Functional Expression in Escherichia coli of the Disulfide-Rich Sea Anemone Peptide APETx2, a Potent Blocker of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Production of Recombinant APETx2 and Its F15A Mutant
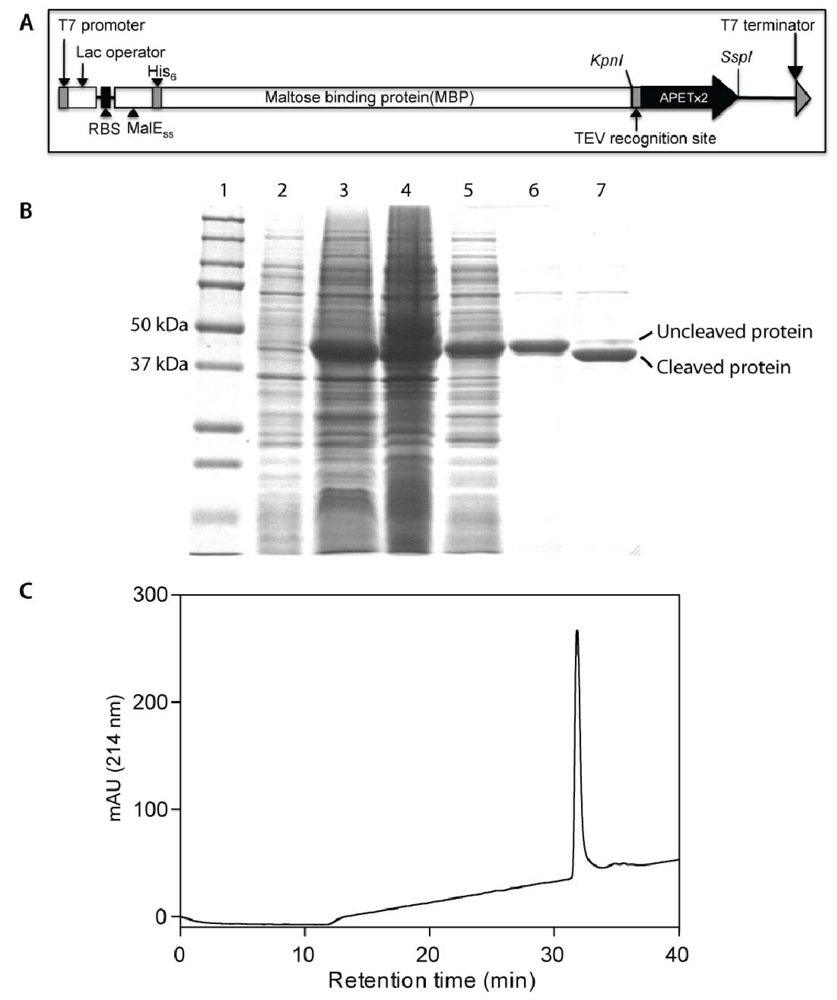
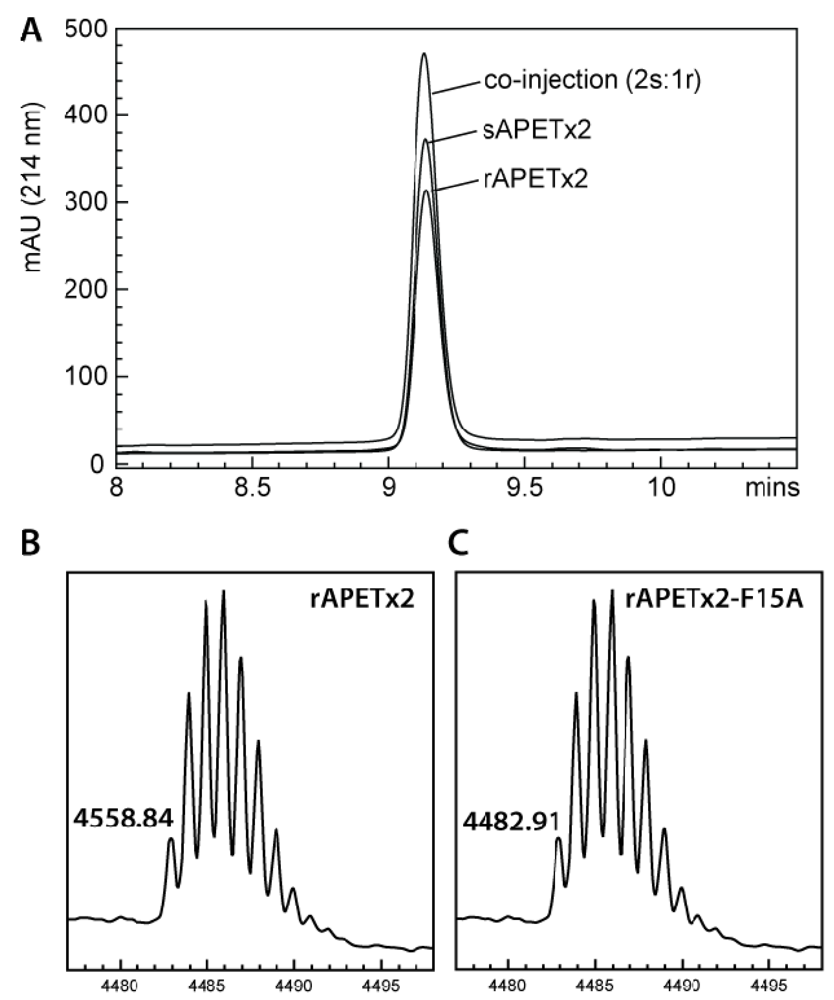
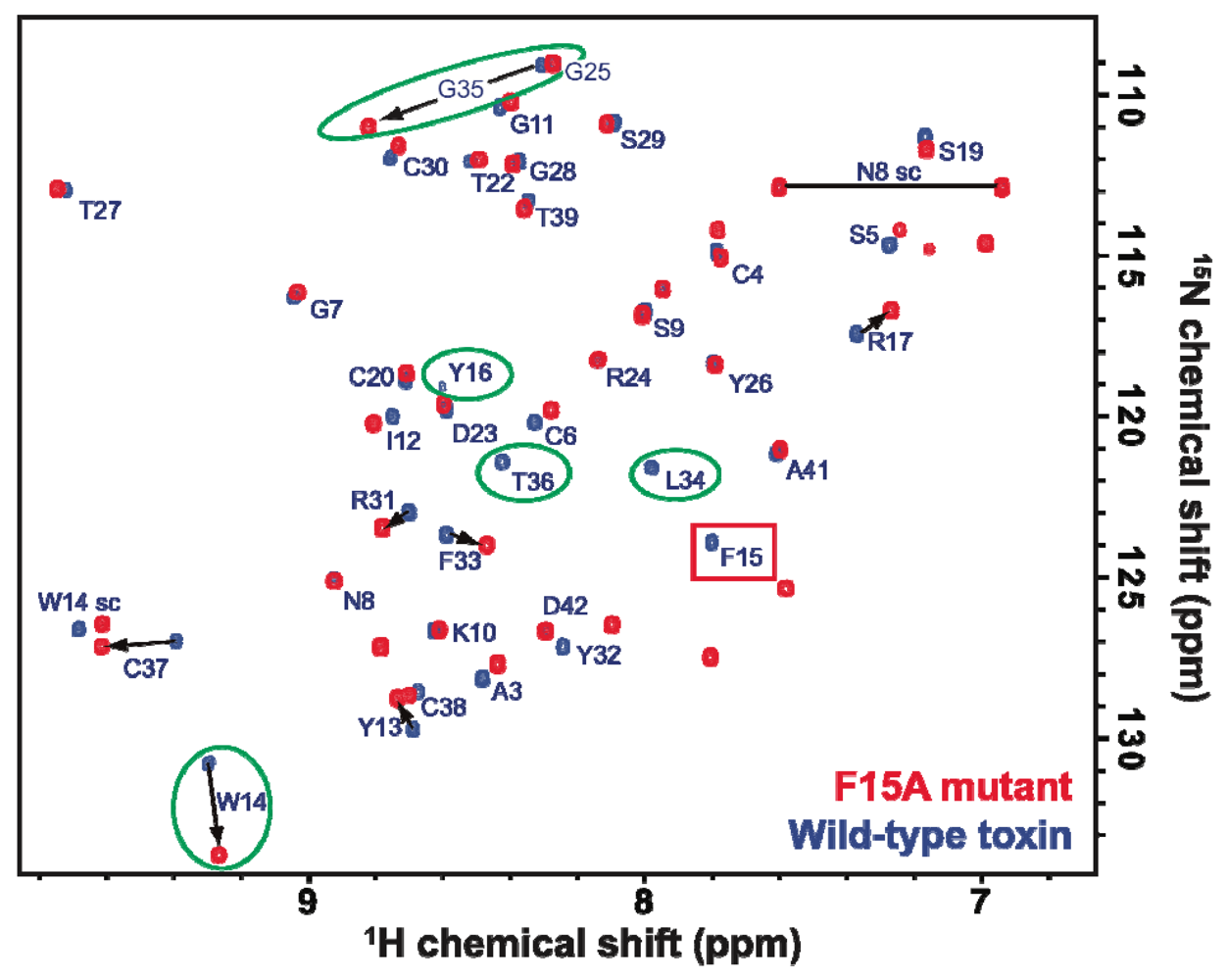
2.2. Activity of Recombinant APETx2 and Its F15A Mutant
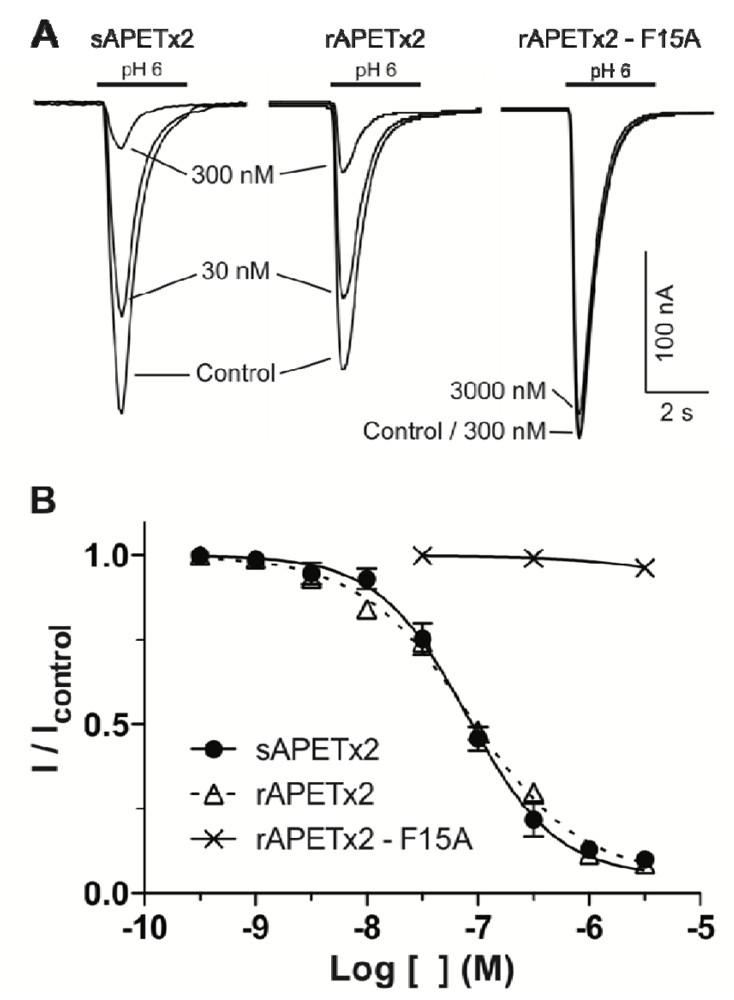
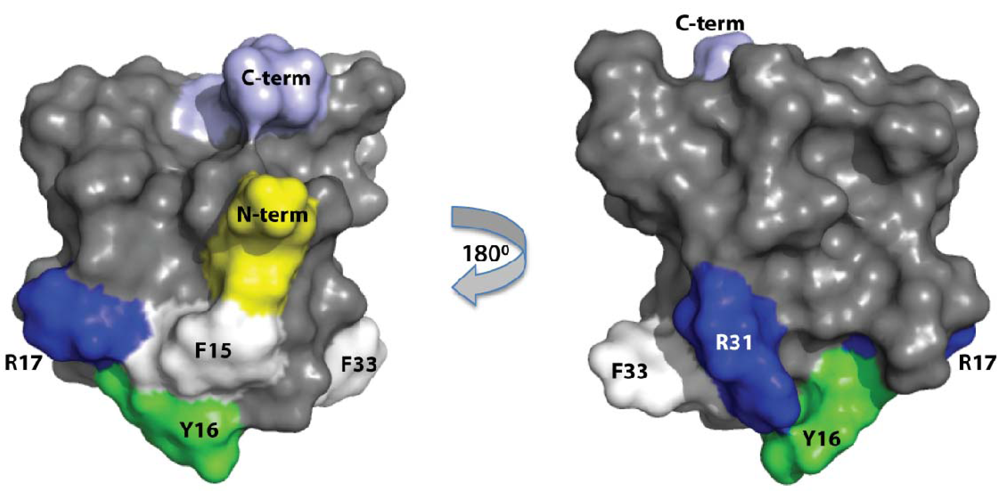
2.3. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Production and Purification of Recombinant APETx2
3.2. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
3.3. NMR Spectroscopy
3.4. Electrophysiological Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Sluka, K.A.; Winter, O.C.; Wemmie, J.A. Acid-sensing ion channels: A new target for pain and CNS diseases. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2009, 12, 693–704. [Google Scholar]
- Wemmie, J.A.; Price, M.P.; Welsh, M.J. Acid-sensing ion channels: Advances, questions and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.G.; Pignataro, G.; Li, M.; Chang, S.Y.; Simon, R.P. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) as pharmacological targets for neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingueglia, E. Acid-sensing ion channels in sensory perception. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17325–17329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Chen, J.; Harding, A.M.; Price, M.P.; Lu, Y.; Abboud, F.M.; Benson, C.J. ASIC2a and ASIC3 heteromultimerize to form pH-sensitive channels in mouse cardiac dorsal root ganglia neurons. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.P.; McIlwrath, S.L.; Xie, J.; Cheng, C.; Qiao, J.; Tarr, D.E.; Sluka, K.A.; Brennan, T.J.; Lewin, G.R.; Welsh, M.J. The DRASIC cation channel contributes to the detection of cutaneous touch and acid stimuli in mice. Neuron 2001, 32, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, S.P.; Benson, C.J.; Adelman, J.P.; McCleskey, E.W. Acid-sensing ion channel 3 matches the acid-gated current in cardiac ischemia-sensing neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 711–716. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, C.J.; Eckert, S.P.; McCleskey, E.W. Acid-evoked currents in cardiac sensory neurons: A possible mediator of myocardial ischemic sensation. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Zimmer, A.; Sun, W.H.; Hall, J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Zimmer, A. A role for ASIC3 in the modulation of high-intensity pain stimuli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8992–8997. [Google Scholar]
- Sluka, K.A.; Price, M.P.; Breese, N.M.; Stucky, C.L.; Wemmie, J.A.; Welsh, M.J. Chronic hyperalgesia induced by repeated acid injections in muscle is abolished by the loss of ASIC3, but not ASIC1. Pain 2003, 106, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanstyne, T.O.; Markowitz, K.; Fan, L.; Gold, M.S. Mechanotransducers in rat pulpal afferents. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagae, M.; Hiraga, T.; Wakabayashi, H.; Wang, L.; Iwata, K.; Yoneda, T. Osteoclasts play a part in pain due to the inflammation adjacent to bone. Bone 2006, 39, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voilley, N.; de Weille, J.; Mamet, J.; Lazdunski, M. Nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit both the activity and the inflammation-induced expression of acid-sensing ion channels in nociceptors. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 8026–8033. [Google Scholar]
- Yiangou, Y.; Facer, P.; Smith, J.A.; Sangameswaran, L.; Eglen, R.; Birch, R.; Knowles, C.; Williams, N.; Anand, P. Increased acid-sensing ion channel ASIC-3 in inflamed human intestine. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 13, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.L.; Cheng, C.F.; Sun, W.H.; Wong, C.W.; Chen, C.C. Targeting ASIC3 for pain, anxiety, and insulin resistance. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A.; Goldin, A.L.; Waxman, S.G. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.G.; Cao, H.; Feng, E.G.; Yu, F.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; Xu, T.L. A nonprotonligand sensor in the acid-sensing ion channel. Neuron 2010, 68, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deval, E.; Gasull, X.; Noël, J.; Salinas, M.; Baron, A.; Diochot, S.; Lingueglia, E. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs): Pharmacology and implication in pain. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 128, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Rash, L.D.; Deval, E.; Escoubas, P.; Scarzello, S.; Salinas, M.; Lazdunski, M. A new sea anemone peptide, APETx2, inhibits ASIC3, a major acid-sensitive channel in sensory neurons. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.S.; Fuentes-Silva, D.; King, G.F. Development of a rational nomenclature for naming peptide and protein toxins from sea anemones. Toxicon 2012, 60, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deval, E.; Noël, J.; Lay, N.; Alloui, A.; Diochot, S.; Friend, V.; Jodar, M.; Lazdunski, M.; Lingueglia, E. ASIC3, a sensor of acidic and primary inflammatory pain. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deval, E.; Noël, J.; Gasull, X.; Delaunay, A.; Alloui, A.; Friend, V.; Eschalier, A.; Lazdunski, M.; Lingueglia, E. Acid-sensing ion channels in postoperative pain. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6059–6066. [Google Scholar]
- Theralpha, Product THA902. Available online: http://www.theralpha.com/index.php?page=tha902 (accessed on 4 May 2012).
- Blanchard, M.G.; Rash, L.D.; Kellenberger, S. Inhibition of voltage-gated Na+ currents in sensory neurones by the sea anemone toxin APETx2. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, I.; Davis, J.L.; Rash, L.D.; Anangi, R.; Mobli, M.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J.; King, G.F. Venomics: A new paradigm for natural products-based drug discovery. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.E.; Durek, T.; Alewood, P.F.; Adams, D.J.; King, G.F.; Rash, L.D. Chemical synthesis and folding of APETx2, a potent and selective inhibitor of acid sensing ion channel 3. Toxicon 2009, 54, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedford, H.W.; Fletcher, J.I.; King, G.F. Functional significance of the β hairpin in the insecticidal neurotoxin ω-atracotoxin-Hv1a. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26568–26576. [Google Scholar]
- Saez, N.J.; Mobli, M.; Bieri, M.; Chassagnon, I.R.; Malde, A.K.; Gamsjaeger, R.; Mark, A.E.; Gooley, P.R.; Rash, L.D.; King, G.F. A dynamic pharmacophore drives the interaction between psalmotoxin-1 and the putative drug target acid-sensing ion channel 1a. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.; Cai, T.F.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.B.; Peng, K.; Liang, S.; Zhang, D.Y. Functional expression of spider neurotoxic peptide huwentoxin-I in E.coli. PLoS One 2011, 6, e21608. [Google Scholar]
- Anangi, R.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, Y.W.; Cheng, Y.R.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chu, Y.P.; Chuang, W.J. Expression in Pichia pastoris and characterization of APETx2, a specific inhibitor of acid sensing ion channel 3. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagot, B.; Escoubas, P.; Diochot, S.; Bernard, C.; Lazdunski, M.; Darbon, H. Solution structure of APETx2, a specific peptide inhibitor of ASIC3 proton-gated channels. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.L.; Chen, F.H.; Lu, W.G.; Li, X. Acid-sensing ion channels 3: A potential therapeutic target for pain treatment in arthritis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 3233–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, M.; Kolker, S.J.; Burnes, L.A.; Walder, R.Y.; Sluka, K.A. Role of ASIC3 in the primary and secondary hyperalgesia produced by joint inflammation in mice. Pain 2008, 137, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walder, R.Y.; Gautam, M.; Wilson, S.P.; Benson, C.J.; Sluka, K.A. Selective targeting of ASIC3 using artificial miRNAs inhibits primary and secondary hyperalgesia after muscle inflammation. Pain 2011, 152, 2348–2356. [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski, J.; Spencer, R.H.; Garsky, V.M.; Liang, A.; Leitl, M.D.; Cato, M.J.; Cook, S.P.; Kane, S.; Urban, M.O. Reversal of acid-induced and inflammatory pain by the selective ASIC3 inhibitor, APETx2. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, A.H.; Mobli, M.; Gooley, P.R.; King, G.F.; Mackay, J.P. Macromolecular NMR spectroscopy for the non-spectroscopist. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoubas, P.; Bernard, C.; Lambeau, G.; Lazdunski, M.; Darbon, H. Recombinant production and solution structure of PcTx1, the specific peptide inhibitor of ASIC1a proton-gated cation channels. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, W.A.; Åslund, F.; Holmgren, A.; Beckwith, J. The role of the thioredoxin and glutaredoxin pathways in reducing protein disulfide bonds in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 15661–15667. [Google Scholar]
- Maggio, F.; King, G.F. Scanning mutagenesis of a Janus-faced atracotoxin reveals a bipartite surface patch that is essential for neurotoxic function. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22806–22813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, L.D.; Dai, W.; Bottomley, S.P. A family of E. coli expression vectors for laboratory scale and high throughput soluble protein production. BMC Biotechnol. 2006, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.F. Venoms as a platform for human drugs: translating toxins into therapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Anangi, R.; Rash, L.D.; Mobli, M.; King, G.F. Functional Expression in Escherichia coli of the Disulfide-Rich Sea Anemone Peptide APETx2, a Potent Blocker of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1605-1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071605
Anangi R, Rash LD, Mobli M, King GF. Functional Expression in Escherichia coli of the Disulfide-Rich Sea Anemone Peptide APETx2, a Potent Blocker of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(7):1605-1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071605
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnangi, Raveendra, Lachlan D. Rash, Mehdi Mobli, and Glenn F. King. 2012. "Functional Expression in Escherichia coli of the Disulfide-Rich Sea Anemone Peptide APETx2, a Potent Blocker of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3" Marine Drugs 10, no. 7: 1605-1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071605
APA StyleAnangi, R., Rash, L. D., Mobli, M., & King, G. F. (2012). Functional Expression in Escherichia coli of the Disulfide-Rich Sea Anemone Peptide APETx2, a Potent Blocker of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3. Marine Drugs, 10(7), 1605-1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071605





