Sinularin from Indigenous Soft Coral Attenuates Nociceptive Responses and Spinal Neuroinflammation in Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Rat Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
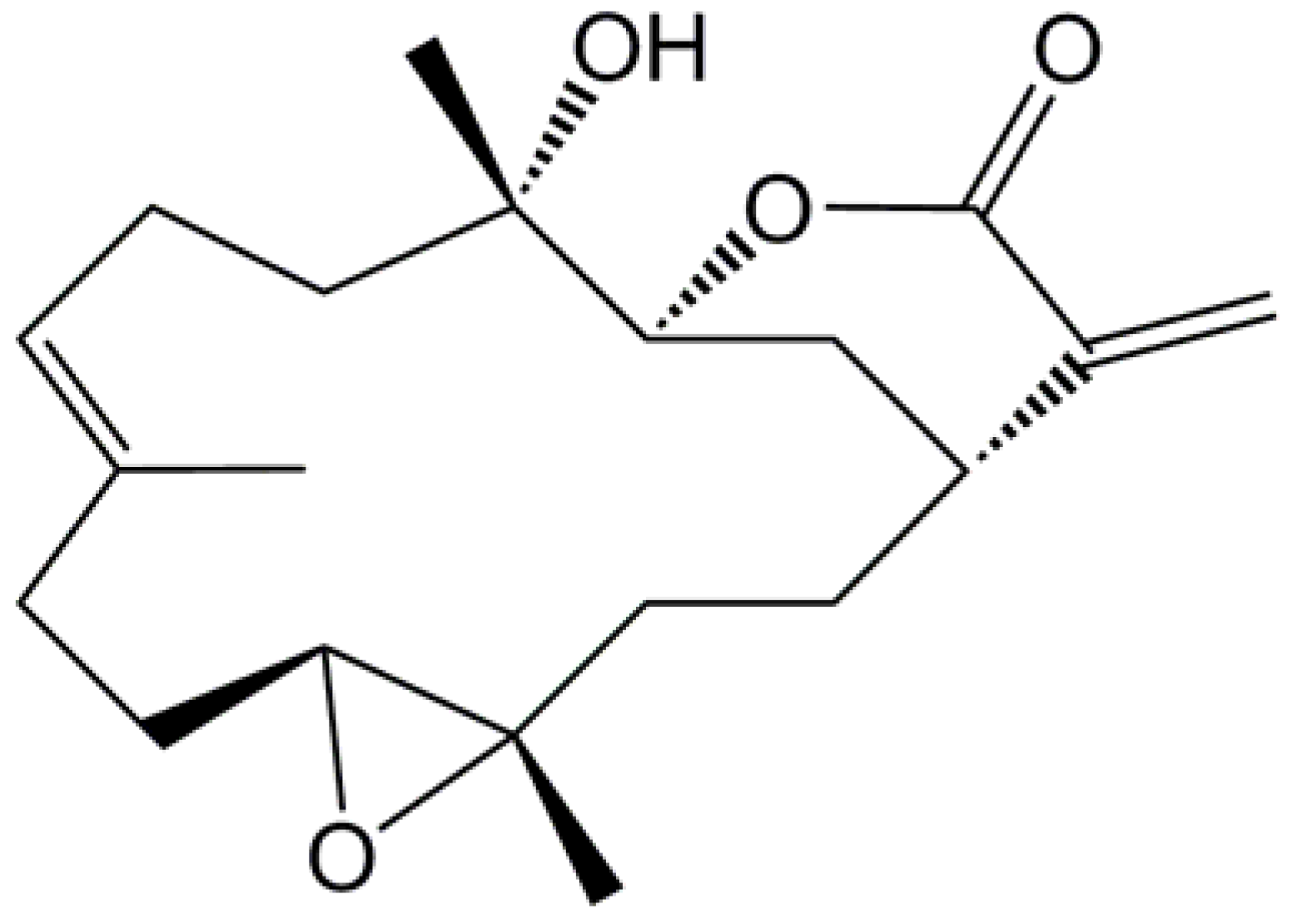
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Sinularin on LPS-Induced iNOS, COX-2, and TGF-β Protein Expression in Macrophages
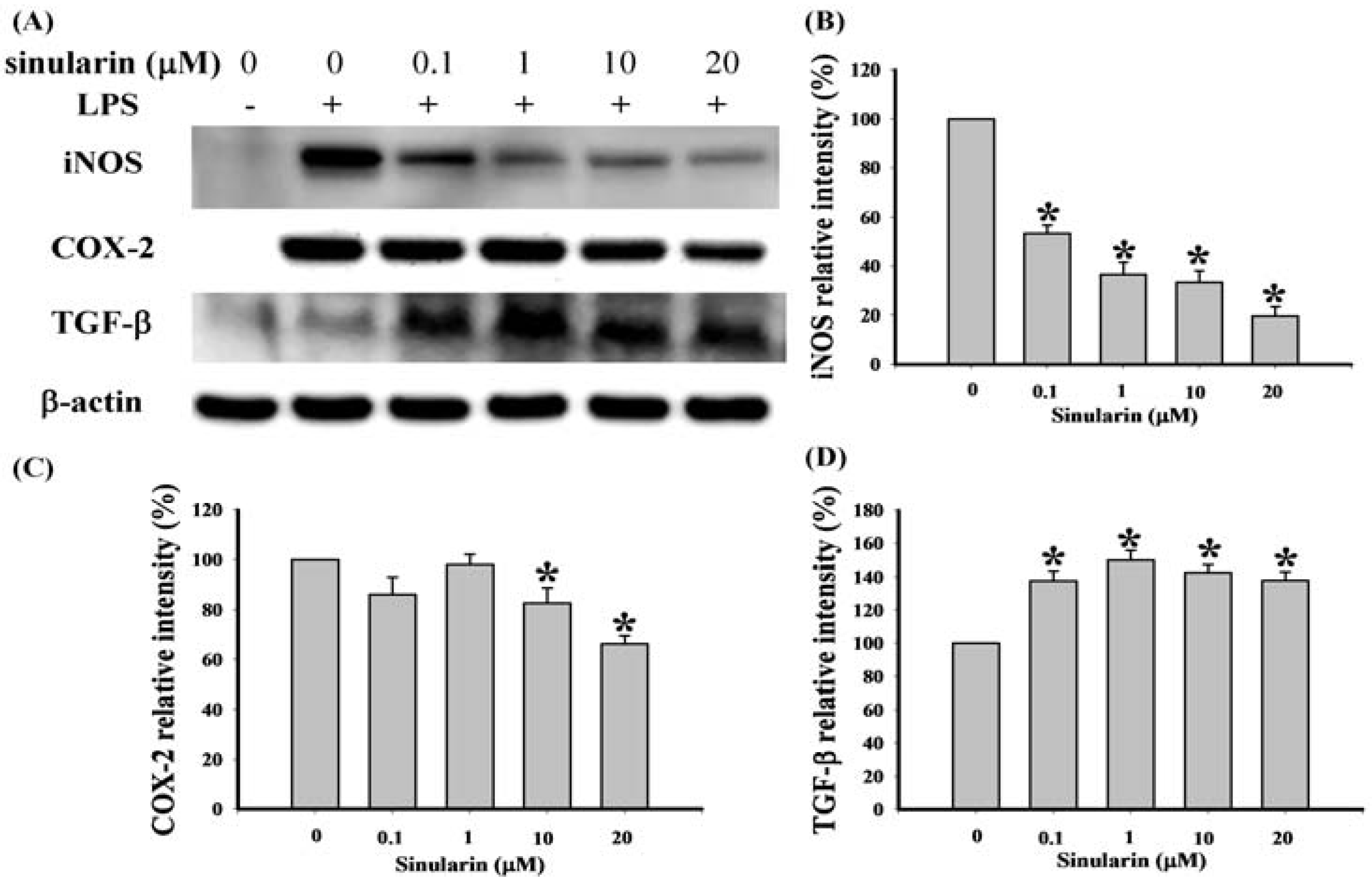
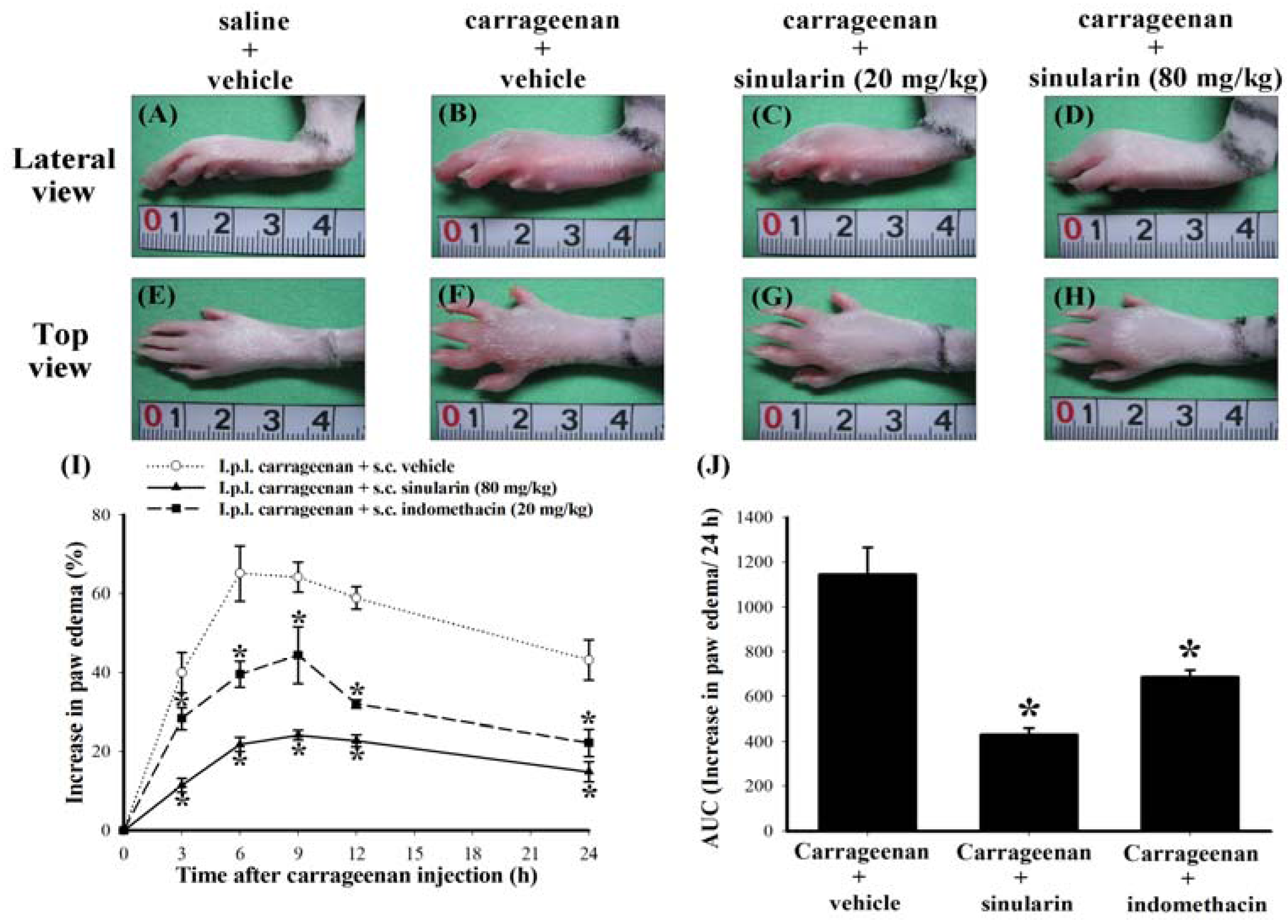
2.2. Effect of Systemic Sinularin Injection on Carrageenan-Induced Redness and Edema of the Paw
2.3. Effect of Systemic Injection of Sinularin on the Carrageenan-Induced Nociceptive Behaviors of Inflammatory Pain
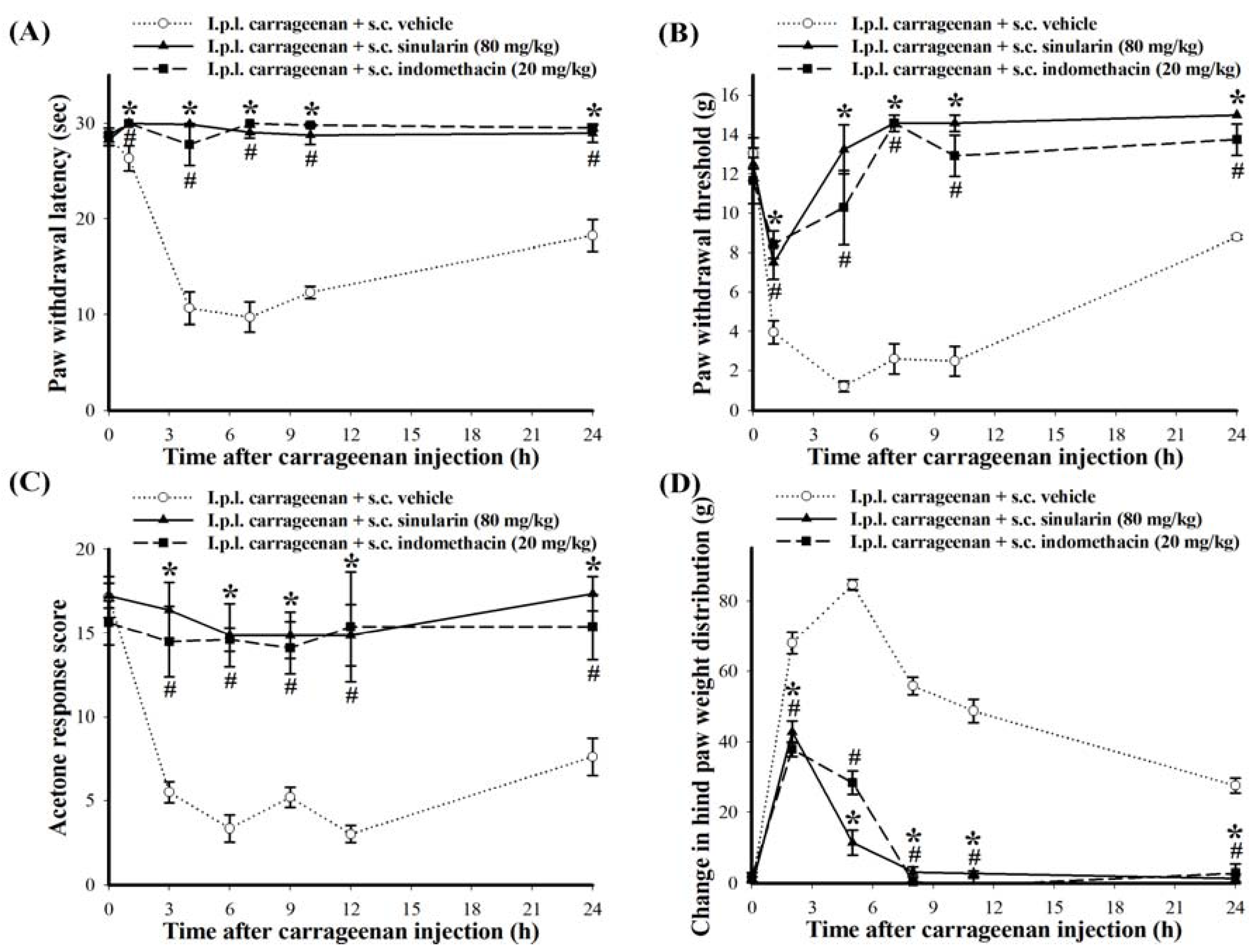
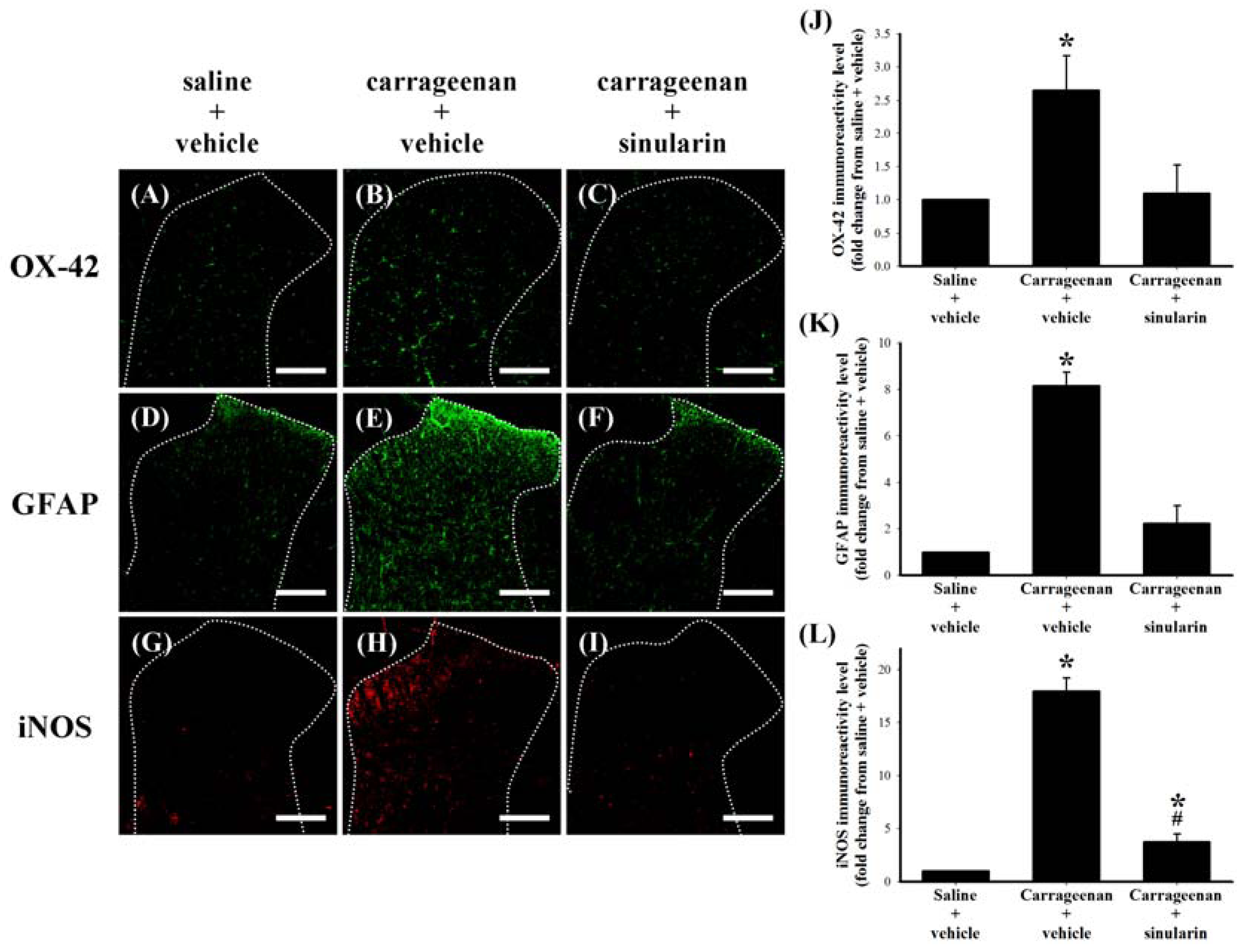
2.4. Effect of Systemic Sinularin Injection on Carrageenan-Induced Spinal Nociceptive Sensitization
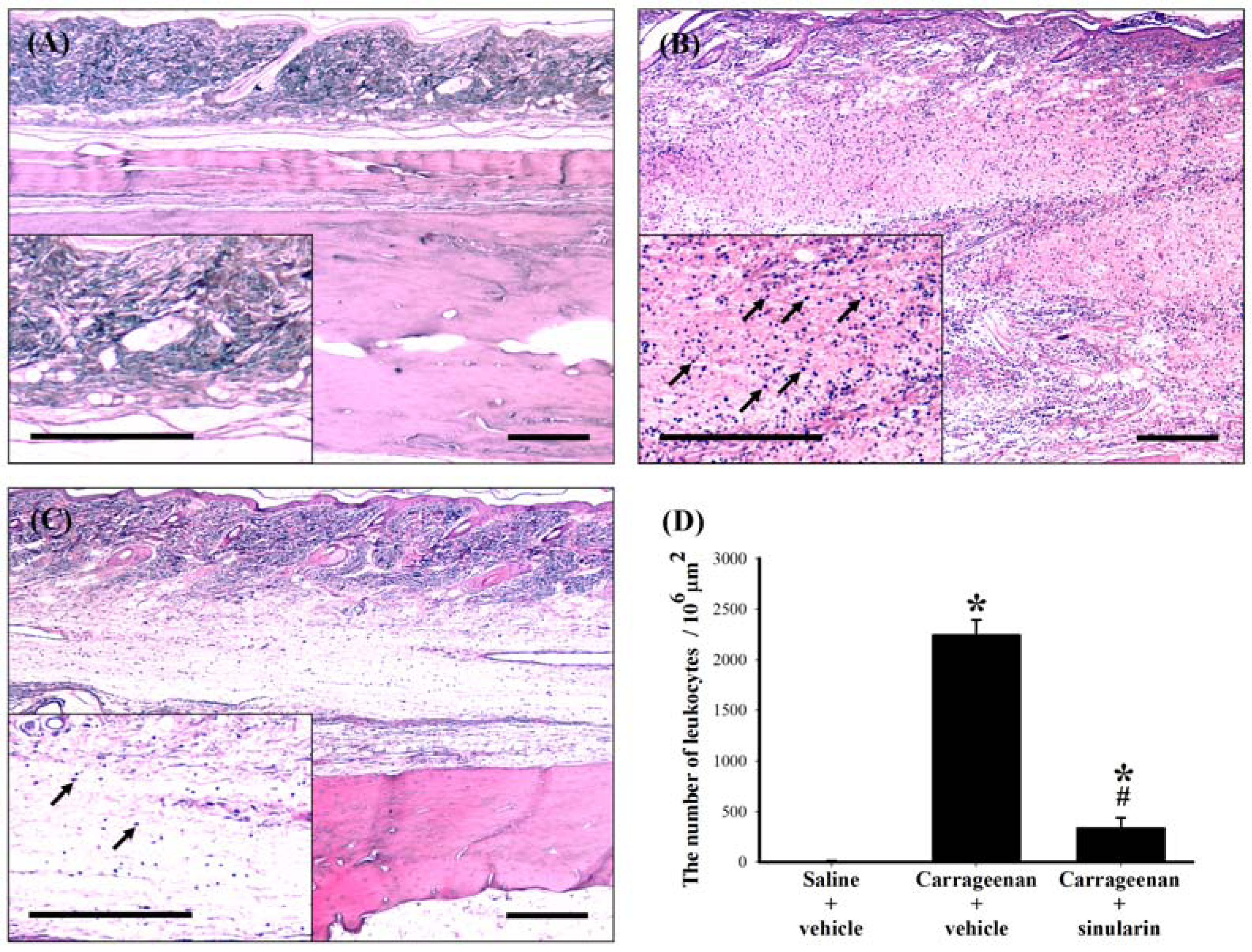
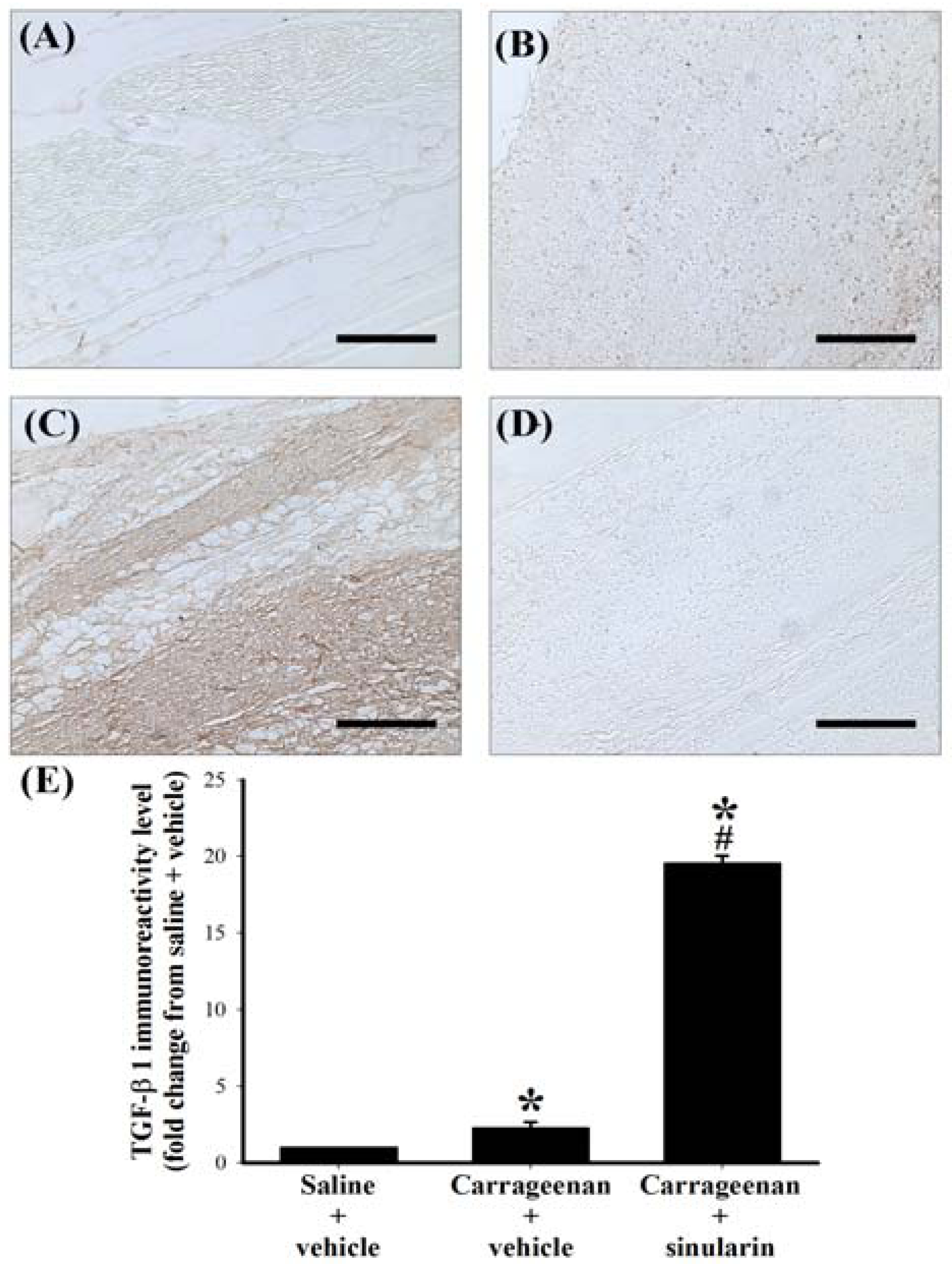
2.5. Effect of Systemic Injection of Sinularin on the Carrageenan-Induced Tissue Inflammatory Responses and TGF-β1 Protein Expression in Paws
3. Discussion
3.1. Summary
3.2. Analgesic Effects of s.c. Sinularin at Behavioral and Spinal Level
3.3. Potential Analgesic Mechanisms of Sinularin
3.4. Advantages and Future Studies of Sinularin
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Assay
4.3. Western Blot Analysis to Determine the Presence of iNOS, COX-2, and TGF-β
4.4. Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema and Behavioral Testing
4.4.1. Paw Edema
4.4.2. Thermal Hyperalgesia
4.4.3. Mechanical Allodynia
4.4.4. Cold Allodynia
4.4.5. Weight-Bearing Deficits
4.5. Spinal Immunohistofluorescence Assay
4.6. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry of Paw Tissues
4.7. Data and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Jean, Y.H.; Chen, W.F.; Duh, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, C.S.; Sung, C.S.; Chen, I.M.; Wen, Z.H. Inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 participate in anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the natural marine compound lemnalol from formosan soft coral Lemnalia cervicorni. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 578, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, Y.H.; Chen, W.F.; Sung, C.S.; Duh, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Tai, M.H.; Tzeng, S.F.; Wen, Z.H. Capnellene, a natural marine compound derived from soft coral, attenuates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 713–725. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Jean, Y.H.; Chen, W.F.; Sung, C.S.; Kao, E.S.; Wang, H.M.; Chakraborty, C.; Duh, C.Y.; Wen, Z.H. Intrathecal lemnalol, a natural marine compound obtained from formosan soft coral, attenuates nociceptive responses and the activity of spinal glial cells in neuropathic rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2011, 22, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.H.; Chao, C.H.; Wu, M.H.; Sheu, J.H. A neuroprotective sulfone of marine origin and the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of an analogue. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5998–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinheimer, A.J.; Matson, J.A.; Hossain, M.B.; van der Helm, D. Marine anticancer agents: Sinularin and dihydrosinularin, new cembranolides from the soft coral, Sinularia flexibilis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 2923–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.T.; Wells, R.J.; Schonholzer, P.; Coll, J.C. Cembranoid constituents from an Australian collection of the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Aust. J. Chem. 1978, 31, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckle, P.J.; Baldo, B.A.; Taylor, K.M. The anti-inflammatory activity of marine natural products—6-n-tridecylsalicylic acid, flexibilide and dendalone 3-hydroxybutyrate. Agents Actions 1980, 10, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Aceret, T.L.; Brown, L.; Miller, J.; Coll, J.C.; Sammarco, P.W. Cardiac and vascular responses of isolated rat tissues treated with diterpenes from Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata: Octocorallia). Toxicon 1996, 34, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Aceret, T.L.; Coll, J.C.; Uchio, Y.; Sammarco, P.W. Antimicrobial activity of the diterpenes flexibilide and sinulariolide derived from Sinularia flexibilis Quoy and Gaimard 1833 (Coelenterata: Alcyonacea, Octocorallia). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1998, 120, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.J.; Su, J.H.; Huang, M.S.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Cladiella krempfi. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H. Bioactive cembrane-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia triangular. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvemini, D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wyatt, P.S.; Bourdon, D.M.; Marino, M.H.; Manning, P.T.; Currie, M.G. Nitric oxide: A key mediator in the early and late phase of carrageenan-induced rat paw inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 118, 829–838. [Google Scholar]
- Seibert, K.; Zhang, Y.; Leahy, K.; Hauser, S.; Masferrer, J.; Perkins, W.; Lee, L.; Isakson, P. Pharmacological and biochemical demonstration of the role of cyclooxygenase 2 in inflammation and pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12013–12017. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi, F.; Mita, Y.; Kamanaka, Y.; Kawao, N.; Matsuya, H.; Taga, C.; Kawabata, A. The potent inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor ONO-1714 inhibits neuronal NOS and exerts antinociception in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 365, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, C.J.; Dougherty, P.M.; Kajander, K.C.; Carlton, S.M. Staining of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in lumbar spinal cord increases following a sciatic nerve constriction injury. Brain Res. 1991, 565, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colburn, R.W.; DeLeo, J.A.; Rickman, A.J.; Yeager, M.P.; Kwon, P.; Hickey, W.F. Dissociation of microglial activation and neuropathic pain behaviors following peripheral nerve injury in the rat. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 79, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colburn, R.W.; Rickman, A.J.; DeLeo, J.A. The effect of site and type of nerve injury on spinal glial activation and neuropathic pain behavior. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 157, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, D.E. Partial peripheral nerve injury leads to activation of astroglia and microglia which parallels the development of allodynic behavior. Glia 1998, 23, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuesse, S.L.; Cruce, W.L.; Lovell, J.A.; McBurney, D.L.; Crisp, T. Microglial proliferation in the spinal cord of aged rats with a sciatic nerve injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 287, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuesse, S.L.; Crisp, T.; McBurney, D.L.; Schechter, J.B.; Lovell, J.A.; Cruce, W.L. Neuropathic pain in aged rats: Behavioral responses and astrocytic activation. Exp. Brain Res. 2001, 137, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweitzer, S.M.; Schubert, P.; DeLeo, J.A. Propentofylline, a glial modulating agent, exhibits antiallodynic properties in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Ledeboer, A.; Sloane, E.M.; Milligan, E.D.; Frank, M.G.; Mahony, J.H.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Minocycline attenuates mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in rat models of pain facilitation. Pain 2005, 115, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraci, F.; Battaglia, G.; Busceti, C.; Biagioni, F.; Mastroiacovo, F.; Bosco, P.; Drago, F.; Nicoletti, F.; Sortino, M.A.; Copani, A. TGF-beta 1 protects against abeta-neurotoxicity via the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 30, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.L.; Smith, P.M.; Lamm, W.J.; Hildebrandt, J. Sampling and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid for chronic studies in awake rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 1983, 54, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi, G.; Adami, M.; Guaita, E.; de Esch, I.J.; Leurs, R. Antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects of the selective histamine H4-receptor antagonists JNJ7777120 and VUF6002 in a rat model of carrageenan-induced acute inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 563, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, I.A.; Khan, R.A.; Gilani, A.U.; Shah, A.J.; Hussain, J.; Ahmad, V.U. The analgesic, anti-inflammatory and calcium antagonist potential of Tanacetum artemisioides. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Fitzsimmons, B.; Steinauer, J.; O’Neill, A.; Newton, A.C.; Hua, X.Y.; Yaksh, T.L. Spinal phosphinositide 3-kinase-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin signaling cascades in inflammation-induced hyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 2113–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Costigan, M.; Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. Neuropathic pain: A maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 32, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.R.; Campana, W.M.; Shubayev, V.I. The role of neuroinflammation in neuropathic pain: Mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, E.D.; Watkins, L.R. Pathological and protective roles of glia in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, F.; Perretti, M.; McMahon, S.B. Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 521–532. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino, G.; La Rana, G.; Russo, R.; Sasso, O.; Iacono, A.; Esposito, E.; Raso, G.M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Lo Verme, J.; Piomelli, D.; et al. Acute intracerebroventricular administration of palmitoylethanolamide, an endogenous peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist, modulates carrageenan-induced paw edema in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Tao, Y.X.; Mao, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, D.; Liaw, W.J.; Raja, S.N.; Johns, R.A. Intact carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Neuroscience 2003, 120, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittner, H.L.; Machelska, H.; Stein, C. Leukocytes in the regulation of pain and analgesia. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 78, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughton-Smith, N.K.; Deakin, A.M.; Follenfant, R.L.; Whittle, B.J.; Garland, L.G. Role of oxygen radicals and arachidonic acid metabolites in the reverse passive arthus reaction and carrageenin paw oedema in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 110, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, T.M.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Schivo, I.R.; Napimoga, M.H.; Parada, C.A.; Poole, S.; Teixeira, M.M.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q. Crucial role of neutrophils in the development of mechanical inflammatory hypernociception. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Takeshita, A.; Hanazawa, S. TGF-beta inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated activity of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in mouse macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1999, 456, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.W.; Kwon, M.Y.; Kang, Y.H.; Chung, H.T.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.P.; Perrella, M.A. Transforming growth factor-beta1 suppression of endotoxin-induced heme oxygenase-1 in macrophages involves activation of Smad2 and downregulation of Ets-2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, F.; Jain, M.K.; Feinberg, M.W.; Sibinga, N.E.; Pellacani, A.; Wiesel, P.; Chin, M.T.; Topper, J.N.; Perrella, M.A.; Lee, M.E. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 inhibition of macrophage activation is mediated via Smad3. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36653–36658. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.Y.; El-Gengaihi, S.E.; Motawea, H.M.; Sleem, A.M. Anti-inflammatory activity of Salvadora persica L. against carrageenan induced paw oedema in rat relevant to inflammatory cytokines. Not. Sci. Biol. 2011, 3, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ronaldson, P.T.; Finch, J.D.; Demarco, K.M.; Quigley, C.E.; Davis, T.P. Inflammatory pain signals an increase in functional expression of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1a4 at the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaldson, P.T.; Demarco, K.M.; Sanchez-Covarrubias, L.; Solinsky, C.M.; Davis, T.P. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling alters substrate permeability and tight junction protein expression at the blood-brain barrier during inflammatory pain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, A.P.; Shah, R.; Hochwald, G.M.; Liggitt, H.D.; Palladino, M.A.; Thorbecke, G.J. Protective effect of transforming growth factor beta 1 on experimental autoimmune diseases in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2918–2921. [Google Scholar]
- Maida, M.; Carroll, A.R.; Coll, J.C. Variability of terpene content in the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata: Octocorallia), and its ecological implications. J. Chem. Ecol. 1993, 19, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Lu, Y.; Yeh, H.C.; Wang, W.H.; Fan, T.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Oxygenated cembranoids from the cultured and wild-type soft corals Sinularia flexibilis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, C.A.; Risley, E.A.; Nuss, G.W. Carrageenin-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for antiiflammatory drugs. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1962, 111, 544–547. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, M.; Tozer, T.N. Assessment of Auc. In Clinical Pharmacokinetics: Concepts and Applications, 3rd; Balado, D., Ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 469–470. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, K.; Dubner, R.; Brown, F.; Flores, C.; Joris, J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 1988, 32, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, L.; Malfetes, N.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Depoortere, R. Chronic restraint stress induces mechanical and cold allodynia, and enhances inflammatory pain in rat: Relevance to human stress-associated painful pathologies. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatters, S.J.; Bennett, G.J. Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel- and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2004, 109, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.H.; Tang, C.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Hsieh, S.P.; Lee, C.H.; Huang, G.S.; Ng, H.F.; Neoh, C.A.; Hsieh, C.S.; et al. Glucosamine sulfate reduces experimental osteoarthritis and nociception in rats: Association with changes of mitogen-activated protein kinase in chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Imaizumi, R.; Sumichika, H.; Tanaka, H.; Goda, M.; Fukunari, A.; Komatsu, H. Sodium iodoacetate-induced experimental osteoarthritis and associated pain model in rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.-Y.; Chen, N.-F.; Chen, W.-F.; Hung, H.-C.; Lee, H.-P.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Wang, H.-M.; Sung, P.-J.; Sheu, J.-H.; Wen, Z.-H. Sinularin from Indigenous Soft Coral Attenuates Nociceptive Responses and Spinal Neuroinflammation in Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Rat Model. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1899-1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10091899
Huang S-Y, Chen N-F, Chen W-F, Hung H-C, Lee H-P, Lin Y-Y, Wang H-M, Sung P-J, Sheu J-H, Wen Z-H. Sinularin from Indigenous Soft Coral Attenuates Nociceptive Responses and Spinal Neuroinflammation in Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Rat Model. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(9):1899-1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10091899
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shi-Ying, Nan-Fu Chen, Wu-Fu Chen, Han-Chun Hung, Hsin-Pai Lee, Yen-You Lin, Hui-Min Wang, Ping-Jyun Sung, Jyh-Horng Sheu, and Zhi-Hong Wen. 2012. "Sinularin from Indigenous Soft Coral Attenuates Nociceptive Responses and Spinal Neuroinflammation in Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Rat Model" Marine Drugs 10, no. 9: 1899-1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10091899
APA StyleHuang, S.-Y., Chen, N.-F., Chen, W.-F., Hung, H.-C., Lee, H.-P., Lin, Y.-Y., Wang, H.-M., Sung, P.-J., Sheu, J.-H., & Wen, Z.-H. (2012). Sinularin from Indigenous Soft Coral Attenuates Nociceptive Responses and Spinal Neuroinflammation in Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Rat Model. Marine Drugs, 10(9), 1899-1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10091899






