Characterisation of Non-Autoinducing Tropodithietic Acid (TDA) Production from Marine Sponge Pseudovibrio Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Culture Conditions Enhance the Production of Bioactive Compounds by Pseudovibrio Species
| Strain | Antagonistic Activity against Pathogen | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y. ruckerri | E. tarda | V. anguillarum | E. coli MUH | E. coli NCIMB 949 | M. morganii | S. Typhimurium LT2 | S. Typhimurium C5369 | P. sporunum | S. arizonae | S. aureus NCDO 949 | |
| JIC5 | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | + | +++ | - | ++ * | + * | + * | ++ |
| JIC6 | + | ++ | + | - | + * | + * | - | - | + * | - | ++ |
| JIC17 | +++ | ++ | + | - | + * | ++ | + * | - | + * | + * | + |
| W10 | +++ | ++ | - | + | - | + * | - | +* | + * | - | + |
| W19 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| W62 | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + * | +++ | - | + * | ++ * | - | ++ |
| W63 | +++ | +++ | - | - | - | - | - | ++ * | +++ * | + * | ++ |
| W64 | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | + | +++ | ++ * | ++ * | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| W65 | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | + | +++ | + * | ++ * | + * | + | ++ |
| W69 | +++ | +++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ * | ++ * | ++ * | ++ * | ++ |
| W71 | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | +++ | + * | ++ * | + * | + | + |
| W89 | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++* | ++ * | ++ * | + | ++ |
| W99 | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | + | +++ | + * | ++ * | + * | + | ++ |
| WC43 | ++ | - | ++ | + * | + | + * | + * | + * | + * | + | ++ |
| W74 | +++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | +++ | + * | ++ * | + * | ++ * | + |
| W85 | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | + * | + | + * | + * | + * | - | ++ |
| W78 | ++ | + | ++ | + * | + * | +++ | +* | + * | + * | - | + |
| W94 | ++ | + | ++ | + * | + * | ++ | + * | + * | + * | + * | ++ |
| W96 | +++ | ++ | ++ | + * | + * | ++ | + * | ++ * | - | ++ * | + |
| WM31 | +++ | ++ | +++ | + * | + * | + | + * | + * | - | - | ++ |
| WM33 | ++ | + | + | + * | + * | - | + | - | - | - | + |
| WM34 | +++ | ++ | +++ | + * | + * | +++ | + * | + * | + * | + * | ++ |
| WM40 | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | - | ++ | ++ * | ++ * | ++ |
| WM50 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| WC13 | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + * | ++ | - | + * | - | + * | ++ |
| WC15 | + | - | + * | - | - | + * | - | - | - | - | + |
| WC21 | ++ | + * | ++ | + | + * | ++ | - | + * | - | + * | ++ |
| WC22 | +++ | + | + | + | + * | + | - | - | - | + * | ++ |
| WC30 | +++ | + | ++ | + | + * | + | - | + * | - | + * | + |
| WC32 | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + * | ++ | - | ++ * | + * | + * | ++ |
| WC41 | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + * | ++ | - | ++ * | - | ++ * | ++ |
| HC6 | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ * | + | +++ | + * | ++ * | + * | + * | ++ |
| HMMA3 | ++ | + | ++ | + * | + * | + * | + * | - | - | - | + |
2.2. Pseudovibrio Species Derived from Marine Sponge Produce Tropodithietic Acid (TDA)

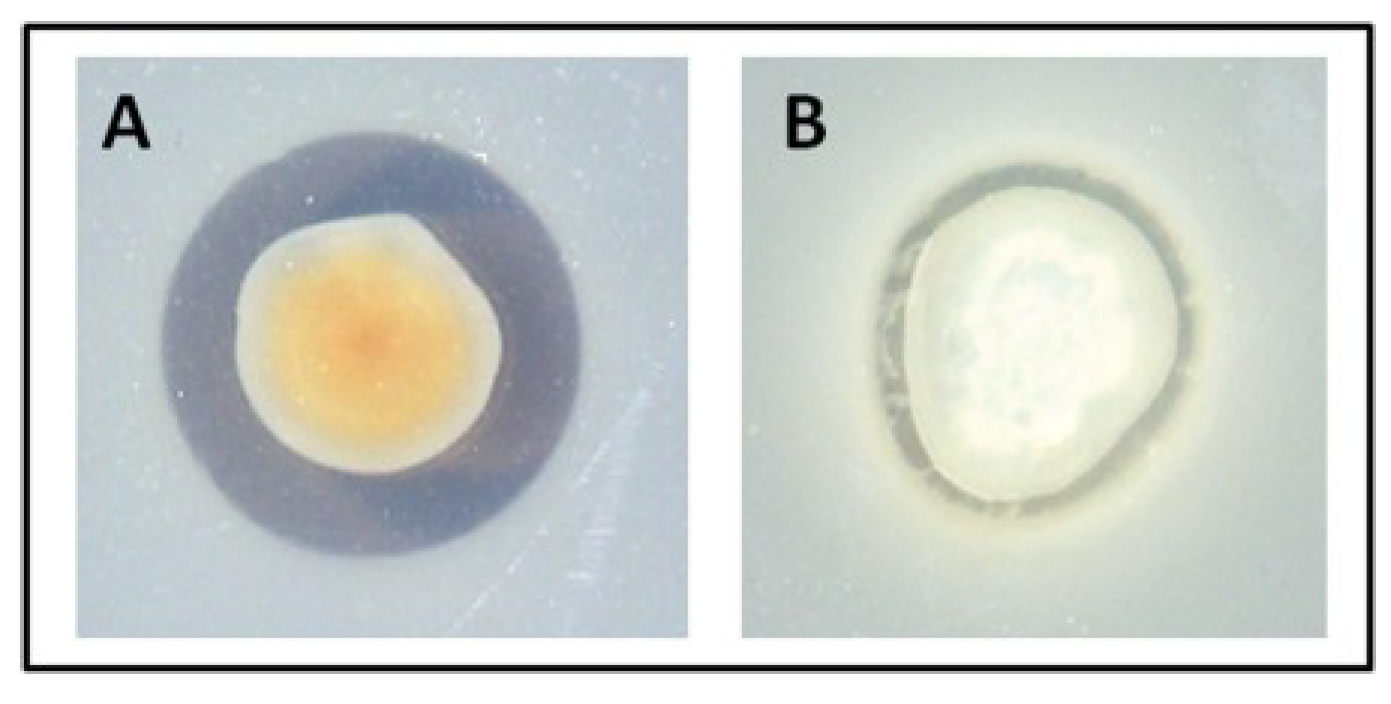
2.3. TDA-Producing Isolate W74 has Limited Activity against Marine Isolates
2.4. TDA Extracted from Pseudovibrio Displays Bioactivity against Cystic Fibrosis (CF) Clinical Isolates
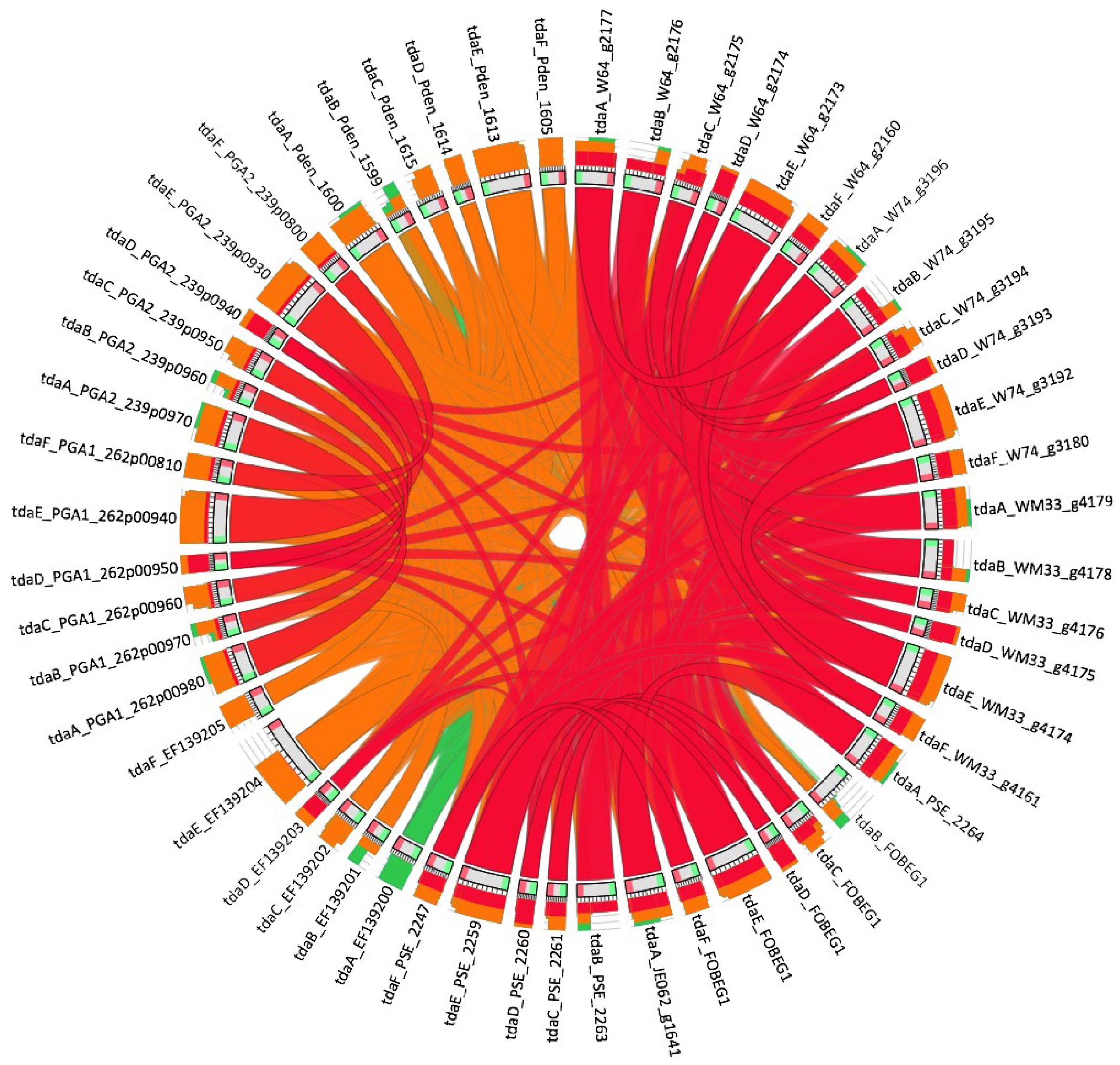
2.5. Genomic Pathway
| Strain | Accession Numbers of tda Genes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tdaA | tdaB | tdaC | tdaD | tdaE | tdaF | |
| W64 | W64_g2177 | W64_g2176 | W64_g2175 | W64_g2174 | W64_g2173 | W64_g2160 |
| W74 | W74_g3196 | W74_g3195 | W74_g3194 | W74_g3193 | W74_g3192 | W74_g3180 |
| WM33 | WM33_g4179 | WM33_g4178 | WM33_g4176 | WM33_g4175 | WM33_g4174 | WM33_g4161 |
| FO-BEG1 [38] | PSE_2264 | PSE_2263 | PSE_2261 | PSE_2260 | PSE_2259 | PSE_2247 |
| JE062 [18] | JE062_g1641 | JE062_g1639 | JE062_g1638 | JE062_g1637 | JE062_g1636 | JE062_g1624 |
| TM1040 [37] | EF139200 | EF139201 | EF139202 | EF139203 | EF139204 | EF139205 |
| Phaeobacter gallaeciensis DSM 17395 [33] | PGA1_262p00980 | PGA1_262p00970 | PGA1_262p00960 | PGA1_262p00950 | PGA1_262p00940 | PGA1_262p00810 |
| Phaeobacter gallaeciensis 2.10 [33] | PGA2_239p0970 | PGA2_239p0960 | PGA2_239p0950 | PGA2_239p0940 | PGA2_239p0930 | PGA2_239p0800 |
| Phaeobacter gallaeciensis 2.10 [39] | Pden_1600 | Pden_1599 | Pden_1615 | Pden_1614 | Pden_1613 | Pden_1605 |
2.6. TDA Expression Occurs during Logarithmic Growth
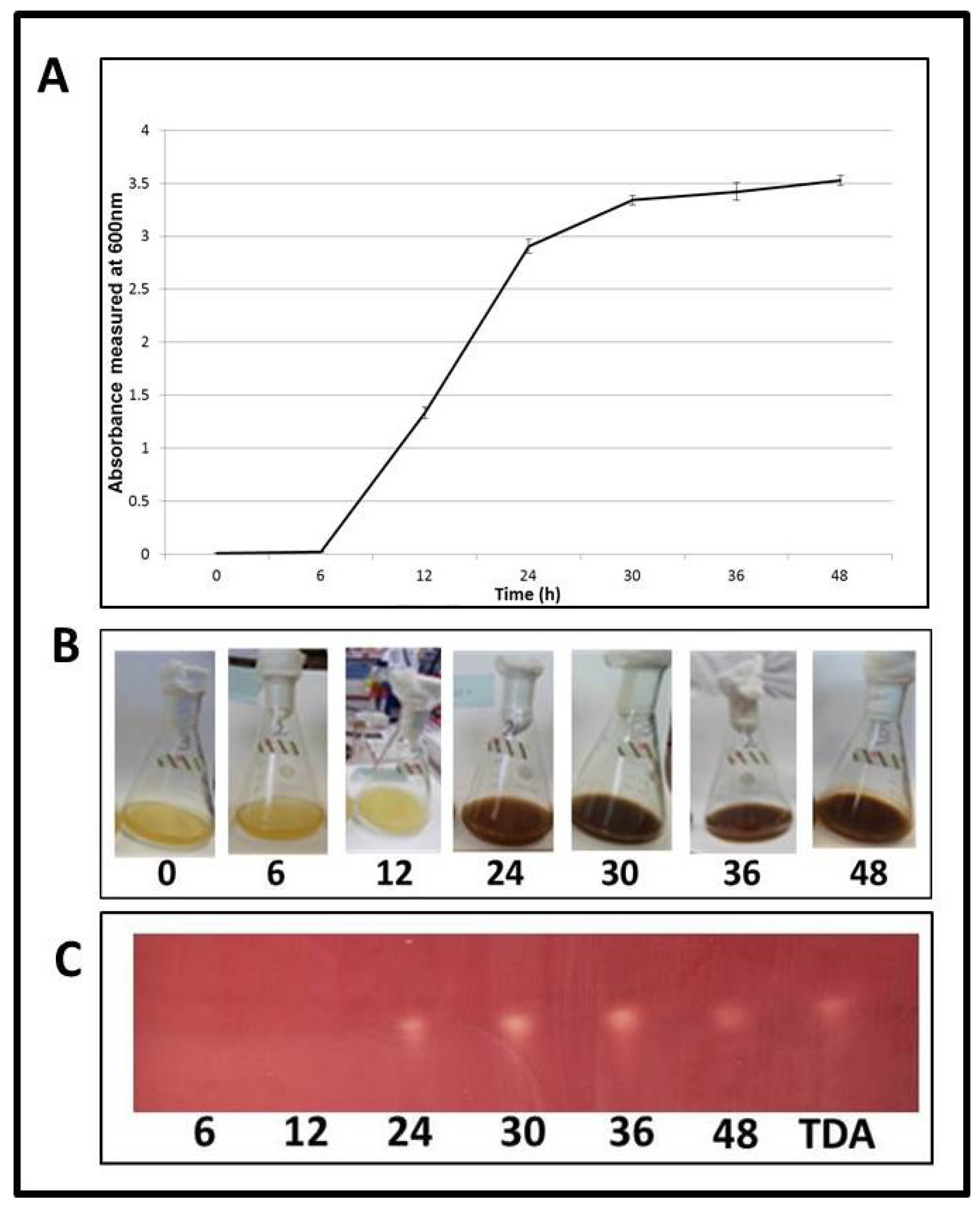
2.7. Induction of TDA Genes in Pseudovibrio is Linked to Bioactivity
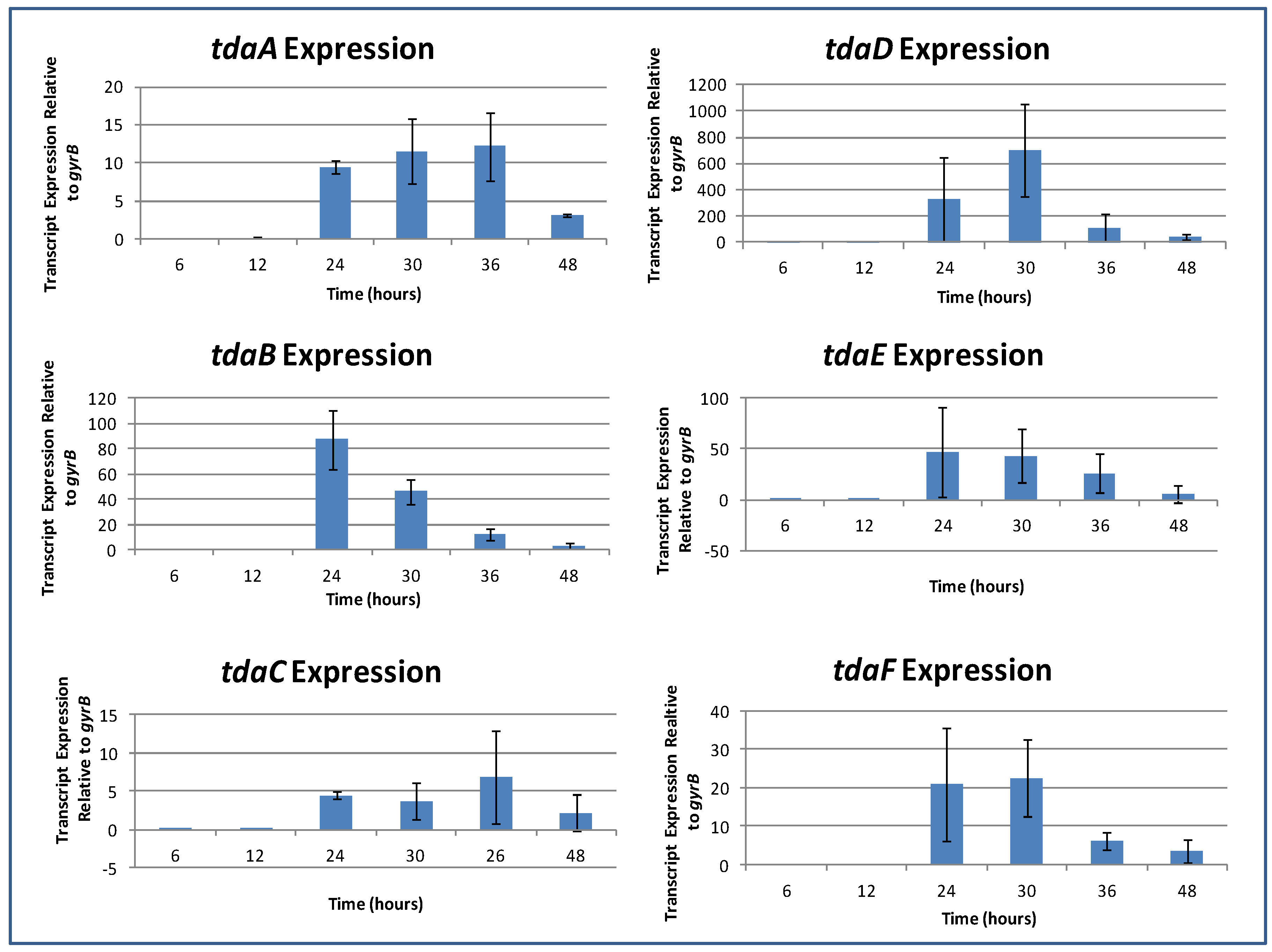
2.8. TDA is Not Autoinduced, or Induced by C10-AHL
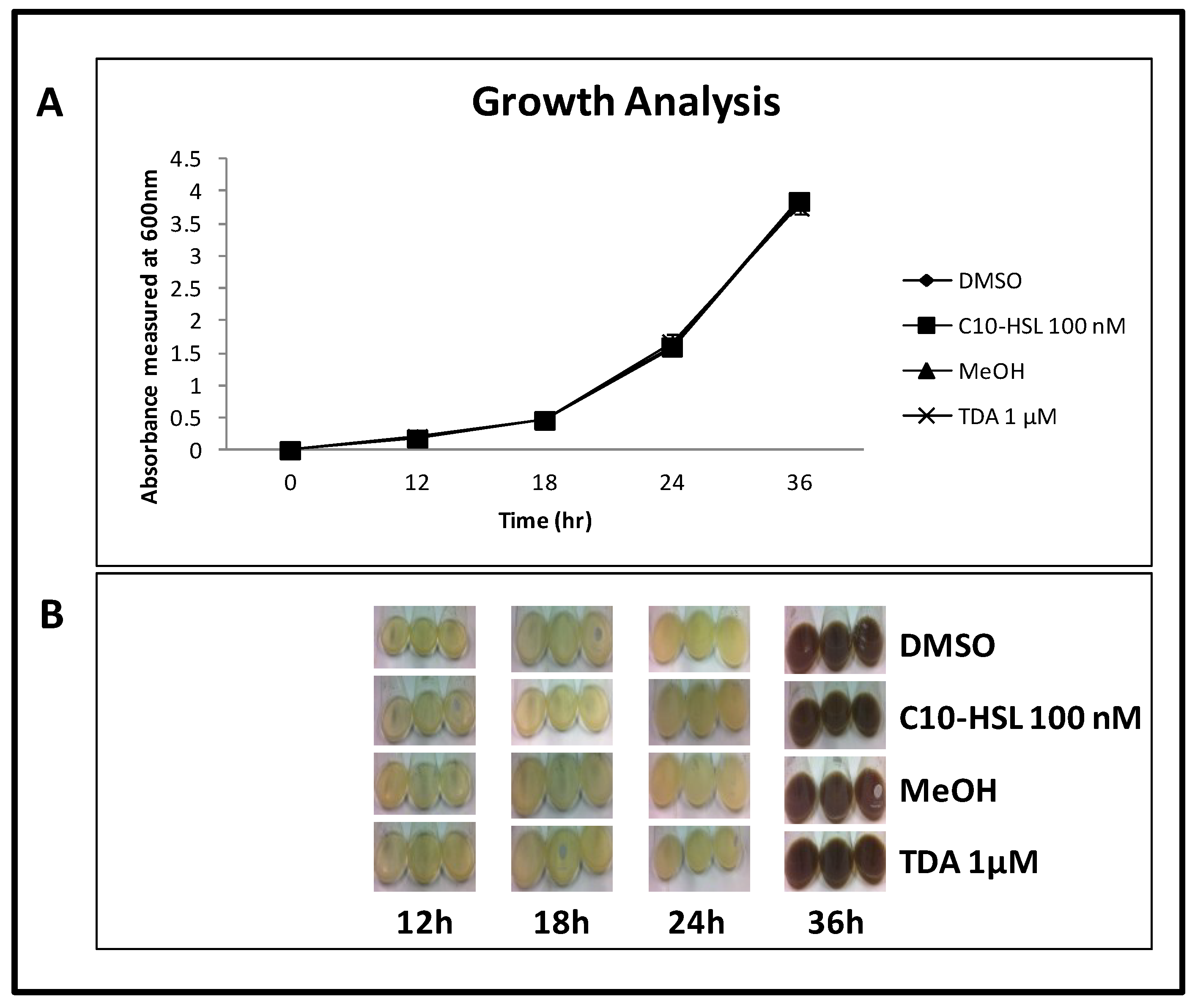
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Growth Conditions
3.2. Antimicrobial Spot-Plate Overlay Assay
3.3. Compound Extraction
3.4. Thin Layer Chromotography (TLC)
3.5. TDA Identification
3.6. Antimicrobial Spot-Plate Overlay Assay for Marine Sponge Isolates
3.7. Pseudovibrio Induction Assay
3.8. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
3.9. RT-PCR
3.10. Genetic Analysis of Pseudovibrio TDA Genes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laport, M.S.; Santos, O.C.; Muricy, G. Marine sponges: Potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.W.; Radax, R.; Steger, D.; Wagner, M. Sponge-associated microorganisms: Evolution, ecology, and biotechnological potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacelet, J.; Donadey, C. Electron microscope study of the association between some sponges and bacteria. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1977, 30, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.P.; Yuan, J.; Sun, L.; She, Z.G.; Wu, J.H.; Lan, X.J.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, S.P. Statistical research on marine natural products based on data obtained between 1985 and 2008. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.C.; Mori, T.; Ruckert, C.; Uria, A.R.; Helf, M.J.; Takada, K.; Gernert, C.; Steffens, U.A.; Heycke, N.; Schmitt, S.; et al. An environmental bacterial taxon with a large and distinct metabolic repertoire. Nature 2014, 506, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, W.Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Jean, W.D. Pseudovibrio denitrificans gen. Nov., sp. Nov., a marine, facultatively anaerobic, fermentative bacterium capable of denitrification. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, Y.; Kurahashi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Yanagi, K.; Yokota, A.; Harayama, S. Pseudovibrio ascidiaceicola sp. Nov., isolated from ascidians (sea squirts). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riesenfeld, C.S.; Murray, A.E.; Baker, B.J. Characterization of the microbial community and polyketide biosynthetic potential in the palmerolide-producing tunicate synoicum adareanum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penesyan, A.; Tebben, J.; Lee, M.; Thomas, T.; Kjelleberg, S.; Harder, T.; Egan, S. Identification of the antibacterial compound produced by the marine epiphytic bacterium Pseudovibrio sp. D323 and related sponge-associated bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Kuo, J.; Sung, P.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Lu, M.C.; Wong, T.Y.; Liu, J.K.; Weng, C.F.; Twan, W.H.; Kuo, F.W. Isolation of marine bacteria with antimicrobial activities from cultured and field-collected soft corals. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 3269–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, C.; Michaud, L.; Hormann, B.; Gerce, B.; Syldatk, C.; Hausmann, R.; de Domenico, E.; lo Giudice, A. Bacteria associated with sabellids (polychaeta: Annelida) as a novel source of surface active compounds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, S.; Carre-Mlouka, A.; Descarrega, F.; Ereskovsky, A.; Longeon, A.; Mouray, E.; Florent, I.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L. Diversity and biological activities of the bacterial community associated with the marine sponge Phorbas tenacior (porifera, demospongiae). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 58, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, A.I.; Hardoim, C.C.; Xavier, J.R.; Goncalves, J.M.; Costa, R. Molecular richness and biotechnological potential of bacteria cultured from Irciniidae sponges in the north-east atlantic. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemer, B.; Kennedy, J.; Margassery, L.M.; Morrissey, J.P.; O’Gara, F.; Dobson, A.D. Diversity and antimicrobial activities of microbes from two irish marine sponges, suberites carnosus and leucosolenia sp. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graca, A.P.; Bondoso, J.; Gaspar, H.; Xavier, J.R.; Monteiro, M.C.; de la Cruz, M.; Oves-Costales, D.; Vicente, F.; Lage, O.M. Antimicrobial activity of heterotrophic bacterial communities from the marine sponge Erylus discophorus (Astrophorida, Geodiidae). PLoS One 2013, 8, e78992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.; Baker, P.; Piper, C.; Cotter, P.D.; Walsh, M.; Mooij, M.J.; Bourke, M.B.; Rea, M.C.; O’Connor, P.M.; Ross, R.P.; et al. Isolation and analysis of bacteria with antimicrobial activities from the marine sponge Haliclona simulans collected from irish waters. Mar. Biotechnol. (NY) 2009, 11, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margassery, L.M.; Kennedy, J.; O’Gara, F.; Dobson, A.D.; Morrissey, J.P. Diversity and antibacterial activity of bacteria isolated from the coastal marine sponges Amphilectus fucorum and Eurypon major. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 55, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enticknap, J.J.; Kelly, M.; Peraud, O.; Hill, R.T. Characterization of a culturable alphaproteobacterial symbiont common to many marine sponges and evidence for vertical transmission via sponge larvae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3724–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscholl-Silberhorn, A.; Thiel, V.; Imhoff, J.F. Abundance and bioactivity of cultured sponge-associated bacteria from the mediterranean sea. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sertan-de Guzman, A.A.; Predicala, R.Z.; Bernardo, E.B.; Neilan, B.A.; Elardo, S.P.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Tasdemir, D.; Ireland, C.M.; Barraquio, W.L.; Concepcion, G.P. Pseudovibrio denitrificans strain z143–1, a heptylprodigiosin-producing bacterium isolated from a Philippine tunicate. Fems. Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 277, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, H.; Belas, R. Expression of tropodithietic acid biosynthesis is controlled by a novel autoinducer. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 4377–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkhoff, T.; Bach, G.; Heidorn, T.; Liang, L.; Schlingloff, A.; Simon, M. Antibiotic production by a roseobacter clade-affiliated species from the german wadden sea and its antagonistic effects on indigenous isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsby, C.H.; Nielsen, K.F.; Gram, L. Phaeobacter and ruegeria species of the roseobacter clade colonize separate niches in a danish turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)-rearing farm and antagonize Vibrio anguillarum under different growth conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7356–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsby, C.H.; Webber, M.A.; Nielsen, K.F.; Piddock, L.J.; Gram, L. Resistance and tolerance to tropodithietic acid, an antimicrobial in aquaculture, is hard to select. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, E.M.; Aebisher, D.; Greer, A.; Bentley, R. Computational studies of the tropone natural products, thiotropocin, tropodithietic acid, and troposulfenin. Significance of thiocarbonyl-enol tautomerism. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cane, D.E.; Wu, Z.; Vanepp, J.E. Thiotropocin biosynthesis—Shikimate origin of a sulfur-containing tropolone derivative. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 8479–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintaka, K.; Ono, H.; Tsubotani, S.; Harada, S.; Okazaki, H. Thiotropocin, a new sulfur-containing 7-membered-ring antibiotic produced by a pseudomonas sp. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1984, 37, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhn, J.B.; Nielsen, K.F.; Hjelm, M.; Hansen, M.; Bresciani, J.; Schulz, S.; Gram, L. Ecology, inhibitory activity, and morphogenesis of a marine antagonistic bacterium belonging to the roseobacter clade. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7263–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alvise, P.W.; Lillebo, S.; Prol-Garcia, M.J.; Wergeland, H.I.; Nielsen, K.F.; Bergh, O.; Gram, L. Phaeobacter gallaeciensis reduces Vibrio anguillarum in cultures of microalgae and rotifers, and prevents vibriosis in cod larvae. PLoS One 2012, 7, e43996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neu, A.K.; Mansson, M.; Gram, L.; Prol-Garcia, M.J. Toxicity of bioactive and probiotic marine bacteria and their secondary metabolites in Artemia sp. And Caenorhabditis elegans as eukaryotic model organisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Halloran, J.A.; Barbosa, T.M.; Morrissey, J.P.; Kennedy, J.; O’Gara, F.; Dobson, A.D. Diversity and antimicrobial activity of Pseudovibrio spp. From irish marine sponges. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gram, L.; Melchiorsen, J.; Bruhn, J.B. Antibacterial activity of marine culturable bacteria collected from a global sampling of ocean surface waters and surface swabs of marine organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. (NY) 2010, 12, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thole, S.; Kalhoefer, D.; Voget, S.; Berger, M.; Engelhardt, T.; Liesegang, H.; Wollherr, A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Daniel, R.; Simon, M.; et al. Phaeobacter gallaeciensis genomes from globally opposite locations reveal high similarity of adaptation to surface life. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2229–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Neumann, A.; Schulz, S.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Tropodithietic acid production in Phaeobacter gallaeciensis is regulated by n-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 6576–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhn, J.B.; Gram, L.; Belas, R. Production of antibacterial compounds and biofilm formation by roseobacter species are influenced by culture conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauernfeind, A.; Horl, G.; Przyklenk, B. Microbiologic and therapeutic aspects of Staphylococcus aureus in cystic fibrosis patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1988, 143, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Bruhn, J.B.; Nielsen, K.F.; Gram, L.; Belas, R. Genetic dissection of tropodithietic acid biosynthesis by marine roseobacters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarev, V.; Richter, M.; Romano, S.; Piel, J.; Schwedt, A.; Schulz-Vogt, H.N. The genus Pseudovibrio contains metabolically versatile bacteria adapted for symbiosis. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2095–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddavattam, D.; Karegoudar, T.B.; Mudde, S.K.; Kumar, N.; Baddam, R.; Avasthi, T.S.; Ahmed, N. Genome of a novel isolate of Paracoccus denitrificans capable of degrading N,N-dimethylformamide. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5598–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darzentas, N. Circoletto: Visualizing sequence similarity with circos. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2620–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sule, P.; Belas, R. A novel inducer of roseobacter motility is also a disruptor of algal symbiosis. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidler, E.; van Noorden, C.J. On the mechanism of the multistep reduction of tetrazolium salts with special reference to the involvement of tetrazolium radicals. Acta Histochem. 1994, 96, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kildgaard, S.; Mansson, M.; Dosen, I.; Klitgaard, A.; Frisvad, J.C.; Larsen, T.O.; Nielsen, K.F. Accurate dereplication of bioactive secondary metabolites from marine-derived fungi by UHPLC-DAD-QTOFMS and a MS/HRMS library. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3681–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Alvise, P.W.; Magdenoska, O.; Melchiorsen, J.; Nielsen, K.F.; Gram, L. Biofilm formation and antibiotic production in ruegeria mobilis are influenced by intracellular concentrations of cyclic dimeric guanosinmonophosphate. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Sato, T.; Weightman, A.J.; Martin, T.A.; Fry, J.C.; Hiom, S.J.; Dymock, D.; Wade, W.G. Design and evaluation of useful bacterium-specific pcr primers that amplify genes coding for bacterial 16s rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Unicersal ProbeLibrary—Roche Life Sciences. Available online: http://lifescience.roche.com/webapp/wcs/stores/servlet/CategoryDisplay?catalogId=10001&tab=&identifier=Universal+Probe+Library&langId=-1#tab-3 (accessed on 2 March 2013).
- Muthusamy, S.; Baltar, F.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Pinhassi, J. Dynamics of metabolic activities and gene expression in the roseobacter clade bacterium Phaeobacter sp. Strain med193 during growth with thiosulfate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6933–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sihto, H.M.; Tasara, T.; Stephan, R.; Johler, S. Validation of reference genes for normalization of qPCR mRNA expression levels in Staphylococcus aureus exposed to osmotic and lactic acid stress conditions encountered during food production and preservation. Fems. Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 356, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. Blast+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformat. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldo, L.; Migliavacca, R.; Regattin, L.; Raglio, A.; Pagani, L.; Nucleo, E.; Spalla, M.; Vailati, F.; Agodi, A.; Mosca, A.; et al. Prevalence of urinary colonization by extended spectrum-beta-lactamase enterobacteriaceae among catheterised inpatients in Italian long term care facilities. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, A.; Reen, F.J.; O’Gara, F.; Callaghan, M.; McClean, S. Inhibition of co-colonizing cystic fibrosis-associated pathogens by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia multivorans. Microbiology 2014, 160, 1474–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Lamas, L.; Rabade Castedo, C.; Martin Romero Dominguez, M.; Barbeito Castineiras, G.; Palacios Bartolome, A.; Perez Del Molino Bernal, M.L. [Pandoraea sputorum colonization in a patient with cystic fibrosis]. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2011, 47, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.B.; Zhao, C.J.; Wang, H.; Cao, B.; Xu, X.L.; Chu, Y.Z.; Hu, Z.D.; Zhuo, C.; Hu, B.J.; Liu, W.E.; et al. An analysis of resistance of nosocomial infection pathogens isolated from 13 teaching hospitals in 2011. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2013, 52, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Bella, S.; Capone, A.; Bordi, E.; Johnson, E.; Musso, M.; Topino, S.; Noto, P.; Petrosillo, N. Salmonella enterica ssp. Arizonae infection in a 43-year-old Italian man with hypoglobulinemia: A case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2011, 5, 323. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelopoulou, G.; Kritas, S.; Govaris, A.; Burriel, A.R. Pork meat as a potential source of Salmonella enterica subsp. Arizonae infection in humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.K.; Khan, S.A.; Chandel, D.S.; Kumar, N.; Hans, C.; Chaudhry, R. Fatal case of Salmonella enterica subsp. Arizonae gastroenteritis in an infant with microcephaly. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5830–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, P.; Klapschinski, T.A.; Brock, N.L.; Citron, C.A.; D’Alvise, P.; Gram, L.; Dickschat, J.S. Synthesis and bioactivity of analogues of the marine antibiotic tropodithietic acid. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harrington, C.; Reen, F.J.; Mooij, M.J.; Stewart, F.A.; Chabot, J.-B.; Guerra, A.F.; Glöckner, F.O.; Nielsen, K.F.; Gram, L.; Dobson, A.D.W.; et al. Characterisation of Non-Autoinducing Tropodithietic Acid (TDA) Production from Marine Sponge Pseudovibrio Species. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5960-5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12125960
Harrington C, Reen FJ, Mooij MJ, Stewart FA, Chabot J-B, Guerra AF, Glöckner FO, Nielsen KF, Gram L, Dobson ADW, et al. Characterisation of Non-Autoinducing Tropodithietic Acid (TDA) Production from Marine Sponge Pseudovibrio Species. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(12):5960-5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12125960
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarrington, Catriona, F. Jerry Reen, Marlies J. Mooij, Fiona A. Stewart, Jean-Baptiste Chabot, Antonio F. Guerra, Frank O. Glöckner, Kristian F. Nielsen, Lone Gram, Alan D. W. Dobson, and et al. 2014. "Characterisation of Non-Autoinducing Tropodithietic Acid (TDA) Production from Marine Sponge Pseudovibrio Species" Marine Drugs 12, no. 12: 5960-5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12125960
APA StyleHarrington, C., Reen, F. J., Mooij, M. J., Stewart, F. A., Chabot, J.-B., Guerra, A. F., Glöckner, F. O., Nielsen, K. F., Gram, L., Dobson, A. D. W., Adams, C., & O'Gara, F. (2014). Characterisation of Non-Autoinducing Tropodithietic Acid (TDA) Production from Marine Sponge Pseudovibrio Species. Marine Drugs, 12(12), 5960-5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12125960