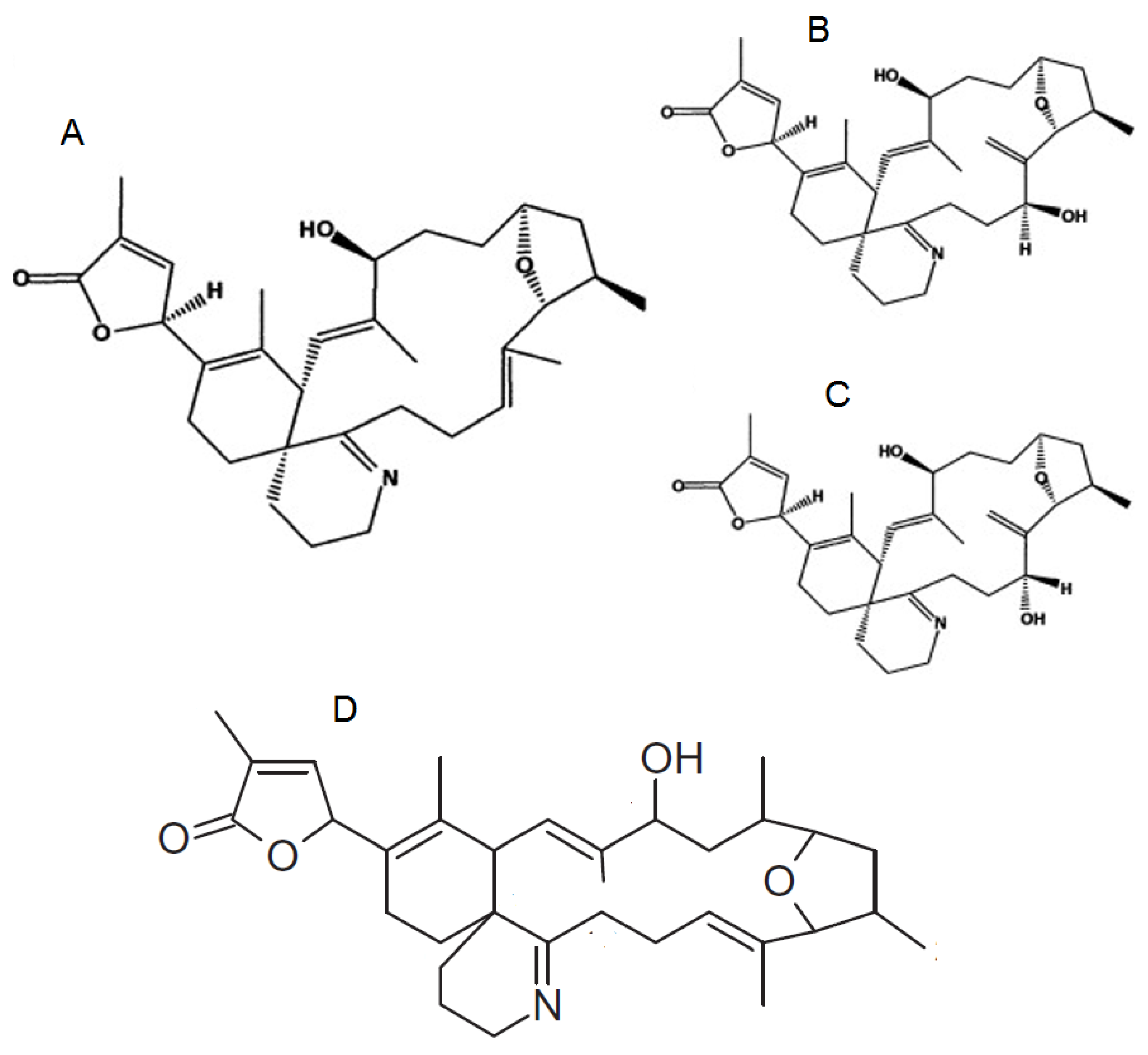
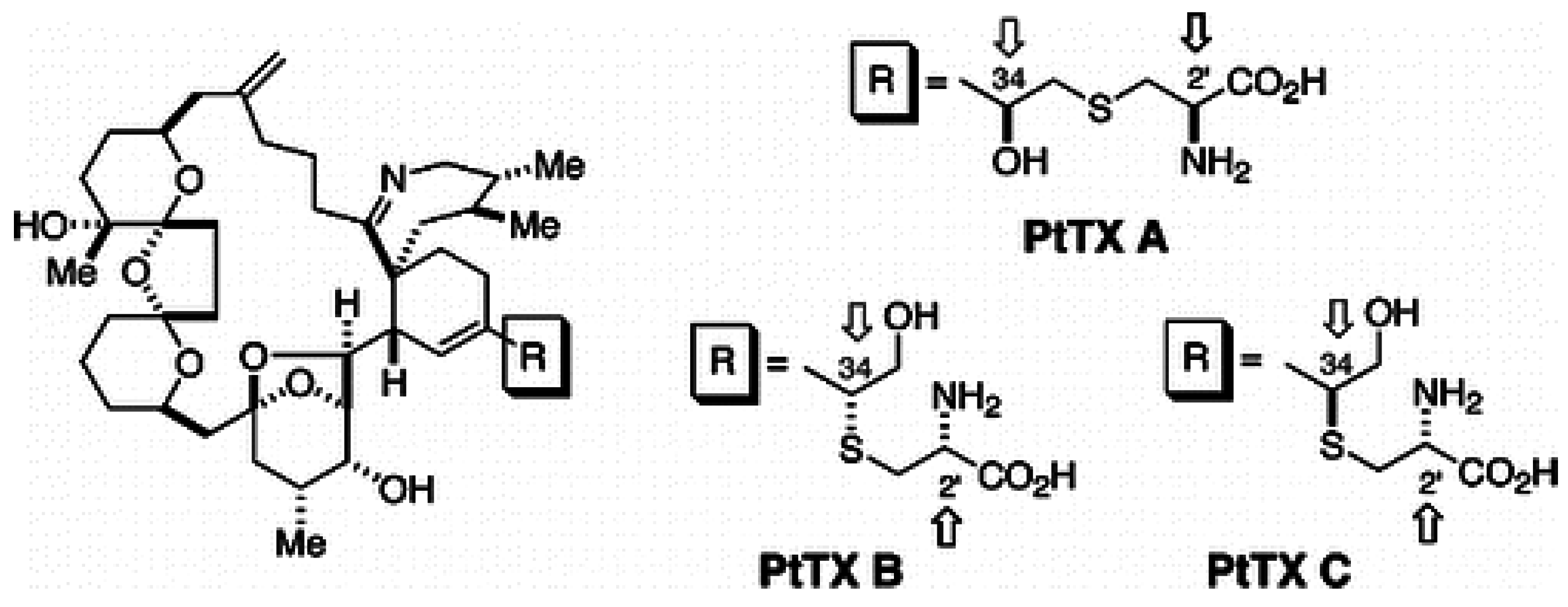
1.4. Pteriatoxins
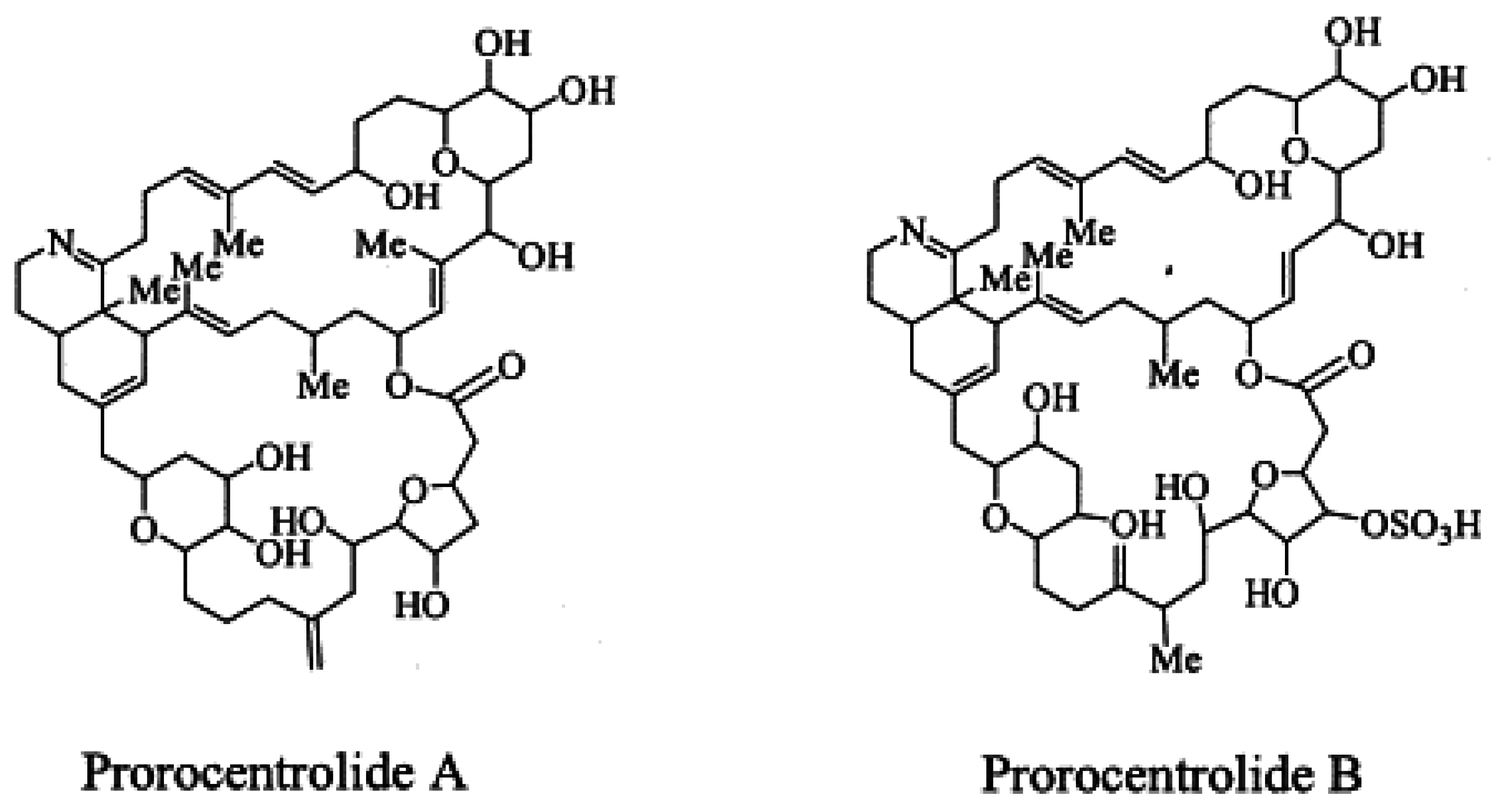
1.5. Prorocentrolides
1.6. Spiro-Prorocentrimine
1.7. Portimine
2. Prevalence of CIs
2.1. Spirolides
2.2. Gymnodimines
2.3. Pinnatoxins
2.4. Pteriatoxins, Prorocentrolides, Spiro-Prorocentrimine
3. Shellfish Accumulation and Depuration
3.1. Spirolides
3.2. Gymnodimines
3.3. Pinnatoxins
4. Potential for Cyclic Imines Becoming Established in the UK
4.1. Alexandrium
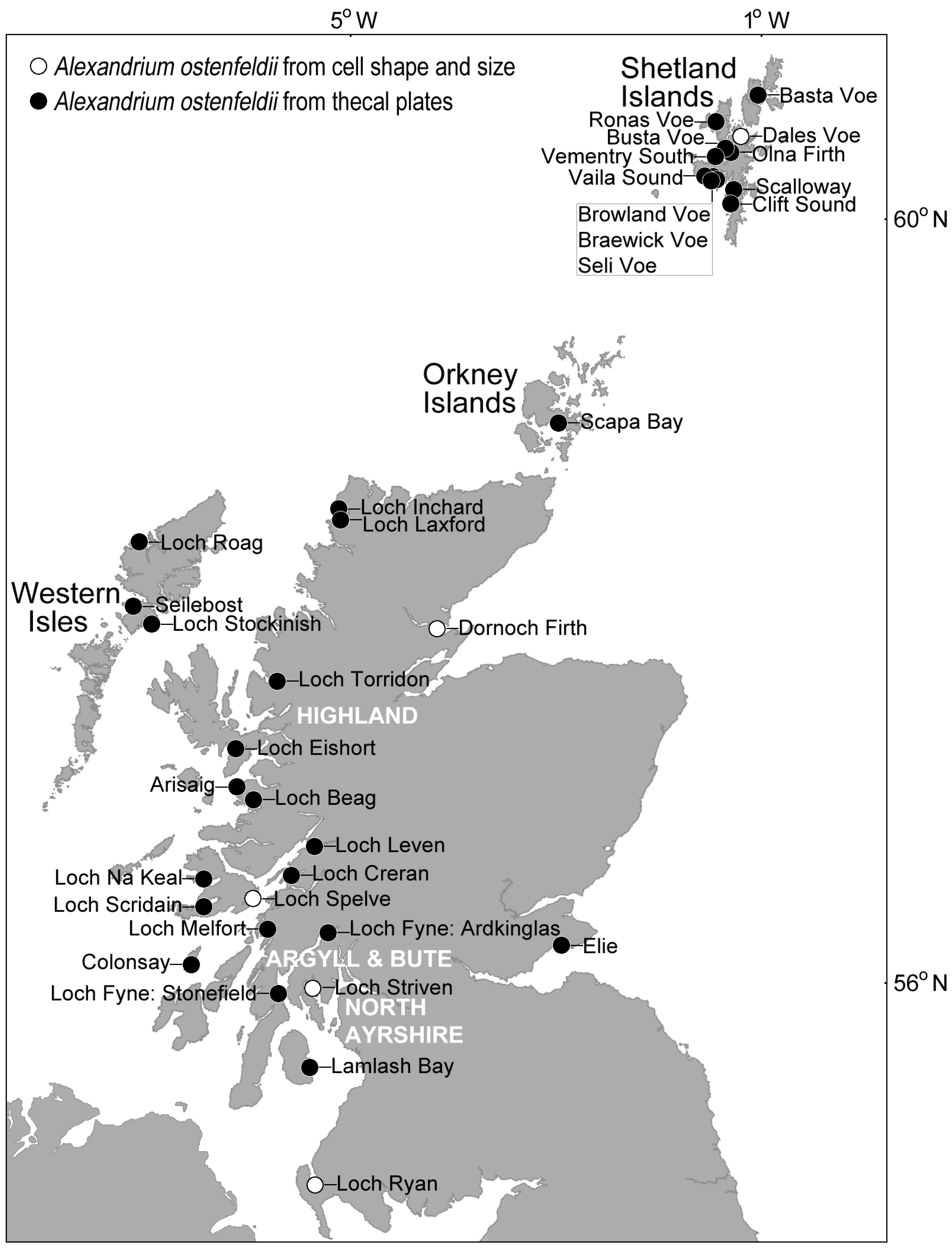
4.2. Other CI Producing Phytoplankton
5. Toxin Testing Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Microscopy |
|
|
| Particle counting methods |
|
|
| Molecular techniques |
|
|
| Mouse bioassay (MBA) |
|
|
| Fluorescence polarization (competitive) |
|
|
| Fluorescence polarization (direct) |
|
|
| Solid-phase receptor-based assays (RBA) |
|
|
| HPLC-UV |
|
|
| LC-MS(MS) |
|
|
5.1. Mouse Bioassays (MBA)
5.2. Bio-Molecular Methods
5.2.1. Fluorescent Polarization (FP)
5.2.2. Solid-Phase Receptor-Based Assay
5.3. Chemical Methods
5.3.1. HPLC
5.3.2. LC-MS Methods
5.4. Suitability of Existing and Potential Methods of CI Analysis
6. Toxicity
6.1. Exposure Assessment
6.2. Toxicokinetics
6.3. Relative Potency of Analogues
7. Conclusions: Summary of Current and Future CI Threats and Options for the Monitoring of Toxins and Their Causative Organisms to Meet Legal Requirements
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cembella, A.D.; Krock, B. Cyclic Imine Toxins: Chemistry, Biogeography, Biosynthesis and Pharmacology, 2nd ed.; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, US, 2008; pp. 561–580. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Oshima, Y.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Watson-Wright, W.M.; Wright, J.L.C. Spirolides B and D, two novel macrocycles isolated from the digestive glands of shellfish. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 2159–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Characterization of biologically inactive spirolides E and F: Identification of the spirolide pharmacophore. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7671–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Satake, M.; MacKenzie, L.; Kaspar, H.F.; Yasumoto, T. Gymnodimine, a new marine toxin of unprecedented structure isolated from New Zealand oysters and the dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 7093–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, D.; Chou, T.; Haino, T.; Nagatsu, A.; Fukuzawa, S.; Zheng, S.; Chen, H. Pinnatoxin A: A toxic amphoteric macrocycle from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1155–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, N.; Umemura, N.; Suenaga, K.; Uemura, D. Structural determination of pteriatoxins A, B and C, extremely potent toxins from the bivalve Pteria penguin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 3495–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torigoe, K.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. Prorocentrolide, a toxic nitrogenous macrocycle from a marine dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum lima. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 7876–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; de Freitas, A.S.; Curtis, J.M.; Oshima, Y.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L. Isolation and structure of prorocentrolide B, a fast-acting toxin from Prorocentrum maculosum. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-K.; Lee, G.-H.; Huang, R.; Chou, H.-N. Spiro-prorocentrimine, a novel macrocyclic lactone from a benthic Prorocentrum sp. of Taiwan. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwood, A.I.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, R.; Shi, F.; Rhodes, L.L.; Holland, P.T. Portimine: A bioactive metabolite from the benthic dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 4705–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Cyclic imines (spirolides, gymnodimines, pinnatoxins and pteriatoxins)/EFSA Panel on contaminants in the food chain (CONTAM)2, 3. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Community Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins (CRLMB). Report on Toxicology Working Group Meeting, Cesenatico, Italy, 24–25 October 2005.
- Pigozzi, S.; Bianchi, L.; Boschetti, L.; Cangini, M.; Ceredi, A.; Magnani, F.; Milandri, A.; Montanari, S.; Pompei, M.; Riccardi, E.; et al. First evidence of spirolide accumulation in Northwestern Adriatic shellfish. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; Moestrup, Ø., Ed.; ISSHA and IOC of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008; pp. 319–322. [Google Scholar]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologia 2000, 39, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. Morphogenetic diversity and biotoxin composition of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) in Irish coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, S.L.; Cembella, A.D.; Quilliam, M.A.; LeBlanc, P.; Lewis, N.I.; Hardstaff, W.R.; Burton, I.W.; Walter, J.A. The characterization of two new spirolides isolated from danish strains of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. In Proceedings of the Xth HAB, International Conference on Harmful Algae 2002, St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 21–25 October 2002; Steidinger, K.A., Landsberg, J.H., Tomas, C.R., Vargo, G.A., Eds.; Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Florida Institute of Oceanography, and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: St. Pete Beach, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 186–188. [Google Scholar]
- Roach, J.S.; Leblanc, P.; Lewis, N.I.; Munday, R.; Quilliam, M.A.; MacKinnon, S.L. Characterization of a dispiroketal spirolide subclass from Alexandrium ostenfeldii. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, J.A.; Hardstaff, W.; Aune, T.; Quilliam, M.A. Discovery of fatty acid ester metabolites of spirolide toxins in mussels from Norway using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucet, E.; Ross, N.N.; Quillam, M.A. Enzymatic hydrolysis of esterified diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins and pectenotoxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, B.; Below, A.; Dreßler, N.; Scheibner, O.; Luckas, B.; Gerdts, G. Are spirolides converted in biological systems?—A Study. Toxicon 2008, 51, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Burton, I.W.; Cembella, A.D.; Curtis, J.M.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Characterization of spirolides A, C, and 13-desmethyl C, new marine toxins isolated from toxic plankton and contaminated shellfish. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, J.; MacKinnon, S.L.; LeBlanc, P.; Walter, J.A.; Hovgaard, P.; Aune, T.; Quilliam, M.A. Detection and identification of spirolides in Norwegian shellfish and plankton. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Grauso, L.; Tartaglione, L.; Guerrini, F.; Pistocchi, R. Spirolide toxin profile of Adriatic Alexandrium ostenfeldii cultures and structure elucidation of 27-hydroxy-13,19-didesmethyl spirolide C. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Iacovo, E.D.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Grauso, L.; Tartaglione, L.; Guerrini, F.; Pezzolesi, L.; Pistocchi, R. Characterization of 27-hydroxy-13-desmethyl spirolide C and 27-oxo-13,19-didesmethyl spirolide C. Further insights into the complex Adriatic Alexandrium ostenfeldii toxin profile. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R. Toxicology of cyclic imines: Gymnodimine, spirolides, pinnatoxins, pteriatoxins, prorocentrolide, spiro-prorocentrimine, and symbioimines. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection, 2nd ed.; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press (Taylor and Francys Group): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 581–594. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.; Murphy, M.; Clausen, J.; Richard, D.; Quilliam, M.; MacKinnon, S.; LaBlanc, P.; Mueller, R.; Pulido, O. Neural injury biomarkers of novel shellfish toxins, spirolides: A pilot study using immunochemical and transcriptional analysis. Neurotoxicology 2003, 24, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, A.J.; Steidinger, K.A.; Truby, E.W.; Bergquist, P.R.; Bergquist, P.L.; Adamson, J.; MacKenzie, L. Comparative morphology and molecular phylogenetic analysis of three new species of the genus Karenia (Dinophyceae) from New Zealand. J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Robinson, W.T.; Hannah, D.J. The absolute stereochemistry of the New Zealand shellfish toxin gymnodimine. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 4889–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Stirling, D.J.; MacKenzie, A.L. New analogue of Gymnodimine from a Gymnodinium species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Stirling, D.J.; MacKenzie, A.L. Gymnodimine C, an isomer of gymnodimine B, from Karenia selliformis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4838–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Naila, I.; Hamza, A.; Gdoura, R.; Diogène, J.; de la Iglesia, P. Prevalence and persistence of gymnodimines in clams from the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia) studied by mouse bioassay and LC-MS/MS. Harmful Algae 2012, 18, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Misner, I.; Tomas, C.R.; Wright, J.L.C. Occurrence of 12-methylgymnodimine in a spirolide-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium peruvianum and the biogenetic implications. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 4243–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrat, R.; Servent, D.; Girard, E.; Ouanounou, G.; Amar, M.; Marrouchi, R.; Benoit, E.; Molgo, J. The marine phycotoxin gymnodimine targets muscular and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes with high affinity. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R.; Towers, N.R.; MacKenzie, L.A.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.T.; Miles, C.O. Acute toxicity of gymnodimine to mice. Toxicon 2004, 44, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.I.; McNabb, P.; van Ginkel, R.; Holland, P.; Munday, R. Production of pinnatoxins by a peridinoid dinoflagellate isolated from Northland, New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezan, E.; Chomerat, N. Vulcanodinium rugosum gen. et sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), un nouveau dinoflagellé marin de la côte méditerranéenne française. Cryptogr. Algol 2011, 32, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.; Osamu, K.; Uemura, D. Relative stereochemistry of pinnatoxin A, a potent shellfish poison from Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 4023–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, N.; Umemura, N.; Suenaga, K.; Chou, T.; Nagatsu, A.; Haino, T.; Yamada, K.; Uemura, D. Pinnatoxins B and C, the most toxic components in the pinnatoxin series from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwood, A.I.; Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; van Ginkel, R.; Munday, R.; Rise, F.; McNabb, P. Isolation and structural determination, and acute toxicity of novel pinnatoxins E, F and G. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6532–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selwood, A.I.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, R.; Gu, H.; Smith, K.F.; Rhodes, L.L.; Rise, F. Pinnatoxin H: A new pinnatoxin analogue from a South China Sea Vulcanodinium rugosum isolate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 5508–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, J.A.; Nagasawa, K.; Lander, P.A.; Mischke, S.G.; Semones, M.A.; Hao, J.; Matsuura, F.; Kishi, Y.; Kita, M.; Uemura, D.; et al. Total synthesis of pinnatoxin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 7647–7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araoz, R.; Servent, D.; Molgo, J.; Iorga, B.I.; Fruchart-Gaillard, C.; Benoit, E.; Gu, Z.; Stivala, C.; Zakarian, A. Total synthesis of pinnatoxins A and G and revision of the mode of action of pinnatoxin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10499–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, F.; Hao, J.L.; Reents, R.; Kishi, Y. Total synthesis and stereochemistry of pinnatoxins B and C. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 3327–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, N.; Gu, H.; Smith, K.F.; Rhodes, L.L.; Selwood, A.I.; Yang, W. The first report of Vulcanodinium rugosum (Dinophyceae) from the South China Sea with a focus on the life cycle. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 46, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundberget, T.; Aasen, J.A.B.; Selwood, A.I.; Miles, C.O. Pinnatoxins and spirolides in Norwegian blue mussels and seawater. Toxicon 2011, 58, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.F.; Munday, R.; Selwood, A.I.; McNabb, P.S.; Holland, P.T.; Bottein, M.-Y. Toxic dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from Rarotonga, Cook Island. Toxicon 2010, 56, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Matsuura, F.; Kishi, Y.; Kita, M.; Uemura, D.; Asai, N.; Iwashita, T. Stereochemistry of Pteriatoxins A, B and C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7742–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R. Toxicology of cyclic imines: Gymnodimine, spirolides, pinnatoxins, pteriatoxins, prorocentrolide, spiro-prorocentrimine, and symbioimines. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection; Botana, L., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sleno, L.; Windust, A.J.; Volmer, D.A. Structural study of spirolide marine toxins by mass spectrometry. Part I. Fragmentation pathways of 13-desmethyl spirolide C by collision-induced dissociation and infrared multiphoton dissociation mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, U.; Cembella, A.; Hummert, C.; Elbrächter, M.; Groben, R.; Medlin, L. Discrimilation of the toxigenic dinoflagellates Alexandrium tamarense and A. ostenfeldii in co-occurring natural populations from Scottish coastal waters. Eur. J. Phycol. 2003, 38, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, K.E.; Keafer, B.A.; Quilliam, M.A.; Cembella, A.D.; Kulis, D.M.; Manahan, A.; Anderson, D.M. Distribution and toxicity of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) in the Gulf of Maine, USA. Deep. Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 2745–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Magno, G.S.; Tartaglione, L.; Grillo, C.; Melchiorrre, N. The Genoa 2005 outbreak. Determination of putative palytoxin in Mediterranean Ostreopsis ovata by a new liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6153–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, P.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Bravo, I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon 2015, 103, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cembella, A.D.; Bauder, A.G.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. Population dynamics and spirolide composition of the toxigenic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii in coastal embayments of Nova Scotia. In Proceedings of the IX International Conference on Harmful Algal Blooms, Hobart, Australia, 7–11 February 2000; Hallegraeff, G.M., Blackburn, S.I., Bolch, C.J.S., Lewis, R.J., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission: Paris, France; pp. 173–176.
- Cembella, A.D.; Bauder, A.G.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. Association of the gonyaulacoid dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii with spirolide toxins in size-fractionated plankton. J. Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruehl, A.; Hummert, C.; Gerdts, G.; Luckas, B. Determination of new algal neurotoxins (spirolides) near the scottish east coast. In Proceedings of the ICES CM 2001/S:09, International Council for the Exploration of the Sea, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4 March–4 April 2001.
- Villar Gonzáles, A.; Rodríguez-Velasco, M.L.; Ben-Gigirey, B.; Botana, L.M. First evidence of spirolides in Spanish shellfish. Toxicon 2006, 48, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amzil, Z.; Sibat, M.; Royer, F.; Masson, N.; Abadie, E. Report on the first detection of pectenotoxin-2, spirolide-A and their derivatives in French shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E.; Avalos, P.; Mariño, C.; Blanco, J. First identification of azaspiracid and spirolides in Mesodesma donacium and Mulinia edulis from Northern Chile. Toxicon 2010, 55, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabb, P.S.; McCoubrey, D.J.; Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.I.; van Ginkel, R.; MacKenzie, A.L.; Munday, R.; Holland, P.T. New perspectives on biotoxin detection in Rangaunu Harbour, New Zealand arising from the discovery of pinnatoxins. Harmful Algae 2012, 13, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yao, J.; Guo, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhai, Y. Distribution of marine lipophilic toxins in shellfish products collected from the chinese market. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4281–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirling, D.J. Survey of historical New Zealand shellfish samples for accumulation of gymnodimine. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2001, 35, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biré, R.; Krys, S.; Fremy, J.M.; Dragacci, S.; Stirling, D.; Kharrat, R. First evidence on occurrence of gymnodimine in clams from Tunisia. J. Nat. Toxins 2002, 11, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marrouchi, R.; Dziri, F.; Belayouni, N.; Hamza, A.; Benoit, E.; Molgo, J.; Kharrat, R. Quantitative determination of gymnodimine-A by high performance liquid chromatography in contaminated clans from Tunisia coastline. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, E.; Yu, Q.; Eaglesham, G.; Connell, D.W.; McBroom, J.; Costanzo, S.; Shaw, G.R. Occurrence and seasonal variations of algal toxins in water, phytoplankton and shellfish from North Stradbroke Island, Queensland, Australia. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 64, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krock, B.; Pitcher, G.C.; Ntuli, J.; Cembella, A.D. Confirmed identification of gymnodimine in oysters from the west coast of South Africa by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 31, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Iglesia, P.; McCarron, P.; Diogene, J.; Quilliam, M.A. Discovery of gymnodimine fatty acid ester metabolites in shellfish using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, C.O.; Rundberget, T.; Sandvik, M.; Aasen, J.A.B.; Selwood, A.I. The Presence of Pinnatoxins in Norwegian Mussels; National Veterinary Institute: Olso, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Medhioub, W.; Lassus, P.; Truquet, P.; Bardouil, M.; Amzil, Z.; Sechet, V.; Sibat, M.; Soudant, P. Spirolide uptake and detoxification by Crassostrea gigas exposed to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Aquaculture 2012, 358–359, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, P.; Abadie, E.; Hervé, F.; Berteaux, T.; Séchet, V.; Aráoz, R.; Molgó, J.; Zakarian, A.; Sibat, M.; Rundberget, T.; et al. Pinnatoxin G is responsible for atypical toxicity in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and clams (Venerupis decussata) from Ingril, a French Mediterranean lagoon. Toxicon 2013, 75, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, P. First report of pinnatoxin in mussels and a novel dinoflagellate, Vulcanodinium rugosum, from France. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Molluscan Shellfish Safety, Charlottetown, PE, Canada, 12–17 June 2011; pp. 12–17.
- García-Altares, M.; Casanova, A.; Bane, V.; Diogène, J.; Furey, A.; de la Iglesia, P. Confirmation of pinnatoxins and spirolides in shellfish and passive samplers from Catalonia (Spain) by liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole and high-resolution hybrid tandem mass spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3706–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, P.; Rourke, W.A.; Hardstaff, W.; Pooley, B.; Quilliam, M.A. Identification of pinnatoxins and discovery of their fatty acid ester metabolites in mussels (Mytilus edulis) from eastern Canada. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jester, R.; Rhodes, L.; Beuzenberg, V. Uptake of paralytic shellfish poisoning and spirolide toxins by paddle crabs (Ovalipes catharus) via a bivalve vector. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, L.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Beuzenberg, V.; Selwood, A.; Suzuki, T. Complex toxin profiles in phytoplankton and Greenshell mussels (Perna canliculus), revealed by LC-MS/MS analysis. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhioub, W.; Ghéguen, M.; Lassus, P.; Bardouil, M.; Truquet, P.; Sibat, M.; Medhioub, N.; Soudant, P.; Kraiem, M.; Amzil, Z. Detoxification enhancement in the gymnodimine-contaminated grooved carpet shell, Ruditapes decussatus (Linné). Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Munday, R.; Hallegraeff, G.M.; Selwood, A.; Molenaar, S.; McNabb, P.; Adamson, J.; Wilkinson, C. Potency of pinnatoxins produced by dinoflagellates isolated from New Zealand and South Australia. In International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO 2013, Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Hersonissos, Greece, 1–5 November 2012; Pagou, P., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; pp. 209–211.
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Magno, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Cangini, M.; Pompei, M.; Guerrini, F.; Boni, L.; Pistocchi, R. Toxin profile of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) from the Northern Adriatic Sea revealed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2006, 47, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.; Bresnan, E.; Graham, J.; Lacaze, J.-P.; Turrell, E.; Colins, C. Distribution, diversity and toxin composition of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) in Scottish waters. Eur. J. Phycol. 2010, 45, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.M.; Paz, B.; Riobo, P.; Pizarro, G.; Figueroa, R.; Fraga, S.; Bravo, I. First report of the production of spirolides by Alexandrium peruvianum (Dinophyceae) from the mediterranean sea. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Copenhagen, Denmark, 4–8 September 2006; p. 174.
- Tomas, C.R.; van Wagoner, R.; Tatters, A.O.; White, K.D.; Hall, S.; Wright, J.L.C. Alexandrium peruvianum (Balech and Mendiola) Balech and Tangen a new toxic species for coastal North Carolina. Harmful Algae 2012, 17, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suikkanen, S.; Kremp, A.; Hautala, H.; Krock, B. Paralytic shellfish toxins or spirolides? The role of environmental and genetic factors in toxin production of the Alexandrium ostenfeldii complex. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Stubbs, B.; Coates, L.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Hatfield, R.G.; Lewis, A.M.; Rowland-Pilgrim, S.; O’Neil, A.; Stubbs, P.; Ross, S.; et al. Variability of paralytic shellfish toxin occurrence and profiles in bivalve molluscs from Great Britain from official control monitoring as determined by pre-column oxidation liquid chromatography and implications for applying immunochemical tests. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utermöhl, H. Neue Wege in der quantitativen Erfassung des Planktons (mit besonderer Berucksichtigung des Ultraplanktons). Verh. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1931, 5, 567–596. [Google Scholar]
- Touzet, N.; Farrell, H.; Ní Rathaille, A.; Rodriguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M.; Raine, R. Dynamics of co-occurring Alexandrium minutum (Global Clade) and A. tamarense (West European) (Dinophyceae) during a summer bloom in Cork Harbour, Ireland (2006). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Davidson, K.; Pete, R.; Flanagan, K.; McCoy, G.R.; Amzil, Z.; Maher, M.; Chapelle, A.; Raine, R. Co-occurrence of the West European (Gr.III) and North American (Gr.I) ribotypes of Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae) in Shetland, Scotland. Protist 2010, 161, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balech, E. The Genus Alexandrium Halim (Dinoflagellata); Sherkin Island Marine Station: Sherkin Island, Co. Cork, Ireland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Balech, E.; Tangen, K. Morphology and taxonomy of toxic species in the tamarensis group (Dinophyceae): Alexandrium excavatum (Braarud) comb. nov. and Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Paulsen) comb. nov. Sarsia 1985, 70, 333–343. [Google Scholar]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. PSP toxin analysis and discrimination of the naturally co-occurring Alexandrium tamarense and A. minutum in Cork Harbour, Ireland. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 51, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremp, A.; Tahvanainen, P.; Litaker, W.; Krock, B.; Suikkanen, S.; Leaw, C.P.; Tomas, C. Phylogenetic relationships, morphological variation, and toxin patterns in the Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) complex: Implications for species boundaries and identities. J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckford-Soper, L.K.; Davidson, K.; Bresnan, E. Identification and quantification of toxic and non-toxic strains of the harmful dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense using fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometry. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2013, 11, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Parenteau, M.; Casas-Monroy, O.; Rochon, A.; Smith, R. Coastal ship traffic: A significant introduction vector for potentially harmful dinoflagellates in eastern Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.; McNabb, P.; Munday, R.; Suda, S.; Molenaar, S.; Hallegraeff, G. Dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum identified as the causative organism of pinnatoxins in Australia, New Zealand and Japan. Phycologia 2011, 50, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, H. Joint FAO/WHO/IOC activities to provide scientific advice on marine biotoxins. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, D.; Arsenault, E.; Cembella, A.D.; Quilliam, M.A. Investigations into the toxicology and pharmacology of spirolides, a novel group of shellfish toxins. In Proceedings of the Harmful Algal Blooms 2000, Habart, Australia, 7–11 February 2000; Hallegraef, G.M., Blackburn, S.I., Bolch, C.J., Lewis, L.R., Eds.; Intergovernmental of Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 383–386. [Google Scholar]
- McCoubrey, D.J. Descriptive Case Study—Pinnatoxin Incidence in Rangaunu Harbour; Aquaculture New Zealand: Nelson, New Zealand, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamaguchi, M. Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoky district. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, R.; Selwood, A.I.; Rhodes, L. Acute toxicity of pinnatoxins E, F and G to mice. Toxicon 2012, 60, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R.; Quilliam, M.A.; LeBlanc, P.; Lewis, N.; Gallant, P.; Sperker, S.A.; Ewart, H.S.; MacKinnon, S.L. Investigations into the toxicology of spirolides, a group of marine phycotoxins. Toxins 2012, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Rodríguez, P.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Cifuentes, J.M.; Bermúdez, R.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Pharmacokinetic and toxicological data of spirolides after oral and intraperitoneal administration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilarino, N.; Fonfria, E.S.; Molgo, J.; Araoz, R.; Botana, L.M. Detection of gymnodimine-A and 13-Desmethyl C spirolides phycotoxins by fluorescence polarization. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2708–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonfria, E.S.; Vilariño, N.; Espiña, B.; Louzao, M.C.; Alvarez, M.; Molgo, J.; Araoz, R.; Botana, L.M. Feasibility of gymnodimine and 13-desmethyl C spirolide detection by fluorescence polarization using a receptor-based assay in shellfish matrixes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 657, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonfría, E.S.; Vilariño, N.; Molgó, J.; Aráoz, R.; Otero, P.; Espiña, B.; Louzao, M.C.; Alvarez, M.; Botana, L.M. Detection of 13,19-didesmethyl C spirolide by fluorescence polarization using Torpedo electrocyte membranes. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 403, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Alfonso, C.; Aráoz, R.; Molgó, J.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. First direct fluorescence polarization assay for the detection and quantification of spirolides in mussel samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 701, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, F.; Kamp, L.; Carpino, J.; Glaze, T.; Faltin, E.; Loftin, K.; Molgó, J.; Aráoz, R. Development and validation of a colorimetric microtiter plate based receptor-binding assays for the determination of freshwater and marine toxins using the nicotinic cholinergic receptor. Toxicon 2014, 91, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.P.; Vilariño, N.; Molgo, J.; Araoz, R.; Antelo, A.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Solid-phase receptor-based assay for the detection of cyclic imines by chemiluminescence, fluorescence or colorimetry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5857–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aráoz, R.; Ramos, S.; Pelissier, F.; Guérineau, V.; Benoit, E.; Vilariño, N.; Botana, L.M.; Zakarian, A.; Molgó, J. Coupling the Torpedo microplate-receptor binding assay with mass spectrometry to detect cyclic imine neurotoxins. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10445–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. Spirolide composition of micro-extracted pooled cells isolated from natural plankton assemblages and from cultures of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-González, A.; Rodríguez-Velasco, M.L.; Ben-Gigirey, B.; Botana, L.M. Lipophilic toxin profile in Galicia (Spain): 2005 toxic episode. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fux, E.; McMillan, D.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Development of an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the detection of lipophilic marine toxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1157, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; McElhinney, M.A.; Mulder, P.P.; Bire, R.; Hess, P.; de Boer, J. Solid phase extraction for removal of matrix effects in lipophilic marine toxin analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.; van Ginkel, R.; Boundy, M.; Harwood, T. Chemical transformation as a detection tool. In Proceedings of the AOAC International Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–15 June 2012.
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.; McElhinney, M.A.; de Boer, J. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of marine lipophilic toxins under alkaline conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.I.; Holland, P.T. Multiresidue method for determination of algal toxins in shellfish: Single-laboratory validation and interlaboratory study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- National Republican Congressional Committee. Certified Reference Materials. Available online: http://www.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/eng/solutions/advisory/crm/biotoxin/list_products.html (accessed on 6 July 2015).
- Molgó, J.; Girard, E.; Benoit, E. Cyclic imines: An insight into this emerging group of bioactive marine toxins. In Phycotoxins: Chemistry and Biochemistry; Botana, L.M., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2007; pp. 319–335. [Google Scholar]
- Molgó, J.; Amar, M.; Araoz, R.; Benoit, E.; Silveira, P.; Schlumberger, S.; Lecardeur, S.; Servent, D. The dinoflagellate toxin 13-Desmethyl Spirolide-C broadly targets muscle and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with high affinity. In Proceedings of the 16th European Section Meeting of the International Society on Toxinology, Leuven, Belgium, 15–19 August 2008.
- Bourne, Y.; Radic, Z.; Aráoz, R.; Talley, T.T.; Benoit, E.; Servent, D.; Taylor, P.; Molgó, J.; Marchot, P. Structural determinants in phycotoxins and AChBP conferring high affinity binding and nicotinic AChR antagonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araoz, R.; Ouanounou, G.; Iorga, B.I.; Goudet, A.; Alili, D.; Amar, M.; Benoit, E.; Molgo, J.; Servent, D. The neurotoxic effect of 13,19-didesmethyl and 13-desmethyl spirolide C phycotoxins is mainly mediated by nicotinic rather than muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espiña, B.; Otero, P.; Louzao, M.C.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M. 13-Desmethyl spirolide C and 13,19-didesmethyl spirolide C trans-epithelial permeabilities: Human intestinal permeability modelling. Toxicology 2011, 287, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, E.; Otero, P.; Vale, C.; Alfonso, A.; Antelo, A.; Gimenez-Llort, L.; Chabaud, L.; Guillou, C.; Botana, L.M. Benefit of 13-desmethyl spirolide C treatment in triple transgenic mouse model of alzheimer disease: β-amyloid and neuronal markers improvement. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2013, 10, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davidson, K.; Baker, C.; Higgins, C.; Higman, W.; Swan, S.; Veszelovszki, A.; Turner, A.D. Potential Threats Posed by New or Emerging Marine Biotoxins in UK Waters and Examination of Detection Methodologies Used for Their Control: Cyclic Imines. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7087-7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127057
Davidson K, Baker C, Higgins C, Higman W, Swan S, Veszelovszki A, Turner AD. Potential Threats Posed by New or Emerging Marine Biotoxins in UK Waters and Examination of Detection Methodologies Used for Their Control: Cyclic Imines. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(12):7087-7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127057
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavidson, Keith, Clothilde Baker, Cowan Higgins, Wendy Higman, Sarah Swan, Andrea Veszelovszki, and Andrew D. Turner. 2015. "Potential Threats Posed by New or Emerging Marine Biotoxins in UK Waters and Examination of Detection Methodologies Used for Their Control: Cyclic Imines" Marine Drugs 13, no. 12: 7087-7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127057
APA StyleDavidson, K., Baker, C., Higgins, C., Higman, W., Swan, S., Veszelovszki, A., & Turner, A. D. (2015). Potential Threats Posed by New or Emerging Marine Biotoxins in UK Waters and Examination of Detection Methodologies Used for Their Control: Cyclic Imines. Marine Drugs, 13(12), 7087-7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127057