Growth and Saxitoxin Production by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) Correlate with Water Hardness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
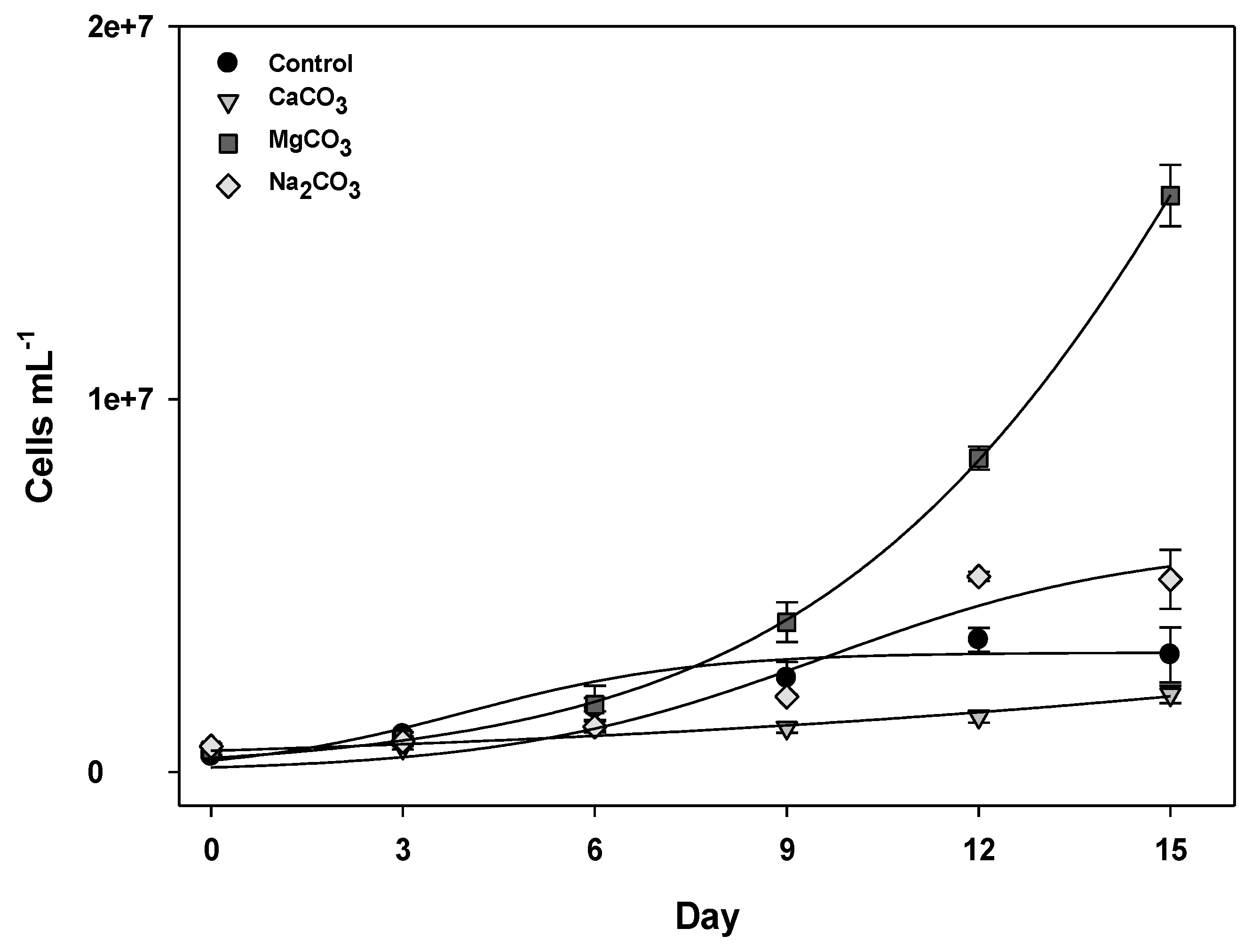
2.1. Growth in Different Conditions
| Growth medium | Conductivity (μS) | pH a,b | Exponential phase | Growth rate (μ) a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration | R2 | ||||
| Control | 568 | 7.43 ± 0.19 | 6 | 0.98 | 0.225 ± 0.03 |
| CaCO3 5 mM | 656 | 7.98 ± 0.12 * | ND | 0.92 | 0.100 ± 0.01 * |
| MgCO3 5 mM | 1196 | 8.66 ± 0.13 ** | 15 | 0.99 | 0.231 ± 0.02 ** |
| Na2CO3 5 mM | 1401 | 8.76 ± 0.09 ** | 15 | 0.95 | 0.162 ± 0.01 ** |
| CaCl2 5 mM | 1436 | 7.51 ± 0.24 | ND | 0.71 | 0.094 ± 0.02 * |
| MgCl2 5 mM | 1484 | 7.45 ± 0.35 | ND | 0.71 | 0.238 ± 0.02 * |
| NaCl 5 mM | 808 | 7.55 ± 0.38 | ND | 0.75 | 0.197 ± 0.02 |
| CaCl2 10 mM | 2550 | 7.55 ± 0.17 | ND | 0.34 | 0.029 ± 0.01 ** |
| MgCl2 10 mM | 2475 | 7.45 ± 0.35 | ND | 0.86 | 0.235 ± 0.02 * |
| NaCl 10 mM | 1350 | 7.53 ± 0.33 | ND | 0.89 | 0.104 ± 0.01 * |
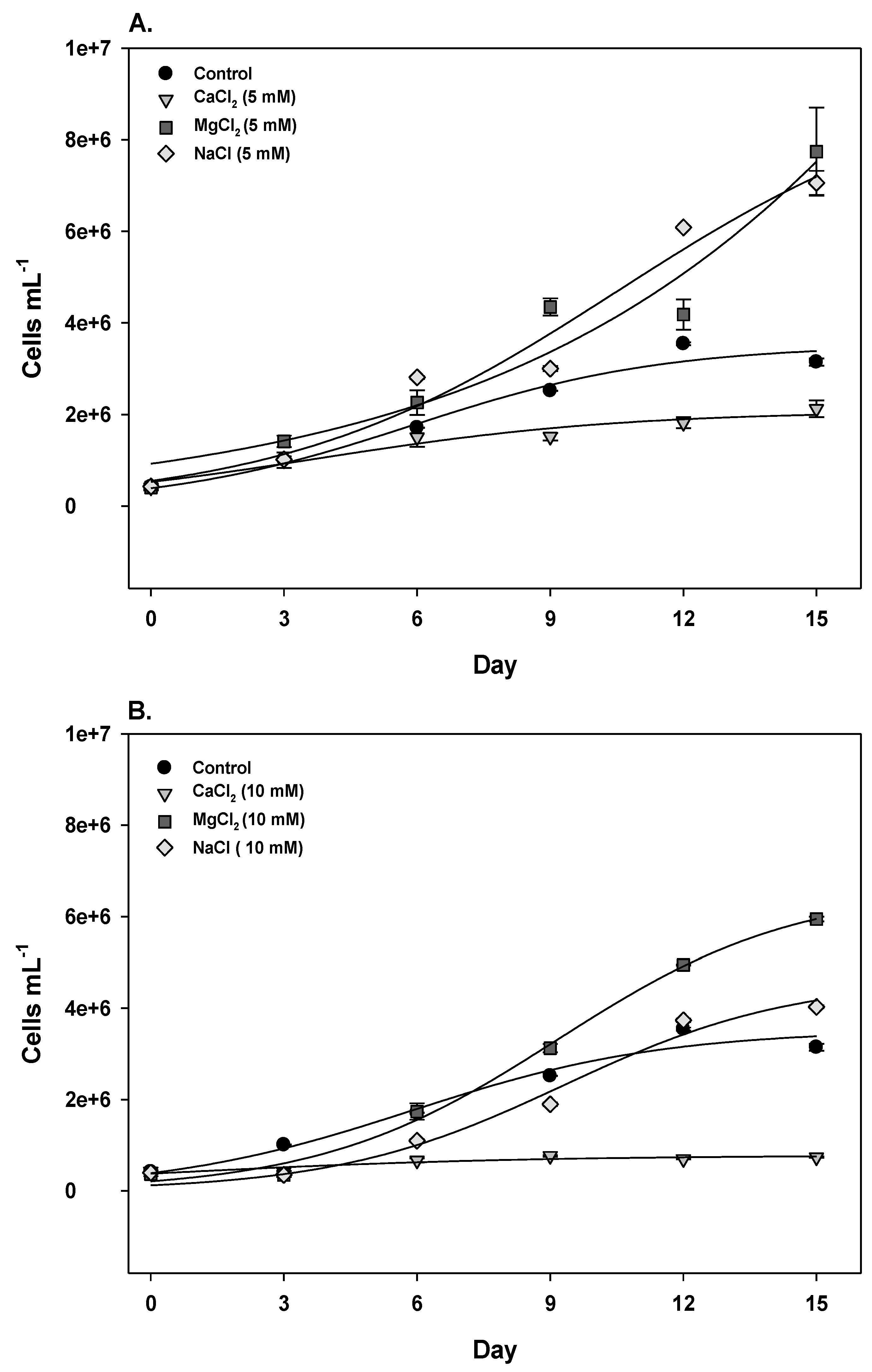
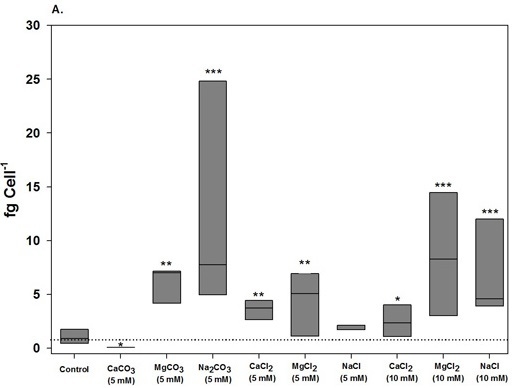
2.2. Saxitoxin Production
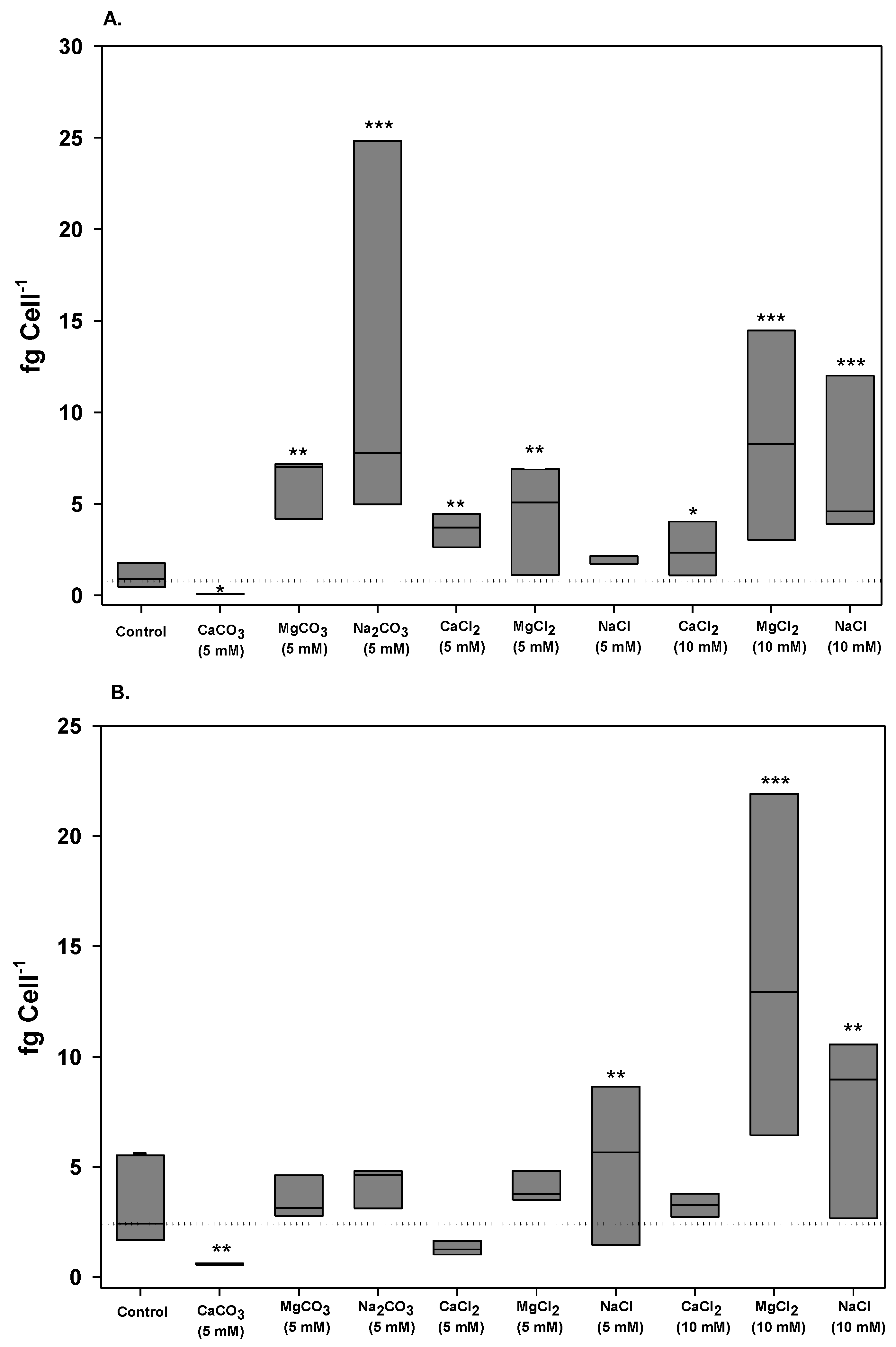
| Growth medium | Fold change from day 6 to 12 a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | neoSTX | STX | |
| Control | +3.1 | +2.9 | +5.6 |
| CaCO3 5 mM | +7.7 | +7.7 | +9.0 |
| MgCO3 5 mM | −1.7 | −1.2 | −13.0 |
| Na2CO3 5 mM | −3.0 | −2.7 | −6.8 |
| CaCl2 5 mM | −2.7 | −2.1 | −7.1 |
| MgCl2 5 mM | −1.1 | −1.3 | +1.44 |
| NaCl 5 mM | +2.6 | +2.1 | +6.2 |
| CaCl2 10 mM | +1.3 | +1.3 | +1.6 |
| MgCl2 10 mM | +1.6 | +1.6 | +1.6 |
| NaCl 10 mM | +1.1 | +1.1 | +1.1 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Strain Maintenance and Growth Conditions
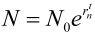 where N is the number of cells at time t, N0 is the initial number of cells and rn is the growth rate [30]. The growth curves were fitted for cell number data to non-linear functions using the logistic curve model as described by Soares et al. [41], where the biovolume was replaced by cells mL−1.
where N is the number of cells at time t, N0 is the initial number of cells and rn is the growth rate [30]. The growth curves were fitted for cell number data to non-linear functions using the logistic curve model as described by Soares et al. [41], where the biovolume was replaced by cells mL−1. 3.2. STX and neoSTX Analysis
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padisák, J. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an expanding highly adaptive blue-green algal species: Worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 1997, 107, 563–593. [Google Scholar]
- Briand, J.F.; Leboulanger, C.; Humbert, J.F. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) invasion at mid-latitudes: Selection, wide physiological tolerance, or global warming? J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedner, C.; Rücker, J.; Brüggemann, R.; Nixford, B. Climate change affects timing and size of populations of an invasive cyanobacterium in temperate regions. Oecologia 2007, 152, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Pearson, L.A.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Orr, P.T.; Neilan, B.A. Increased incidence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in temperate zones is climate change responsible? Water Res. 2012, 46, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenik, A.; Hadas, O.; Kaplan, A.; Quesada, A. Invasion of Nostocales (cyanobacteria) to subtropical and temperate freshwater lakes—Physiological, regional, and global driving forces. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, I.; Moore, R.E.; Runnegar, M.T.C. Cylindrospermopsin: A potent hepatotoxin from the blue-green alga Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 7941–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, N.; Onodera, H.; Zagatto, P.A.; Andrinolo, D.O.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Oshima, Y. The first evidence of paralytic shellfish toxins in the freshwater cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolated from Brazil. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, R.J.R.; Onodera, H.; Garcia, C.; Andrinolo, D.; Nascimento, S.; Meguro, H.; Oshima, Y.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Lagos, N. Toxins in freshwater cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyceae) isolated from Tabocas reservoir in Caruaru, Brazil, including demonstration of a new saxitoxin analogue. Phycologia 2002, 41, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, R.J.R.; Oliveira, E.J.A.; Carvalho, P.V.V.C.; Costa, A.P.N.S.F.; Cunha, M.C.C.; Melo, G.L.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Ocurrence of saxitoxins and anatoxin-a(s)-like anticholinesterase in Brazilian drinking water supply. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Salata, J.J.; Bennett, P.B. Saxitoxin is a gating modifier of HERG K+ Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2003, 121, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Sheets, M.; Ishida, H.; Li, F.; Barry, W.H. Saxitoxin blocks l-type ICa. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 324–329. [Google Scholar]
- Chonudomkul, D.; Yongmanitchai, W.; Theeragool, G.; Kawachi, M.; Kasai, F.; Kaya, K.; Watanabe, M.M. Morphology, genetic diversity, temperature tolerance and toxicity of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) strains from Thailand and Japan. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, C.; Aubriot, L.; Fabre, A.; Amaral, V.; González-Piana, M.; Figueiredo, C.C.; Giani, A.; Kruk, C.; Bonilla, S. Genetic and eco-physiological differences of South American Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolates support the hypothesis of multiple ecotypes. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L.; Soares, M.C.S.; González-Piana, M.; Fabre, A.; Huszar, V.L.; Lürling, M.; Antoniades, D.; Padisák, J. What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isvánovics, V.; Shafik, H.M.; Présing, M.; Juhos, S. Growth and phosphate uptake kinetics of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyceae) in throughflow cultures. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 43, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.M.A.; Marinho, M.M.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Which Factors Are Related to the Success of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Brazilian Aquatic Systems? In Cyanobacteria: Ecology, Toxicology and Management; Ferrão-Filho, A.S., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, I.A.S.; Cunha, S.R.S.; Panosso, R.; Araújo, M.F.F.; Melo, J.L.S.; Eskinazi-Sant’Anna, E.M. Dinâmica de cianobactérias em reservatórios eutróficos do semi-árido do Rio Grande do Norte. Oecologia Bras. 2009, 13, 382–401. [Google Scholar]
- Bouvy, M.; Molica, R.J.R.; Oliveira, S.; Marinho, M.; Becker, B. Dynamics of a toxic cyaobacterial bloom (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) in a shalow reservoir in the semi-arid region of northeast Brazil. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 20, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvy, M.; Falcão, D.; Marinho, M.; Pagano, M.; Moura, A. Ocurrence of Cylindrospermopis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) in 39 Brazilian tropical reservoirs during the 1998 drought. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 23, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvy, M.; Nascimento, S.M.; Molica, R.J.R.; Ferreira, A.; Huszar, V.L.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Limnological features in Tapucurá reservoir (Northeast Brazil) during a severe drought. Hydrobiologia 2003, 493, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappa, N.T.; Costa, M.A.M. Dominant and co-existing species of cyanobacteria from a eutrophicated reservoir of Rio Grande do Norte State, Brazil. Acta Oecologica 2003, 24, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1985; p. 391. [Google Scholar]
- Mol, B.A.R.; Barbosa, A.B.; Silva, R.R. Água dura em sabão mole. Quím. Nova Esc. 1995, 2, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology; Saunders Book Company: Phyladelphia, PA, USA, 1981; p. 743. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, C.R.; Barbosa, J.E.L.; Ceballos, B.S.O. Temporal variability (Nicthemeral and Sazonal) of limnological conditions of the Semi-arid dams. Rev. Biol. Cienc. Terra 2006, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pomati, F.; Rosseti, C.; Manarolla, G.; Burns, B.P.; Neilan, B.A. Interactions between intracellular Na+ levels and saxitoxin production in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii T3. Microbiology 2004, 150, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisander, P.H.; McClinton, E., III; Paerl, H.W. Salinity effects on growth, photosynthetic parameters, and nitrogenase activity in estuarine planktonic cyanobacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 43, 432–442. [Google Scholar]
- Callandrino, E.S.; Pearl, H.W. Determining the potential for the proliferation of the harmful cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Currituck Sound, North Carolina. Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Liebe, K.; Méndez, M.A.; Fuenzalida, L.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A.; Vásquez, M. PSP toxin release from the cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis brookii D9 (Nostocales) can be induced by sodium and potassium ions. Toxicon 2012, 60, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Ecology of Phytoplankton: Ecology, Biodiversity and Conservation; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 535. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, A.G.M.; Bryant, D.A. Chlorophyll biosynthesis in bacteria: The origins of structural and functional diversity. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobotka, R.; Dühring, U.; Komenda, J.; Peter, E.; Gardian, Z.; Tichy, M.; Grimm, B.; Wilde, A. Importance of the cyabacterial Gun4 protein for chlorophyll metabolism and assembly of photosynthetic complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25794–25802. [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Liebe, K.; Murillo, A.A.; Krock, B.; Stucken, K.; Fuentes-Valdés, J.J.; Trefault, N.; Cembella, A.; Vásquez, M. Reassessment of the toxin profile of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii T3 and function of putative sulfotransferases in synthesis of sulfated and sulfonated PSP toxins. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1350–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, R.L.; Santos, M.E.V.; Pacheco, A.B.F.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Effects of light intensity and light quality on growth and circadian rhythm of saxitoxins production in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, M.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic alkaloids: Saxitoxin and its analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the European Commission on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Saxitoxin group. EFSA J. 2009, 1019, 1–76.
- Carneiro, R.L.; Alípio, A.C.N.; Bisch, P.M.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Pacheco, A.B.F. The inhibitory effect of calcium on Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) metabolism. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellman, R.; Neilan, B.A. Biochemical characterization of paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis in vitro. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorhan, P.; Maclachlav, J.R.; Hammer, V.T.; Kim, W.K. Isolation and culture of toxic strains of Anabaena flos-aquae (Lyngb.) de Bréb. Verein. Limnol. 1964, 15, 796–804. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, R.L.; Dörr, F.A.; Dörr, F.; Bortoli, S.; Delherbe, N.; Vásquez, A.; Pinto, E. Co-occurrence of microcystin and microginin congeners in Brazilian strains of Microcystis sp. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Lürling, M.; Huszar, V.L.M. Growth and temperature-related phenotypic plasticity in the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Phycol. Res. 2013, 61, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y. Postcolumn derivatization liquid chromatographic method for paralytic shellfish toxins. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 528–532. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Carneiro, R.L.; Pacheco, A.B.F.; De Oliveira e Azevedo, S.M.F. Growth and Saxitoxin Production by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) Correlate with Water Hardness. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2949-2963. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082949
Carneiro RL, Pacheco ABF, De Oliveira e Azevedo SMF. Growth and Saxitoxin Production by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) Correlate with Water Hardness. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(8):2949-2963. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082949
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarneiro, Ronaldo Leal, Ana Beatriz Furlanetto Pacheco, and Sandra Maria Feliciano De Oliveira e Azevedo. 2013. "Growth and Saxitoxin Production by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) Correlate with Water Hardness" Marine Drugs 11, no. 8: 2949-2963. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082949
APA StyleCarneiro, R. L., Pacheco, A. B. F., & De Oliveira e Azevedo, S. M. F. (2013). Growth and Saxitoxin Production by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) Correlate with Water Hardness. Marine Drugs, 11(8), 2949-2963. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082949