Managing Mortality: Key Factors Influencing Hemiarthroplasty Outcomes in Geriatric Patients with Proximal Femur Fractures
Abstract
1. Introduction
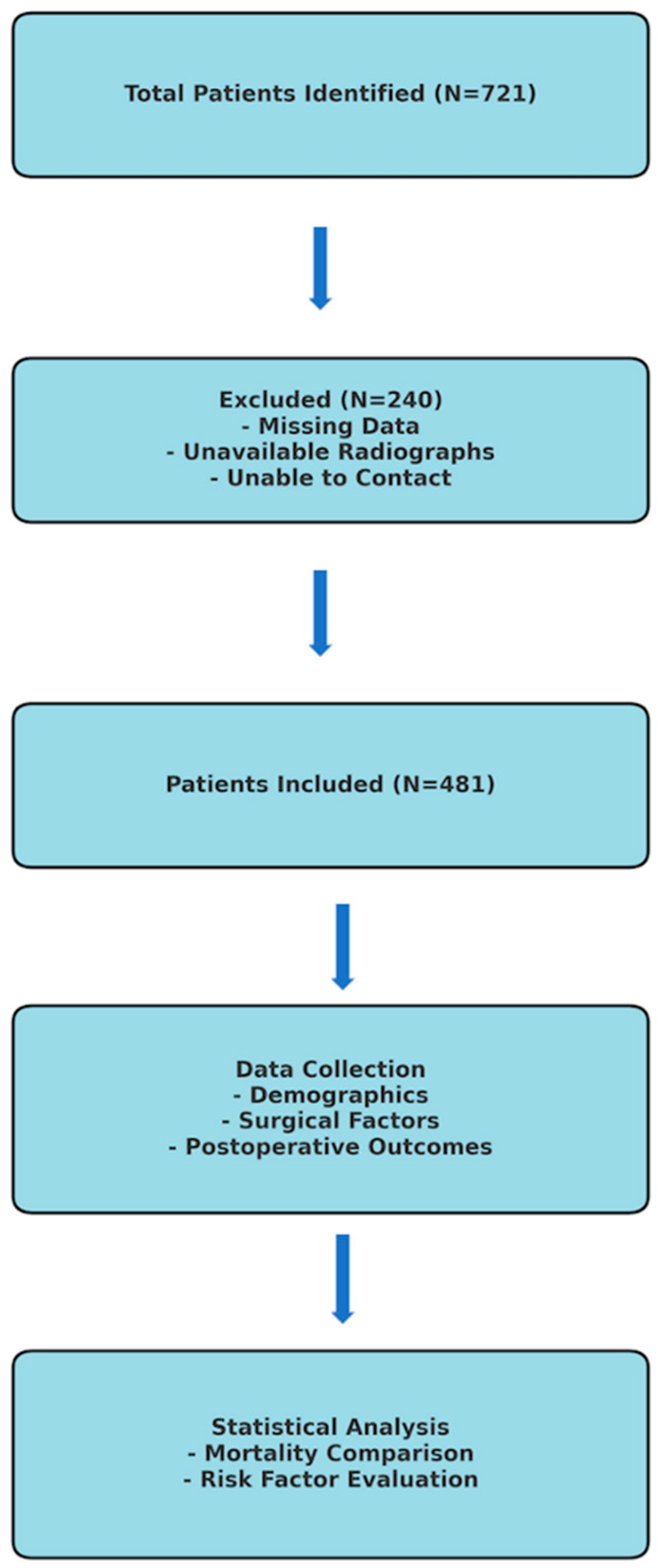
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Parameters Examined in the Study
2.3. Statistical Analysis
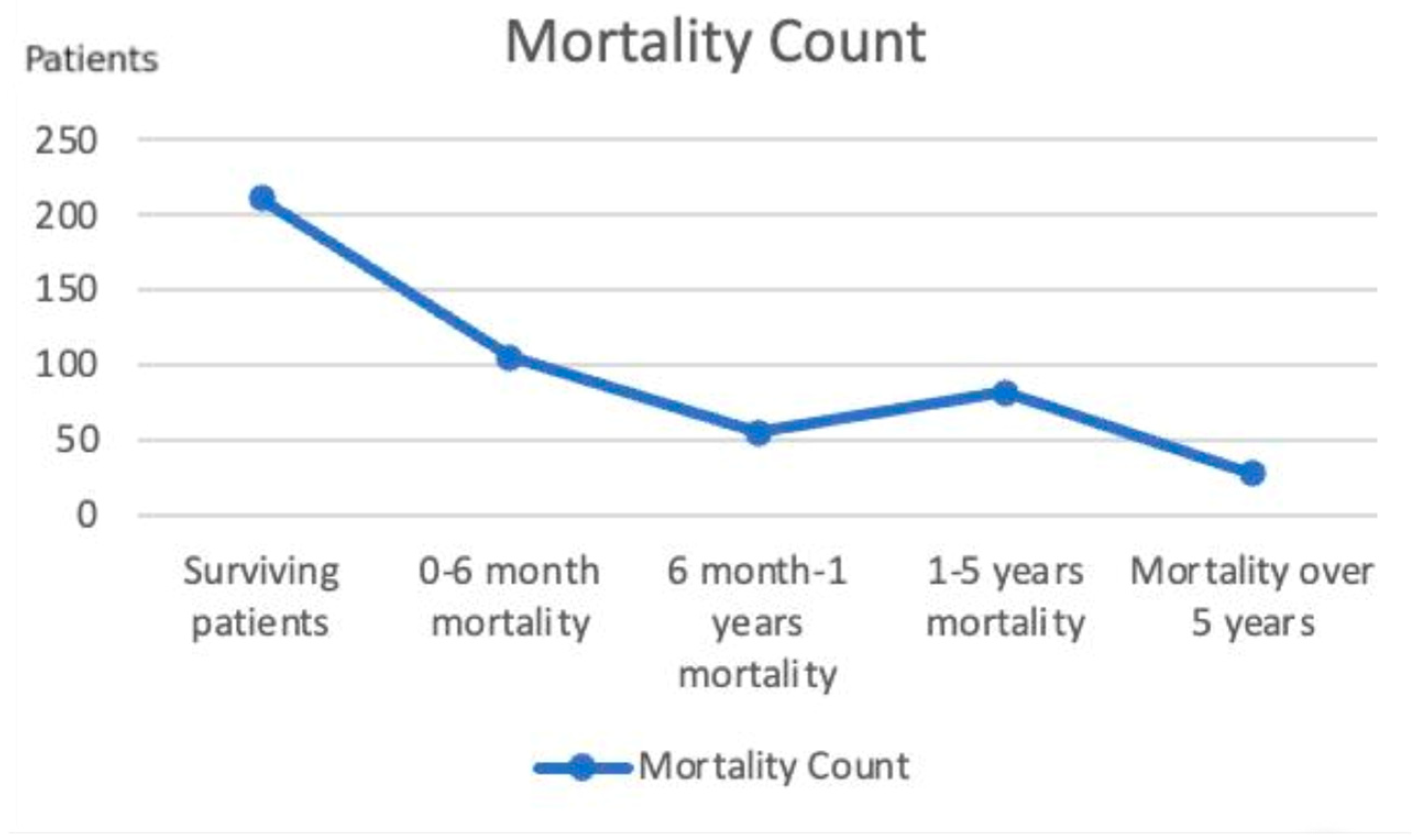
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Factors and Mortality
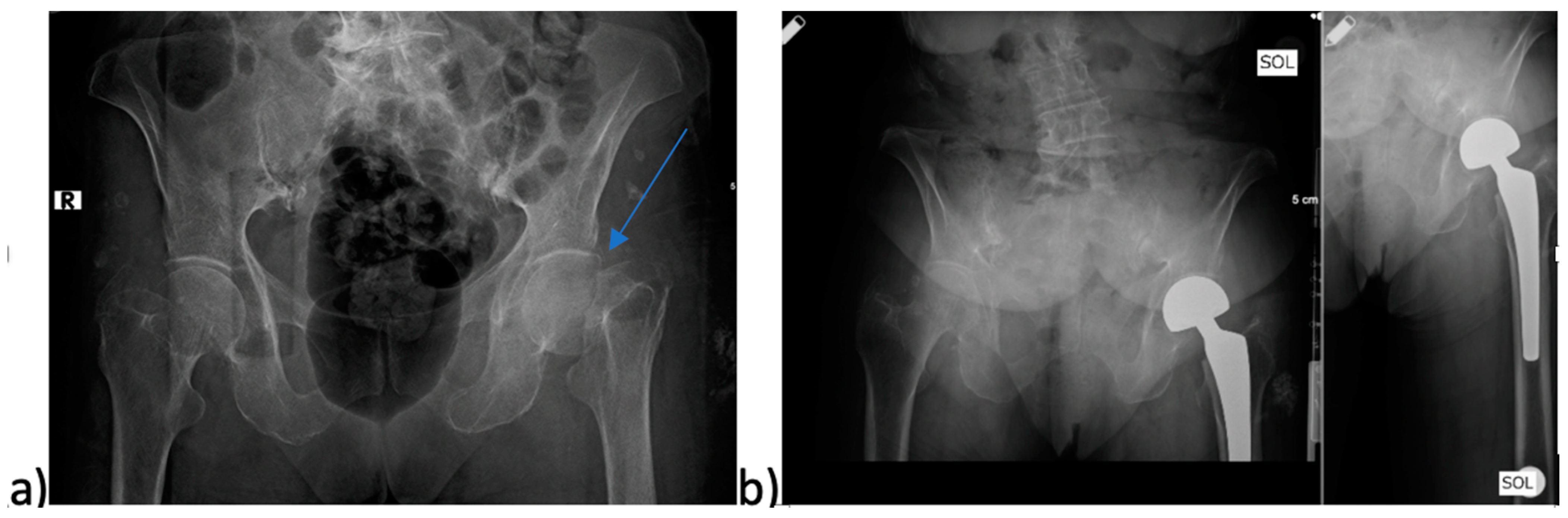
3.2. Surgical Factors and Mortality
3.3. Postoperatives Outcomes and Mortality
4. Discussion
4.1. Demographic Factors and Mortality
4.2. Surgical Factors and Mortality
4.3. Postoperative Outcomes and Mortality
- -
- Early surgical intervention: Patients should undergo surgery within 48 h of admission to minimize complications and improve survival rates.
- -
- Strict infection control protocols: Preoperative and postoperative infection prevention strategies, including appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis and sterile surgical environments, should be strictly followed.
- -
- Optimized perioperative management: Preoperative stabilization of patient conditions can improve surgical outcomes.
- -
- Postoperative early mobilization: Encouraging immediate postoperative mobilization through physical therapy can significantly reduce mortality rates.
- -
- Shorter hospital stays: Efforts should be made to discharge patients as soon as they are medically stable to reduce the risk of hospital-acquired complications.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, F.F.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, B.; Lin, C.H.; Zheng, K. Cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails. Medicine 2019, 98, e14634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Bradman, H.; Fraser, C.; Holt, G. The management of intracapsular hip fractures. Orthop. Trauma 2016, 30, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, C.-W.; Cheung, C.-L. Hip Fracture Burden to Nearly Double Worldwide by 2050. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2023, 38, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, J.; Kostakopoulou, K.; Cool, W.; Ford, D. One-year outcome for elderly patients with displaced intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck managed non-operatively. Injury 2010, 41, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.; Cromwell, D. Statistical Methods Developed for the National Hip Fracture Database Annual Report; Royal College of Surgeons of England: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.; Neelapala, V.; Andrew, J. Results of non-operative treatment following hip fracture compared to surgical intervention. Injury 2009, 40, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogmark, C.; Johnell, O.; Sernbo, I. A prospective randomised trial of internal fixation versus arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the neck of the femur: Functional outcome for 450 patients at two years. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2002, 84, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, R.F. Fractures of the proximal part of the femur. JBJS 1994, 76, 924–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekerom, M.P.V.D.; Sierevelt, I.N.; Bonke, H.; Raaymakers, E.L. The natural history of the hemiarthroplasty for displaced intracapsular femoral neck fractures: 302 patients followed until revision or death. Acta Orthop. 2013, 84, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-D.; Yoo, J.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Kim, T.-Y.; Jung, K.-H.; Kim, Y.-K. Bipolar hemiarthroplasty for hip fractures in patients aged over 90 years-the factors influencing the postoperative mortality. J. Korean Hip Soc. 2010, 22, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A.P.; Hoff, M.; Skoie, I.M.; Hochberg, M.; Haugeberg, G. Short-and long-term mortality in males and females with fragility hip fracture in Norway. A population-based study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Atay, T.; Aydoğan, N.H. Risk factors for mortality and survival rates in elderly patients undergoing hemiarthroplasty for hip fracture. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2020, 54, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Ireland, A.W.; Kelly, P.J.; Cumming, R.G. Risk factor profiles for early and delayed mortality after hip fracture: Analyses of linked Australian Department of Veterans’ Affairs databases. Injury 2015, 46, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, J.; Wenn, R.T.; Sahota, O.; Moran, C.G. Effect of comorbidities and postoperative complications on mortality after hip fracture in elderly people: Prospective observational cohort study. BMJ 2005, 331, 1374. [Google Scholar]
- D’Angelo, F.; Giudici, M.; Molina, M.; Margaria, G. Mortality rate after hip hemiarthroplasty: Analysis of risk factors in 299 consecutives cases. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2005, 6, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri-Tehrani, M.M.; Yavari, P.; Pakdaman, M.; Eslami, S.; Nourian, S.M.A. Comparison of surgical complications following hip hemiarthroplasty between the posterolateral and lateral approaches. Int. J. Burn. Trauma 2021, 11, 406. [Google Scholar]
- Mutlu, H.; Bilgili, F.; Mutlu, S.; Karaman, O.; Cakal, B.; Ozkaya, U. The effects of preoperative non-invasive cardiac tests on delay to surgery and subsequent mortality in elderly patients with hip fracture. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2016, 29, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.; Brown, P.; Webb, M. The use of fast-setting cement in hip hemiarthroplasty significantly reduces operating time without an increase in the rate of complications: 0036. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 47, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Toker, S.; Erturer, E.; Aksoy, B.; Seckin, F. Analysis of risk factors affecting mortality in elderly patients (aged over 65 years) operated on for hip fractures. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2008, 42, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzora, J.E.; Mccarthy, R.E.; Drennan, L.J.; Sledge, C.B. Hip fracture mortality: Relation to age, treatment, preoperative illness, time of surgery, and complications. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. (1976–2007) 1984, 186, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, J.M.; Gomez, G.I.; Chatterjee, M.; Shapiro, L.M.; Morris, A.M.; Gardner, M.J.; Sox-Harris, A.H.S.; Baker, L.; Koltsov, J.C.B.; Castillo, T.; et al. Contextual Determinants of Time to Surgery for Patients with Hip Fracture. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2347834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, T.; Wajima, Z.I.; Ohe, Y. Is operative delay associated with increased mortality of hip fracture patients? Systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Can. J. Anesth. 2008, 55, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, G.; Smith, R.; Duncan, K.; Finlayson, D.; Gregori, A. Early mortality after surgical fixation of hip fractures in the elderly: An analysis of data from the scottish hip fracture audit. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2008, 90, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollmann, C.T.; Dahl, F.A.; Røtterud, J.H.M.; Gjertsen, J.-E.; Årøen, A. Surgical site infection after hip fracture–mortality and risk factors: An observational cohort study of 1709 patients. Acta Orthop. 2020, 91, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Singletary, R.; Schmader, K.; Anderson, D.J.; Bolognesi, M.; Kaye, K.S. Surgical site infection in the elderly following orthopaedic surgery: Risk factors and outcomes. JBJS 2006, 88, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, J.; Syrjälä, H.; Vähänikkilä, H.; Jalovaara, P. Impact of deep infection after hip fracture surgery on function and mortality. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 62, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.; da Casa, C.; Fidalgo, H.; García-Iglesias, M.; González-Garcia, L.; Burón-Alvarez, I.; Sañudo, S.; García-Alonso, M. Effect of hip hemiarthroplasty dislocation on mortality after hip fracture surgery. Rev. Esp. Cir. Ortop. Traumatol. 2023, 67, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, K.; Shannak, O.; Scammell, B.; Moran, C. Predictors and outcomes of treatment in hip hemiarthroplasty dislocation. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2014, 96, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sexson, S.B.; Lehner, J.T. Factors affecting hip fracture mortality. J. Orthop. Trauma 1987, 1, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunovic, N.; Devereaux, P.; Bhandari, M. Surgery for hip fractures: Does surgical delay affect outcomes? Indian J. Orthop. 2011, 45, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, H.C.; Harris, I.A.; McEvoy, L.; Todorova, T. Delay to surgery and mortality after hip fracture. ANZ J. Surg. 2007, 77, 889–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniksar, Ö.; Kacmaz, O.; Yüksek, A.; Aydin, A.; Öz, H. Intensive Care Unit Admission Predictors of Geriatric Patients Who Underwent Hemiarthroplasty due to Hip Fracture. J. Crit. Intensive Care 2021, 12, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
| Mortality/Age | Age/Mean ± SD | Age/Median (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|
| No mortality | 76.96 ± 8.92 | 78 (37–95) |
| 0–6-month mortality | 81.3 ± 10.11 | 84 (48–101) |
| 6-month–1-year mortality | 76.58 ± 7.70 | 78 (54–91) |
| 1–5-year mortality | 80.78 ± 6.89 | 82 (56–96) |
| +5-year mortality | 77.79 ± 6.18 | 78 (66–90) |
| Overall | 78.56 ± 8.82 | 79 (37–101) |
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3 | Type 4 | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients/percentage | 38 (7.9%) | 110 (22.9%) | 73 (15.2%) | 260 (54.1%) | 481 (100%) |
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients/percentage | 364 (75.7%) | 117 (24.3%) | 481 (100%) |
| Supported Mobilization | Unsupported Mobilization | Immobilization | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First postoperative month | 339 (70.5%) | 26 (5.4%) | 116 (24.1%) | 481 (100%) |
| Sixth postoperative month | 168 (34.9%) | 224 (46.6%) | 89 (18.5%) | 481 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayar, E.; Cengiz, T.; Aydın Şimşek, Ş.; Albayrak, B.; Büyükceran, İ.; Tomak, Y. Managing Mortality: Key Factors Influencing Hemiarthroplasty Outcomes in Geriatric Patients with Proximal Femur Fractures. Medicina 2025, 61, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040568
Bayar E, Cengiz T, Aydın Şimşek Ş, Albayrak B, Büyükceran İ, Tomak Y. Managing Mortality: Key Factors Influencing Hemiarthroplasty Outcomes in Geriatric Patients with Proximal Femur Fractures. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040568
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayar, Ercan, Tolgahan Cengiz, Şafak Aydın Şimşek, Bedirhan Albayrak, İsmail Büyükceran, and Yılmaz Tomak. 2025. "Managing Mortality: Key Factors Influencing Hemiarthroplasty Outcomes in Geriatric Patients with Proximal Femur Fractures" Medicina 61, no. 4: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040568
APA StyleBayar, E., Cengiz, T., Aydın Şimşek, Ş., Albayrak, B., Büyükceran, İ., & Tomak, Y. (2025). Managing Mortality: Key Factors Influencing Hemiarthroplasty Outcomes in Geriatric Patients with Proximal Femur Fractures. Medicina, 61(4), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040568






