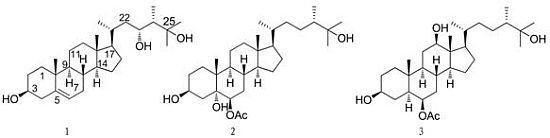
Polyoxygenated Sterols from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
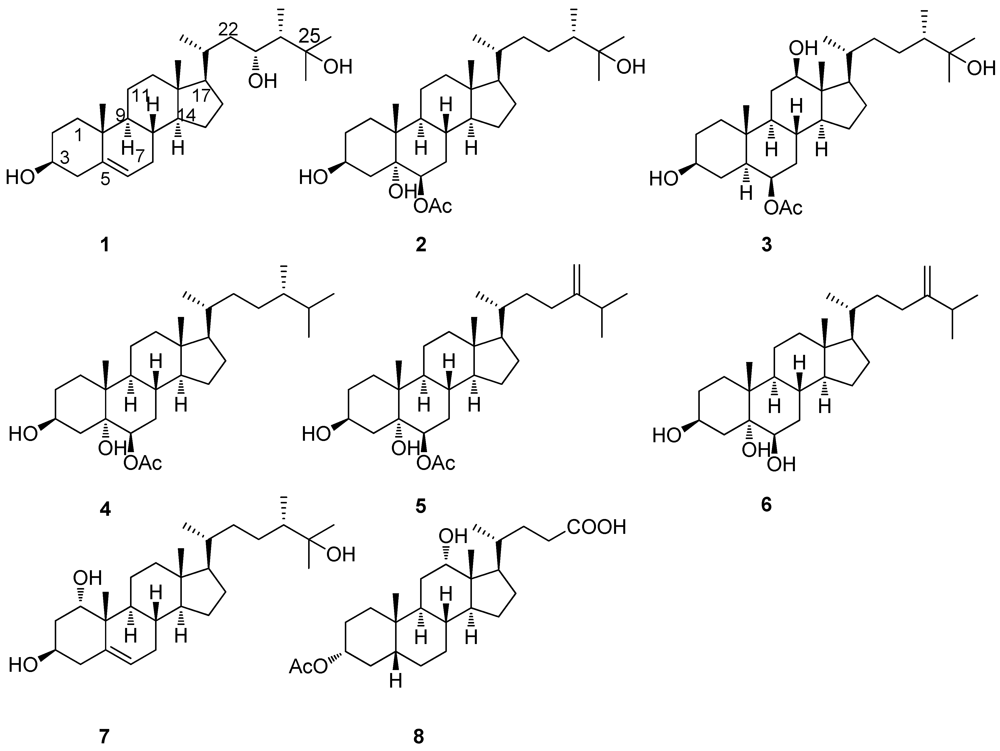
2. Results and Discussion
| H# | 1, δH (J in Hz) a | 2, δH (J in Hz) b | 3, δH (J in Hz) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.82 (1H, d, J = 4.8 Hz, H-ax) | 1.75 (1H, br d, J = 12.0 Hz, H-ax) | 1.82 (1H, br d, J = 4.8 Hz, H-ax) |
| 1.12 (1H, m, H-eq) | 1.18 (1H, m, H-eq) | 1.27 (1H, m, H-eq) | |
| 2 | 2.30 (1H, ddd, J = 13.2, 4.8, 1.8 Hz, H-ax) | 2.01 (1H, dt, J = 12.0, 2.4 Hz, H-ax) | 1.99 (1H, 1H, dt, J = 12.6, 2.4 Hz, H-ax) |
| 1.49 (1H, m, H-eq) | 1.51 (1H, m, H-eq) | 1.49 (1H, m, H-eq) | |
| 3 | 3.56 (1H, m) | 3.99 (1H, m) | 4.09 (1H, m) |
| 4 | 2.22 (1H, td, J = 12.6, 2.4 Hz, H-ax) | 1.77 (1H, br d, J = 12.0 Hz, H-ax ) | 1.84 (1H, br d, J = 12.0 Hz, H-ax) |
| 1.48 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-eq) | 1.53 (1H, m, H-eq) | 1.54 (1H, m, H-eq) | |
| 5 | – | – | 1.61 (1H, m) d |
| 6 | 5.34 (1H, br d, J = 4.8 Hz) | 4.68 (1H, t, J = 2.4 Hz) | 4.70 (1H, m) |
| 7 | 2.02 (1H, dt, J = 12.6, 4.8 Hz, H-ax) | 1.68 (1H, dd, J =13.8, 2.4 Hz, H-ax) | 1.64 (1H, m) |
| 1.96 (1H, m, H-eq) | 1.47 (1H, d, J = 2.4, H-eq) | 1.61 (1H, m) d | |
| 8 | 1.52 (1H, m) | 1.52 (1H, m) | 1.29 (1H, m) |
| 9 | 1.16 (1H, m) | 1.63 (1H, m) | 1.68 (1H, m) |
| 10 | – | – | – |
| 11 | 1.43 (1H, m) | 1.34 (1H, m) | 1.73 (1H, dd, J = 14.4, 7.2 Hz H-ax) |
| 1.32 (1H, m) | 1.32 (1H, m) | 0.77 (1H, m, H-eq) | |
| 12 | 1.28 (1H, m) | 1.58 (1H, m) | 4.31 (1H, td, J = 7.2, 0.6 Hz) |
| 0.97 (1H, m) | 1.42 (1H, m) | ||
| 13 | – | – | – |
| 14 | 1.33 (1H, m) | 1.25 (1H, m) | 1.30 (1H, m) |
| 15 | 1.44 (1H, m) | 1.55 (1H, m) | 1.51 (1H, m) |
| 0.94 (1H, m) | 1.03 (1H, m) | 1.02 (1H, m) | |
| 16 | 1.88 (1H, m) | 1.89 (1H, m) | 1.86 (1H, m) |
| 1.45 (1H, m) | 1.50 (1H, m) | 1.40 (1H, m) | |
| 17 | 1.15 (1H, m) | 1.05 (1H, m) | 1.10 (1H, m) |
| 18 | 0.70 (3H, s) | 0.78 (3H, s) | 0.68 (3H, s) |
| 19 | 1.00 (3H, s) | 1.14 (3H, s) | 1.16 (3H, s) |
| 20 | 1.50 (1H, m) | 1.36 (1H, m) | 1.39 (1H, m) |
| 21 | 1.08 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz) | 0.94 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz) | 0.93 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz) |
| 22 | 1.84 (1H, m) | 1.62 (1H, m) | 1.62 (1H, m) |
| 1.10 (1H, m) | 1.01 (1H, m) | 1.08 (1H, m) | |
| 23 | 3.71 (1H, ddd, J = 12.0, 8.4, 3.0 Hz) | 1.68 (1H, m) | 1.86 (1H, m) |
| 0.77 (1H, m) | 0.78 (1H, m) | ||
| 24 | 1.56 (1H, m) | 1.27 (1H, m) | 1.28 (1H, m) |
| 25 | – | – | – |
| 26 | 1.23 (3H, s) c | 1.09 (3H, s) | 1.15 (3H, s) e |
| 27 | 1.23 (3H, s) c | 1.10 (3H, s) | 1.15 (3H, s) e |
| 28 | 0.81 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz) | 0.87 (3H, d, J = 7.2 Hz) | 0.89 (3H, d, J = 7.2 Hz) |
| OAc | – | 2.02 (3H, s, CH3CO–) | 2.06 (3H, s, CH3CO–) |
| C# | 1, a δC, type | 2, b δC, type | 3, a δC, type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37.2, CH2 | 33.2, CH2 | 34.9, CH2 |
| 2 | 24.3, CH2 | 22.2, CH2 | 21.1, CH2 |
| 3 | 71.8, CH | 67.9, CH | 67.3, CH |
| 4 | 42.3, CH2 | 31.6, CH2 | 28.2, CH2 |
| 5 | 140.8, C | 75.5, C | 30.7, CH |
| 6 | 121.6, CH | 77.8, CH | 76.1, CH |
| 7 | 31.7, CH2 | 32.5, CH2 | 31.4, CH2 |
| 8 | 31.9, CH | 32.2, CH | 31.9, CH |
| 9 | 50.1, CH | 46.2, CH | 45.2, CH |
| 10 | 36.5, C | 39.6, C | 38.5, C |
| 11 | 21.1, CH2 | 29.1, CH2 | 40.5, CH2 |
| 12 | 39.7, CH2 | 41.0, CH2 | 73.7, CH |
| 13 | 42.5, C | 43.9, C | 42.7, C |
| 14 | 56.6, CH | 57.3, CH | 55.8, CH |
| 15 | 21.0, CH2 | 25.2, CH2 | 24.1, CH2 |
| 16 | 28.5, CH2 | 29.3, CH2 | 29.7, CH2 |
| 17 | 57.3, CH | 57.4, CH | 55.9, CH |
| 18 | 11.8, CH3 | 12.6, CH3 | 12.2, CH3 |
| 19 | 19.4, CH3 | 17.1, CH3 | 16.5, CH3 |
| 20 | 35.0, CH | 37.8, CH | 36.3, CH |
| 21 | 23.2, CH3 | 15.3, CH3 | 19.0, CH3 |
| 22 | 44.2, CH2 | 36.3, CH2 | 39.9, CH2 |
| 23 | 75.8, CH | 29.1, CH2 | 30.6, CH2 |
| 24 | 48.9, CH | 46.4, CH | 45.4, CH |
| 25 | 75.2, C | 74.2, C | 75.3, C |
| 26 | 30.7, CH3 | 26.0, CH3 | 26.2, CH3 |
| 27 | 30.7, CH3 | 27.2, CH3 | 27.2, CH3 |
| 28 | 14.1, CH3 | 19.6, CH3 | 14.8, CH3 |
| CH3CO | – | 21.4, CH3 | 21.4, CH3 |
| CH3CO | – | 172.1, C | 164.5, C |
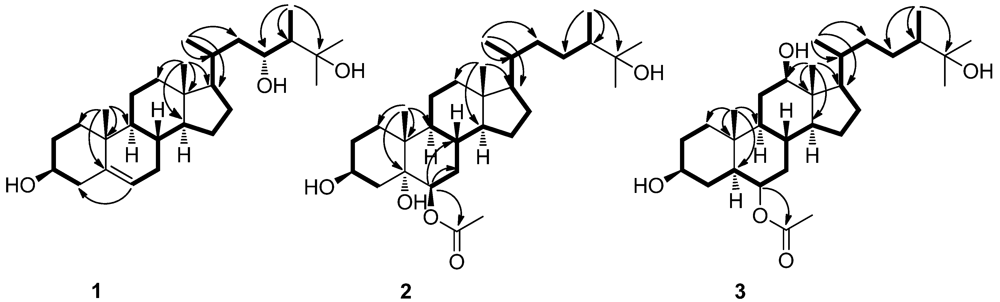
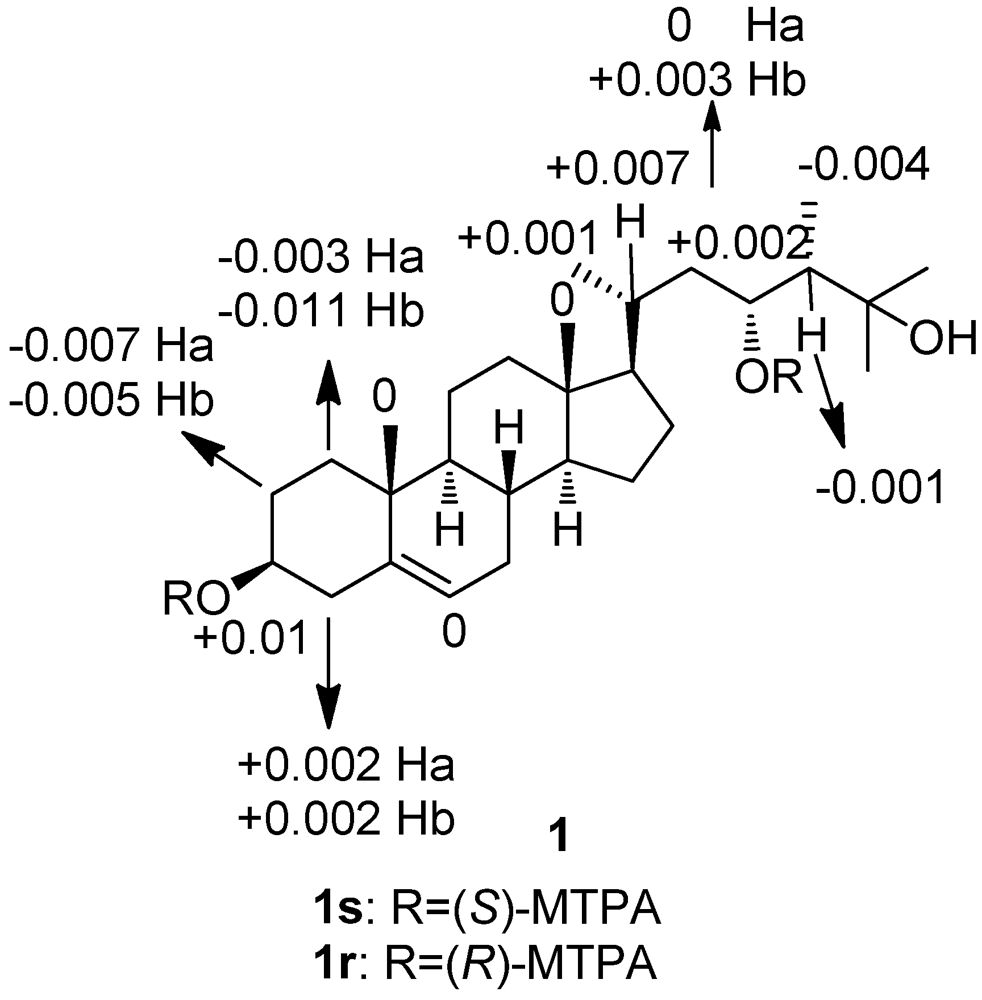
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Preparation of the (S)-and (R)-MTPA Esters of 1
3.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 26–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, S.P.; Lu, C.K.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Sinularianins A and B, novel sesquiterpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 5889–5891. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.H.; Schmitz, F.J. Cytotoxic acylated spermidine from a soft coral, Sinularia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojika, M.; Islam, M.K.; Shintani, T.; Zhang, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Sakagami, Y. Three new cytotoxic acylspermidines from the soft coral, Sinularia sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbs, A.B.; Yakovleva, I.M.; Pham, L.Q. Distribution of lipids and fatty acids in the zooxanthellae and host of the soft coral Sinularia sp. Fish. Sci. 2010, 76, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, S.P.; Lu, C.K.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Novel cyclic sesquiterpene peroxides from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 2175–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Sheu, J.H.; Chang, K.C.; Duh, C.Y. A cytotoxic 5α,8α-epidioxysterol from a soft coral Sinularia species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Guo, Y.W.; Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Cimino, G. Two new polyhydroxylated steroids from the Hainan soft coral Sinularia sp. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Takaki, H.; Koganemaru, R.; Iwakawa, Y.; Higuchi, R.; Miyamoto, T. Inhibitory effect of norditerpenes on LPS-induced TNF-α production from the Okinawan soft coral, Sinularia sp. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, N.; Umeyama, A.; Arihara, S. A novel norditerpenoid from the Okinawan soft coral Sinularia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Chen, A.N.; Shao, C.L.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Qian, P.Y. Chemical constituents of soft coral Sarcophyton infundibuliforme from the South China Sea. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2011, 39, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Huang, H.; Shao, C.L.; Liu, Q.A.; Qi, J.; Sun, X.P.; Zhai, P.; Gu, Y.C. A new pregnane analogue from Hainan soft coral Scleronephthya gracillimum Kuekenthal. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sheng, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.B.; Huang, H.; Li, X.B.; Li, J.; Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Guo, Y.W. Diterpenes from the Hainan soft coral Lobophytum cristatum Tixier-Durivault. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L.; Li, L.; Li, X.B.; Chen, M.; Qian, P.Y. Chemical constituents of the soft coral Sarcophyton infundibuliforme from the South China Sea. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L.; Guo, Y.W.; Li, G.Q.; Sun, X.P.; Han, L.; Huang, H.; Guan, H.S. Sarcoglycosides A-C, new O-glycosylglycerol derivatives from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton infundibuliforme. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L.; Han, L.; Sun, X.P.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.W.; Huang, H.; Guan, H.S. Two new metabolites from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 11, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, M.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Tursch, B. Chemical studies of marine invertebrates. XVIII. Four novel polyhydroxylated steroids from Sinularia dissecta (Coelenterata, Octocorallia, Alcyonacea). Bull. Soc. Chim. Belges 1976, 85, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.J.; Su, J.Y.; Zeng, L.M. Studies on the secondary metabolites of the soft coral, Sinularia sp. collected from the South China Sea. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2003, 42, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yeffet, D.; Rudi, A.; Ketzinel, S.; Benayahu, Y.; Kashman, Y. Auroside, a xylosyl-sterol, and patusterol A and B, two hydroxylated sterols, from two soft corals Eleutherobia aurea and Lobophytum patulum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumi, T.; Fujita, Y.; Ohtani, I.; Kakisawa, H. Anomaly in the modified Mosher’s method: Absolute configurations of some marine cembranolides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 2923–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M.; Hayashi, T.; Hayashi, K.; Tanabe, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Mitsuhashi, H. Marine sterols. XI. Polyhydroxysterols of the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum: Isolation and synthesis of 5-cholestane-1α,3β,5,6β-tetrol. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Ayyad, S.N.; Shaher, F.; Alarif, W.M. Antibacterial sphingolipid and steroids from the black coral Antipathes dichotoma. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Alcfizar, V.; Prados, P.; Mendoza, J.D. Synthetic receptors for uronic acid salts based on bicyclic guanidinium and deoxycholic acid subunits. Tetrahedron 1999, 53, 13119–13128. [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita, Y.; Amemiya, K.; Ohnuma, H.; Furumura, K.; Masaki, A.; Matsuki, T.; Kikuchi, M. Sterol constituents from five edible mushrooms. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, T.; Yaoita, Y.; Kikuchi, M. Sterol constituents from the fruit bodies of Grifola frondosa (Fr.) S. F. Gray. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; McMahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, P.N.; Wright, C.W.; Anderson, M.M.; Gupta, M.P.; Phillipson, J.D. A microwell cytotoxicity assay using Artemia salina (brine shrimp). Planta Med. 1993, 59, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.N.; Ferrigni, N.R.; Putnam, J.E.; Jacobson, L.B.; Nicols, D.E.; Mclaughlin, J.L. Brine shrimp: A convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Planta Med. 1982, 45, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
Supplementary Files
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Shao, C.-L.; Qi, X.; Li, X.-B.; Li, J.; Sun, L.-L.; Wang, C.-Y. Polyoxygenated Sterols from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1422-1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071422
Li R, Shao C-L, Qi X, Li X-B, Li J, Sun L-L, Wang C-Y. Polyoxygenated Sterols from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia sp. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(7):1422-1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071422
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rui, Chang-Lun Shao, Xin Qi, Xiu-Bao Li, Jing Li, Ling-Ling Sun, and Chang-Yun Wang. 2012. "Polyoxygenated Sterols from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia sp." Marine Drugs 10, no. 7: 1422-1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071422
APA StyleLi, R., Shao, C.-L., Qi, X., Li, X.-B., Li, J., Sun, L.-L., & Wang, C.-Y. (2012). Polyoxygenated Sterols from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia sp. Marine Drugs, 10(7), 1422-1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071422