Scoping Review—The Effectiveness of Clear Aligners in the Management of Anterior Open Bite in Adult Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Map the literature on treatment protocols (e.g., anterior extrusion, posterior intrusion and refinement procedures) employed with CAs;
- -
- Evaluate clinical outcomes comparing incisor and molar movements, overbite correction and mandibular rotation effects;
- -
- Identify key influencing factors—patient compliance, clinician expertise and aligner material properties—and outline potential limitations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Question & Protocol
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- -
- Population: adult patients (≥18 years) with anterior open-bite malocclusion;
- -
- Intervention: treatment with CA;
- -
- Study Designs: case reports/series, retrospective and prospective observational studies and randomized controlled trial studies (RCTs);
- -
- Language: articles published in English from January 2000 to December 2024.
- -
- Studies focusing on pediatric/adolescent patients (due to differences in growth dynamics);
- -
- Studies lacking detailed methodological descriptions concerning treatment planning and outcome evaluation;
- -
- Narrative reviews, systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.4. Selection of Sources of Evidence
2.5. Data Charting Process
- -
- Publication data;
- -
- Study design, type of intervention and sample size;
- -
- Description of the clear aligner treatment protocol (treatment phases, including anterior extrusion, posterior intrusion, refinements and auxiliary devices);
- -
- Outcome measures: overbite correction, incisor extrusion and molar intrusion values, mandibular rotation and treatment duration;
- -
- Reported limitations and recommendations;
- -
- Main conclusions as reported by the study authors.
2.6. Synthesis of Results
3. Results
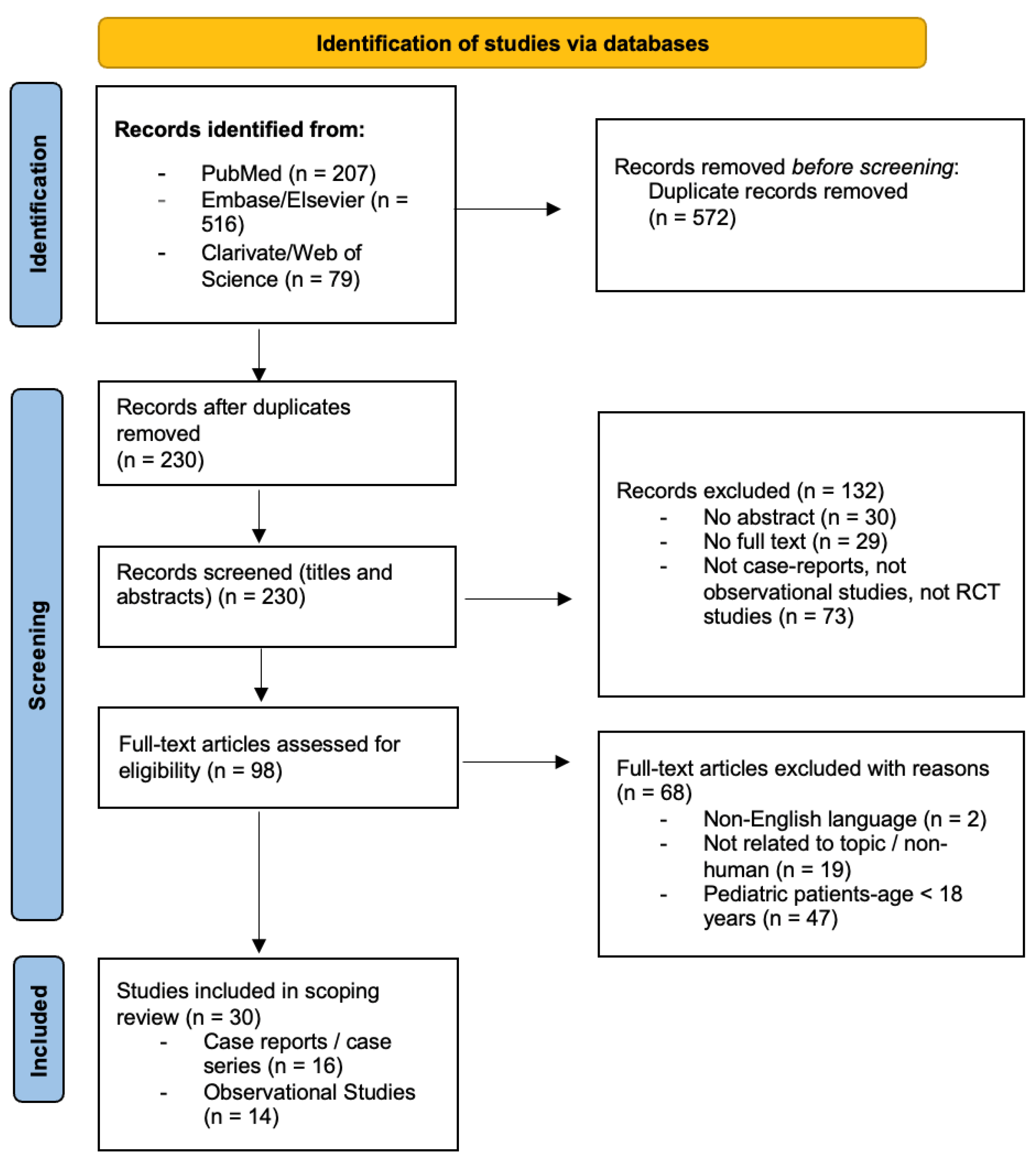
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
4. Discussion
4.1. Treatment Goals
4.1.1. Desired Tooth Movements
4.1.2. Posterior Intrusion and/or Anterior Extrusion
4.1.3. Refinements and Treatment Adjustments
4.1.4. Retention Protocol
4.2. Influencing Factors and Treatment Outcomes
4.2.1. Patient-Related Factors
4.2.2. Clinician-Related Factors
4.2.3. Technology-Related Factors
4.3. Outcome Measures and Comparative Effectiveness
4.4. Recommendations for Improved Aligner Use
4.5. Study Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torkan, S.; Firth, F.; Fleming, P.S.; Kravitz, N.D.; Farella, M.; Huang, G.J. Retention: Taking a more active role. Br. Dent. J. 2021, 230, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C.L. Efficacy of clear aligners in controlling orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, G.M.; Huang, G.J.; Chen, S.S.; Chen, J.; Koepsell, T.; Hujoel, P. Stability of treatment for anterior open-bite malocclusion: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 139, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Kaur, H.; Fagundes, N.C.F.; Romanyk, D.; Major, P.; Flores Mir, C. Effectiveness of clear aligner therapy for orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 23, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, S.P.; Zafra, J.L. Vertical problems. In Aligner Techniques in Orthodontics; Moya, S.P., Zafra, J.L., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 355–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, B.S.; Mahood, K.; Nguyen, M.; Al-Katheeb, A.; Liu, S.; Boyd, R.; Oh, H. Cephalometric comparison of adult anterior open bite treatment using clear aligners and fixed appliances. Angle Orthod. 2019, 89, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, S.; Araújo, E.A.; McCray, J.F.; Thiesen, G.; Kim, K.B. Cephalometric evaluation of adult anterior open bite non-extraction treatment with Invisalign®. Dent. Press. J. Orthod. 2017, 22, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.; Ojima, K.; Dan, C.; Upadhyay, M.; Alshehri, A.; Kuo, C.L.; Mu, J.; Uribe, F.; Nanda, R. Evaluation of open bite closure using clear aligners: A retrospective study. Prog. Orthod. 2020, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, H.L.; Weir, T.; Byrne, G. Predictability of anterior open bite treatment with Invisalign®. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 164, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.; Garnett, B.S.; Mahood, K.; Boyd, R.L.; Oh, H. Short-term stability of anterior open bite treatment with clear aligners in adults. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 164, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorna, M.; Marek, I.; Kučera, J.; Tycová, H.; Tvardek, J. Cephalometric changes following clear aligner treatment in patients with anterior open bite. J. Aligner Orthod. 2022, 6, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Rask, H.; English, J.D.; Colville, C.; Kasper, F.K.; Gallerano, R.; Jacob, H.B. Cephalometric evaluation of changes in vertical dimension and molar position in adult non-extraction treatment with clear aligners and traditional fixed appliances. Dent. Press. J. Orthod. 2021, 26, e2119360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kau, C.H.; Feinberg, K.B.; Christou, T. Effectiveness of clear aligners in treating patients with anterior open bite: A retrospective analysis. J. Clin. Orthod. 2017, 51, 454–460. [Google Scholar]
- Todoki, L.S.; Finkleman, S.A.; Funkhouser, E.; Greenlee, G.M.; Choi, K.W.; Ko, H.C.; Wang, H.F.; Shapiro, P.A.; Khosravi, R.; Baltuck, C.; et al. The National Dental Practice-Based Research Network Adult Anterior Open Bite Study: Treatment success. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 158, e137–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, T.; Santos, M. Skeletal open bite treated with clear aligners and miniscrews. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 159, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxler, R. Correcting skeletal open bite with clear aligners and miniscrews. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 160, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, Y.; Goyal, M.; Kumar, M.; Kaur, A. Skeletal open bite treated with clear aligners and miniscrews. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 160, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadera, K.J.; Jagtap, S.B.; Shah, Y.A.; Deshmukh, S.V. Nonsurgical management of skeletal Class III malocclusion and dentoalveolar open bite with clear aligners. AJO-DO Clin. Companion 2023, 3, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancotti, A.; Garino, F.; Mampieri, G. Use of clear aligners in open bite cases: An unexpected treatment option. J. Orthod. 2017, 44, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalikkattil, T.L.; Batra, N.; Vivek, C.R.; Reddy, V.; Manimegalan, P.; Tom, A. Effectiveness of Invisalign Treatment on Open Bite Correction. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16, S850–S852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, B.P.; Pandis, N.; Darendeliler, M.A.; Papadopoulou, A.K. A comparative assessment of the dentoskeletal effects of clear aligners vs miniplate-supported posterior intrusion with fixed appliances in adult patients with anterior open bite. A multicenter, retrospective cohort study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2022, 162, 214–228.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burashed, H. The efficacy of anterior open bite closure when using Invisalign®’s optimized extrusion versus conventional attachments. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2023, 12, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, R.; Cohanim, B.; Hujoel, P.; Daher, S.; Neal, M.; Liu, W.; Huang, G. Management of overbite with the Invisalign appliance. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 691–699.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberland, S.; Nataf, N. Noninvasive conservative management of anterior open bite treated with TADs versus clear aligner therapy. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2024, 28, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangalli, L. Invisalign System as a Treatment of a Skeletal Open Bite. A Case Report with a 5-Year Follow-up. J. Dent. Rep. 2021, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bialy, T. The Use of High Frequency Vibration and Clear Aligners in Management of an Adult Patient with Class III Skeletal Malocclusion with Open Bite and Severe Bimaxillary Protrusion: Case Report. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarneri, M.P.; Oliverio, T.; Silvestre, I.; Lombardo, L.; Siciliani, G. Open bite treatment using clear aligners. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, W.; Haubrich, J.; Neumann, I. Treatment of anterior open bite with the Invisalign system. J. Clin. Orthod. 2010, 44, 501–507. [Google Scholar]
- Gudhimella, S.; Gandhi, V.; Schiro, N.L.; Janakiraman, N. Management of Anterior Open Bite and Skeletal Class II Hyperdivergent Patient with Clear Aligner Therapy. Turk. J. Orthod. 2022, 35, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.; Rossini, G.; Rombolà, A. Simplifying the approach of open bite treatment with aligners and selective micro-osteoperforations: An adult case report. Int. Orthod. 2021, 19, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouni, W.; Venugopal, A.; Adel, S.M.; Vaid, N. Correction of anterior open bite of varying severity using clear aligner therapy—A case series. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepedino, M.; Iancu Potrubacz, M.; Esposito, R.; Staderini, E.; Ciavarella, D. Open Bite Treatment with Combined Aligners and Myofunctional Appliances: A Case Report. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, H.L. Nonextraction treatment of a Class II open bite in an adult patient. J. Clin. Orthod. 2012, 46, 367–371. [Google Scholar]
- Haubrich, J.; Schupp, W. Open bite treatment with aligner orthodontics. J. Aligner Orthod. 2023, 7, 195–216. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Niu, Q.; Wang, A.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Jin, Z. Clear aligner treatment for an adult with severe anterior open bite malocclusion. AJO-DO Clin. Companion 2022, 2, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, K.; Dan, C.; Watanabe, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Nanda, R. The biomechanics of aligner orthodontics in open-bite cases. J. Clin. Orthod. 2019, 53, 699–712. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, R.M. Space closure using aligners. Dent. Press. J. Orthod. 2020, 25, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, N.D.; Kusnoto, B.; BeGole, E.; Obrez, A.; Agran, B. How well does Invisalign work? A prospective clinical study evaluating the efficacy of tooth movement with Invisalign®. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagravère, M.O.; Flores-Mir, C. The treatment effects of Invisalign orthodontic aligners: A systematic review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2005, 136, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampieri, G.; Condò, R.; Di Caccamo, G.; Pirelli, P.; Giancotti, A. Clear Aligner Treatments in Orthoperio Patients. Case Rep. Dent. 2022, 2022, 8932770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, S.; Martini, M.; Bordegoni, M.; Razionale, A.V. Predictability of root movements using virtual root setup in a patient with periodontal disease treated with clear aligners. Open Dent. J. 2021, 15, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.L. Periodontal and restorative considerations with clear aligner treatment to establish a more favorable restorative environment. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2009, 30, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caruso, S.; Darvizeh, A.; Zema, S.; Gatto, R.; Nota, A. Management of a Facilitated Aesthetic Orthodontic Treatment with Clear Aligners and Minimally Invasive Corticotomy. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelotti, A.; Rongo, R.; D’Antò, V.; Bucci, R. Occlusion, orthodontics, and temporomandibular disorders: Cutting edge of the current evidence. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2020, 9, S15–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castroflorio, T.; Bargellini, A.; Lucchese, A.; Manuelli, M.; Casasco, F.; Cugliari, G.; Cioffi, I.; Deregibus, A. Effects of clear aligners on sleep bruxism: Randomized controlled trial. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, T.; Tran, J.; Castroflorio, T.; Tassi, A.; Cioffi, I. Evaluation of masticatory muscle response to clear aligner therapy using ambulatory electromyographic recording. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 159, e25–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, L.H.; Farrag, G.; Baxmann, M.; Schwendicke, F. Factors influencing patient compliance during clear aligner therapy: A retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.L.; Waskalic, V. Three-dimensional diagnosis and orthodontic treatment of complex malocclusions with the Invisalign appliance. Semin. Orthod. 2001, 7, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Keilig, L.; Schwarze, J.; Jung, B.A.; Bourauel, C. Treatment outcome and efficacy of an aligner technique—Regarding incisor torque, premolar derotation and molar distalization. BMC Oral. Health 2014, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, S.; Paoli, A.; Razionale, A.V.; Savignano, R. Computational design and engineering of polymeric orthodontic aligners. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2017, 33, e2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putrino, A.; Barbato, E.; Galluccio, G. Clear aligners: Between evolution and efficiency—A scoping review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampakis, O.; Iliadi, A.; Ueno, H.; Oliver, D.R.; Kim, K.B. Accuracy of clear aligners: A retrospective study of patients who needed refinement. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2018, 154, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, A.; Mousoulea, S.; Gkantidis, N.; Kloukos, D. Clinical effectiveness of Invisalign® orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Prog. Orthod. 2018, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.W.; Ko, H.C.; Todoki, L.S.; Finkleman, S.A.; Khosravi, R.; Wang, H.F.; Funkhouser, E.; Baltuck, C.; Raj, V.; Allareddy, V.; et al. The National Dental Practice-Based Research Network adult anterior open bite study: A description of the practitioners and patients. Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, N.; Kishorekumar, S. Efficacy of Clear Aligners in Correcting Anterior Open Bite-A Systematic Review. Indian J. Med. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2020, 14, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, T. Clear aligners in orthodontic treatment. Aust. Dent. J. 2017, 62, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovard, S.; Leroux, B.; Greenlee, G.; Huang, G. Bias in the superimposition of lateral cephalograms in adult patients with anterior open bite. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 163, 222–232.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshorne, J.; Wertheimer, M.B. Emerging insights and new developments in clear aligner therapy: A review of the literature. AJO-DO Clin. Companion 2022, 2, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Palone, M.; Carlucci, A.; Siciliani, G. Clear aligner hybrid approach: A case report. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2020, 9, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Topic | Supporting References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observational Studies | Case Report/Series Studies | |||
| Retrospective Studies (13 Studies) | Prospective Cohort Studies (1 Studies) | Case Report Studies (13 Studies) | Case Series Studies (3 Studies) | |
| Posterior intrusion | [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14] | [15] | [16,17,18,19] | [20] |
| Anterior extrusion | [7,9,10,11,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25] | [19,26,27] | ||
| Refinements and treatment adjustments | [9] | [16] | ||
| Retention protocol | [11] | [28,29,30] | ||
| Patient-related factors | [8,12,13,21,22] | [15] | [27,30,31,32,33] | [20,32] |
| Clinician-related factors | [7,8,9,11,23] | [15] | [33] | |
| Technology-related factors | [10] | [19,30,33,34] | [35] | |
| Patient-Related Factors | Effects and Action | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Failure to use the aligners correctly or continuously | Lingual attachments for upper- and lower-anterior teeth | [8,21,30,31] |
| Periodontal disease | High-frequency vibration and corticotomy in addition to clear aligner treatment | [27] |
| Bruxism | Awake bruxism during clear aligner treatment has no significant impact on outcomes | [12] |
| Previous treatment with fixed appliances | A possible cause of open bites and a reason for patients’ choice of CAs or poor compliance | [20,31,32] |
| Smile and facial appearance | In hyperdivergent facial types, upper-incisor extrusion should not exceed 1–2 mm due to the risk of excessive gingival display | [13,22,33] |
| Orthodontist-Related Factors | Effects and Action | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment planning | Skills and willingness to use computer-aided planning | [10] |
| Training and level of experience | An annual minimum of 100 clear aligner treatments Orthodontist’s unique working style → uniform materials and methods and yet a source of research bias | [7,8,9,15,23] |
| Post-treatment follow-up | Tongue posture reeducation and tooth clenching | [11,33] |
| Study Design | Treatment Period | Study Objective | Participants Sample Size | Mechanism of Anterior Open-bite Correction | Clear Aligner Efficacy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Garnett et al., 2019 [7], comparative retrospective study | Fixed Appliance Group: 2008–2014; Clear Aligner Group: 2011–2014 | To compare fixed appliances and clear-aligner therapy in correcting anterior open bite and in controlling the vertical dimension in adult patients with hyperdivergent skeletal patterns. | 17 fixed-appliance patients and 36 clear-aligner patients. | Retro inclination of the upper and lower incisors while maintaining the vertical position of the upper and lower molars. | The clear aligner group showed a slightly greater amount of lower incisor extrusion (p = 0.009). Mean overbite changes of 2.28 ± 1.55 mm, not significantly higher than in the fixed-appliance group. |
| 2 | Moshiri et al., 2017 [8], retrospective study | 18 months | The purpose of this study was to evaluate, by means of cephalometric appraisal, the vertical effects of non-extraction treatment of adult anterior open bite with CA. | Lateral cephalograms of 30 adult patients with a Class I or II open bite. | Bite closure was mainly achieved by a combination of counterclockwise rotation of the mandibular plane, lower molar intrusion and lower incisor extrusion. | An average overbite change of 3.4 ± 1.4 mm. |
| 3 | Harris et al., 2020 [9], single-center retrospective study | - | To evaluate the dental and skeletal effects that occur in the correction of anterior open bite with CA. | 45 adult patients with an average open bite of −1.21 ± 1.15 mm. | Anterior retraction and extrusion and posterior molar intrusion, with slight mandibular autorotation. | An average overbite change of 3.27 ± 1.09 mm. |
| 4 | Blundell et al., 2023 [10], multicenter retrospective study | - | The objective of this study was to investigate and determine the accuracy of Invisalign® treatment in correcting anterior open bite by comparing the predicted outcome from ClinCheck® Pro 6.0 to the achieved outcome for the initial aligner sequence. | 76 adult patients with a mean overbite of −1.48 mm ± 1.21 mm. | Anterior extrusion | An average of 66.7% of the programmed ClinCheck® Pro 6.0 open-bite closure. |
| 5 | Steele B.P. et al. (2022) [22], retrospective cohort study | To compare the dentoskeletal effects and treatment outcomes of clear aligner therapy versus miniplate-supported posterior intrusion (MSPI) combined with fixed appliances in adult patients with anterior open bite. | Invisalign group: 29 patients; MSPI group: 24 patients. | Anterior extrusion | MSPI resulted in significantly greater maxillary molar intrusion (1.5 mm) compared to Invisalign. | |
| 6 | Suh et al., 2023 [11], retrospective cohort study | - | This study aimed to examine the stability of anterior open-bite (AOB) treatment with CA. | 52 adult patients with an initial overbite of less than −0.5 mm, evaluated at least 1-year posttreatment. | Anterior extrusion, with minor maxillary molar intrusion leading to mandibular counterclockwise rotation. | A mean retention period of 2.1 ± 1.1 years with a mean change in overbite of 3.3 ± 1.5 mm and 94% stability. |
| 7 | Pokorna et al., 2022 [12], retrospective study | 20 months | The study aimed to assess the cephalometric changes in patients with a clinically proven anterior open bite after clear aligner treatment (Invisalign®). The amount of planned movement was also compared with the amount of movement that actually occurred, measured as 8 on the radiographs. | 30 adult patients with a bite depth of <0 mm. | Intrusion of the lateral segments and anterior extrusion. | A mean bite deepening of 2.71 mm. Anterior extrusion of 0.95 to 1.06 mm in the maxilla and 0.38 mm in the mandible. Molar intrusion occurred in the maxilla (0.66 to 0.83 mm) during treatment. |
| 8 | Todoki et al., 2020 [15], observational prospective cohort study | 30 months | This study reports on the overall success rate of anterior open-bite orthodontic treatment in the adult population across the United States, as well as 4 major treatment modalities and other factors that may influence treatment success. | 29 adult patients with a mean open bite of −2.35 mm in the total number of 254 orthodontic patients. | Posterior intrusion | Similar success rates of 81% for aligner and fixed-appliance treatment. |
| 9 | Burashed et al., 2023 [23], retrospective cohort study | - | The aim of this retrospective study was to compare the efficacy of anterior open-bite correction with Invisalign® when using optimized extrusion versus conventional attachments. | 86 adult patients with an overbite of ≤0 mm on all 4 incisors. | Conventional horizontal and rectangular attachments or optimized extrusion attachments on incisors. | An efficacy of anterior open-bite correction of 58.4%, with similar results in patients with conventional versus optimized attachments, the latter having a shorter treatment duration. |
| 10 | Khosravi et al., 2017 [24], retrospective study | - | To assess the nature of overbite changes with the Invisalign® appliance. The study sample included 68 patients with normal overbites, 40 with deep bites and 12 with open bites. | 12 adult patients with mild to moderate open bites. | Anterior extrusion | A median deepening of overbite of 1.5 mm ± 0.5 mm. |
| 11 | Kau et al., 2017 [14], retrospective study | - | A comparison of pre-treatment and posttreatment scores was conducted using the PAR index and ICON. | Invisalign® 2 groups: Anterior open-bite patients: 23; Control group: 77. | Posterior intrusion and anterior extrusion. | Invisalign is effective in correcting anterior open bites, achieving outcomes comparable to non-open-bite patients when well-planned and well-executed. |
| 12 | Chamberland & Nataf, 2024 [25], retrospective comparative study | This study aimed to compare the treatment effect and mechanisms of open-bite closure between patients treated with braces and TADs double-arch intrusion and those treated with CAs. | The TAD group included 18 consecutively treated patients from the main author. The CAT group consisted of 16 selected patients from three different orthodontists. | Anterior extrusion | A significant reduction in vertical dimensions temporary only in skeletal device treatment, whereas clear aligner treatment showed a significant extrusion of 1.22 ± 0.42 mm of the lower incisors. | |
| 13 | Rask K et al., 2021 [13], retrospective study | - | The purpose of this study was to compare changes promoted by CAs and traditional fixed appliances in cephalometric measurements of the vertical dimension and molar position in adult patients with Class I malocclusion treated with non-extraction. | Pre- and post-treatment lateral cephalometric radiographs of adult patients treated with either CAs (n = 44) or traditional fixed appliances (n = 22). | Posterior intrusion and anterior extrusion. | Clear aligners can effectively control the vertical dimension and aid in anterior open-bite closure in adults, potentially better than fixed appliances in non-extraction protocols. |
| 14 | Karalikkattil, T.L. et al., 2024 [21], retrospective cohort study | 18 months | This study aims to contribute to the existing body of knowledge by evaluating the effectiveness of Invisalign® treatment on open-bite correction through a retrospective analysis of patient records. | A retrospective analysis was conducted on a cohort of 50 patients with open bites who underwent Invisalign treatment. | Anterior extrusion | Treatment evaluation showed that the mean overbite improved to +1.5 mm (SD = 0.8). |
| Study | Year | Study Design and Invisalign® Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Garnett et al. [7] | 2019 | Retrospective Comparative—compared Invisalign® vs. fixed appliances |
| Moshiri et al. [8] | 2017 | Observational Retrospective—cephalometric evaluation of Invisalign® |
| Harris et al. [9] | 2020 | Retrospective—evaluated open-bite closure using Invisalign® |
| Waxler et al. [17] | 2021 | Case Report—skeletal open-bite corrected with Invisalign® + TADs |
| Vadera et al. [19] | 2023 | Case Report—skeletal Class III malocclusion + dentoalveolar anterior open bite using CA |
| Blundell et al. [10] | 2023 | Retrospective—predictability of anterior open bite with Invisalign® |
| Giancotti et al. [20] | 2017 | Case Series—Invisalign® used in open-bite cases |
| Schupp et al. [29] | 2010 | Case Series—focused on Invisalign® system |
| Suh et al. [11] | 2023 | Observational Longitudinal—studied short-term stability of Invisalign® treatment |
| Karalikkattil al. [21] | 2024 | Retrospective—Invisalign® effectiveness for anterior open bite |
| Steele et al. [22] | 2022 | Retrospective—clinical dentoskeletal effects and treatment outcomes of Invisalign® patients versus miniplate-supported posterior intrusion (MSPI) combined with fixed appliances |
| Burashed et al. [23] | 2023 | Comparative Retrospective—Invisalign® optimized vs. conventional attachments |
| Khosravi et al. [24] | 2017 | Retrospective—overbite management with Invisalign® |
| Rodriguez et al. [34] | 2012 | Case Report—non-extraction open-bite treatment with Invisalign® |
| Haubrich et al. [35] | 2023 | Case Series—follow-up on aligner open-bite treatments |
| Kau et al. [14] | 2017 | Retrospective—Invisalign® effectiveness for anterior open bite |
| Recommendation | Details |
|---|---|
| Improve Patient Compliance Including Long Term Treatments |
|
| Address Orthodontic Extractions and Surgical Concerns |
|
| Monitor Periodontal Health |
|
| Manage Bruxism and Jaw Tension |
|
| Consider Previous Orthodontic Treatment |
|
| Meet Esthetic Demands in Complex Cases |
|
| Enhance Esthetic and Functional Outcomes |
|
| Category | Clinical Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive Treatment Planning |
|
| Clinician Expertise and Experience |
|
| Case Selection & Bias Considerations |
|
| Managing Open-Bite Cases |
|
| Patient-Centered Approach |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olteanu, N.D.; Romanec, C.; Cernei, E.R.; Karvelas, N.; Nastri, L.; Zetu, I.N. Scoping Review—The Effectiveness of Clear Aligners in the Management of Anterior Open Bite in Adult Patients. Medicina 2025, 61, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061113
Olteanu ND, Romanec C, Cernei ER, Karvelas N, Nastri L, Zetu IN. Scoping Review—The Effectiveness of Clear Aligners in the Management of Anterior Open Bite in Adult Patients. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061113
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlteanu, Nicolae Daniel, Cristian Romanec, Eduard Radu Cernei, Nikolaos Karvelas, Livia Nastri, and Irina Nicoleta Zetu. 2025. "Scoping Review—The Effectiveness of Clear Aligners in the Management of Anterior Open Bite in Adult Patients" Medicina 61, no. 6: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061113
APA StyleOlteanu, N. D., Romanec, C., Cernei, E. R., Karvelas, N., Nastri, L., & Zetu, I. N. (2025). Scoping Review—The Effectiveness of Clear Aligners in the Management of Anterior Open Bite in Adult Patients. Medicina, 61(6), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061113








