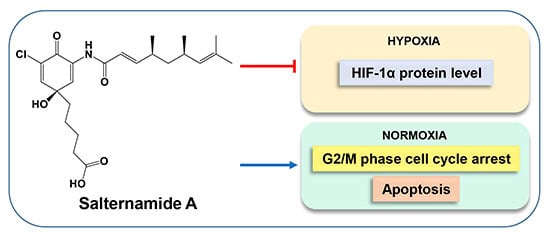
Salternamide A Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Accumulation of HIF-1α and Induces Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Salternamide A Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced HIF-1α Protein Accumulation in Various Cancer Cells
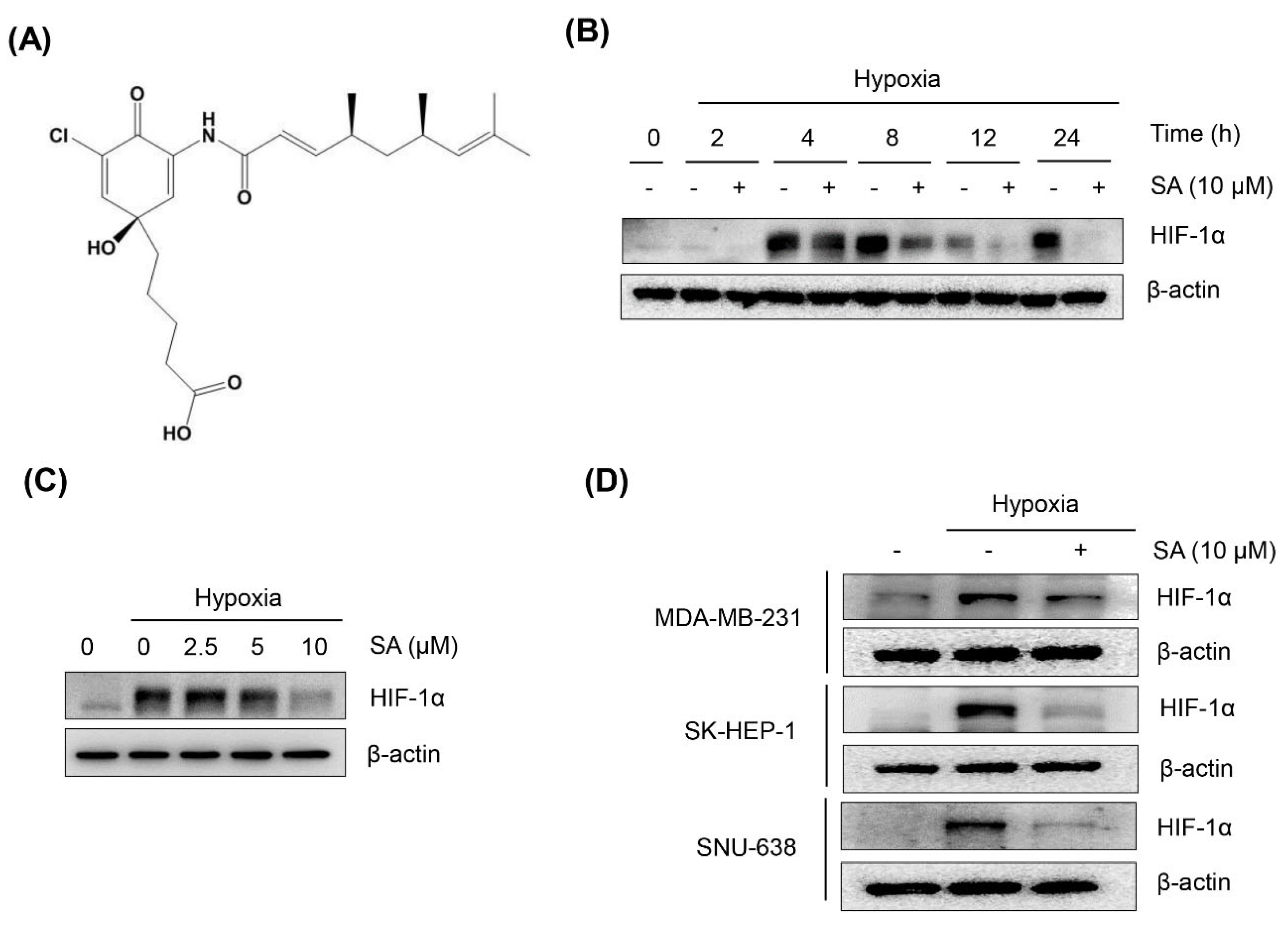
2.2. Suppression of HIF-1α Accumulation by Salternamide A in HCT116 Cells Is Independent of Proteasomal Degradation

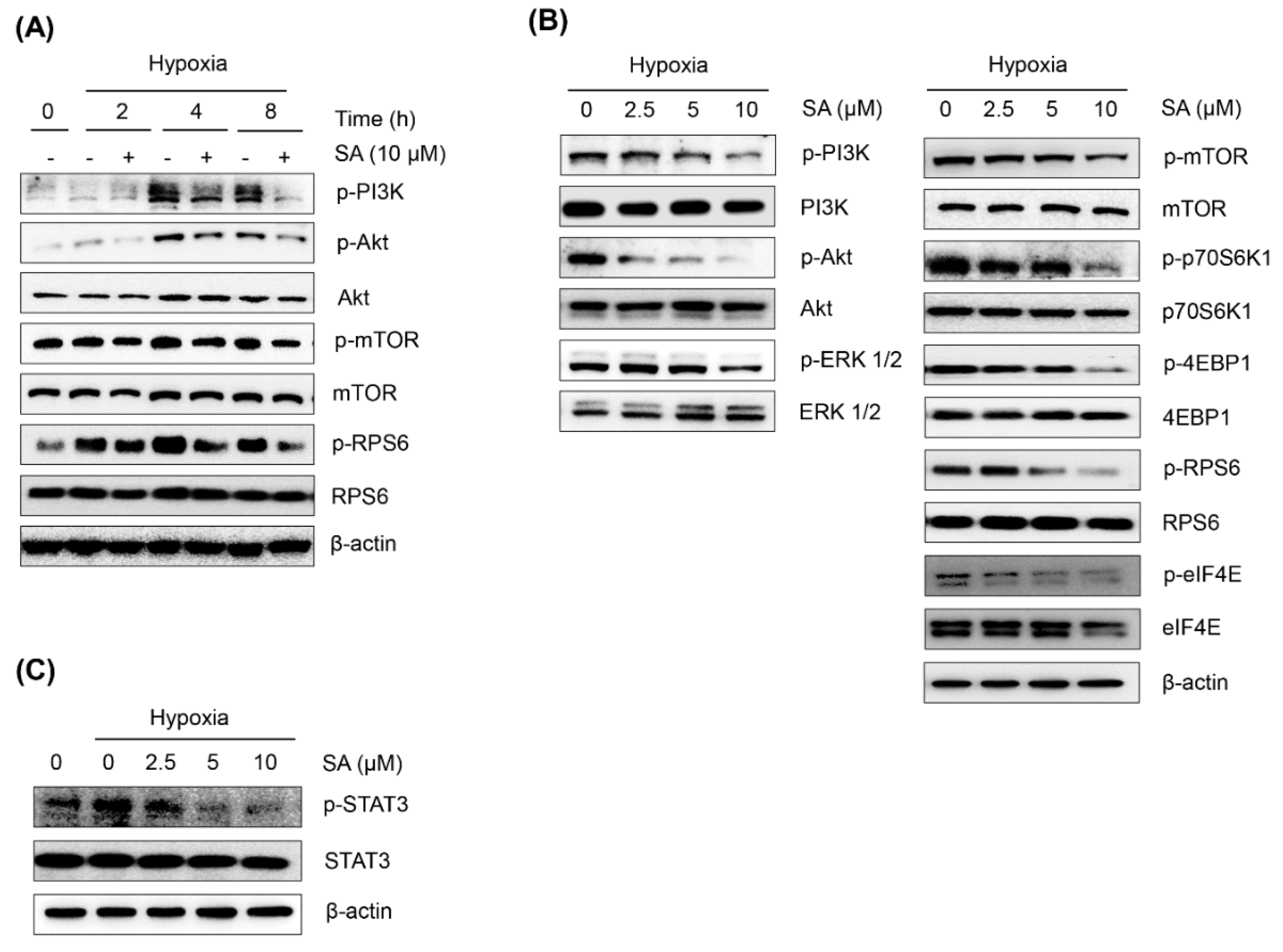
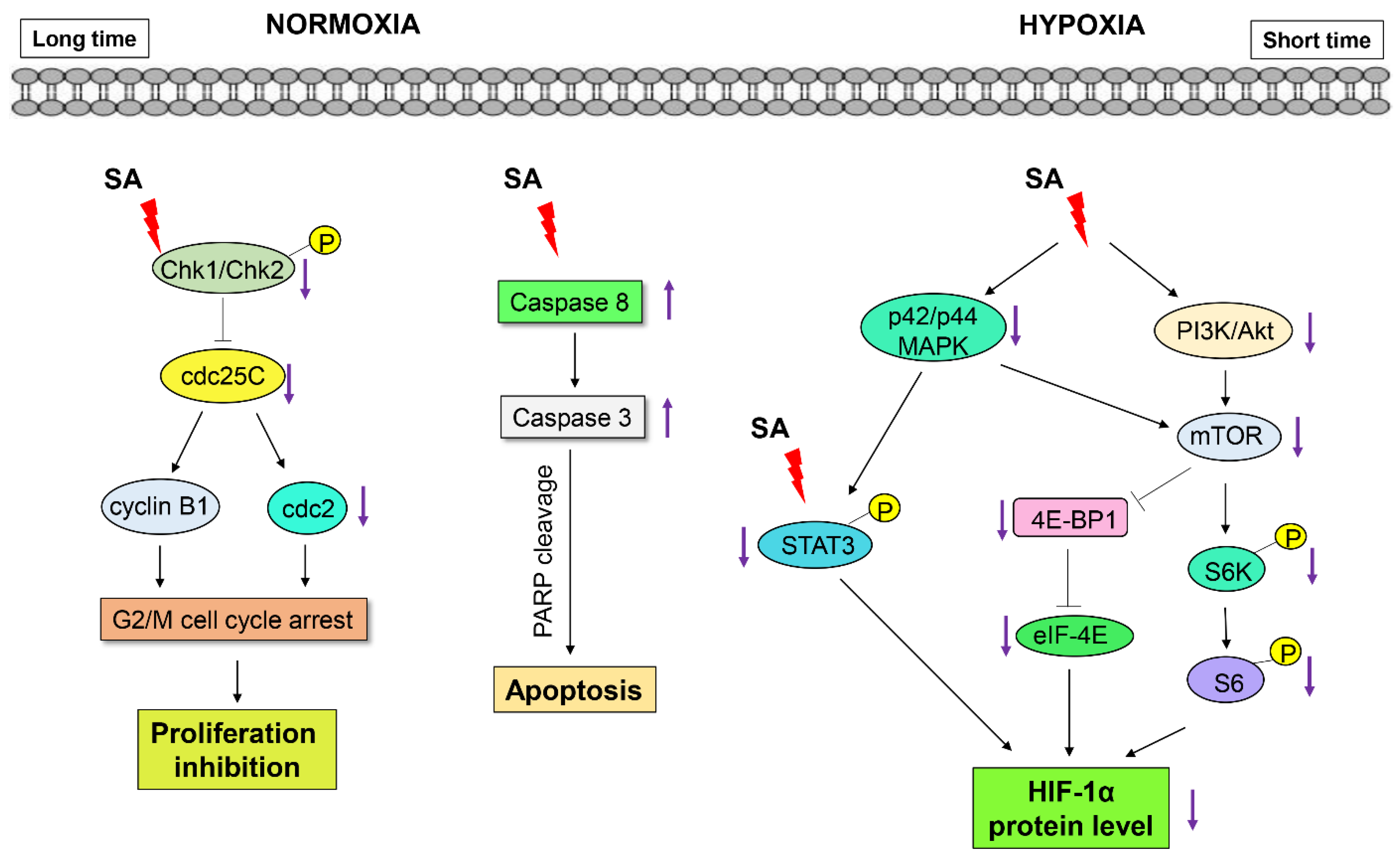
2.3. Salternamide A Suppresses the Hypoxia-Induced Accumulation of HIF-1α via the Regulation of Signal Transduction Pathways
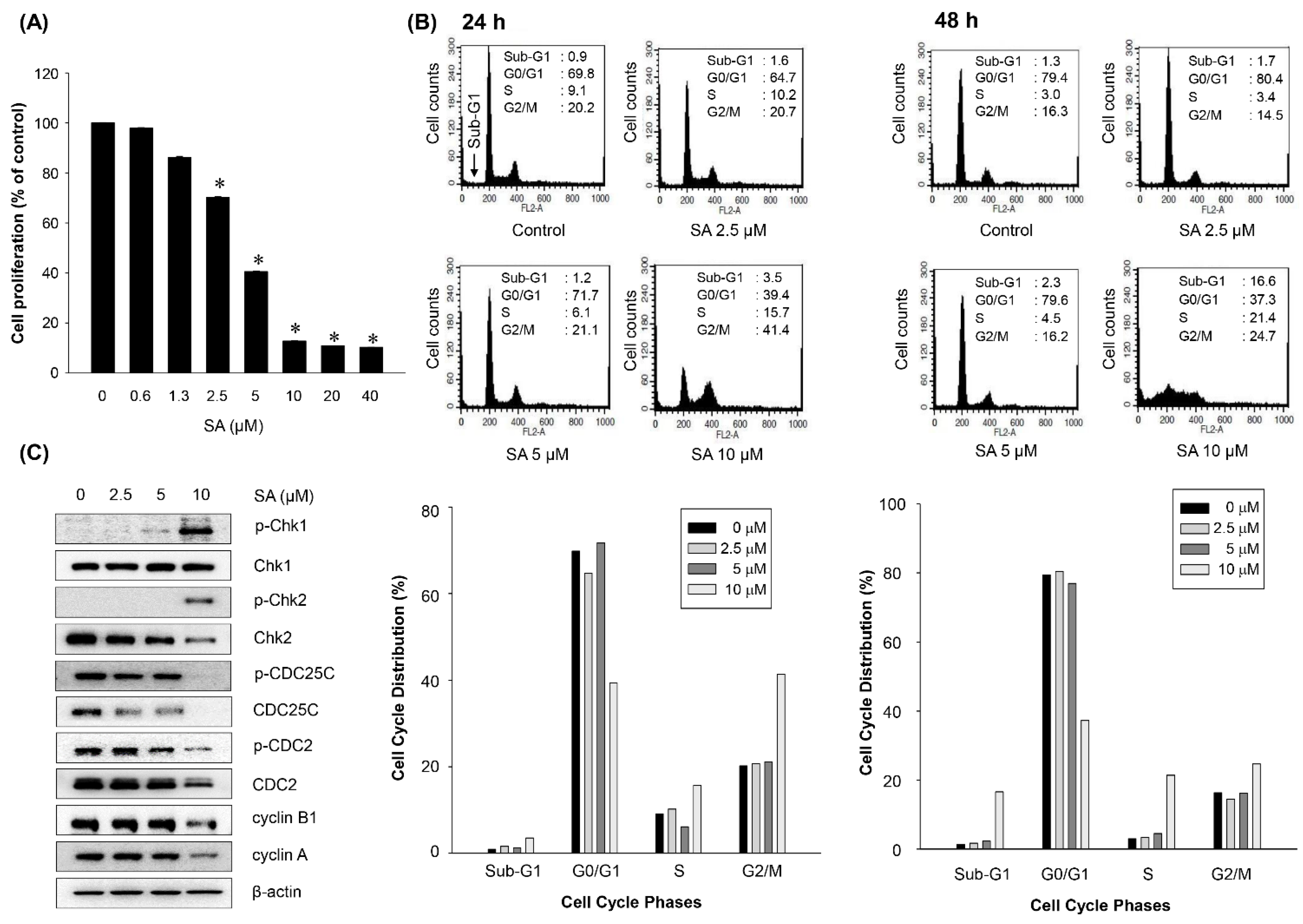
2.4. Salternamide A Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
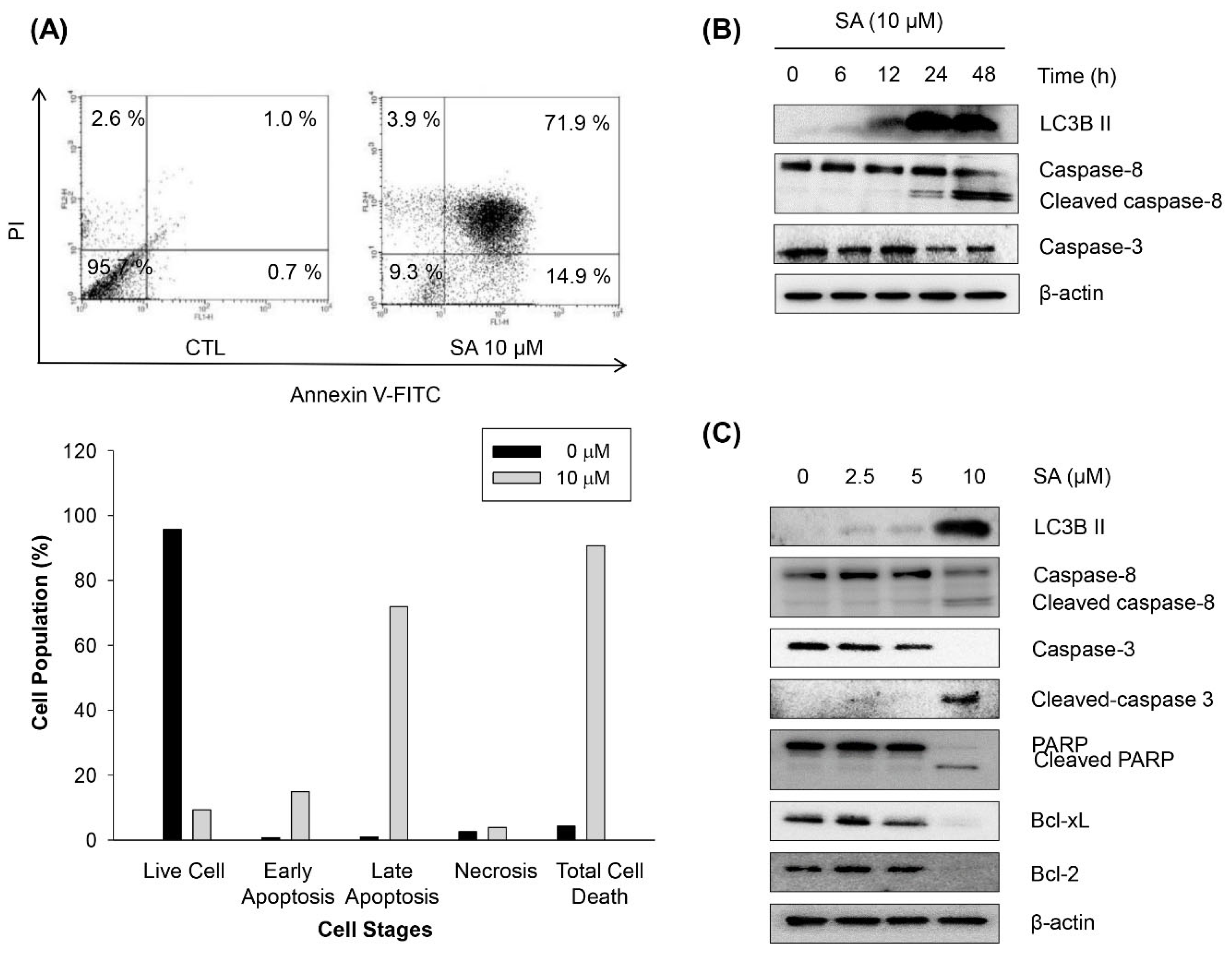
2.5. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Sulforhodamine B Assay
3.4. Flow Cytometry for Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Analysis
3.5. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Reverse Transcript-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
3.6. Western Blot Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Feldser, D.; Agani, F.; Iyer, N.V.; Pak, B.; Ferreira, G.; Semenza, G.L. Reciprocal positive regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and insulin-like growth factor 2. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 3915–3918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krishnamachary, B.; Berg-Dixon, S.; Kelly, B.; Agani, F.; Feldser, D.; Ferreira, G.; LaRusch, J.; Iyer, N.; Pak, B.; Taghavi, P.; et al. Regulation of colon carcinoma cell invasion by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: Role of the HIF system. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Pore, N.; Behrooz, A.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Maity, A. Regulation of glut1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9519–9525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L.; Shimoda, L.A.; Prabhakar, N.R. Regulation of gene expression by HIF-1. Novartis Found. Symp. 2006, 272, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; de Marzo, A.M.; Laughner, E.; Lim, M.; Hilton, D.A.; Zagzag, D.; Buechler, P.; Isaacs, W.B.; Semenza, G.L.; Simons, J.W. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5830–5835. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Talks, K.L.; Turley, H.; Gatter, K.C.; Maxwell, P.H.; Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Harris, A.L. The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 and human disease: One highly involved factor. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1983–1991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Chiles, K.; Feldser, D.; Laughner, E.; Hanrahan, C.; Georgescu, M.M.; Simons, J.W.; Semenza, G.L. Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: Implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richard, D.E.; Berra, E.; Gothie, E.; Roux, D.; Pouyssegur, J. p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32631–32637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, N.; Stiehl, D.P.; Bohensky, J.; Leshchinsky, I.; Srinivas, V.; Caro, J. MAPK signaling up-regulates the activity of hypoxia-inducible factors by its effects on p300. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14013–14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee Koh, M.; Spivak-Kroizman, T.R.; Powis, G. HIF-1 regulation: Not so easy come, easy go. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.E.; Lee, H.G.; Cho, I.H.; Chung, D.H.; Yoon, S.H.; Yang, Y.M.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, S.; Park, J.W.; Ye, S.K.; et al. STAT3 is a potential modulator of HIF-1-mediated VEGF expression in human renal carcinoma cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, C.S.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, Y.N.; Kang, G.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Juhnn, Y.S.; Kim, S.J.; Park, J.W.; et al. STAT3 inhibits the degradation of HIF-1alpha by pVHL-mediated ubiquitination. Exp. Mol. Med. 2008, 40, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, K.B.; Lee, S.K.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.C. Salternamides A-D from a Halophilic Streptomyces sp. Actinobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, L.O.; Friedler, A.; Freund, S.; Rudiger, S.; Fersht, A.R. Two sequence motifs from HIF-1alpha bind to the DNA-binding site of p53. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10305–10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creighton-Gutteridge, M.; Cardellina, J.H., 2nd; Stephen, A.G.; Rapisarda, A.; Uranchimeg, B.; Hite, K.; Denny, W.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Melillo, G. Cell type-specific, topoisomerase II-dependent inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein accumulation by NSC 644221. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.V.; Baek, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Diez, R.; Cole, R.N.; Semenza, G.L. RACK1 competes with HSP90 for binding to HIF-1alpha and is required for O(2)-independent and HSP90 inhibitor-induced degradation of HIF-1alpha. Mol. Cell 2007, 25, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zundel, W.; Schindler, C.; Haas-Kogan, D.; Koong, A.; Kaper, F.; Chen, E.; Gottschalk, A.R.; Ryan, H.E.; Johnson, R.S.; Jefferson, A.B.; et al. Loss of PTEN facilitates HIF-1-mediated gene expression. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noman, M.Z.; Buart, S.; van Pelt, J.; Richon, C.; Hasmim, M.; Leleu, N.; Suchorska, W.M.; Jalil, A.; Lecluse, Y.; el Hage, F.; et al. The cooperative induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and STAT3 during hypoxia induced an impairment of tumor susceptibility to CTL-mediated cell lysis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3510–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlus, M.R.; Wang, L.; Hu, C.J. STAT3 and HIF1alpha cooperatively activate HIF1 target genes in MDA-MB-231 and RCC4 cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.; Kuzontkoski, P.M.; Groopman, J.E.; Prasad, A. Cannabidiol induces programmed cell death in breast cancer cells by coordinating the cross-talk between apoptosis and autophagy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, F.A.; Rathmell, W.K.; Arsham, A.M.; Gnarra, J.; Keith, B.; Simon, M.C. Loss of pVHL is sufficient to cause HIF dysregulation in primary cells but does not promote tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranchie, J.K.; Vasselli, J.R.; Riss, J.; Bonifacino, J.S.; Linehan, W.M.; Klausner, R.D. The contribution of VHL substrate binding and HIF1-alpha to the phenotype of VHL loss in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Beucken, T.; Koritzinsky, M.; Wouters, B.G. Translational control of gene expression during hypoxia. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, G.; Briggs, J.; Deng, J.; Ma, Y.; Lee, H.; Kortylewski, M.; Kujawski, M.; Kay, H.; Cress, W.D.; Jove, R.; et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha RNA expression in both tumor cells and tumor-associated myeloid cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlus, M.R.; Wang, L.; Murakami, A.; Dai, G.; Hu, C.J. STAT3 or USF2 contributes to HIF target gene specificity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.W.; Ko, S.W.; Tsai, H.Y.; Chung, J.G.; Chiang, J.H.; Chen, K.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, J.S. Cantharidin induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer colo 205 cells through inhibition of CDK1 activity and caspase-dependent signaling pathways. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doree, M.; Galas, S. The cyclin-dependent protein kinases and the control of cell division. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Graves, P.R.; Thoma, R.S.; Wu, Z.; Shaw, A.S.; Piwnica-Worms, H. Mitotic and G2 checkpoint control: Regulation of 14-3-3 protein binding by phosphorylation of Cdc25C on serine-216. Science 1997, 277, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Grant, S. New insights into checkpoint kinase 1 in the DNA damage response signaling network. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarzadeh, E.; Sandoghchian Shotorbani, S.; Baradaran, B. Herbal medicine as inducers of apoptosis in cancer treatment. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gump, J.M.; Thorburn, A. Autophagy and apoptosis: What is the connection? Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livesey, K.M.; Kang, R.; Vernon, P.; Buchser, W.; Loughran, P.; Watkins, S.C.; Zhang, L.; Manfredi, J.J.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Li, L.; et al. p53/HMGB1 complexes regulate autophagy and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bach, D.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Hong, J.-Y.; Park, H.J.; Oh, D.-C.; Lee, S.K. Salternamide A Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Accumulation of HIF-1α and Induces Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6962-6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116962
Bach D-H, Kim S-H, Hong J-Y, Park HJ, Oh D-C, Lee SK. Salternamide A Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Accumulation of HIF-1α and Induces Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(11):6962-6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116962
Chicago/Turabian StyleBach, Duc-Hiep, Seong-Hwan Kim, Ji-Young Hong, Hyen Joo Park, Dong-Chan Oh, and Sang Kook Lee. 2015. "Salternamide A Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Accumulation of HIF-1α and Induces Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells" Marine Drugs 13, no. 11: 6962-6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116962
APA StyleBach, D.-H., Kim, S.-H., Hong, J.-Y., Park, H. J., Oh, D.-C., & Lee, S. K. (2015). Salternamide A Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Accumulation of HIF-1α and Induces Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs, 13(11), 6962-6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116962