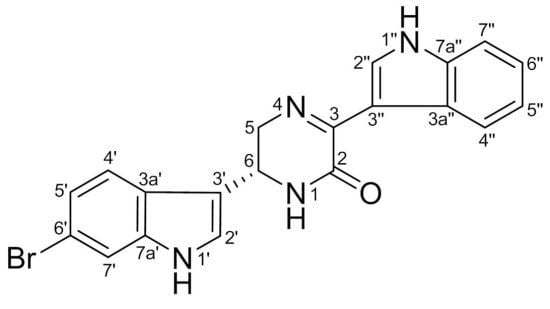
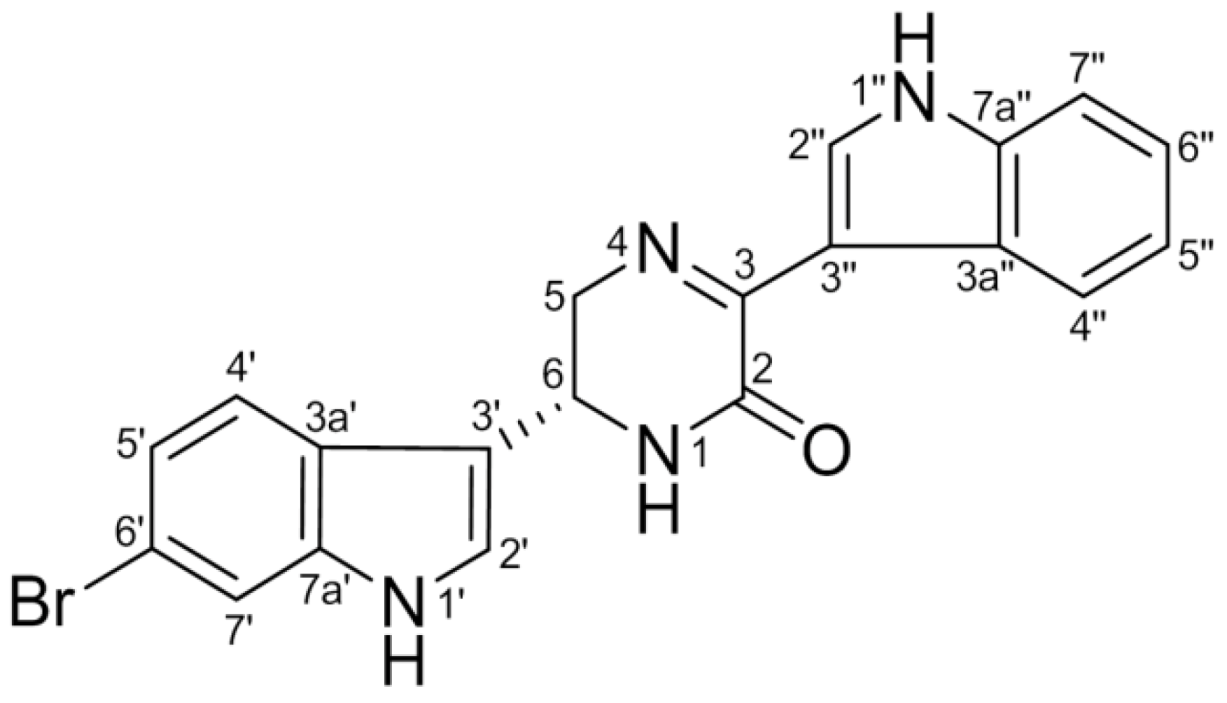
6″-Debromohamacanthin A, a Bis (Indole) Alkaloid, Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting the VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
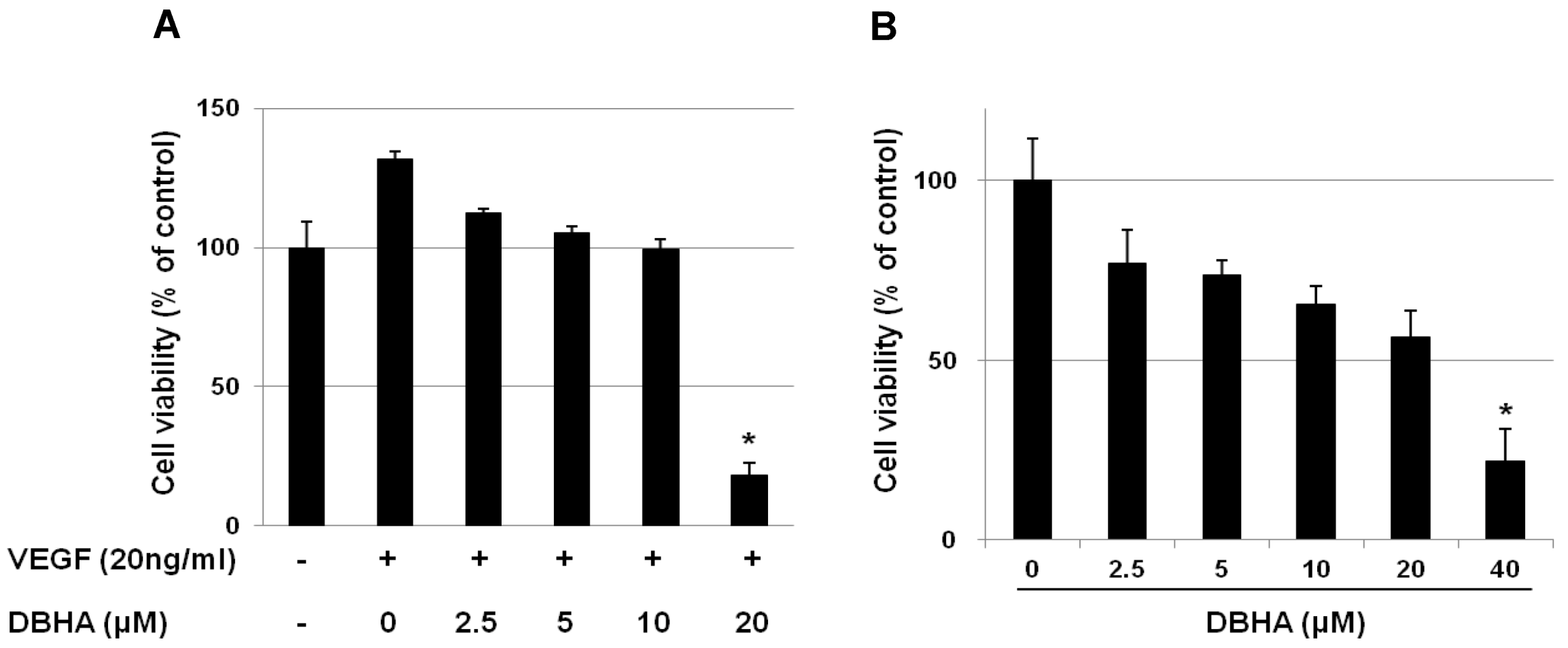
2.1. DBHA Inhibits the Viability of VEGF-Induced HUVEC and mES-Derived Endothelial-Like Cells
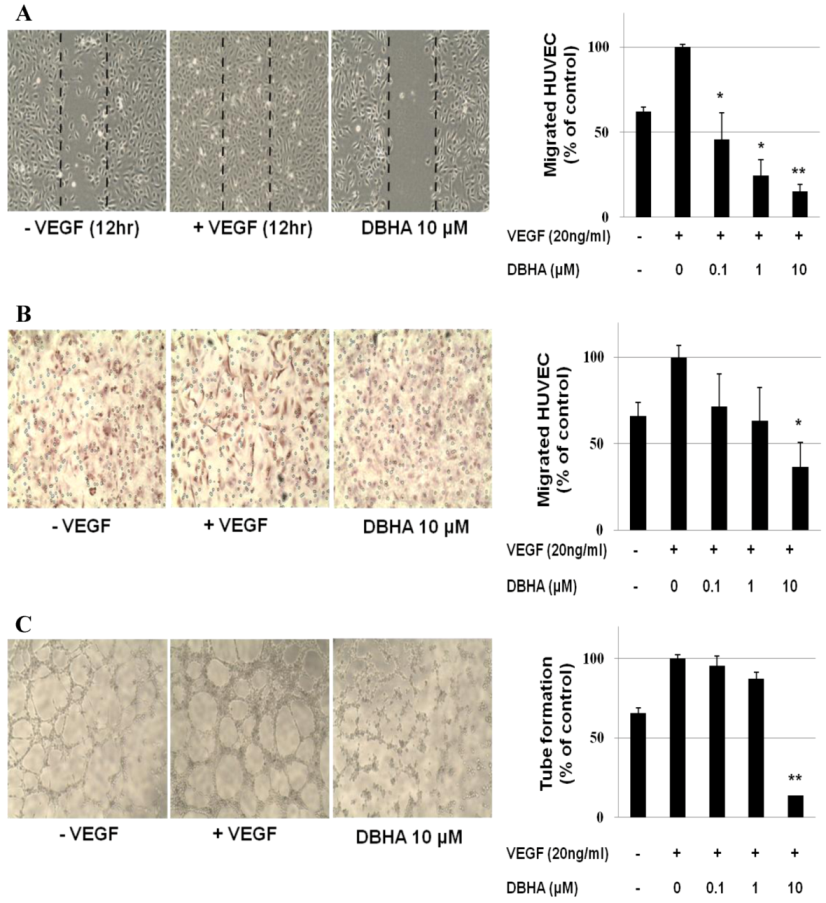
2.2. DBHA Inhibits the VEGF-Induced Cell Migration and Tube Formation of HUVEC
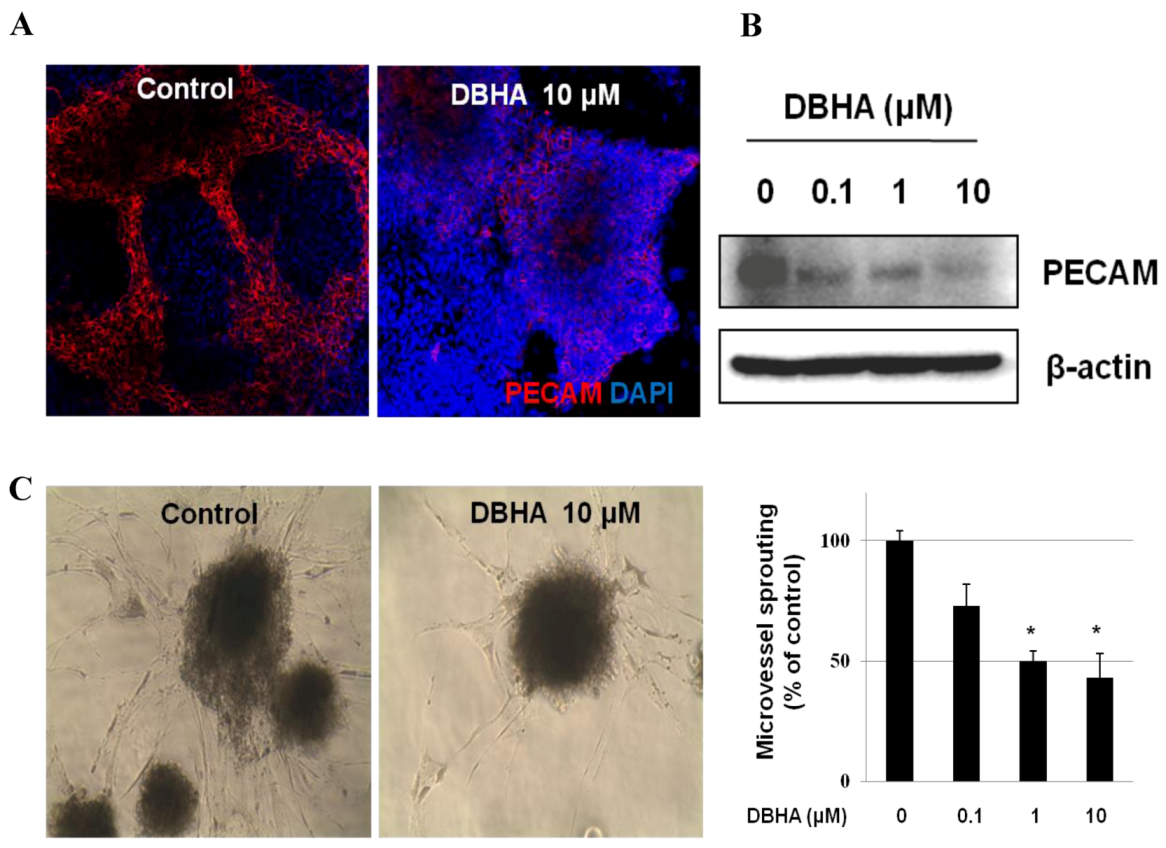
2.3. DBHA Suppresses PECAM Expression and Capillary Sprouting of mES Cell-Derived Embryoid Bodies
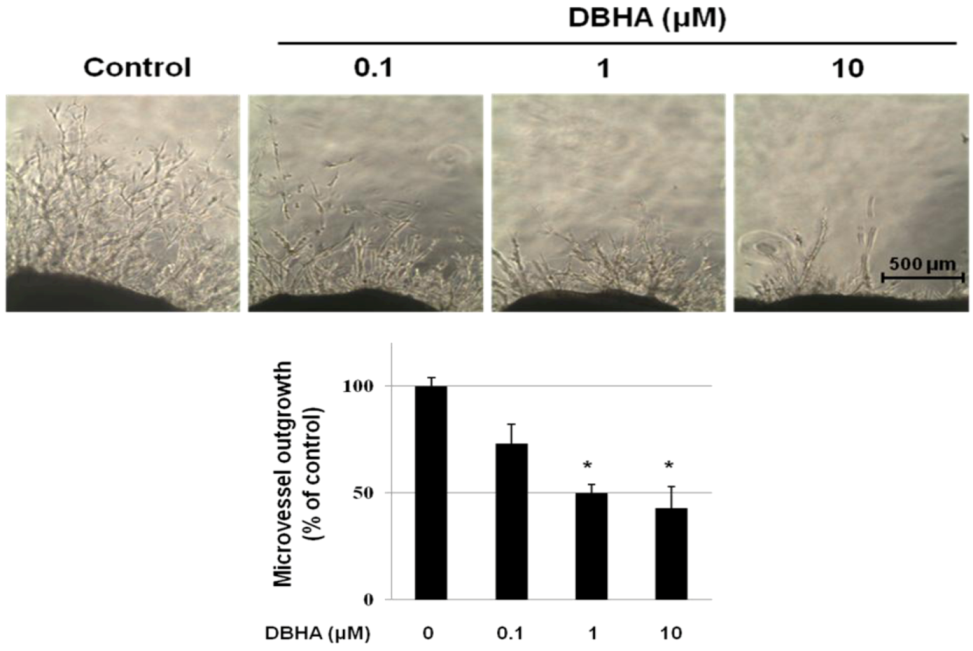
2.4. DBHA Inhibits Capillary Spouting in the Mouse Aortic Ring Assay

2.5. DBHA Inhibits MAPKs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in VEGF-Stimulated HUVEC and mES-Derived Endothelial-Like Cells
2.6. Global Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagent
3.2. Endothelial Cell Culture
3.3. Culture and Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
3.4. Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Scratch-Wound Migration Assay
3.6. Transwell Migration Assay
3.7. Tube Formation Assay with HUVEC Cells on Matrigel
3.8. Western Blot Analysis
3.9. Immunocytochemistry
3.10. 3-Dimensional Collagen Type-I Sprouting Angiogenesis Model
3.11. Aortic Ring Assay
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Folkman, J. Endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors. APMIS 2004, 112, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.F.; Cho, S.G.; Yi, Z.F.; Pang, X.F.; Rodriguez, M.; Wang, Y.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Liu, M.Y. Thymoquinone inhibits tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth through suppressing akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plate, K.H.; Breier, G.; Weich, H.A.; Risau, W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 1992, 359, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.E.; Perez-Soler, R. Mechanisms of resistance to vascular endothelial growth factor blockade. Cancer 2012, 118, 3455–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Ohgimoto, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Shibuya, M. Essential role of flk-1 (VEGF receptor 2) tyrosine residue 1173 in vasculogenesis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, T.A.; Garrett, M.D.; Walton, M.I.; Raynaud, F.; de Bono, J.S.; Workman, P. Targeting the pi3k-akt-mtor pathway: Progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 393–412. [Google Scholar]
- Bohmer, C.; Wehner, F. The epithelial Na(+) channel (enac) is related to the hypertonicity-induced Na(+) conductance in rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 2001, 494, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, C.; Poncet, G.; Villaume, K.; Blanc, M.; Gadot, N.; Walter, T.; Lepinasse, F.; Hervieu, V.; Cordier-Bussat, M.; Scoazec, J.Y.; et al. Targeting the pi3k/mtor pathway in murine endocrine cell lines: In vitro and in vivo effects on tumor cell growth. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, Y. Science of symptomatology: Spasms. Physiopathology of motor function disorders. Kango Gijutsu 1980, 26, 2047–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalingam, D.; Sankhala, K.; Mita, A.; Giles, F.J.; Mita, M.M. Targeting the mtor pathway using deforolimus in cancer therapy. Futur. Oncol. 2009, 5, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.A. Leukocyte-endothelial-cell interactions in leukocyte transmigration and the inflammatory response. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.R. Isolation of a pluripotent cell-line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem-cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 7634–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.D.; Bae, S.Y.; Park, H.J.; Bae, K.; Lee, S.K. Honokiol inhibits vascular vessel formation of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells via the suppression of pecam and mapk/mtor signaling pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phife, D.W.; Ramos, R.A.; Feng, M.; King, I.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Wright, A.; Patel, M.; Pachter, J.A.; Coval, S.J. Marine sponge bis(indole) alkaloids that displace ligand binding to α1 adrenergic receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 2103–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.Q.; Sun, Q.S.; Yao, X.S.; Hong, J.K.; Lee, C.O.; Sim, C.J.; Im, K.S.; Jung, J.H. Cytotoxic bisindole alkaloids from a marine sponge Spongosorites sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A.; Cross, S.S.; Mccarthy, P. A new bis(indole) alkaloid from a deep-water marine sponge of the genus spongosorites. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 4772–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakemi, S.; Sun, H.H. Nortopsentins A, B, and C. Cytotoxic and antifungal imidazolediylbis [indoles] from the sponge Spongosorites ruetzleri. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 4304–4307. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, S.A.; Andersen, R.J. Brominated bis(indole) alkaloids from the marine sponge Hexadella sp. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; McCarthy, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Hamacanthins A and B, new antifungal bis indole alkaloids from the deep-water marine sponge, Hamacantha sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kouko, T.; Totsuka, H.; Hiramatsu, K. Synthesis of marine bisindole alkaloids, hamacanthins a and b through intramolecular transamidation-cyclization. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 8849–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achab, S. A three-component coupling approach to the marine bis-indole alkaloids: Topsentin, deoxytopsentin and bromotopsentin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 5503–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, I.; Yamashita, M.; Ohta, S. Total synthesis of nortopsentins a–d, marine alkaloids. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Arai, M.; Fujita, M.; Kobayashi, M. Pyripyropenes, fungal sesquiterpenes conjugated with α-pyrone and pyridine moieties, exhibits anti-angiogenic activity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Seo, Y.; Cho, K.W.; Rho, J.R.; Sim, C.J. New bis(indole) alkaloids of the topsentin class from the sponge Spongosorites genitrix. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.B.; Mar, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, M.N.; Kim, J.G.; Shin, D.; Sim, C.J.; Shin, J. Bis(indole) alkaloids as sortase a inhibitors from the sponge Spongosorites sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4927–4931. [Google Scholar]
- Tozer, G.M.; Kanthou, C.; Baguley, B.C. Disrupting tumour blood vessels. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, E.A.; Duray, P.H.; Tsokos, M.G.; Venzon, D.J.; Libutti, S.K.; Dixon, S.C.; Rudek, M.A.; Pluda, J.; Allegra, C.; Figg, W.D. Endostatin inhibits microvessel formation in the ex vivo rat aortic ring angiogenesis assay. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 268, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.J.; Claesson-Welsh, L. FGF and VEGF function in angiogenesis: Signalling pathways, biological responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1216–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.G.; Zhang, X.W.; Geng, M.Y.; Yue, J.M.; Xin, X.L.; Tian, F.; Shen, X.; Tong, L.J.; Li, M.H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Pseudolarix acid b, a new tubulin-binding agent, inhibits angiogenesis by interacting with a novel binding site on tubulin. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Murphy, D.A.; Lassoued, W.; Thurston, G.; Feldman, M.D.; Lee, W.M.F. Activated stat3 is a mediator and biomarker of VEGF endothelial activation. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1994–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.F.; Luo, J.C.; Rana, J.S.; Laham, R.; Sellke, F.W.; Li, J. Involvement of cox-2 in VEGF-induced angiogenesis via p38 and jnk pathways in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, K.N.; Bryant, P.; Vincent, P.A.; Pumiglia, K.M. Activated ras induces a proangiogenic phenotype in primary endothelial cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, S.; Oda, N.; Abe, M.; Terai, Y.; Ito, M.; Shitara, K.; Tabayashi, K.; Shibuya, M.; Sato, Y. Roles of two vegf receptors, flt-1 and kdr, in the signal transduction of VEGF effects in human vascular endothelial cells. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiojima, I.; Walsh, K. Role of akt signaling in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Jo, S.A.; Ryou, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Chung, J.; Jo, I. Troglitazone acutely inhibits protein synthesis in endothelial cells via a novel mechanism involving protein phosphatase 2a-dependent p70 s6 kinase inhibition. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C317–C326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.; Perez, C.A.; Moretti, L.; Lu, B. The mtor signaling network: Insights from its role during embryonic development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1192–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.G.; Acosta-Jaquez, H.A.; Romeo, Y.; Ekim, B.; Soliman, G.A.; Carriere, A.; Roux, P.P.; Ballif, B.A.; Fingar, D.C. Regulation of mtor complex 1 (mtorc1) by raptor ser863 and multisite phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risau, W.; Sariola, H.; Zerwes, H.G.; Sasse, J.; Ekblom, P.; Kemler, R.; Doetschman, T. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in embryonic-stem-cell-derived embryoid bodies. Development 1988, 102, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Wartenberg, M.; Gunther, J.; Hescheler, J.; Sauer, H. The embryoid body as a novel in vitro assay system for antiangiogenic agents. Lab. Invest. 1998, 78, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, K.; Magnusson, P.; Dixelius, J.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Cross, M.J. Angiostatin and endostatin inhibit endothelial cell migration in response to FGF and VEGF without interfering with specific intracellular signal transduction pathways. FEBS Lett. 2003, 536, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, H.; Gunther, J.; Hescheler, J.; Wartenberg, M. Thalidomide inhibits angiogenesis in embryoid bodies by the generation of hydroxyl radicals. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Tsark, W.; Holmes, K.V.; Shively, J.E. Role of ceacam1 in VEGF induced vasculogenesis of murine embryonic stem cell-derived embryoid bodies in 3D culture. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1668–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.D.; Kim, G.J.; Seok, J.H.; Chung, H.M.; Chee, K.M.; Rhee, G.S. Differentiation of endothelial cells derived from mouse embryoid bodies: A possible in vitro vasculogenesis model. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 180, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.D.; Rhee, G.S.; Chung, H.M.; Chee, K.M.; Kim, G.J. Cytotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil: Effect on endothelial differentiation via cell cycle inhibition in mouse embryonic stem cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festag, M.; Viertel, B.; Steinberg, P.; Sehner, C. An in vitro embryotoxicity assay based on the disturbance of the differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells into endothelial cells. II. Testing of compounds. Toxicol. In Vitro 2007, 21, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Yi, Z.; Cho, S.G.; Luo, J.; Pandey, M.K.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Liu, M. Gambogic acid inhibits angiogenesis and prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1843–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Robinson, S.D.; Lechertier, T.; Barber, P.R.; Tavora, B.; D’Amico, G.; Jones, D.T.; Vojnovic, B.; Hodivala-Dilke, K. Use of the mouse aortic ring assay to study angiogenesis. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.D.; Cheong, O.J.; Bae, S.Y.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.K. 6″-Debromohamacanthin A, a Bis (Indole) Alkaloid, Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting the VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1087-1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041087
Kim GD, Cheong OJ, Bae SY, Shin J, Lee SK. 6″-Debromohamacanthin A, a Bis (Indole) Alkaloid, Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting the VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(4):1087-1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041087
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Gi Dae, Oug Jae Cheong, Song Yi Bae, Jongheon Shin, and Sang Kook Lee. 2013. "6″-Debromohamacanthin A, a Bis (Indole) Alkaloid, Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting the VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways" Marine Drugs 11, no. 4: 1087-1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041087
APA StyleKim, G. D., Cheong, O. J., Bae, S. Y., Shin, J., & Lee, S. K. (2013). 6″-Debromohamacanthin A, a Bis (Indole) Alkaloid, Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting the VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs, 11(4), 1087-1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041087