Prediction Model for Risk of Death in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Kidney Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Database
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.1.1. Categorical Variables
3.1.2. Continuous Variables
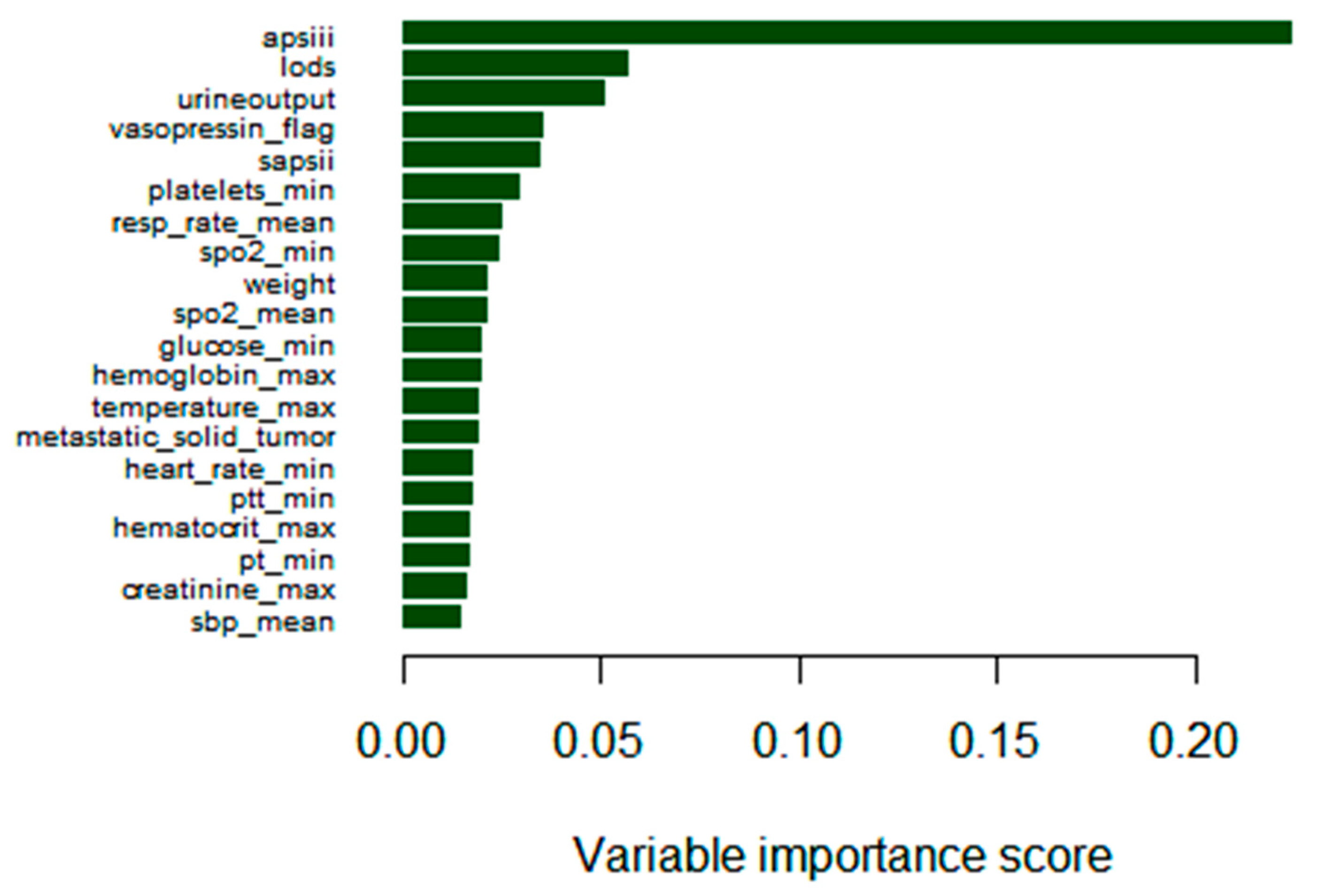
3.2. Model Construction
3.3. Model Comparison
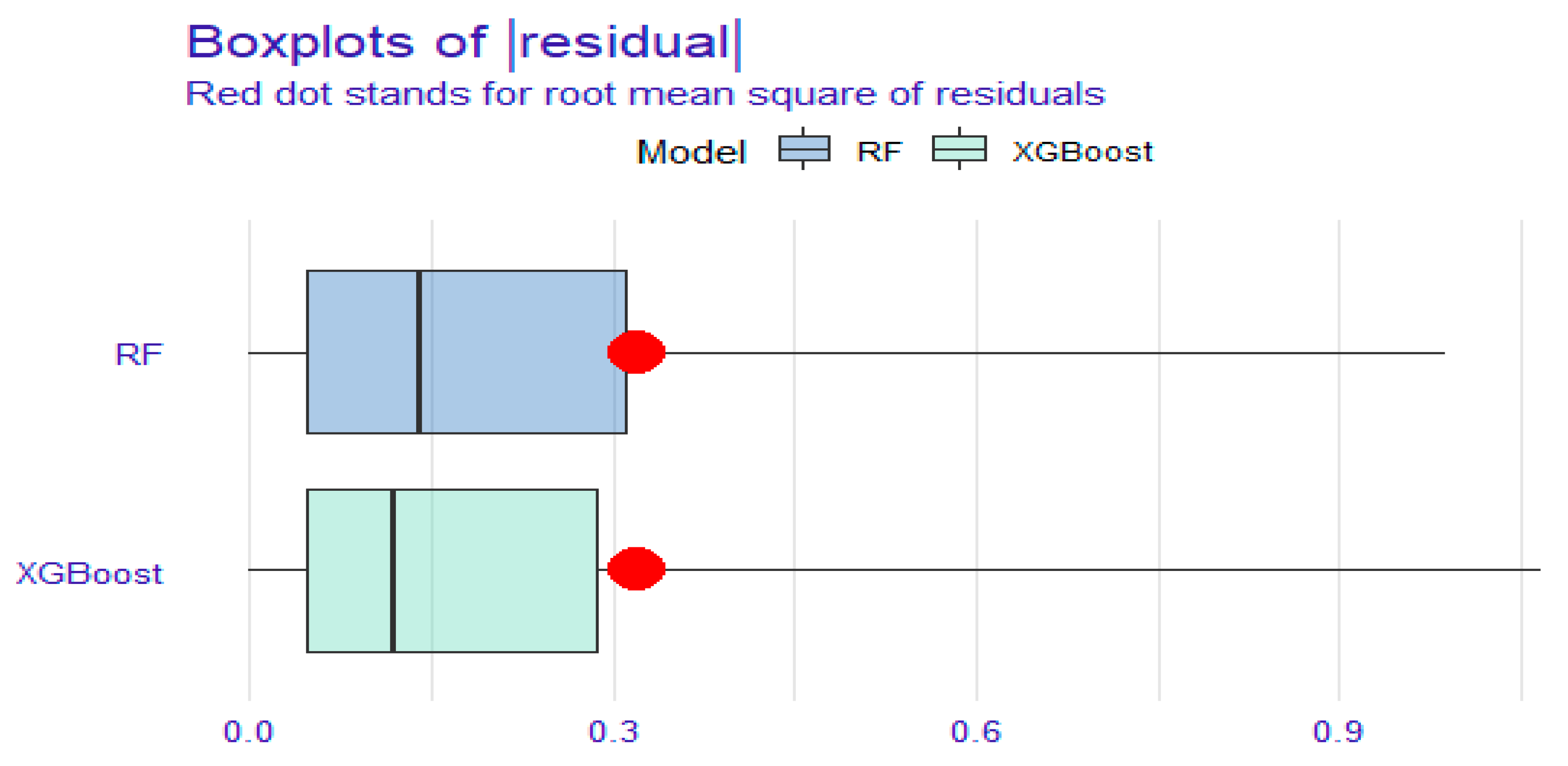
3.3.1. Differentiation and Calibration
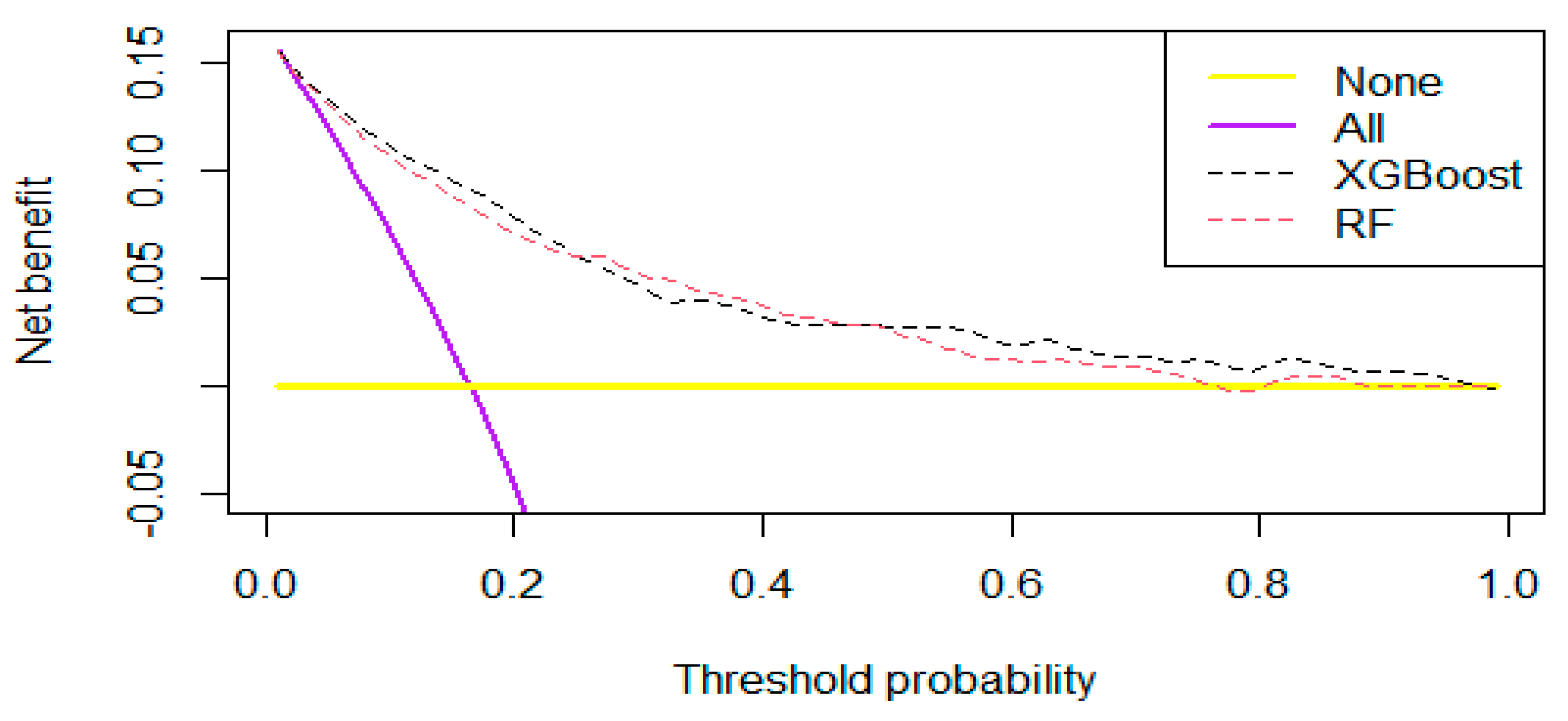
3.3.2. Clinical Utility and Degree of Fit
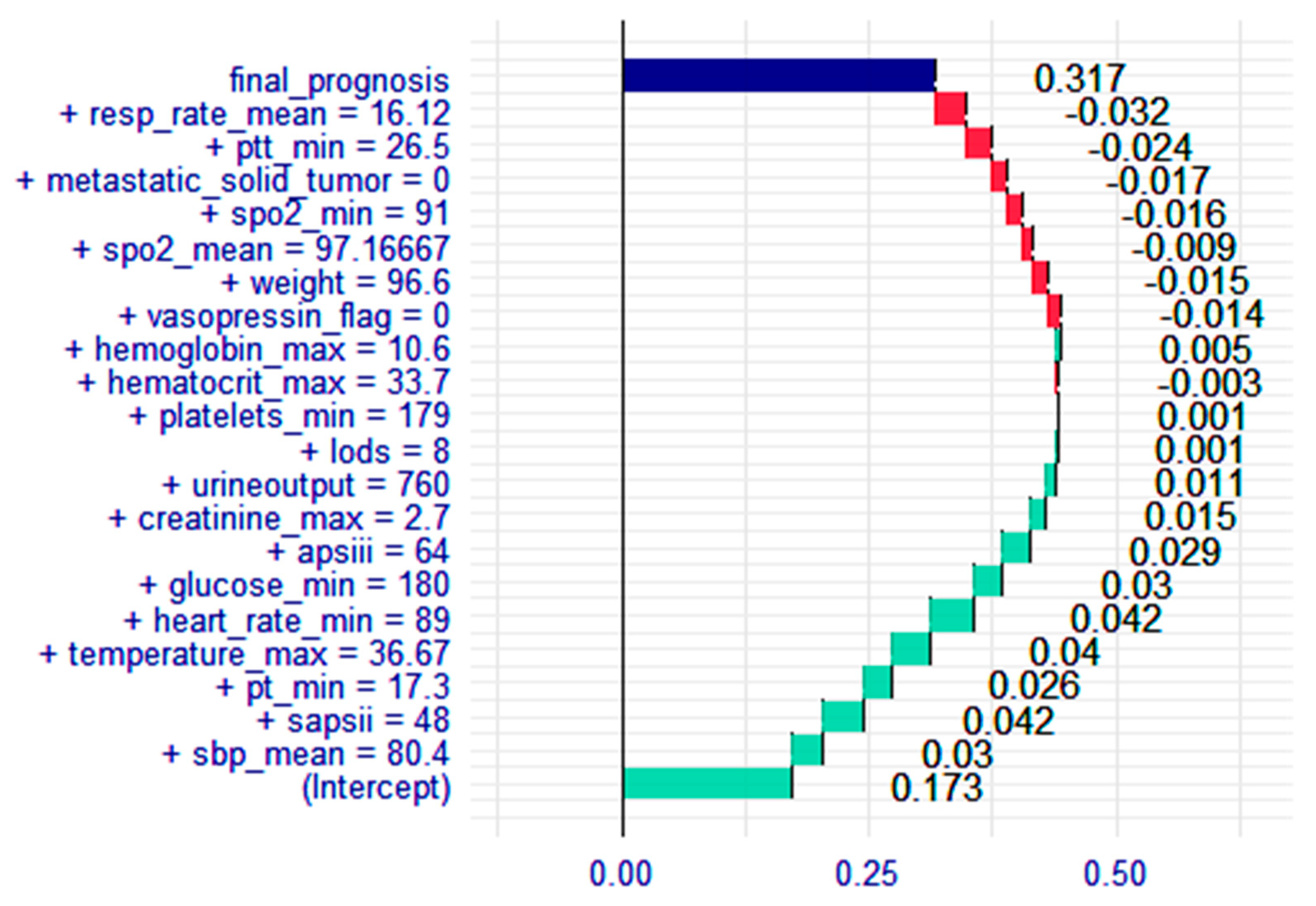
3.4. Breakdown Plot for the XGBoost Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sobamowo, H.; Prabhakar, S.S. The kidney in aging: Physiological changes and pathological implications. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 146, 303–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khow, K.S.; Lau, S.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Yong, T.Y. Diuretic-associated electrolyte disorders in the elderly:risk factors, impact, management and prevention. Curr. Drug Saf. 2014, 9, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clingan, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Caserta, M.P.; Cox, K.L.; Gupta, V.; Baumgarten, D.A.; Zhai, Q.; Alexander, L.F. Imaging Patients with Kidney Failure. Radiographics 2023, 43, e220116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deo, R.C. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Houwelingen, S. Ridge Estimators in Logistic Regression. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C 1992, 41, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Chen, Q. Entity recognition in Chinese clinical text using attention-based CNN-LSTM-CRF. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19 (Suppl. S3), 74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Shan, B.; He, M.; Xu, J. XGBoost Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Outcome in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 659–667. [Google Scholar]
- Zhanshan, L.I.; Liu, Z. Feature selection algorithm based on XGBoost. J. Commun. 2019, 40, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q.; Li, W.; Chen, X. Identification the source of fecal contamination for geographically unassociated samples with a statistical classification model based on support vector machine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124821. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Duan, Z.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, W.; Xu, L.; Wang, T.; Su, L.; et al. Oral Microbiome Alterations Associated with Early Childhood Caries Highlight the Importance of Carbohydrate Metabolic Activities. mSystems 2019, 4, e00450-19. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Bajorath, J. Evolution of Support Vector Machine and Regression Modeling in Chemoinformatics and Drug Discovery. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2022, 36, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, E215–E220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.S. Comparative analysis strategy of classified data. Chin. J. Nurs. 2011, 46, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kattan, M.W.; Vickers, A.J. Statistical Analysis and Reporting Guidelines for CHEST. Chest 2020, 158, S3–S11. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Mao, H.; Xing, C. Incidence and diagnosis of Acute kidney injury in hospitalized adult patients: A retrospective observational study in a tertiary teaching Hospital in Southeast China. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 203. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, X.; Wen, Y.; Du, B.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, B.; Xi, X. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in intensive care units in Beijing: The multi-center BARFT study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 468. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Ma, A.; Kang, Y. Machine learning model for predicting acute kidney injury progression in critically ill patients. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, S.; Guo, F.; Xue, H.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xie, W.; Zhu, F. Predicting renal function recovery and short-term reversibility among acute kidney injury patients in the ICU: Comparison of machine learning methods and conventional regression. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Meng, X. Recent Advances in Epigenetics of Age-Related Kidney Diseases. Genes 2022, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeros, A.; Lange, K. Algorithms for Sparse Support Vector Machines. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2023, 32, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Jiang, K.; Yan, T.A.; Chen, G.H. XGBoost: An Optimal Machine Learning Model with Just Structural Features to Discover MOF Adsorbents of Xe/Kr. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9066–9076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, W.; Wu, J. Machine learning for the prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.H.; Luo, X.Q.; Yan, P.; Zhang, N.Y.; Liu, Y.; Duan, S.B. Outcome prediction for acute kidney injury among hospitalized children via eXtreme Gradient Boosting algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8956. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, C. Comparison of machine learning and logistic regression models in predicting acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2021, 151, 104484. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Peng, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, T.; Xie, L. Explainable ensemble machine learning model for prediction of 28-day mortality risk in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1165129. [Google Scholar]
- Shiba, A.; Uchino, S.; Fujii, T.; Takinami, M.; Uezono, S. Association Between Intraoperative Oliguria and Acute Kidney Injury After Major Noncardiac Surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 127, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.X.; Du, B. Fluid management of acute kidney injury. J. Cardiopulm. Vasc. Dis. 2019, 38, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, L.M.; Balkawade, R. Thermoneutral Regulation and Acute Injury: Implications for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2022, 146, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- MacLaughlin, H.L.; Pike, M.; Selby, N.M.; Siew, E.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Guide, A.; Stewart, T.G.; Himmelfarb, J.; Go, A.S.; Parikh, C.R.; et al. Body mass index and chronic kidney disease outcomes after acute kidney injury: A prospective matched cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.F.; Wang, J.Y.; Chou, T.C.; Lin, S.H. Vasoactive mediators and renal haemodynamics in exertional heat stroke complicated by acute renal failure. QJM Int. J. Med. 2003, 96, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, T.Y.; Liaw, C.C. Retrospective Analysis of Mortality Cases in Advanced and Metastatic Solid Tumors With Concurrent Prerenal Azotemia. Vivo 2020, 34, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chancharoenthana, W.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Acute kidney injury spectrum in patients with chronic liver disease: Where do we stand. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3684–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, T.J.; Johnson, A.E.W.; Raffa, J.D.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G.; Badawi, O. The eICU Collaborative Research Database, a freely available multi-center database for critical care research. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Death | Survival | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 1385 | 6625 | |
| Gender (%) | 0.02 | ||
| Female | 643 (46.43) | 2842 (42.90) | |
| Male | 742 (53.57) | 3783 (57.10) | |
| Ethnicity (%) | 0.003 | ||
| Caucasian | 994 (71.77) | 4682 (70.67) | |
| African American | 115 (8.30) | 725 (10.94) | |
| Asian | 41 (2.96) | 188 (2.84) | |
| Other | 235 (16.97) | 1030 (15.55) | |
| Marital status (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Single | 245 (17.69) | 1179 (17.80) | |
| Married | 632 (45.63) | 3102 (46.82) | |
| Other | 508 (36.68) | 2344 (35.38) | |
| First care unit (%) | <0.001 | ||
| MICU | 350 (25.27) | 1631 (24.62) | |
| SICU | 320 (23.10) | 1237 (18.67) | |
| Other | 715 (51.63) | 3757 (56.71) | |
| Dialysis (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 67 (4.84) | 131 (1.98) | |
| No | 1318 (95.16) | 6494 (98.02) | |
| Antibiotic (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 1314 (94.87) | 5694 (85.95) | |
| No | 71 (5.13) | 931 (14.05) | |
| Dobutamine (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 100 (7.22) | 159 (2.40) | |
| No | 1285 (92.78) | 6466 (97.60) | |
| Dopamine (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 126 (9.10) | 300 (4.53) | |
| No | 1259 (90.90) | 6325 (95.47) | |
| Nerve blockers (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 80 (5.78) | 91 (1.37) | |
| No | 1305 (94.22) | 6534 (98.63) | |
| Epinephrine (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 141 (10.18) | 358 (5.40) | |
| No | 1244 (89.82) | 6267 (94.60) | |
| Norepinephrine (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 738 (53.29) | 1780 (26.87) | |
| No | 647 (46.71) | 4845 (73.13) | |
| Phenylephrine (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 425 (30.69) | 1182 (17.84) | |
| No | 960 (69.31) | 5443 (82.16) | |
| Vasopressor (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 392 (28.30) | 465 (7.02) | |
| No | 993 (71.70) | 6160 (92.98) | |
| Myocardial infarct (%) | 0.32 | ||
| Yes | 398 (28.74) | 1816 (27.41) | |
| No | 987 (71.26) | 4809 (72.59) | |
| Congestive heart failure (%) | 0.05 | ||
| Yes | 749 (54.08) | 3392 (51.20) | |
| No | 636 (45.92) | 3233 (48.80) | |
| Peripheral vascular disease (%) | 0.03 | ||
| Yes | 256 (18.52) | 1067 (16.11) | |
| No | 1129 (81.48) | 5558 (83.89) | |
| Cerebrovascular disease (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 240 (17.33) | 896 (13.52) | |
| No | 1145 (82.67) | 5729 (86.48) | |
| Dementia (%) | 0.90 | ||
| Yes | 109 (7.87) | 528 (7.97) | |
| No | 1276 (92.13) | 6097 (92.03) | |
| Chronic pulmonary disease (%) | 0.04 | ||
| Yes | 473 (34.15) | 2077 (31.35) | |
| No | 912 (65.85) | 4548 (68.65) | |
| Rheumatic disease (%) | 0.89 | ||
| Yes | 65 (4.69) | 305 (4.60) | |
| No | 1320 (95.31) | 6320 (95.40) | |
| Peptic ulcer disease (%) | 0.26 | ||
| Yes | 65 (4.69) | 267 (4.03) | |
| No | 1320 (95.31) | 6358 (95.97) | |
| Diabetes complicated (%) | 0.15 | ||
| Yes | 395 (28.52) | 2020 (30.49) | |
| No | 990 (71.48) | 4605 (69.51) | |
| Mild liver disease (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 253 (18.27) | 602 (9.09) | |
| No | 1132 (81.73) | 6023 (90.91) | |
| Paraplegia (%) | 0.005 | ||
| Yes | 69 (4.98) | 227 (3.43) | |
| No | 1316 (95.02) | 6398 (96.57) | |
| Malignant cancer (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 368 (26.57) | 1024 (15.46) | |
| No | 1017 (73.43) | 5601 (84.54) | |
| Severe liver disease (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 129 (9.31) | 236 (3.56) | |
| No | 1256 (90.69) | 6389 (96.44) | |
| Metastatic solid tumor (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 205 (14.80) | 391 (5.90) | |
| No | 1180 (85.20) | 6234 (94.10) | |
| Aids (%) | 0.48 | ||
| Yes | 3 (0.21) | 9 (0.14) | |
| No | 1382 (99.78) | 6616 (99.86) |
| Death | Survival | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 1385 | 6625 | |
| Age, year | 79.40 (72.66, 86.48) | 78.13 (71.46, 84.91) | <0.001 |
| Weight, kg | 74.80 (63.50, 87.90) | 77.90 (66.30, 91.47) | <0.001 |
| Length of stay in the ICU, day | 5.09 (2.50, 10.27) | 3.09 (1.91, 6.01) | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit_min (%) | 27.40 (23.70, 32.20) | 28.40 (24.50, 33.00) | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit_max (%) | 31.70 (28.00, 35.90) | 32.50 (29.10, 36.90) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin_min (g/dL) | 8.80 (7.60, 10.50) | 9.30 (8.00, 10.80) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin_max (g/dL) | 10.20 (8.90, 11.60) | 10.60 (9.40, 12.10) | <0.001 |
| Platelets_min (k/uL) | 165.00 (100.00, 226.00) | 167.00 (121.00, 224.00) | <0.001 |
| Platelets_max (k/uL) | 199.00 (132.00, 266.00) | 201.00 (153.00, 266.00) | <0.001 |
| WBC_min (k/uL) | 9.80 (7.00, 13.50) | 9.50 (6.90, 12.50) | <0.001 |
| WBC_max (k/uL) | 12.9 (10.00, 18.00) | 12.70 (9.20, 17.10) | <0.001 |
| AG_min (mEq/L) | 14.00 (12.00, 17.00) | 13.00 (11.00, 15.00) | <0.001 |
| AG_max (mEq/L) | 17.00 (15.00, 21.00) | 17.00 (14.00, 19.00) | <0.001 |
| Bicarbonate_min (mEq/L) | 20.00 (16.00, 23.00) | 21.00 (18.00, 24.00) | <0.001 |
| Bicarbonate_max (mEq/L) | 23.00 (20.00, 26.00) | 23.00 (21.00, 26.00) | <0.001 |
| BUN_min (mg/dL) | 33.00 (24.00, 50.00) | 30.00 (21.00, 42.00) | <0.001 |
| BUN_max (mg/dL) | 39.00 (29.00, 58.00) | 36.00 (25.00, 50.00) | <0.001 |
| Calcium_min (EU/dL) | 8.00 (7.50, 8.50) | 8.10 (7.70, 8.60) | <0.001 |
| Calcium_max (EU/dL) | 8.60 (8.00, 9.00) | 8.60 (8.10, 9.00) | 0.09 |
| Chloride_min (mEq/L) | 101.00 (97.00, 106.00) | 102.00 (98.00, 106.00) | <0.001 |
| Chloride_max (mEq/L) | 105.00 (101.00, 109.00) | 106.00 (102.00, 109.00) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine_min (g/dL) | 1.30 (1.10, 2.00) | 1.30 (1.00, 1.70) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine_max (g/dL) | 1.60 (1.30, 2.30) | 1.60 (1.30, 2.10) | <0.001 |
| Sodium_min (mEq/L) | 137.00 (134.00, 140.00) | 137.00 (134.00, 140.00) | 0.05 |
| Sodium_max (mEq/L) | 140.00 (137.00, 143.00) | 140.00 (137.00, 143.00) | 0.30 |
| Potassium_min (mEq/L) | 4.00 (3.60, 4.50) | 4.00 (3.60, 4.40) | 0.33 |
| Potassium_max (mEq/L) | 4.60 (4.20, 5.20) | 4.60 (4.10, 5.10) | 0.04 |
| PT_min (s) | 13.70 (13.10, 16.20) | 13.50 (12.30, 14.80) | <0.001 |
| PT_max (s) | 14.90 (14.10, 18.30) | 14.60 (13.00, 16.50) | <0.001 |
| PTT_min (s) | 29.30 (27.30, 34.70) | 29.20 (26.30, 32.60) | <0.001 |
| PTT_max (s) | 32.70 (30.60, 43.80) | 32.70 (28.60, 38.00) | <0.001 |
| Glucose_min (mg/dL) | 105.00 (87.00, 131.00) | 104.50 (88.00, 124.00) | 0.02 |
| Glucose_max (mg/dL) | 168.00 (135.00, 217.00) | 168.00 (133.00, 211.00) | 0.14 |
| Urine output (ml) | 850.00 (405.00, 1495.00) | 1378.00 (863.00, 2120.00) | <0.001 |
| Heart rate_min (min−1) | 73.00 (63.00, 86.00) | 69.00 (60.00, 78.00) | <0.001 |
| Heart rate_max (min−1) | 107.00 (94.00, 124.00) | 99.00 (87.00, 114.00) | <0.001 |
| Heart rate_mean (min−1) | 89.22 (77.26, 101.69) | 81.93 (72.32, 92.81) | <0.001 |
| SBP_min (mmHg) | 84.00 (75.00, 92.00) | 88.00 (80.00, 98.00) | <0.001 |
| SBP_max (mmHg) | 141.00 (126.00, 156.00) | 144.00 (132.00, 160.00) | <0.001 |
| SBP_mean (mmHg) | 108.07 (100.52, 117.83) | 113.53 (105.52, 125.10) | <0.001 |
| DBP_min (mmHg) | 41.00 (34.00, 47.00) | 43.00 (37.00, 49.00) | <0.001 |
| DBP_max (mmHg) | 84.00 (72.00, 97.00) | 84.00 (72.00, 97.00) | 0.35 |
| DBP_mean (mmHg) | 57.80 (51.72, 64.28) | 58.50 (52.48, 65.63) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory rate_min (min−1) | 13.00 (11.00, 16.00) | 13.00 (11.00, 15.00) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory rate_max (min−1) | 30.00 (26.00, 34.00) | 28.00 (24.00, 32.00) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory rate_mean (min−1) | 20.44 (18.04, 23.61) | 19.24 (17.13, 21.80) | <0.001 |
| Body temperature_min (°C) | 36.39 (36.06, 36.56) | 36.39 (36.17, 36.61) | <0.001 |
| Body temperature_max (°C) | 37.11 (36.83, 37.50) | 37.11 (36.89, 37.44) | 0.13 |
| Body temperature_mean (°C) | 36.72 (36.47, 36.95) | 36.74 (36.54, 36.97) | <0.001 |
| SpO2_min (%) | 91.00 (87.00, 94.00) | 92.00 (89.00, 94.00) | <0.001 |
| SpO2_max (%) | 100.00 (100.00, 100.00) | 100.00 (99.00, 100.00) | 0.04 |
| SpO2_mean (%) | 96.77 (95.08, 98.33) | 96.90 (95.50, 98.24) | 0.01 |
| SOFA | 8.00 (6.00, 12.00) | 5.00 (4.00, 8.00) | <0.001 |
| APSIII | 75.00 (59.00, 97.00) | 50.00 (41.00, 64.00) | <0.001 |
| LODS | 9.00 (6.00, 11.00) | 5.00 (4.00, 7.00) | <0.001 |
| OASIS | 40.00 (34.00, 47.00) | 33.00 (28.00, 39.00) | <0.001 |
| SAPSII | 52.00 (43.00, 62.00) | 41.00 (35.00, 49.00) | <0.001 |
| SIRS | 3.00 (2.00, 3.00) | 3.00 (2.00, 3.00) | <0.001 |
| Mode | AUC | Brier | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | 0.835 | 0.206 | 0.730 | 0.631 |
| RF | 0.839 | 0.158 | 0.805 | 0.761 |
| SVM | 0.784 | 0.217 | 0.794 | 0.556 |
| XGBoost | 0.851 | 0.102 | 0.837 | 0.734 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Ye, F.; Du, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y. Prediction Model for Risk of Death in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Kidney Failure. Medicina 2025, 61, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040640
Zeng J, Ye F, Du J, Zhang M, Yang J, Wu Y. Prediction Model for Risk of Death in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Kidney Failure. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040640
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jinping, Feng Ye, Jiaolan Du, Min Zhang, Jun Yang, and Yinyin Wu. 2025. "Prediction Model for Risk of Death in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Kidney Failure" Medicina 61, no. 4: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040640
APA StyleZeng, J., Ye, F., Du, J., Zhang, M., Yang, J., & Wu, Y. (2025). Prediction Model for Risk of Death in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Kidney Failure. Medicina, 61(4), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040640







