Cytotoxic Sesterterpenoids from a Sponge Hippospongia sp.
Abstract
1. Introduction

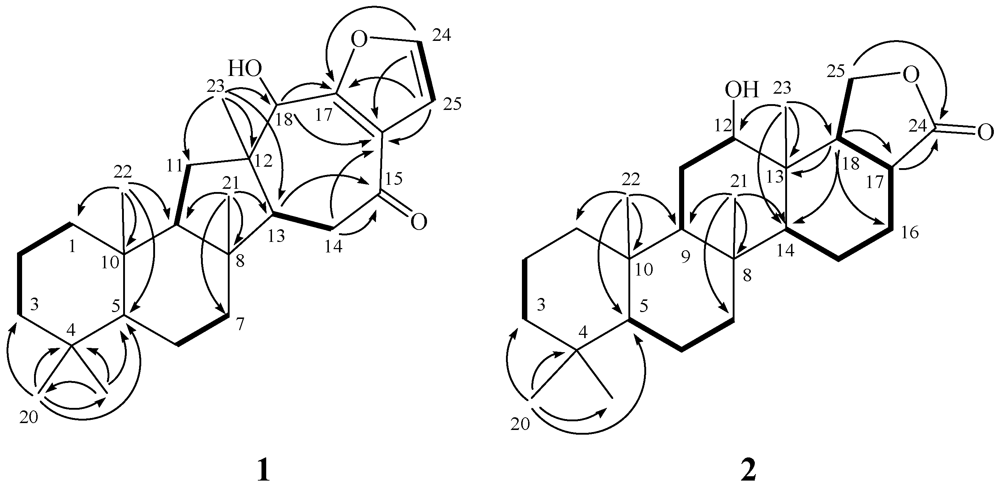
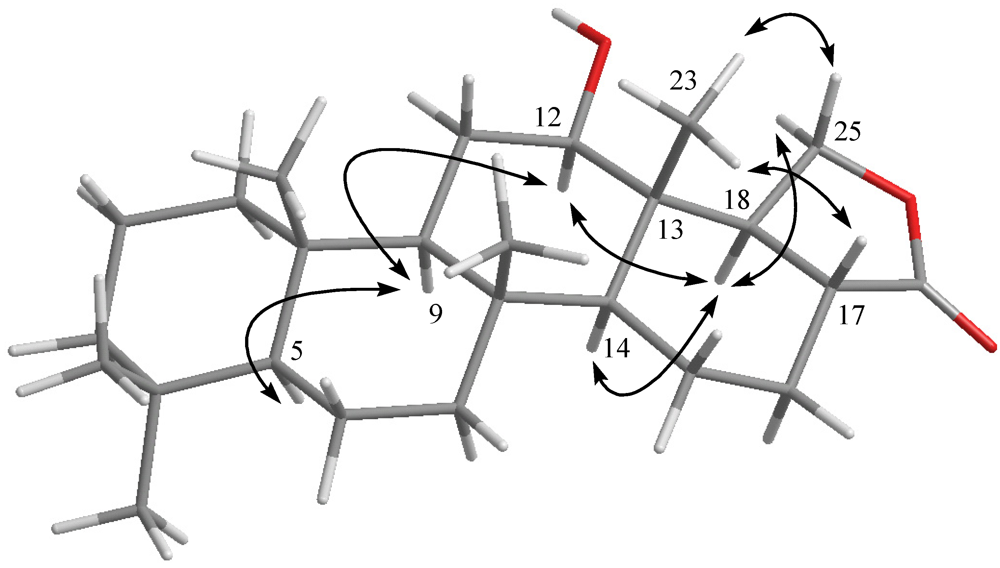
2. Results and Discussion
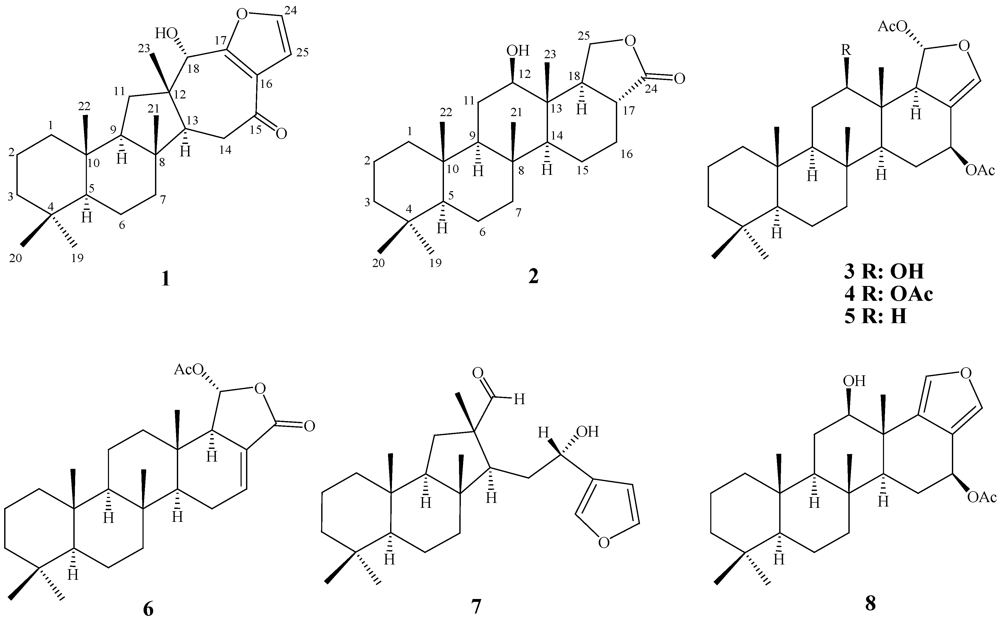
| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) a | δC (mult.) b | δH (J in Hz) a | δC (mult.) b | |
| 1 | 1.46 m; 0.98 m | 40.2 (CH2) c | 1.65 m | 39.9 (CH2) |
| 2 | 1.65 m; 1.40 m | 18.4 (CH2) | 1.54 m; 1.38 m | 18.2 (CH2) |
| 3 | 1.38 m; 1.19 m | 42.5 (CH2) | 1.36 m; 1.12 m | 42.0 (CH2) |
| 4 | 33.1 (C) | 33.3 (C) | ||
| 5 | 0.92 m | 57.6 (CH) | 0.80 m | 56.5 (CH) |
| 6 | 1.57 m; 1.38 m | 18.8 (CH2) | 1.61 m; 1.42 m | 18.6 (CH2) |
| 7 | 1.68 m; 1.10 m | 40.1 (CH2) | 1.74 m; 0.90 m | 41.7 (CH2) |
| 8 | 44.8 (C) | 37.3 (C) | ||
| 9 | 1.45 m | 61.0 (CH) | 0.88 m | 58.9 (CH) |
| 10 | 36.8 (C) | 37.5 (C) | ||
| 11 | 1.99 d (6.0); 1.43 m | 35.0 (CH2) | 1.70 m; 1.45 m | 27.5 (CH2) |
| 12 | 43.0 (C) | 3.40 br d (10.5) | 80.5 (CH) | |
| 13 | 2.20 dd (13.0, 2.5) | 47.5 (CH) | 42.0 (C) | |
| 14 | 2.64 dd (13.5, 13.0) | 39.6 (CH2) | 0.80 m | 58.1(CH) |
| 2.54 dd (13.5, 2.5) | ||||
| 15 | 196.8 (C) | 1.78 m; 1.36 m | 20.0 (CH2) | |
| 16 | 122.9 (C) | 2.20 m; 1.22 m | 25.6 (CH2) | |
| 17 | 159.0 (C) | 2.22 m | 39.2 (CH) | |
| 18 | 4.58 s | 75.9 (CH) | 1.86 m | 55.3 (CH) |
| 19 | 0.85 s | 33.5 (CH3) | 0.84 s | 33.2 (CH3) |
| 20 | 0.84 s | 21.3 (CH3) | 0.80 s | 21.3 (CH3) |
| 21 | 0.85 s | 16.2 (CH3) | 0.84 s | 17.3 (CH3) |
| 22 | 0.87 s | 15.6 (CH3) | 0.84 s | 16.3 (CH3) |
| 23 | 1.14 s | 23.4 (CH3) | 0.91 s | 9.8 (CH3) |
| 24 | 7.33 d (1.5) | 142.3 (CH) | 177.8 (C) | |
| 25 | 6.76 d (1.5) | 110.9 (CH) | 4.38 dd (9.5, 7.0) | 70.0 (CH2) |
| 4.09 dd (11.0, 10.0) | ||||

| Compound | Cell Lines | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLD-1 | HCT-116 | T-47D | K562 | |
| 1 | – a | – a | – a | – a |
| 2 | – a | – a | – a | – a |
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 4 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 0.3 | 0.05 |
| 5 | 1.1 | 8.0 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 6 | – a | – a | – a | – a |
| 7 | – a | – a | – a | – a |
| 8 | – a | – a | – a | – a |
| Actinomycin D | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.03 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Separation
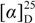 −66 (c 0.1, CHCl3); IR (neat) νmax 3386, 2922, 2854, 1715, 1642, 1455 and 1385 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 407 (100, [M + Na]+); HRESIMS m/z 407.2560 (calcd for C25H36O3Na, 407.2562).
−66 (c 0.1, CHCl3); IR (neat) νmax 3386, 2922, 2854, 1715, 1642, 1455 and 1385 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 407 (100, [M + Na]+); HRESIMS m/z 407.2560 (calcd for C25H36O3Na, 407.2562).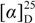 −3 (c 0.05, CHCl3); IR (neat) νmax 3436, 2927, 1753, 1461 and 1383 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 411 (80, [M + Na]+); HRESIMS m/z 411.2878 (calcd for C25H40O3Na, 411.2875).
−3 (c 0.05, CHCl3); IR (neat) νmax 3436, 2927, 1753, 1461 and 1383 cm−1; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; ESIMS m/z 411 (80, [M + Na]+); HRESIMS m/z 411.2878 (calcd for C25H40O3Na, 411.2875).3.4. Cytotoxicity Testing
3.5. Molecular Mechanics Calculations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- González, M.A. Scalarane sesterterpenoids. Curr. Bioact. Comp. 2010, 6, 178–206. [Google Scholar]
- Kashman, Y.; Rudi, A. The 13C NMR spectrum and stereochemistry of heteronemin. Tetrahedron 1977, 33, 2997–2998. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, P.; Bescansa, P. Sesterterpenes from a common marine sponge, Hyrtios erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 1986, 49, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-G.; Bi, K.-S.; Gue, Y.-W. Hyrtiosins A–E, five new scalarane sesterterpenes from the South China Sea sponge Hyrtios erecta. HeIv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonganuchitmeta, S.-N.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Keawpradub, N.; Plubrukarn, A. Antitubercular sesterterpenes from the Thai sponge Brachiaster sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1767–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, K.; Shimada, Y.; Yamada, Y. Hyrtiosal, a new sesterterpenoid with a novel carbon skeleton from the Okinawan marine sponge Hyrtios erectus. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 522–524. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, R.P.; Thompson, J.E.; Faulkner, D.J. Sesterterpenes from Spongia idia. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 4976–4979. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Yamaki, R.K.; Kelly, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Salmahyrtisol A, a novel cytotoxic sesterterpene from the Red Sea sponge Hyrtios erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahidol, C.; Prawat, H.; Sangpetsiripan, S.; Ruchirawat, S. Bioactive scalaranes from the Thai sponge Hyrtios gumminae. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Fattorusso, E.; Magno, S.; Santacroce, C.; Sica, D. Scalarin, a new pentacyclic C-25 terpenoid from the sponge Cacospongia scalaris. Tetrahedron 1972, 28, 5993–5997. [Google Scholar]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abbott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar]
- Scudiero, D.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Paull, K.D.; Monks, A.; Tierney, S.; Nofziger, T.H.; Currens, M.J.; Seniff, D.; Boyd, M.R. Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar]
- Chem3D Ultra, version 9.0.1, CambridgeSoft Corporation: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005.
- Lee, H.-S.; Lee, T.-H.; Yang, S.H.; Shin, H.J.; Shin, J.; Oh, K.-B. Sesterterpene sulfates as isocitrate lyase inhibitors from tropical sponge Hippospongia sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2483–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, K.S.; Williams, D.E.; Hollander, I.; Frommer, E.; Mallon, R.; Collins, K.; Wojciechowicz, D.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Novel sesterterpenoid and norsesterterpenoid RCE-protease inhibitors isolated from the marine sponge Hippospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 4801–4808. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Namikoshi, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Yao, X.; Cai, G. Sesquiterpene quinones from a marine sponge Hippospongia sp. that inhibit maturation of starfish oocytes and induce cell cycle arrest with HepG2 cells. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-H. New sesquiterpene hydroquinones from a Taiwanese marine sponge, Hippospongia metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 801–803. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Cheng, J.-f.; Nakamura, H.; Hirata, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Metachromins A and B, novel antineoplastic sesquiterpenoids from the Okinawan sponge Hippospongia cf. metachromia. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 2855–2858. [Google Scholar]
- Musman, M.; Ohtani, I.I.; Nagaoka, D.; Tanaka, J.; Higa, T. Hipposulfates A and B, new sesterterpene sulfates from an Okinawan sponge, Hippospongia cf. metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.-J.; Zhang, H.-J.; Lu, H.-Y.; Yang, F.; Jiao, W.-H.; Yi, Y.-H.; Chen, W.-S.; Lin, H.-W. Hippolides A–H, acyclic manoalide derivatives from the marine sponge Hippospongia lachne. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Oda, T.; Wang, W.; Fujita, A.; Mochizuki, M.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Promotion of IL-8 production in PMA-stimulated HL-60 cells by sesquiterpene quinones from a marine sponge, Hippospongia sp. J. Nat. Med. 2007, 61, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaio, A.; Piccialli, V.; Sica, D.; Corriero, G. New polyhydroxysterols from the dictyoceratid sponges Hippospongia communis, Spongia officinalis, Ircinia variabilis, and Spongionella gracilis. J. Nat. Prod. 1989, 52, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaio, A.; Notaro, G.; Piccialli, V.; Sica, D. Minor 5,6-secosterols from the marine sponge Hisppospongia communis. Isolation and synthesis of (7Z,22E,24R)-24-methyl-5,6-secocholesta-7,22-diene-3β,5β,6-triol. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 565–572. [Google Scholar]
- Cimino, G.; de Stefano, S.; Minale, L. Furospongin-1, a new C-21 furanoterpene from the sponges Spongia officinalis and Hippospongia communzs. Tetrahedron 1971, 27, 4673–4679. [Google Scholar]
- Cimino, G.; de Stefano, S.; Minale, L. Minor C-21 furanoterpenes from the sponges Spongia officinalis and Hippospongia communis. Tetrahedron 1972, 28, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Madaio, A.; Piccialli, V.; Sica, D. Hipposterol, a unique trihydroxylated 5,6-secosterol from the marine sponge Hippospongia communis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, 5999–6000. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Murayama, T.; Ohizumi, Y. Metachromin C, a new cytotoxic sesquiterpenoid from the Okinawan marine sponge Hippospongia metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 1989, 52, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Naitoh, K.; Saaski, T.; Shigemori, H. Metachromins D-H, new cytotoxic sesquiterpenoids from the Okinawan marine sponge Hippospongia metachromia. J. Org. Chen. 1992, 57, 5773–5776. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Shinonaga, H.; Shigemori, H.; Sasaki, T. Untenospongin C, a new C21 furanoterpene from the Okinawan marine sponge Hippospongia sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 381–382. [Google Scholar]
- Rochfort, S.J.; Atkin, D.; Hobbs, L.; Capon, R.J. Hippospongins A-F: New furanoterpenes from a Southern Australian marine sponge Hippospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Hirata, Y. Hippospongin, a novel furanosesterterpene possessing antispasmodic activity from the Okinawan marine sponge Hippospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 2113–2116. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, S.; Uno, M.; Tokumasu, M.; Hiraga, Y.; Ikegami, S. Hippospongic acid A: An unusual triterpenoic acid from a marine sponge, Hippospongia sp., which inhibits gastrulation of starfish embryos. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7765–7766. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.W.; Trivellone, E. Ent-untenospongin A, a new C21 furanoterpene from the Indian marine sponge Hippospongia sp. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2000, 11, 327–330. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H.; Deng, S.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, Y. Dictyoceratin-A and -B, novel antimicrobial terpenoids from the Okinawan marine sponge Hippospongia sp. Tetrahedron 1986, 42, 4197–4201. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiyama, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Ogawa, A.; Yoshida, S.; Kobayashi, J. Taurospongin A, a novel acetylenic fatty acid derivative inhibiting DNA polymerase and HIV reverse transcriptase from sponge Hippospongia sp. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 3831–3836. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.-W.; Trivellone, E. New hurgamides from a Red Sea sponge of the genus Hippospongia. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 2, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Samples Availability: Not available.
Supplementary Files
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.-C.; Tseng, S.-W.; Liu, L.-L.; Chou, Y.; Ho, Y.-S.; Lu, M.-C.; Su, J.-H. Cytotoxic Sesterterpenoids from a Sponge Hippospongia sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 987-997. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10050987
Chang Y-C, Tseng S-W, Liu L-L, Chou Y, Ho Y-S, Lu M-C, Su J-H. Cytotoxic Sesterterpenoids from a Sponge Hippospongia sp. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(5):987-997. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10050987
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yu-Chia, Shang-Wei Tseng, Li-Lian Liu, Yalan Chou, Yuan-Shing Ho, Mei-Chin Lu, and Jui-Hsin Su. 2012. "Cytotoxic Sesterterpenoids from a Sponge Hippospongia sp." Marine Drugs 10, no. 5: 987-997. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10050987
APA StyleChang, Y.-C., Tseng, S.-W., Liu, L.-L., Chou, Y., Ho, Y.-S., Lu, M.-C., & Su, J.-H. (2012). Cytotoxic Sesterterpenoids from a Sponge Hippospongia sp. Marine Drugs, 10(5), 987-997. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10050987





