Anti-Inflammatory Components of the Starfish Astropecten polyacanthus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
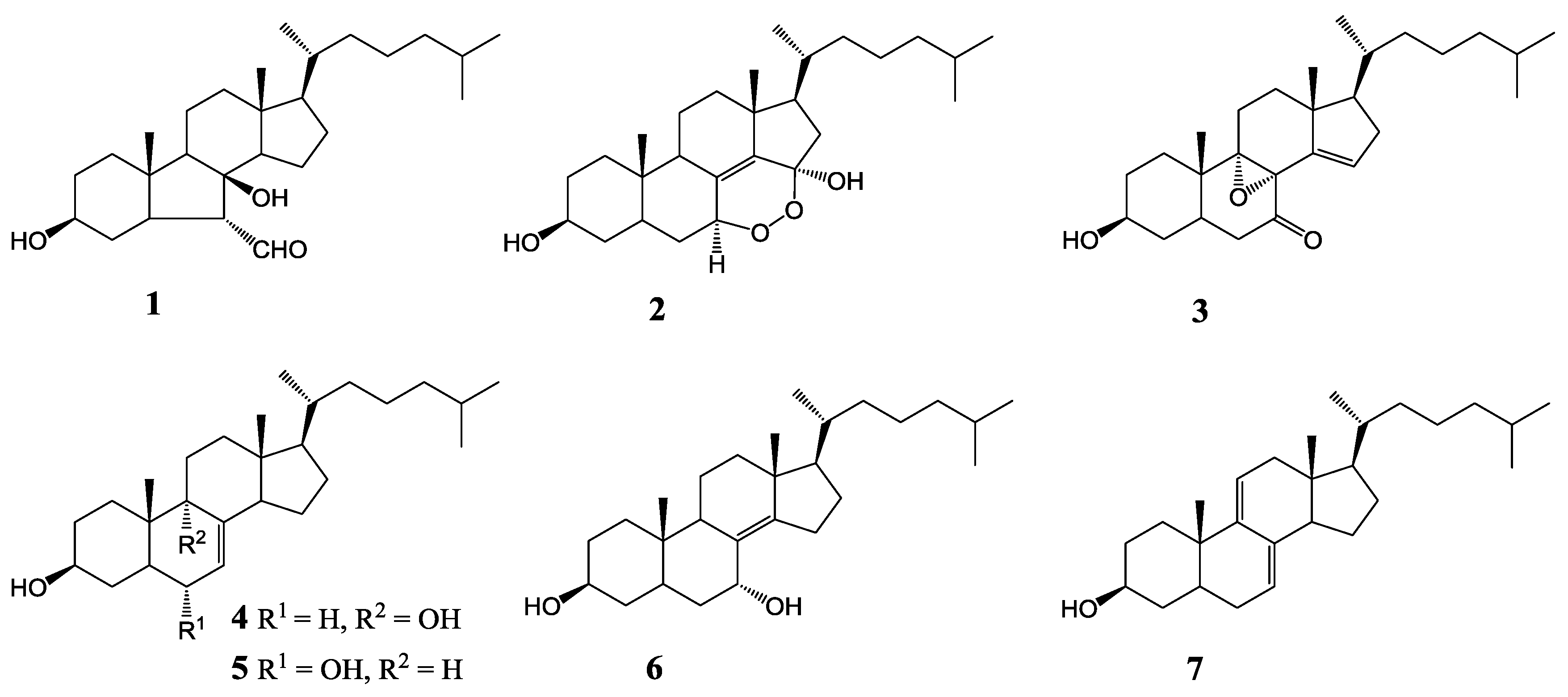
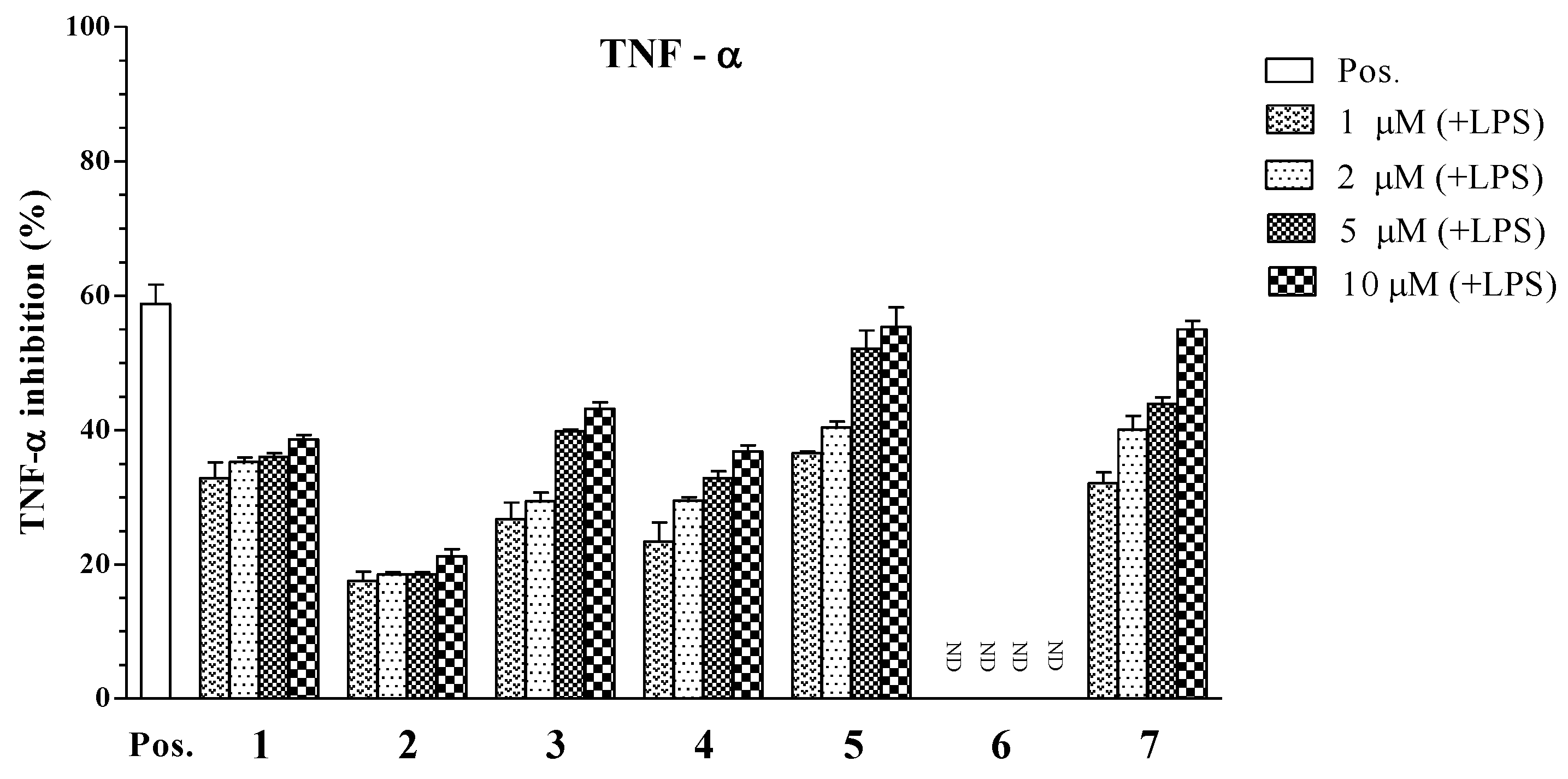
2. Results and Discussion
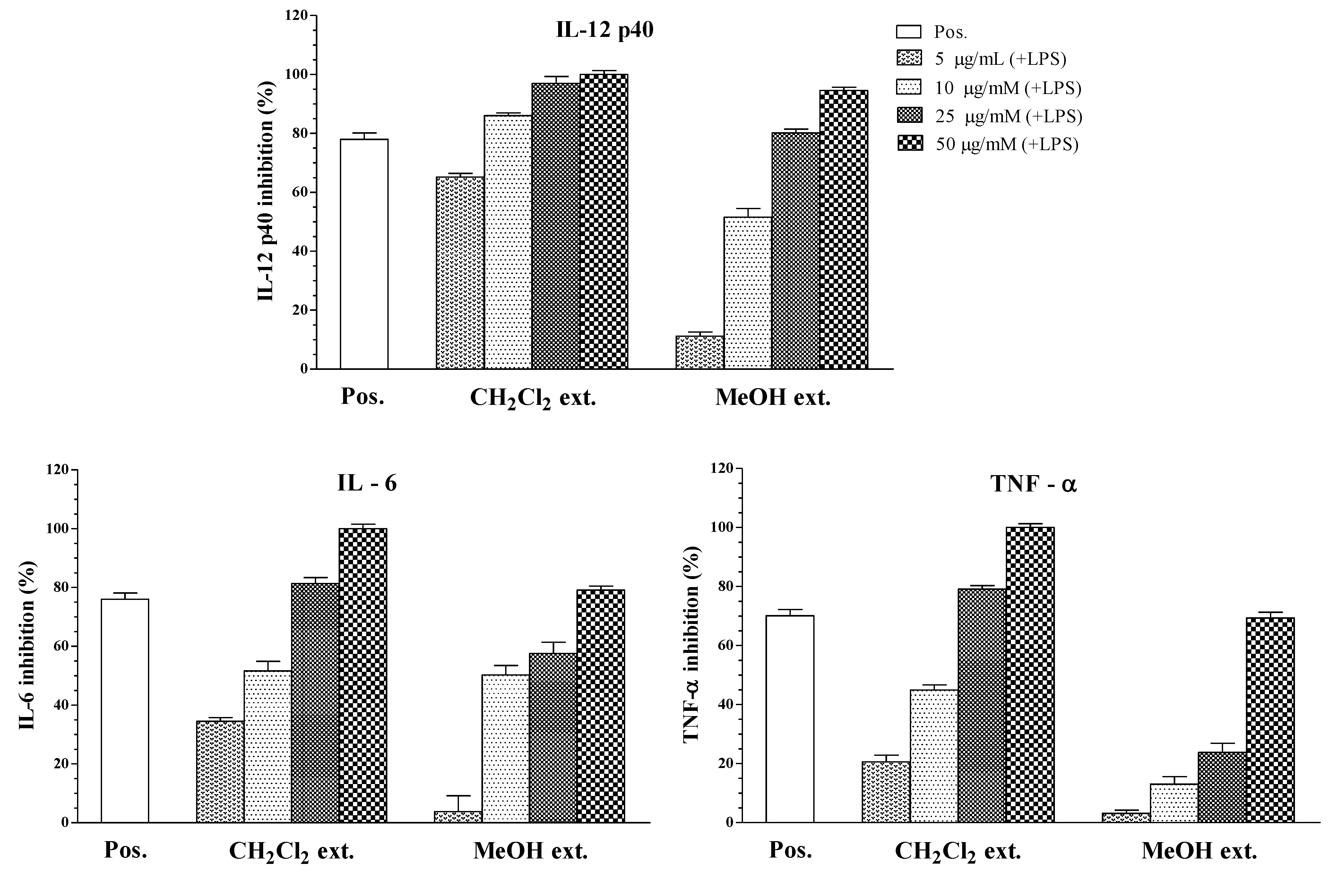
| Fraction Extracts | IC50 Values (μg/mL) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-12 p40 | IL-6 | TNF-α | |
| CH2Cl2 extract | 1.27 ± 0.11 | 8.82 ± 0.18 | 11.48 ± 0.16 |
| Crude MeOH extract | 11.47 ± 0.16 | 20.28 ± 0.22 | 36.99 ± 0.24 |
| SB203580 b | 2.52 ± 0.12 | 1.67 ± 0.13 | 3.65 ± 0.12 |
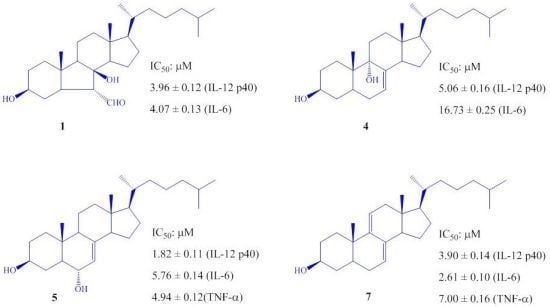
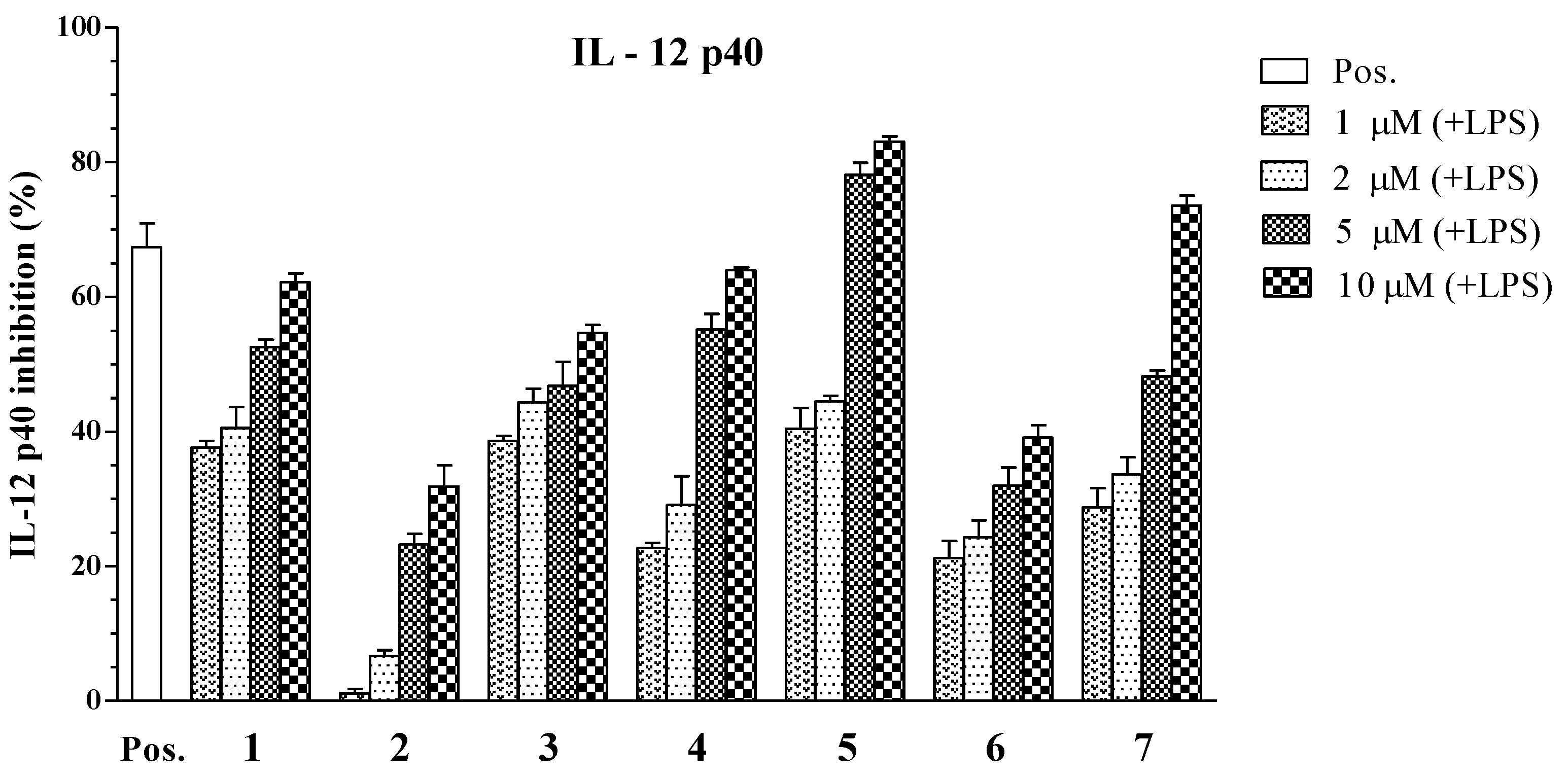
| Compounds | IC50 Values (μM) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-12 p40 | IL-6 | TNF-α | |
| 1 | 3.96 ± 0.12 | 4.07 ± 0.13 | >100 |
| 2 | 34.86 ± 1.31 | >100 | >100 |
| 3 | 6.55 ± 0.18 | >100 | 22.80 ± 0.21 |
| 4 | 5.06 ± 0.16 | 16.73 ± 0.25 | >100 |
| 5 | 1.82 ± 0.11 | 5.76 ± 0.14 | 4.94 ± 0.12 |
| 6 | 79.05 ± 2.05 | >100 | >100 |
| 7 | 3.90 ± 0.14 | 2.61 ± 0.10 | 7.00 ± 0.16 |
| SB203580 b | 5.00 ± 0.16 | 3.50 ± 0.12 | 7.20 ± 0.13 |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Biological
3.2. Cell Cultures and Measurement of Cytokine Production

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Nathan, C. Points of control in inflammation. Nature 2002, 420, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgio, T. Interleukin-12: A proinflammatory cytokine with immunoregulatory functions that bridge innate resistance and antigen-specific adaptive immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1995, 13, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T. IL-6: From its discovery to clinical applications. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood 1989, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, T. Interleukin-6 and its relation to inflammation and disease. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1992, 62, S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Hirata, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Minamoto, S.; Aono, A.; Nishimoto, N.; Kajita, T.; Taga, T.; Yoshizaki, K.; et al. Structure and function of a new STAT-induced STAT inhibitor. Nature 1997, 387, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, C.A.; Bost, K.L.; Boulware, D.W.; Levy, L.S. Mechanisms of pathogenesis in scleroderma. I. Overproduction of interleukin 6 by fibroblasts cultured from affec ted skin sites of patients with scleroderma. J. Rheum. 1992, 19, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.R. TNF-Mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waage, A.; Halstensen, A.; Espevik, T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet 1987, 1, 355–357. [Google Scholar]
- Robak, T.; Gladalska, A.; Stepien, H. The tumour necrosis factor family of receptors/ligands in the serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 1998, 9, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Xu, T.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of starfish. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 740–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, N.; Gammone, M.A.; Gemello, E.; Girolamo, M.D.; Cusenza, S.; Riccioni, G. Marine bioactives: Pharmacological properties and potential applications against inflammatory diseases. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2005–6: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigucgi, R.; Inoue, S.; Inagaki, K.; Sakai, M.; Miyamoto, T.; Komori, T.; Inagaki, M.; Isobe, R. Biologically active glycosides from Asteroidea, 42. Isolation and structure of a new biologically active ganglioside molecular species from the starfish Asterina pectinifera. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Ham, J.H.; Lee, N.J.; Park, C.H.; Shin, Y.H.; Lee, D.U. Antimutagenic activity of 5α-cholest-7-en-3β-ol, a new component from the starfish Asterina pectinifera. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 1247–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zheng, J.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, F.; Ju, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Polyhydroxy steroids and saponins from China sea starfish Asterina pectinifera and their biological activities. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.P.; Cuong, N.X.; Luyen, B.T.T.; Nam, N.H.; Cuong, P.V.; Thanh, N.V.; Nhiem, N.X.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kang, H.K.; et al. Steroidal constituents from the starfish Astropecten polyacanthus and their anticancer effects. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Thao, N.P.; Nam, N.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Quang, T.H.; Tung, P.T.; Tai, B.H.; Luyen, B.T.T.; Chae, D.; Kim, S.; Koh, Y.S.; et al. Diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia maxima and their inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated production of proinflammatory cytokines in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Thao, N.P.; Nam, N.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Quang, T.H.; Tung, P.T.; Dat, L.D.; Chae, D.; Kim, S.; Koh, Y.S.; Kiem, P.V.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory norditerpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia maxima. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.P.; Nam, N.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Tai, B.H.; Quang, T.H.; Ngan, N.T.T.; Luyen, B.T.T.; Yang, S.Y.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, S.; et al. Steroidal constituents from the soft coral Sinularia dissecta and their inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.P.; Dat, L.D.; Ngoc, N.T.; Tu, V.A.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Huong, P.T.T.; Nhiem, N.X.; Tai, B.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; et al. Pyrrole and furan oligoglycosides from the starfish Asterina batheri and their inhibitory effect on the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, P.A.; Tsujimoto, H.; Bahjat, F.R.; Ungaro, R.; Debernardis, J.; Tannahill, C.; Baker, H.V.; Edwards, C.K.; Moldawer, L.L. Differential maturation of murine bone-marrow derived dendritic cells with lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Endotoxin. Res. 2005, 11, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, T.L.; Cleveland, M.G.; Kulesza, P.; Magram, J.; Murphy, K.M. Regulation of Interleukin 12 p40 expression through an NF-κB half-site. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Plevy, S.E.; Gembreling, J.H.M.; Hsu, S.; Dorner, A.J.; Smale, S.T. Multiple control elements mediate activation of the murine and human interleukin 12 p40 promoters: Evidence of functional synergy between C/EBP and rel proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 4572–4588. [Google Scholar]
- Barrie, A.M.; Plevy, S.E. The interleukin-12 family of cytokines: Therapeutic targets for inflammatory disease mediation. Clin. Appl. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 5, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Laydon, J.T.; Mcdonnell, P.C.; Gallagher, T.F.; Kumar, S.; Green, D.; Mcnulty, D.; Blumenthal, M.J.; Keys, J.R.; Vatter, S.W.L.; et al. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature 1994, 372, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.E.; Hong, H.J.; Dearth, A.; Kobayashi, K.S.; Koh, Y.S. Intracellular invasion of orientia tsutsugamushi activates inflammasome in ASC-dependent manner. PLoS One 2012, 7, e39042. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Thao, N.P.; Cuong, N.X.; Luyen, B.T.T.; Quang, T.H.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Kim, S.; Koh, Y.-S.; Nam, N.H.; Van Kiem, P.; Van Minh, C.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Components of the Starfish Astropecten polyacanthus. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2917-2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082917
Thao NP, Cuong NX, Luyen BTT, Quang TH, Hanh TTH, Kim S, Koh Y-S, Nam NH, Van Kiem P, Van Minh C, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Components of the Starfish Astropecten polyacanthus. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(8):2917-2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082917
Chicago/Turabian StyleThao, Nguyen Phuong, Nguyen Xuan Cuong, Bui Thi Thuy Luyen, Tran Hong Quang, Tran Thi Hong Hanh, Sohyun Kim, Young-Sang Koh, Nguyen Hoai Nam, Phan Van Kiem, Chau Van Minh, and et al. 2013. "Anti-Inflammatory Components of the Starfish Astropecten polyacanthus" Marine Drugs 11, no. 8: 2917-2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082917
APA StyleThao, N. P., Cuong, N. X., Luyen, B. T. T., Quang, T. H., Hanh, T. T. H., Kim, S., Koh, Y.-S., Nam, N. H., Van Kiem, P., Van Minh, C., & Kim, Y. H. (2013). Anti-Inflammatory Components of the Starfish Astropecten polyacanthus. Marine Drugs, 11(8), 2917-2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082917