Evaluation of Passive Samplers as a Monitoring Tool for Early Warning of Dinophysis Toxins in Shellfish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
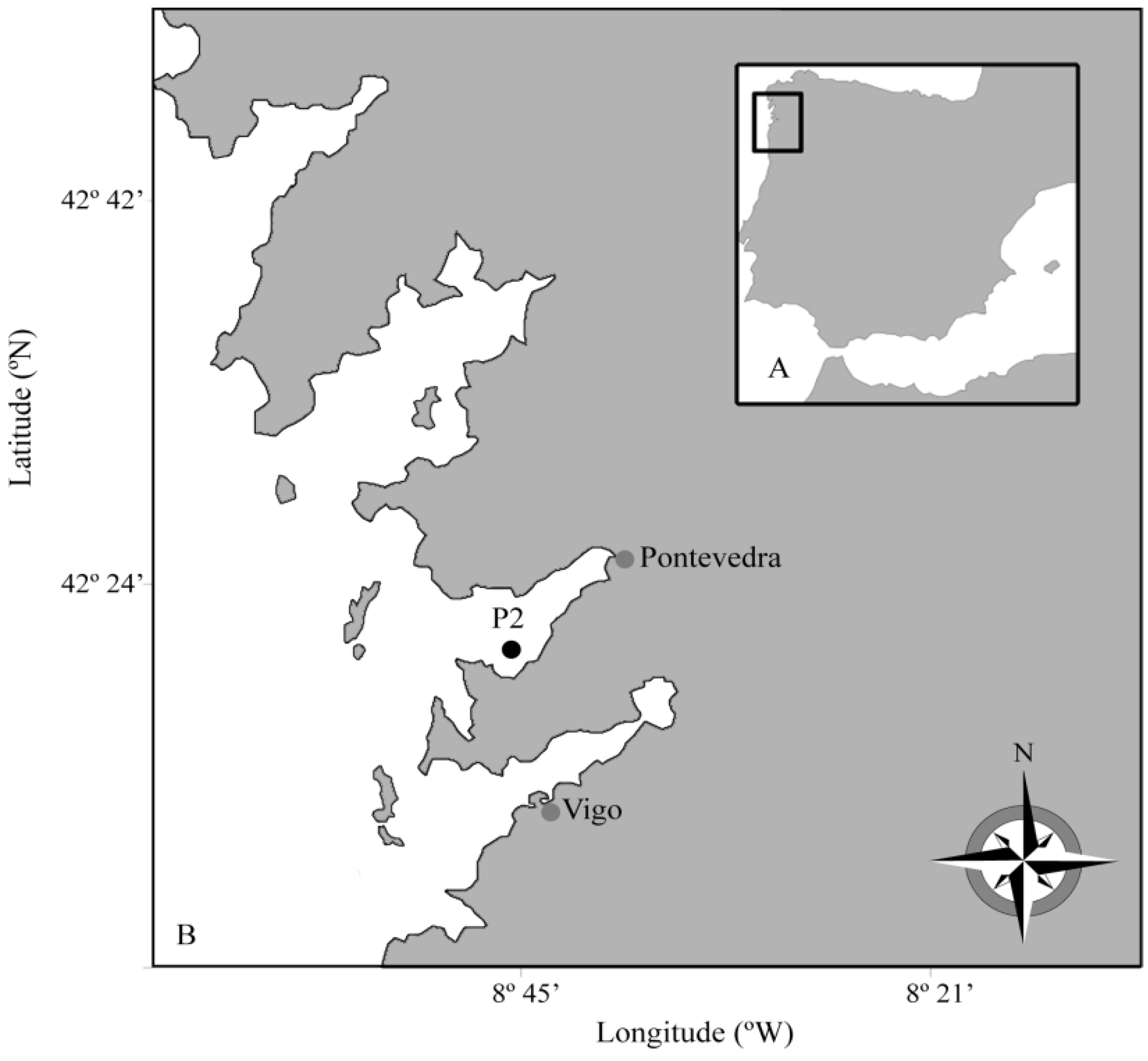
2. Results
2.1. Seasonal Distribution of Dinophysis Species
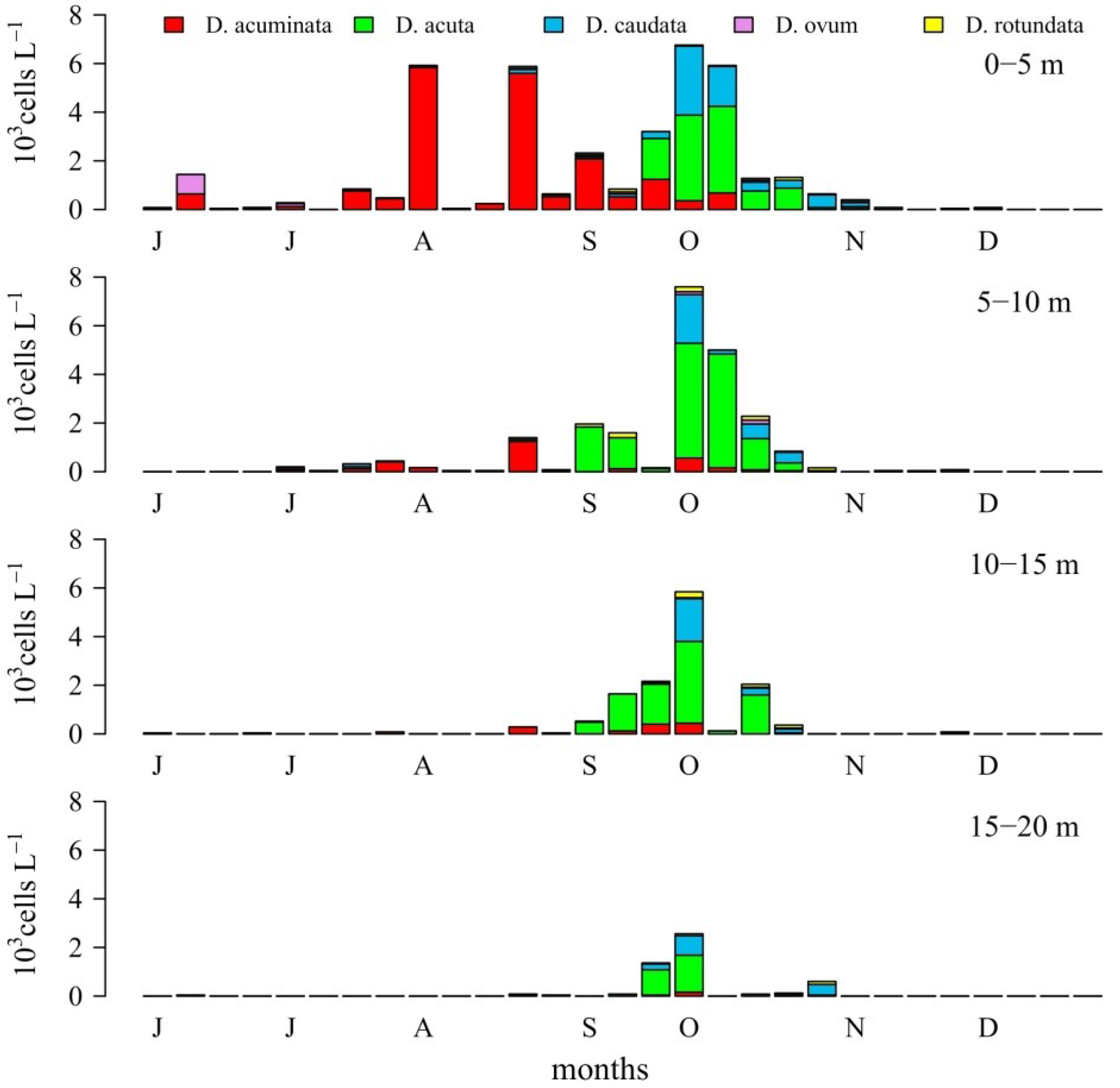
2.2. Dinophysis spp. in the Concentrated (Pump) Phytoplankton Samples
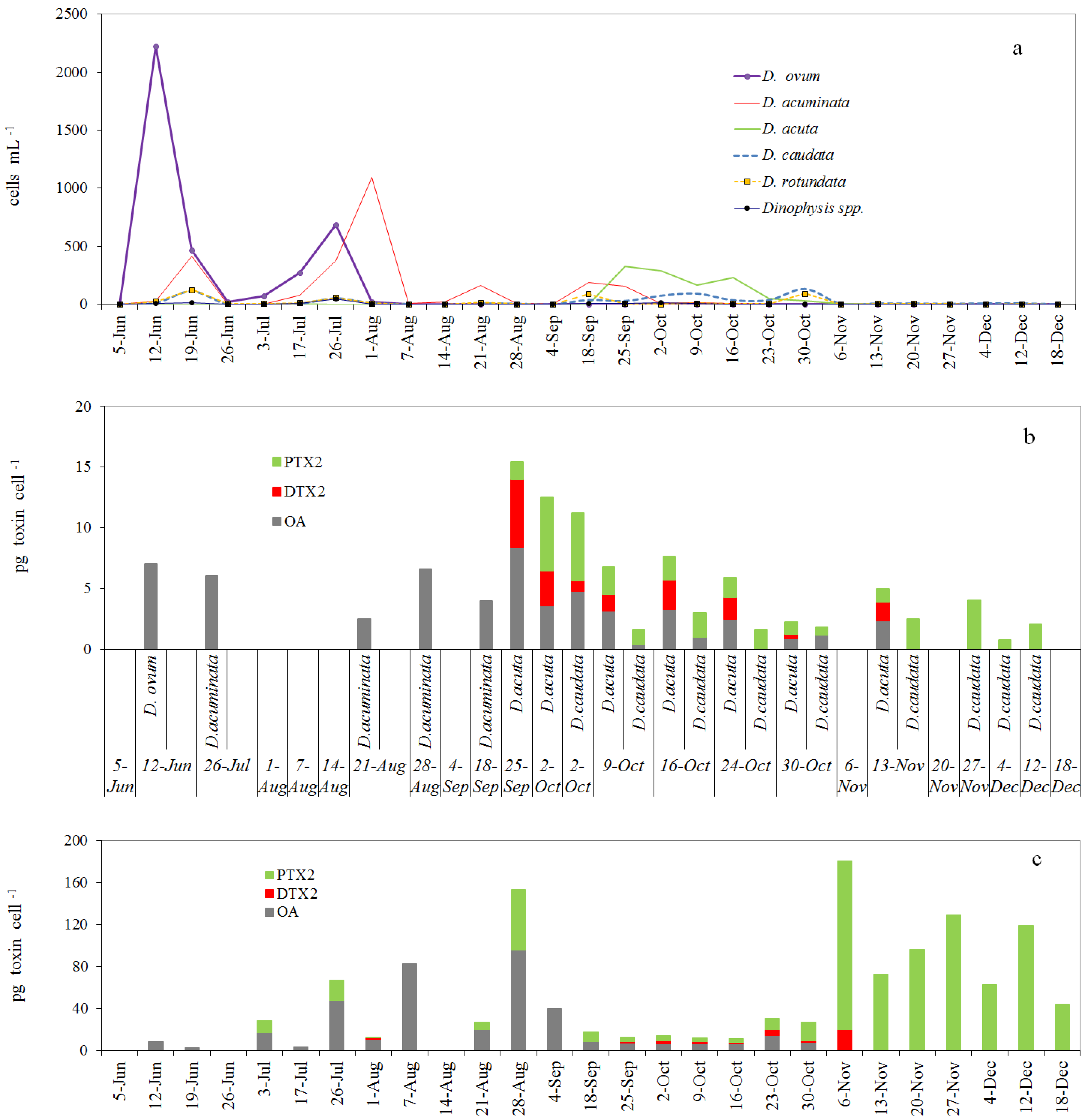
2.3. Toxin Profile and Content in Picked Cells of Dinophysis from the Pump Concentrates
2.4. Toxin Profiles and Content per Cell of Dinophysis in the Size-Fractioned Plankton Concentrates
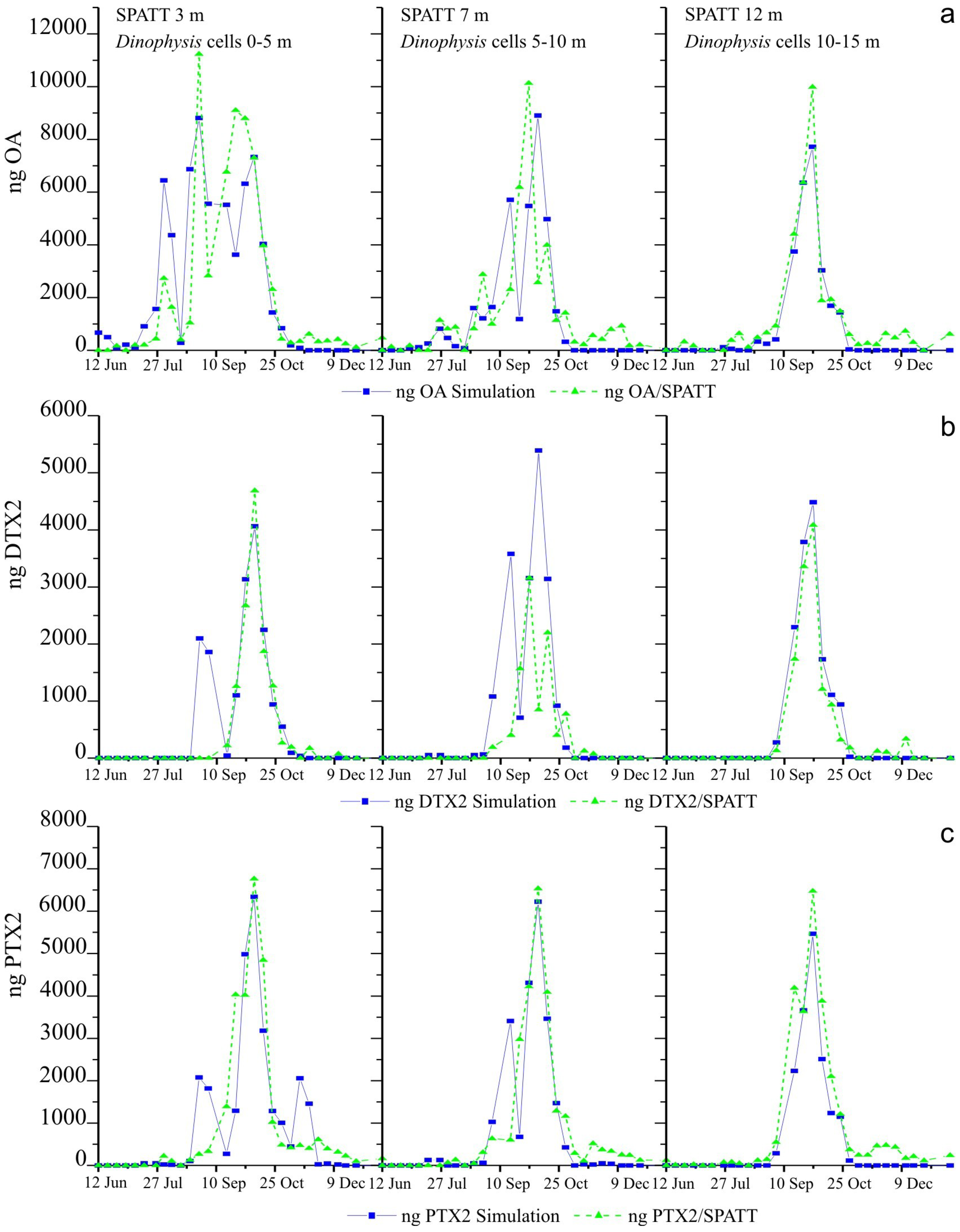
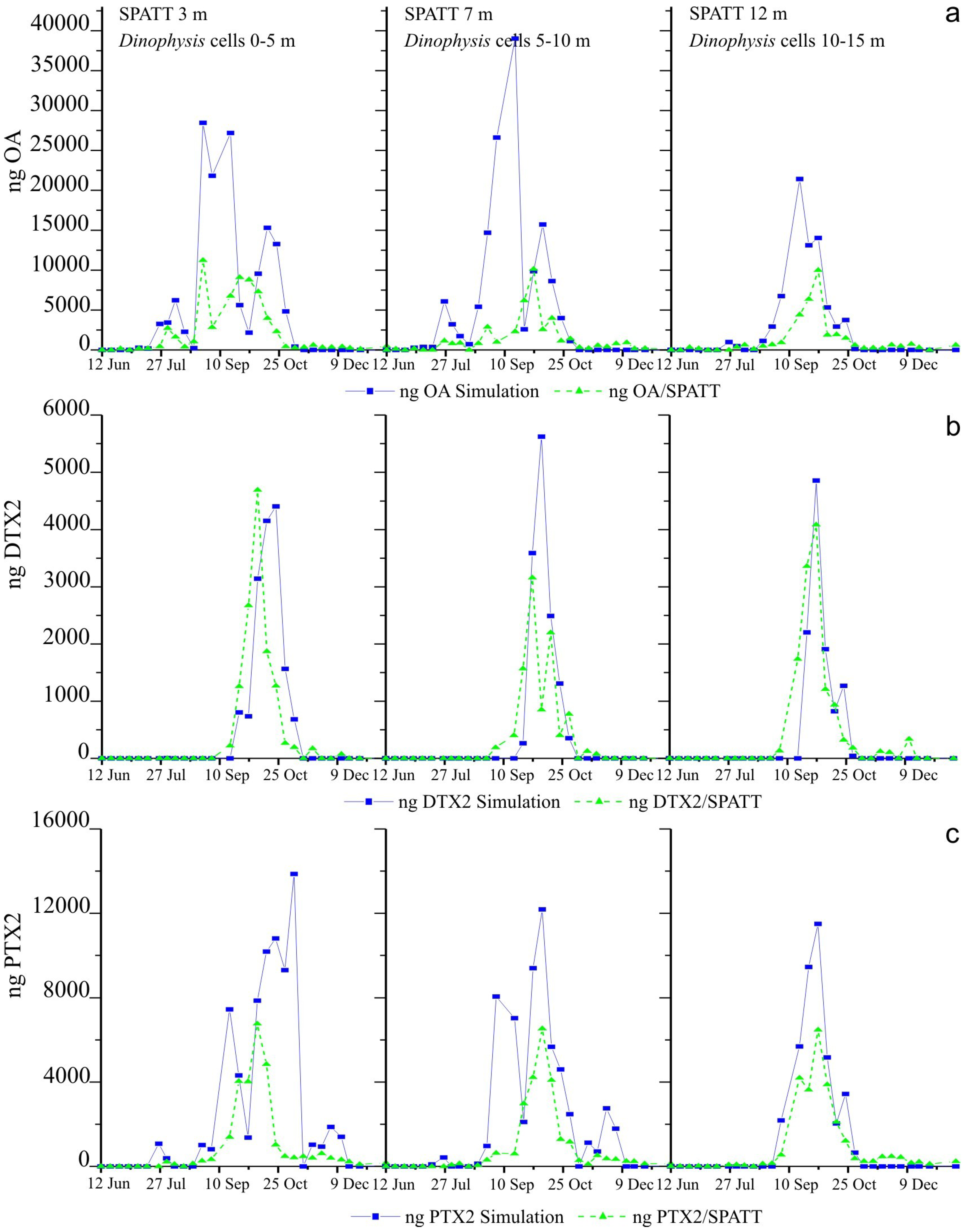
2.5. Weekly Adsorption of Toxins in the SPATT Discs and Its Relation with Dinophysis Populations
2.5.1. SPATT at 3 m versus Dinophysis Cells at 0–5 m
2.5.2. SPATT Discs at 7 m versus Dinophysis Cells at 5–10 m

2.5.3. SPATT Discs at 12 m versus Dinophysis Cells at 10–15 m
2.6. Simulations of Toxin Adsorption by SPATT at 3 m, 7 m and 12 m
| Toxin | Source of toxin data | SPATT, 3 m | SPATT, 7 m | SPATT, 12 m | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (pg cell−1) | r2 | slope | r2 | slope | r2 | slope | |
| OA | picked cells | 0.62 | 0.70 | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.95 | 0.87 |
| plankton | 0.44 | 1.74 | 0.07 | 1.35 | 0.68 | 1.96 | |
| DTX2 | picked cells | 0.74 | 0.90 | 0.39 | 1.18 | 0.98 | 1.14 |
| plankton | 0.46 | 0.82 | 0.44 | 1.16 | 0.78 | 0.92 | |
| PTX2 | picked cells | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.79 |
| plankton | 0.19 | 1.13 | 0.65 | 1.70 | 0.90 | 1.75 | |
3. Discussion
3.1. Seasonal and Annual Variability of the Toxin Profile and Content in Picked Cell of Dinophysis
| Cellular toxin content (pg cell−1), mean ± SD | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dinophysis species | year | OA | DTX2 | PTX2 | n | Location | Reference |
| D. acuminata | 2002 | 12.1 | nd | nd | 1 | Bueu | [19] |
| 2003 | 1.0 | nd | nd | 1 | Bueu | [19] | |
| 2005 | 1.3 ± 1.0 | nd | nd | 15 | Bueu | [19] | |
| 2006 | 3.7 ± 1.8 | nd | nd | 8 | Bueu | this work | |
| D. skagii | 2006 | nd | nd | nd | 1 | Bueu | this work |
| D. acuta | 2005 | 3.8 ± 2.5 | 3.7 ± 2.4 | 1.5 ± 1.0 | 11 | Bueu | [19] |
| 2006 | 2.9 ± 2.0 | 1.9 ± 1.5 | 2.8 ± 2.7 | 12 | Bueu | this work | |
| D. caudata | 2003 | nd | nd | 44.4 ± 15.1 | 2 | Bueu | [19] |
| 2005 | nd | nd | 3.9 | 1 | D13 | [19] | |
| 2006 | 0.6 | 2.8 | 5.0 | 1 | Moaña | this work | |
| D. rotundata | 2003 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | nd | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 5 | Bueu | [18] |
| 2005 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.5 ± 0.6 | nd | 2 | Bueu | [18] | |
| 2007 | nd | nd | nd | 4 | Bueu | [18] | |
3.2. Simulations of Toxin Accumulation in the SPATT versus the Actual Observations: What Is the Source of the SPATT-Accumulated Toxins?
3.3. Assessment of the Use of SPATT as a Tool in Research and Monitoring of Lipophilic Toxin Outbreaks
4. Experimental Section
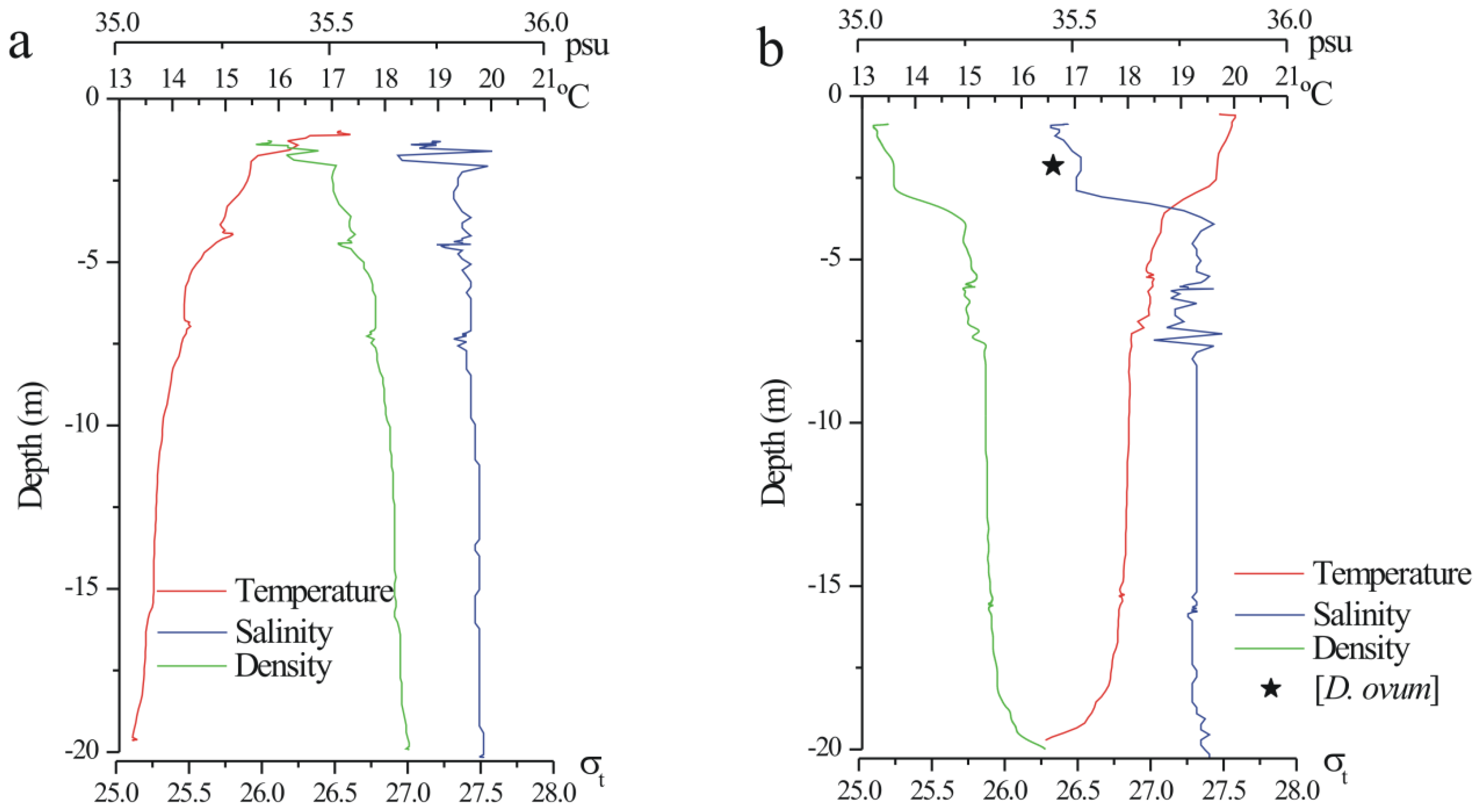
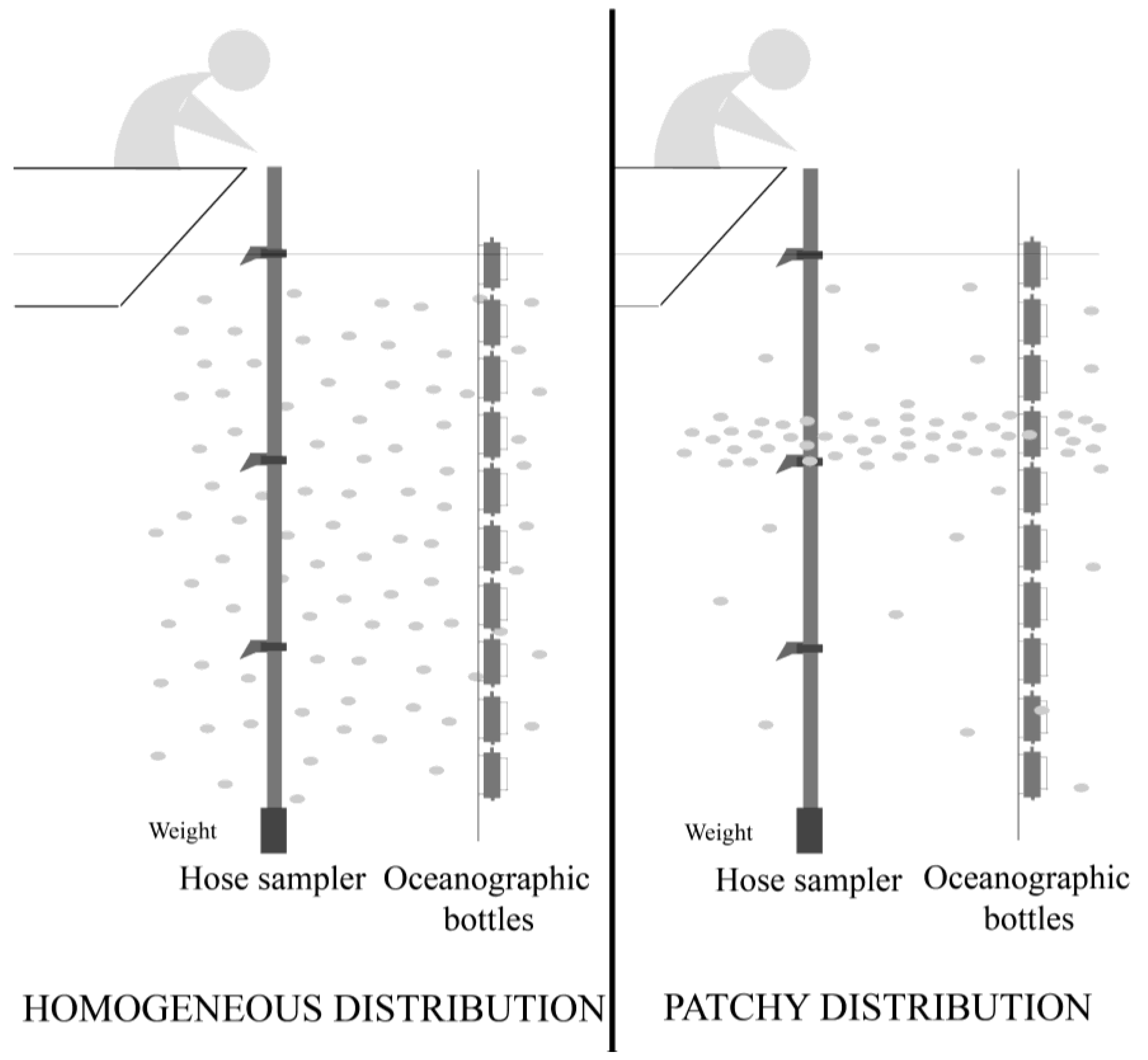
4.1. Field Sampling

4.2. Phytoplankton Counts
4.3. Toxin Extraction from Phytoplankton Pump-Concentrates, Picked Cells and SPATT Resins
4.4. LC-MS Analyses
4.5. Simulation of Toxins Adsorption by the SPATT Discs
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yasumoto, T.; Murata, M.; Oshima, Y.; Sano, M.; Matsumoto, G.; Clardy, J. Diarrhetic shellfish toxins. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Moroño, A.; Pazos, Y.; Maneiro, J.; Mariño, J. Trends and Variations of the Abundance of Main PSP and DSP Producing Species in the Galician Rías: Environmental and Biological Influences. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, H.; Gentien, P.; Fernand, L.; Lunven, M.; Reguera, B.; González-Gil, S.; Raine, R. Scales characterising a high density thin layer of Dinophysis acuta Ehrenberg and its transport within a coastal jet. Harmful Algae 2012, 15, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalera, L.; Pazos, Y.; Doval, M.D.; Reguera, B. A comparison of integrated and discrete depth sampling for monitoring Dinophysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No. 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004. Off. J. Eur. Union 2004, L139, 55–205.
- Reguera, B.; Pizarro, G. Planktonic Dinoflagellates which Produce Polyether Toxins of the Old “DSP Complex”. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection, 2nd ed.; Botana, L.M., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2008; pp. 257–284. [Google Scholar]
- Reguera, B.; Velo-Suárez, L.; Raine, R.; Park, M.G. Harmful Dinophysis species: A review. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, E.; Smith, J.L.; Tong, M.; Guzmán, L.; Anderson, D.M. Toxin profiles of five geographical isolates of Dinophysis spp. from North and South America. Toxicon 2011, 57, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; González-Gil, S.; Franco, J.M.; Reguera, B. Seasonal variability of lipophilic toxins during a Dinophysis acuta bloom in Western Iberia: Differences between picked cells and plankton concentrates. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, O.; Lundve, B.; Johansen, M. Toxicity of Dinophysis spp. in relation to population density and environmental conditions on the Swedish west coast. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, L.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Selwood, A. Solid phase adsorption toxin tracking (SPATT): A new monitoring tool that simulates the biotoxin contamination of filter feeding bivalves. Toxicon 2004, 44, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, E.; Marcaillou, C.; Mondeguer, F.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Field and mesocosm trials on passive sampling for the study of adsorption and desorption behaviour of lipophilic toxins with a focus on OA and DTX1. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaze, J.P. Solid-phase adsorption passive sampling: Review of a monitoring tool tracking in situ marine and freshwater toxins. In New Trends in Marine and Freshwater Toxins: Food and Safety Concerns; Cabado, A.G., Vieites, J.M., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 91–113. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, G.; Escalera, L.; González-Gil, S.; Franco, J.M.; Reguera, B. Growth, behavior and cell toxin quota of Dinophysis acuta Ehrenberg during a daily cycle. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 353, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raho, N.; Pizarro, G.; Escalera, L.; Reguera, B.; Marín, I. Morphology, toxin composition and molecular analysis of Dinophysis ovum Schutt, a dinoflagellate of the “Dinophysis acuminata complex”. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, R.; Dines, M.H.; Hawkes, A.D.; Briggs, L.R.; Sandvik, M.; Jensen, D.J.; Cooney, J.M.; Holland, P.T.; et al. Isolation of pectenotoxin-2 from Dinophysis acuta and its conversion to pectenotoxin-2 seco acid, and preliminary assessment of their acute toxicities. Toxicon 2004, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Mackenzie, L.; Stirling, D.; Adamson, J. Pectenotoxin-2 seco acid: A toxin converted from pectenotoxin-2 by the New Zealand Greenshell mussel, Perna canaliculus. Toxicon 2001, 39, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gil, S.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Velo-Suárez, L.; Reguera, B. Considerations on the toxigenic nature and prey sources of Phalacroma rotundatum. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 64, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, G. Estudio, Mediante LC-MS, de la Variabilidad del Perfil y Contenido de Toxinas en Poblaciones de Dinophysis spp. Agentes de Episodios DSP en las Rías Baixas Gallegas. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Vigo, Vigo, Spain, 29 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, M.M.; Kulis, D.M.; Fux, E.; Smith, J.L.; Hess, P.; Zhou, Q.X.; Anderson, D.M. The effects of growth phase and light intensity on toxin production by Dinophysis acuminata from the northeastern United States. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Krock, B.; Hansen, P.J. Effects of light and food availability on toxin production, growth and photosynthesis in Dinophysis acuminata. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 471, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Krock, B.; Hansen, P.J. Production and excretion of okadaic acid, pectenotoxin-2 and a novel dinophysistoxin from the DSP-causing marine dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta—Effects of light, food availability and growth phase. Harmful Algae 2013, 23, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J. Modelling as a Mitigation Strategy for Harmful Algal Blooms. In Shellfish Safety and Quality; Shumway, S.E., Rodrick, G.E., Eds.; Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition 167; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 200–227. [Google Scholar]
- Rossignoli, A.E. Acumulación de Toxinas DSP en el mejillón Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 18 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.; Tong, M.; Fux, E.; Anderson, D.M. Toxin production, retention, and extracellular release by Dinophysis acuminata during extended stationary phase and culture decline. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, B.; Riobó, P.; Fernández, M.L.; Fraga, S.; Franco, J.M. Production and release of yessotoxins by the dinoflagellates Protoceratium reticulatum and Lingulodinium polyedrum in culture. Toxicon 2004, 44, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, B.; Vázquez, J.A.; Riobó, P.; Franco, J.M. Study of the effect of temperature, irradiance and salinity on growth and yessotoxin production by the dinoflagellate Protoceratium reticulatum in culture by using a kinetic and factorial approach. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 62, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.L.; Reguera, B.; González-Gil, S.; Míguez, A. Pectenotoxin-2 in single-cell isolates of Dinophysis caudata and Dinophysis acuta from the Galician Rías (NW Spain). Toxicon 2006, 48, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, E.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Comparative accumulation and composition of lipophilic marine biotoxins in passive samplers and in mussels (M. edulis) on the West Coast of Ireland. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroño, A.; Arévalo, F.; Fernández, M.L.; Maneiro, J.; Pazos, Y.; Salgado, C.; Blanco, J. Accumulation and transformation of DSP toxins in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis during a toxic episode caused by Dinophysis acuminata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, E.; Gonzalez-Gil, S.; Lunven, M.; Gentien, P.; Hess, P. Production of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins and pectenotoxins at depths within and below the euphotic zone. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, O. A dividable hose for phytoplankton sampling. In ICES Report of the Working Group on Exceptional Algal Blooms; ICES C.M. 1986/L:26, Annex 3; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1986; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Utermöhl, H. Neue wege in der quantitativen Erfassung des Planktons (mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Ultraplanktons). Verh. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1931, 5, 567–596. [Google Scholar]
- Van Trijp, J.M.P.; Roos, A.H. Model for the Calculation of Calibration Curves; RIKILT Report 91.02; RIKILT-DLO: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pizarro, G.; Moroño, Á.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Pazos, Y.; Reguera, B. Evaluation of Passive Samplers as a Monitoring Tool for Early Warning of Dinophysis Toxins in Shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3823-3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103823
Pizarro G, Moroño Á, Paz B, Franco JM, Pazos Y, Reguera B. Evaluation of Passive Samplers as a Monitoring Tool for Early Warning of Dinophysis Toxins in Shellfish. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(10):3823-3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103823
Chicago/Turabian StylePizarro, Gemita, Ángeles Moroño, Beatriz Paz, José M. Franco, Yolanda Pazos, and Beatriz Reguera. 2013. "Evaluation of Passive Samplers as a Monitoring Tool for Early Warning of Dinophysis Toxins in Shellfish" Marine Drugs 11, no. 10: 3823-3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103823
APA StylePizarro, G., Moroño, Á., Paz, B., Franco, J. M., Pazos, Y., & Reguera, B. (2013). Evaluation of Passive Samplers as a Monitoring Tool for Early Warning of Dinophysis Toxins in Shellfish. Marine Drugs, 11(10), 3823-3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11103823




