Complication Profile and Safety Outcomes of Aquablation in the Management of BPH
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
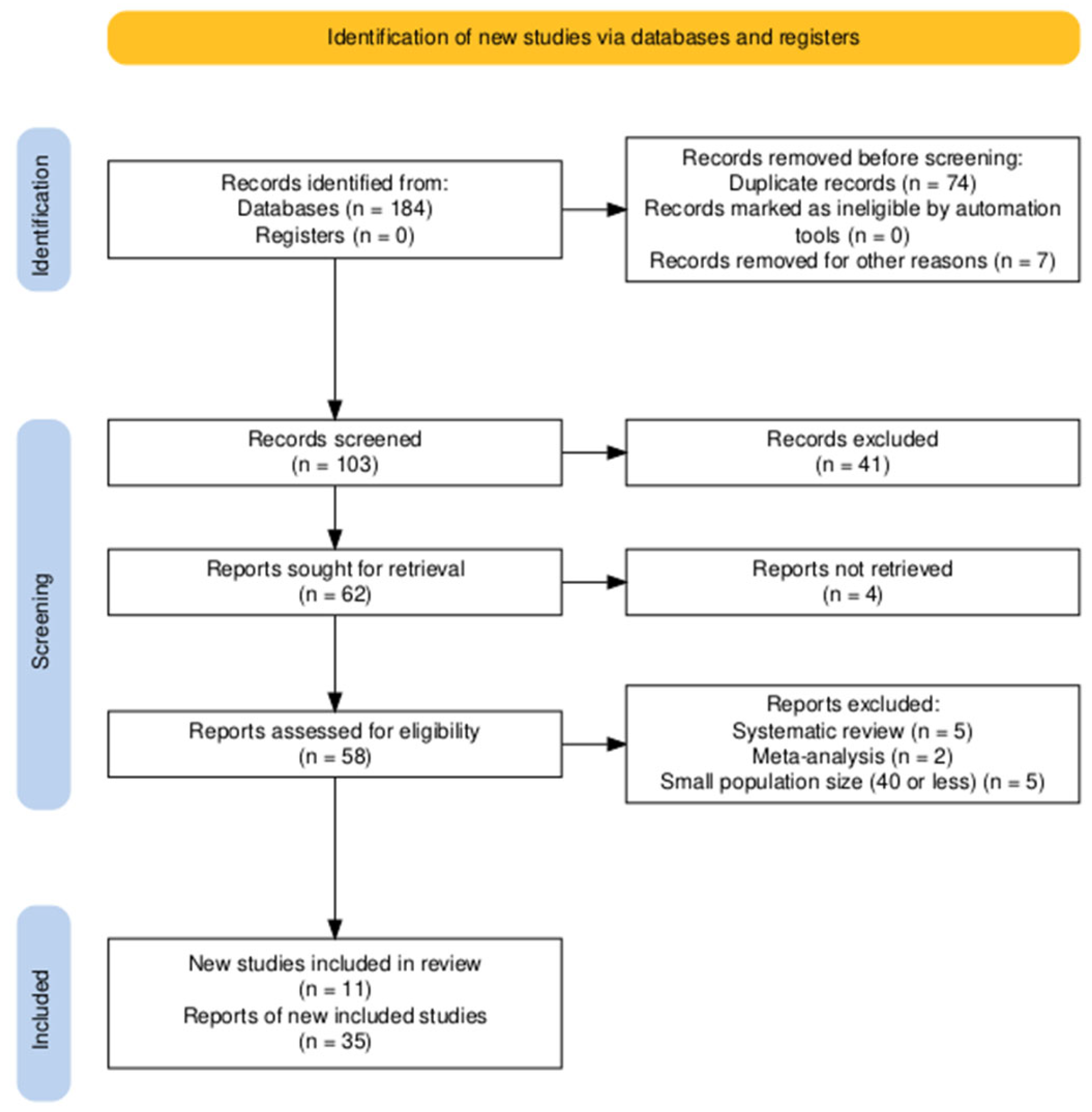
2.4. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Data Synthesis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPH | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia |
| CD | Clavien-Dindo |
| HoLEP | Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate |
| iTIND | Temporary Implantable Nitinol Device |
| LUTS | Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms |
| MIST | Minimally Invasive Surgical Therapy |
| TURP | Transurethral Resection of the Prostate |
| Rezūm | Convective Water Vapor Thermal Therapy |
| UroLift | Prostatic Urethral Lift |
References
- Colvin, H.; Johnston, M.; Ripa, F.; Sinha, M.M.; Pietropaolo, A.; Brewin, J.; Fiori, C.; Gozen, A.; Somani, B.K. Transurethral Resection and Other Minimally Invasive Treatment Options for BPH: Would We Treat Ourselves as We Treat Our Patients? Results from EAU Section of Uro-Technology (ESUT) Decision-Making Survey among Urologists. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2024, 77, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.; Harper, P.; Somani, B.K. Treatment Algorithm for Management of Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Overview of Current Techniques. Life 2023, 13, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacqua, L.V.; Vanzulli, A.; Di Meo, R.; Pellegrino, G.; Lavorato, R.; Vitale, G.; Carrafiello, G. Minimally Invasive Treatment in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, K.; Savin, Z.; Bashi, T.; Dekalo, S.; Hendel, H.; Ehrlich, Y.; Anis, O.; Dotan, Z.; Verhovsky, G.; Genessin, E.; et al. Transformations in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Surgical Practices: A Longitudinal Study of Trends and Predictions. Urol. Int. 2024, 109, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilling, P.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Anderson, P.; Sutton, M.; Aho, T.; Kramolowsky, E.; Thomas, A.; Cowan, B.; Kaufman, R.P.J.; et al. WATER: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Aquablation® vs Transurethral Resection of the Prostate in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilling, P.J.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Anderson, P.; Sutton, M.; Aho, T.; Kramolowsky, E.; Thomas, A.; Kaufman, R.P.J.; Badlani, G.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes for Aquablation Therapy Compared to TURP: Results from a Double-Blind, Randomized Trial in Men with LUTS Due to BPH. Can. J. Urol. 2022, 29, 10960–10968. [Google Scholar]
- Gilling, P.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Anderson, P.; Sutton, M.; Aho, T.; Kramolowsky, E.; Thomas, A.; Cowan, B.; Kaufman, R.P., Jr.; et al. Three-year outcomes after Aquablation therapy compared to TURP: Results from a blinded randomized trial. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2020, 27, 10072–10079. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, M.; Bidair, M.; Bhojani, N.; Trainer, A.; Arther, A.; Kramolowsky, E.; Doumanian, L.; Elterman, D.; Kaufman, R.P.J.; Lingeman, J.; et al. WATER II (80–150 mL) Procedural Outcomes. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, T.; Gilling, P.; El Hajj, A.; Anderson, P.; Barber, N. First Multi-Center All-Comers Study for the Aquablation Procedure. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidele, O.O.; Siegal, A.S.; Roshandel, R.; Te, A.E.; Kaplan, S.A. Aquablation at 4-Years: Real World Data from the Largest Single-Center Study with Associated Outcomes Follow-Up. Urology 2024, 194, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringler, R.; Gangwish, D.; Horning, P.; Kuperus, J.; Palmateer, G.; Zwaans, B.M.M.; Hafron, J.; Peters, K.M. Does Size Matter? A Single Institution’s Comparison of Aquablation in Prostates Greater than or Less than 150mL. Prostate 2025, 85, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo Quintas, J.; García Rojo, E.; García Gómez, B.; Lista Mateos, F.; Otta Oshiro, R.J.; Peña Vallejo, E.; Manfredi, C.; Bozzini, G.; Rodríguez Antolín, A.; Romero-Otero, J. Aquablation vs. Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A 150-Patients Prospective Comparative Multicenter Study. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2025, 77, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinata, N.; Fujisawa, M.; Yamaguchi, R.; Katsura, D.; Kitano, H.; Sekino, Y.; Yoshioka, K.; Koike, S.; Odagaki, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; et al. AQUABEAM Robotic System Use-Results Survey: Aquablation for the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in the Japanese Population. Int. J. Urol. 2025, 32, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, T.; Giannakis, I.; Bachmann, A.; Fiori, C.; Gomez-Sancha, F.; Herrmann, T.R.W.; Netsch, C.; Rieken, M.; Scoffone, C.M.; Tunc, L.; et al. Aquablation of the Prostate: Single-Center Results of a Non-Selected, Consecutive Patient Cohort. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, M.; Mansour, M.; Abdallah, N.; Jaafar, R.; Wazzan, W.; Bulbul, M.; El-Hajj, A. Aquablation for Benign Prostatic Obstruction: Single Center Technique Evolution and Experience. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2021, 62, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasraeian, A.; Alcantara, M.; Alcantara, K.M.; Altamirando, J.A.; Kasraeian, A. Aquablation for BPH. Can. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 10378–10381. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, M.M.; Singh, A.; Abhishek, S.; Laddha, A.; Pandya, H.; Ashrafi, A.N.; Ganpule, A.P.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Thomas, A.J.; Desai, M.; et al. Aquablation Therapy for Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Single-Centre Experience in 47 Patients. BJU Int. 2018, 121, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.; Gilling, P.; Tan, A. Multicenter Experience of a Novel Treatment for BPH.; Aquablation-Image Guided Robotassisted Water-Jet Ablation of the Prostate: 1 Year Follow-Up. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2016, 15, e1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assad, A.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Gilling, P.; Anderson, P.; Badlani, G.; Humphreys, M.; Kaplan, S.; Kaufman, R.; et al. WATER vs WATER II 3-Year Update: Comparing Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in 30–80 Cc and 80–150 Cc Prostates. Urology 2022, 165, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, T.; Barber, N.; Elterman, D.; Humphreys, M.; Bhojani, N.; Zorn, K.C.; Te, A.; Chughtai, B.; Kaplan, S. Aquablation Outcomes in Men with LUTS Due to BPH Following Single Versus Multi-Pass Treatments. Urology 2022, 169, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berjaoui, M.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Daher, K.; Saud Almoussa, S.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Gilling, P.; Anderson, P.; Zorn, K.; Badlani, G.; et al. WATER vs. WATER II 5-Year Update: Comparing Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in 30–80 Cm3 and 80–150 Cm3 Prostates. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2024, 18, S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berjaoui, M.B.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Almousa, S.; Daher, K.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Gilling, P.; Anderson, P.; Zorn, K.C.; Badlani, G.; et al. WATER versus WATER II 5-Year Update: Comparing Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in 30–80-Cm(3) and 80–150-Cm(3) Prostates. BJUI Compass 2024, 5, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojani, N. Water Ii: Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Men with Large Prostates (80–150 cc): 6-Month Safety and Efficacy Results. J. Urol. 2019, 201, e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojani, N.; Elterman, D.; Paterson, R.; So, A.; Goldenberg, S.; Kaufman, R.; Lingeman, J.; Kaplan, S.; Humphreys, M.; Zorn, K.; et al. WATER II: Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (80-150 Cc) 12-Month Safety and Efficacy Results. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2019, 13, S77. [Google Scholar]
- Bhojani, N.; Bidair, M.; Kramolowsky, E.; Desai, M.; Doumanian, L.; Zorn, K.C.; Elterman, D.; Kaufman, R.P.J.; Eure, G.; Badlani, G.; et al. Aquablation Therapy in Large Prostates (80–150 mL) for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Final WATER II 5-Year Clinical Trial Results. J. Urol. 2023, 210, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojani, N.; Bidair, M.; Zorn, K.C.; Trainer, A.; Arther, A.; Kramolowsky, E.; Doumanian, L.; Elterman, D.; Kaufman, R.P.; Lingeman, J.; et al. Aquablation for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Large Prostates (80–150 Cc): 1-Year Results. Urology 2019, 129, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, I.; Chakraborty, A.; Nguyen, D.D.; Arezki, A.; Oumedjbeur, K.; Bhojani, N.; Elterman, D.; Chughtai, B.; Gilling, P.; Barber, N.; et al. Aquablation in Patients on Antithrombotics: Assessment of Safety, Postoperative Bleeding Rates and Clinical Outcomes. Urology 2023, 181, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, D.; Colicchia, M.; Corsi, P.; Romagnoli, D.; Del Rosso, A.; Modonutti, D.; Busetto, G.M.; Ferro, M.; Schiavina, R.; Molinaroli, E.; et al. The Combination of Waterjet Ablation (Aquabeam®) and Holmium Laser Power for Treatment of Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Early Functional Results. Cent. European J. Urol. 2021, 74, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cillis, S.; Amparore, D.; Quarà, A.; Checcucci, E.; Piana, A.; Volpi, G.; Piramide, F.; Sica, M.; Ortenzi, M.; Manfredi, M.; et al. Evaluation of LUTS of the Filling Phase after Aquablation: A Prospective Single Center Experience. Front. Urol. 2022, 2, 1001710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Laddha, A.; Mishra, S.; Desai, M.; Sabnis, R.; Singh, A. Single-Center Experience Utilizing Second Generation Aquabeam System for the Targeted, Heat-Free Removal of Prostate Tissue, during the Treatment of BPH. J. Urol. 2016, 195, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Bidair, M.; Zorn, K.C.; Trainer, A.; Arther, A.; Kramolowsky, E.; Doumanian, L.; Elterman, D.; Kaufman, R.P.J.; Lingeman, J.; et al. Aquablation for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Large Prostates (80–150 mL): 6-Month Results from the WATER II Trial. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilling, P.J.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Anderson, P.; Sutton, M.; Aho, T.; Kramolowsky, E.; Thomas, A.; Cowan, B.; Roehrborn, C. Randomized Controlled Trial of Aquablation versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: One-Year Outcomes. Urology 2019, 125, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloger, S.; Schueller, L.; Paulics, L.; Bach, T.; Ubrig, B. Aquablation with Subsequent Selective Bipolar Cauterization versus Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) with Regard to Perioperative Bleeding. Can. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 10685–10690. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, A.J.; Lipp, M.J.; Baumbach, R.; Becker, B.; Vogt, K.; Rosenbaum, C.; Netsch, C. Rectal Perforation after Aquablation of the Prostate: Lessons Learned the Hard Way. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 3441–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Intraoperative Blood Loss in Patients Undergoing Aquablation NCT06710327. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT06710327 (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Nguyen, D.-D.; Zorn, K.; Bhojani, N. WATER vs. WATER II: Three-Year Comparison of Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in 30–80 Cc Prostates and 80–150 Cc Prostates. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2021, 15, S197. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.-D.; Zorn, K.; Elterman, D.; Bhojani, N. WATER vs. WATER II: Two-Year Comparison of Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2020, 14, S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.-D.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Gilling, P.; Anderson, P.; Zorn, K.C.; Badlani, G.; Humphreys, M.; Kaplan, S.; Kaufman, R.; et al. Waterjet Ablation Therapy for Endoscopic Resection of Prostate Tissue Trial (WATER) vs WATER II: Comparing Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in 30–80 and 80–150 mL Prostates. BJU Int. 2020, 125, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.-D.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Gilling, P.; Anderson, P.; Zorn, K.C.; Badlani, G.; Humphreys, M.; Kaplan, S.; Kaufman, R.; et al. WATER versus WATER II 2-Year Update: Comparing Aquablation Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in 30–80-Cm(3) and 80–150-Cm(3) Prostates. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2021, 25, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumedjbeur, K.; Ibrahim, A.; Matta, I.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Arezki, A.; Sadri, I.; Bouhadana, D.; Elsherbini, T.; Gilling, P.; Barber, N.; et al. Aquablation Therapy® vs. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate: 5-Year Outcomes of the WATER Randomized Clinical Trial for Medium-Sized Prostates. Eur. Urol. 2023, 83, S1638–S1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.; Zeldin, A.; Farkas, A.; Chertin, B. Severe Hemorrhage Post Robotic-Assisted Aquablation: A Case Report. Urol. Case Rep. 2025, 61, 103059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plante, M.; Gilling, P.; Barber, N.; Bidair, M.; Anderson, P.; Sutton, M.; Aho, T.; Kramolowsky, E.; Thomas, A.; Cowan, B.; et al. Symptom Relief and Anejaculation after Aquablation or Transurethral Resection of the Prostate: Subgroup Analysis from a Blinded Randomized Trial. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrborn, C.; Anderson, P.; Gilling, P. The WATER Study Clinical Results-a Subgroup Analysis of Larger Prostates from the Phase III Blinded Randomized Trial of Aquablation versus TURP. BJU Int. 2018, 121, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanneru, K.; Jazayeri, S.B.; Alam, M.U.; Kumar, J.; Bazargani, S.; Kuntz, G.; Palayapalayam Ganapathi, H.; Bandyk, M.; Marino, R.; Koochekpour, S.; et al. An Indirect Comparison of Newer Minimally Invasive Treatments for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Network Meta-Analysis Model. J. Endourol. 2021, 35, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, D.; Ng, K.L.; Barber, N. Initial Single Centre Experience of Aquablation of the Prostate Using the AquaBeam System with Athermal Haemostasis for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: 1-Year Outcomes. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafi, F.A.; Tallman, C.T.; Seard, M.L.; Jordan, M.L. Aquablation Outcomes for the U.S. Cohort of Men with LUTS Due to BPH in Large Prostates (80–150 Cc). Int. J. Impot. Res. 2018, 30, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, K.C.; Bidair, M.; Trainer, A.; Arther, A.; Kramolowsky, E.; Desai, M.; Doumanian, L.; Elterman, D.; Kaufman, R.P.J.; Lingeman, J.; et al. Aquablation Therapy in Large Prostates (80–150 Cc) for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: WATER II 3-Year Trial Results. BJUI Compass 2022, 3, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, K.C.; Chakraborty, A.; Chughtai, B.; Mehan, R.; Elterman, D.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Bouhadana, D.; Glaser, A.P.; Marhamati, S.; Barber, N.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Same Day Discharge for Men Undergoing Contemporary Robotic-Assisted Aquablation Prostate Surgery in an Ambulatory Surgery Center Setting-First Global Experience. Urology 2025, 195, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, K.C.; Goldenberg, S.L.; Paterson, R.; So, A.; Elterman, D.; Bhojani, N. Aquablation among Novice Users in Canada: A WATER II Subpopulation Analysis. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2019, 13, E113–E118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquablation Therapy. WATER III Randomized-Controlled Trial Results Announced at European Association of Urology Comparing Aquablation ® Therapy to Laser Enucleation. Available online: https://aquablation.co.uk/blog/water-iii-randomised-controlled-trial-results-announced-at-european-association-of-urology-comparing-aquablation-therapy-to-laser-enucleation/ (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Sandhu, J.S.; Bixler, B.R.; Dahm, P.; Goueli, R.; Kirkby, E.; Stoffel, J.T.; Wilt, T.J. Management of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Attributed to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): AUA Guideline Amendment 2023. J. Urol. 2024, 211, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EAU Guidelines, Edn. Presented at the EAU Annual Congress Paris April 2024. ISBN 978-94-92671-23-3. EAU Guidelines Office, Arnhem, the Netherlands. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guidelines (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Cantiello, F.; Crocerossa, F.; Alba, S.; Carbonara, U.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Falagario, U.; Veccia, A.; Ucciero, G.; Ferro, M.; Mondaini, N.; et al. Refining Surgical Strategies in ThuLEP for BPH: A Propensity Score Matched Comparison of En-Bloc, Three Lobes, and Two Lobes Techniques. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year | Design | Single- or Multi-Centered | Population | Use of Clavien-Dindo Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bach et al. [15] | 2019 | prospective, observational | single | 118 | yes |
| Bach et al. [10] | 2020 | prospective, single-arm clinical trial (OPEN WATER) | multi | 178 | yes |
| Desai et al. [18] | 2018 | prospective, single-arm clinical trial (AQUABEAM India Study) | single | 47 | yes |
| Desai et al. [9] | 2019 | prospective, single-arm clinical trial (WATER II) | multi | 101 | yes |
| Gilling et al. [6] | 2018 | randomized, controlled clinical trial (WATER) | multi | 117 vs. 67 (TURP) | yes |
| Hinata et al. [14] | 2025 | prospective, observational | single | 103 | yes |
| Kasraeian et al. [17] | 2020 | prospective, observational | single | 55 | no |
| Labban et al. [16] | 2021 | prospective, observational | single | 59 | yes |
| Omidele et al. [11] | 2024 | prospective, observational | single | 330 | no |
| Quintas et al. [13] | 2025 | prospective, comparative | multi | 75 vs. 75 (HoLEP) | yes |
| Ringler et al. [12] | 2025 | prospective, observational | single | 174 | yes |
| Study | Randomization Process | Deviations from Intended Interventions | Missing Outcome Data | Measurement of the Outcome | Selection of the Reported Result | Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gilling et al. 2018 [6] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Study | Confounding | Selection of Participants | Classification of Interventions | Deviations from Intended Interventions | Missing Data | Measurement of Outcomes | Selection of Reported Result | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quintas et al. 2025 [13] | Serious | Serious | Low | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Low | Serious |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Triantafyllou, P.; Arseniou, P.; Katsimperis, S.; Kyriazis, I.; Manolitsis, I.; Juliebø-Jones, P.; Somani, B.; Tsaturyan, A.; Karagiotis, T.; Markopoulos, T.; et al. Complication Profile and Safety Outcomes of Aquablation in the Management of BPH. Medicina 2025, 61, 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122076
Triantafyllou P, Arseniou P, Katsimperis S, Kyriazis I, Manolitsis I, Juliebø-Jones P, Somani B, Tsaturyan A, Karagiotis T, Markopoulos T, et al. Complication Profile and Safety Outcomes of Aquablation in the Management of BPH. Medicina. 2025; 61(12):2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122076
Chicago/Turabian StyleTriantafyllou, Panagiotis, Polyvios Arseniou, Stamatios Katsimperis, Ioannis Kyriazis, Ioannis Manolitsis, Patrick Juliebø-Jones, Bhaskar Somani, Arman Tsaturyan, Theodoros Karagiotis, Titos Markopoulos, and et al. 2025. "Complication Profile and Safety Outcomes of Aquablation in the Management of BPH" Medicina 61, no. 12: 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122076
APA StyleTriantafyllou, P., Arseniou, P., Katsimperis, S., Kyriazis, I., Manolitsis, I., Juliebø-Jones, P., Somani, B., Tsaturyan, A., Karagiotis, T., Markopoulos, T., Tzelves, L., & Skolarikos, A. (2025). Complication Profile and Safety Outcomes of Aquablation in the Management of BPH. Medicina, 61(12), 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61122076






