AI and Machine Learning for Precision Medicine in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic and Differential Diagnostics in Acute Pancreatitis
3. Prediction of Severity and Complications
4. Radiomics in Acute Pancreatitis
5. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
6. Acute Kidney Injury
7. Survival and Mortality
8. Recurrence
9. Surgical Timing
10. Discussion
11. Conclusions
12. Future Directions
- Model Generalizability
- Multimodal Data Integration
- Real-Time Clinical Applications
- Personalized Medicine and Predictive Analytics
- Advancing Imaging Techniques
- Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
- Expanding Applications Beyond Prediction and global health
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Acronyms and Definitions
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| APACHE | Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation Score |
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BC | Bayesian Classifier |
| BISAP | Bedside Index for Severity in Acute Pancreatitis |
| BUN | Blood Urea Nitrogen |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CTGAN | Conditional Tabular Generative Adversarial Networks |
| CTSI | Computed Tomography Severity Index |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| EA | Auto-encoder |
| EASY-APP | Early AI Model for Pancreatitis Severity Prediction |
| GBM | Gradient Boosting Machine |
| GNB | Gaussian Naive Bayes |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| LightGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| MCTSI | Modified Computed Tomography Severity Index |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NECRO-APP | AI-Based Necrosis Prediction Model |
| PANCREATIA | Predictive Model for Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis |
| PrismSAP | Multimodal AI Model for Acute Pancreatitis |
| RF | Random Forest |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SANRA | Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles |
| SIRS | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
| SMOTE | Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| VAEs | Variational Autoencoders |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the man-agement of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2013, 13 (Suppl. S2), e1–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X. Predictive value of the Ranson and BISAP scoring systems for the severity and prognosis of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, M.W.; Jiang, H. A deep learning-powered diagnostic model for acute pancreatitis. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.X.; Zhao, C.F.; Wang, S.L.; Tu, X.Y.; Huang, W.B.; Chen, J.N.; Xie, Y.; Chen, C.R. Acute pancreatitis: A review of diagnosis, severity prediction and prognosis assess-ment from imaging technology, scoring system and artificial intelligence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 5268–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q. Advances in the clinical application of machine learning in acute pancreatitis: A review. Front. Med. 2025, 11, 147271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Lan, L.; You, L.; Chen, K.; Peng, L.; Zhao, W.; Song, B.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, X. Automated CT pancreas segmentation for acute pancreatitis patients by combining a novel object detection approach and U-Net. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 81, 104430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Jiao, K.; Li, X.; Feng, L.; Tian, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, K.; Chen, S.; Yang, B.; et al. Artificial intelligence-based tools with automated segmentation and measurement on CT im-ages to assist accurate and fast diagnosis in acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 97, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandili, S.; Shayesteh, S.; Fouladi, D.F.; Blanco, A.; Chu, L.C. Emerging imaging techniques for acute pancreatitis. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, R.; Parekh, V.S.; Faghih, M.; Singh, V.K.; Jacobs, M.A.; Zaheer, A. Radiomic features of the pancreas on CT imaging accurately differentiate functional abdominal pain, recurrent acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancreatitis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 123, 108778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Iqbal, Z.; Garikipati, A.; Siefkas, A.; Hoffman, J.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Early prediction of severe acute pancreatitis using machine learning. Pancreatology 2022, 22, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Qiu, M.; Pan, S.; Basharat, Z.; Zippi, M.; Fiorino, S.; Hong, W. Comparison of an interpretable extreme gradient boosting model and an artificial neu-ral network model for prediction of severe acute pancreatitis. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2024, 134, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Ji, M.; Wang, S.; Wen, X.; Huang, P.; Shen, L.; Xu, J. Machine learning model identifies aggressive acute pancreatitis within 48 h of admis-sion: A large retrospective study. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Duan, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, L.; et al. Development and validation of a multimodal model in predicting severe acute pan-creatitis based on radiomics and deep learning. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2024, 184, 105341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kui, B.; Pintér, J.; Molontay, R.; Nagy, M.; Farkas, N.; Gede, N.; Vincze, Á.; Bajor, J.; Gódi, S.; Czimmer, J.; et al. EASY-APP: An artificial intelligence model and application for early and easy prediction of severity in acute pancreatitis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villasante, S.; Fernandes, N.; Perez, M.; Cordobés, M.A.; Piella, G.; Martinez, M.; Gomez-Gavara, C.; Blanco, L.; Alberti, P.; Charco, R.; et al. Prediction of Severe Acute Pancreatitis at a Very Early Stage of the Disease Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques, Without Laboratory Data or Imaging Tests: The PANCREATIA study. Ann. Surg. 2024. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.N.; Mu, D.; Zheng, S.C.; Tian, W.; Wu, Z.Y.; Meng, J.; Wang, R.F.; Zheng, T.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Windsor, J.; et al. Machine learning improves prediction of severity and outcomes of acute pancreatitis: A prospective multi-center cohort study. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 1934–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Nian, Y.J.; Guo, Y.; Tang, L.; Lu, N.; Wen, L.Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, D.F.; Liu, K.J. Development and validation of three machine-learning models for predicting multiple organ failure in moderately severe and severe acute pancreatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, R.; Duff, M.D.; Madhavan, K.K.; Garden, O.J.; Parks, R.W. Identification of severe acute pancreatitis using an artificial neural network. Surgery 2007, 141, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Chen, C.J.; Ma, Y.S.; Shen, Y.T.; Sung, M.I.; Hsu, C.C.; Lin, H.J.; Chen, Z.C.; Huang, C.C.; Liu, C.F. Real-time artificial intelligence predicts adverse outcomes in acute pancreatitis in the emergency department: Comparison with clinical decision rule. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2024, 31, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yao, J.; Liu, C.; Shou, S. Construction and validation of machine learning models for sepsis prediction in patients with acute pancreatitis. BMC Surg. 2023, 23, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.X.Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, H.; Hu, C.; Huang, Z.; Tan, Q.; Song, B.; Deng, L. Deep Learning Models for Severity Prediction of Acute Pancreatitis in the Early Phase From Abdominal Nonenhanced Computed Tomography Images. Pancreas 2023, 52, e45–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Wang, M.; Wen, Y.; Du, F.; Jiang, L.; Geng, X.; Tang, L.; Yan, H. Predicting acute pancreatitis severity with enhanced computed tomography scans using convolutional neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, S.; Pintér, J.; Molontay, R.; Nagy, M.; Farkas, N.; Sipos, Z.; Fehérvári, P.; Pecze, L.; Földi, M.; Vincze, Á.; et al. Early prediction of acute necrotizing pancreatitis by artificial intelligence: A prospective cohort-analysis of 2387 cases. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Ren, W.; Huang, S.; Jiang, J.; Xu, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Y.; Lü, M.; Tang, X. The role of artificial neural networks in prediction of severe acute pancreatitis associ-ated acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective study. Medicine 2023, 102, E34399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pang, M. Early prediction of acute respiratory distress syndrome complicated by acute pancreatitis based on four machine learning models. Clinics 2023, 78, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Lu, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Leng, X.; Chi, L.; Jin, P.; Bian, J. Predictive model of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with acute pancreatitis: A machine learning approach using the MIMIC-IV database. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2303395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhao, L.; Kang, J.; Wen, C.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Song, J.; et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for acute kidney injury in patients with moderately severe and severe acute pancreatitis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2022, 26, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yin, M.; Jiang, A.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, L. Automated machine learning for early predic-tion of acute kidney injury in acute pancreatitis. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, Q.; Cao, L.; Wang, B.; Jin, X.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, M. Machine learning for the prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with acute pancreatitis admitted to the intensive care unit. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 2886–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Guo, C.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chai, X. An Artificial Neural Networks Model for Early Predicting In-Hospital Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis in MIMIC-III. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6638919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, X. Risk Factors and Prediction of 28-Day-All Cause Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients with Acute Pancreatitis Using Machine Learning Techniques: A Retro-spective Analysis of Multi-Institutions. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 4611–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, M.A.B.; Alamgir, Z. Improving mortality prediction in Acute Pancreatitis by machine learning and data augmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.L.W.; Zou, K.; Huang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W.; Shi, X.; Shi, L.; Zhong, X.; Peng, Y.; Tang, X. Prediction of in-hospital Mortality of Intensive Care Unit Patients with Acute Pancreatitis Based on an Explainable Machine Learning Algorithm. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 58, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthra, A.K.; Porter, K.; Hinton, A.; Chao, W.L.; Papachristou, G.I.; Conwell, D.L.; Krishna, S.G. A Comparison of Machine Learning Methods and Conventional Logistic Regres-sion for the Prediction of In-Hospital Mortality in Acute Biliary Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2022, 51, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gao, L.; Gong, H.; Cao, L.; Zhou, J.; Ke, L.; Liu, Y.; Tong, Z.; Li, W. Recurrence rates and risk factors for recurrence after first episode of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 116, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, T.W.; Wu, C.Q.; Lin, Q.; Hu, R.; Xie, C.L.; Zuo, H.D.; Wu, J.L.; Mu, Q.W.; Fu, Q.-S.; et al. Radiomics model of contrast-enhanced computed tomography for predicting the re-currence of acute pancreatitis. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4408–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Zou, K.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Luo, B.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, X.; Shi, L.; Zhong, X.; et al. Application of a Machine Learning Predictive Model for Recur-rent Acute Pancreatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 58, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Lu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X. Classification of Infected Necrotizing Pancreatitis for Surgery Within or Beyond 4 Weeks Using Machine Learning. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Lan, L.; Peng, L.; Li, M.; Lu, H.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X. Predicting Timing of Surgical Intervention Using Recurrent Neural Network for Necrotiz-ing Pancreatitis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 207905–207913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Sun, H.; Su, N.; Pan, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, L. Machine learning improves early prediction of organ failure in hyperlipidemia acute pancreatitis using clinical and abdominal CT features. Pancreatology 2024, 24, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Long, H.; Lai, Q.; Zhou, Y. Machine Learning Predictive Model for Septic Shock in Acute Pancreatitis with Sepsis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
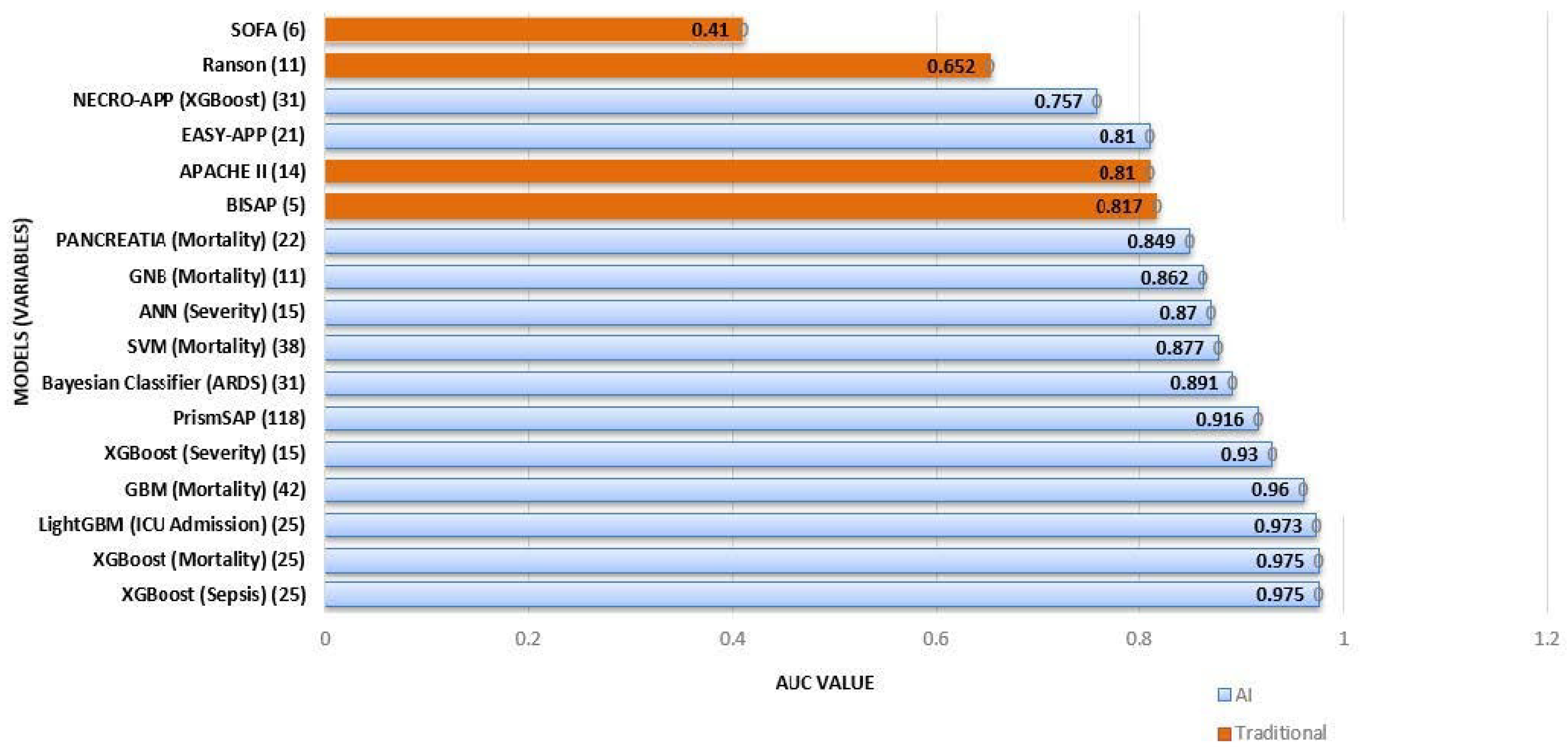
| Characteristic | Traditional Models (Ranson, BISAP, APACHE II, and SOFA) | AI-Based Models |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Variables | 5–12 | 15–116 |
| Type of Data Used | Clinical + Lab | Clinical + Lab + Imaging + Radiomics |
| Predictive Accuracy (AUC) | 0.65–0.82 | 0.85–0.97 |
| Adaptability | Fixed criteria, no adaptation to real-time data | Dynamic, learns from new data |
| Real-Time Analysis | No | Yes |
| Use of Imaging Data | Limited (CTSI only) | Extensive (Uses advanced radiomics and multimodal data) |
| Complexity | Low (Simple scoring systems) | High (Uses complex algorithms) |
| Interpretability | High (Easily interpretable) | Moderate (Requires explainability techniques) |
| Clinical Integration | Widely used, easy to apply | Emerging, requires integration with hospital systems |
| Limitations | Lower accuracy, limited data integration | Requires large datasets, potential bias, regulatory hurdles |
| Model | Prediction Target | Patients Included (N) | Total Variables (N) | Statistically Significant Features for the Prediction Target and Model | AUC Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EASY-APP | Severity | 1184 | 21 | Age, gender, RR, BT, AMR, glucosa | 0.81 | Kui et al. [15] |
| NECRO-APP (XGBoost) | Necrosis | 2387 | 31 | PCR, Glucose, Total WBC, Hb, RBC, LDH | 0.757 | Kiss et al. [24] |
| PrismSAP | Severity | 1221 | 9 + 107 (radiomics) | PE, SIRS, HT, RDW | 0.916 | Yin et al. [14] |
| XGBoost | Severity | 648 | 15 | BUN, PE, HDL-C | 0.93 | Lu et al. [12] |
| ANN | Severity | 648 | 15 | Glucose, albumin, PE | 0.87 | Lu et al. [12] |
| XGBoost | Sepsis | 8274 | 25 | ND | 0.975 | Chang [20] |
| XGBoost | Mortality | 8274 | 25 | ND | 0.975 | Chang et al. [20] |
| LightGBM | ICU Admission | 8274 | 25 | Amylase | 0.973 | Chang et al. [20] |
| PANCREATIA | Mortality | 594 | 22 | Advanced age, ASA, tachycardia, satO2/FiO2, BUN | 0.849 | Villasante et al. [16] |
| Support vector machine (SVM) | Mortality | 534 | 38 | WBC, platelet count, temperature, age, BUN, RDW, SpO2, Hb | 0.877 | Cai et al. [32] |
| Bayesian Classifier (BC) | Acute Respiratory Distress | 460 | 31 | PaO2, PCR, Procalcitonin, Calcium, NRL, WBC, LA, Amylase | 0.891 | Zhang et al. [26] |
| Gaussian Naive Bayes (GNB) | Mortality | 1281 | 11 | MCDW, satO2/FiO2, SIRS, BUN | 0.862 | Ren et al. [34] |
| Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) | Mortality | 97027 | 42 | Increasing age | 0.96 | Anjuli K Luthra et al. [35] |
| Random Forest (RF) | Organ Failure | 143 | 7 + 4 (radiomics) | HDL-C, Calcium, amylase, Apo-AI, lipasa | 0.915 | Lin et al. [41] |
| Auto-encoder (EA) | Septic shock | 604 | 11 | Heart Rate, respiratory rate, lactate, base excess, cystatin | 0.900 | Xia et al. [42] |
| BISAP | Severity | 8274 | 25 | ND | 0.817 | Chang et al. [20] |
| Ranson | Severity | 337 | 12 | ND | 0.652 | Ding et al. [31] |
| APACHE II | Severity | 664 | 10 | SIRS, hypotension, Age > 60 | 0.81 | Mofidi et al. [19] |
| SOFA | Severity | 337 | 12 | ND | 0.41 | Ding et al. [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López Gordo, S.; Ramirez-Maldonado, E.; Fernandez-Planas, M.T.; Bombuy, E.; Memba, R.; Jorba, R. AI and Machine Learning for Precision Medicine in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review. Medicina 2025, 61, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040629
López Gordo S, Ramirez-Maldonado E, Fernandez-Planas MT, Bombuy E, Memba R, Jorba R. AI and Machine Learning for Precision Medicine in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040629
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez Gordo, Sandra, Elena Ramirez-Maldonado, Maria Teresa Fernandez-Planas, Ernest Bombuy, Robert Memba, and Rosa Jorba. 2025. "AI and Machine Learning for Precision Medicine in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review" Medicina 61, no. 4: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040629
APA StyleLópez Gordo, S., Ramirez-Maldonado, E., Fernandez-Planas, M. T., Bombuy, E., Memba, R., & Jorba, R. (2025). AI and Machine Learning for Precision Medicine in Acute Pancreatitis: A Narrative Review. Medicina, 61(4), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040629






