Chronic Toxicity Study of Neosaxitoxin in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
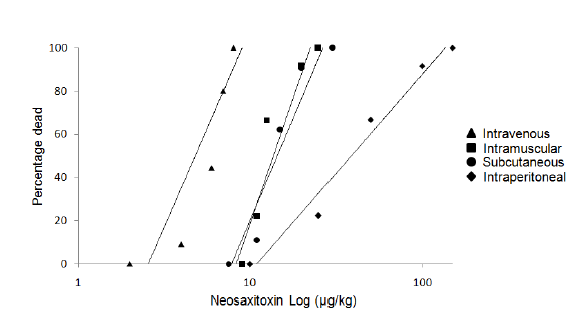
2.1. Acute Toxicity, Physical and Clinical Observations
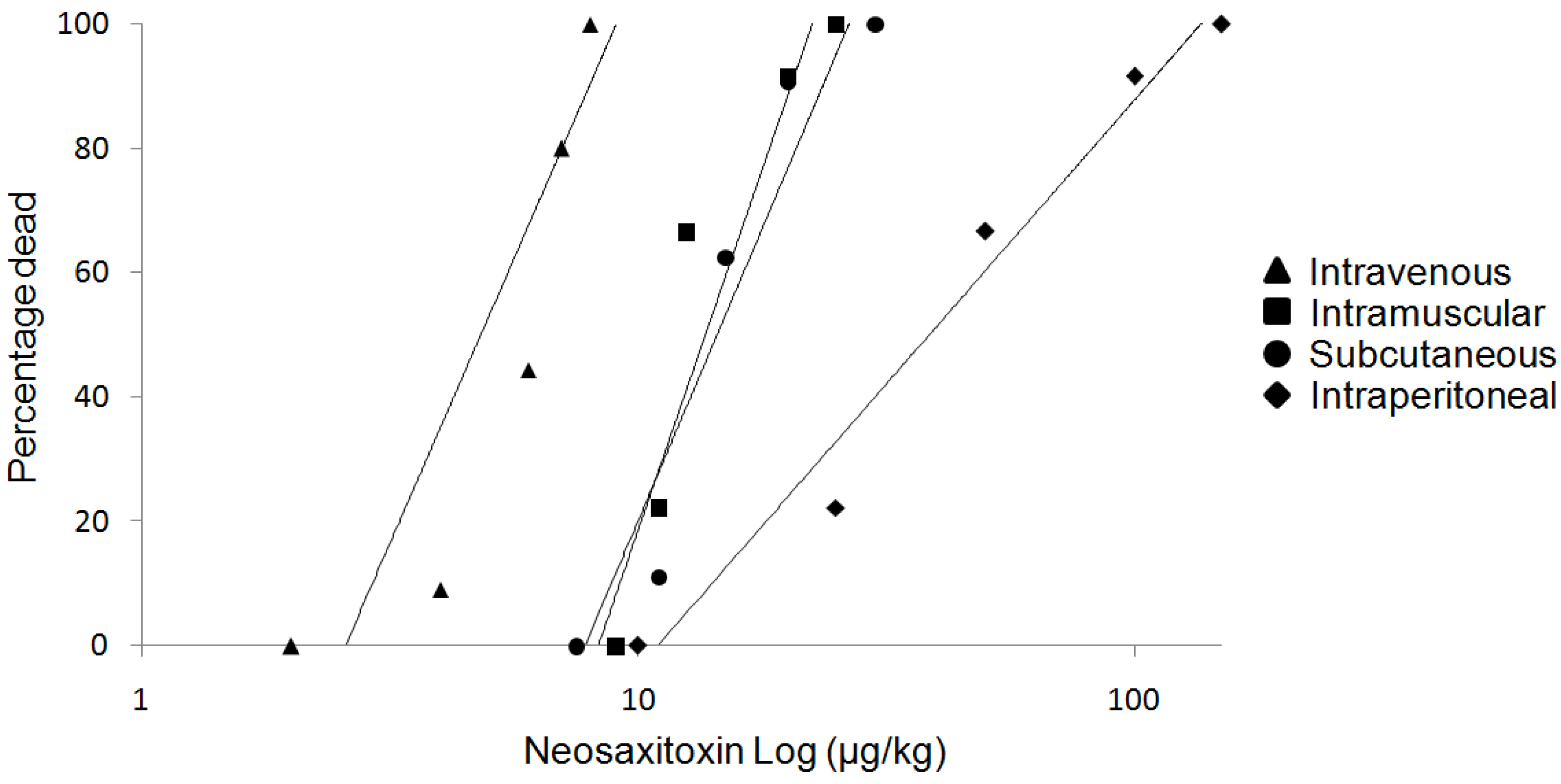
| Intravenous | Intramuscular | Subcutaneous | Intraperitoneal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD50 (μg/kg) | 6.06 | 11.4 | 12.41 | 30.35 |
| Upper 95% CL | 8.14 | 13.69 | 16.15 | 46.51 |
| Lower 95% CL | 4.51 | 9.49 | 9.55 | 19.81 |
2.2. Plasmatic Concentration of NeoSTX
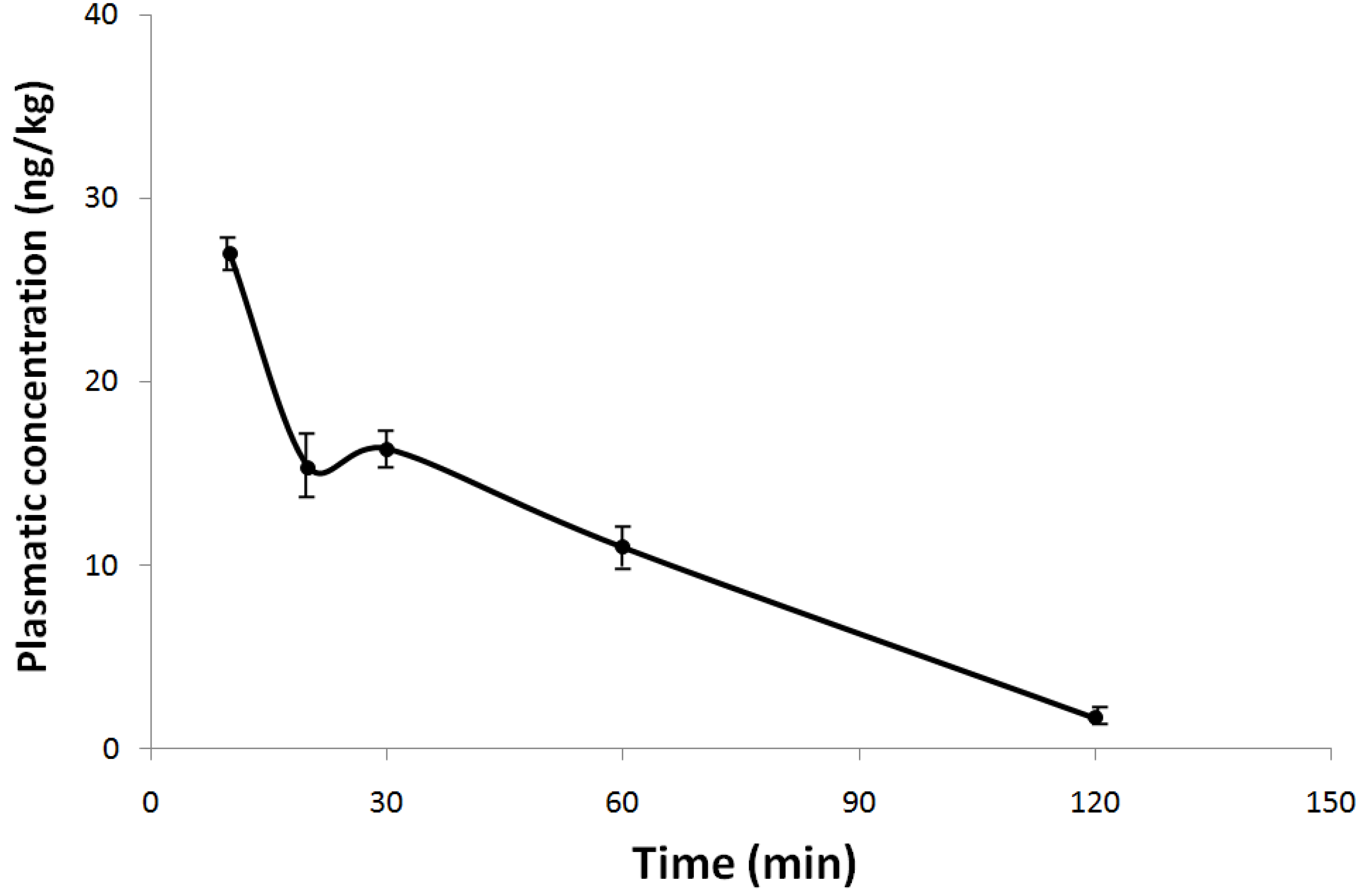
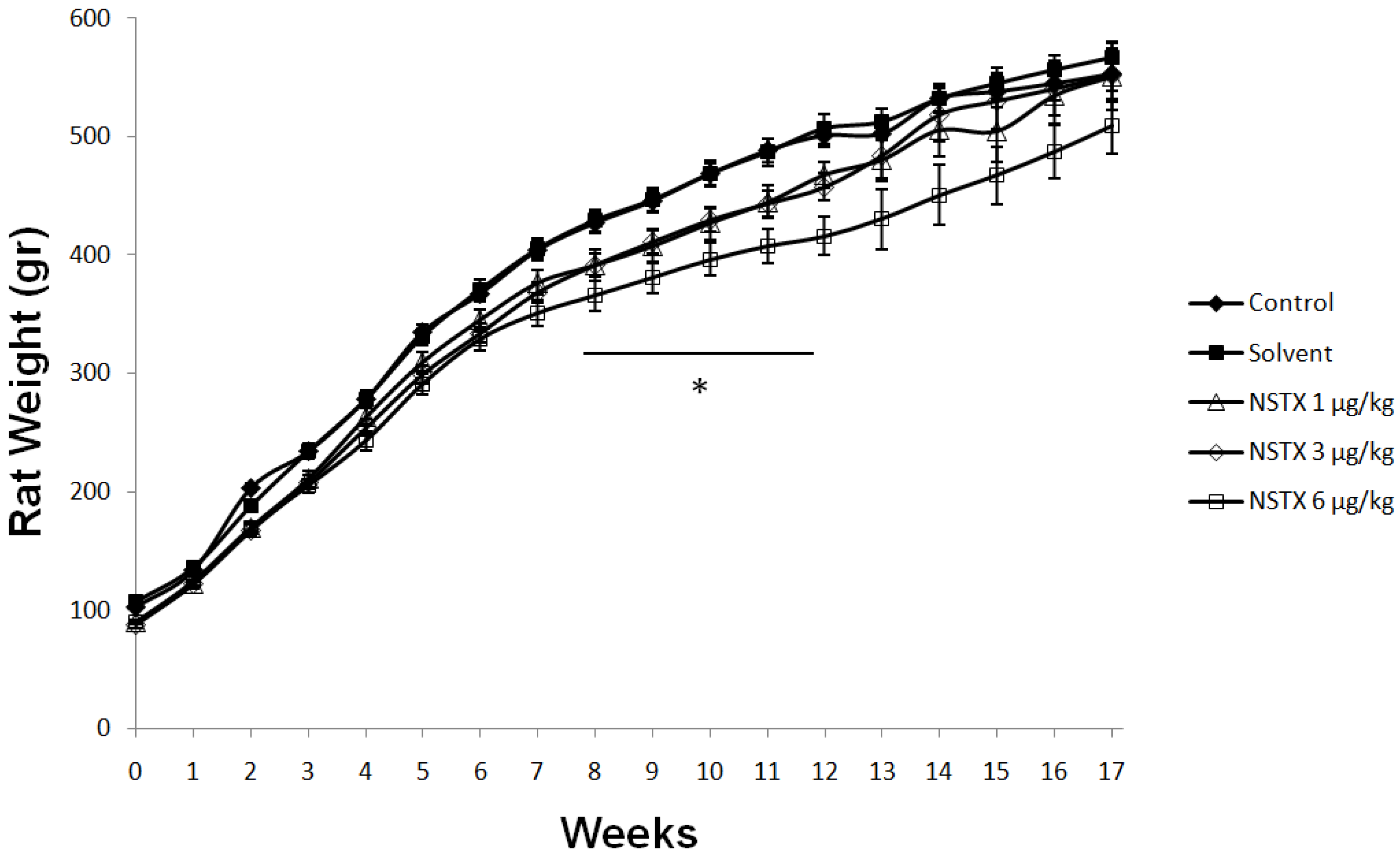
2.3. Effect of NeoSTX on Body Weight, Food and Water Intake
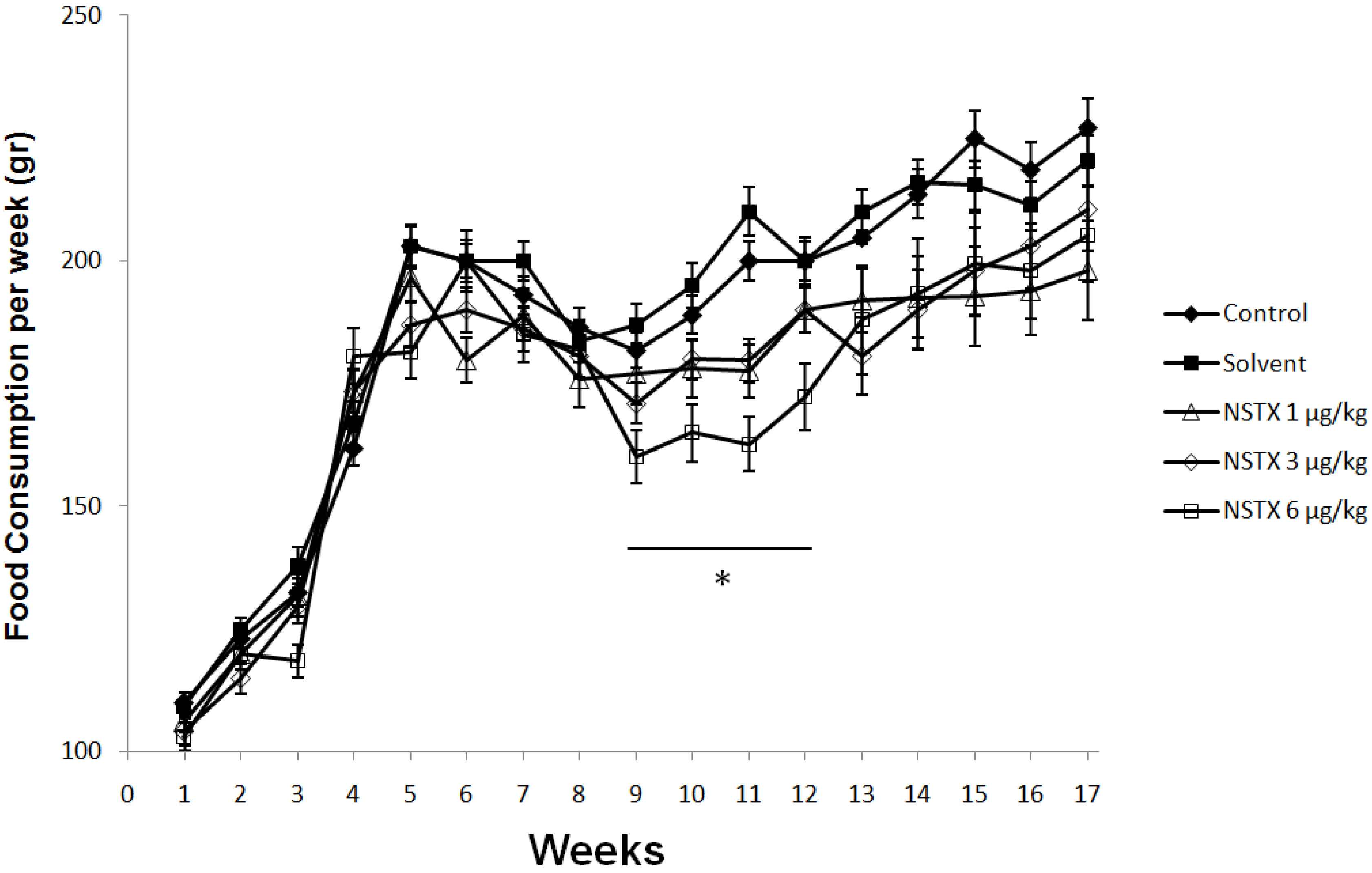

2.4. Effect on Weight of Vital Organs
| Heart | Spleen | Stomach | Liver | Lung | Kidney | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.07 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 3.04 ± 0.08 | 0.47 ± 0.08 | 0.69 ± 0.05 |
| Solvent | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 3.27 ± 0.44 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 0.70 ± 0.03 |
| NeoSTX 1 μg/kg | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 2.97 ± 0.10 | 0.46 ± 0.02 | 0.64 ± 0.03 |
| NeoSTX 3 μg/kg | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.47 ± 0.03 | 2.84 ± 0.19 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 0.65 ± 0.07 |
| NeoSTX 6 μg/kg | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 2.06 ± 0.11 | 3.47 ± 0.62 | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 0.75 ± 0.05 |
| Heart | Spleen | Stomach | Liver | Lung | Kidney | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 0.42 ± 0.06 | 2.89 ± 0.16 | 0.44 ± 0.07 | 0.65 ± 0.03 |
| Solvent | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.40 ± 0.07 | 3.13 ± 0.27 | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 0.66 ± 0.05 |
| NeoSTX 1 μg/kg | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 2.68 ± 0.49 | 0.41 ± 0.06 | 0.58 ± 0.12 |
| NeoSTX 3 μg/kg | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.40 ± 0.08 | 2.40 ± 0.42 | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 0.57 ± 0.06 |
| NeoSTX 6 μg/kg | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 0.45 ± 0.14 | 3.48 ± 0.86 | 0.44 ± 0.07 | 0.64 ± 0.11 |
2.5. Effect of NeoSTX on Hematological Parameters
| Control | Solvent | NSTX 1 μg/kg | NSTX 3 μg/kg | NSTX 6 μg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (%) | 15.0 ± 2.3 | 15.4 ± 1.7 | 15.8 ± 3.4 | 16.4 ± 2.6 | 15.5 ± 1.9 |
| RBC Count (106/μL) | 9.36 ± 0.30 | 9.40 ± 0.84 | 9.05 ± 0.22 | 9.23 ± 0.13 | 8.42 ± 1.30 |
| Hemotocrite (%) | 52.0 ± 1.4 | 52.9 ± 1.8 | 52.2 ± 2.2 | 52.3 ± 0.6 | 53.1 ± 2.1 |
| MCV (fL) | 55.5 ± 0.5 | 56.0 ± 4.3 | 57.6 ± 1.6 | 56.7 ± 0.6 | 55.1 ±2.3 |
| MCH (pg) | 16.9 ± 0.2 | 17.8 ± 0.3 | 17.1 ± 0.2 | 17.5 ± 0.4 | 17.2 ± 0.5 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 30.4 ± 0.4 | 32.0 ± 2.6 | 31.4 ± 0.8 | 31.7 ± 0.2 | 32.4 ± 1.2 |
| Platelet count (103/μL) | 1238 ± 360 | 1145 ± 407 | 995 ± 330 | 1050 ± 200 | 1090 ± 180 |
| WBC (103/μL) | 3.9 ± 0.9 | 4.5 ± 2.3 | 5.3 ± 2.3 | 4.8 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.8 |
| Reticulocyte (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Neutrophils (%) | 12 ± 6 | 5 ± 2 | 7 ± 3 | 4 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 |
| Lynphocytes (%) | 88 ± 6 | 92 ± 2 | 92 ± 3 | 93 ± 3 | 91 ± 4 |
| Eosinophils (%) | 0 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 | 2 ± 2 |
| Monocytes (%) | 0 | 1 ± 1 | 0 | 2 ± 2 | 0 |
| Basophils (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control | Solvent | NeoSTX 1 μg/kg | NeoSTX 3 μg/kg | NeoSTX 6 μg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (%) | 15.4 ± 2.6 | 14.7 ± 1.5 | 15.2 ± 2.4 | 15.7 ± 2.4 | 15.9 ± 2.3 |
| RBC Count (106/μL) | 8.78 ± 0.50 | 9.32 ± 0.94 | 9.35 ± 0.78 | 9.32 ± 1.03 | 8.82 ± 1.55 |
| Hematocrit(%) | 51.9 ± 2.1 | 52.5 ± 1.2 | 52.7 ± 2.3 | 52.6 ± 1.1 | 53.2 ± 2.4 |
| MCV (fL) | 56.5 ± 1.5 | 56.5 ± 2.3 | 56.4 ± 1.8 | 56.3 ± 0.9 | 55.7 ± 1.8 |
| MCH (pg) | 17.5 ± 0.4 | 17.7 ± 0.6 | 17.0 ± 0.4 | 17.8 ± 0.4 | 17.1 ± 0.5 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 31.4 ± 0.6 | 32.3 ± 1.7 | 31.7 ± 0.8 | 32.4 ± 1.1 | 32.2 ± 1.4 |
| Platelet count (103/μL) | 1145 ± 242 | 1275 ± 322 | 1035 ± 240 | 1100 ± 220 | 1140 ± 245 |
| WBC (103/μL) | 4.9 ± 1.5 | 4.4 ± 1.3 | 4.8 ± 1.9 | 5.4 ± 1.2 | 4.3 ± 1.2 |
| Reticulocyte (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Neutrophils (%) | 8 ± 4 | 6 ± 3 | 6 ± 2 | 5 ± 3 | 6 ± 3 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 91 ± 7 | 92 ± 4 | 92 ± 3 | 92 ± 4 | 90 ± 3 |
| Eosinophils (%) | 0 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 |
| Monocytes (%) | 0 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 | 1 ± 1 |
| Basophils (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
2.6. Effect of NeoSTX on Serum Biochemical Parameters
| Control | Solvent | NeoSTX 1 μg/kg | NeoSTX 3 μg/kg | NeoSTX 6 μg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 326.2 ± 82.4 | 367.8 ± 59.95 | 289.6 ± 45.23 | 303.8 ± 47.21 | 307.8 ± 117.78 |
| Ureic Nitrogen (mg/dL) | 15.5 ± 2.1 | 18.8 ± 1.17 | 17.4 ± 1.85 | 15.6 ± 1.6 | 18.4 ± 1.4 |
| Ureic acid (mg/dL) | 1.02 ± 0.25 | 1.12 ± 0.44 | 0.88 ± 0.44 | 1.04 ± 0.32 | 4.5 ± 4.00 |
| Total Protein (g/dL) | 6.42 ± 0.12 | 6.26 ± 0.36 | 6.46 ± 0.28 | 6.44 ± 0.36 | 6.65 ± 0.37 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.28 ± 0.21 | 3.2 ± 0.16 | 3.28 ± 0.22 | 3.38 ± 0.15 | 3.59 ± 0.24 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 58.2 ± 6.58 | 61.2 ± 5.71 | 72.4 ± 13.66 | 64.8 ± 7.76 | 68.6 ± 5.38 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 35.4 ± 5.78 | 39.2 ± 3.41 | 46.8 ± 6.23 | 41.2 ± 5.27 | 46.6 ± 8.69 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 7.72 ± 5.06 | 14.28 ± 16.98 | 9.42 ± 5.63 | 12.76 ± 4.59 | 10.08 ± 5.79 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 75.8 ± 28.13 | 132.5 ± 107.88 | 107.4 ± 70.43 | 54.2 ± 20.88 | 91.2 ± 40.36 |
| LDH (U/L) | 2383.8 ± 760.51 | 2356.6 ± 1024.64 | 2475.2 ± 528.45 | 2302.6 ± 727.33 | 4015.5 ± 2497.87 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.52 ± 0.04 | 0.54 ± 0.05 | 0.54 ± 0.05 | 0.46 ± 0.05 | 0.54 ± 0.08 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.03 * |
| Direct Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.30 ± 0.07 * |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (U/L) | 206.4 ± 56.57 | 238.2 ± 62.31 | 293.4 ± 30.72 | 292.2 ± 68.38 | 237.4 ± 67.93 |
| GGT (U/L) | 7.2 ± 3.53 | 7.4 ± 0.84 | 7.5 ± 0.87 | 8.2 ± 4.17 | 12.5 ± 2.75 * |
| SGOT (UI/dL) | 91.2 ± 8.45 | 88.6 ± 12.12 | 95.7 ± 10.92 | 81.2 ± 11.07 | 142.8 ± 15.42 * |
| SGPT (UI/dL) | 67.8 ± 6.96 | 60.9 ± 6.93 | 61.0 ± 4 | 75.4 ± 12.81 | 80.2 ± 15.32 |
| Control | Solvent | NeoSTX 1 μg/kg | NeoSTX 3 μg/kg | NeoSTX 6 μg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 334.7 ± 61.3 | 352.5 ± 45.67 | 297.5 ± 53.2323 | 335.8 ± 52.32 | 325.8 ± 52.46 |
| Ureic Nitrogen (mg/dL) | 16.3 ± 1.73 | 17.6 ± 1.49 | 15.9 ± 1.57 | 18.4 ± 2.1 | 18.1 ± 1.6 |
| Ureic acid (mg/dL) | 0.92 ± 0.42 | 1.22 ± 0.54 | 0.96 ± 0.51 | 1.10 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.57 |
| Total Protein (g/dL) | 6.32 ± 0.24 | 6.36 ± 0.26 | 6.42 ± 0.26 | 6.46 ± 0.5 | 6.35 ± 0.47 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.30 ± 0.19 | 3.24 ± 0.17 | 3.28 ± 0.19 | 3.32 ± 0.22 | 3.29 ± 0.20 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 59.3 ± 7.38 | 62.6 ± 6.52 | 64.4 ± 6.35 | 63.8 ± 5.8 | 62.8 ± 6.18 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 38.6 ± 4.52 | 43.1 ± 4.43 | 42.9 ± 5.36 | 43.5 ± 6.10 | 41.8 ± 6.12 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 10.53 ± 4.34 | 12.58 ± 6.33 | 10.5 ± 5.42 | 11.34 ± 4.87 | 10.54 ± 4.90 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 93.5 ± 23.4 | 102.3 ± 36.4 | 90.6 ± 22.4 | 76.8 ± 25.66 | 105.2 ± 32.10 |
| LDH (U/L) | 2525.4 ± 665.50 | 2248.6 ± 735.42 | 2160.8 ± 460.76 | 2650.2 ± 643.55 | 2540.9 ± 580.32 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.53 ± 0.05 | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 0.52 ± 0.04 | 0.51 ± 0.05 | 0.53 ± 0.05 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.03 |
| Direct Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (U/L) | 226.8 ± 48.37 | 242.9 ± 54.35 | 248.9 ± 42.52 | 225.2 ± 45.55 | 235.6 ± 49.76 |
| GGT (U/L) | 7.2 ± 1.51 | 7.3 ± 1.22 | 7.4 ± 0.91 | 7.8 ± 2.45 | 7.4 ± 1.73 |
| SGOT (UI/dL) | 89.5 ± 11.55 | 91.6 ± 11.83 | 96.4 ± 10.65 | 88.9 ± 10.88 | 95.8 ± 12.45 |
| SGPT (UI/dL) | 65.4 ± 5.87 | 65.2 ± 4.22 | 62.3 ± 4.55 | 68.2 ± 5.28 | 70.1 ± 8.77 |
2.7. Effect of NeoSTX on Serum Electrolyte
| Control | Solvent | NeoSTX 1 μg/kg | NeoSTX 3 μg/kg | NeoSTX 6 μg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.90 ± 0.41 | 9.88 ± 0.28 | 9.92 ± 0.14 | 9.84 ± 0.17 | 10.26 ± 0.81 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 7.33 ± 0.94 | 7.66 ± 0.69 | 7.59 ± 0.59 | 7.45 ± 0.72 | 9.71 ± 3.72 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 142.1 ± 1.41 | 140.8 ± 2.56 | 141.2 ± 2.13 | 142.4 ± 0.84 | 143.4 ± 4.84 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 5.32 ± 1.11 | 5.32 ± 0.25 | 5.35 ± 0.36 | 4.96 ± 0.57 | 7.66 ± 2.81 |
| Chloride (mEq/L) | 108.6 ± 1.28 | 106.2 ± 2.99 | 106.4 ± 1.59 | 107.8 ± 0.98 | 87.6 ± 37.90 |
| Control | Solvent | NeoSTX 1 μg/kg | NeoSTX 3 μg/kg | NeoSTX 6 μg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.85 ± 0.43 | 9.78 ± 0.38 | 9.9 ± 0.24 | 9.82 ± 0.17 | 9.82 ± 0.31 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 7.44 ± 0.62 | 7.45 ± 0.59 | 7.60 ± 0.67 | 7.52 ± 0.62 | 7.7 ± 0.72 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 142.3 ± 1.75 | 141.5 ± 1.86 | 142.1 ± 2.05 | 141.8 ± 1.71 | 141.4 ± 2.10 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 5.29 ± 0.65 | 5.31 ± 0.42 | 5.32 ± 0.47 | 5.33 ± 0.66 | 5.35 ± 0.93 |
| Chloride (mEq/L) | 107.5 ± 1.45 | 106.8 ± 1.95 | 107.1 ± 1.7 | 106.2± 1.11 | 106.6 ± 1.90 |
2.8. Effect of NeoSTX on Histopathological Presentations and Macro Anatomical Features
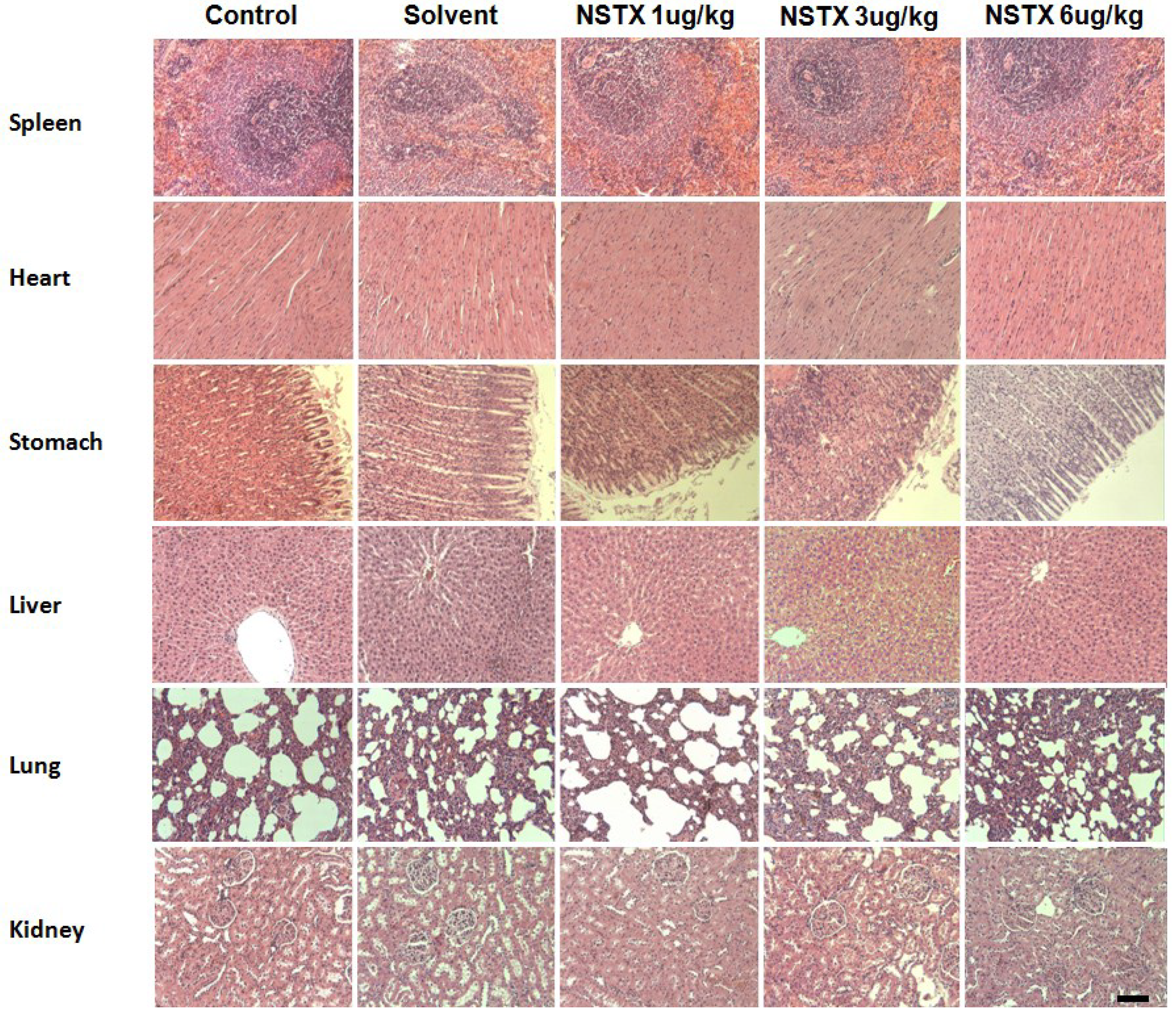
2.9. Mortality
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals
4.2. Acute Toxicity Study
4.3. Chronic Toxicity Study
4.4. Hematological Analysis
4.5. Biochemical Analysis
4.6. Histopathological Assessment
4.7. Pharmacokinetic Study
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bricelj, V.M.; Connell, L.; Konoki, K.; Macquarrie, S.P.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A.; Trainer, V.L. Sodium channel mutation leading to saxitoxin resistance in clams increases risk of PSP. Nature 2005, 434, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, L.E. Saxitoxin, a toxic marine natural product that targets a multitude of receptors. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 200–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, M.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic alkaloids: Saxitoxin and its analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 20, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.; Vale, C.; Alonso, E.; Alfonso, C.; Rodriguez, P.; Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Vale, P.; Hirama, M.; Vieytes, M.R.; et al. A comparative study of the effect of ciguatoxins on voltage-dependent Na+ and K+ channels in cerebellar neurons. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlinck, R.G.; Kossuga, M.H. Natural guanidine derivatives. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 516–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, R.J.S.; Stüken, A.; Murray, S.A.; Jakobsen, K.S. Evolution and distribution of saxitoxin biosynthesis in dinoflagellates. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2814–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein-Barash, H.; Shichor, I.; Kwon, A.H.; Hall, S.; Lawlor, M.W.; Langer, R.; Kohane, D.S. Prolonged duration local anesthesia with minimal toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7125–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Bai, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, W.O.; Shin, Y.S.; Lee, K.Y. The duration of intrathecal bupivacaine mixed with lidocaine. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 107, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, J., 4th. Mechanisms of local anesthetic action. Anesth. Analg. 1996, 82, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, G.; Shang, L.; Li, X.; Dudley, S.C., Jr. Energetic localization of saxitoxin in its channel binding site. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Navarro, A.J.; Lagos, N. Neosaxitoxin as a local anesthetic: Preliminary observation from a first human trial. Anesthesiology 2007, 106, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Navarro, A.J.; Lagos, M.; Figueroa, C.; Garcia, C.; Recabal, P.; Silva, P.; Iglesias, V.; Lagos, N. Potentiation of Local Anesthetic activity on Neosaxitoxin with bupivacaine or epinephrine: Development of a long acting pain blocker. Neurotox. Res. 2009, 16, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Navarro, A.J.; Lagos, N.; Lagos, M.; Braghetto, I.; Csendes, A.; Hamilton, J.; Berger, Z.; Wiedmaier, G.; Henriquez, A. Intrasphincteric neosaxitoxin injection: Evidence of lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in achalasia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2667–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Navarro, A.J.; Berde, C.B.; Wiedmaier, G.; Mercado, A.; Garcia, C.; Iglesias, V.; Zurakowski, D. Comparison of neosaxitoxin versus bupivacaine via port infiltration for postoperative analgesia following laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A randomized, double-blind trial. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2011, 36, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, N.A.; Lapointe, B.; Ong-Lam, M.; Dubuc, B.; Walde, D.; Gagnon, B.; Love, R.; Goel, R.; Hawley, P.; Ngoc, A.H.; et al. A multicentre open-label safety and efficacy study of tetrodotoxin for cancer pain. Curr. Oncol. 2011, 18, e109–e116. [Google Scholar]
- Kohane, D.S.; Lu, N.T.; Gökgöl-Kline, A.C.; Shubina, M.; Kuang, Y.; Hall, S.; Strichartz, G.R.; Berde, C.B. The local anesthetic properties and toxicity of saxitonin homologues for rat sciatic nerve block in vivo. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2000, 25, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kleinhaus, A.L.; Siegman, M.J. Vasomotor and respiratory depressant actions of tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1967, 165, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borison, H.L.; Culp, W.J.; Gonsalves, S.F.; McCarthy, L.E. Central respiratory and circulatory depression caused by intravascular saxitoxin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1980, 68, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervenka, R.; Zarrabi, T.; Lukacs, P.; Todt, H. The Outer vestibulae of the Na+ channel-toxin receptor and modulator of permeation as well as gating. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1373–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R.; Thomas, K.; Gibbs, R.; Murphy, C.; Quilliam, M.A. Acute toxicities of saxitoxin, neosaxitoxin, decarbamoylsaxitoxin and gonyautoxins 1&4 and 2&3 to mice by various routes of administration. Toxicon 2013, 76, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, P.L.; Müller, M.; Sturm, E. Genes and cholestasis. Hepatology 2001, 34, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, K.N.; Müller, M.; Jansen, P.L. Drug transport proteins in the liver. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchell, B.; Soars, M.; Monaghan, G.; Cassidy, A.; Smith, D.; Ethell, B. Drug-mediated toxicity caused by genetic deficiency of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 15, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchell, B. Genetic variation of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase: Implications in disease and drug glucuronidation. Am. J. Pharmacogenomics 2003, 3, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, C.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.; Díaz, J.C.; Torres, R.; Lagos, N. Evidence of in vitro glucuronidation and enzymatic transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins by healthy human liver microsomes fraction. Toxicon 2009, 53, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, C.; Barriga, A.; Díaz, J.C.; Lagos, M.; Lagos, N. Route of metabolization and detoxication of paralytic shellfish toxins in humans. Toxicon 2010, 55, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, P.V. Hyperbilirubinemia of fasting. JAMA 1971, 217, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauner, M.; Boyer, J.L. Bile salt transporters: Molecular characterization, function, and regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 633–671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barrett, P.V. The effect of diet and fasting on the serum bilirubin concentration in the rat. Gastroenterology 1971, 60, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gronwall, R.; Mia, A.S. Fasting hyperbilirubinemia in horses. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1976, 17, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, C.E.; Freedland, R.A. Fasting hyperbilirubinemia in normal squirrel monkeys. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1992, 42, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Test No. 425: Acute Oral Toxicity: Up-and-Down Procedure; OECD: Paris, France, 2008; ISBN: 9789264071049. [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, J.T.; Wilcoxon, F. A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1949, 96, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basavaiah, K.; Charan, V.S. Titrimetric and spectrophotometric assay of some antihistamines through the determination of the chloride of their hydrochlorides. Farmaco 2002, 57, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokazono, E.; Osawa, S.; Nakano, T.; Kawamoto, Y.; Oguchi, Y.; Hotta, T.; Kayamori, Y.; Kang, D.; Cho, Y.; Shiba, K.; et al. Development of a new measurement method for serum calcium with chlorophosphonazo-III. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 46, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Riet, J.M.; Gibbs, R.S.; Chou, F.W.; Muggah, P.M.; Rourke, W.A.; Burns, G.; Thomas, K.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid chromatographic post-column oxidation method for analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins in mussels, clams, scallops, and oysters: Single-laboratory validation. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1690–1704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zepeda, R.J.; Candiracci, M.; Lobos, N.; Lux, S.; Miranda, H.F. Chronic Toxicity Study of Neosaxitoxin in Rats. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5055-5071. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12095055
Zepeda RJ, Candiracci M, Lobos N, Lux S, Miranda HF. Chronic Toxicity Study of Neosaxitoxin in Rats. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(9):5055-5071. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12095055
Chicago/Turabian StyleZepeda, Ramiro J., Manila Candiracci, Nicolas Lobos, Sebastian Lux, and Hugo F. Miranda. 2014. "Chronic Toxicity Study of Neosaxitoxin in Rats" Marine Drugs 12, no. 9: 5055-5071. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12095055
APA StyleZepeda, R. J., Candiracci, M., Lobos, N., Lux, S., & Miranda, H. F. (2014). Chronic Toxicity Study of Neosaxitoxin in Rats. Marine Drugs, 12(9), 5055-5071. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12095055