Abstract
Four novel amicoumacins, namely lipoamicoumacins A–D (1–4), and one new bacilosarcin analog (5) were isolated from culture broth of a marine-derived bacterium Bacillus subtilis, together with six known amicoumacins. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic (2D NNR, IR, CD and MS) analysis and in comparison with data in literature.
1. Introduction
Highly diverse marine microbes not only act as a driving force of material cycles in the marine ecosystems but also serve as an excellent source of novel compounds with great potential for biomedical and ecological applications [1,2]. However, natural product discoveries from marine microbes in the Red Sea remain largely unexplored. Accordingly, we have recently initiated a program to discover bioactive natural products from microorganisms isolated from some under-explored ecological niches in the Red Sea. Based on the cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities of the crude extract of its fermented broth, strain B1779, identified as Bacillus subtilis based on 16s DNA gene sequence, was chosen for further chemical investigation. Previous chemical studies of the Genus Bacillus have led to the isolation and identification of six isocoumarin type metabolites [3]. Some of these exhibit different biological activities, such as cytotoxic [4,5], antibacterial [5,6], antiulcer [7,8,9] and plant-growth inhibitory activities [10]. Our ongoing chemical investigation of B. subtilis strain B1779 resulted in the isolation of 11 amicoumacins, including four novel lipoamicoumacins that were designated as lipoamicoumacins A–D (1–4), one new bacisarcin C (5) and six known analogues (6–11). Compounds 6–7 showed significant cytotoxic activity against HeLa cells and strong antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus and Loktanella hongkongensi. In this paper, we report the fermentation, isolation, structures elucidation, and cytotoxic and antibacterial activities of isolated compounds from a Bacillus subtilis strain B1779.
2. Results and Discussion
Strain Bacillus subtitlis B1779 was cultivated in a sea salt-based medium for 4 days with vigorous shaking (160 rpm). The UPLC-MS and bioassay guided fractionation revealed that the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extract of its fermentation broth contained bioactive secondary metabolites with molecular weights ranging from m/z: 390 to 730. Moreover, analysis of the 1H NMR and UV spectra of this extract revealed that the bioactive fractions were mainly comprised of isocoumacin-type compounds with characteristic spectral features and UV absorptions similar to those of amicoumcin A (7). Further separation with semi-preparative HPLC resulted in the isolation of 11 constituents with similar UV and NMR features, including five new compounds (1–5); their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic analysis and upon comparison with data in the literature. Compounds 1–4 were identified as novel lipo-amicoumacins, which are referred to herein as Lipoamicoumacin A–D (1–4).
2.1. Structure Elucidation of New Amicoumacins
Lipoamicoumacin A (1) was obtained as a white amorphous solid. Based on HRESIMS (m/z 703.3921 [M + H]+) data we established its molecular formula as C36H54N4O10, indicating twelve degrees of unsaturation. The IR absorptions at 3432, 1667 and 1545 cm−1 in association with the 13C NMR spectroscopic data suggested the presence of hydroxyl, carbonyl and aromatic groups. The 1H NMR spectra exhibited three aromatic proton singlets for a tri-substituted aromatic unit at δH 7.47 (1H, dd, H-6), 6.85 (1H, d, H-7) and 6.81 (1H, d, H-5), three oxymethines at δH 4.79 (1H, t, H-9'), 4.68 (1H, dd, H-3) and 4.42 (1H, d, H-8'), three nitrogen-bond methines at δH 4.51 (1H, dt, H-10'), 4.65 (1H, dd, H-15') and 4.29 (1H, m, H-5'), a broad peak at δH 1.30 (10H, brs, H4''~8'') and four methyl resonances at δH 0.97 (3H, d, H-2'), 0.89 (3H, d, H-1') and 0.88 (6H, d, H-11'', H-12''). The 13C NMR spectra provided five ester/amide carbonyl resonances at δC (171.2–178.1), six aromatic carbons for a trisubstituted aromatic ring, three oxymethines and three nitrogen-bonded sp3 carbons. In addition, the UV spectrum was nearly identical to that reported for amicoumacins (λmax 206, 247 and 314 nm) [8], suggesting that 1 possessed a similar dihydroisocoumarin chromophore. The gross structure of 1 was further established by analyses of the 1H, 13C, 1H–1H COSY, HMQC and HMBC NMR spectral data (Figure 1 and Figure 2), indicating an amicoumacin unit was linked to a fatty acid chain. The NMR spectroscopic data of 1 were highly similar to those from the combination of amicoumacin C (9) and lipoamide B [8,11] with the exceptions of the Δδ = 1.6 ppm upfield shift of C-10' (δC 48.6) and Δδ = 0.23 ppm downfield shift of H-10' (δH 4.51). The differences were due to the linkage of the lipoamide group at C-10' in compound 1 when comparing it with 9. These assignments were also supported by HMBC correlations from H-10' to C-14' and ESI-MS fragmentations (Figure 3). The ESI-MS spectrum showed fragment ions corresponding to the loss of an acyl group from the iso C12 fatty acid side strain (m/z 521) and sequential loss of asparagine (Asn) (m/z 407) and dihydroisocoumarin fragment ion (m/z 250). The relative configuration of 1 was determined by NOE correlations of H-3/H-4' and H-5'/H-8', which shares similar stereochemical configurations with amicoumacin C (9). To further confirm the absolute configuration of the dihydroisocoumarin unit, the CD spectrum of 1 and 9 was compared. The CD spectrum of 1 showed positive Cotton effects at 221 and 240 nm and negative Cotton effects at 260 and 310 nm, which were in good agreement with those for compound 8 and 9 [9,10]. Thus, the structure of 1 was determined as illustrated in Figure 1.
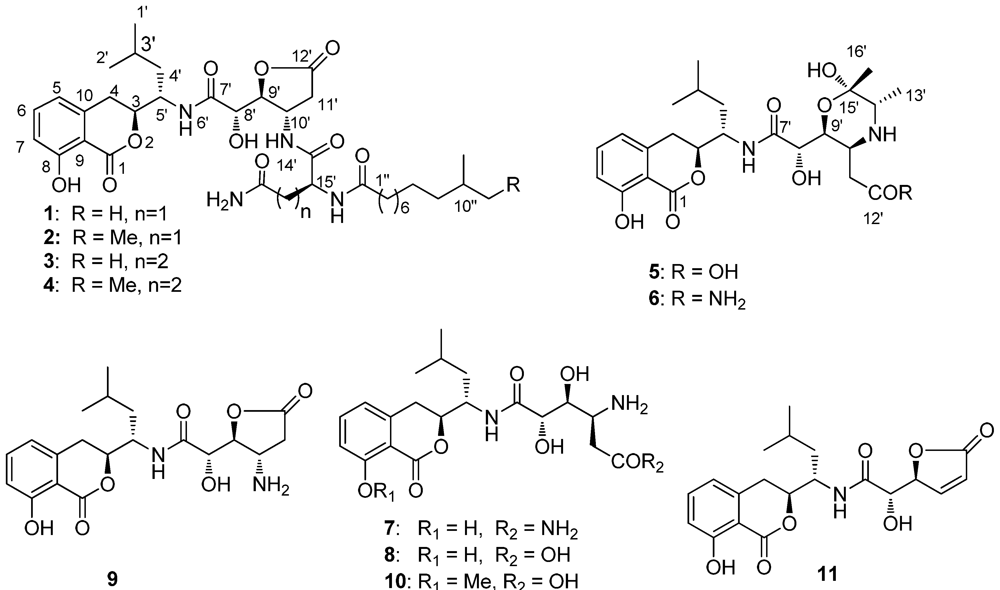
Figure 1.
Amicoumacins (1–11) isolated from Bacillus subtilis strain B1779.
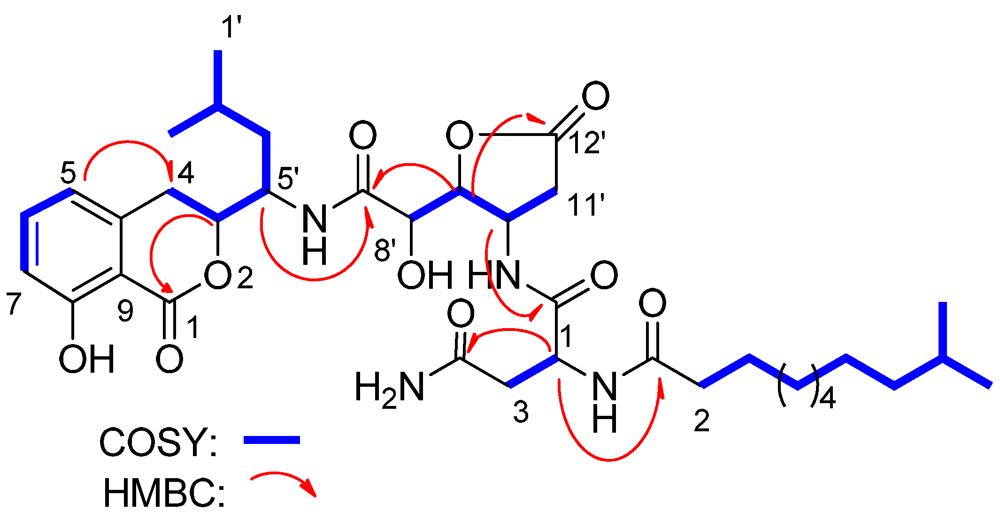
Figure 2.
Select HMBC and COSY correlations of lipoamicoumacin A (1).
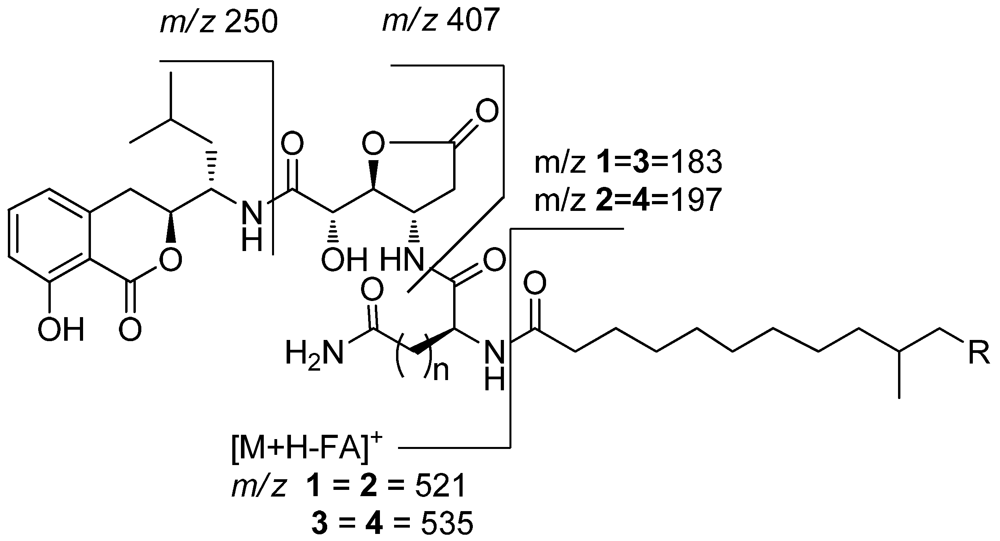
Figure 3.
ESI-MS fragmentations of lipoamicoumacins A–D (1–4).
The molecular formula of lipoamicoumacin B (2) was established as C37H56N4O10, based on the HRESIMS (m/z 717.4062 [M + H]+, calcd. 717.4069), which was 14 amu higher than that of 1. The NMR spectroscopic data of 2 (Supporting Information, Table 1) indicated that its structure was closely related to that of 1. The only difference was the presence of an additional methyl group (δH 0.86, δC 11.9) in 2, located at C-11''. HMBC correlation between H-12'' and C-10'' and COSY correlations from H-12'' to H-11'', H-11'' to H-10'' and H-10'' to H-13'' confirmed that the structure of 2 was a C-11'' methylated analog of 1, seen also with the ESIMS fragmentation analysis.

Table 1.
NMR data of lipoamicoumacins A (1).
| lipoamicoumacins A (1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δC, mult | δH, (J in Hz) | HMBC | Position | δC, mult | δH, (J in Hz) | HMBC |
| 1 | 171.2, C | 11' | 36.7, CH2 | 2.45, dd (2.6, 18.0), 3.01 m | 12' | ||
| 3 | 82.7, CH | 4.68, m | 1 | 12' | 178.1, C | ||
| 4 | 30.8, CH2 | 2.98, dd (3.5, 16.0), 3.06, m | 5, 9, 10 | Asparagine | |||
| 5 | 119.8, CH | 6.81, d (7.6) | 4, 7, 9 | 14' | 173.3, C | ||
| 6 | 137.8, CH | 7.47, dd (7.5, 8.4) | 8, 10 | 15' | 51.3, CH | 4.65, dd (6.5, 7.0) | 14', 1'' |
| 7 | 116.9, CH | 6.85, d (8.4) | 5, 8, 9 | 16' | 38.2, CH2 | 2.57, dd (7.1, 15.2), 2.67, dd (6.4,15.2) | 14', 17' |
| 8 | 163.3, C | 17' | 174.8, C | ||||
| 9 | 109.6, C | 18' | |||||
| 10 | 141.4, C | Fatty acid | |||||
| 1' | 22.1, CH3 | 0.89, d (6.6) | 2', 4' | 1'' | 176.3, C | ||
| 2' | 24.0, CH3 | 0.97, d (6.6) | 1', 4' | 2'' | 37.0, CH2 | 2.24, t (8.0) | 1'' |
| 3' | 26.0, CH3 | 1.68, m | 3'' | 27.0, CH2 | 1.60, m | ||
| 4' | 40.4, CH2 | 1.43, m, 1.82, m | 4''~8'' | 30.5–31.2 | 1.30, brs | ||
| 5' | 50.7, CH | 4.29, m | 7' | 9'' | 38.3, CH2 | 1.17 m, 1.30 m | |
| 7' | 172.8, C | 10'' | 27.0, CH | 1.53 m | |||
| 8' | 73.6, CH | 4.42, d (2.5) | 7', 10' | 11'' | 23.2, CH3 | 0.88, t (6.8) | 9'' |
| 9' | 87.9, CH | 4.79, t (2.4) | 7', 12' | 12'' | 23.2, CH3 | 0.88, t (6.8) | 9'' |
| 10' | 48.6, CH | 4.51, dt (9.1, 2.0) | 14' | ||||
Lipoamicoumacin C (3) had a molecular formula of C37H56N4O10, which was established by the HRESIMS data (m/z 717.4062 [M + H]+, calcd. 717.4069). The NMR data of 3 (Supporting Information, Table 1) were comparable to those of 1, with the exception of an additional methylene at δH 2.25 (2H, t, H-17') and the Δδ = 3.1 ppm downfield shift of C-18' (δC 177.8). Analysis of ESIMS fragmentation ions (Figure 3) revealed the presence of a glutamine group (∆m/z 535–407) in 3, instead of an asparagine group (∆m/z 521–407) in 1. The suggestion was further confirmed by HMBC correlations of H-10'/C-14', H-15'/C-1'' and 1H–1H COSY correlations of H-17'/H-16' and H-16'/H-15'.
Lipoamicoumacin D (4) had a molecular formula of C38H58N4O10, which was established from the HRESIMS (m/z 731.4215 [M + H]+, calcd. 731.4222). The molecular weight of 4 was also 14 amu higher than that of 3. The NMR and MS spectroscopic data of 4 indicated that its structure is nearly identical to that of 3, with the exception of an additional methyl group located at C-11'' in 4.
Bacilosarcin C (5) had a molecular formula of C24H34N2O9, which was established from the HRESIMS (m/z 495.2344 [M + H]+, calcd. 495.2337). The 1H NMR spectrum exhibited three aromatic proton singlets for one aromatic spin system at δH 7.46 (1H, dd, H-6), 6.85 (1H, d, H-7) and 6.82 (1H, d, H-5), three oxymethines at δH 4.68 (1H, dd, H-9'), 4.66 (1H, dd, H-3) and 4.14 (1H, d, H-8'), two nitrogen-bonded methines at δH 4.34 (1H, dt, H-5'), 3.91 (1H, m, H-10') and 3.43 (1H, q, H-14'), two methylenes at δH 3.10 (1H, dd, H-4) and 2.96 (1H, dd, H-4), δH 3.06 (1H, dd, H-11') and 2.92 (1H, dd, H-11'), and four methyl resonances at δH 1.28 (3H, d, H-13'), 1.26 (3H, s, H-16'), 0.98 (3H, d, H-2') and 0.94 (3H, d, H-1'). The UV absorptions at λmax 206, 247 and 314 nm in association with the NMR data suggested that compound 5 also possesses an amicoumacin unit. The NMR data of 5 (Supporting Information, Table 2) were mostly the same as bacilosarcin B (6) [10], except for the Δδ = 0.20 ppm downfield shift of H-11' (δH 3.06). The difference was due to the linkage of a hydroxyl group (5) as opposed to an amide group (6) at C-12'. These assignments were also supported by molecular composition and a HRESI-MS fragment ion (m/z: 477.2238 [M − H2O + H]+) corresponding to the intermolecular dehydration between C-9' and C-12'. The relative configurations of 5 were determined by the NOE correlations of H-4'/H-9', H-12'/H-8' and H-12'/14', which were in good agreement with those for compound 6. The stereochemistry of 5 was assigned to be the same as that of 6 based on their similar Cotton effects observed in the CD spectrum and similar levo specific rotation.
Based on spectroscopic analyses and the comparison of their spectroscopic data with those reported in the literature, six known compounds were identified as bacilosarcin B (6) [10], amicoumacin A–C (7–9) [6,9], 6-[[1-(3,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-l-oxo-1H-2-benzopyran-3-yl)-3-methylbutyl]amino]-4,5-dihydroxy-6-oxo-3-ammoniohexanoate (10) and AI-77-F (11) [8].
2.2. Biological Evaluation
All isolated compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against human cervical carcinoma epithelioid cell line HeLa using MTT methods, and for their antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Loktanella hongkongensis, Peseudomonas aeruginosa and Chromobacterium violaceum by MIC assay .Only compounds amicoumacin A (7) and bacilosarcin B (6), which have an amide functional group at C-12', exhibited cytotoxicity against the HeLa cells with IC50 values of 33.60 and 4.32 μM respectively, indicating that the C-12' amide group of amicoumcin plays a critical role in cytotoxicity. This was further supported by comparision of cytotoxicity between compounds 7 and 8 and between compounds 5 and 6. Compound 7, with an IC50 value of 4.32 μM showed 30-fold higher cytotoxicity than 8. Previous research also reported that C-12 amide groups of amicoumacin played a critical role in antibacterial activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) [12], which was based on the comparison of amicoumacin A (7) and amicoumacin B (8). Herein, we studied the antibacterial structure-activity relationships based on 11 amicoumacins against three target bacterial strains. Our results indicate that only those compounds with C-12' amide groups exhibited antibacterial activities against B. subtilis, S. aureus and L. hongkongensis (Supporting Information, Table 3), which strongly supported that the C-12' amide group of amicoumcin acts as a pharmacophore in antibacterial activities. This conclusion was further supported by comparing antibacterial activities between compounds 7 and 8 and between compound 5 and 6. Compound 7 exhibited antibacterial activities against B. subtilis, S. aureus and L. hongkongensis, which were about six-fold higher than those of compound 8.
While microbial secondary metabolites have been extensively used as antimicrobial or antitumor therapeutic agents, the biological functions of the metabolites in microbes that produce them have only been studied in a few cases. For instance, xenocoumacin-1, the major antimicrobial compound produced by Xenorhabdus nematophila, was shown to suppress their competitors of the host and subsequently convert xenocoumacin-2, which has a much weaker antimicrobial activity, to avoid self-toxicity [13]. In Bacillus genus, surfactins were produced to serve as signaling molecules to activate the pathway related to biofilm information [14], while sporulenes was shown to serve as a chemical barrier against oxidative stress [15]. However, the biological role of amicoumacins in the life cycle of B. subtillis is far from being understood. It will therefore be intriguing to investigate the chemical ecology of amicoumacins in the future.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotations were recorded on an Autopol III Rudolph research automatic polarimeter, whereas IR spectra were obtained on a Thermo Nicolet Nexus 470 FT-IR spectrometer. NMR spectra were measured on a Bruker Avance-500/700 FT 500/700 MHz NMR spectrometer using trimethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard. CD spectra were recorded on J-810-150s spectropolarimeter (Jasco, Germany). HRESIMS spectra were recorded on a Bruker micrOTOF II ESI-TOF-MS spectrometer. Sephadex LH-20 (18–110 μm) was purchased from Pharmacia Co (Japan), whereas octadecylsilane (ODS) (50 μm) was purchased from YMC Co. (Japan). HPLC was performed on a Waters 600 apparatus using a semi-preparative C-18 Phenomenex Luna 5 μm (10 mm × 250 mm) column and monitored by a UV detector (Waters 2475).
3.2. Bacterial Material and Identification
The Bacillus subtilis strain B1779 was isolated from a marine sediment sample which was collected by a multicore sampler at a depth of 1000 m in the Red Sea, in April 2010. This strain was isolated by a standard dilution-plating technique. Bacteria in the sediment were released by vigorous shaking in autoclaved filtered seawater and inoculated in a serial dilution on 1.5% agar composed of 10 g starch and 2 g yeast extract dissolved in 1 L filtered seawater. According to its 16S rRNA gene sequence (accession number: HM585050.1), this strain belongs to Bacillus subitlis group. A voucher strain of this Bacillus subtilis strain has been preserved at the Costal Marine Lab, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology. Genomic DNA was extracted from the cells using the TaKaRa MiniBEST Bacterial Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (TaKaRa, China). The 16S rRNA gene of B1779 was amplified by a pair of primers of 8F (5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3') and 1525R (5'-AAGGAGTGWTCCARCC-3') with Vent DNA polymerase (NEB) and sequenced using Applied Biosystems 3100 automated DNA sequencer, as previously described [16,17]. The resulting 16S rRNA gene sequence was compared with sequences obtained from the NCBI nucleotide database using BLAST search [18] to locate approximate phylogenetic affiliation.
3.3. Fermentation and Extraction
The bacterium was cultured in multiple 3 L flasks containing SYT culture medium (1% of starch, 0.4% of yeast extract and 0.2% tryptone) in seawater at 25 °C with agitation (160 rpm) for 4 days until the stationary phase was reached. In total, 20 L of fermented broth were obtained. The bacterial culture broth was extracted with an equal volume of ethyl acetate (EtOAc) three times and gave a total of 11 g of crude extract.
3.4. Isolation
The crude EtOAc extract (11.0 g) was fractionated by ODS open column chromatography eluting with a step gradient from 40% methanol in water to 100% methanol to give six fractions (F1–F6). UPLC-MS analysis and cytotoxicity bio-assay showed that bioactive isocoumacins were mainly concentrated in fractions 3 and 4 (named as F3 and F4). F3 (0.39 g) was separated by semi-preparative HPLC with a gradient mobile phase (MeCN-H2O, from 30 % to 50 %) to obtain 5 (3.6 mg), 6 (4.7 mg), 7 (25.0 mg), 8 (11.5 mg), 9 (18.0 mg), 10 (22 mg) and 11(6.2 mg), respectively. F4 (0.42 g) was subjected to Sephadex LH-20 and subsequently separated with semi-preparative HPLC eluting with a gradient mobile phase (MeCN-H2O, from 60% to 80%) to yield the compounds 1 (1.9 mg), 2 (1.6 mg), 3 (3.5 mg) and 4 (4.8 mg), respectively.
3.5. Spectroscopic Data of Compounds
3.5.1. Lipoamicoumacin A (1)
White amorphous powder; [α]27D −12.0 (c 0.20, MeOH); IR (KBr) νmax 3432, 3047, 2955, 2925, 2101, 1794, 1667, 1545, 1462, 1371, 1026 and 974 cm−1; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 206 (4.22), 247 (3.44) and 314 (3.29) nm; for 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HREIMS m/z 703.3921 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C36H55N4O10, 703.3913); ESI-MS fragmental ions (m/z 521.2, 407.2, 297.2, 250.1).
3.5.2. Lipoamicoumacin B (2)
White amorphous powder;[α]27D 4.0 (c 0.20, MeOH); IR (KBr) νmax 3433, 3304, 2924, 2853, 1790, 1663, 1540, 1461, 1370, 1020 and 873 cm−1; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 206 (4.18), 247 (3.45) and 314 (3.32) nm; for 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 in Supporting Information; HREIMS m/z 717.4062 [M + H]+, (calcd. for C37H57N4O10, 717.4069); ESI-MS fragmental ions (m/z 521.2, 407.2, 311.2, 250.1).
3.5.3. Lipoamicoumacin C (3)
White amorphous powder; [α]27D −25.0 (c 0.20, MeOH); IR (KBr) νmax 3424, 3314, 3068, 2926, 2856, 1793, 1665, 1541, 1463, 1371, 1220, 1166, 1112 and 872 cm−1; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 206 (4.13), 247 (3.43) and 314 (3.29) nm; for 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 in Supporting Information 1; HREIMS m/z 717.4062 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C37H57N4O10, 717.4069); ESI-MS fragmental ions (m/z 535.3, 407.2, 311.2, 250.1, 183.2).
3.5.4. Lipoamicoumacin D (4)
White amorphous powder; [α]27D −19.2 (c 0.20, MeOH); IR (KBr) νmax 3432, 3045, 2924, 2856, 1792, 1664, 1538, 1462, 1368, 1115 and 873 cm−1; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 206 (4.15), 247 (3.43) and 314 (3.30) nm; for 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1 in Supporting Information 1; HREIMS m/z 731.4215 [M + H]+, (calcd. for C38H59N4O10, 731.4222); ESI-MS fragmental ions (m/z 535.3, 407.2, 325.3, 250.1, 197.2).
3.5.5. Bacilosarcin C (5)
White amorphous powder; [α]27D −18.0 (c 0.20, MeOH); IR (KBr)νmax 3400, 2959, 2880, 1676, 1620, 1586, 1464, 1388, 1205, 1138, 1040, 966 and 804 cm−1; UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 206 (4.06), 247 (3.35) and 314 (3.23) nm; for 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 2 in Supporting Information 1; HREIMS m/z 495.2344 [M + H]+, (calcd. for C24H35N2O9, 495.2337); ESI-MS fragmental ions (m/z 477.2, 285.3, 250.1).
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
Human HeLa cells were used in the assay; 80 μL of 1 × 105/mL cells were planted into 96-microwell plates. Twelve hours later the cells were treated with testing samples at various concentrations and then incubated at 37 °C for 48 hours. Afterward, the supernatant was removed and 20 μL of MTT (2.5 mg mL−1) were added to each well. After incubation at 37 °C for 4 hours, 100 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were added to each well and incubated for an additional 20 min. The absorbance of each well was then measured at 570 nm by a Thermo scientific Multiskan FC multiplate photometer (Waltham, MA, USA).
3.7. Antibacterial Assay
The antibacterial activities of compound 1–11 were evaluated by MIC assay against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Loktanella hongkongensis, Peseudomonas aeruginosa and Chromobacterium violaceum. Briefly, the bacterial strains were inoculated in YP broth (0.2% yeast extract, 0.1% peptone and 1.7% sea salts) and were incubated at 28 °C for 12 h. The stock solution of samples were prepared at 50 mg/mL in DMSO and further diluted to varying concentrations in 96 well plates that contained the incubated microbial strains. After incubation at 28 °C for 24 hours, the absorbance of each well was then measured at 600 nm by a Thermo scientific Multiskan FC multiplate photometer.
4. Conclusion
Bioassay guided investigation of the Red Sea bacterium Bacillus subtilis has resulted in the isolation of four novel lipoamicoumacins, lipoamicoumacin A–D (1–4), together with one new bacilosarcin C and six known amicoumacins. Study of the structure-activity relationship indicated that the C-12' amide functional groups play a critical role in cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities of these amicoumacins. It is particularly noteworthy to mention that lipoamicoumacin A–D (1–4) is the first subclass of amicoumacin with a lipoamide side chain to be reported from a natural source.
Acknowledgements
This publication was based on work supported in part by Award No. SA-C0040/UK-C001, made by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) to P.Y. Qian.
Supplementary Files
References
- Imhoff, J.F.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J. Bio-mining the microbial treasures of the ocean: New natural products. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 468–482. [Google Scholar]
- Dobretsov, S.; Dahms, H.U.; Qian, P.Y. Natural products as antifouling compounds: Recent progress and future perspectives. Biofouling 2006, 22, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdache, A.; Lamarti, A.; Aleu, J.; Collado, I.G. Non-peptide metabolites from the genus Bacillus. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 893–899. [Google Scholar]
- Canedo, L.M.; Puentes, J.L.P.; Baz, J.P.; Acebal, C.; De La Calle, F.; Garcia, D.G.; De Quesada, T.G. PM-94128, a new isocoumarin antitumor agent produced by a marine bacterium. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 175–176. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.F.; Li, L.H.; Tian, L.; Qiao, L.; Hua, H.M.; Pei, Y.H. Sg17-1-4, a novel isocoumarin from a marine fungus Aternaria tenuis Sg17-1. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 355–357. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, J.; Omoto, S.; Shomura, T.; Nishizawa, N.; Miyado, S.; Yuda, Y.; Shibata, U.; Inouye, S. Amicoumacin-A, a new antibiotic with strong anti-inflammatory and antiulcer activity. J. Antibiot. 1981, 34, 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, J.; Omoto, S.; Shomura, T.; Nishizawa, N.; Miyado, S.; Yuda, Y.; Shibata, U.; Inouye, S. Isolation, physicochemical properties and biological activities of amicoumacins produced by Bacillus pumilus. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1982, 46, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Shimojima, Y.; Hayashi, H. 1H-2-Benzopyran-1-one derivatives, microbial products with pharmacological activity. Relationship between structure and activity in 6-[[1S-(3S,4-dihydro-8-hydroxy-1-oxo-1H-2-benzopyranon-3-yl)-3-methylbutyl]amino]-4S,5S-dihydroxy-6-oxo-3S-ammoniohexanoate. J. Med. Chem. 1983, 26, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojima, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Ooka, T.; Shibukawa, M. (Studies on AI-77s, microbial products with pharmacological activity) structures and the chemical nature of AI-77s. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 5435–5438. [Google Scholar]
- Azumi, M.; Ogawa, K.; Fujita, T.; Takeshita, M.; Yoshida, R.; Furumai, T.; Igarashi, Y. Bacilosarcins A and B, novel bioactive isocoumarins with unusual heterocyclic cores from the marine-derived bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 6420–6425. [Google Scholar]
- Berrue, F.; Ibrahim, A.; Boland, P.; Kerr, R.G. Newly isolated marine Bacillus pumilus (SP21): A source of novel lipoamides and other antimicrobial agents. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, M.; Taguchi, T.; Nishida, S.; Ueno, K.; Koizumi, K.; Aburada, M.; Ichinose, K. Isolation of 8'-phosphate ester derivatives of amicoumacins: Structure-activity relationship of hydroxy amino acid moiety. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 752–756. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.; Ciezki, K.; van der Hoeven, R.; Singh, S.; Reimer, D.; Bode, H.B.; Forst, M. Genetic analysis of xenocoumacin antibiotic production in the mutualistic bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophila. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 73, 938–949. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, D.; Fischbach, M.A.; Chu, F.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Structurally diverse natural products that cause potassium leakage trigger multicellularity in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kontnik, R.; Bosak, T.; Butcher, R.A.; Brocks, J.J.; Losick, R.; Clardy, J.; Pearson, A. Sporulenes, heptaprenyl metabolites from Bacillus subtilis Spores. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 3551–3554. [Google Scholar]
- Shrout, J.D.; Scheetz, T.E.; Casavant, T.L.; Parkin, G.F. Isolation and characterization of autotrophic, hydrogen-utilizing, perchlorate-reducing bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.W.; Ng, C.Y.; Ren, J.; Lau, S.C.; Qian, P.Y.; Wong, P.K.; Lau, T.C.; Wu, M. Owenweeksia hongkongensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel marine bacterium of the phylum “Bacteroidetes”. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).