CT Imaging Features of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Typical and Atypical Radiological Features and Their Differential Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Etiology and Diagnosis
2.1. Diagnostic Criteria and Imaging Modalities
2.2. Histopathologic Confirmation
2.3. The Role of Pulmonary Function Tests
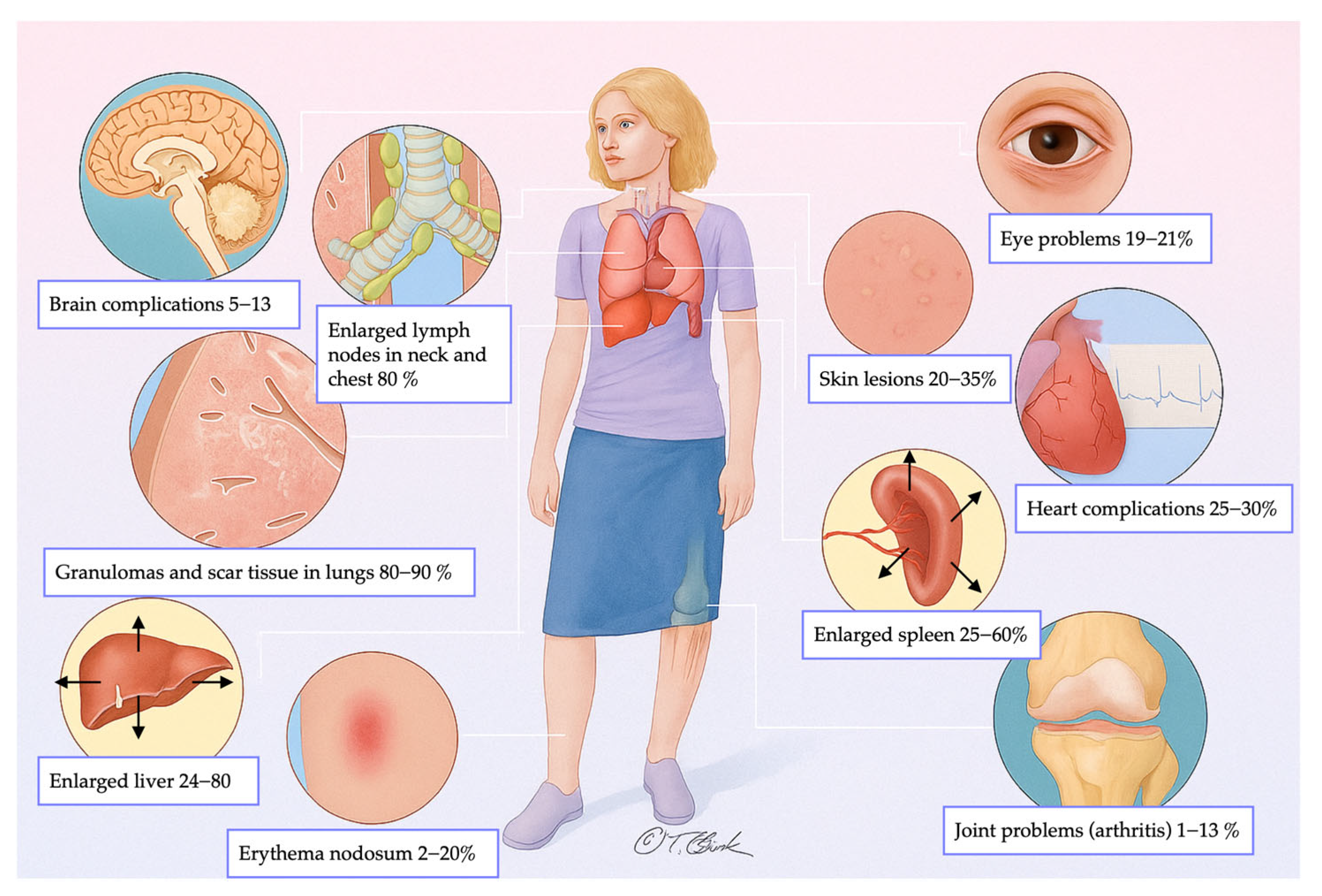
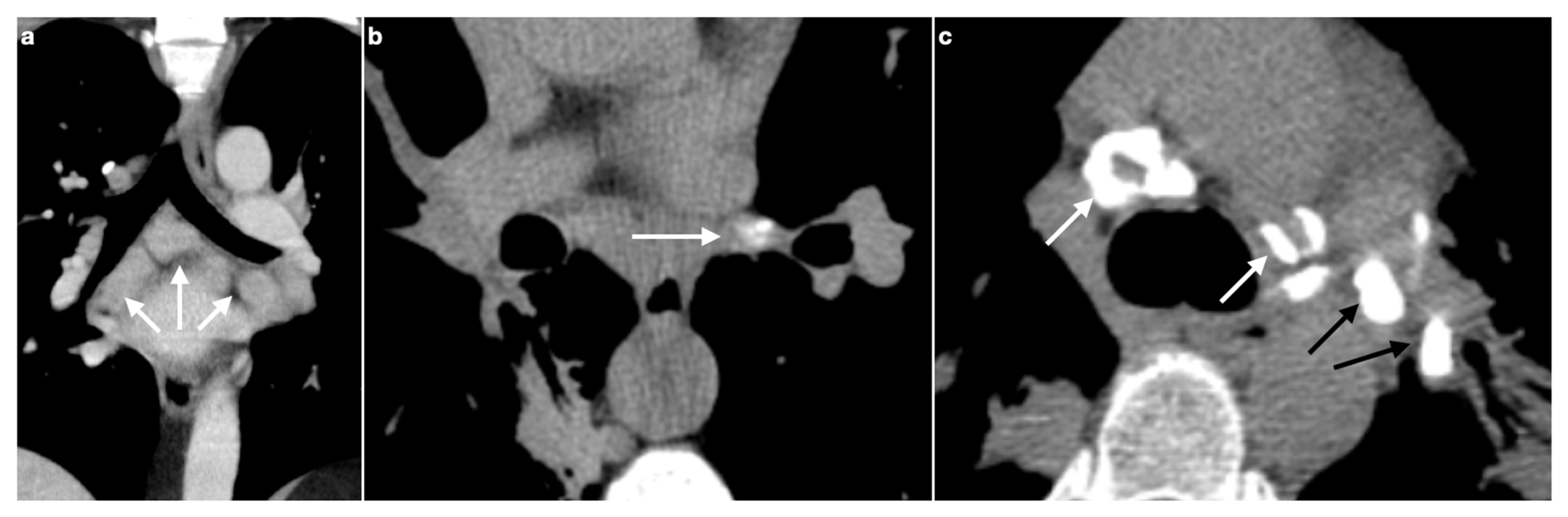
3. Lymphadenopathy
3.1. Typical Imaging
Calcifications
3.2. Atypical Imaging
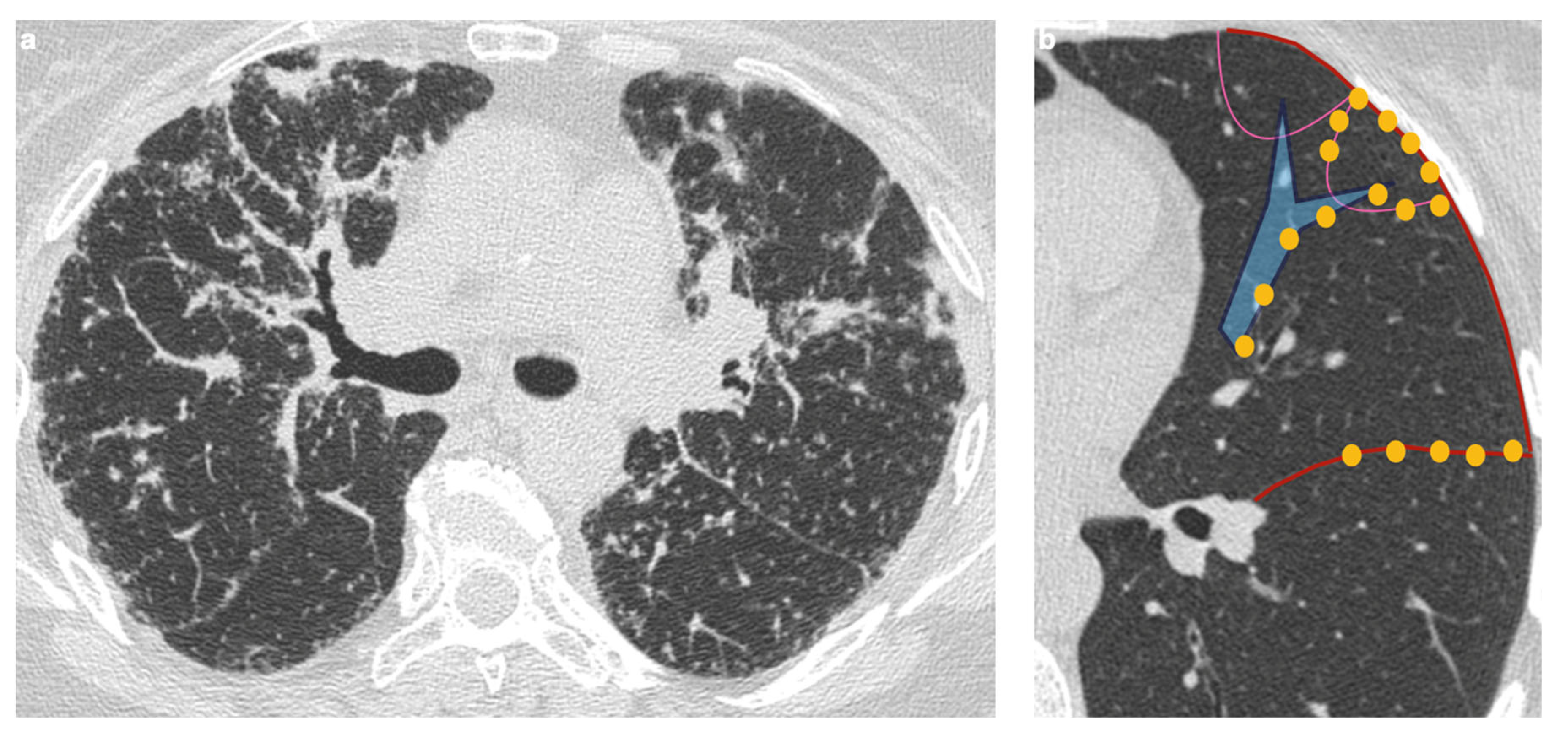
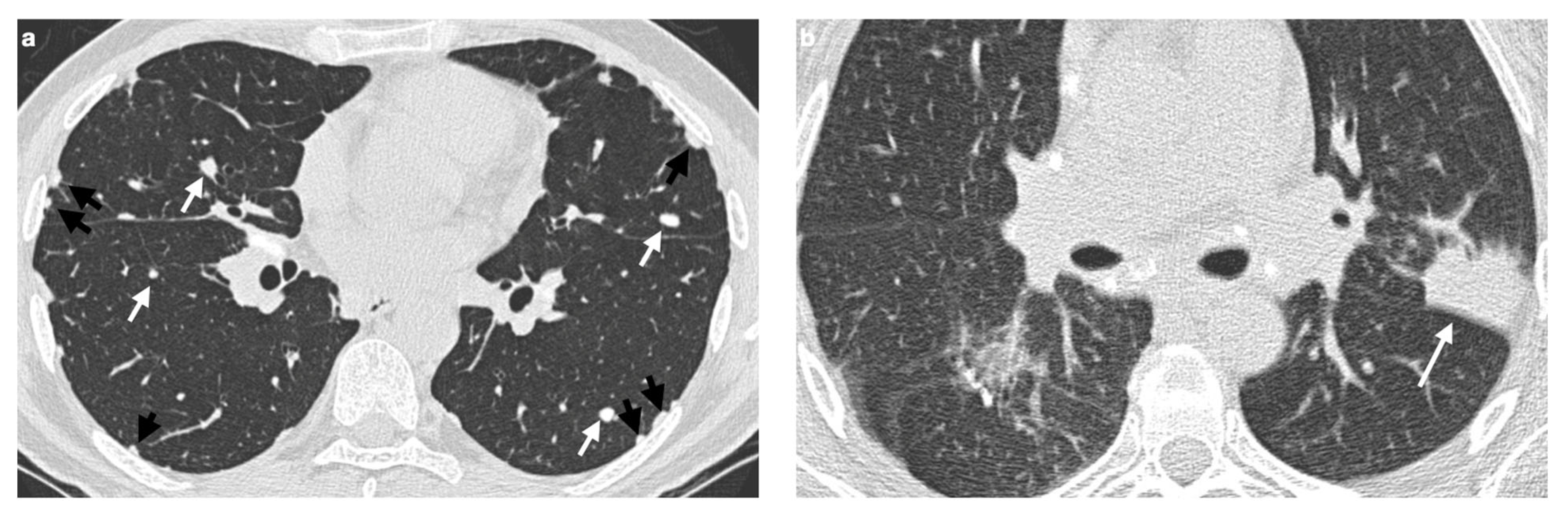
4. Pulmonary Interstitium
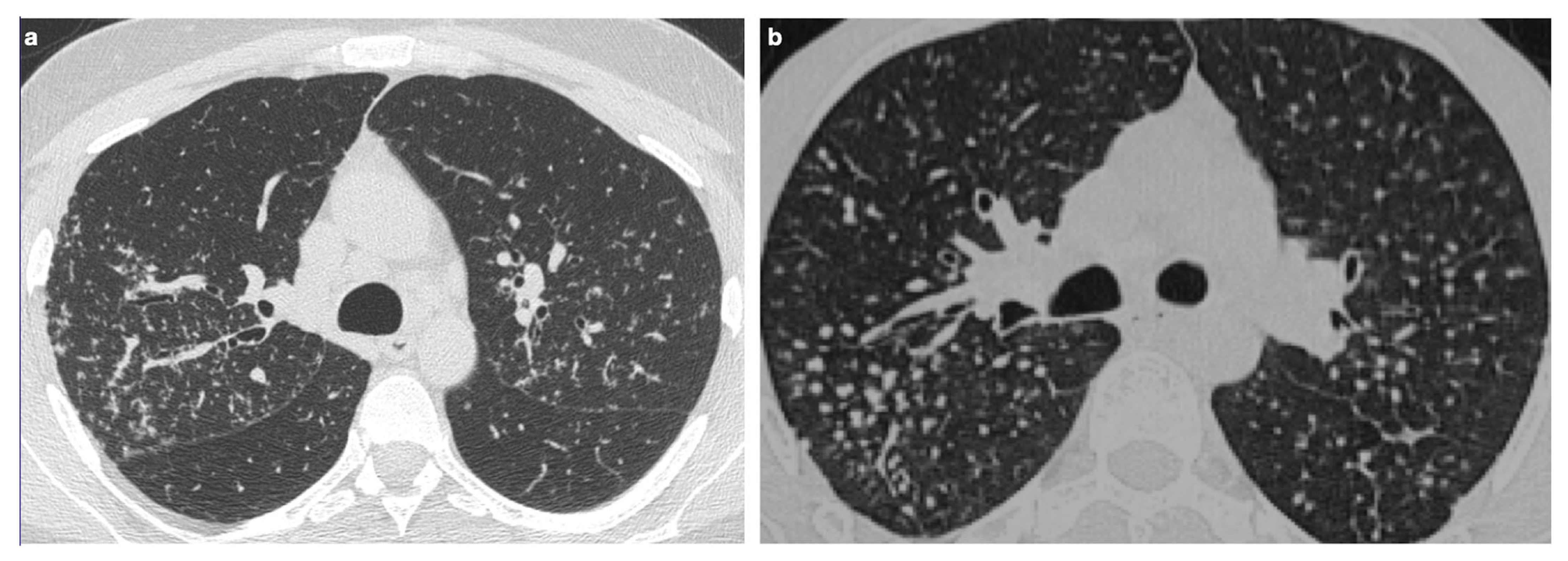
4.1. Typical Imaging
4.2. Atypical Imaging
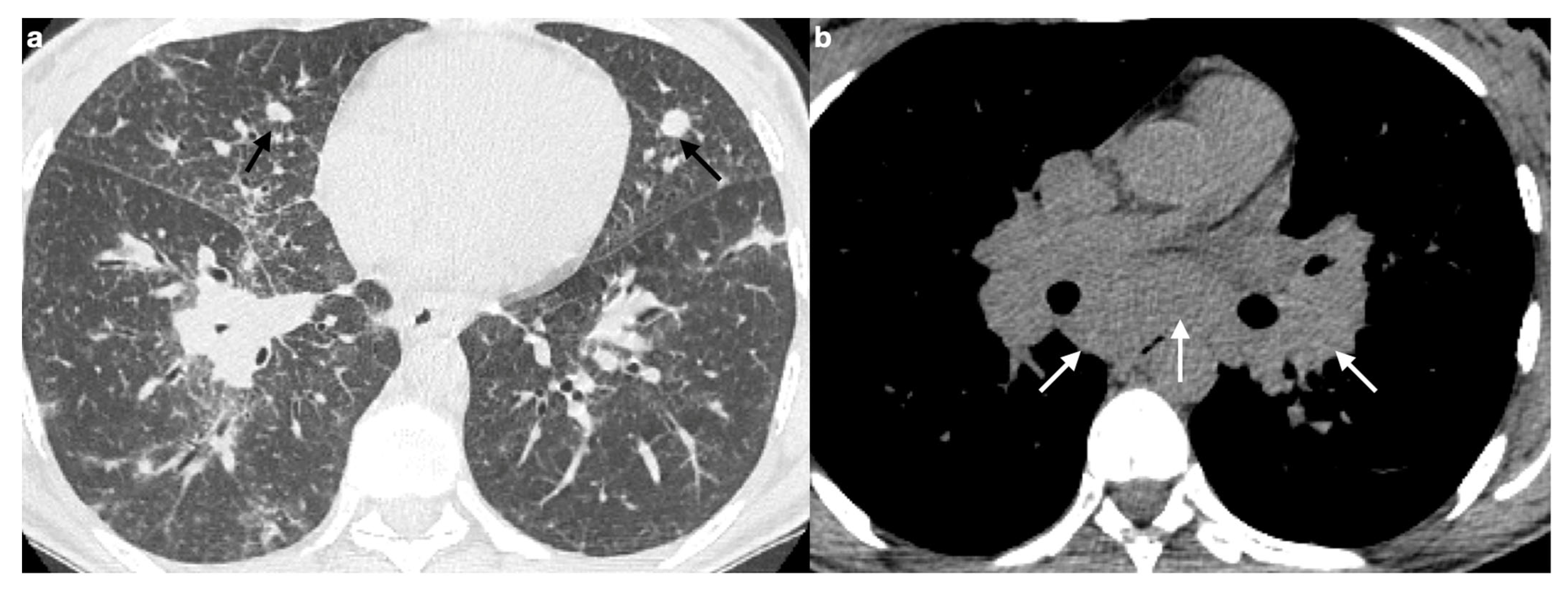
4.2.1. Nodules and Masses
4.2.2. Patchy Parenchymal Consolidation
4.2.3. Ground-Glass Opacities
4.2.4. Miliary Opacities
5. Fibrosis
5.1. Progressive Fibrosing Form
5.2. Association with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
6. Airways
7. Pulmonary Hypertension
8. Main Differential Diagnoses
8.1. Pulmonary Metastases
8.2. Carcinomatous Lymphangitis
8.3. Tuberculosis
8.4. Organizing Pneumonia
8.5. Silicosis
8.6. Common Variable Immunodeficiency
9. Sarcoidosis and Neoplasms
9.1. Possible Correlations Between Neoplasms and Concurrent Onset of Sarcoidosis
9.2. Drug-Induced Sarcoidosis-like Reactions
10. Rare Complications of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis
10.1. Cavitation
10.2. Fungal Colonization
10.3. Pleural Pathologies
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GLD | Granulomatous lung disease |
| CXR | Chest radiography |
| HRCT | High-resolution computed tomography |
| 18-FDG PET/CT | Positron-emission tomography with fluorodeoxyglucose |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| EBUS-TBNA | Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration |
| PFT | Pulmonary function test |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in one second |
| DLCO | Diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide |
| 6MWT | Six-minute walking test |
| GGO | Ground-glass opacities |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| CSIPF | Combined sarcoidosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| OP | Organizing pneumonia |
| CVID | Common variable immunodeficiency |
| GLILD | Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease |
| SLR | Sarcoid-like reaction |
| MGUS | Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance |
| DISR | Drug-induced sarcoidosis-like reaction |
| cART | Combination antiretroviral therapy |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| IFN | Interferon |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
References
- Chopra, A.; Avadhani, V.; Tiwari, A.; Riemer, E.C.; Sica, G.; Judson, M.A. Granulomatous lung disease: Clinical aspects. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, E.; Sánchez, M.; Ramírez, J.; Arguis, P.; De Caralt, T.M.; Perea, R.J.; Xaubet, A. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Typical and Atypical Manifestations at High-Resolution CT with Pathologic Correlation. RadioGraphics 2010, 30, 1567–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshimo, S.; Guzman, J.; Costabel, U.; Bonella, F. Differential diagnosis of granulomatous lung disease: Clues and pitfalls: Number 4 in the Series “Pathology for the clinician” Edited by Peter Dorfmüller and Alberto Cavazza. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belperio, J.A.; Fishbein, M.C.; Abtin, F.; Channick, J.; Balasubramanian, S.A.; Lynch Iii, J.P. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: A comprehensive review: Past to present. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 149, 103107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshan, D.; Menias, C.O.; Lubner, M.G.; Pickhardt, P.J.; Sandrasegaran, K.; Bhalla, S. Sarcoidosis from Head to Toe: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Radiographics 2018, 38, 1180–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statement on Sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 736–755. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.P.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Gay, S.E. Pulmonary sarcoidosis. Clin. Chest Med. 1997, 18, 755–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baughman, R.P.; Teirstein, A.S.; Judson, M.A.; Rossman, M.D.; Yeager, H.; Bresnitz, E.A.; DePALO, L.; Hunninghake, G.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Johns, C.J.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Patients in a Case Control Study of Sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1885–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifazi, M.; Gasparini, S.; Alfieri, V.; Renzoni, E. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 38, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsaeidi, M.; Machado, R.F.; Schraufnagel, D.; Sweiss, N.J.; Baughman, R.P. Racial Difference in Sarcoidosis Mortality in the United States. Chest 2015, 147, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozier, Y.C. Assessing the worldwide epidemiology of sarcoidosis: Challenges and future directions. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, B.A.; Major, M.; Popovich, J.; Maliarik, M.J.; Iannuzzi, M.C. Racial differences in sarcoidosis incidence: A 5-year study in a health maintenance organization. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, M.C.; Rybicki, B.A.; Teirstein, A.S. Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.-C.; Truong, K.-T.; Afshar, K. Key management considerations in sarcoidosis from the American Thoracic Society 2016 Conference. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, S569–S572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouranos, V.; Jacob, J.; Wells, A.U. Severe Sarcoidosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2015, 36, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costabel, U.; Bonella, F.; Ohshimo, S.; Guzman, J. Diagnostic Modalities in Sarcoidosis: BAL, EBUS, and PET. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 31, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Palomares, L.; Caballero-Eraso, C.; Gutierrez, C.; Donate, A.; Antonio, J. Clinical Manifestations of Sarcoidosis. In Sarcoidosis; Eishi, Y., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1027-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hours, S.; Nunes, H.; Kambouchner, M.; Uzunhan, Y.; Brauner, M.W.; Valeyre, D.; Brillet, P.-Y. Pulmonary Cavitary Sarcoidosis: Clinico-Radiologic Characteristics and Natural History of a Rare Form of Sarcoidosis. Medicine 2008, 87, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratella, E.; Borghesi, A.; Calandriello, L.; Cortese, G.; Della Casa, G.; Giraudo, C.; Grassedonio, E.; Larici, A.R.; Palmucci, S.; Romei, C.; et al. Quantification of progressive pulmonary fibrosis by visual scoring of HRCT images: Recommendations from Italian chest radiology experts. Radiol. Med. 2025, 130, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Ji, Q.; Zhou, Y. Pulmonary Function in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keijsers, R.G.M.; Verzijlbergen, J.F.; van Diepen, D.M.; van den Bosch, J.M.M.; Grutters, J.C. 18F-FDG PET in sarcoidosis: An observational study in 12 patients treated with infliximab. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2008, 25, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Mostard, R.L.M.; van Kroonenburgh, M.J.P.G.; Drent, M. The role of the PET scan in the management of sarcoidosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2013, 19, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, R.K. Management strategies for pulmonary sarcoidosis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2009, 5, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teirstein, A.S.; Machac, J.; Almeida, O.; Lu, P.; Padilla, M.L.; Iannuzzi, M.C. Results of 188 whole-body fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography scans in 137 patients with sarcoidosis. Chest 2007, 132, 1949–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostard, R.L.M.; Verschakelen, J.A.; van Kroonenburgh, M.J.P.G.; Nelemans, P.J.; Wijnen, P.A.H.M.; Vöö, S.; Drent, M. Severity of pulmonary involvement and (18)F-FDG PET activity in sarcoidosis. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.J.; Kessler, R.; Constantinesco, A.; Imperiale, A. 18F-FDG PET/CT in sarcoidosis management: Review and report of 20 cases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostard, R.L.; Prompers, L.; Weijers, R.E.; van Kroonenburgh, M.J.; Wijnen, P.A.; Geusens, P.P.; Drent, M. F-18 FDG PET/CT for detecting bone and bone marrow involvement in sarcoidosis patients. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chareonthaitawee, P.; Beanlands, R.S.; Chen, W.; Dorbala, S.; Miller, E.J.; Murthy, V.L.; Birnie, D.H.; Chen, E.S.; Cooper, L.T.; Tung, R.H.; et al. Joint SNMMI-ASNC Expert Consensus Document on the Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Cardiac Sarcoid Detection and Therapy Monitoring. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, G.; Leung, E.; Mylonas, I.; Nery, P.; Williams, K.; Wisenberg, G.; Gulenchyn, K.Y.; Dekemp, R.A.; Dasilva, J.; Birnie, D.; et al. The use of 18F-FDG PET in the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis: A systematic review and metaanalysis including the Ontario experience. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.; Chan, M.V.; Urzua Fresno, C.; Farrell, A.; Islam, N.; McInnes, M.D.F.; Iwanochko, M.; Balter, M.; Moayedi, Y.; Thavendiranathan, P.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Cardiac MRI versus FDG PET for Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology 2022, 304, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauczor, H.-U.; Ley-Zaporozhan, J.; Ley, S. Imaging of pulmonary pathologies: Focus on magnetic resonance imaging. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2009, 6, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetikkurt, C.; Yanardag, E.; Bilir, M.; Yanardag, H.; Kimyon, U. Diagnostic yield of the Kveim test in sarcoidosis patients. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2024, 41, e2024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grutters, J.C. Establishing a Diagnosis of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaquen, S.; Matta, A.; Sultan, S.; Sarvottam, K. Role of Bronchoscopy in Diagnosis of Sarcoidosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2024, 45, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, A.R.; Shadid, A.M. The Role of Bronchoscopy in the Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.G.; Cheung, W.Y.; Hutchings, H.A. Sarcoidosis: A long-term follow up study. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2000, 17, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Baughman, R.P.; Nunes, H.; Sweiss, N.J.; Lower, E.E. Established and experimental medical therapy of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 1424–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Drent, M.; Culver, D.A.; Grutters, J.C.; Handa, T.; Humbert, M.; Judson, M.A.; Lower, E.E.; Mana, J.; Pereira, C.A.; et al. Endpoints for clinical trials of sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2012, 29, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, T.; Nagai, S.; Fushimi, Y.; Miki, S.; Ohta, K.; Niimi, A.; Mishima, M.; Izumi, T. Clinical and radiographic indices associated with airflow limitation in patients with sarcoidosis. Chest 2006, 130, 1851–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, O.P.; Johnson, R. Airway obstruction in sarcoidosis. A study of 123 nonsmoking black American patients with sarcoidosis. Chest 1988, 94, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, K.C.; Strek, M.E. Pulmonary fibrosis in sarcoidosis. Clinical features and outcomes. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abehsera, M.; Valeyre, D.; Grenier, P.; Jaillet, H.; Battesti, J.P.; Brauner, M.W. Sarcoidosis with pulmonary fibrosis: CT patterns and correlation with pulmonary function. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 174, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.L.; Wells, A.U.; Sverzellati, N.; Keir, G.J.; Calandriello, L.; Antoniou, K.M.; Copley, S.J.; Devaraj, A.; Maher, T.M.; Renzoni, E.; et al. An integrated clinicoradiological staging system for pulmonary sarcoidosis: A case-cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkil, G.; Lower, E.E.; Baughman, R.P. Predictors of Mortality in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Chest 2018, 153, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savale, L.; Huitema, M.; Shlobin, O.; Kouranos, V.; Nathan, S.D.; Nunes, H.; Gupta, R.; Grutters, J.C.; Culver, D.A.; Post, M.C.; et al. WASOG statement on the diagnosis and management of sarcoidosis-associated pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 210165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeny, F.; Bernaudin, J.-F.; Cohen Aubart, F.; Brillet, P.-Y.; Bouvry, D.; Nunes, H.; Valeyre, D. Diagnosis issues in sarcoidosis. Respir. Med. Res. 2020, 77, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baughman, R.P.; Engel, P.J.; Taylor, L.; Lower, E.E. Survival in sarcoidosis-associated pulmonary hypertension: The importance of hemodynamic evaluation. Chest 2010, 138, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlobin, O.A.; Nathan, S.D. Management of end-stage sarcoidosis: Pulmonary hypertension and lung transplantation. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlobin, O.A.; Kouranos, V.; Barnett, S.D.; Alhamad, E.H.; Culver, D.A.; Barney, J.; Cordova, F.C.; Carmona, E.M.; Scholand, M.B.; Wijsenbeek, M.; et al. Physiological predictors of survival in patients with sarcoidosis-associated pulmonary hypertension: Results from an international registry. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, C.E.; Henke, G.; Elveback, L.R.; Beard, M.; Ballard, D.J.; Kurland, L.T. The Epidemiology of sarcoidosis in rochester, minnesota: A population-based study of incidence and survival. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 123, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, J.M. Mortality of Intrathoracic Sarcoidosis in Referral vs. Population-Based Settings. Chest 2002, 121, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, M.A. (Ed.) Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: A Guide for the Practicing Clinician; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4614-8926-9. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.J.; Jung, J.I.; Chung, M.H.; Song, S.W.; Kim, H.L.; Baik, J.H.; Han, D.H.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, K.-Y. Typical and Atypical Manifestations of Intrathoracic Sarcoidosis. Korean J. Radiol. 2009, 10, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouranos, V.; Hansell, D.M.; Sharma, R.; Wells, A.U. Advances in imaging of cardiopulmonary involvement in sarcoidosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2015, 21, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockoff, S.; Rohatgi, P. Unusual manifestations of thoracic sarcoidosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1985, 144, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamper, U.M.; Fishman, E.K.; Khouri, N.F.; Johns, C.J.; Wang, K.P.; Siegelman, S.S. Typical and Atypical CT Manifestations of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1986, 10, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, E.F.; Glickstein, M.F.; Mahar, P.; Miller, W.T. Pulmonary sarcoidosis in the older patient: Conventional radiographic features. Radiology 1988, 169, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.H.; Rosado-de-Christenson, M.L.; McAdams, H.P.; Fishback, N.F. Thoracic sarcoidosis: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 1995, 15, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Ueda, H.; Togashi, K.; Umeoka, S.; Kataoka, M.; Nagai, S. Radiologic Manifestations of Sarcoidosis in Various Organs. RadioGraphics 2004, 24, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, N.; Kullnig, P.; Miller, R. The CT findings of pulmonary sarcoidosis: Analysis of 25 patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1989, 152, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverosi, R.; Russo, R.; Coran, A.; Battista, A.; Agostini, C.; Pomerri, F.; Giraudo, C. Typical and atypical pattern of pulmonary sarcoidosis at high-resolution CT: Relation to clinical evolution and therapeutic procedures. Radiol. Med. 2014, 119, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsu, M.; Hatabu, H.; Morikawa, K.; Uematsu, H.; Ohno, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Nagai, S.; Izumi, T.; Konishi, J.; Itoh, H. Large Coalescent Parenchymal Nodules in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: “Sarcoid Galaxy” Sign. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 178, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herráez Ortega, I.; Alonso Orcajo, N.; López González, L. El “cúmulo sarcoideo”. Un nuevo signo en tomografía computarizada de tórax de alta resolución. Radiología 2009, 51, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S. Webb, Müller and Naidich’s High-Resolution CT of the Lung, 6th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-9751-4443-2. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, I.M.; Libshitz, H.I.; Glassman, L.M.; Israel, H.L. Sarcoidosis. Typical and atypical thoracic manifestations and complications. Clin. Radiol. 1970, 21, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Itoh, H.; Kitaichi, M.; Nagai, S.; Izumi, T. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: Correlation of CT and histopathologic findings. Radiology 1993, 189, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zompatori, M.; Poletti, V.; Battista, G.; Diegoli, M. Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia (BOOP), presenting as a ring-shaped opacity at HRCT (the atoll sign). A case report. Radiol. Med. 1999, 97, 308–310. [Google Scholar]
- Marten, K.; Rummeny, E.J.; Engelke, C. The CT halo: A new sign in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. Br. J. Radiol. 2004, 77, 1042–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A. High resolution computed tomography in sarcoidosis: A clinical perspective. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 1998, 15, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Bonham, C.A.; Strek, M.E.; Patterson, K.C. From granuloma to fibrosis: Sarcoidosis associated pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2016, 22, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, R.A.; Al-Ani, M.A.Z.; Altmayer, S.; Dias Prodigios, J.; Mehrad, B.; Marchiori, E.; Patel, D.; Zanon, M.; Mohammed, T.-L.; Moreno, M.; et al. Multimodality Imaging for the Diagnosis and Evaluation of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2025, 7, e240294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, M.; Han, J.; Wada, N.; Song, J.W.; Hwang, J.; Lee, H.Y.; Hata, A.; Franquet, T.; Chung, M.P.; Tomiyama, N.; et al. Advances in Concept and Imaging of Interstitial Lung Disease. Radiology 2025, 315, e241252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marll, M.; Fawaz, A.; Shaver, A. An Updated Review on Treatment of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis and Multisystem Disease Monitoring. Curr. Pulmonol. Rep. 2025, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.R.; Sivarasan, N.; Johannson, K.A.; George, P.M.; Culver, D.A.; Devaraj, A.; Lynch, D.A.; Milne, D.; Renzoni, E.; Nunes, H.; et al. High-resolution CT phenotypes in pulmonary sarcoidosis: A multinational Delphi consensus study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Kim, G.H.; Salisbury, M.L.; Barber, D.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Brown, K.K.; Conoscenti, C.S.; De Backer, J.; Flaherty, K.R.; Gruden, J.F.; et al. Computed Tomographic Biomarkers in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. The Future of Quantitative Analysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoud, T.C.; Little, B.P. Thoracic Radiology: Recent Developments and Future Trends. Radiology 2023, 306, e223121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, C.C.W.; Bates, J.H.T.; Driehuys, B.; Fain, S.B.; Goldin, J.G.; Hoffman, E.A.; Hogg, J.C.; Levin, D.L.; Lynch, D.A.; Ochs, M.; et al. Quantitative Imaging Metrics for the Assessment of Pulmonary Pathophysiology: An Official American Thoracic Society and Fleischner Society Joint Workshop Report. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2023, 20, 161–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.K.; Martinez, F.J.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Thannickal, V.J.; Prasse, A.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Goeldner, R.-G.; Clerisme-Beaty, E.; Tetzlaff, K.; Cottin, V.; et al. The natural history of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, W.; Clark, M. Sarcoidosis; a clinicopathologic review of 300 cases, including 22 autopsies. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1949, 19, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, G.L.; Wells, A.U.; Desai, S.R. Imaging of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis-A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polychronopoulos, V.S.; Prakash, U.B.S. Airway Involvement in Sarcoidosis. Chest 2009, 136, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Lower, E.E.; Tami, T. Upper airway.4: Sarcoidosis of the upper respiratory tract (SURT). Thorax 2010, 65, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.G.; Barter, S.; Jash, D.; MacKinnon, D.M.; Carstairs, L.S. Sarcoidosis of the upper respiratory tract (SURT). J. Laryngol. Otol. 1982, 96, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udwadia, Z.F.; Pilling, J.R.; Jenkins, P.F.; Harrison, B.D. Bronchoscopic and bronchographic findings in 12 patients with sarcoidosis and severe or progressive airways obstruction. Thorax 1990, 45, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkless, H.A.; Chodoff, R.J. Middle Lobe Syndrome Due to Sarcoidosis. Dis. Chest 1956, 30, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenique, F.; Brauner, M.W.; Grenier, P.; Battesti, J.P.; Loiseau, A.; Valeyre, D. CT assessment of bronchi in sarcoidosis: Endoscopic and pathologic correlations. Radiology 1995, 194, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huitema, M.P.; Spee, M.; Vorselaars, V.M.M.; Boerman, S.; Snijder, R.J.; Van Es, H.W.; Reesink, H.J.; Grutters, J.C.; Post, M.C. Pulmonary artery diameter to predict pulmonary hypertension in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israël-Biet, D.; Pastré, J.; Nunes, H. Sarcoidosis-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeyre, D.; Brauner, M.; Bernaudin, J.-F.; Carbonnelle, E.; Duchemann, B.; Rotenberg, C.; Berger, I.; Martin, A.; Nunes, H.; Naccache, J.-M.; et al. Differential diagnosis of pulmonary sarcoidosis: A review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1150751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauner, M.W.; Lenoir, S.; Grenier, P.; Cluzel, P.; Battesti, J.P.; Valeyre, D. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: CT assessment of lesion reversibility. Radiology 1992, 182, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauner, M.W.; Grenier, P.; Mompoint, D.; Lenoir, S.; De Crémoux, H. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: Evaluation with high-resolution CT. Radiology 1989, 172, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, O.; Johkoh, T.; Ichikado, K.; Yoshida, S.; Mihara, N.; Higashi, M.; Tomiyama, N.; Maeda, M.; Hamada, S.; Naito, H.; et al. Comparison of High Resolution CT Findings of Sarcoidosis, Lymphoma, and Lymphangitic Carcinoma: Is There Any Difference of Involved Interstitium? J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1999, 23, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Sekiguchi, H.; Yi, E.S. Pulmonary manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiori, E.; Zanetti, G.; Barreto, M.M.; De Andrade, F.T.A.; Rodrigues, R.S. Atypical distribution of small nodules on high resolution CT studies: Patterns and differentials. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voloudaki, A.E.; Bouros, D.E.; Froudarakis, M.E.; Datseris, G.E.; Apostolaki, E.G.; Gourtsoyiannis, N.C. Crescentic and Ring-Shaped Opacities: CT Features in Two Cases of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Organizing Pneumonia (BOOP). Acta Radiol. 1996, 37, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.S.; Ryu, Y.H.; Yoon, Y.C.; Choe, K.O.; Kim, T.S.; Sung, K.J. Reversed halo sign on high-resolution CT of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: Diagnostic implications. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Kullnig, P.; Hartman, T.E.; Müller, N.L. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: CT findings in 43 patients. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 162, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare Mehrjardi, M.; Kahkouee, S.; Pourabdollah, M. Radio-pathological correlation of organizing pneumonia (OP): A pictorial review. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.W.; Rose, C.S.; Lynch, D.A. State of the Art: Imaging of Occupational Lung Disease. Radiology 2014, 270, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.M.; Pope, K.; Meek, L.; Chung, J.H.; Hobbs, S.B.; Walker, C.M. Sarcoidosis: A Diagnosis of Exclusion. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardinello, N.; Petrarulo, S.; Balestro, E.; Cocconcelli, E.; Veltkamp, M.; Spagnolo, P. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patuzzo, G.; Barbieri, A.; Tinazzi, E.; Veneri, D.; Argentino, G.; Moretta, F.; Puccetti, A.; Lunardi, C. Autoimmunity and infection in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Levinson, A.I. Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Clin. Immunol. 2010, 134, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Sverzellati, N.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M. Imaging aspects of the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grados, A.; Ebbo, M.; Bernit, E.; Veit, V.; Mazodier, K.; Jean, R.; Coso, D.; Aurran-Schleinitz, T.; Broussais, F.; Bouabdallah, R.; et al. Sarcoidosis Occurring After Solid Cancer: A Nonfortuitous Association: Report of 12 Cases and Review of the Literature. Medicine 2015, 94, e928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenter, V.; Albert, N.L.; Ahmaddy, F.; Unterrainer, M.; Hornung, J.; Ilhan, H.; Bartenstein, P.; Spitzweg, C.; Kneidinger, N.; Todica, A. The diagnostic challenge of coexistent sarcoidosis and thyroid cancer—A retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, J.; Begent, R.H.; Meyer, T. Sarcoidosis and testicular cancer: A case series and literature review. Urol. Oncol. 2010, 28, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, A.M.; Pasciuto, G.; Verrecchia, E.; Sicignano, L.L.; Gerardino, L.; Massaro, M.G.; Urbani, A.; Manna, R. Sarcoidosis and Cancer: The Role of the Granulomatous Reaction as a Double-Edged Sword. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, S.; Kantarjian, H.; O’Brien, S.; Cohen, P.R.; Pierce, S.; Talpaz, M. Immune-mediated and unusual complications during interferon alfa therapy in chronic myelogenous leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 2401–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; Anzai, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Tsuchiya, J.; Shirai, T.; Shibata, S.; Sakakibara, R.; Mitsumura, T.; Honda, T.; et al. Deep convolutional neural network for differentiating between sarcoidosis and lymphoma based on [18F]FDG maximum-intensity projection images. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 34, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, G.; Itani, M.; Shah, H.; Ahuja, J.; Yilmaz Gunes, B.; Assaker, R.; Behnia, F. PET/CT in the Diagnosis and Workup of Sarcoidosis: Focus on Atypical Manifestations. RadioGraphics 2018, 38, 1536–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincker, H. The sarcoidosis-lymphoma syndrome. Br. J. Cancer 1986, 54, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincker, H. Sarcoid Reactions and Sarcoidosis in Hodgkin’s Disease and Other Malignant Lymphomata. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miedema, J.; Nunes, H. Drug-induced sarcoidosis-like reactions. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2021, 27, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Pleuvry, A.; Cole, D.C. Global burden of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis complicating sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Cadranel, J.; Beigelman-Aubry, C.; Ader, F.; Chakrabarti, A.; Blot, S.; Ullmann, A.J.; Dimopoulos, G.; Lange, C.; European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases and European Respiratory Society. Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: Rationale and clinical guidelines for diagnosis and management. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollschlager, C.; Khan, F. Aspergillomas complicating sarcoidosis. A prospective study in 100 patients. Chest 1984, 86, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szwarcberg, J.B.; Glajchen, N.; Teirstein, A.S. Pleural involvement in chronic sarcoidosis detected by thoracic CT scanning. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2005, 22, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Froudarakis, M.E.; Bouros, D.; Voloudaki, A.; Papiris, S.; Kottakis, Y.; Constantopoulos, S.H.; Siafakas, N.M. Pneumothorax as a first manifestation of sarcoidosis. Chest 1997, 112, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomm, S.A. An unusual presentation of sarcoidosis—Spontaneous haemopneumothorax. Postgrad. Med. J. 1984, 60, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, H.-P.; Xu, L.-L.; Li, X. Recurrent pneumothorax as a presenting manifestation of active sarcoidosis: A case report and literature review. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 1615–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Omori, H.; Asahi, H.; Irinoda, T.; Itabashi, T.; Saito, K. Pneumothorax as a presenting manifestation of early sarcoidosis. Jpn. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 52, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
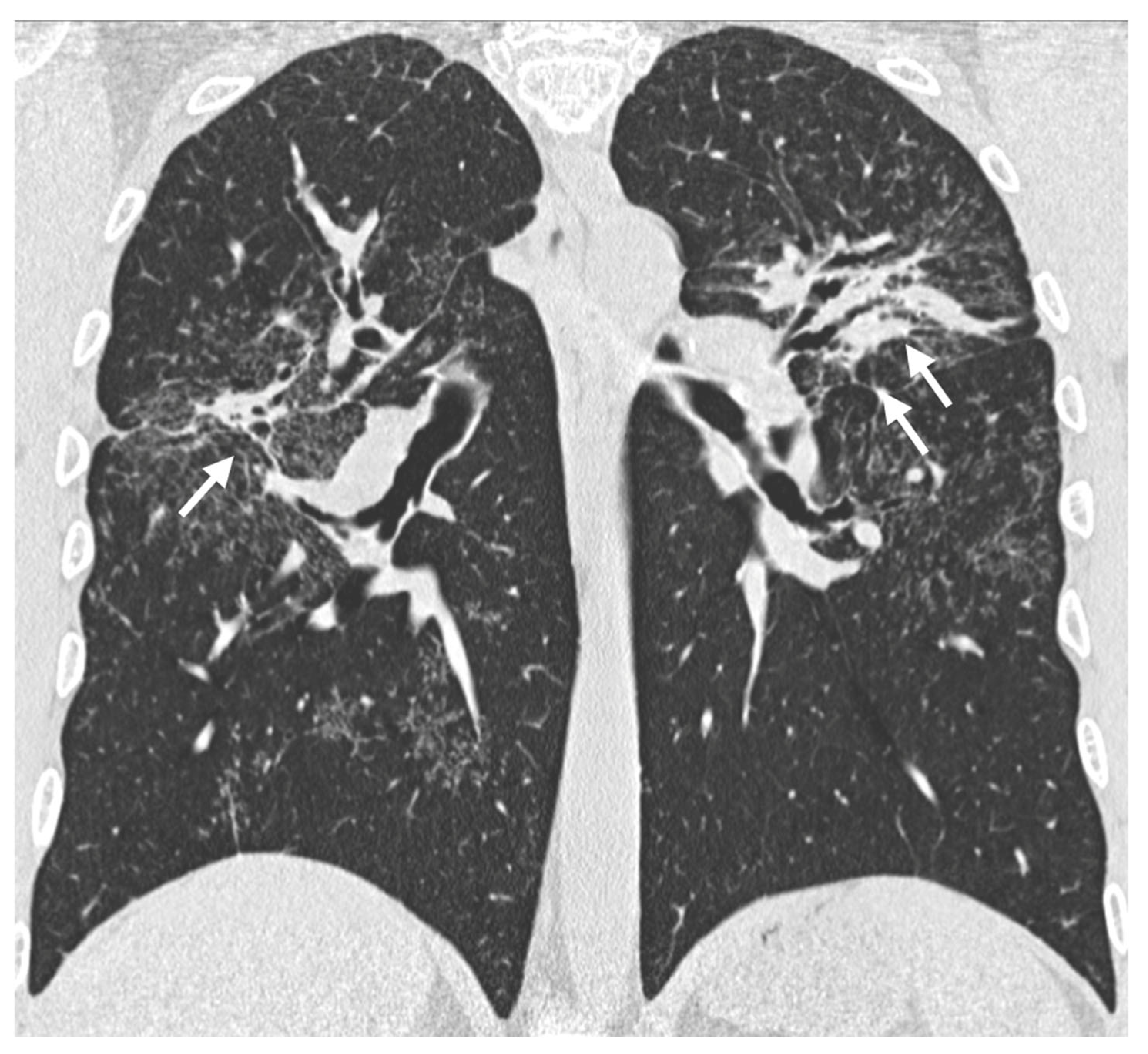
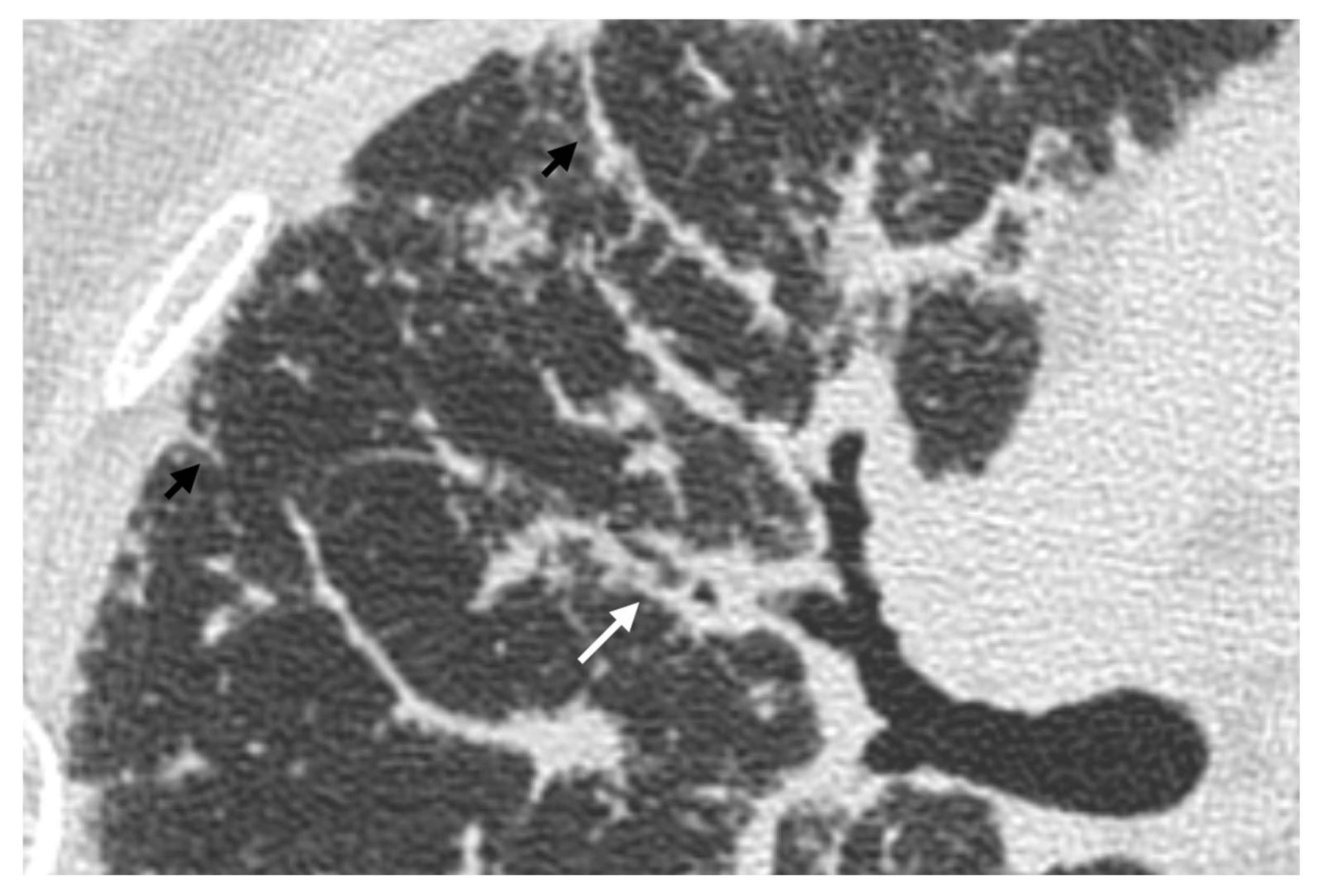
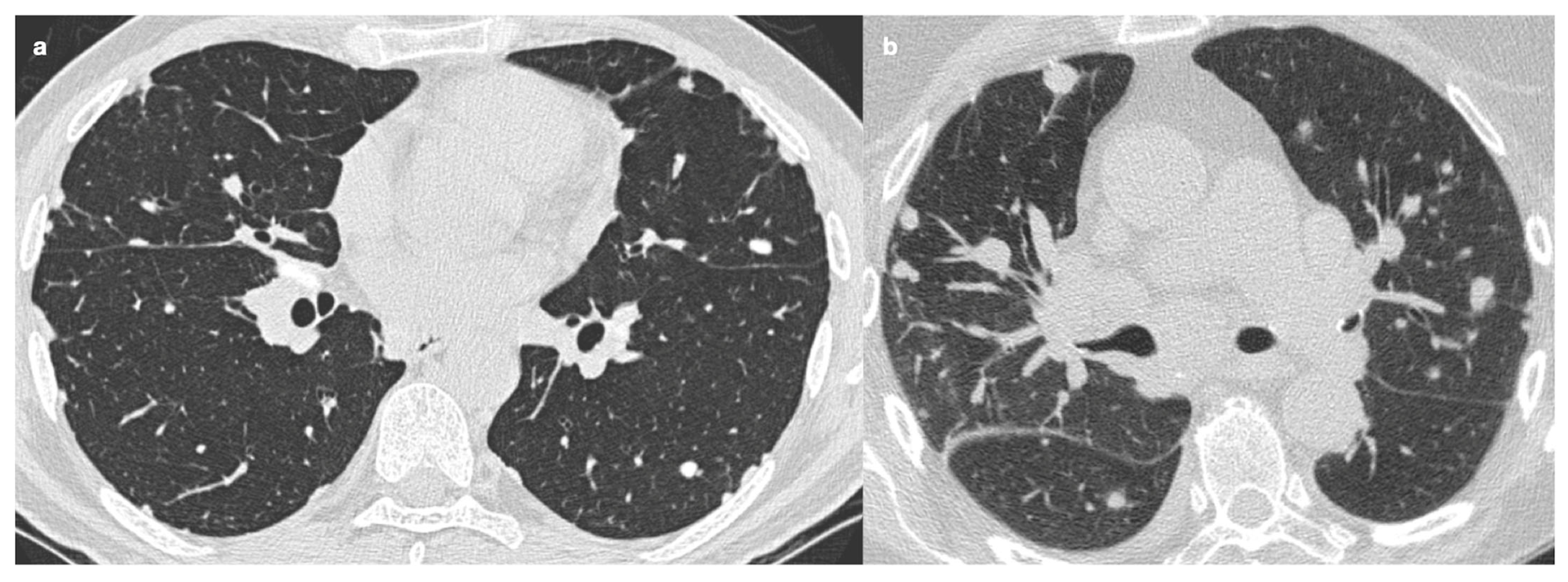
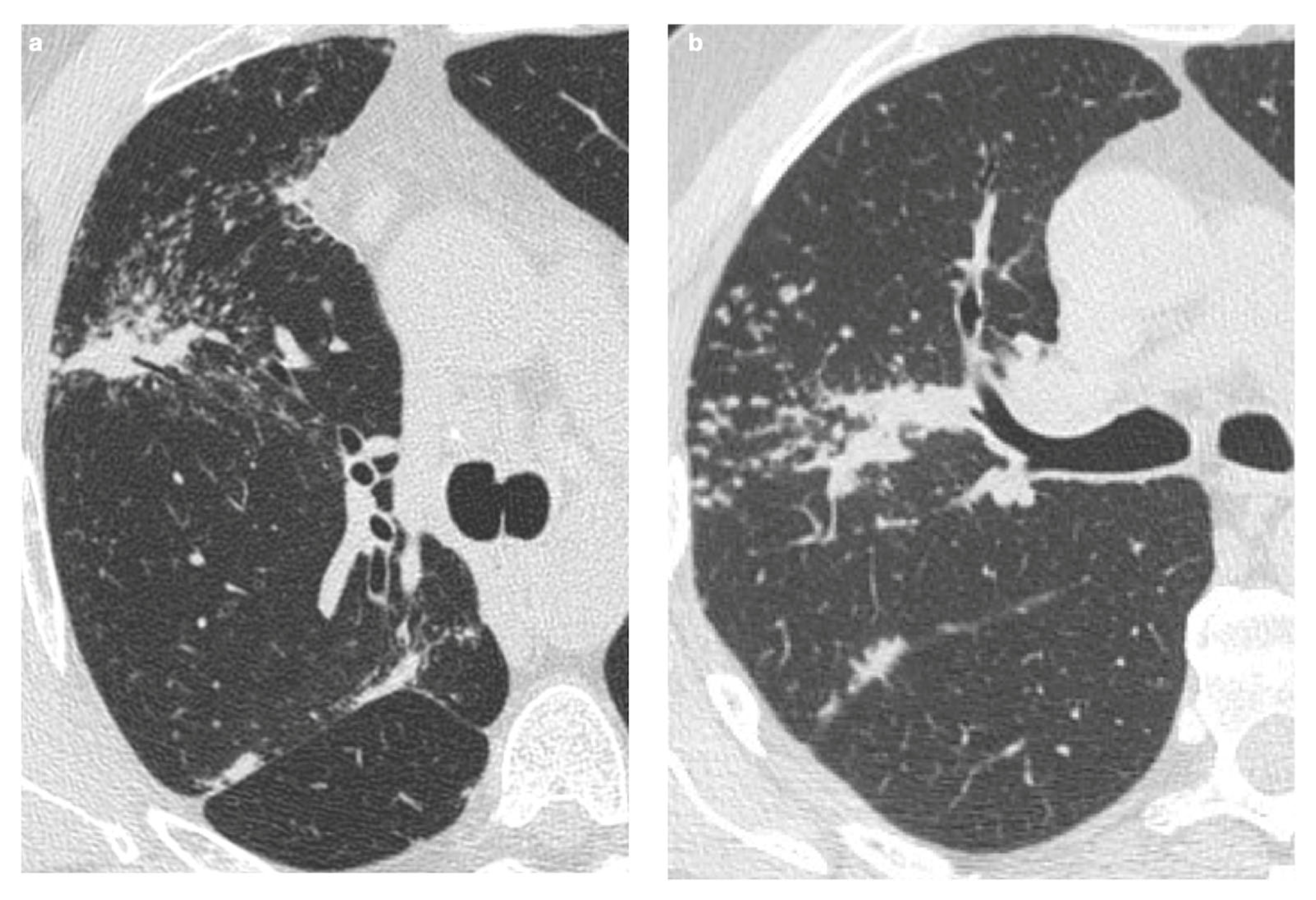
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage 0 | Normal chest radiograph, no evidence of disease. |
| Stage I | Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, often associated with enlargement of right para-tracheal lymph nodes, without parenchymal lung alterations. |
| Stage II | Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy accompanied by reticular parenchymal opacities. |
| Stage III | Reticular parenchymal opacities without hilar lymphadenopathy. |
| Stage IV | Reticular opacities associated with pulmonary volume loss, predominantly involving the upper lobes. Possible presence of traction bronchiectasis, calcifications, cavitations, or cystic formations. |
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Distribution | Perilympathic (75–90% of cases); bilateral and symmetric involvement, especially in the middle and upper lobes |
| Nodule size | Micronodules 2–4 mm in diameter |
| Morphology | Nodules with well-defined margins, round shape |
| HRCT localization | Peribronchovascular interstitium, interlobar fissures, interlobular septa |
| Evolution | Possible coalescence of micronodules into macronodules over time |
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Incidence | Approximately 20% of patients with sarcoidosis |
| Origin | Chronic inflammation, long-lasting disease, or phenotypic susceptibility |
| Alterations | Linear opacities, traction bronchiectasis, architectural distortion |
| Distribution | Predominantly in the upper lobes and peribronchovascular regions |
| Honeycombing | Present in about 10% of patients, typically localized in middle-upper lobes |
| Characteristic | Sarcoidosis | Pulmonary Metastases |
|---|---|---|
| Presence of nodules or masses | Rarely presents a single mass or solitary nodule | Frequently presents multiple well-defined, rounded nodules |
| Appearance of nodules | May have macronodules (>5 mm), multiple, well-defined, simulating metastases | Multiple, well-circumscribed nodules distributed across various lobes |
| Differential diagnosis | Difficult to distinguish from metastatic disease with imaging alone | Often requires exclusion of granulomatous diseases |
| Granuloma localization | Granulomas may appear near tumors, but also in distant sites | Metastatic nodules develop from a known or unknown primary tumor |
| Diagnostic strategy | Search for granulomas in other sites and confirm via biopsy/histology in doubtful cases | Diagnosis based on oncological history and histopathological confirmation, if necessary |
| Characteristic | Sarcoidosis | Carcinomatous Lymphangitis |
|---|---|---|
| Interlobular septa thickening | Marked | Moderate or absent |
| Involvement of subpleural interstitium | Extensive | Limited |
| Distribution | Often asymmetric, irregular | Symmetric, bilateral |
| Peribronchovascular nodules | Rare | Frequent (perilymphatic distribution) |
| Nodules > 1 cm | Rare | Infrequent |
| Overall appearance | Infiltrative, along the lymphatic vessels | Nodular, well-defined |
| Characteristic | Sarcoidosis | Tuberculosis |
|---|---|---|
| Etiological agent | Non-infectious, immunologic | Infectious (mainly Mycobacterium tuberculosis) |
| Lung parenchyma | Frequently affected | Frequently affected |
| Galaxy sign | Variably present (14–54%) | Rare (<5%) |
| Sarcoid mass sign | Variably present (10–20%) | Infrequent (5–10%) |
| Nodular distribution | More regular, mainly along the bronchovascular bundle | Random, especially in miliary TB |
| Unilateral calcified lymphadenopathy | Less common (23%) | Common (61%) |
| Bilateral lymph node calcifications | Common (65%) | Rare (8%) |
| “Reverse halo” (or “atoll”) sign | May be present (5–10%) | May be present (<5%) |
| Differential diagnosis | Requires exclusion of infection | Requires infectious history and specific tests (active vs. latent TB) |
| Characteristic | Sarcoidosis | Silicosis |
|---|---|---|
| Type of opacity | Perilobar conglomerate opacities | Perilobar conglomerate opacities, possible calcifications and cavitations |
| Origin and extension | From the hilar region, extending posteriorly | Fibrotic areas with bands extending to the periphery |
| Other radiological signs | Reticulation, traction bronchiectasis, architectural distortion | Dense fibrosis |
| Preferred location | Middle-upper regions | Upper and perilobar regions |
| History | Not specifically occupational | Occupational exposure (e.g., silica) |
| Characteristic | Sarcoidosis | CVID |
|---|---|---|
| Type of disease | Granulomatous inflammation of unknown origin | Primary immunodeficiency with granulomatous and lymphoproliferative manifestations |
| Immunoglobulins levels | Normal | Reduced (e.g., hypogammaglobulinemia) |
| History | Generally, absence of recurrent infections | Presence of recurrent bacterial infections |
| Typical CT appearance | Perilymphatic nodules, hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy | Poorly defined nodules, centrilobular or random distribution |
| Atypical/overlapping CT appearance | Macronodules, sometimes coalescent, and unilateral hilar lymphadenopathy | Possible perilymphatic nodules, with lymphadenopathy similar to sarcoidosis |
| Pulmonary involvement | Common, with perilymphatic distribution | Common, with involvement of small airways and interstitium (GLILD) |
| Granulomas | Non-necrotizing | Non-necrotizing |
| Distinctive features | Absence of organized pneumonia or follicular bronchiolitis | Presence of organized pneumonia and follicular bronchiolitis |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, clinical and radiological context | Biopsy, immunohistochemical tests (i.e., CD3, CD4, CD8, CD20) and clonality evaluation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baratella, E.; di Luca, V.; Oliva, A.; Fiorese, I.; Segalotti, A.; Troian, M.; Lovadina, S.; Ruaro, B.; Salton, F.; Polverosi, R.; et al. CT Imaging Features of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Typical and Atypical Radiological Features and Their Differential Diagnosis. Medicina 2025, 61, 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122094
Baratella E, di Luca V, Oliva A, Fiorese I, Segalotti A, Troian M, Lovadina S, Ruaro B, Salton F, Polverosi R, et al. CT Imaging Features of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Typical and Atypical Radiological Features and Their Differential Diagnosis. Medicina. 2025; 61(12):2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122094
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaratella, Elisa, Valeria di Luca, Alessandra Oliva, Ilaria Fiorese, Antonio Segalotti, Marina Troian, Stefano Lovadina, Barbara Ruaro, Francesco Salton, Roberta Polverosi, and et al. 2025. "CT Imaging Features of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Typical and Atypical Radiological Features and Their Differential Diagnosis" Medicina 61, no. 12: 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122094
APA StyleBaratella, E., di Luca, V., Oliva, A., Fiorese, I., Segalotti, A., Troian, M., Lovadina, S., Ruaro, B., Salton, F., Polverosi, R., & Cova, M. A. (2025). CT Imaging Features of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: Typical and Atypical Radiological Features and Their Differential Diagnosis. Medicina, 61(12), 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122094








