Evaluation of the Relationship Between Albuminuria and Triglyceride Glucose Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Collection and Laboratory Measurements
2.5. Triglyceride Glucose Index Measurement and Calculation
2.6. Study Variables
2.7. Outcomes
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TyG | triglyceride glucose index |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| DKD | diabetic kidney disease |
| ACR | albumin-to-creatinine ratio |
| ESRD | end-stage renal disease |
| IR | insulin resistance |
| HOMA-IR | homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance |
| ADA | American diabetes association |
| BMI | body mass index |
| FBG | fasting blood glucose |
| HbA1c | glycated hemoglobin |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HDLc | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDLc | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | area under curve |
| PV | predictive value |
| CI | confidence interval |
| OR | odds ratio |
| SD | standard deviation |
| IQR | interquartile range |
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; The International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.C.; Brownlee, M.; Susztak, K.; Sharma, K.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A.; Zoungas, S.; Rossing, P.; Groop, P.H.; Cooper, M.E. Diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2015, 1, 15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, K.L.; Chertow, G.M.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Ishani, A.; Israni, A.; Ku, E.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Obrador, G.T.; et al. US Renal Data System 2022 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 81 (Suppl. 1), A8–A11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Chronic Kidney Disease Surveillance System—United States. Available online: https://nccd.cdc.gov/CKD/ (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Gheith, O.; Farouk, N.; Nampoory, N.; Halim, M.A.; Kentab, O. Diabetic kidney disease: Worldwide difference in prevalence and risk factors. J. Nephropharmacol. 2015, 4, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.T.; Xu, X.; Lim, P.S.; Hung, K.Y. Worldwide Epidemiology of Diabetes-Related End-Stage Renal Disease, 2000–2015. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnudi, L.; Coward, R.J.M.; Long, D.A. Diabetic Nephropathy: Perspective on Novel Molecular Mechanisms. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, P.; Maxwell, A.P.; Brazil, D.P. The Potential of Albuminuria as a Biomarker of Diabetic Complications. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2021, 35, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Shahid, I.; Anker, S.D.; Fonarow, G.C.; Fudim, M.; Hall, M.E.; Hernandez, A.; Morris, A.A.; Shafi, T.; Weir, M.R.; et al. Albuminuria and Heart Failure: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, P.; Jialal, I. Diabetic Nephropathy; StatPearls: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Huh, H.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Jung, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.-N.; Paek, J.H.; Park, W.Y.; Jin, K.; et al. Impact of albuminuria on the various causes of death in diabetic patients: A nationwide population-based study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Marco, L.; Guerra-Torres, X.; Viejo, I.; Lopez-Romero, L.; Yugueros, A.; Bermídez, V. Non-albuminuric Diabetic Kidney Disease Phenotype: Beyond Albuminuria. touchREV Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Ni, L.; Gao, L.; Wu, X. Comparison of Nonalbuminuric and Albuminuric Diabetic Kidney Disease Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 871272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Liu, T.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, L.; Mao, H.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Zhan, Y. Oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: Role of polyphenols. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1185317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.E.; Brunt, V.E.; Shiu, Y.T.; Bunsawat, K. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: A clinical perspective. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2025, 329, H135–H153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niskanen, L.; Laakso, M. Insulin resistance is related to albuminuria in patients with type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 1993, 42, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cosmo, S.; Minenna, A.; Ludovico, O.; Mastroianno, S.; Di Giorgio, A.; Pirro, L.; Trischitta, V. Increased urinary albumin excretion, insulin resistance, and related cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes: Evidence of a sex-specific association. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.I.; Kim, C.H.; Choi, C.S.; Chung, Y.E.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, S.I.; Park, J.Y.; Hong, S.K.; Lee, K.U. Microalbuminuria is associated with the insulin resistance syndrome independent of hypertension and type 2 diabetes in the Korean population. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2001, 52, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lai, X. Association between the triglyceride glucose index, triglyceride-glucose body mass index and diabetic kidney disease in adults with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1328601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y. Associations of the TyG index with albuminuria and chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Liu, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-T.; Wu, J.-Y.; Tsai, W.-W.; Hung, K.; Chen, I.; Feng, P.-H. Diagnostic efficacy of the triglyceride-glucose index in the prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy following percutaneous coronary intervention. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1282675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Cao, J. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and its composite obesity indexes and cardio-renal disease: Analysis of the NHANES 2013–2018 cycle. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1505808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Su, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Evaluating the impact of chronic kidney disease and the triglyceride-glucose index on cardiovascular disease: Mediation analysis in the NHANES. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. The product of fasting glucose and triglycerides as surrogate for identifying insulin resistance in apparently healthy subjects. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2008, 6, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasques, A.C.; Novaes, F.S.; de Oliveira, M.d.a.S.; Souza, J.R.; Yamanaka, A.; Pareja, J.C.; Tambascia, M.A.; Saad, M.J.; Geloneze, B. TyG index performs better than HOMA in a Brazilian population: A hyperglycemic clamp validated study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, e98–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Han, J.H. Comparison of triglyceride-glucose index and HOMA-IR for predicting prevalence and incidence of metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.H. The triglyceride-glucose index is a more powerful surrogate marker for predicting the prevalence and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus than the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 180, 109042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qian, H.; Zhong, S.; Gu, T.; Xu, M.; Yang, Q. The relationship between triglyceride-glucose index and albuminuria in United States adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1215055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; He, F.; Liu, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, E. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Shi, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, W.; Bao, H.; Cheng, X. Triglyceride-glucose index change and chronic kidney disease progression in a Chinese hypertensive population. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1342408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Pu, J.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, L.; Tao, L.; Peng, Z. The prognostic value of triglyceride-glucose index to adverse renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Results from the cohort study of ACCORD. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.; Brozek, W.; Concin, H.; Nagel, G.; Kerschbaum, J.; Lhotta, K.; Ulmer, H.; Zitt, E. The Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Obesity-Related Risk of End-Stage Kidney Disease in Austrian Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e212612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipoorashrafi, S.A.; Adeli, A.; Seyedi, S.A.; Rabizadeh, S.; Bahri, R.A.; Mohammadi, F.; Yadegar, A.; Nakhjavani, M.; Esteghamati, A. Comparison of insulin resistance indices in predicting albuminuria among patients with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, P.M.; Ma, X.Y.; Sun, X.J.; Lv, W.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.G. Association of serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol with microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, J.; Qian, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, C.; Zhao, L. A Population-Based Study of the Mediating Role of WBC, NEUT and PLT in the Relationship Between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Urinary Albumin Excretion. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 10613–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 11. Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. 1), S219–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Seidu, S.; Kurl, S.; Laukkanen, J.A. Baseline and usual triglyceride-glucose index and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A prospective cohort study. Geroscience 2024, 46, 3035–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xia, R.; Song, X.; Zhang, B.; He, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Yuan, G. Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, A.A.; Altay, F.P.; Demir, P.; Ozdemir, D.; Topaloglu, O.; Ersoy, R.; Cakır, B. The Association Between Diabetic Nephropathy and Triglyceride/Glucose Index and Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, S.; Pek, S.; Moh, A.; Ang, K.; Khoo, J.; Shao, Y.-M.; Tang, W.E.; Lim, Z.; Subramaniam, T.; Sum, C.F.; et al. Triglyceride-glucose index is prospectively associated with chronic kidney disease progression in Type 2 diabetes-mediation by pigment epithelium-derived factor. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2022, 19, 14791641221113784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Xu, B.T.; Wan, S.R.; Ma, X.M.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z.Z. The role of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, C. Oxidative Stress: A Culprit in the Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H. Lipid abnormalities associated with urinary albumin excretion rate in Taiwanese type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Liu, L.; Qi, Y.; Han, N.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Shang, X.; Han, T.; Zha, Y.; Wei, X.; et al. Joint association of TyG index and high sensitivity C-reactive protein with cardiovascular disease: A national cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Pan, Q.; Du, L.-L.; Song, J.-J.; Liu, Y.-P.; Meng, X.-B.; Zhang, K.; Gao, J.; Shao, C.-L.; Wang, W.-Y.; et al. Association of triglyceride-glucose index with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and mortality among familial hypercholesterolemia patients. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Gao, S.; Chen, W.; Yang, R.; Yu, C. Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in different metabolic states in patients with coronary heart disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1447072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, S.; Chi, C.; Fan, X.; Tang, J.; Ji, H.; Teliewubai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Association between macro- and microvascular damage and the triglyceride glucose index in community-dwelling elderly individuals: The Northern Shanghai Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Yu, D.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, Z.; Simmons, D. The triglyceride glucose index can predict newly diagnosed biopsy-proven diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: A nested case control study. Medicine 2019, 98, e17995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Gong, L.; Wu, J.; Luo, W.; Shen, Y.; Han, S.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Chongqing Diabetes Registry Group. Relationship Between the TyG Index and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Jiang, M.; Han, L.; Zheng, X. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and chronic kidney disease: A cohort study and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
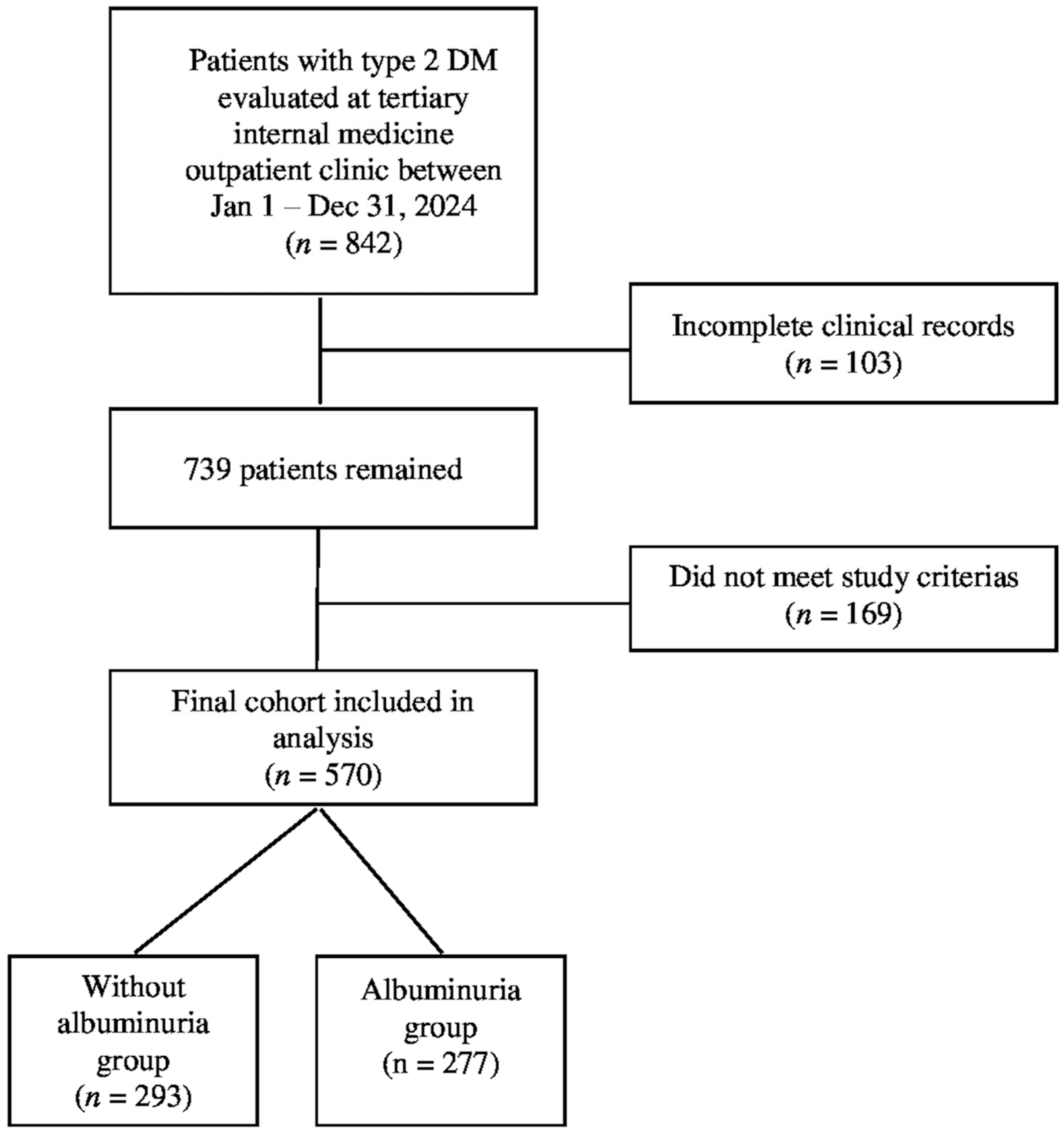
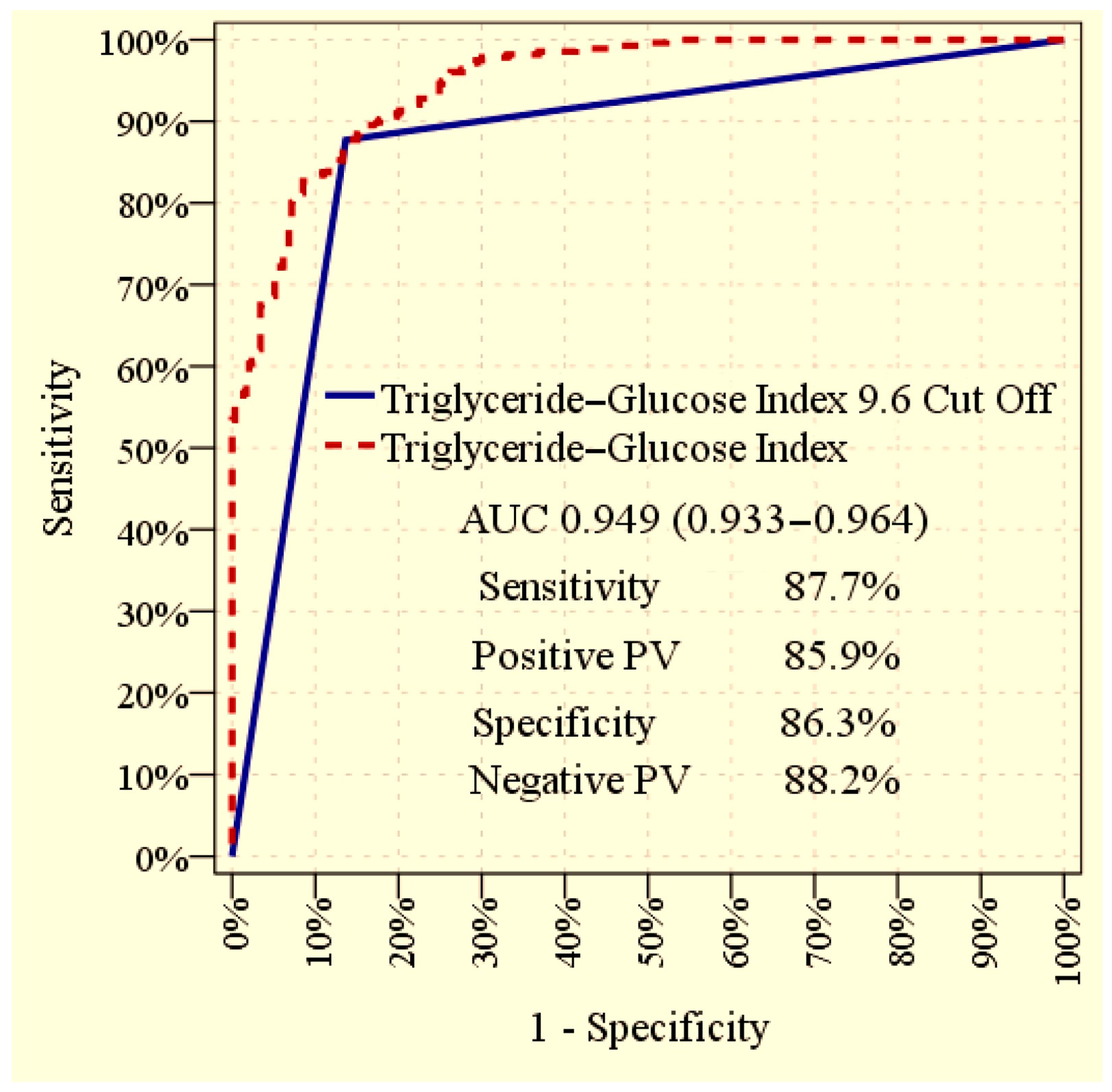
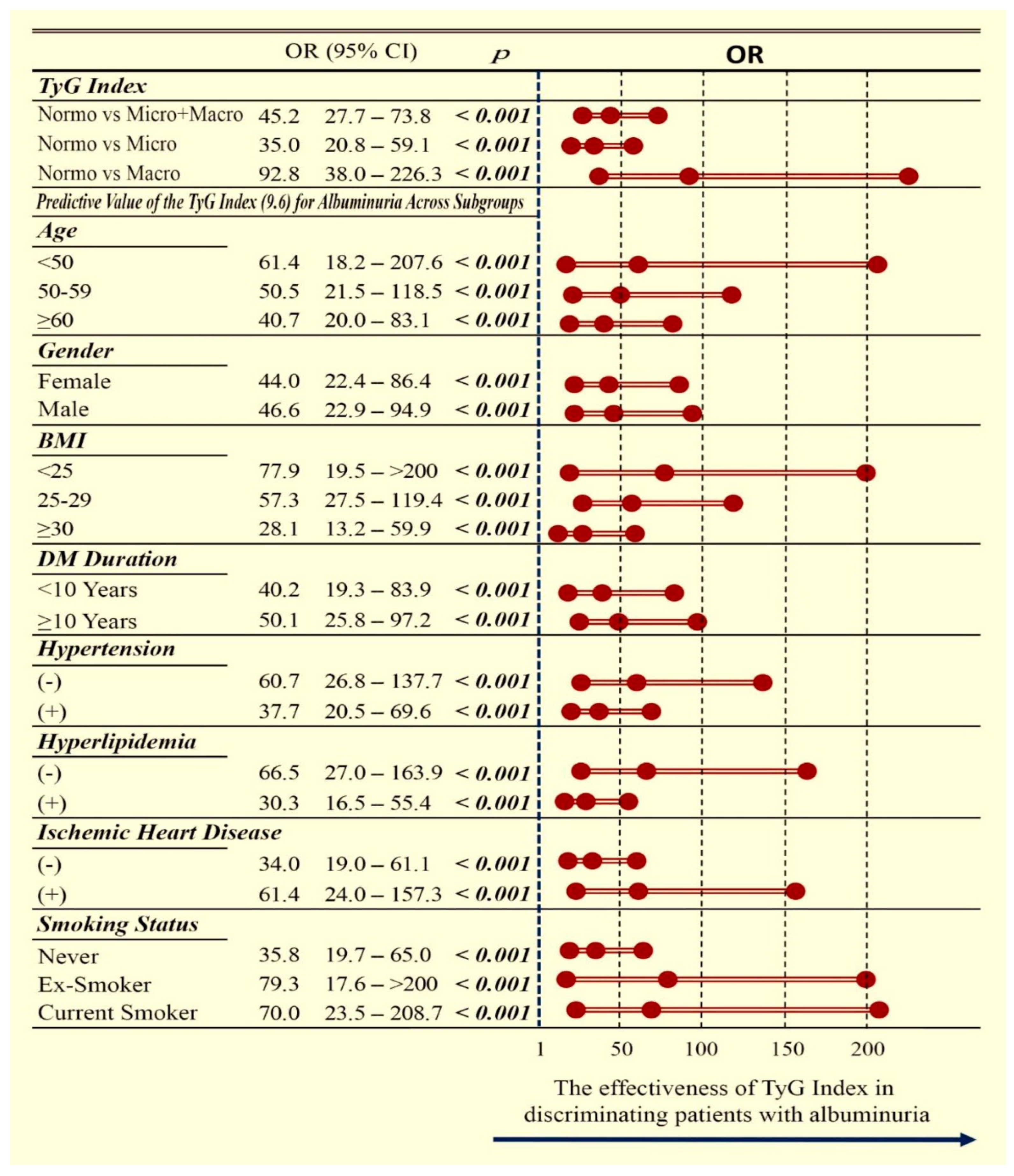
| Without Albuminuria (n = 293) | With Albuminuria (n = 277) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 59 (52–65) | 59 (52–66) | 0.832 |
| Gender, n (%) | |||
| 154 (52.6) | 143 (51.6) | 0.823 |
| 139 (47.4) | 134 (48.4) | |
| Weight, kg | 76 (70–85) | 78 (71–87) | 0.073 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 28.7 (26–31) | 28.9 (26–31) | 0.870 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 130 (120–140) | 130 (120–140) | 0.225 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 85 (75–90) | 85 (75–90) | 0.433 |
| Diabetes duration, years | 10 (6–15) | 11 (8–15) | 0.176 |
| Comorbid diseases, n (%) | |||
| 177 (60.4) | 165 (59.6) | 0.837 |
| 125 (42.7) | 213 (76.9) | <0.001 |
| 58 (19.8) | 135 (48.7) | <0.001 |
| Smoking status, n (%) | |||
| 186 (63.5) | 169 (61) | 0.774 |
| 70 (23.9) | 68 (24.5) | |
| 37 (12.6) | 40 (14.4) | |
| Medication, n (%) | |||
| 185 (63.1) | 170 (61.4) | 0.663 |
| 33 (11.3) | 37 (13.4) | 0.446 |
| 71 (24.2) | 68 (24.5) | 0.930 |
| 156 (53.2) | 150 (54.2) | 0.828 |
| 125 (42.7) | 213 (76.9) | <0.001 |
| Parameter | Without Albuminuria (n = 293) | With Albuminuria (n = 277) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triglyceride–glucose index | 9.1 (8.7–9.4) | 10 (9.7–10.4) | <0.001 |
| Fasting blood glucose, mg/dL | 142 (111–177) | 207 (175–265) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin A1c, % | 7.9 (6.8–9.3) | 9 (7.8–10) | <0.001 |
| Urea, mg/dL | 30.3 (25–37) | 34 (26–41) | 0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.79 (0.7–0.9) | 0.95 (0.7–1.2) | <0.001 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 101 (96–105) | 75 (57–90) | <0.001 |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 4.5 (3.7–5.5) | 4.8 (4–6.4) | 0.014 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase, U/L | 16 (13–20) | 16 (13–20) | 0.684 |
| Alanine aminotransferase, U/L | 17 (13–22) | 17 (13–21) | 0.418 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 185 (157–213) | 196 (166–231) | 0.011 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 120 (94–157) | 217 (186–275) | <0.001 |
| HDL-c, mg/dL | 45 (38–52) | 43 (36–49) | 0.009 |
| LDL-c, mg/dL | 108 (81–138) | 116 (90–146) | 0.031 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/L | 2.5 (1–6) | 3.5 (1.4–8) | 0.031 |
| Leukocyte, 103/mm3 | 7.9 (6.7–9.8) | 8.3 (7.1–10) | 0.035 |
| UACR, mg/g | 11.2 (5.9–20.3) | 109.7 (50–454) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Univariate Model | Multivariate Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | |||||
| Hyperlipidemia | 4.473 | 3.112 | – | 6.430 | <0.001 | 2.628 | 1.240 | – | 5.569 | 0.012 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 3.852 | 2.656 | – | 5.586 | <0.001 | |||||
| Lipid-lowering drugs | 0.224 | 0.156 | – | 0.321 | <0.001 | |||||
| Glucose, mg/dL | 1.020 | 1.016 | – | 1.024 | <0.001 | |||||
| Hemoglobin A1c, % | 1.311 | 1.190 | – | 1.443 | <0.001 | |||||
| Urea, mg/dL | 1.020 | 1.007 | – | 1.032 | 0.002 | |||||
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 63.28 | 25.22 | – | 158.74 | <0.001 | |||||
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 0.858 | 0.834 | – | 0.882 | <0.001 | 0.852 | 0.815 | – | 0.891 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol mg/dL | 1.006 | 1.002 | – | 1.009 | 0.001 | |||||
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 1.031 | 1.026 | – | 1.037 | <0.001 | |||||
| HDL-c, mg/dL | 0.982 | 0.966 | – | 0.997 | 0.019 | |||||
| LDL-c, mg/dL | 1.006 | 1.001 | – | 1.010 | 0.010 | |||||
| Triglyceride–glucose index | 351.09 | 126.03 | – | 978.01 | <0.001 | 245.5 | 68.2 | – | 883.5 | <0.001 |
| Normo-Albuminuria (n = 293) | Micro-Albuminuria (n = 183) | Macro-Albuminuria (n = 94) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG Index | 9.1 2,3 (8.7–9.4) | 9.9 3 (9.7–10.2) | 10.2 (9.9–10.6) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yilmaz, O.; Erinc, O. Evaluation of the Relationship Between Albuminuria and Triglyceride Glucose Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101803
Yilmaz O, Erinc O. Evaluation of the Relationship Between Albuminuria and Triglyceride Glucose Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101803
Chicago/Turabian StyleYilmaz, Ozgur, and Osman Erinc. 2025. "Evaluation of the Relationship Between Albuminuria and Triglyceride Glucose Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101803
APA StyleYilmaz, O., & Erinc, O. (2025). Evaluation of the Relationship Between Albuminuria and Triglyceride Glucose Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina, 61(10), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101803






