Abstract
Nuclear receptors (NRs) are important pharmaceutical targets because they are key regulators of many metabolic and inflammatory diseases, including diabetes, dyslipidemia, cirrhosis, and fibrosis. As ligands play a pivotal role in modulating nuclear receptor activity, the discovery of novel ligands for nuclear receptors represents an interesting and promising therapeutic approach. The search for novel NR agonists and antagonists with enhanced selectivities prompted the exploration of the extraordinary chemical diversity associated with natural products. Recent studies involving nuclear receptors have disclosed a number of natural products as nuclear receptor ligands, serving to re-emphasize the translational possibilities of natural products in drug discovery. In this review, the natural ligands of nuclear receptors will be described with an emphasis on their mechanisms of action and their therapeutic potentials, as well as on strategies to determine potential marine natural products as nuclear receptor modulators.
1. Introduction
Natural products, including compounds from plants, microbes, and marine species, have become major resources for bioactive agents and play a key role in the discovery of lead compounds for new drug research. The high hit rates in lead drug screening and large-scale structural diversity make marine natural products ideal candidates for drug discovery. However, these natural products are often in limited supply, and total synthesis remains difficult. Thus, the bottleneck is a shortage of raw material, which has made it very challenging for drug development from marine natural products. Driven by new developments in analytical technology, spectroscopy, and high-throughput screening, recent years have witnessed a renaissance in marine-based drug discovery since the first marine drug (Ziconotide) came out [1,2]. In addition to Ziconotide for the treatment of pain, Trabectedin is another successful marine drug for anticancer therapies [3,4].
One key approach in drug discovery is to identify a drug target associated with a particular disease and to screen for lead compounds that are able to appropriately regulate this target protein. A drug target is a functional region of a protein for which a significant fraction of family members have been successfully targeted by drugs. The most important feature of drug targets is that they are able to respond to small molecules including intracellular metabolites and xenobiotics, such as certain drugs. Rhodopsin-like GPCRs, certain ion-channel domains, and nuclear receptors (NRs) are the most successful molecular targets in the history of drug discovery [5]. Nuclear receptors, consisting of 48 members in humans, are important transcriptional factors that play fundamental roles in a broad range of biological processes, from development and metabolism to reproductive health [6]. Direct ligand binding induces a conformational change in the receptor, allowing it to recruit cofactors in regulating transcription [7,8]. The ligands for nuclear receptors include metabolites, vitamins, and hormones, as well as xenobiotics. Many nuclear receptors already have one or more ligands currently used as medicines, and nuclear receptors represent well-validated drug targets for several human diseases, including metabolic syndrome and hormone-dependent cancers (Table 1).
Two important concerns for drug development are efficacy and clinical safety, which are often associated with cross-activity of the compounds with undesired targets. Therefore, all lead compounds or drug candidates need to be assessed for toxicity to and selectivity for related targets. A major goal in nuclear receptor-targeting drug development has been to obtain ligands that exhibit regulatory activity in a receptor-selective manner with reduced adverse side effects. In this review, strategies to determine potential marine natural products as nuclear receptor modulators, the interaction between marine natural products and nuclear receptors, and potential marine natural products for drug development will be discussed and explored.

Table 1.
Disease relevance and drug development of human nuclear receptors.
| NR | Related Diseases | Drug Development |
|---|---|---|
| CAR | cholestatic liver disease [9] | Phenobarbital [12] |
| type 2 diabetes [10] | ||
| hematopoietic malignancies [11] | ||
| ER(α, β) | breast cancer [13] ovarian cancer, colon cancer [14] prostate cancer [15] | Bazedoxifene [16] |
| Tamoxifen [17] | ||
| Raloxifene [18] | ||
| Lasofoxifene [19] | ||
| FXR | biliary cirrhosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [9] | Fexaramine GW4064 [20] |
| INT-747 [21] | ||
| GR | allergic, inflammatory, haematological disorders [22] | Dexamethasone [23] |
| RU486 [24] | ||
| HNF4α | maturity onset diabetes of the young [25] | MEDICA 16 [26] |
| LXR(α, β) | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [27] | GW3965 [31] N-Acylthiadiazolines [32] T00901317 [33] |
| Alzheimer’s disease [28] | ||
| breast cancer [29] | ||
| atherosclerosis [30] | ||
| PPAR(α, β, γ) | dyslipidemia [34] diabetes [35] | Fibrates [36] |
| GW9662, GW501516 [37] | ||
| Rosiglitazone [38] | ||
| Thiazolidinediones [39] | ||
| PXR | endothelial detoxification [40] | Rifampicin [43] |
| liver injury [41] | ||
| cholestatic liver disease [9] | ||
| cancers [42] | ||
| RXR | metabolic diseases [44] | Bexarotene [46] |
| cancers [45] | ||
| TR(α, β) | thyroid hormone resistance syndrome [47] | Levothyroxine [49] |
| thyroid cancer [48] | Liothyronine | |
| VDR | diabetic nephropathy, hypertension, atherosclerosis [50,51,52] | Doxercalciferol [53] |
| MR | cardiovascular disease [54] | |
| chronic kidney disease [55,56] | ||
| vascular Disease [57] | ||
| PR | breast cancer [58,59] | RU-486 [24] |
| endometriosis [60] | ||
| AR | androgen insensitivity syndrome [61] | |
| prostate cancer [62] | ||
| osteoporosis [63] | ||
| RAR(α, β, γ) | acute promyelocytic leukemia [64] | |
| kidney disease [65] | ||
| Alzheimer’s Disease [66] | ||
| skin diseases [67] | ||
| cancer [44] |
2. Nuclear Receptors: Structure and Function
Nuclear receptors can be divided into three groups: hormone receptors, adopted orphan receptors, and orphan receptors. They share high sequence identity and conserved domains. A typical nuclear receptor usually contains four functional regions: The A/B region (N-terminal activation function-1 domain, AF-1), the C region (DNA-binding domain, DBD), the D region (hinge region), and the E/F region (ligand-binding domain, LBD) (Figure 1A,B) [8]. Among these regions, the DBD and LBD are the most conserved. The LBD contains dimerization motifs and an activation function-2 (AF-2), located at the C-terminus of the receptor, in which conformation is highly dependent on ligand binding (Figure 1C). The LBD interacts with ligands and mediates transcriptional activation in a ligand-dependent fashion. Specifically, the binding of ligands to the LBD determines the recruitment of transcriptional coregulators that trigger the induction or repression of target genes (Figure 1D). As ligand binding and ligand-mediated cofactor recruitment are crucial for functions mediated by nuclear receptors, the LBD plays a critical role in nuclear receptor signaling. Thus, the LBD has been the focus of structural study, which has revealed important clues to the binding of ligands and cofactors [68,69,70,71].
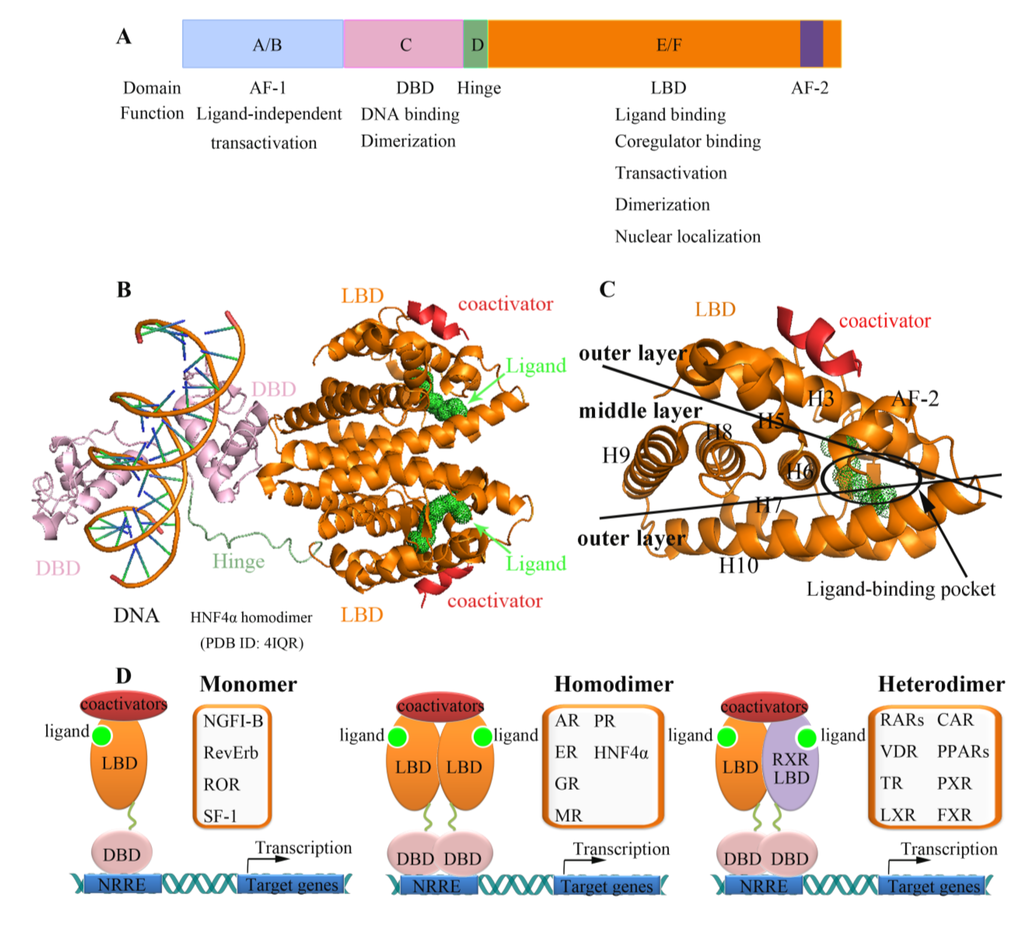
Figure 1.
Structural and functional organization of nuclear receptors. (A) Schematic diagram for a common domain structure of NR. N-terminal A/B domain includes activation function 1 (AF-1), which mediates ligand-independent transcriptional activation. DNA binding domain (DBD) dictates specific response element recognition. Hinge region (Hinge) links DBD and LBD. C-terminal E/F domain encompasses the ligand-binding domain, which mediates ligand-dependent coactivator interactions; (B) Multi-domain structure of the HNF4α/DNA complex in cartoon representation. The crystal structure of HNF4α homodimer (PDB 4IQR) includes DBD (pink), Hinge (green), LBD (orange) in complex with response DNA sequence (left) and ligand (green dots); (C) Enlarged view of HNF4α LBD monomer, which clearly shows the three layer sandwich structure; (D) Metabolic regulation of NR. Ligand-activated NR complex recruits coactivator proteins that increase transcriptional activity of the gene. NRs bind DNA as monomers, homodimers or heterodimers.
Figure 1.
Structural and functional organization of nuclear receptors. (A) Schematic diagram for a common domain structure of NR. N-terminal A/B domain includes activation function 1 (AF-1), which mediates ligand-independent transcriptional activation. DNA binding domain (DBD) dictates specific response element recognition. Hinge region (Hinge) links DBD and LBD. C-terminal E/F domain encompasses the ligand-binding domain, which mediates ligand-dependent coactivator interactions; (B) Multi-domain structure of the HNF4α/DNA complex in cartoon representation. The crystal structure of HNF4α homodimer (PDB 4IQR) includes DBD (pink), Hinge (green), LBD (orange) in complex with response DNA sequence (left) and ligand (green dots); (C) Enlarged view of HNF4α LBD monomer, which clearly shows the three layer sandwich structure; (D) Metabolic regulation of NR. Ligand-activated NR complex recruits coactivator proteins that increase transcriptional activity of the gene. NRs bind DNA as monomers, homodimers or heterodimers.
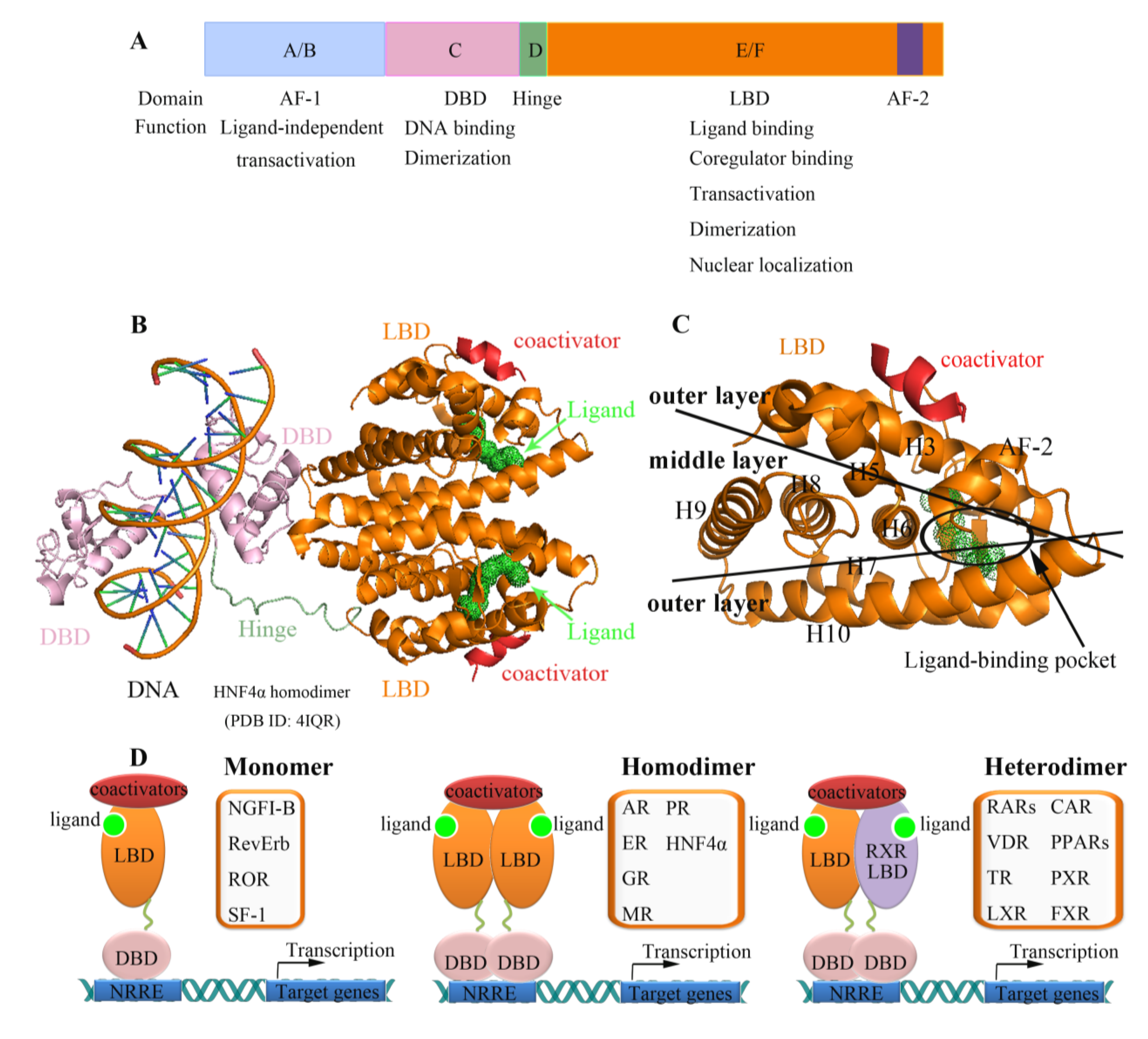
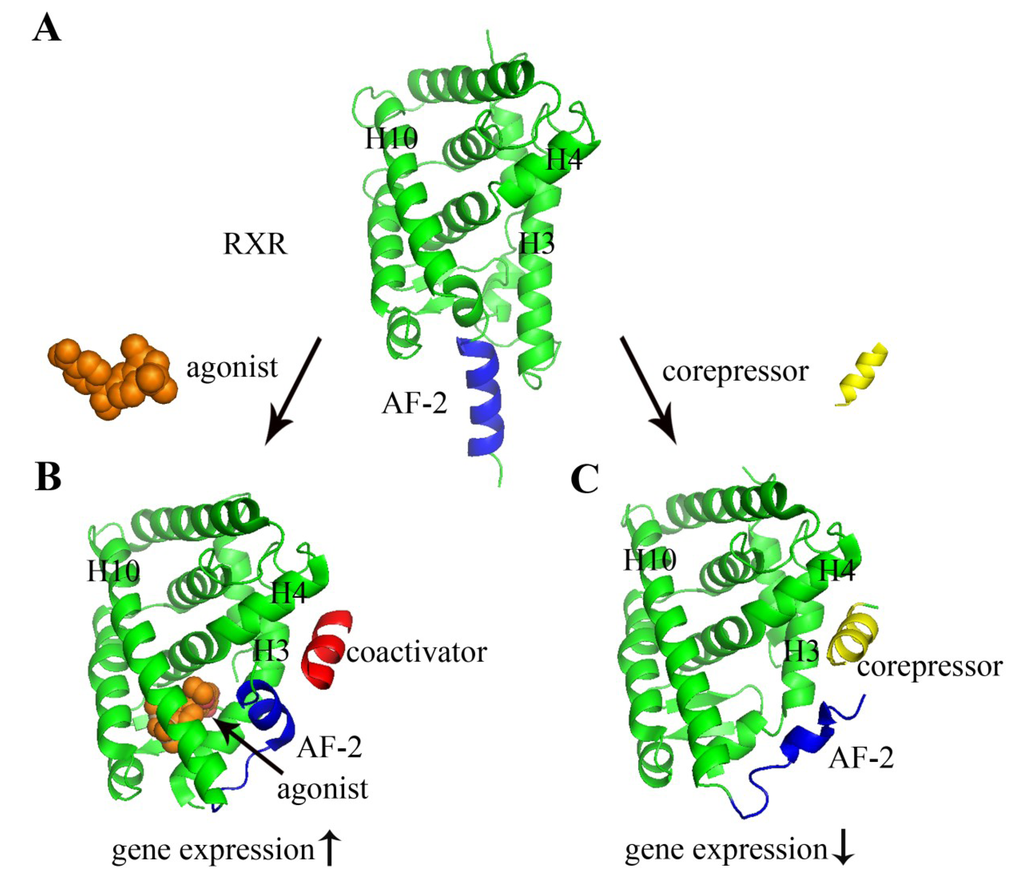
Figure 2.
Structural basis of nuclear receptor ligand binding and cofactor recruitment. The structures shown here are the LBD of RXR (green image in the diagram). (A) Apo-RXR (no ligand bound, PDB 1LBD) [72]; (B) RXR complexed with agonist BMS649 (PDB 2ZY0) [73]; (C) RXR complexed with corepressor SMRT (silencing mediator for retinoid or thyroid-hormone receptors) (PDB 3R29) [74]. The agonist, coactivator, and corepressor are depicted as orange space filling spheres, a red image, and a yellow image, respectively. When an agonist is bound to a NR, the C-terminal α helix of the LBD (AF-2, blue) changes its position so that a coactivator protein (red) can bind to the surface of the LBD (B). Antagonist occupies the same ligand-binding cavity of the NR (antagonist not shown). However, antagonist ligands in addition have a side chain extension, which sterically pushes AF-2 to move towards outside, and corepressor (yellow) occupies roughly the same position in space as coactivators bind. Hence, coactivator binding to the LBD is blocked.
Figure 2.
Structural basis of nuclear receptor ligand binding and cofactor recruitment. The structures shown here are the LBD of RXR (green image in the diagram). (A) Apo-RXR (no ligand bound, PDB 1LBD) [72]; (B) RXR complexed with agonist BMS649 (PDB 2ZY0) [73]; (C) RXR complexed with corepressor SMRT (silencing mediator for retinoid or thyroid-hormone receptors) (PDB 3R29) [74]. The agonist, coactivator, and corepressor are depicted as orange space filling spheres, a red image, and a yellow image, respectively. When an agonist is bound to a NR, the C-terminal α helix of the LBD (AF-2, blue) changes its position so that a coactivator protein (red) can bind to the surface of the LBD (B). Antagonist occupies the same ligand-binding cavity of the NR (antagonist not shown). However, antagonist ligands in addition have a side chain extension, which sterically pushes AF-2 to move towards outside, and corepressor (yellow) occupies roughly the same position in space as coactivators bind. Hence, coactivator binding to the LBD is blocked.
All nuclear receptors exhibit similar structural features (Figure 1B). Nuclear receptor LBD structures contain 11–13 α-helices that are arranged into a three-layer antiparallel α-helical sandwich [75,76]. The three long helices (H3, 7, and 10) form the two outer layers, and the middle layer of helices (H5, 6, 8, and 9) is present only in the top half of the domain, thereby creating a cavity for ligand binding, the so-called ligand-binding pocket (Figure 1C). The AF-2 also forms a helix that can adopt multiple conformations depending on different bound ligands (Figure 2). The first step of nuclear receptor activation is initiated by ligand binding, which induces a conformational change in the receptor; thus, the ligand-binding pocket is an important structural feature of nuclear receptors. Upon the binding of an agonist, nuclear receptors use a charge clamp pocket, in part composed of the C-terminal AF-2 helix, to form a hydrophobic groove for binding of the LXXLL motif of coactivators, such as SRCs (steroid receptor coactivators) and GRIP1 (glucocorticoid receptor interacting protein 1), leading to the modulation and promotion of gene transcription (Figure 1D). Antagonists block the effect of agonist through competitive binding to the same binding site in the nuclear receptor. Therefore, the antagonist-bound receptor is in an inactive state and preferentially binds corepressor proteins, leading to the repression of gene transcription [77,78]. The corepressors bind to LBDs via a conserved LXXXIXXXL/I motif, which is longer than LXXLL coactivator motif and adopts a three-turn α helix. The binding of corepressor motif induces major conformation change of AF-2 helix to accomadate the larger corepressor helix. The conformational flexibility of AF-2 helix allows the NR to sense the presence of the bound ligand, either an agonist or an antagonist, and to recruit the coactivator or corepressors that ultimately determine the transcriptional activation or repression of NRs (Figure 2) [8].
There is a pressing need to develop detailed structure–function relationships (SAR) of nuclear receptor and ligand interaction to facilitate the discovery of potent ligands. Structural comparison and analysis show that several features of the ligand-binding pocket have contributed to the ligand binding affinity and specificity. The ligand-binding pocket is the least conserved region on LBD, in which size and shape varies greatly from receptor subtype to subtype, to further accommodate specific ligands. The small pocket seen in the ERRα (estrogen-related receptor α) suggests that only ligands with four to five carbon atoms or less can fit [79]. In contrast, the large pocket in PXR (pregnane X receptor) allows the binding of antibiotic rifampicin, one of the largest structural ligands for nuclear receptors [80]. The overall hydrophobic nature of the ligand-binding pocket allows the NRs to interact with many lipid soluble ligands [81,82]. Given the plastic nature of the ligand-binding pockets, NRs respond differently to distinct ligands and readily exchange their ligands in different environments. From the drug discovery point of view, NRs may possess even greater potential as the flexible ligand-binding pocket allowing them to interact with a wider array of pharmacophores. As such, the ligand-binding pockets of nuclear receptors are promising sites for drug discovery research.
NR dimerization is critical in many regulatory processes, as NRs can bind to their cognate sequence-specific promoter elements on target genes either as monomers [83,84,85,86], homodimers [72,87,88,89,90,91,92,93], or heterodimers with RXRs (retinoid X receptor α, β, and γ) [75,94,95,96,97,98,99,100] (Figure 1D). Cooperative DNA binding and distinct recognition sites of homodimer and heterodimer make dimerization a general mechanism to increase binding site affinity, specificity, and diversity [101]. NR LBD stabilizes the dimers, while NR DBD contributes to response element selection by dictating the response element repertoire for monomer, homodimer, or heterodimer receptors. The steroid receptors appear to function as homodimers, such as ER (estrogen receptor) [88], PR (progesterone receptor) [102], AR (androgens receptor) [103], GR (glucocorticoids receptor) [93], and MR (mineralocorticoid receptor) [71]. HNF4α (Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha) is rather unique in that it binds DNA exclusively as a homodimer and, yet, behaves as the subtype nuclear receptors that localized primarily in the nucleus and usually activated as heterodimer with RXR [92]. One third of known NRs act as heterodimers with RXR, including RARs (retinoic acid receptors) [94,95], VDR (vitamin D receptors) [104,105], TR (thyroid hormone receptors) [96], LXR (liver X receptor) [97], CAR (constitutive androstane receptor) [98,99], PPARs (peroxisome proliferator activated receptors) [75,100], PXR, and FXR (farnesoid X receptor). Further, RXR self-associates into a homodimer or a homotetramer in the active or auto-repressed state [106]. It is suggested that RXR exists predominately in inactive homotetramer in the absence of ligand in vivo and dissociates upon ligand binding to form homodimer or heterodimers with other NRs [107]. Crystal structures of homodimers and heterodimers of NRs have revealed the structural organization of NR dimers. The NR dimerizations are mainly mediated by the dimerization surface located on the LBDs, which are topologically conserved. The dimeric arrangements are closely related, with residues from helices H7, H9, and H10, and loops L8–9 and L9–10 of each protomer, forming an interface comprising a network of complementary hydrophobic and charged residues [94]. NGFI-B (Nerve Growth factor IB) [84], RevErb [85], ROR (RAR-related orphan receptor) [83], SF-1 (steroidogenic factor 1) [86], and several other orphan NRs have been shown to bind DNA as monomers. Interestingly, some NRs have been reported to function in multiple patterns. For example, TR can bind to DNA as monomers, homodimers, or heterodimers. A single surface mutation, D355R, was shown to be crucial for converting the modestly stable monomeric TR LBD into a stable dimer [108]. LXR have been reported both as homodimers and heterodimers, and the comparison of these two different dimer patterns explains differences in dimer affinity and leads us to propose a model for allosteric activation in LXR dimers, in which an unactivated RXR partner provides an inhibitory tail wrap to the cofactor binding pocket of LXR [109]. When activated, ER translocates into the nucleus, binding to DNA either as a αα homodimer or as a αβ heterodimer [110,111].
3. Nuclear Receptors as Drug Targets in Related Disease Signaling
Extensive studies have revealed that nuclear receptors are involved in many metabolic and inflammatory diseases, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, cirrhosis, and fibrosis [112,113,114,115,116,117]. As ligands play a pivotal role in modulating nuclear receptor activity, agonists or antagonists of nuclear receptors have been suggested for pharmaceutical development. The examples of disease relevance of NRs and drug development are listed in Table 1. As most marine natural ligands have been reported to target PPARs, FXR, PXR, and RARs, the following discussion focuses on the drug discovery targeting these well-described NRs as well as their therapeutic uses.
3.1. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR)
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs, isoforms α, β/δ, and γ) are ligand-activated nuclear receptors that play essential roles in lipid homeostasis [34], adipocyte differentiation [118], and insulin responses [119]. A large ligand-binding pocket is a distinguishing feature of PPARs, which allows them to bind a variety of chemical ligands including fatty acids, fibrates, and the thiazolidinedione class of antidiabetic drugs with diverse shapes, sizes, and compositions. The binding of ligands causes a conformational change in PPARs and the recruitment of coregulators, such as PGC1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha), which results in the transcriptional regulation of downstream target genes [120,121,122,123]. These genes in turn regulate many metabolic pathways involved in glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. PPARα is expressed in the liver, heart, muscle, and kidneys, and it regulates fatty acid metabolism and transport. PPARγ is expressed in adipose, muscle, and macrophage and is critical for adipogenesis and lipid storage. PPARδ is broadly expressed in the body and is involved in fat oxidation, energy expenditure, and lipid storage. These biological roles have made PPARs important targets in the treatment of metabolic syndrome and diabetes.
The most extensively studied ligands for PPARs are thiazolidinediones (TZDs), a class of drugs used to increase insulin sensitivity. TZDs can decrease insulin resistance, modify adipocyte differentiation, and induce lipoprotein lipase (LPL) by regulating the expression of PPARγ target genes [124,125,126,127]. However, TZDs are clinically limited due to severe adverse effects, such as fluid retention, weight gain, liver toxicity, and cardiovascular disease [38,128,129]. Therefore, it is imperative to develop improved PPARs ligands that retain the benefits in improving insulin resistance but that have reduced side effects. Current approaches include multi-target strategies (ligands targeting more than one PPAR isoform) and selectivity strategies (selective PPARγ modulators (SPPARMs)). Some SPPARMs with partial or no agonism in transcriptional activity have shown similar glucose-lowering effects to rosiglitazone but with reduced side effects [69,130,131,132]. Recently, we reported two novel ligands for PPARs (RU486 and ionomycin) as partial agonists for PPARγ [69,133], which may provide promising therapeutic agents targeting PPARs.
3.2. Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR)
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), also known as bile acid receptor, is important in maintaining bile acid and cholesterol homeostasis. FXR regulates the expression of transporters and biosynthetic enzymes, such as cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1), which is crucial for the physiological maintenance of bile acid homeostasis [134,135,136]. FXR is highly expressed in the liver, intestine, kidneys, and adrenal gland [137,138,139] and is activated by chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and other bile acids [140,141]. Following ligand binding, the transcriptional function of FXR is mediated through the recruitment of coactivators such as SRC1 or through the release of specific corepressors such as NCoR1 (nuclear receptor corepressor 1) and SMRT [142,143,144]. FXR regulates lipid metabolism, possibly by interacting with PPARα and PPARγ, as well as repressing sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) [145,146,147]. Activation of FXR by an agonist or hepatic overexpression of FXR lowered blood glucose levels in both diabetic db/db and high-fat diet-fed wild-type mice, and FXR-null mice exhibited glucose intolerance and insulin insensitivity [148].
Given the important roles of FXR in physiological and pathological processes, FXR ligands have become promising therapeutic agents for different diseases. Synthetic agonists of FXR (including GW4064, INT-747, and fexaramine) have been developed to treat primary biliary cirrhosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [149]. However, synthetic FXR ligands have limitations owing to side effects and uncertain bioavailability. The application of known natural FXR ligands, such as bile acid CDCA, is also limited by their poor selectivity and low affinity [144].
3.3. Retinoic Acid Receptor (RAR)
Retinoic acid receptors (RARs) exist as three subtype isoforms (α, β, and γ) that collectively contribute to a response to both natural and synthetic ligands [150,151]. RARα is associated with differentiation therapy for human acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) [44,152]. RARβ plays a crucial role in limiting the growth of different tumor cell types and is thus a promising target for the treatment of breast and other cancers [153]. RARγ is primarily expressed in the skin and is involved in skin diseases, such as psoriasis and acne [67].
RARs activate transcription in a ligand-dependent manner by binding to DNA as heterodimers with RXR. Ligand activation of RAR/RXR heterodimers drives physical interactions with co-regulatory proteins (corepressors and coactivators) and binding to retinoic acid response elements (RAREs) present in the promoter or enhancer regions of target genes. RAR ligand retinoids, which include vitamin A and its derivatives, have demonstrated some success as therapeutic agents for a wide range of diseases [150,151,154,155,156,157,158]. Retinoids exert their therapeutic effect by activating retinoid receptors, including RARs (α, β, and γ) and RXRs (α, β, and γ) [159,160,161]. For instance, the use of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), a retinoid panspecific for all RARs, has been very successful in the treatment of APL by inducing differentiation of leukemic cells.
Due to their teratogenic properties, retinoids can result in a number of undesired side effects, such as increased serum triglycerides and bone toxicity, presumably due to their panspecific activation of all RAR isoforms. Further, the occurrence of RA resistance in a variety of cancer cells is also one of the major concerns with retinoid treatments, which hampers RA-based chemotherapy [33]. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop ligands against RARs distinct from retinoids, which may yield more efficacious RAR-targeted drugs with less adverse effects.
3.4. Pregnane X Receptor (PXR)
By sensing the presence of foreign toxic substances, PXR can up-regulate the expression of proteins involved in the detoxification and clearance of these substances from the body [162]. In addition to detoxification and metabolism of xenobiotics, PXR is also involved in various physiological and pathophysiological processes, such as lipid metabolism [163], glucose homeostasis, and inflammatory response [164]. Recent studies suggest that PXR may be a useful target for pharmacological therapies in various conditions, including liver disease [165], and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), encompassing Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) [164,166]. PXR is activated by a large number of endogenous and exogenous chemicals including steroids, antibiotics, antimycotics, bile acids, and many other herbal compounds [162]. Following ligand binding, PXR forms a heterodimer with RXR and binds to specific PXR response elements (PXREs), located in the N-terminal flanking regions of PXR target genes, resulting in their transcriptional activation [167]. Primary targets of PXR activation are P450 enzymes (CYP3A, CYP2C, and CYP2B), important phase I oxidative enzymes that are responsible for the metabolism of many drugs [167,168]. In addition, PXR up-regulates the expression of phase II conjugating enzymes that improve solubility of phase I metabolites (glutathione S-transferases [169], sulfotransferases, and UDP-glucoronosyltransferases [170,171]) and phase III transport uptake and efflux proteins, such as OATP2 [172] and MDR1 [173,174].
PXR LBD shows a typical NRs organization, but its ligand-binding pocket is substantially larger than those of many other NRs [175,176]. Therefore, PXR is able to bind both small and large ligands. The number of chemicals that are reported to activate PXR has grown rapidly, including many drugs currently in use, such as statins, the antibiotic rifampicin, antihypertensive drugs nifedipine and spironolactone, anticancer compounds, HIV protease inhibitors, calcium channel modulators, diverse environmental toxicants, such as plasticizers and pesticides [177]. Rifampicin, a semisynthetic PXR agonist, is currently used in the treatment of cholestatic liver disease and its exact mechanism of action is still under investigation. Notably, most PXR ligands reported show agonism properties, whereas to date only few PXR antagonists have been identified [178].
4. Strategies for the Discovery of Novel Ligands for Nuclear Receptors
The discovery of novel ligands for nuclear receptors represents an interesting and promising therapeutic approach to various diseases. Both indirect and direct methodologies have been developed to identify compounds that bind to nuclear receptors in vitro, generally involving the LBDs. Direct approaches are the use of high-throughput screening (HTS) assays to identify compounds capable of regulating nuclear receptors; these assays have become increasingly popular because they can rapidly and accurately distinguish compounds among large chemical libraries [179]. Improved methods for the synthesis of chemical libraries have created a need for increased sensitivity and throughput in screening [180,181]. In the field of HTS, there are often various biochemical assays and cell-based assays available for efficiently measuring a particular nuclear receptor-ligand interaction; such choices are fluorescence polarization (FP), AlphaScreen assays, and transactivation reporter gene assays.
4.1. Fluorescence Polarization (FP) and Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
Fluorescence polarization (FP) is one of the standard ligand-binding assays, and it is commonly deployed in a high-throughput format to measure the rotational speed of a fluorophore during its fluorescence lifetime, defined as the duration of time post-excitation by plane-polarized light but prior to light emission [182]. In an FP assay, compounds are screened for their ability to compete with a labeled, validated LBD-binding ligand. Either an agonist or antagonist can be detected in this type of competitive binding assay [183]. A small coactivator peptide alone, containing an LXXLL motif and a fluorophore label, rotates quickly, and exhibits low polarization. Ligand binding of nuclear receptors induces the formation of a ligand-nuclear receptor-coactivator complex, which is larger and rotates more slowly, resulting in the emission of more highly polarized light. Therefore, ligand binding can be quantitatively monitored based on the difference in polarization.
The FRET assay was developed from the FP assay, in which the fluorescent signal intensity depends upon the interaction between a fluorescently labeled LBD and coactivator proteins. A fluorescent signal is obtained when the LBD is in close proximity to the coactivator proteins through its interaction with a putative agonist. In a time-resolved FRET (TR-FRET) assay, lanthanide chelates are used as the donor fluorophore and may be used to label either the protein directly or an antibody to a common protein tag. A receptor ligand is labeled with fluorescein or some other suitable acceptor fluorophore. Potential ligands that compete for LBD binding will result in an associated decrease in the TR-FRET signal. TR-FRET assays can greatly reduce data variability because they are able to measure both lanthanide and acceptor fluorophore emissions to generate FRET ratios. The FRET ratio is disrupted when a competitor ligand binds to the LBD and displaces the bound fluorescein-labeled tracer molecule. TR-FRET assays can minimize the nonspecific interference derived from short fluorescent lifetime components such as plate plastics, compound autofluorescence, and diffusion-enhanced FRET. Moreover, selecting the proper donor and acceptor fluorophores and wavelength filters allows for the monitoring of two simultaneous processes [184]. However, FP assays also have several disadvantages, including their high level of background, which translates into a lower signal-to-noise ratio and decreased sensitivity, and their inability to distinguish between agonists and antagonists [185].
4.2. AlphaScreen (Cofactor Binding Assays)
AlphaScreen, used mostly in high throughput screening, is a homogenous assay technology similar to TR-FRET. AlphaScreen technology was first described in 1994 and is based on the principle of luminescent oxygen channeling [186,187]. AlphaScreen is a bead-based, nonradioactive amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay in which a donor and an acceptor pair of 250-nm-diameter reagent-coated polystyrene microbeads are brought into proximity by a molecular interaction of binding partners immobilized to these beads [187,188,189]. The detection system of AlphaScreen can be time-gated, as the signal is long lived, thus, eliminating short-lived background signals. The high sensitivity of the assay derives from the very low background fluorescence. Furthermore, the detection wavelength is shorter than the excitation wavelength, thereby further reducing the potential for fluorescence interference.
The larger diffusion distance of the singlet oxygen makes the available detection of binding distance 200 nm, whereas TR-FRET is limited to 9 nm [190]. The most important advantage of AlphaScreen over TR-FRET is that the AlphaScreen can distinguish between an agonist and an antagonist by the selective usage of coactivator or corepressor peptides. The AlphaScreen system is generally applicable over a wide variety of biomolecular targets, which can supplant solid-support binding assays in many applications, such as receptor-ligand interactions [191], lipid signaling [192], protein kinase monitoring [193], and other types of signaling [194].
The unique advantages of AlphaScreen have made it an excellent alternative to TR-FRET for the measurement of ligand-induced nuclear receptor-cofactor interactions [195]. A comparison study between AlphaScreen and TR-FRET suggested that AlphaScreen would be better because of its increased sensitivity, decreased plate reading time, and increased proximity limits [195]. The large signal/background ratio and increased sensitivity in the AlphaScreen assay enable a significant reduction in the quantities of nuclear receptor protein and biotinyl-cofactor required for screening. For the AlphaScreen format, acceptable data can be obtained with five-fold less of these reagents compared to the TR-FRET assays. In recent years, more and more NR ligands have been identified by AlphaScreen. Our lab also uses AlphaScreen to determine the binding of the various cofactor peptide motifs to nuclear receptor LBDs in response to ligands. By using a hexahistidine detection kit from PerkinElmer (including the N-terminal biotinyl peptides, His-tag fusion LBD, and compound libraries) [68,69,133,196,197,198], several ligands for various nuclear receptors have been identified, including two PPARγ agonists [69,133], a marine natural product as an RAR agonist [196], an existing drug as an FXR agonist [68], a dual PPARα and PPARδ agonist [198], and a natural compound as an agonist for orphan receptor RORγ [197].
4.3. Transactivation Reporter Gene Assays (Transient Transfection Assays)
Cell-based systems are also widely used for identifying ligands that interact with nuclear receptors. Transient and stable transfections are two types of cell-based systems for assessing nuclear receptor transactivation. The most common method for evaluating nuclear receptor activation is transient reporter gene assay, through transient transfection of a nuclear receptor together with a cognate response element-reporter gene construct. In Gal4-driven reporter assays, the cells are transfected with Gal4-LBDs of various nuclear receptors and pG5Luc reporter. In native promoter reporter assays, the cells are co-transfected with plasmids encoding full-length nuclear receptors and their cognate luciferase reporters (e.g., PPARs and PPRE). Many cell lines are available to serve as recipients of these plasmids, including COS7, HuH7, HEK293, HepG2, and other stable tumor cell lines. Many nuclear receptor agonists have been identified using transient transactivation systems [199,200,201]. The advantages of reporter gene assays are their ease of use, efficiency, and reproducibility, as well as their ability to differentiate mechanisms of action in the nuclear receptor application. Similar to biochemical studies, the cell based transactivation assays can also be employed to obtain EC50 values that reflect the potency of a compound. This is important as clinical models are based upon EC50 and Emax values to rank a compound’s potency [202].
The biochemical assays, including FP, FRET, and AlphaScreen assays are straightforward, fast and easy to set up, with reasonable cost, enabling the high-throughput screening of a large number of chemical libraries. Following biochemical screening, it’s also necessary to perform cell-based assays, like a transactivation reporter assay, to validate the functional relevance of the hit compounds. To further characterize the underlying molecular mechanisms, various other biological assays and structure-activity relationships (SAR) analysis are often critical to gather more insights to optimize the hit compounds for future drug discovery. For example, Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is a type of immunoprecipitation experimental technique used to investigate coactivators and corepressors recruitment modulated by ligands [200,203,204], while real-time PCR allows precise quantification for the expression pattern of nuclear receptor target genes regulated by the hit compounds [68,69,200,204].
5. Search for Marine Natural Products Targeting Nuclear Receptors
The value of natural products from marine species has been recognized for over half a century, but it is only in recent years there has been a renewed interest in this potential source of new medicines [205]. Chemical, structural, and pharmacological characterizations of marine nature products libraries have successfully identified many hit compounds that regulate NRs. Recent research has been focusing on the development of novel drugs specifically targeting nuclear receptors for treating a variety of diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, dyslipidemia, fatty liver disease, drug hepatotoxicity, and cholestasis. Searching for novel nuclear receptor ligands (agonists and antagonists) from marine natural products with improved selectivity will prompt the exploration of the extraordinary chemical diversity associated with natural products. The marine environment has provided a rich source of nuclear receptor ligands, and a number of natural products have been shown to display remarkable affinity for nuclear receptors, in some cases with unique modes of action (Table 2). These nuclear receptors proven to be targets of marine natural products include RAR [196], FXR [206], PPARs [207,208], AR [209], GR [210], VDR [211], PR [212], and PXR [213]. In this section, selected examples of the marine natural ligands for NRs will be described with an emphasis on their therapeutic potentials.

Table 2.
List of marine natural molecules targeting nuclear receptors signaling.
| Compounds | Origin | Target(s) | Comments/References | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| luffariellolide | Marine sponges Luffariella sp. and Fascaplysinopsis | RAR | agonist of RAR with inhibitory effects on cancer cells [196] | AlphaScreen |
| 7-hydroxy retinoic acid | cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Spirulina sp. | RAR | agonist of RAR [214] | yeast two hybrid |
| SQA | Brown alga Sargassum yezoense | PPARα/γ | PPARα/γ dual agonists [207] | transfection assay |
| SHQA | Brown alga Sargassum yezoense | PPARα/γ | PPARα/γ dual agonists [207] | transfection assay |
| Ionomycin | Streptomyces conglobatus | PPARγ | partial agonist of PPARγ [69] | AlphaScreen |
| Tuberatolide A | Korean marine tunicate Botryllus tuberatus | FXR | antagonized the (CDCA)-activated FXR [206] | transfection assay |
| Meroterpenoids tuberatolide B | Korean marine tunicate Botryllus tuberatus | FXR | antagonized the (CDCA)-activated FXR [206] | transfection assay |
| 2′-epi-tuberatolide B | Korean marine tunicate Botryllus tuberatus | FXR | antagonized the (CDCA)-activated FXR [206] | transfection assay |
| yezoquinolide | Korean marine tunicate Botryllus tuberatus | FXR | antagonized the (CDCA)-activated FXR [206] | transfection assay |
| (R)-sargachromenol | Korean marine tunicate Botryllus tuberatus | FXR | antagonized the (CDCA)-activated FXR [206] | transfection assay |
| (S)-sargachromenol | Korean marine tunicate Botryllus tuberatus | FXR | antagonized the (CDCA)-activated FXR [206] | transfection assay |
| Compounds 1–5 | marine sponge Spongia sp. | FXR | FXR antagonistic activity [215] | transfection assay |
| 4-methylenesterols | marine sponge Theonellaswinhoei | FXR, PXR | potent agonists of PXR and antagonists of FXR [213,216] | transfection assay |
| Conicasterol E | marine sponge Theonella swinhoei | FXR, PXR | dual FXR and PXR agonist [217] | transfection assay |
| Malaitasterol A | marine sponge Theonella swinhoei | PXR | potent agonists of PXR [218] | transfection assay |
| suvanine | marine sponge | FXR | antagonist of FXR [200] | transfection assay |
| sulfated sterol (compound 8) | marine invertebrates | FXR | antagonist of FXR [219] | transfection assay |
| solomonsterols A and B | marine sponge Theonellaswinhoei | PXR | agonist of PXR [220] | transfection assay |
| okadaic acid | microalgae | CiVDR/PXRa, hPXR | activation at nanomolar concentration [211] | transfection assay |
| pectenotoxin-2 | microalgae | CiVDR/PXRa | activation at nanomolar concentration [211] | transfection assay |
| Phosphoiodyns A | Korean marine sponge Placospongia sp. | PPARδ | highly potent hPPARδ activity (EC50 = 23.7 nm) [208] | NMR spectrum |
| Herdmanine I and K | marine ascidian Herdmania momus | PPARγ | similar PPARγ agonistic activities to rosiglitazone [221] | transfection assay |
| gracilioether B and plakilactone C | marine sponge Plakinastrella mamillaris | PPARγ | selective PPARγ ligands [222] | transfection assay |
| Niphatenones | Marine sponge Niphates digitalis | AR | block androgen receptor transcriptional activity in prostate cancer cells [209] | transfection assay |
| Psammaplin A | marine sponge Pseudoceratina rhax | PPARγ | activates PPARγ in a MCF-7 cell-based reporter assay [223] | transfection assay |
| chlorinated peptides sintokamides A to E | sponge Dysidea sp. | AR | inhibitor of N-terminus transactivation of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells [224] | transfection assay |
| theonellasterol | marine sponge Theonella swinhoei | FXR | FXR antagonist [225] | transfection assay |
| steroids 3-oxocholest-1,22-dien-12beta-ol and 3-oxocholest-1,4-dien-20beta-ol | soft coral Dendronephthya gigantea | FXR | inhibitory activity against FXR with IC(50)’s 14 and 15 µM [226] | transfection assay |
| Bendigoles D | marine sponge derived bacterium Actinomadura sp. SBMs009 | GR | inhibitor of GR [210] | transfection assay |
| (3R)-cyclocymopol monomethyl ether | marine alga Cymopolia barbata | PR | PR antagonist [212] | transfection assay |
| (3S)-cyclocymopol monomethyl ether | marine alga Cymopolia barbata | PR | PR agonist [212] | transfection assay |
5.1. Luffariellolide and RARs
Very few reports on natural ligands of RARs have been reported so far in the literature [196,214,227]. Among these natural ligands, 7-hydroxy retinoic acid and luffariellolide were isolated from marine organisms. 7-hydroxy retinoic acid is an analog of ATRA isolated from cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Spirulina sp., and its relative RAR agonistic activity was lower than ATRA [214]. Due to its similar structure with RA and RA resistance in a variety of cancer cells, further exploration of 7-hydroxy retinoic acid in therapy has been limited [228]. Therefore, the search for new RAR ligands other than retinoids with distinct activity profiles and fewer side effects may provide a new rational drug design strategy targeting nuclear receptor RARs. Meeting these criteria, luffariellolide may be an ideal hit compound for drug design [196].
Considering the structural diversity, lower toxicity, and abundance of marine natural products, our laboratory set out to search for novel ligands for RARs present in marine products libraries by using the AlphaScreen biochemical assay [196]. The marine natural product luffariellolide, a hexane extract isolated from sponges of Luffariella sp. and Fascaplysinopsis, was identified as a positive RARα activator. Notably, the chemical structure of luffariellolide shows a unique γ-hydroxybutenolide ring terminus instead of a carboxylic acid moiety for retinoids, thus, representing a novel approach for an RAR ligand design strategy distinct from the retinoid scaffold. In the follow-up study, cell-based bioassays were used to attain characteristics of luffariellolide in activating nuclear receptors, and the results have shown that luffariellolide was a selective agonist for all three RARs, but not for other NRs, including the heterodimer partner RXRα.
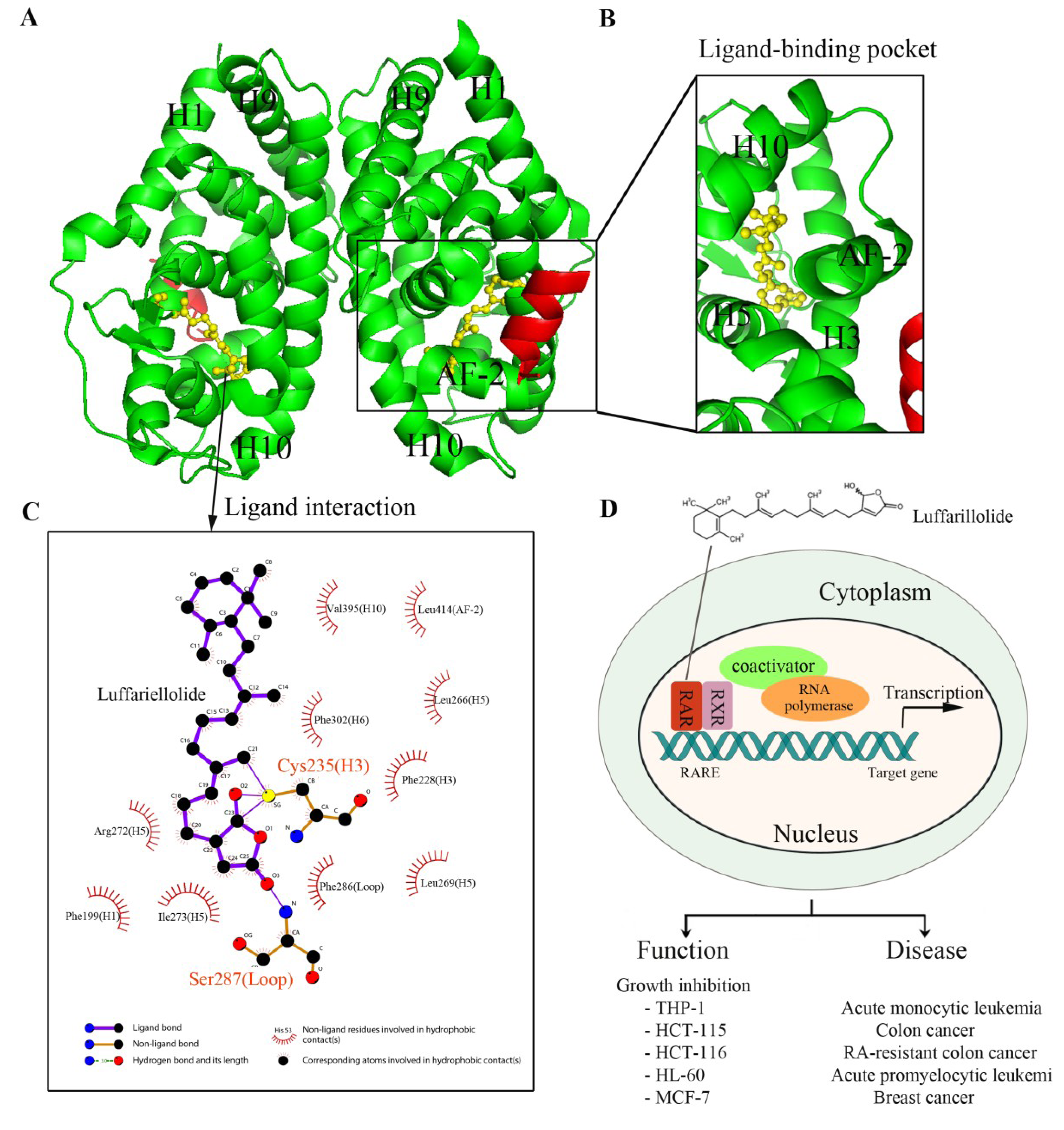
The ability of luffariellolide to promote recruitment of coactivator motifs by RARs was determined and the results were consistent with that of the cell reporter assay. Moreover, we were also able to obtain the crystal structure of luffariellolide bound to the LBD of RARα, which revealed the molecular basis for the binding of luffariellolide by RARs (Figure 3A,B). By structural comparison between the luffariellolide-RARα complex and the ATRA-RARα complex, a unique binding mode of luffariellolide to RARα was identified. Strikingly, the luffariellolide-RARα structure revealed a covalent interaction between the ligand and the receptor, in addition to several hydrophobic and van der Waals interactions. Specifically, a covalent bond formed between the Cys235 in RARα and the ketone on the unique γ-hydroxybutenolide group of luffariellolide (Figure 3C). The covalent interaction has been further confirmed by mass spectrometry (MS) and by mutagenesis studies of RARα LBD. Incubation of RARα LBD with luffariellolide yielded a mass addition corresponding to the molecular mass of the luffariellolide ligand. In the mutagenesis study, both the C235A and C235L mutations abolished the activation of RARα by luffariellolide, suggesting the critical roles of this covalent modification for the receptor-luffariellolide interaction.
Next, several cell-based experiments were conducted to assess the roles of luffariellolide in regulating the physiological functions of RARs. Luffariellolide could reduce cell proliferation and induce known RA-inducible genes in various cancer cells (Figure 3D). Of significance is the observation that in an RA-resistant HCT-116 cell line, in which retinoids failed to show effect, luffariellolide was able to function as an RAR agonist, reducing cell proliferation and switching on target genes. In future studies, it will be worth investigating if luffariellolide can act in suitable in vivo disease models with the downstream target gene responsible for overcoming RA-resistance using luffariellolide as a probe.
Taken together, as a novel RAR agonist, marine natural product luffariellolide may provide an alternative drug design strategy for non-retinoid compounds with advantages over current RA drugs. The unique characteristics of the γ-hydroxybutenolide ring may represent a new pharmacophore that can be optimized for selectively targeting RARs.
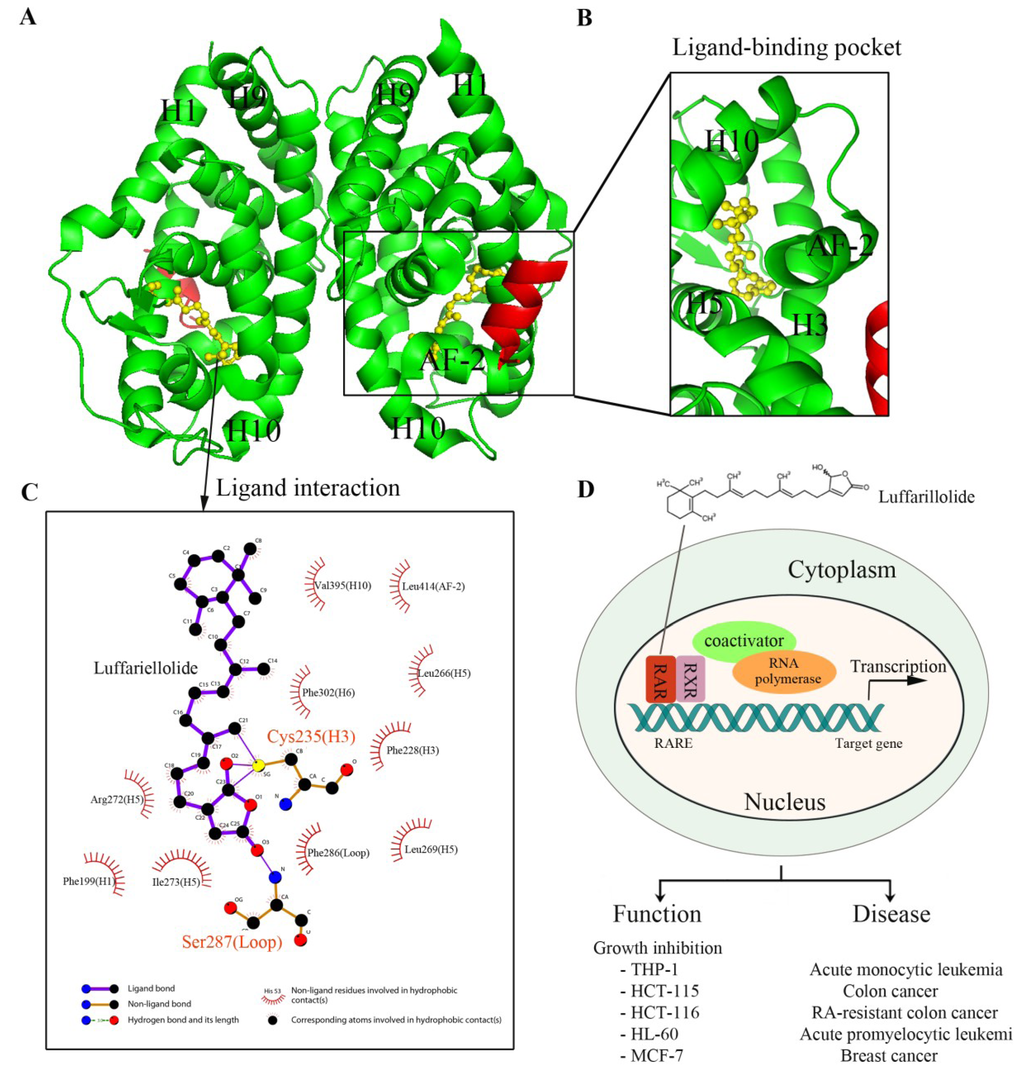
Figure 3.
The structure and gene regulation of luffariellolide bound RARα. (A) Intact structure of RARα LBD-Luffariellolide complex. Luffariellolide-bound RARα adopts a dimer fold. The RARα LBD (green) and coactivator SRC1 (red) motif are depicted in image representation, and luffariellolide is shown in yellow ball and stick representation; (B) Enlarged view of the ligand-binding pocket of RARα. AF-2, together with Helix 3, Helix 5, and Helix 10, form a ligand-binding pocket for luffariellolide; (C) Interaction analysis of luffariellolide by Ligplot [229]. Cys235 from Helix 3 of RARα LBD forms a covalent bond with the ketone group of the γ-hydroxybutenolide ring terminus from luffariellolide; (D) Gene regulation by RARα in the presence of luffariellolide. Luffariellolide treatment can inhibit the cell proliferation of monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1, RA-sensitive colon cancer cell line HCT-115, RA-resistant colon cancer cell line HCT-116, promyeloid leukemic cell line HL-60, and breast carcinoma line MCF-7 [196].
Figure 3.
The structure and gene regulation of luffariellolide bound RARα. (A) Intact structure of RARα LBD-Luffariellolide complex. Luffariellolide-bound RARα adopts a dimer fold. The RARα LBD (green) and coactivator SRC1 (red) motif are depicted in image representation, and luffariellolide is shown in yellow ball and stick representation; (B) Enlarged view of the ligand-binding pocket of RARα. AF-2, together with Helix 3, Helix 5, and Helix 10, form a ligand-binding pocket for luffariellolide; (C) Interaction analysis of luffariellolide by Ligplot [229]. Cys235 from Helix 3 of RARα LBD forms a covalent bond with the ketone group of the γ-hydroxybutenolide ring terminus from luffariellolide; (D) Gene regulation by RARα in the presence of luffariellolide. Luffariellolide treatment can inhibit the cell proliferation of monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1, RA-sensitive colon cancer cell line HCT-115, RA-resistant colon cancer cell line HCT-116, promyeloid leukemic cell line HL-60, and breast carcinoma line MCF-7 [196].
5.2. Marine Products Targeting FXR
Marine sponges Theonella species have been proven to be an extraordinary source of unusual new chemical entities, mainly peptides and macrolides, with impressive biological activities [217]. Apart from anti-inflammatory peptides [230] and cytotoxic macrolides [231], recent chemical and pharmacological analysis of several Theonella extracts has furnished a large family of molecules able to target FXR and PXR, including solomonsterols [220,232] and a large number of 4-methylenesteroids [213,216,217,218]. Solomonsterols A and B were identified to stimulate the expression of CYP3A4 and MDR1, two well characterized PXR responsive genes, making them potential hit compounds for the treatment of human disorders characterized by inflammation and dysregulation of innate immunity [220,232]. Further pharmacological studies in animal models of colitis demonstrated that synthetic solomonsterol A effectively protects against development of clinical signs and symptoms of colitis and reduces the generation of TNFα, a signature cytokine for this disorder [232]. Within the family of 4-methylenesteroids, theonellasterol, the major component of the steroidal fraction of Theonella swinhoei, was identified as a highly selective FXR antagonist with pharmacological potential in the treatment of cholestasis [204]. Theonellasterol directly inhibits FXR transactivation caused by CDCA and reverses the effect of CDCA on the expression of canonical FXR target genes. In rodent models of cholestasis, theonellasterol attenuates liver injury caused by bile duct ligation. Interestingly, 4-methylenesterols derived from marine sponge Theonella swinhoei, was found to have potent PXR agonist activity and FXR antagonist activity [213,216,217,218]. The dual behaviors of these marine natural compounds may lead to combination therapies involving lower drug doses and therefore reduced side effects.
Hepatic FXR activation leads to both beneficial actions and potentially undesirable side effects such as the inhibitions of bile acids synthesis and basolateral efflux of bile acids [233]. These findings have raised the notion that FXR antagonists might be useful in the treatment of liver disorders caused by impairment of bile secretion [204]. However, only few FXR antagonists are known and the main contribution is derived from terrestrial and marine natural compounds [228]. Most of the FXR antagonists have a steroid skeleton [219,220,232,234,235]. The steroidal FXR antagonists may also regulate steroid receptors and are unsuitable for studying FXR physiology. Therefore, the discovery of nonsteroidal FXR antagonists is highly desirable.
Six nonsteroidal FXR antagonists from the Korean marine tunicate Botryllus tuberatus were identified, including the isoprenoid tuberatolide A, a pair of diastereomeric meroterpenoids (tuberatolide B and 2′-epi-tuberatolide B), and three meroterpenoids (yezoquinolid, (R)-sargachromenol, and (S)-sargachromenol) [206]. They show potent inhibition of FXR transactivation without significant cytotoxicity. More importantly, these compounds have no effects on steroid receptors in transactivation experiments. Structurally, the six compounds all have γ-lactones or carboxylic acids at the C-15 position, suggesting that the carbonyl group at C-15 may enhance the FXR antagonistic effects and may help to unravel the controversial function of FXR in atherosclerosis [206].
Sesterterpenes isolated from marine sponges are particularly interesting from their pharmacological properties. There is no report of biological activity of scalaranes in regard to metabolic disorders until the discovery of five novel scalarane sesterterpenes with FXR inhibitory activities [215]. All five sesterterpenes were isolated from marine sponge Spongia sp. and showed inhibitory activities against FXR transactivation. Notably, 12,24-diacetoxy-deoxoscalarin showed the most potent inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 8.1 µM without any significant cytotoxicity [215]. In addition, suvanine, a furano sesterterpene sulfate from the marine sponge Coscinoderma mathewsi, was reported as a novel antagonist of the mammalian bile acid sensor FXR [200].
5.3. Marine Products Targeting PPARs and AR
As for PPARs, a master regulator of adipocyte differentiation, psammaplin A from the sponge Pseudoceratina rhax and herdmanine from the marine ascidian Herdmania momus were both revealed to activate PPARγ [223]. In addition, the marine natural products sargaquinoic acid (SQA) and sargahydroquinoic acid (SHQA) from Sargassum yezoense were reported as novel PPARα/γ dual agonists. SQA and SHQA increased adipocyte differentiation accompanied by increased expression of adipogenic marker genes, suggesting that these PPARα/γ dual agonists may reduce insulin resistance through regulating adipogenesis [207]. SQA, also named aleglitazar, already entered phase III clinical trials for the treatment of type 2 diabetes but failed due to its inacceptable side effects related to bone fractures, heart failure, and gastrointestinal bleeding [236]. Gracilioether B and plakilactone C isolated from the marine sponge Plakinastrella mamillaris were identified as selective PPARγ ligands in transactivation assays. Both agents regulate the expression of PPARγ-dependent genes in the liver and inhibit the generation of inflammatory mediators by macrophages. More importantly, these two marine natural compounds covalently bind to the PPARγ LBD through a Michael addition reaction involving a cysteine residue and the α,β-unsaturated ketone in their side chains, suggesting the possibility to develop novel PPARγ modulators as potential agents in the treatment of inflammatory disorders [222].
Interestingly, several marine natural products with antagonism activities interact with AR at its N-terminal domain, not the LBD, including a group of glycerol ethers (niphatenones) from the sponge Niphates digitalis [209] and a group of chlorinated peptides, termed sintokamides, from the sponge Dysidea sp. [224]. These two AR antagonists demonstrate the possibility of targeting regions other than the traditional LBDs to modulate NR activity, thus, providing an alternative method for NR ligand screening to overcome hormone resistance.
6. Conclusions
As the pathogenesis of diseases is complicated, the development of safe and effective drugs against diseases is full of challenges. Currently, nuclear receptors have been engaged in hit compound discovery as important targets involved in disease. In comparison with synthetic compounds, natural products possess multiple advantages for their large-scale structures and target diversity both in single target and signaling pathway-based drug discovery strategies. In addition, the complex structures of natural products lead to great target diversity. Therefore, natural molecules often function as good probe candidates for exploring novel targets or pathways involved in diseases.
The marine environment has long been known to be species-rich. Recent studies have revealed more and more marine natural products as nuclear receptor modulators, which highlights the translational possibilities of natural products in drug discovery. Many emerging strategies have been developed to speed up the drug discovery process, including natural product isolation technologies, compound synthesis and optimization methods, and high-throughput screening technologies. It is reasonable to expect that interaction between marine natural products and nuclear receptors will continue to provide more hit compounds, as well as a mechanistic understanding for drug discovery targeting nuclear receptors, thereby, greatly facilitating the development of therapeutic reagents against human diseases.
Taken together, the discovery of NR ligands in marine natural products and their derivatives opens a promising approach for the design and preparation of new potential leads in the pharmacological treatment of NR-mediated human diseases.
Acknowledgments
We thank the grants support from the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program: 2012CB910104 to Y. Li), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31200571 to C. Yang and 31270776 to Y. Li).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Koehn, F.E.; Carter, G.T. The evolving role of natural products in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljanich, G.P. Ziconotide: Neuronal calcium channel blocker for treating severe chronic pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adis International Limited. Trabectedin: Ecteinascidin 743, Ecteinascidin-743, ET 743, ET-743, NSC 684766. Drugs R D 2006, 7, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overington, J.P.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Hopkins, A.L. How many drug targets are there? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Thummel, C.; Beato, M.; Herrlich, P.; Schutz, G.; Umesono, K.; Blumberg, B.; Kastner, P.; Mark, M.; Chambon, P.; et al. The nuclear receptor superfamily: The second decade. Cell 1995, 83, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lambert, M.H.; Xu, H.E. Activation of nuclear receptors: A perspective from structural genomics. Structure 2003, 11, 741–746. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Li, Y. Structural and functional insights into nuclear receptor signaling. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halilbasic, E.; Baghdasaryan, A.; Trauner, M. Nuclear receptors as drug targets in cholestatic liver diseases. Clin. Liver Dis. 2013, 17, 161–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xie, W. Role of the constitutive androstane receptor in obesity and type 2 diabetes: A case study of the endobiotic function of a xenobiotic receptor. Drug Metab. Rev. 2013, 45, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, L.; Yang, H.; Ferguson, S.S.; Baer, M.R.; Gartenhaus, R.B.; Wang, H. The constitutive androstane receptor is a novel therapeutic target facilitating cyclophosphamide-based treatment of hematopoietic malignancies. Blood 2013, 121, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, P.; Brodie, M.J. Phenobarbital for the treatment of epilepsy in the 21st century: A critical review. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnwald, L.K.; Rossing, M.A.; Li, C.I. Hormone receptor status, tumor characteristics, and prognosis: A prospective cohort of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Thompson, M.; Lynch, I.J.; Bhardwaj, B. Expression of estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes and ERbeta isoforms in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 632–640. [Google Scholar]
- Bonkhoff, H.; Fixemer, T.; Hunsicker, I.; Remberger, K. Estrogen receptor expression in prostate cancer and premalignant prostatic lesions. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskobing, D.M. Update on bazedoxifene: A novel selective estrogen receptor modulator. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 299–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Carlsson, B.; Grandien, K.; Enmark, E.; Haggblad, J.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 863–870. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, S.R.; Eckert, S.; Krueger, K.A.; Grady, D.; Powles, T.J.; Cauley, J.A.; Norton, L.; Nickelsen, T.; Bjarnason, N.H.; Morrow, M.; et al. The effect of raloxifene on risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women: Results from the MORE randomized trial. Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation. JAMA 1999, 281, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, S.R.; Ensrud, K.; Delmas, P.D.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Vukicevic, S.; Reid, D.M.; Goldstein, S.; Sriram, U.; Lee, A.; Thompson, J.; et al. Lasofoxifene in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yan, L.; Gao, M.; Liu, D. Synthetic FXR agonist GW4064 prevents diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudaliar, S.; Henry, R.R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Morrow, L.; Marschall, H.U.; Kipnes, M.; Adorini, L.; Sciacca, C.I.; Clopton, P.; Castelloe, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the farnesoid X receptor agonist obeticholic acid in patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quax, R.A.; Manenschijn, L.; Koper, J.W.; Hazes, J.M.; Lamberts, S.W.; van Rossum, E.F.; Feelders, R.A. Glucocorticoid sensitivity in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 670–686. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Nelson, R.K.; Tabor, D.E.; Zhang, Y.; Akhter, M.P.; Gould, K.A.; Wang, D. Dexamethasone prodrug treatment prevents nephritis in lupus-prone (NZB × NZW)F1 mice without causing systemic side effects. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 4029–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.; Young, A.H. Mifepristone (RU-486) treatment for depression and psychosis: A review of the therapeutic implications. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2006, 2, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Arya, V.B.; Rahman, S.; Senniappan, S.; Flanagan, S.E.; Ellard, S.; Hussain, K. HNF4A mutation: Switch from hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia to maturity-onset diabetes of the young, and incretin response. Diabet. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalderon, B.; Mayorek, N.; Ben-Yaacov, L.; Bar-Tana, J. Adipose tissue sensitization to insulin induced by troglitazone and MEDICA 16 in obese Zucker rats in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E795–E803. [Google Scholar]
- Ducheix, S.; Montagner, A.; Theodorou, V.; Ferrier, L.; Guillou, H. The liver X receptor: A master regulator of the gut-liver axis and a target for non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, R.K.; Singh, N. Liver X receptors: Emerging therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 72, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Roz, A.; Bard, J.M.; Huvelin, J.M.; Nazih, H. LXR agonists and ABCG1-dependent cholesterol efflux in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: Relation to proliferation and apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 3007–3013. [Google Scholar]
- Kappus, M.S.; Murphy, A.J.; Abramowicz, S.; Ntonga, V.; Welch, C.L.; Tall, A.R.; Westerterp, M. Activation of liver X receptor decreases atherosclerosis in Ldlr−/− mice in the absence of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in myeloid cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, B.; Zondlo, S.; Gibbs, S.; Cromley, D.; Hosagrahara, V.P.; Kirchgessner, T.G.; Billheimer, J.; Mukherjee, R. Raising HDL cholesterol without inducing hepatic steatosis and hypertriglyceridemia by a selective LXR modulator. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, V.; Li, X.; Nabakka, J.; Liang, F.; Wityak, J.; Koder, A.; Vargas, L.; Romeo, R.; Mitro, N.; Mak, P.A.; et al. N-Acylthiadiazolines, a new class of liver X receptor agonists with selectivity for LXRbeta. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 4255–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grefhorst, A.; Elzinga, B.M.; Voshol, P.J.; Plosch, T.; Kok, T.; Bloks, V.W.; van der Sluijs, F.H.; Havekes, L.M.; Romijn, J.A.; Verkade, H.J.; et al. Stimulation of lipogenesis by pharmacological activation of the liver X receptor leads to production of large, triglyceride-rich very low density lipoprotein particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34182–34190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, H.; Dreyer, C.; Medin, J.; Mahfoudi, A.; Ozato, K.; Wahli, W. Fatty acids and retinoids control lipid metabolism through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 2160–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarstedt, A.; Andersson, C.X.; Rotter Sopasakis, V.; Smith, U. The effect of PPARgamma ligands on the adipose tissue in insulin resistance. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2005, 73, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonjans, K.; Peinado-Onsurbe, J.; Lefebvre, A.M.; Heyman, R.A.; Briggs, M.; Deeb, S.; Staels, B.; Auwerx, J. PPARalpha and PPARgamma activators direct a distinct tissue-specific transcriptional response via a PPRE in the lipoprotein lipase gene. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5336–5348. [Google Scholar]
- Dressel, U.; Allen, T.L.; Pippal, J.B.; Rohde, P.R.; Lau, P.; Muscat, G.E. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta agonist, GW501516, regulates the expression of genes involved in lipid catabolism and energy uncoupling in skeletal muscle cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 2477–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K. Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2457–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentz, A.J.; Friedmann, P.S. Type 2 diabetes, psoriasis and thiazolidinediones. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2006, 60, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, L.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.S.; Shyy, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; et al. Shear stress activation of nuclear receptor PXR in endothelial detoxification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13174–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yu, R.T.; Atkins, A.R.; Downes, M.; Tukey, R.H.; Evans, R.M. Targeting the pregnane X receptor in liver injury. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondugula, S.R.; Mani, S. Pregnane xenobiotic receptor in cancer pathogenesis and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, G.V.; Ball, C.S.; Mowat, A.P.; Mieli-Vergani, G. Effect of rifampicin in the treatment of pruritus in hepatic cholestasis. Arch. Dis. Child. 1993, 69, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altucci, L.; Leibowitz, M.D.; Ogilvie, K.M.; de Lera, A.R.; Gronemeyer, H. RAR and RXR modulation in cancer and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; de Luca, L.M. Therapeutic potential of “rexinoids” in cancer prevention and treatment. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4945–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, D.J.; Duvic, M.; Horwitz, S.M.; Hymes, K.; Goy, A.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.J.; Feldman, T.; Wegner, B.; Myskowski, P.L. Final results of phase II trial of doxorubicin HCl liposome injection followed by bexarotene in advanced cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzani, A.; Moia, S.; Prodam, F.; Walker, G.E.; Bellone, S.; Petri, A.; Bona, G. A novel familial variation of the thyroid hormone receptor beta gene (I276N) associated with resistance to thyroid hormone. Thyroid 2012, 22, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.D.; Privalsky, M.L. Thyroid hormone receptor mutations in cancer and resistance to thyroid hormone: Perspective and prognosis. J. Thyroid Res. 2011, 2011, 361304:1–361304:20. [Google Scholar]
- Negro, R.; Formoso, G.; Mangieri, T.; Pezzarossa, A.; Dazzi, D.; Hassan, H. Levothyroxine treatment in euthyroid pregnant women with autoimmune thyroid disease: Effects on obstetrical complications. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 2587–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L. Protective role of the vitamin D receptor. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 279, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- hakhtoura, M.; Azar, S.T. The role of vitamin d deficiency in the incidence, progression, and complications of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, D.G.; Chen, S.; Glenn, D.J. Vitamin D and the heart. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R969–R977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, S.M.; Ho, L.T. Oral doxercalciferol therapy for secondary hyperparathyroidism in a peritoneal dialysis patient. Clin. Nephrol. 2002, 58, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.J. Targeting the mineralocorticoid receptor in cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.J.; Bomback, A.S.; Klemmer, P.J. Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2011, 13, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocchio, J.P.; Warnock, D.G.; Jaisser, F. Mineralocorticoid receptor activation and blockade: An emerging paradigm in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, A.P.; McCurley, A.; Preston, I.R.; Jaffe, I.Z. Mineralocorticoid receptors in vascular disease: Connecting molecular pathways to clinical implications. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2013, 15, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Nawaz, Z. Progesterone receptors—Animal models and cell signaling in breast cancer: Role of steroid receptor coactivators and corepressors of progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqua, S.A.; Cui, Y.; Lee, A.V.; Osborne, C.K.; Horwitz, K.B. Insights into the role of progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 931–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kurita, T.; Bulun, S.E. Progesterone action in endometrial cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and breast cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 130–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Cruz-Rodriguez, O.; Bolton, E.; Iniguez-Lluhi, J.A. The in vivo role of androgen receptor SUMOylation as revealed by androgen insensitivity syndrome and prostate cancer mutations targeting the proline/glycine residues of synergy control motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 31195–31206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Sakari, M.; Okada, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Takahashi, S.; Kouzmenko, A.; Kato, S. The androgen receptor in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolagas, S.C.; O’Brien, C.A.; Almeida, M. The role of estrogen and androgen receptors in bone health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, J.D. Reconstructing a disease: What essential features of the retinoic acid receptor fusion oncoproteins generate acute promyelocytic leukemia? Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Evans, T.; Chuang, P.; Das, B.; He, J.C. Novel retinoic acid receptor alpha agonists for treatment of kidney disease. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27945. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.P.; Casadesus, G.; Zhu, X.; Lee, H.G.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Gustaw-Rothenberg, K.; Lerner, A. All-trans retinoic acid as a novel therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Molecular mechanisms of retinoid actions in skin. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Feng, X.; Rong, H.; Pan, Z.; Inaba, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zheng, W.; Lin, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Feng, X.; Qiu, L.; Pan, Z.; Wang, R.; Lin, S.; Hou, D.; Jin, L.; Li, Y. Identification of the antibiotic ionomycin as an unexpected peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligand with a unique binding mode and effective glucose-lowering activity in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita-Sato, S.; Ito, S.; Isobe, T.; Ohyama, T.; Wakabayashi, K.; Morishita, K.; Ando, O.; Isono, F. Structural basis of digoxin that antagonizes RORgamma t receptor activity and suppresses Th17 cell differentiation and interleukin (IL)-17 production. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31409–31417. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Suino, K.; Daugherty, J.; Xu, H.E. Structural and biochemical mechanisms for the specificity of hormone binding and coactivator assembly by mineralocorticoid receptor. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguet, W.; Ruff, M.; Chambon, P.; Gronemeyer, H.; Moras, D. Crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the human nuclear receptor RXR-alpha. Nature 1995, 375, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, W.P.; Burschka, C.; Gotz, K.; Kaupp, M.; Ivanova, D.; Gaudon, C.; Sato, Y.; Antony, P.; Rochel, N.; Moras, D.; et al. Silicon analogues of the RXR-selective retinoid agonist SR11237 (BMS649): Chemistry and biology. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; Shen, X. Structural basis for retinoic X receptor repression on the tetramer. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24593–24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampe, R.T., Jr.; Montana, V.G.; Lambert, M.H.; Miller, A.B.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Milburn, M.V.; Kliewer, S.A.; Willson, T.M.; Xu, H.E. Asymmetry in the PPARgamma/RXRalpha crystal structure reveals the molecular basis of heterodimerization among nuclear receptors. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, R.T.; Wisely, G.B.; Westin, S.; Cobb, J.E.; Lambert, M.H.; Kurokawa, R.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Willson, T.M.; Glass, C.K.; Milburn, M.V. Ligand binding and co-activator assembly of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Nature 1998, 395, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.E.; Stanley, T.B.; Montana, V.G.; Lambert, M.H.; Shearer, B.G.; Cobb, J.E.; McKee, D.D.; Galardi, C.M.; Plunket, K.D.; Nolte, R.T.; et al. Structural basis for antagonist-mediated recruitment of nuclear co-repressors by PPARalpha. Nature 2002, 415, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, C.A.; Gampe, R.T., Jr.; Lambert, M.H.; Parks, D.J.; Montana, V.; Bynum, J.; Broderick, T.M.; Hu, X.; Williams, S.P.; Nolte, R.T.; et al. Structure of Rev-erbalpha bound to N-CoR reveals a unique mechanism of nuclear receptor-co-repressor interaction. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallen, J.; Schlaeppi, J.M.; Bitsch, F.; Filipuzzi, I.; Schilb, A.; Riou, V.; Graham, A.; Strauss, A.; Geiser, M.; Fournier, B. Evidence for ligand-independent transcriptional activation of the human estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha): Crystal structure of ERRalpha ligand binding domain in complex with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 49330–49337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrencik, J.E.; Orans, J.; Moore, L.B.; Xue, Y.; Peng, L.; Collins, J.L.; Wisely, G.B.; Lambert, M.H.; Kliewer, S.A.; Redinbo, M.R. Structural disorder in the complex of human pregnane X receptor and the macrolide antibiotic rifampicin. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, S.W.; Suino-Powell, K.; Zhou, X.E.; Kretschman, J.E.; Reynolds, R.; Vonrhein, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; et al. Identification of COUP-TFII orphan nuclear receptor as a retinoic acid-activated receptor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowski, M.D.; Ni, A.; Hagey, L.R.; Ekins, S. Evolution of promiscuous nuclear hormone receptors: LXR, FXR, VDR, PXR, and CAR. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 334, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguere, V.; McBroom, L.D.; Flock, G. Determinants of target gene specificity for ROR alpha 1: Monomeric DNA binding by an orphan nuclear receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, T.E.; Fahrner, T.J.; Milbrandt, J. The orphan receptors NGFI-B and steroidogenic factor 1 establish monomer binding as a third paradigm of nuclear receptor-DNA interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 5794–5804. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, H.P.; Lazar, M.A. The monomer-binding orphan receptor Rev-Erb represses transcription as a dimer on a novel direct repeat. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 4791–4802. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Choi, M.; Cavey, G.; Daugherty, J.; Suino, K.; Kovach, A.; Bingham, N.C.; Kliewer, S.A.; Xu, H.E. Crystallographic identification and functional characterization of phospholipids as ligands for the orphan nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor-1. Mol. Cell 2005, 17, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisi, B.F.; Xu, W.X.; Otwinowski, Z.; Freedman, L.P.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Sigler, P.B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature 1991, 352, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, J.W.; Chapman, L.; Finch, J.T.; Rhodes, D. The crystal structure of the estrogen receptor DNA-binding domain bound to DNA: How receptors discriminate between their response elements. Cell 1993, 75, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Khorasanizadeh, S.; Miyoshi, Y.; Lazar, M.A.; Rastinejad, F. Structural elements of an orphan nuclear receptor-DNA complex. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, A.M.; Pike, A.C.; Dauter, Z.; Hubbard, R.E.; Bonn, T.; Engstrom, O.; Ohman, L.; Greene, G.L.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Carlquist, M. Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature 1997, 389, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greschik, H.; Wurtz, J.M.; Sanglier, S.; Bourguet, W.; van Dorsselaer, A.; Moras, D.; Renaud, J.P. Structural and functional evidence for ligand-independent transcriptional activation by the estrogen-related receptor 3. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Huang, P.; Potluri, N.; Wu, D.; Kim, Y.; Rastinejad, F. Multidomain integration in the structure of the HNF-4alpha nuclear receptor complex. Nature 2013, 495, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledsoe, R.K.; Montana, V.G.; Stanley, T.B.; Delves, C.J.; Apolito, C.J.; McKee, D.D.; Consler, T.G.; Parks, D.J.; Stewart, E.L.; Willson, T.M.; et al. Crystal structure of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain reveals a novel mode of receptor dimerization and coactivator recognition. Cell 2002, 110, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguet, W.; Vivat, V.; Wurtz, J.M.; Chambon, P.; Gronemeyer, H.; Moras, D. Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogenberg, V.; Guichou, J.F.; Vivat-Hannah, V.; Kammerer, S.; Perez, E.; Germain, P.; de Lera, A.R.; Gronemeyer, H.; Royer, C.A.; Bourguet, W. Characterization of the interaction between retinoic acid receptor/retinoid X receptor (RAR/RXR) heterodimers and transcriptional coactivators through structural and fluorescence anisotropy studies. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Putcha, B.D.; Wright, E.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Fernandez, E.J. Structural basis for negative cooperativity within agonist-bound TR:RXR heterodimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6084–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, S.; Ostberg, T.; Jacobsson, M.; Norstrom, C.; Stefansson, K.; Hallen, D.; Johansson, I.C.; Zachrisson, K.; Ogg, D.; Jendeberg, L. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric complex of LXRalpha and RXRbeta ligand-binding domains in a fully agonistic conformation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suino, K.; Peng, L.; Reynolds, R.; Li, Y.; Cha, J.Y.; Repa, J.J.; Kliewer, S.A.; Xu, H.E. The nuclear xenobiotic receptor CAR: Structural determinants of constitutive activation and heterodimerization. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 893–905. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.X.; Lambert, M.H.; Wisely, B.B.; Warren, E.N.; Weinert, E.E.; Waitt, G.M.; Williams, J.D.; Collins, J.L.; Moore, L.B.; Willson, T.M.; et al. A structural basis for constitutive activity in the human CAR/RXRalpha heterodimer. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Huang, P.; Hamuro, Y.; Raghuram, S.; Wang, Y.; Burris, T.P.; Rastinejad, F. Structure of the intact PPAR-gamma-RXR- nuclear receptor complex on DNA. Nature 2008, 456, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Khorasanizadeh, S.; Rastinejad, F. Nuclear-receptor interactions on DNA-response elements. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.P.; Sigler, P.B. Atomic structure of progesterone complexed with its receptor. Nature 1998, 393, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, J.S.; Kish, K.F.; Wang, C.; Attar, R.M.; Kiefer, S.E.; An, Y.; Wu, G.Y.; Scheffler, J.E.; Salvati, M.E.; Krystek, S.R., Jr.; et al. Crystallographic structures of the ligand-binding domains of the androgen receptor and its T877A mutant complexed with the natural agonist dihydrotestosterone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4904–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chalmers, M.J.; Stayrook, K.R.; Burris, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Busby, S.A.; Pascal, B.D.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.D.; Bruning, J.B.; Istrate, M.A.; et al. DNA binding alters coactivator interaction surfaces of the intact VDR-RXR complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, I.; Rochel, N.; Moras, D.; Klaholz, B.P. Structure of the full human RXR/VDR nuclear receptor heterodimer complex with its DR3 target DNA. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S.; Dong, D.; Lee, W.; Reczek, P.R.; Noy, N. Auto-silencing by the retinoid X receptor. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 284, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S.; Kelleher, D.; Chambon, P.; Gronemeyer, H.; Noy, N. Retinoid X receptor alpha forms tetramers in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8645–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouravel, N.; Sablin, E.; Togashi, M.; Baxter, J.D.; Webb, P.; Fletterick, R.J. Molecular basis for dimer formation of TRbeta variant D355R. Proteins 2009, 75, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Fradera, X.; Vu, D.; Nimz, O.; Skene, R.; Hosfield, D.; Wynands, R.; Cooke, A.J.; Haunso, A.; King, A.; Bennett, D.J.; et al. X-ray structures of the LXRalpha LBD in its homodimeric form and implications for heterodimer signaling. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 399, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, S.M.; Hoare, S.; Mosselman, S.; Parker, M.G. Estrogen receptors alpha and beta form heterodimers on DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 19858–19862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chambon, P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell 1988, 55, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.; Lin, C.Y. Oestrogen receptors in breast cancer: Basic mechanisms and clinical implications. Ecancermedicalscience 2013, 7, 370. [Google Scholar]
- Aranda, A.; Alonso-Merino, E.; Zambrano, A. Receptors of thyroid hormones. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2013, 11, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, P.D.; Gucalp, A.; Traina, T.A. The role of the androgen receptor in triple-negative breast cancer. Womens Health 2013, 9, 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsuka, A.; Wada, J.; Makino, H. Cell cycle abnormality in metabolic syndrome and nuclear receptors as an emerging therapeutic target. Acta Med. Okayama 2013, 67, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadian, M.; Suh, J.M.; Hah, N.; Liddle, C.; Atkins, A.R.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. PPARgamma signaling and metabolism: The good, the bad and the future. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 557–566. [Google Scholar]
- Cermenati, G.; Brioschi, E.; Abbiati, F.; Melcangi, R.C.; Caruso, D.; Mitro, N. Liver X receptors, nervous system, and lipid metabolism. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2013, 36, 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Tontonoz, P.; Hu, E.; Graves, R.A.; Budavari, A.I.; Spiegelman, B.M. mPPAR gamma 2: Tissue-specific regulator of an adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribon, V.; Johnson, J.H.; Camp, H.S.; Saltiel, A.R. Thiazolidinediones and insulin resistance: Peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor gamma activation stimulates expression of the CAP gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14751–14756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, R.B.; Huss, J.M.; Kelly, D.P. The coactivator PGC-1 cooperates with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha in transcriptional control of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation enzymes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 1868–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, K.; Suruga, K.; Fukami, H.; Kiso, Y.; Takase, S.; Goda, T. Selectivity of fatty acid ligands for PPARalpha which correlates both with binding to cis-element and DNA binding-independent transactivity in Caco-2 cells. Life Sci. 2006, 80, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.M.; Barish, G.D.; Wang, Y.X. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feige, J.N.; Gelman, L.; Michalik, L.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. From molecular action to physiological outputs: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are nuclear receptors at the crossroads of key cellular functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 120–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, J.J.; Ludvik, B.; Beerdsen, P.; Joyce, M.; Olefsky, J. Improvement in glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in obese subjects treated with troglitazone. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Bailey, P.; Biswas, C.; Cullinan, C.A.; Doebber, T.W.; Hayes, N.S.; Saperstein, R.; Smith, R.G.; Leibowitz, M.D. Thiazolidinediones produce a conformational change in peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma: Binding and activation correlate with antidiabetic actions in db/db mice. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 4189–4195. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Nagashima, I.; Taira, K.; Hikita, M.; Tamura, K.; Bujo, H.; Morisaki, N.; Saito, Y. A novel frameshift mutation in exon 6 (the site of Asn 291) of the lipoprotein lipase gene in type I hyperlipidemia. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1999, 285, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, A.; Tamemoto, H.; Tobe, K.; Ueki, K.; Mori, Y.; Iwamoto, K.; Umesono, K.; Akanuma, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Horikoshi, H.; et al. Troglitazone increases the number of small adipocytes without the change of white adipose tissue mass in obese Zucker rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yki-Jarvinen, H. Thiazolidinediones. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchi, A.; Maillard, M.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Vinciguerra, M.; Deleaval, P.; Nussberger, J.; Burnier, M.; Pechere-Bertschi, A. Effects of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma agonist pioglitazone on renal and hormonal responses to salt in diabetic and hypertensive individuals. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.; Zhang, F.; Moodie, S.A.; Clemens, L.E.; Smith, A.; Gregoire, F.; Bell, A.; Muscat, G.E.; Gustafson, T.A. Halofenate is a selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulator with antidiabetic activity. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2523–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lavan, B.E.; Gregoire, F.M. Selective modulators of PPAR-gamma activity: Molecular Aspects related to obesity and side-effects. PPAR Res. 2007, 2007, 32696. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, L.S.; Depaoli, A.M. Selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) modulation as a strategy for safer therapeutic PPARgamma activation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 267S–272S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Han, Y.; Shi, Y.; Rong, H.; Zheng, S.; Jin, S.; Lin, S.Y.; Lin, S.C.; Li, Y. Revealing a steroid receptor ligand as a unique PPARgamma agonist. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, B.; Jones, S.A.; Price, R.R.; Watson, M.A.; McKee, D.D.; Moore, L.B.; Galardi, C.; Wilson, J.G.; Lewis, M.C.; Roth, M.E.; et al. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, T.; Choi, M.; Moschetta, A.; Peng, L.; Cummins, C.L.; McDonald, J.G.; Luo, G.; Jones, S.A.; Goodwin, B.; Richardson, J.A.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005, 2, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Chen, W.D.; Moore, D.D.; Huang, W. FXR: A metabolic regulator and cell protector. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makishima, M.; Okamoto, A.Y.; Repa, J.J.; Tu, H.; Learned, R.M.; Luk, A.; Hull, M.V.; Lustig, K.D.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Shan, B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science 1999, 284, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.J.; Blanchard, S.G.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Chandra, G.; Consler, T.G.; Kliewer, S.A.; Stimmel, J.B.; Willson, T.M.; Zavacki, A.M.; Moore, D.D.; et al. Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science 1999, 284, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, J.W.; Liddle, C.; Downes, M. FXR and PXR: Potential therapeutic targets in cholestasis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 130, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, B.M.; Goode, E.; Chen, J.; Oro, A.E.; Bradley, D.J.; Perlmann, T.; Noonan, D.J.; Burka, L.T.; McMorris, T.; Lamph, W.W.; et al. Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by farnesol metabolites. Cell 1995, 81, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Hollister, K.; Sowers, L.C.; Forman, B.M. Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 543–553. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Li, T.; Ellis, E.; Strom, S.; Chiang, J.Y. A novel bile acid-activated vitamin D receptor signaling in human hepatocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Blackford, J.A., Jr.; Song, L.N.; Huang, Y.; Cho, S.; Simons, S.S., Jr. Equilibrium interactions of corepressors and coactivators with agonist and antagonist complexes of glucocorticoid receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 1376–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, P.; Cariou, B.; Lien, F.; Kuipers, F.; Staels, B. Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in metabolic regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 147–191. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda Torra, I.; Claudel, T.; Duval, C.; Kosykh, V.; Fruchart, J.C.; Staels, B. Bile acids induce the expression of the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha gene via activation of the farnesoid X receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Castellani, L.W.; Sinal, C.J.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Edwards, P.A. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) regulates triglyceride metabolism by activation of the nuclear receptor FXR. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Houten, S.M.; Wang, L.; Moschetta, A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Heyman, R.A.; Moore, D.D.; Auwerx, J. Bile acids lower triglyceride levels via a pathway involving FXR, SHP, and SREBP-1c. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lee, F.Y.; Barrera, G.; Lee, H.; Vales, C.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Willson, T.M.; Edwards, P.A. Activation of the nuclear receptor FXR improves hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Pellicciari, R.; Gioiello, A.; Costantino, G.; Sadeghpour, B.M.; Rizzo, G.; Meyer, U.; Parks, D.J.; Entrena-Guadix, A.; Fiorucci, S. Back door modulation of the farnesoid X receptor: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a series of side chain modified chenodeoxycholic acid derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4208–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette-Egly, C.; Germain, P. Dynamic and combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs). Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2009, 7, e005. [Google Scholar]
- Theodosiou, M.; Laudet, V.; Schubert, M. From carrot to clinic: An overview of the retinoic acid signaling pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1423–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soprano, D.R.; Qin, P.; Soprano, K.J. Retinoic acid receptors and cancers. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2004, 24, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.A.; Sigman, C.C.; Andreola, F.; Ross, S.A.; Kelloff, G.J.; de Luca, L.M. Retinoids in chemoprevention and differentiation therapy. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, M.; Kojima, S.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Tsurumi, H.; Muto, Y.; Friedman, S.L.; Moriwaki, H. Retinoids in cancer chemoprevention. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2004, 4, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moise, A.R.; Noy, N.; Palczewski, K.; Blaner, W.S. Delivery of retinoid-based therapies to target tissues. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 4449–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, P.; Chambon, P.; Eichele, G.; Evans, R.M.; Lazar, M.A.; Leid, M.; de Lera, A.R.; Lotan, R.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Gronemeyer, H. International Union of Pharmacology. LX. Retinoic acid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, M.; Ghyselinck, N.B.; Chambon, P. Function of retinoic acid receptors during embryonic development. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2009, 7, e002. [Google Scholar]
- Samarut, E.; Rochette-Egly, C. Nuclear retinoic acid receptors: Conductors of the retinoic acid symphony during development. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 348, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, R.F.; Gudas, L.J. Retinoic acid receptor isotype specificity in F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells results from the differential recruitment of coregulators to retinoic response elements. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 33421–33434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongan, N.P.; Gudas, L.J. Diverse actions of retinoid receptors in cancer prevention and treatment. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2007, 75, 853–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Kliewer, S.A.; Kakizuka, A.; Umesono, K.; Evans, R.M. Retinoid receptors. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 1993, 48, 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Goodwin, B.; Willson, T.M. The nuclear pregnane X receptor: A key regulator of xenobiotic metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, A.; Vilarem, M.J.; Maurel, P.; Pascussi, J.M. Xenoreceptors CAR and PXR activation and consequences on lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and inflammatory response. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarelli, A.; Migliorati, M.; Barbanti, M.; Cipriani, S.; Palladino, G.; Distrutti, E.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S. Pregnane-X-receptor mediates the anti-inflammatory activities of rifaximin on detoxification pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizaki, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takizawa, D.; Negishi, M. New insights on the xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptors in liver diseases—CAR and PXR. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Shah, Y.M.; Ma, X.; Pang, X.; Tanaka, T.; Kodama, T.; Krausz, K.W.; Gonzalez, F.J. Therapeutic role of rifaximin in inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical implication of human pregnane X receptor activation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertilsson, G.; Heidrich, J.; Svensson, K.; Asman, M.; Jendeberg, L.; Sydow-Backman, M.; Ohlsson, R.; Postlind, H.; Blomquist, P.; Berkenstam, A. Identification of a human nuclear receptor defines a new signaling pathway for CYP3A induction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12208–12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.M.; McKee, D.D.; Watson, M.A.; Willson, T.M.; Moore, J.T.; Kliewer, S.A. The human orphan nuclear receptor PXR is activated by compounds that regulate CYP3A4 gene expression and cause drug interactions. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, K.C.; Pinaire, J.A.; Xiao, G.H.; Geoghegan, T.E.; Prough, R.A. Regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase A2 gene by glucocorticoids: Involvement of both the glucocorticoid and pregnane X receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 611–619. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, J.M.; Johnson, M.D.; Lippman, M.E.; Flockhart, D.A. Rifampin is a selective, pleiotropic inducer of drug metabolism genes in human hepatocytes: Studies with cDNA and oligonucleotide expression arrays. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda, J.; Xie, W.; Rosenfeld, J.M.; Barwick, J.L.; Guzelian, P.S.; Evans, R.M. Regulation of a xenobiotic sulfonation cascade by nuclear pregnane X receptor (PXR). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13801–13806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, J.L.; Goodwin, B.; Jones, S.A.; Hawkins-Brown, D.; MacKenzie, K.I.; LaTour, A.; Liu, Y.; Klaassen, C.D.; Brown, K.K.; Reinhard, J.; et al. The nuclear receptor PXR is a lithocholic acid sensor that protects against liver toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3369–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synold, T.W.; Dussault, I.; Forman, B.M. The orphan nuclear receptor SXR coordinately regulates drug metabolism and efflux. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geick, A.; Eichelbaum, M.; Burk, O. Nuclear receptor response elements mediate induction of intestinal MDR1 by rifampin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14581–14587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R.E.; Wisely, G.B.; Moore, L.B.; Collins, J.L.; Lambert, M.H.; Williams, S.P.; Willson, T.M.; Kliewer, S.A.; Redinbo, M.R. The human nuclear xenobiotic receptor PXR: Structural determinants of directed promiscuity. Science 2001, 292, 2329–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Moore, L.B.; Orans, J.; Peng, L.; Bencharit, S.; Kliewer, S.A.; Redinbo, M.R. Crystal structure of the pregnane X receptor-estradiol complex provides insights into endobiotic recognition. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekins, S.; Chang, C.; Mani, S.; Krasowski, M.D.; Reschly, E.J.; Iyer, M.; Kholodovych, V.; Ai, N.; Welsh, W.J.; Sinz, M.; et al. Human pregnane X receptor antagonists and agonists define molecular requirements for different binding sites. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Poulton, E.J.; Grun, F.; Bammler, T.K.; Blumberg, B.; Thummel, K.E.; Eaton, D.L. The dietary isothiocyanate sulforaphane is an antagonist of the human steroid and xenobiotic nuclear receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 220–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, L.; Ma, W.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, G. One-pot synthesis of glycopolymer-porphyrin conjugate as photosensitizer for targeted cancer imaging and photodynamic therapy. Macromol. Biosci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meanwell, N.A. Improving drug candidates by design: A focus on physicochemical properties as a means of improving compound disposition and safety. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1420–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, T.J.; Loniello, K.R.; Beebe, J.A.; Ervin, K.M. Development and application of fluorescence polarization assays in drug discovery. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2003, 6, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xie, W.; Agler, M.; Banks, M. Coactivators in assay design for nuclear hormone receptor drug discovery. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2003, 1, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.J.; Nguyen, D.T.; Macarthur, R.; Simeonov, A.; Frazee, W.J.; Hallis, T.M.; Marks, B.D.; Singh, U.; Eliason, H.C.; Printen, J.; et al. Identification of pregnane X receptor ligands using time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer and quantitative high-throughput screening. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2009, 7, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cali, J.J.; Niles, A.; Valley, M.P.; O’Brien, M.A.; Riss, T.L.; Shultz, J. Bioluminescent assays for ADMET. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, E.F.; Kirakossian, H.; Switchenko, A.C.; Ishkanian, J.; Ericson, M.; Wartchow, C.A.; Pirio, M.; Pease, J.; Irvin, B.R.; Singh, S.; et al. Luminescent oxygen channeling assay (LOCI): Sensitive, broadly applicable homogeneous immunoassay method. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Ullman, E.F.; Kirakossian, H.; Singh, S.; Wu, Z.P.; Irvin, B.R.; Pease, J.S.; Switchenko, A.C.; Irvine, J.D.; Dafforn, A.; Skold, C.N.; et al. Luminescent oxygen channeling immunoassay: Measurement of particle binding kinetics by chemiluminescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5426–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafforn, A.; Kirakossian, H.; Lao, K. Miniaturization of the luminescent oxygen channeling immunoassay (LOCI(TM)) for use in multiplex array formats and other biochips. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.P.; de Keczer, S.; Alexander, S.; Pirio, M.; Davalian, D.; Kurn, N.; Ullman, E.F. Homogeneous, rapid luminescent oxygen channeling immunoassay (LOCI(TM)) for homocysteine. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1506–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Mathis, G.; Socquet, F.; Viguier, M.; Darbouret, B. Homogeneous immunoassays using rare earth cryptates and time resolved fluorescence: Principles and specific advantages for tumor markers. Anticancer Res. 1997, 17, 3011–3014. [Google Scholar]
- Marchese, A.; George, S.R.; Kolakowski, L.F., Jr.; Lynch, K.R.; O’Dowd, B.F. Novel GPCRs and their endogenous ligands: Expanding the boundaries of physiology and pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Olsson, H.; Batty, I.H.; Priganica, L.; Peter Downes, C. Nonradioactive methods for the assay of phosphoinositide 3-kinases and phosphoinositide phosphatases and selective detection of signaling lipids in cell and tissue extracts. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 313, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenat, S.; Rouleau, N.; Bielmann, C.; Bedard, J.; Maurer, F.; Allaman-Pillet, N.; Nicod, P.; Bielefeld-Sevigny, M.; Beckmann, J.S.; Bonny, C.; et al. Homogeneous and nonradioactive high-throughput screening platform for the characterization of kinase inhibitors in cell lysates. J. Biomol. Screen. 2006, 11, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Choi, M.; Suino, K.; Kovach, A.; Daugherty, J.; Kliewer, S.A.; Xu, H.E. Structural and biochemical basis for selective repression of the orphan nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog 1 by small heterodimer partner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9505–9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glickman, J.F.; Wu, X.; Mercuri, R.; Illy, C.; Bowen, B.R.; He, Y.; Sills, M. A comparison of ALPHAScreen, TR-FRET, and TRF as assay methods for FXR nuclear receptors. J. Biomol. Screen. 2002, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.; Zheng, W.; Wang, R.; Jin, S.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Li, Y. Revealing a natural marine product as a novel agonist for retinoic acid receptors with a unique binding mode and inhibitory effects on cancer cells. Biochem. J. 2012, 446, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Martynowski, D.; Zheng, S.; Wada, T.; Xie, W.; Li, Y. Structural basis for hydroxycholesterols as natural ligands of orphan nuclear receptor RORgamma. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Lin, S.; Rong, H.; Zheng, S.; Jin, S.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Structural basis for iloprost as a dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/delta agonist. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31473–31479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Huang, H.; Sundarababu, S.; Liu, W.; Kalpana, G.; Smith, A.B.; Horwitz, S.B. Activation of the steroid and xenobiotic receptor (human pregnane X receptor) by nontaxane microtubule-stabilizing agents. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6359–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, F.S.; Festa, C.; D’Amore, C.; de Marino, S.; Renga, B.; D’Auria, M.V.; Novellino, E.; Limongelli, V.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Binding mechanism of the farnesoid X receptor marine antagonist suvanine reveals a strategy to forestall drug modulation on nuclear receptors. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4701–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhu, R.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, D.; et al. Identification of chemerin as a novel FXR target gene down-regulated in the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, V.; Einolf, H.J.; Evers, R.; Kumar, G.; Moore, D.; Ripp, S.; Silva, J.; Sinha, V.; Sinz, M.; Skerjanec, A. In vitro and in vivo induction of cytochrome p450: A survey of the current practices and recommendations: A pharmaceutical research and manufacturers of america perspective. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 1339–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, W.; Theodorou, V.; Kok, M.; Canisius, S.; Linn, S.; Carroll, J.S. Oestrogen receptor-co-factor-chromatin specificity in the transcriptional regulation of breast cancer. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4764–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; D’Amore, C.; Cipriani, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Sepe, V.; Chini, M.G.; Monti, M.C.; Bifulco, G.; Zampella, A.; et al. Discovery that theonellasterol a marine sponge sterol is a highly selective FXR antagonist that protects against liver injury in cholestasis. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, I.J. What lies beneath: Natural products from marine organisms as nuclear receptor modulators. Biochem. J. 2012, 446, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Hwang, H.; Chin, J.; Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Nam, S.J.; Lee, B.C.; Rho, B.J.; Kang, H. Tuberatolides, potent FXR antagonists from the Korean marine tunicate Botryllus tuberatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.N.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, W.; Park, G.M.; Shin, W.S.; Kim, Y.K. Sargaquinoic acid and sargahydroquinoic acid from Sargassum yezoense stimulate adipocyte differentiation through PPARalpha/gamma activation in 3T3-L1 cells. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chin, J.; Choi, H.; Baek, K.; Lee, T.G.; Park, S.E.; Wang, W.; Hahn, D.; Yang, I.; Lee, J.; et al. Phosphoiodyns A and B, unique phosphorus-containing iodinated polyacetylenes from a Korean sponge Placospongia sp. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meimetis, L.G.; Williams, D.E.; Mawji, N.R.; Banuelos, C.A.; Lal, A.A.; Park, J.J.; Tien, A.H.; Fernandez, J.G.; de Voogd, N.J.; Sadar, M.D.; et al. Niphatenones, glycerol ethers from the sponge Niphates digitalis block androgen receptor transcriptional activity in prostate cancer cells: Structure elucidation, synthesis, and biological activity. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, L.; Kaufmann, K.; Garcia, R.; Schwar, G.; Huch, V.; Muller, R. Bendigoles D–F, bioactive sterols from the marine sponge-derived Actinomadura sp. SBMs009. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6570–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, A.E.; Holland, P.T.; Reschly, E.J.; Ekins, S.; Krasowski, M.D. Activation of a tunicate (Ciona intestinalis) xenobiotic receptor orthologue by both natural toxins and synthetic toxicants. Toxicon 2012, 59, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Pathirana, C.; Stein, R.B.; Berger, T.S.; Fenical, W.; Ianiro, T.; Mais, D.E.; Torres, A.; Goldman, M.E. Nonsteroidal human progesterone receptor modulators from the marine alga Cymopolia barbata. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 630–635. [Google Scholar]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; Petek, S.; Fiorucci, S.; et al. 4-Methylenesterols from Theonella swinhoei sponge are natural pregnane-X-receptor agonists and farnesoid-X-receptor antagonists that modulate innate immunity. Steroids 2012, 77, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, K.; Shiraishi, F.; Uchida, H.; Sano, T. A novel retinoic acid analogue, 7-hydroxy retinoic acid, isolated from cyanobacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S.J.; Ko, H.; Shin, M.; Ham, J.; Chin, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Shin, K.; Choi, H.; Kang, H. Farnesoid X-activated receptor antagonists from a marine sponge Spongia sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 5398–5402. [Google Scholar]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Theonellasterols and conicasterols from Theonella swinhoei. Novel marine natural ligands for human nuclear receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Debitus, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Conicasterol E, a small heterodimer partner sparing farnesoid X receptor modulator endowed with a pregnane X receptor agonistic activity, from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Sepe, V.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; Petek, S.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Towards new ligands of nuclear receptors. Discovery of malaitasterol A, an unique bis-secosterol from marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4856–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Discovery of sulfated sterols from marine invertebrates as a new class of marine natural antagonists of farnesoid-X-receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; de Marino, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Petek, S.; Zampella, A. Solomonsterols A and B from Theonella swinhoei. The first example of C-24 and C-23 sulfated sterols from a marine source endowed with a PXR agonistic activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Xiao, B.; Park, M.; Yoo, E.S.; Shin, S.; Hong, J.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, J.H. PPAR-gamma agonistic metabolites from the ascidian Herdmania momus. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; Lauro, G.; de Marino, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Monti, M.C.; Casapullo, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; Petek, S.; et al. Plakilactones from the marine sponge Plakinastrella mamillaris. Discovery of a new class of marine ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8303–8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, F.D.; Jones, D.K.; Desai, P.V.; Patny, A.; Avery, M.A.; Feller, D.R.; Smillie, T.; Zhou, Y.D.; Nagle, D.G. Bioassay for the identification of natural product-based activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma): The marine sponge metabolite psammaplin A activates PPARgamma and induces apoptosis in human breast tumor cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadar, M.D.; Williams, D.E.; Mawji, N.R.; Patrick, B.O.; Wikanta, T.; Chasanah, E.; Irianto, H.E.; Soest, R.V.; Andersen, R.J. Sintokamides A to E, chlorinated peptides from the sponge Dysidea sp. that inhibit transactivation of the N-terminus of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4947–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Marino, S.D.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Nakao, Y.; et al. Preliminary structure-activity relationship on theonellasterol, a new chemotype of FXR antagonist, from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2448–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Chin, J.; Hahn, D.; Lee, J.; Hwang, H.; Won, D.H.; Ham, J.; Choi, H.; Kang, E.; Kim, H.; et al. Sterols from a soft coral, Dendronephthya gigantea as farnesoid X-activated receptor antagonists. Steroids 2012, 77, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Nishimaki-Mogami, T.; Kawai, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Shinozaki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Asakawa, Y.; Inoue, K.; Ohno, Y.; et al. Screening of novel nuclear receptor agonists by a convenient reporter gene assay system using green fluorescent protein derivatives. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, M.V.; Sepe, V.; Zampella, A. Natural ligands for nuclear receptors: Biology and potential therapeutic applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 637–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. LIGPLOT: A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng. 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; de Marino, S.; Sepe, V.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Debitus, C.; Bucci, M.; Vellecco, V.; Zampella, A. Solomonamides A and B, new anti-inflammatory peptides from Theonella swinhoei. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Festa, C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Cresteil, T.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Swinholide J, a potent cytotoxin from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Mencarelli, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Total synthesis and pharmacological characterization of solomonsterol A, a potent marine pregnane-X-receptor agonist endowed with anti-inflammatory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 4590–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renga, B.; Migliorati, M.; Mencarelli, A.; Cipriani, S.; D’Amore, C.; Distrutti, E.; Fiorucci, S. Farnesoid X receptor suppresses constitutive androstane receptor activity at the multidrug resistance protein-4 promoter. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1809, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urizar, N.L.; Liverman, A.B.; Dodds, D.T.; Silva, F.V.; Ordentlich, P.; Yan, Y.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Heyman, R.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Moore, D.D. A natural product that lowers cholesterol as an antagonist ligand for FXR. Science 2002, 296, 1703–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, T.P.; Montrose, C.; Houck, K.A.; Osborne, H.E.; Bocchinfuso, W.P.; Yaden, B.C.; Cheng, C.C.; Zink, R.W.; Barr, R.J.; Hepler, C.D.; et al. The hypolipidemic natural product guggulsterone is a promiscuous steroid receptor ligand. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 948–954. [Google Scholar]
- Younk, L.M.; Uhl, L.; Davis, S.N. Pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety of aleglitazar for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with high cardiovascular risk. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2011, 7, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
