Immunoglobulin G Trough Levels and Infection Risk in Adults with Inborn Errors of Immunity Receiving Immunoglobulin Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Immunoglobulin Therapy and Dose Adjustments
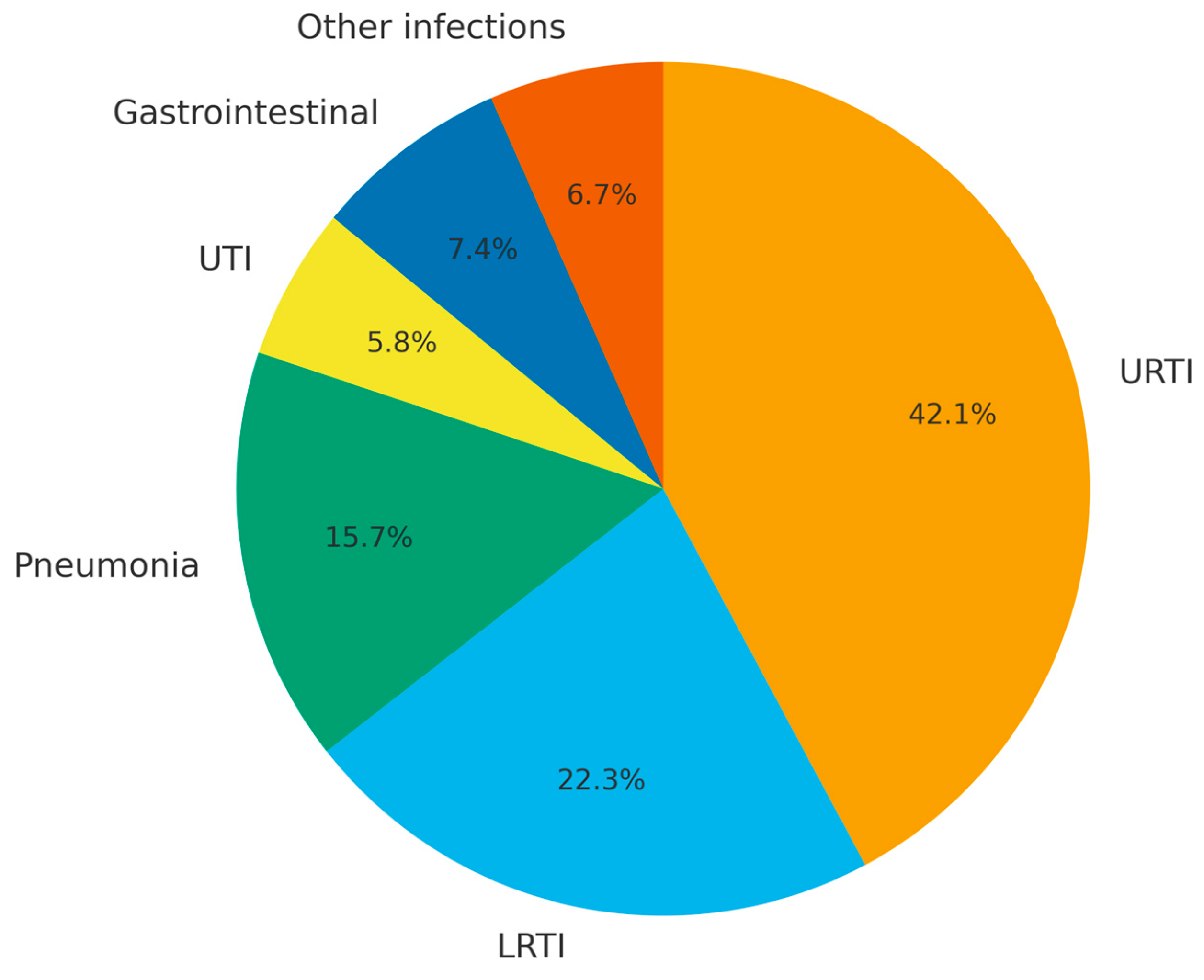
3.3. Infection Outcomes and Association with IgG Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IEI | Inborn Errors Of Immunity |
| PID | Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases |
| PAD | Primary Antibody Deficiency |
| SCID | Severe Combined Immunodeficiency |
| IVIG | Intravenous Immunoglobulin G |
| SCIG | Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin |
| ESID | European Society For Immunodeficiencies |
| CVID | Common Variable Immunodeficiency |
| XLA | X-linked agammaglobulinemia |
References
- Tangye, S.G.; Al-Herz, W.; Bousfiha, A.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Oksenhendler, E.; Picard, C.; et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2022 Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1473–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Frange, P.; Blanche, S.; Casanova, J.L. Pathogenesis of infections in HIV-infected individuals: Insights from primary immunodeficiencies. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 48, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiding, J.W.; Forbes, L.R. Mechanism-Based Precision Therapy for the Treatment of Primary Immunodeficiency and Primary Immunodysregulatory Diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivan, G.; Jolles, S.; Granados, E.L.; Paolantonacci, P.; Ouaja, R.; Cissé, O.A.; Bernatowska, E. New insights in the use of immunoglobulins for the management of immune deficiency (PID) patients. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 6, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Durandy, A.; Kracker, S.; Fischer, A. Primary antibody deficiencies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, E.E.; Orange, J.S.; Bonilla, F.; Chinen, J.; Chinn, I.K.; Dorsey, M.; El-Gamal, Y.; Harville, T.O.; Hossny, E.; Mazer, B.; et al. Update on the use of immunoglobulin in human disease: A review of evidence. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S1–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolhassani, H.; Asgardoon, M.H.; Rezaei, N.; Hammarstrom, L.; Aghamohammadi, A. Different brands of intravenous immunoglobulin for primary immunodeficiencies: How to choose the best option for the patient? Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, F.A.; Khan, D.A.; Ballas, Z.K.; Chinen, J.; Frank, M.M.; Hsu, J.T.; Keller, M.; Kobrynski, L.J.; Komarow, H.D.; Mazer, B.; et al. Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1186–1205.e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleba, T.; Ensom, M.H. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous immunoglobulin: A systematic review. Pharmacotherapy 2006, 26, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roifman, C.M.; Berger, M.; Notarangelo, L.D. Management of primary antibody deficiency with replacement therapy: Summary of guidelines. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2008, 28, 875–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, J.S.; Grossman, W.J.; Navickis, R.J.; Wilkes, M.M. Impact of trough IgG on pneumonia incidence in primary immunodeficiency: A meta-analysis of clinical studies. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 137, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, P.; Karmacharya, P.; Wang, Z.; Donato, A.; Joshi, A.Y. Impact of IVIG vs. SCIG on IgG trough level and infection incidence in primary immunodeficiency diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.L.; Mohamed Shah, N.; Makmor-Bakry, M.; Islahudin, F.H.; Alias, H.; Noh, L.M.; Mohd Saffian, S. A Systematic Review and Meta-regression Analysis on the Impact of Increasing IgG Trough Level on Infection Rates in Primary Immunodeficiency Patients on Intravenous IgG Therapy. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 682–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dropulic, L.K.; Cohen, J.I. Severe viral infections and primary immunodeficiencies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, M.; Lee, M.; Lortan, J.; Lopez-Granados, E.; Misbah, S.; Chapel, H. Infection outcomes in patients with common variable immunodeficiency disorders: Relationship to immunoglobulin therapy over 22 years. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1354–1360.e1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.A. The Preparation of Future Statistically Oriented Physicians: A Single-Center Experience in Saudi Arabia. Medicina 2024, 60, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.; Stanworth, S.; Burton, J.; Jones, A.; Peckham, D.G.; Green, T.; Hyde, C.; Chapel, H. Recognition, clinical diagnosis and management of patients with primary antibody deficiencies: A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 149, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, D.; Bhattad, S.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, A.; Rawat, A.; Sehgal, S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, S. Serial Serum Immunoglobulin G (IgG) Trough Levels in Patients with X-linked Agammaglobulinemia on Replacement Therapy with Intravenous Immunoglobulin: Its Correlation with Infections in Indian Children. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Grimbacher, B.; Boecking, C.; Chee, R.; Allgar, V.; Holding, S.; Wong, G.; Huissoon, A.; Herriot, R.; Doré, P.; et al. Serum trough IgG level and annual intravenous immunoglobulin dose are not related to body size in patients on regular replacement therapy. Drug Metab. Lett. 2011, 5, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoraro, A.; Ricci, S.; Vultaggio, A.; Boggia, G.M.; Spadaro, G. Correlations Among Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin Dosage, Immunoglobulin G Serum Pre-infusional Levels and Body Mass Index in Primary Antibody Deficiency Patients: A Pooled Analysis from the SHIFT/IBIS Studies. Clin. Drug Investig. 2020, 40, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.K.; Betschel, S.D. Timing of infections in patients with primary immunodeficiencies treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg). Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballow, M. Optimizing immunoglobulin treatment for patients with primary immunodeficiency disease to prevent pneumonia and infection incidence: Review of the current data. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111, S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M. Incidence of infection is inversely related to steady-state (trough) serum IgG level in studies of subcutaneous IgG in PIDD. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro-Sampaio, M.; Coutinho, A. Immunity to microbes: Lessons from primary immunodeficiencies. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 12 (38.7%) |
| Male | 19 (61.3%) |
| Mean age, years (SD) | 36.4 ± 14.2 Median: 37.5 (range: 19–69) |
| Diagnosis | |
| Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) | 29 (93.5%) |
| X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) | 2 (6.5%) |
| Mean age at diagnosis, years (SD) | 28.1 ± 17 Median: 30 (range: 2–63) |
| Follow-up duration, months | Median: 13 (range: 6–72) |
| Comorbidities At least one comorbidity | 23 (74.2%) |
| Autoimmune disease | 18 (58.1%) |
| Bronchiectasis | 13 (41.9%) |
| Asthma | 5 (16.3%) |
| Lymphoma | 2 (6.5%) |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 5 (16.1%) |
| No comorbidity | 8 (25.8%) |
| Baseline IgG level, mg/dL (SD) | 366 ± 248 |
| Mean IgG trough level, mg/dL (SD) | 815.8 ± 205.9 |
| Mean IVIG dose, mg/kg/month (SD) | 498.8 ± 93.0 Median: 477.2 (range: 365.9–692.3) |
| Infection frequency, n (%) | |
| At least one major infection | 14 (45.2%) |
| Only minor infections | 17 (54.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aktaş, Ö.Ö.; Özer, N.O.; Kaplankıran, C.; Akın, B.G.; Ozturk, B.O.; Durmaz, M.S.B.; Kalkan, F.; Soyyiğit, Ş. Immunoglobulin G Trough Levels and Infection Risk in Adults with Inborn Errors of Immunity Receiving Immunoglobulin Therapy. Medicina 2025, 61, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091549
Aktaş ÖÖ, Özer NO, Kaplankıran C, Akın BG, Ozturk BO, Durmaz MSB, Kalkan F, Soyyiğit Ş. Immunoglobulin G Trough Levels and Infection Risk in Adults with Inborn Errors of Immunity Receiving Immunoglobulin Therapy. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091549
Chicago/Turabian StyleAktaş, Özge Öztürk, Nagihan Orhan Özer, Ceren Kaplankıran, Begüm Görgülü Akın, Betul Ozdel Ozturk, Makbule Seda Bayrak Durmaz, Fikriye Kalkan, and Şadan Soyyiğit. 2025. "Immunoglobulin G Trough Levels and Infection Risk in Adults with Inborn Errors of Immunity Receiving Immunoglobulin Therapy" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091549
APA StyleAktaş, Ö. Ö., Özer, N. O., Kaplankıran, C., Akın, B. G., Ozturk, B. O., Durmaz, M. S. B., Kalkan, F., & Soyyiğit, Ş. (2025). Immunoglobulin G Trough Levels and Infection Risk in Adults with Inborn Errors of Immunity Receiving Immunoglobulin Therapy. Medicina, 61(9), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091549








