Selective Cytopheretic Device Therapy in the Context of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Selective Cytopheretic Device (SCD) Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
3. Preclinical Experience: SCD/LMOD in ECMO and CPB
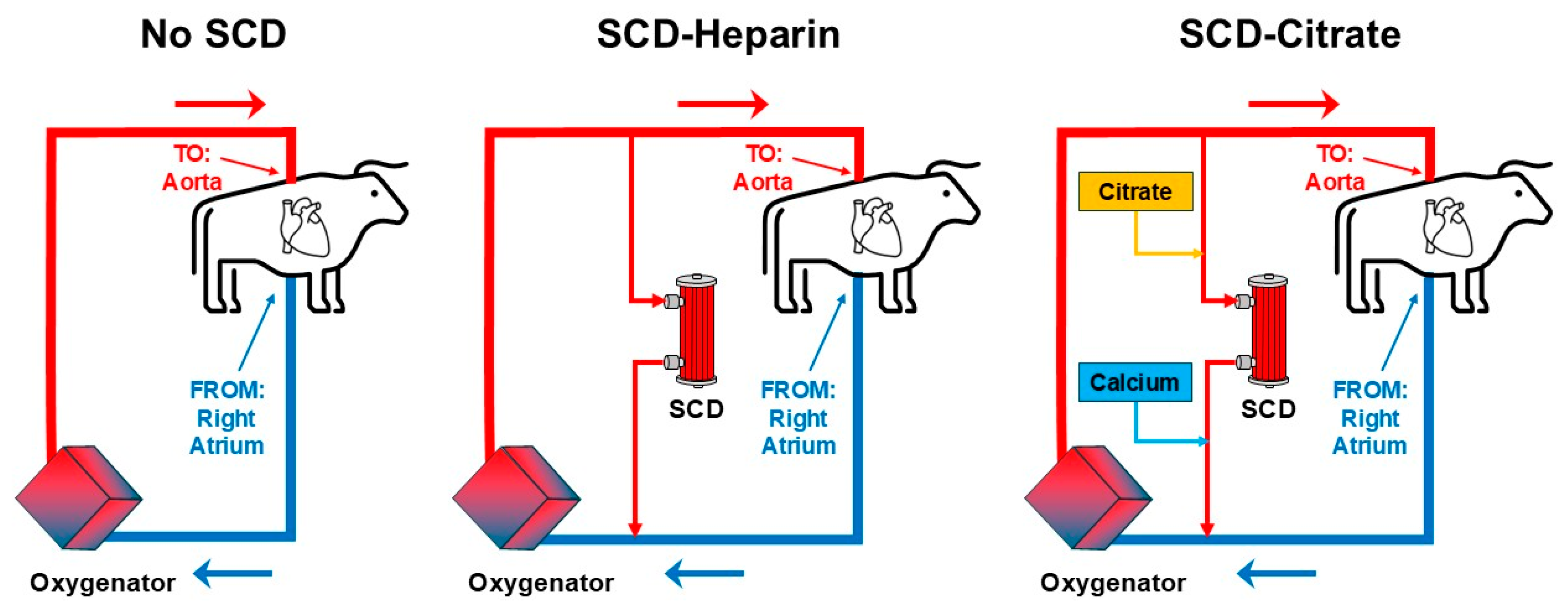
4. Preclinical Bovine CPB Model
5. Preclinical Porcine CPB Model
6. Preclinical Porcine Model of Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (EPR) Supported with ECMO
7. Pediatric Clinical Data
8. Clinical: Adult Patient Data Gathered to Date
9. Discussion
9.1. Issues in Clinical Trial Design
9.2. SCD/LMOD Addresses Several Mechanisms of Action
9.3. LMOD/SCD Circuit Considerations
9.4. Future Directions: Use of ECMO and SCD to Improve Transplantation
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | angiotensin converting enzyme |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ARDS | acute respiratory dysfunction syndrome |
| BFR | blood flow rate |
| BTT | bridge to transplant |
| CKRT | continuous kidney replacement therapy |
| CPB | cardiopulmonary bypass |
| CPR | cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| CVVH | continuous veno-venous hemofiltration |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
| ECPR | extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| ESRD | end stage renal disease |
| EUA | emergency use authorization |
| FDA | Federal Drug Administration |
| HDE | humanitarian use device exemption |
| HLH | hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
| HRS | hepatorenal syndrome |
| iCa | ionized calcium |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| IDE | investigational device exemption |
| IRI | ischemia reperfusion injury |
| LE | leukocyte |
| LF | leukofilter |
| LMOD | Leukocyte Modulating Device |
| LVAD | left ventricular assist device |
| MO | monocyte |
| MOD | multiple organ dysfunction |
| MODS | multiple organ dysfunction syndrome |
| MOF | multiple organ failure |
| NET | neutrophil extracellular trap |
| NICU | neonatal intensive care unit |
| NE | neutrophil |
| PICU | pediatric neonatal intensive care unit |
| RAD | Renal Assist Device |
| RCA | regional citrate anticoagulation |
| SCD | Selective Cytopheretic Device |
| SIRS | systemic inflammatory response syndrome |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor α |
| VA ECMO | venous–arterial ECMO |
| VV ECMO | veno-venous ECMO |
References
- Ortiz-Prado, E.; Izquierdo-Condoy, J.S.; Vasconez-Gonzalez, J.; Lopez-Cortes, A.; Salazar-Santoliva, C.; Vargas Michay, A.R.; Velez-Paez, J.L.; Unigarro, L. From pandemic onset to present: Five years of insights into ARDS caused by COVID-19. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2025, 19, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklienka, P.; Bursa, F.; Frelich, M.; Maca, J.; Romanova, T.; Vodicka, V.; Strakova, H.; Bilena, M.; Jor, O.; Neiser, J.; et al. Lessons Learned From Awake ECMO Approach in COVID-19-Related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome—A Scoping Review. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2025, 21, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijeiro-Paradis, R.; Gannon, W.D.; Fan, E. Complications Associated With Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation-What Can Go Wrong? Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, M.; Filipsky, R.; Bukowski, N.; Gerger, G.; Hermann, A.; Krenn, K.; Teufel, A.; Kimberger, O.; Laxar, D.; Maleczek, M.; et al. Long-Term Health-Related Quality of Life Following Survival of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Due to COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursu, E.; Mikolic, A.; Tong, B.; Silverberg, N.D.; Parag, N.; Foster, D.; Sekhon, M.S.; Panenka, W.; Thiara, S.; Griesdale, D.E.G. Functional outcomes among the survivors of veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during the COVID-19 pandemic: A historical cohort study. Can. J. Anaesth. 2025, 72, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Yao, C.; Xu, G.; Wang, J.; Shou, S.; Jin, H. Research progress on the pathogenesis of AKI complicated by ECMO. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2025, 29, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skogby, M.; Adrian, K.; Friberg, L.G.; Mellgren, G.; Mellgren, K. Influence of hemofiltration on plasma cytokine levels and platelet activation during extra corporeal membrane oxygenation. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2000, 34, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, R.E.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, K.; Jeon, J.; Jang, H.R.; Chung, C.R.; Cho, Y.H.; Park, T.K.; Lee, J.M.; Song, Y.B.; et al. The effects of extracorporeal blood purification (oXiris(R)) in patients with cardiogenic shock who require VA-ECMO (CLEAN ECMO): A prospective, open-label, randomized controlled pilot study. Crit. Care 2025, 29, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, S.; Ying, J.; Qu, Y. Neutrophils: A key component in ECMO-related acute organ injury. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1432018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boodram, S.; Evans, E. Use of leukocyte-depleting filters during cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: A review. J. Extra Corpor. Technol. 2008, 40, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Song, J.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Lou, L.; Wang, M.; Charles, L.; Westover, A.; Smith, P.L.; Pino, C.J.; Buffington, D.A.; et al. A biomimetic membrane device that modulates the excessive inflammatory response to sepsis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, C.J.; Westover, A.J.; Johnston, K.A.; Buffington, D.A.; Humes, H.D. Regenerative Medicine and Immunomodulatory Therapy: Insights From the Kidney, Heart, Brain, and Lung. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortenberry, J.D.; Bhardwaj, V.; Niemer, P.; Cornish, J.D.; Wright, J.A.; Bland, L. Neutrophil and cytokine activation with neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Pediatr. 1996, 128 Pt 1, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, T.; Palmer, B.F. Review of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and Dialysis-Based Liver Support Devices for the Use of Nephrologists. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 46, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amerson, S.J.; Hoffman, M.; Abouzahr, F.; Ahmad, M.; Sterling, R.K.; Gidwani, H.; Sousse, L.E.; Dellavolpe, J.D. Sequential Extracorporeal Therapy of Pathogen Removal Followed by Cell-Directed Extracorporeal Therapy in Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Refractory to Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Case Report. Crit. Care Explor. 2024, 6, e1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, H.D.; MacKay, S.M.; Funke, A.J.; Buffington, D.A. The bioartificial renal tubule assist device to enhance CRRT in acute renal failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1997, 30 (Suppl. S4), S28–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumlin, J.; Wali, R.; Williams, W.; Murray, P.; Tolwani, A.J.; Vinnikova, A.K.; Szerlip, H.M.; Ye, J.; Paganini, E.P.; Dworkin, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of renal tubule cell therapy for acute renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumlin, J.A.; Chawla, L.; Tolwani, A.J.; Mehta, R.; Dillon, J.; Finkel, K.W.; DaSilva, J.R.; Astor, B.C.; Yevzlin, A.S.; Humes, H.D. The effect of the selective cytopheretic device on acute kidney injury outcomes in the intensive care unit: A multicenter pilot study. Semin. Dial. 2013, 26, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, C.J.; Yevzlin, A.S.; Lee, K.; Westover, A.J.; Smith, P.L.; Buffington, D.A.; Humes, H.D. Cell-based approaches for the treatment of systemic inflammation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westover, A.J.; Humes, H.D.; Pino, C.J. Immunomodulatory effects of a cell processing device to ameliorate dysregulated hyperinflammatory disease states. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, C.J.; Johnston, K.A.; Westover, A.J.; Humes, H.D. Selective Cytopheretic Device (QUELimmune): A Leukocyte Processing, Immunomodulatory Device. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2025, 36, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhuja, A.; McCarthy, P.; Hayanga, J.A.; Turley, S.; Smith, G.; Kellum, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Patients: National Analysis of Impact of Age. Blood Purif. 2022, 51, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.A.; Westover, A.J.; Rojas-Pena, A.; Haft, J.W.; Toomasian, J.M.; Johnson, T.; Buffington, D.A.; Humes, H.D. Novel Leukocyte Modulator Device Reduces the Inflammatory Response to Cardiopulmonary Bypass. ASAIO J. 2019, 65, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, C.J.; Lou, L.; Smith, P.L.; Ding, F.; Pagani, F.D.; Buffington, D.A.; Humes, H.D. A selective cytopheretic inhibitory device for use during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Perfusion 2012, 27, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanZalen, J.J.; Nakashima, T.; Phillips, A.; Hill, J.E.; Westover, A.J.; Lou, L.; Liao, J.; Mergos, J.; Fogo, G.; Sanderson, T.H.; et al. Leukocyte filtration and leukocyte modulation therapy during extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a porcine model of prolonged cardiac arrest. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salis, S.; Mazzanti, V.V.; Merli, G.; Salvi, L.; Tedesco, C.C.; Veglia, F.; Sisillo, E. Cardiopulmonary bypass duration is an independent predictor of morbidity and mortality after cardiac surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2008, 22, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, J.W.; James, M.T.; Palmer, S.C. Acute kidney injury and prognosis after cardiopulmonary bypass: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesouhaitier, M.; Belicard, F.; Tadie, J.M. Cardiopulmonary bypass and VA-ECMO induced immune dysfunction: Common features and differences, a narrative review. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.L.; Askenazi, D.J.; Basu, R.K.; Selewski, D.T.; Paden, M.L.; Krallman, K.A.; Kirby, C.L.; Mottes, T.A.; Terrell, T.; Humes, H.D. Use of the Selective Cytopheretic Device in Critically Ill Children. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.L.; Ollberding, N.J.; Askenazi, D.J.; Basu, R.K.; Selewski, D.T.; Krallman, K.A.; Yessayan, L.; Humes, H.D. Selective Cytopheretic Device Use in Continuous Kidney Replacement Therapy in Children: A Cohort Study With a Historical Comparator. Kidney Med. 2024, 6, 100792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yessayan, L.; Szamosfalvi, B.; Napolitano, L.; Singer, B.; Kurabayashi, K.; Song, Y.; Westover, A.; Humes, H.D. Treatment of Cytokine Storm in COVID-19 Patients With Immunomodulatory Therapy. ASAIO J. 2020, 66, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yessayan, L.T.; Neyra, J.A.; Westover, A.J.; Szamosfalvi, B.; Humes, H.D. Extracorporeal Immunomodulation Treatment and Clinical Outcomes in ICU COVID-19 Patients. Crit. Care Explor. 2022, 4, e0694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yessayan, L.; Humes, H.D.; Scribe, E.C.; Iyer, S.P.N.; Chung, K.K. Rationale and Design of NEUTRALIZE-AKI: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled, Pivotal Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of a Selective Cytopheretic Device in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury Requiring Continuous Kidney Replacement Therapy. Nephron 2024, 148, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Marmol, G.; Moyon, Q.; Combes, A. Temporary circulatory support for cardiogenic shock. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2025, 31, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiritano, F.; Serraino, G.F.; Ten Cate, H.; Fina, D.; Matteucci, M.; Mastroroberto, P.; Lorusso, R. Platelets and extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation in adult patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccioli, E.; Terzi, S.; Pangoni, A.; Lomangino, I.; Rossi, S.; Lloret, A.; Cannone, G.; Marino, C.; Catelli, C.; Dell’Amore, A. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in lung transplantation: Indications, techniques and results. World J. Transplant. 2021, 11, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipograf, Y.; Salna, M.; Minko, E.; Grogan, E.L.; Agerstrand, C.; Sonett, J.; Brodie, D.; Bacchetta, M. Outcomes of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Bridge to Lung Transplantation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabrias Fernandez de Sevilla, R.; Sanchez Cervino, A.C.; Laporta Hernandez, R.; Aguilar Perez, M.; Garcia Fadul, C.; Garcia-Masedo Fernandez, S.; Sanchez Guerrero, A.; Ussetti Gil, M.P. Impact of Neutropenia on Clinical Outcomes after Lung Transplantation. Med. Sci. 2024, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, H.D.; Westover, A.J. Experience With Pediatric Medical Device Development. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Somer, F.; Swol, J. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation from last resort to indispensable tool in the treatment of respiratory and/or circulatory failure. Perfusion 2024, 39 (Suppl. S1), 3S–4S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swol, J. An extracorporeal membrane oxygenation journey from rescue to standard and protective organ support. Perfusion 2024, 39, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukreja, J.; Tsou, S.; Chen, J.; Trinh, B.N.; Feng, C.; Golden, J.A.; Hays, S.; Deuse, T.; Singer, J.P.; Brzezinski, M. Risk Factors and Outcomes of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Bridge to Lung Transplantation. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 32, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprarola, S.D.; Ng, D.K.; Carroll, M.K.; Tekes, A.; Felling, R.J.; Salorio, C.F.; Almuqati, R.; Schwartz, J.M.; Everett, A.D.; Bembea, M.M. Pediatric ECMO: Unfavorable outcomes are associated with inflammation and endothelial activation. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.E.; Fanning, J.P.; McDonald, C.I.; McAuley, D.F.; Fraser, J.F. The inflammatory response to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO): A review of the pathophysiology. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.P.N.; Pino, C.J.; Yessayan, L.T.; Goldstein, S.L.; Weir, M.R.; Westover, A.J.; Catanzaro, D.A.; Chung, K.K.; Humes, H.D. Increasing Eligibility to Transplant Through the Selective Cytopheretic Device: A Review of Case Reports Across Multiple Clinical Conditions. Transplant. Direct 2024, 10, e1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasasna, I.; Andrew, B.; Rothenberg, P.; Platten, M.; Rajjoub, H.; White, D.; Ganoe, A.; Sappington, P.; McCarthy, P.; Hayanga, J.W.A. Surviving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Is a Longitudinal Process: Exploring a Survivorship Model to Improve Quality of Life. Ann. Thorac. Surg. Short. Rep. 2025, 3, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, H.D.; Aaronson, K.D.; Buffington, D.A.; Sabbah, H.N.; Westover, A.J.; Yessayan, L.T.; Szamosfalvi, B.; Pagani, F.D. Translation of immunomodulatory therapy to treat chronic heart failure: Preclinical studies to first in human. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0273138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szamosfalvi, M.; Pino, C.J.; Humes, H.D. Selective Cytopheretic Device Therapy in the Context of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Medicina 2025, 61, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091513
Szamosfalvi M, Pino CJ, Humes HD. Selective Cytopheretic Device Therapy in the Context of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091513
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzamosfalvi, Marton, Christopher J. Pino, and H. David Humes. 2025. "Selective Cytopheretic Device Therapy in the Context of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091513
APA StyleSzamosfalvi, M., Pino, C. J., & Humes, H. D. (2025). Selective Cytopheretic Device Therapy in the Context of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Medicina, 61(9), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091513







