Abstract
Four new polycyclic antibiotics, citreamicin θ A (1), citreamicin θ B (2), citreaglycon A (3), and dehydrocitreaglycon A (4), were isolated from marine-derived Streptomyces caelestis. The structures of these compounds were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR spectra. All four compounds displayed antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtillis. Citreamicin θ A (1), citreamicin θ B (2) and citreaglycon A (3) also exhibited low MIC values of 0.25, 0.25, and 8.0 μg/mL, respectively, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ATCC 43300.
1. Introduction
The marine environment is a plentiful source of bioactive natural products with potential for development as new pharmaceutical agents. To date, the success rate of drug discovery from the marine world is seven approved drugs out of 22,000 discovered molecular entities, which is approximately 1.7 to 3.3-fold higher than the industry average [1]. Among the diverse spectrum of marine organisms, culturable marine bacteria are prime candidates due to their production of bioactive natural products for possible use in chemical and clinical research [2].
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a traditional nosocomial opportunistic pathogen, has spread from hospitals to the community in the last few decades [3]. Compared with methicillin-susceptible S. aureus bacteremia, MRSA bacteremia cases are associated with greater lengths of hospital stay, significantly higher mortality, and increased costs, posing a heavy burden on healthcare systems [4,5,6]. In the United States, the standardized mortality rate from MRSA infection in 2005 was 6.3 per 100,000 [7]. MRSA contains a mutant gene that manufactures a protein that protects the bacterium from the binding of penicillin [8]. Due to the current prevalence of multidrug-resistant bacteria such as MRSA in many countries, the discovery of new antibiotics with novel modes of action is crucial to tackle the threat of multidrug-resistant bacteria [9].
Citreamicins are polycyclic xanthones isolated from Streptomyces, and have been reported to show antibacterial activity against a variety of Gram-positive bacteria, including MRSA and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE). To date, 10 citreamicins have been reported by several research groups [10,11,12,13,14]. Citreamicins share a common 5/6/6/6/6/6/6 seven-ring system, and identifying their respective structures is usually difficult due to the existence of multiple quaternary carbon atoms.
With the aim of discovering novel antibacterial natural products from marine bacteria, we examined a rarely explored area of rich biodiversity—the Red Sea. We performed a systematic biological and chemical analysis of the secondary metabolites produced by bacteria isolated from the Red Sea based on various bioassays, ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) analysis, and UV profile analysis. One of the hits resulting from our efforts was identified by its 16S rRNA gene as the strain Streptomyces caelestis. The genus Streptomyces belongs to the actinomycete family, which is responsible for producing about half of all of the discovered secondary metabolites known to have broad biological activity, such as antibacterial, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory activity [15,16,17,18,19]. Bioassay-Guided fractionation of the S. caelestis extract led to the isolation of four new compounds (1–4), all of which showed antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus subtillis. Citreamicin θ A (1), citreamicin θ B (2), and citreaglycon A (3) also exhibited low minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 0.25, 0.25, and 8.0 μg/mL, respectively, against methicillin-resistant strain Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ATCC 43300. Compounds 1 and 2 also displayed cytotoxic activity against HeLa cells. Here, we report the fermentation, isolation, structural elucidation, and bioactivity evaluation of these isolated compounds from S. caelestis.
2. Results and Discussion
Compound 1 was isolated as a red crystal with the molecular formula C30H25NO11, based on a high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy (HRESIMS) of 576.1508 for the [M + H]+ value (calcd 576.1506), indicating 19 degrees of unsaturation. The UV spectrum showed the existence of conjugation based on absorption at λmax 237, 278, 323, and 441 nm. Analysis of the 13C NMR spectra indicated the presence of three carbonyls (δC 183.1, 173.7, 166.3), including a ketone at δC 183.1; 18 sp2 carbons in the down field region (three methines (δC 122.6, 118.2, 107.7) and fifteen quaternary carbons); and two sp3 quaternary carbons (δC 93.6, 65.5), four methylene groups (δC 61.6, 40.4, 29.4, 23.6), two methyl groups (δC 26.5, 19.2) and one methoxy (δC 57.3) in the high field region. Together, these signals reveal a skeleton of xanthones very similar to that identified in citreamicin ε (5) [13] (Figure 1). A fragment ion at m/z 475 in ion source collision-induced dissociation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ISCID ESIMS) corresponding to citeamicin ε (5) without the G ring ion was also observed (Figure 2).
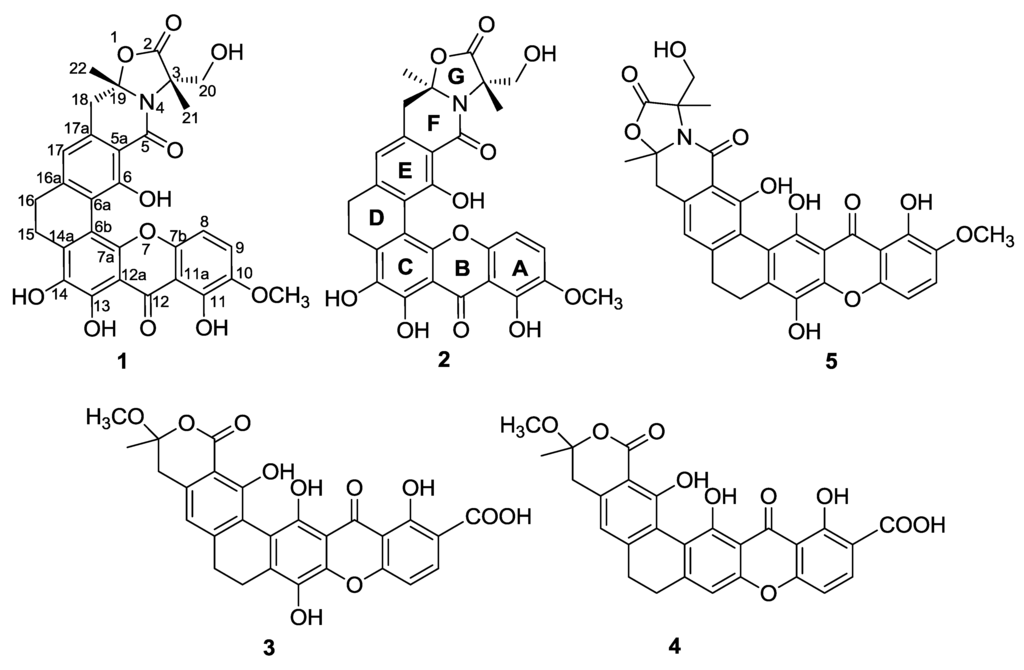
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1–5.
Further comparison of the 1D and 2D NMR data of compound 1 and citreamicin ε [13] indicated that they are structural isomers with the same molecular weight and similar chemical shifts. Heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) correlations from the methyl group at δH 1.61 (H-21) to carbons at δC 173.7 (C-2), 65.5 (C-3), and 61.6 (C-20), together with HMBC correlations from δH 1.67 (H-22) to δC 40.4 (C-18) and 93.6 (C-19), reveal the G ring. However, as rings B and C are constituted by quaternary carbons, it was difficult to obtain an unambiguous structure through 2D NMR analysis. To determine the exact difference in the constituent parts of compound 1 and citreamicin ε, we attempted to culture a single crystal of compound 1. From the crystal data [20], we were able to identify two ortho-phenolic hydroxyls at positions 13 and 14 and to determine the planar structure of compound 1 as that shown in Figure 1.
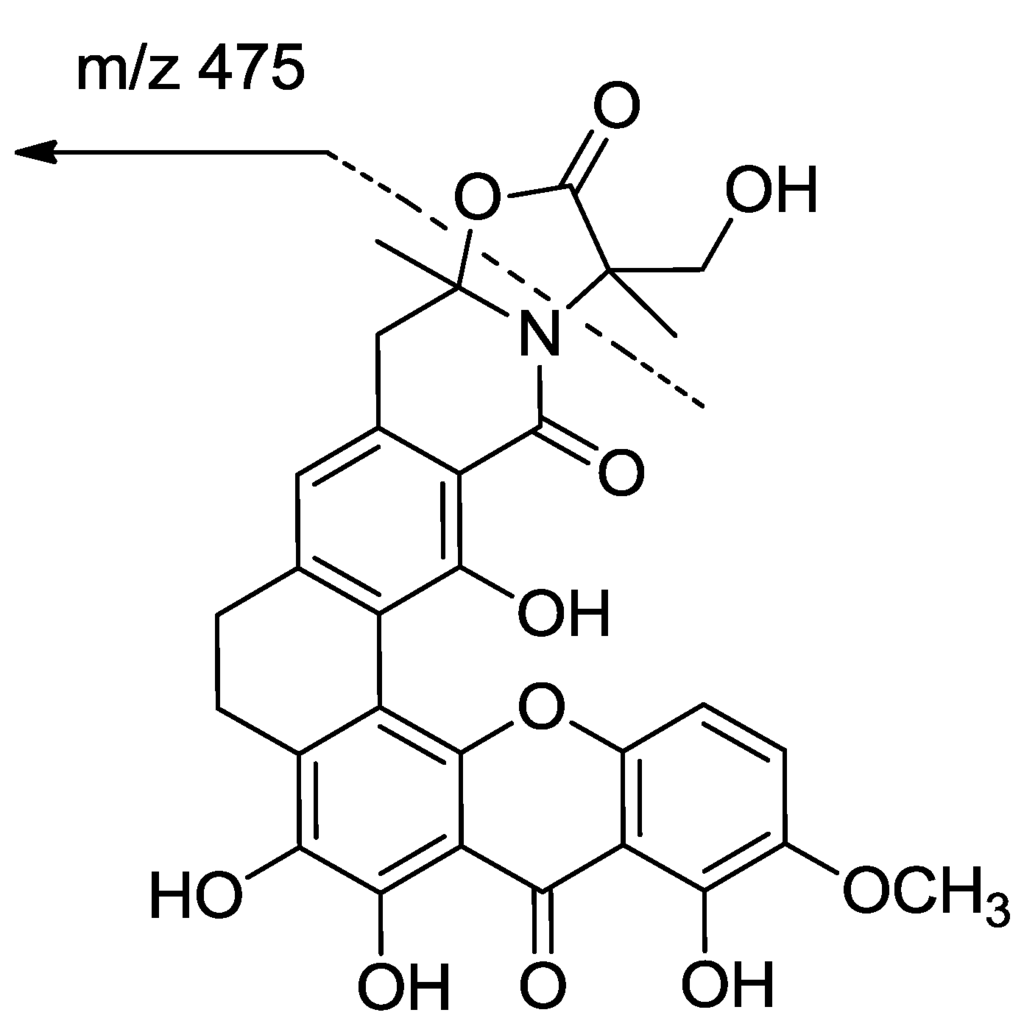
Figure 2.
Ion source collision-induced dissociation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry fragmentations of compounds 1 and 2.
Compound 2 was also isolated as a red crystal with an identical UV profile to that of compound 1 with absorption at λmax 237, 278, 323, and 441 nm. Its molecular formula of C30H25NO11 ([M + H]+ 576.1500 calcd 576.1506) obtained from HRESIMS and the 1H and 13C NMR data (Table 1) are very similar to those of 1, with the significant differences being the methylene signals at position 18 (δH 3.37 in 1 and δH 3.45 in 2) and at position 20 (δH 3.55/4.31, δC 61.6 in 1 and δH 3.69/4.10, δC 63.4 in 2) in the 1D NMR spectra. Further analysis of the 2D NMR spectra of compound 2 showed that a proton signal at δH 7.54 (H-9) had a H1-H1 correlation (H1-H1 COSY) to δH 6.82 (H-8) and HMBC correlations to δC 145.5 (C-7), 149.1 (C-10), 143.3 (C-11). Together, these data elucidate the construction of the A and B rings. HMBC correlations from the methyl group at δH 1.61 (H-21) to carbons at δC 173.4 (C-2), 65.6 (C-3) and 63.4 (C-20), together with HMBC correlations from δH 1.69 (H-22) to δC 40.0 (C-18) and 93.7 (C-19) reveal the G ring. The similar HMBC correlations in 2 to those observed in 1 suggest that they are a pair of diastereomers.

Table 1.
1H and 13C NMR data for compounds 1 and 2 in DMSO-d6.
| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC a | δH (J in Hz) b | δC a | δH (J in Hz) b | |
| 2 | 173.7, qC | 173.4, qC | ||
| 3 | 65.5, qC | 65.6, qC | ||
| 5 | 166.3, qC | 166.0, qC | ||
| 5a | 109.6, qC | 109.2, qC | ||
| 6 | 147.2, qC | 146.9, qC | ||
| 6a | 118.3, qC | 118.1, qC | ||
| 6b | 102.6, qC | 102.1, qC | ||
| 7a | 150.6, qC | 150.2, qC | ||
| 7b | 145.9, qC | 145.5, qC | ||
| 8 | 107.7, CH | 6.87, d (8.8) | 107.2, CH | 6.82, d (8.9) |
| 9 | 122.6, CH | 7.57, d (8.8) | 122.3, CH | 7.54, d (8.9) |
| 10 | 149.5, qC | 149.1, qC | ||
| 11 | 143.7, qC | 143.3, qC | ||
| 11a | 106.4, qC | 105.9, qC | ||
| 12 | 183.1, qC | 182.7, qC | ||
| 12a | 108.3, qC | 107.9, qC | ||
| 13 | 159.2, qC | 158.7, qC | ||
| 14 | 137.3, qC | 136.7, qC | ||
| 14a | 134.6, qC | 134.9, qC | ||
| 15 | 23.6, CH2 | 4.09, m | 23.2, CH2 | 4.05, m |
| 16 | 29.4, CH2 | 3.72, m | 29.6, CH2 | 3.69, m |
| 16a | 142.3, qC | 142.0, qC | ||
| 17 | 118.2, CH | 6.90, s | 117.8, CH | 6.87, s |
| 17a | 141.8, qC | 141.4, qC | ||
| 18 | 40.4, CH2 | 3.37, m | 40.0, CH2 | 3.45, m |
| 19 | 93.6, qC | 93.7, qC | ||
| 20 | 61.6, CH2 | 3.55, d (10.9) | 63.4, CH2 | 3.69, d (11.1) |
| 4.31, d (10.9) | 4.10, d (11.1) | |||
| 21 | 19.2, CH3 | 1.61, s | 18.6, CH3 | 1.61, s |
| 22 | 26.5, CH3 | 1.67, s | 25.0, CH3 | 1.69, s |
| -OCH3 | 57.3, CH3 | 3.85, s | 56.9, CH3 | 3.82, s |
| 6-OH | 12.01, s | 12.01, s | ||
| 11-OH | 11.77, s | 11.75, s | ||
| 14-OH | 9.23, s | 9.23, s | ||
a Recorded at 500 MHz; b Recorded at 125 MHz.
As both compounds 1 and 2 possess two stereogenic centers, there were two possibilities regarding the directions of the two methyl groups at C-3 and C-19. The relative configuration of 2 was determined from the nuclear overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY). The structures of 1 and 2 were optimized by the molecular modeling (MM2) force field and the calculated distance between the H3-21 (δH 1.61) and H-18 (δH 3.45) are shown in Figure 3. The distances between protons beyond 4 Å would give no or only very weak nuclear overhauser effect (NOE) signals [21]. Although, the two protons at position 18 were not distinguished, the distance between H3-21 and one of the H-18 is 4.658 Å that is beyond the cutoff of 4 Å [21]. The NOE correlation between H3-21 (δH 1.61) and H-18 (δH 3.45) revealed that they are on the same side of the molecule, which indicates that the methyl groups at positions C-3 and C-19 have opposite orientations (Figure 3).
The circular dichroism (CD) spectrum of compound 1 displayed a negative Cotton effect with weak minima at short wavelengths and a maximum at higher wavelengths [λmax 220 nm (Δε −0.41), λmax 248 nm (Δε +1.14)] (Figure 4). However, the CD spectrum of compound 2 showed an almost opposite Cotton effect to that of compound 1. The CD spectra of compounds 1 and 2 confirmed that these two compounds were diastereomers [22,23].
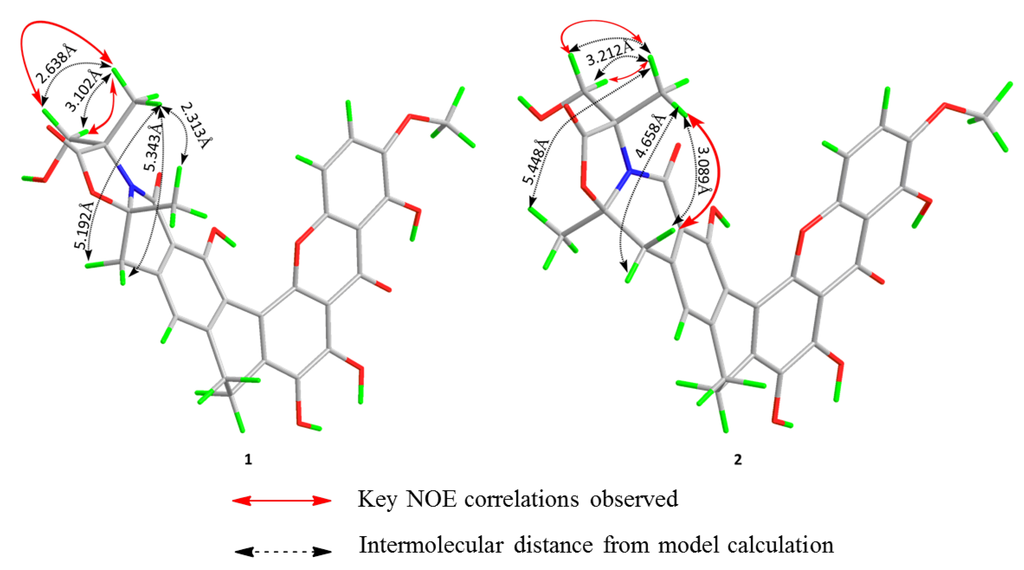
Figure 3.
Key nuclear overhauser effect correlations of compounds 1 and 2 and the optimized 3D model structures.
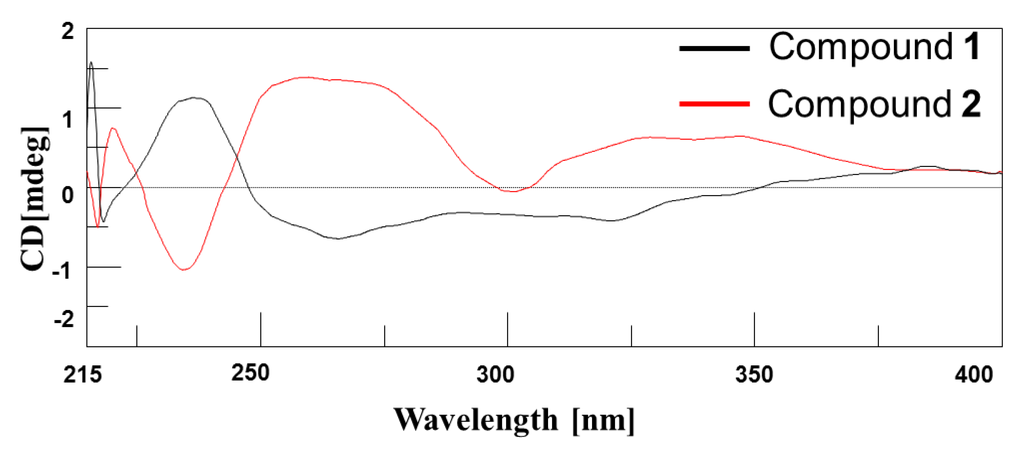
Figure 4.
The circular dichroism spectra of compounds 1 and 2.
Compound 3 has the molecular formula of C27H20O11, as established by the HRESIMS of the pseudomolecular ion peak at m/z 521.1079 [M + H]+ (calcd for 521.1084). The UV spectrum displayed absorption at λmax 238, 298, 412 nm, which is similar to the findings for compound 1. The 1H NMR spectrum revealed the presence of four phenolic protons (δH 9.29, 10.3, 11.7, 12.6), three aromatic protons (δH 6.82, 7.49, 7.63), one methoxy group (δH 3.31), one methyl (δH 1.66), and three methylene groups (Table 2). The 13C NMR spectrum displayed 27 carbon signals, which were classified as three carbonyls (δC 167.5, 169.0, 180.9); nineteen carbons between δC 160 and 100, indicating multiple aromatic rings; three methylene (δC 23.1, 29.6, 36.8), one methoxy (δC 50.1); and one methyl group (δC 21.7). Compound 3 had the same xanthone skeleton as compound 1, but without the G ring.

Table 2.
1H and 13C NMR data for compounds 3 and 4 in DMSO-d6.
| Position | 3 | 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC a | δH (J in Hz) b | δC a | δH (J in Hz) b | |
| 2 | 169.0, qC | 169.2, qC | ||
| 2a | 106.6, qC | 106.7, qC | ||
| 3 | 158.4, qC | 158.0, qC | ||
| 3a | 118.3, qC | 118.8, qC | ||
| 3b | 112.5, qC | 110.5, qC | ||
| 4 | 150.2, qC | 149.9, qC | ||
| 4a | 106.6, qC | 106.7, qC | ||
| 5 | 180.9, qC | 181.2, qC | ||
| 5a | 117.4, qC | 117.9, qC | ||
| 6 | 150.1, qC | 149.9, qC | ||
| 7 | 116.7, qC | 115.9, qC | ||
| 8 | 125.1, CH | 7.49, d (9.1) | 125.6, CH | 7.45, d (9.1) |
| 9 | 119.3, CH | 7.63, d (9.1) | 119.3, CH | 7.37, d (9.1) |
| 9a | 148.6, qC | 147.1, qC | ||
| 10a | 144.1, qC | 144.9, qC | ||
| 11 | 137.5, qC | 118.7, qC | 6.90, s | |
| 11a | 132.3, qC | 135.9, qC | ||
| 12 | 23.1, CH2 | 2.24, m | 23.0, CH2 | 2.23, m |
| 3.31, overlap | 3.25, m | |||
| 13 | 29.6, CH2 | 2.63, m | 29.2, CH2 | 2.64, m |
| 13a | 148.8, qC | 148.9, qC | ||
| 14 | 117.5, CH | 6.82, s | 117.9, CH | 6.84, s |
| 14a | 137.4, qC | 137.7, qC | ||
| 15 | 36.8, CH2 | 3.16, m | 37.8, CH2 | 3.22, m |
| 3.38, m | 3.41, m | |||
| 16 | 106.1, qC | 106.4, qC | ||
| 17 | 21.7, CH3H | 1.66, s | 22.4, CH3 | 1.69, s |
| 18 | 167.5, qC | 167.6, qC | ||
| –OCH3 | 50.1 | 3.31, s | 50.1 | 3.35, s |
| 3-OH | 11.7, s | 11.8, s | ||
| 4-OH | 12.6, s | 12.8, s | ||
| 11-OH | 9.29, s | 9.22, s | ||
| 18-OH | 10.3, s | 10.3, s | ||
a Recorded at 500 MHz; b Recorded at 125 MHz.
The HMBC spectrum of 3 revealed correlations from δH 3.31 and δH 1.66 to δC 106.1 (C-16), indicating the attachment of the methyl and methoxy group at C-16. The downfield chemical shift of C-16 suggests that this quaternary carbon attaches to an additional oxygen. The construction of the F ring was verified by an HMBC correlation from δH 1.66 to carbonyl carbon δC 169.0 (C-2) and δC 36.8 (C-15). HMBC correlation from δH 7.49 (H-8) to δC 167.5 (C-18) provided evidence for the presence of a carboxylic acid group at C-7 (Figure 5), and the planar structure of compound 3 was thus determined to be that shown in Figure 1. However, the relative structure of 3 at C-16 remains unconfirmed due to the limited signals in the NOESY spectrum. Furthermore, since the single crystal of compound 3 was not obtainable, and no CD signal was observed, the absolute configuration of compound 3 is still undetermined.
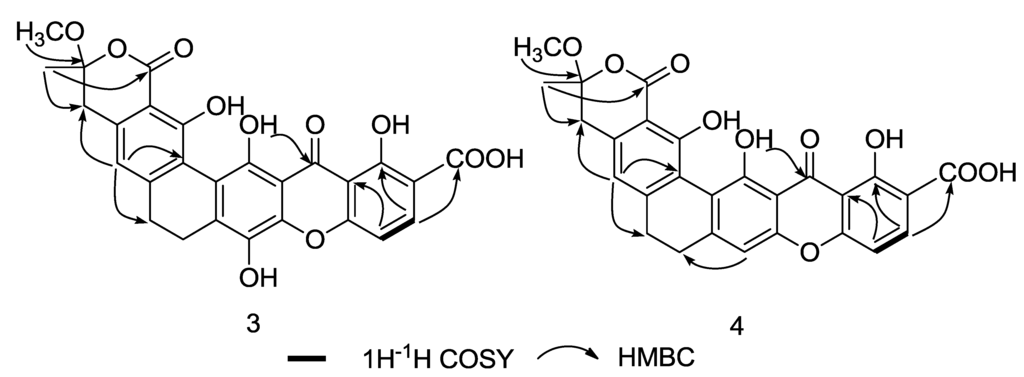
Figure 5.
Key 1H-1H COSY and HMBC correlations of compounds 3 and 4.
Compound 4 has the molecular formula C27H20O10, as deduced from its HRESIMS data ([M + H]+ at m/z 505.1130, calcd for 505.1135), which is 16 Dalton less than the value for compound 3. Comparison of the 1H and 13C NMR spectral data (Table 2) indicates close similarities between 4 and 3, with the only difference occurring at C-11. The phenolic hydroxyl group at C-11 in compound 3 is replaced by an aromatic proton in compound 4, as confirmed by an HMBC correlation in compound 4 from δH 6.90 (H-11) to δC 22.4 (C-12). These findings revealed the structure of 4 to be that shown in Figure 1. The relative configuration at C-16 was again undetermined due to insufficient NOESY key correlations. The absolute configuration of 4 was still unconfirmed due to the absent of single crystal data and the CD signal.
The antibacterial and cytotoxic activity of compounds 1–4 was evaluated. The diastereomers—compounds 1 and 2—showed similar antibacterial activity against four strains: B. subtillis 769, S. haemolyticus UST950701-004, S. aureus UST950701-005, and S. aureus ATCC 43300, with MIC values of ≤1.0 μg/mL. Compounds 3 and 4 also displayed similar biological activity against these bacterial strains, except that compound 4 revealed no activity against S. aureus ATCC 43300. The cytotoxic activity of these four compounds was also assessed against HeLa cells by the standard 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay [24]. Compounds 1 and 2 displayed significant cytotoxic activity at nanomolar concentrations, whereas compounds 3 and 4 showed no activity (Table 3). Compounds 1 and 2 displayed much stronger antibacterial activity than compounds 3 and 4, suggesting that the five-member nitrogen heterocycle, which is absent from compounds 3 and 4, is essential for activity. The five-member nitrogen heterocycle is quite similar to that in oxazolidinones, which are an approved class of antibiotics [25,26]. The mode of action of compounds 1 and 2 with the five-member nitrogen heterocycle is currently being studied.

Table 3.
Antibacterial and cytotoxic activity of compounds 1–4.
| Compound | Antibacterial (MIC, μg/mL) | Cytotoxicity (IC50μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus UST950701-004 | Staphylococcus aureus UST950701-005 | Bacillus subtillis 769 | Staphylococcus aureus ATCC43300 | HeLa cells | |
| 1 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.055 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.072 |
| 3 | 8.0 | 16.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | >40 |
| 4 | 8.0 | 16.0 | 8.0 | NA | >40 |
| Penicillin G | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.13 | NA | NT |
| Streptomycin | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | NA | NT |
| Cisplatin | NT | NT | NT | NT | 18.14 |
NA means MIC > 50 μg/mL, NT means NOT test.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
The 1H, 13C, and 2D NMR spectral data were obtained with Varian Inova 500 MHz and Bruker 700 MHz NMR spectrometers. The ESI and high-resolution mass spectra were acquired from ultra-performance liquid chromatography-time of fly-mass spectrometry (UPLC-TOF-MS). The UPLC system was a Waters ACQUITY UPLC system (Waters, Manchester, UK) coupled with a Bruker microTOF-q II mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics GmbH, Bremen, Germany). The X-ray diffraction study was carried out using a Bruker SMART APEX-2 CCD (Bruker, Rheinstetten, Germany), and the semi-preparative HPLC was performed using a C18 (2) column that was 5 μm and 250 × 10 mm in size. The optical density (OD) measurements in the experiments were recorded at 595 nm on a Thermo scientific Multiskan FC multiplate photometer (Waltham, MA, USA).
3.2. Sample Collection and Microbial Material
The Streptomyces sp. was isolated from the coastal water of the Red Sea by the side of a fish market near Jeddah (21′29.622N 39′09.617E). The total genomic DNA preparation of the strain was carried out following the procedure in the literature [27]. The Blast program was used to assess the DNA similarities in the NCBI Databases. The strain displayed 99% similarity with Streptomyces caelestis strain NRRL 2418. The complete 16S rDNA sequence data suggests that the strain is most closely related to Streptomyces caelestis [28]. The sequence of the strain has been deposited in GenBank with the accession number: JX204833.
3.3. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation
The strain was cultured in 37 × 1.0 L volume of media (10 g/L of starch, 2 g/L of peptone, 4 g/L of yeast extract and 20 g/L sea salt) at 23 °C for 5 days. Each flask contained about 100 glass beads (3 mm in diameter). The spent fermentation culture (37.0 L) was filtered with 8 layers of cheesecloth. The broth was then extracted with ethyl acetate, and the mycelia were extracted with acetone and methanol (1:2 v/v). The extracts from the broth and the mycelia were combined and partitioned between water and hexane three times. The resulting aqueous residue was further extracted with ethyl acetate (EtOAc). The separation of the EtOAc soluble constituents (15.3 mg) was achieved by reverse phase C18 flash chromatography, and elution with solvent mixtures of H2O–MeOH (9:1), H2O–MeOH (7:3), H2O–MeOH (5:5), H2O–MeOH (3:7), H2O–MeOH (9:1), and 100% MeOH. The fraction that was eluted with H2O–MeOH (3:7, v/v) was evaporated, to yield a residue (labeled Fraction (Fr.) B, 630 mg). The Fr. B fraction was then subjected to Sephadex LH-20 eluted with MeOH to yield 14 sub-fractions (named Fr. B-1 to Fr. B-14). The final purification of Fr. B-6 was achieved by reverse-phase semi-preparative HPLC and elution with MeCN–H2O (50:50, (v/v), flow rate: 3 mL/min), to give compounds 1 (2.3 mg) and 2 (3.1 mg) at a retention time of 24.0 min and 29.4 min, respectively. The Fr. B-13 was further purified by the same column and eluted with MeCN–H2O (37:63–50:50, (v/v)) to obtain pure compounds 3 (10.2 mg) and 4 (7.4 mg).
Citreamicin θ A (1): red crystal; [α]25D +59 (c 0.02, MeOH); mp 341.1–349.1 °C; UV λmax(MeOH) nm 237, 278, 323, 441; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1: HRESIMS m/z 576.1508 [M + H]+ (calcs for C30H25NO11 576.1506).
Citreamicin θ B (2): red crystal; [α]25D −43 (c 0.02, MeOH); mp 341.1–349.1 °C; UV λmax (MeOH) nm 237, 278, 323, 441; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1: HRESIMS m/z 576.1500 [M + H]+ (calcs for C30H25NO11 576.1506).
Citreaglycon A (3): red powder; UV λmax (MeOH) nm 238, 298, 412; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 2: HRESIMS m/z 521.1079 [M + H]+ (calcs for C27H20O11 521.1084).
Dehydrocitreaglycon A (4): red powder; UV λmax (MeOH) nm 237, 298, 411; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 2: HRESIMS m/z 505.1130 [M + H]+ (calcs for C27H20O10 505.1135).
3.4. Antibacterial Assays
The minimum inhibitory concentration values (MIC) of compounds 1–4 were determined using a modification of the microdilution method described [29]. In brief, the strains B. subtillis 769, S. haemolyticus UST950701-004, S. aureus UST950701-005, and S. aureus ATCC 43300 were inoculated in Lysogeny broth (LB) (10 g of tryptone, 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of NaCl, 1 L of dd H2O) and were incubated at 28 °C for 12 h. Stock solution of the samples were prepared at 40 mg/mL in DMSO and then further diluted with LB broth to varying concentrations in 96-well plates. The bacteria were incubated at 28 °C overnight. Cell growth was checked by measuring the optical density at 595 nm, with Penicillin G and Streptomycin as positive controls.
3.5. Cytotoxic Assays
The cytotoxicity tests were carried out according to the method previously described by Li et al. [30]. Briefly, HeLa cells were seeded and cultured in 96-well plates 12 h before the addition of the test samples. The compounds were dissolved in DMSO and diluted in the assay media. After incubation of the test samples for 48 h, the cell viability was assayed by the MTT method.
4. Conclusions
Four new xanthones were isolated from a marine-derived Streptomyces caelestis. Compounds 1 and 2, named citreamicin θ A and B, are a pair of diasteromers that possess a 5/6/6/6/6/6/6 seven-ring system. It is the first report of the citreamicins with such a unique ring system that is bending with an acute angle. The similar MIC values of citreamicin θ A (1) and B (2) to those of B. subtillis, S. haemolyticus, and S. aureus, and the MRSA strain indicate that these two diasteromers possess equal antibacterial activity. Citreaglycon A and dehydrocitreaglycon A showed weaker antibacterial activity than citreamicin θ A (1) and citreamicin θ B (2). The greater antibacterial activity of citreamicin θ A (1) and B (2) may be due to the five-member nitrogen heterocycle. The role of this nitrogen heterocycle in citreamicins merits further study.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Hongping He of the Kunming Institute of Botany, China and Rui Feng of Division of Life Science of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology for taking the NMR spectra. This work was supported by a research grant (DY125-15-T-02) from the China Ocean Mineral Resources Research and Development Association and Award No SA-C0040/UK-C001 from the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST).
Supplementary Files
References and Notes
- Gerwick, W.; Moore, B. Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural products drug discovery and chemical biology. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bhakuni, D.S.; Rawat, D.S. Bioactive Marine Natural Products; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2005; pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Seybold, U.; Kourbatova, E.V.; Johnson, J.G.; Halvosa, S.J.; Wang, Y.F.; King, M.D.; Ray, S.M.; Blumberg, H.M. Emergence of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 genotype as a major cause of health care associated blood stream infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, S.E.; Sakoulas, G.; Perencevich, E.N.; Schwaber, M.J.; Karchmer, A.W.; Carmeli, Y. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engemann, J.J.; Carmeli, Y.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Fowler, V.G.; Bronstein, M.Z.; Trivette, S.L.; Briggs, J.P.; Sexton, D.J.; Kaye, K.S. Adverse clinical and economic outcomes attributable to methicillin resistance among patients with Staphylococcus aureus surgical site infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, S.E.; Qi, Y.; Kaye, K.S.; Harbarth, S.; Karchmer, A.W.; Carmeli, Y. The impact of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia on patient outcomes: Mortality, length of stay, and hospital charges. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 2, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Klevens, R.M.; Morrison, M.A.; Nadle, J.; Petit, S.; Gershman, K.; Ray, S.; Harrison, L.H.; Lynfield, R.; Dumyati, G.; Townes, M.; et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA 2007, 298, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Deresinski, S. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An evolutionary, epidemiologic, and therapeutic odyssey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeb, M. Antibiotics: A shot in the arm. Nature 2004, 431, 892–893. [Google Scholar]
- Maiese, W.M.; Lechevalier, M.P.; Lechevalier, H.A.; Korshalla, J.; Goodman, J.; Wildey, M.J.; Kuck, N.; Greenstein, M. LL-E19085 alpha, a novel antibiotic from Micromonospora citrea: Taxonomy, fermentation and biological activity. J. Antibiot. 1989, 42, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.T.; Nietsche, J.A.; Williams, D.R.; Borders, D.B. Citreamicins, novel antibiotics from Micromonospora citrea: Isolation, characterization, and structure determination. J. Antibiot. 1990, 43, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.F.; Lee, V.J.; Ashcroft, J.; Morton, G.O. An unusual cyclization product from the reaction of citreamicin η with sulfene. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 5288–5290. [Google Scholar]
- Hopp, D.C.; Milanowski, D.J.; Rhea, J.; Jacobsen, D.; Rabenstein, J.; Smith, C.; Romari, K.; Clarke, M.; Francis, L.; Irigoyen, M.; et al. Citreamicins with potent gram-positive activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 2032–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Peoples, A.J.; Zhang, Q.; Millett, W.P.; Rothfeder, M.T.; Pescatore, B.C.; Madden, A.A.; Ling, L.L.; Moore, C.M. Neocitreamicins I and II, novel antibiotics with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococci. J. Antibiot. 2009, 61, 457–463. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Xu, Y.; McConnell, O.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Qi, S.; Huang, X.; Qian, P. Two antimycin A analogues from marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces lusitanus. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, X.; Niu, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Ju, J.; Zhang, C. Pseudonocardians A–C, new diazaanthraquinone derivatives from a deep-sea Actinomycete Pseudonocardia sp. SCSIO 01299. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, T.; Ren, X.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Sun, A.; Ma, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, C.; Ju, J. Cytotoxic angucycline class glycosides from the deep sea actinomycete Streptomyces lusitanus SCSIO LR32. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleissner, C.; Perez, M.; Losada, A.; Rodriguez, P.; Crespo, C.; Zuniga, P.; Fernandez, R.; Reyes, F.; De la Calle, F. Antitumor actinopyranones produced by Streptomyces albus POR-04-15-053 isolated from a marine sediment. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratyuk, T.P.; Park, E.J.; Yu, R.; Van Breemen, R.B.; Asolkar, R.N.; Murphy, B.T.; Fenical, W.; Pezzuto, J.M. Novel marine phenazines as potential cancer chemopreventive and anti-inflammatory agents. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X-ray crystallogrphic analysis of compound 1: red crystal, 0.05 × 0.06 × 0.28, C30H23NO10, Mr = 557.49, monoclinic, space group P21/c, a = 15.307(3) Å, b = 7.9472(16) Å, c = 24.715(5) Å, β = 97.18(3)°, V = 2983.0(10) Å3, Z = 4, dx = 1.241 g/cm3, F(000) = 1160, μ(Cu Kα) = 0.795 mm−1. The data collection was performed on a Bruker SMART APEX-II using graphite-monochromated radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å), with 4797 unique reflections collected to θmax = 66.98°, where 2116 reflections were observed [F2 > 2σ(F2)]. The structures were solved by direct methods (SHELXTL, 2008) and refined by full-matrix least-squares on F2. The final R = 0.2224, Rw = 0.5021, and S = 1.848. The final model was not very accurate because of the small size of the crystal. The coordinates of the five-member ring and its side chain could not be determined very precisely.
- Schneider, H.J.; Hacket, F.; Rüdiger, V.; Ikeda, H. NMR studies of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1755–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamese, S.; Manna, L.; Scivoli, G. Chiral HPLC separation and CD spectra of the C-2 diastereomers of naringin in grapefruit during maturation. Chirality 2003, 15, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, R.V.; Monde, K.; Humpf, H.; Berova, N.; Nakanishi, K. A new approach in exciton-coupled circular dichroism (ECCD)—insertion of an auxiliary stereogenic center. Chirality 1995, 7, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bozdogan, B.; Appelbaum, P.C. Oxazolidinones: Activity, mode of action, and mechanism of resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, U.; Yan, Y.P.; Hobbs, F.W., Jr.; Kaczmarczyk, J.; Slee, A.M.; Pompliano, D.L.; Kurilla, M.G.; Bobkova, E.V. Oxazolidinones mechanism of action: Inhibition of the first peptide bond formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37199–37205. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 914–923. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Fluit, A.C.; Lückefahr, M.; Engler, B.; Hofmann, B.; Verhoef, J.; Heinz, H.P.; Hadding, U.; Jones, M.E. The effect of reserpine, an inhibitor of multidrug efflux pumps, on the in vitro activities of ciprofloxacin, sparfloxacin and moxifloxacin against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1998, 42, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Han, Z.; Lai, P.Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, W.; Qian, P.Y. Five new amicoumacins isolated from a marine-derived bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).