The Effect of the Nasal Airflow Reducer on Parasympathetic Activity in Adults: A Pilot and Exploratory Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
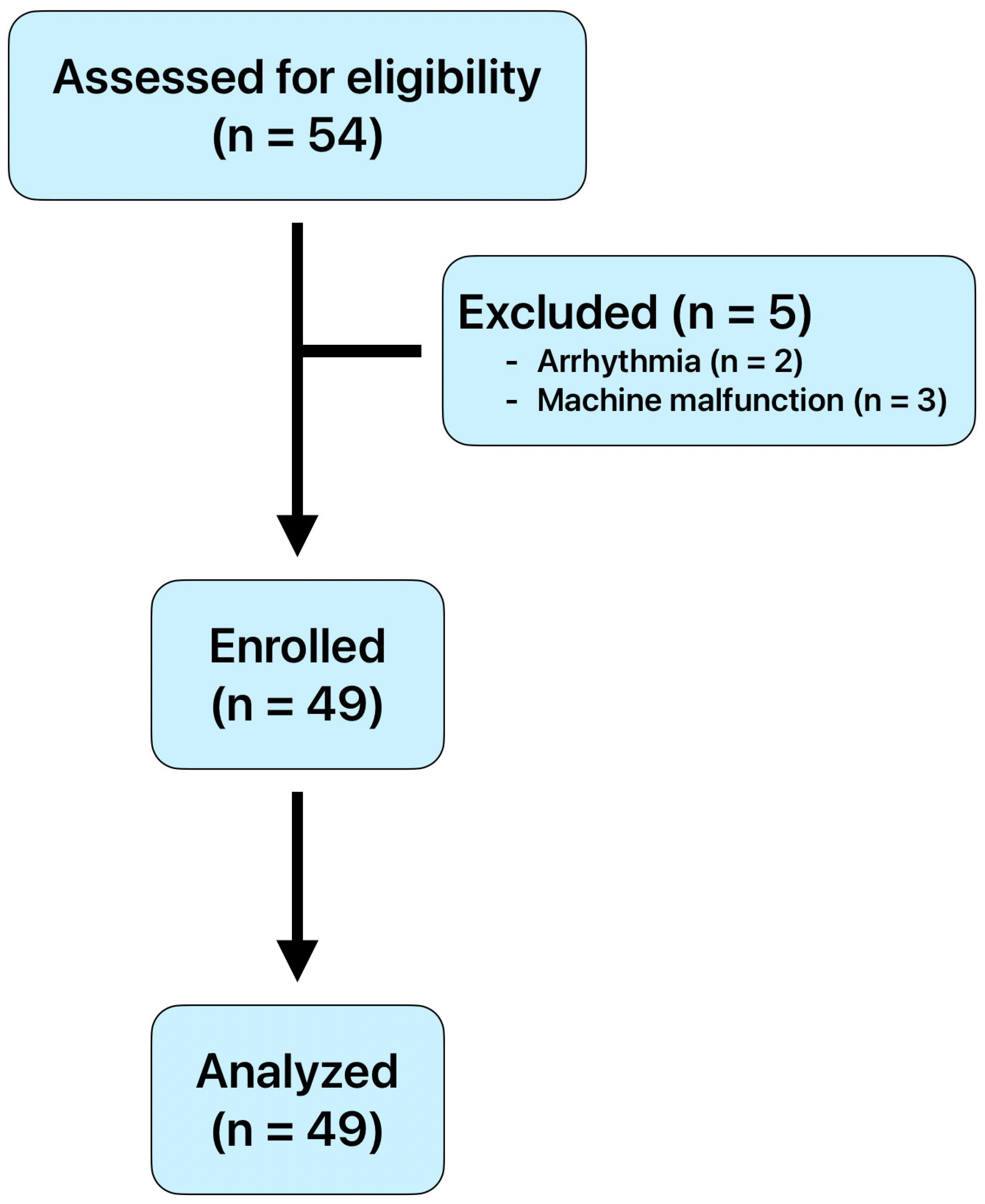
2.1. Study Design
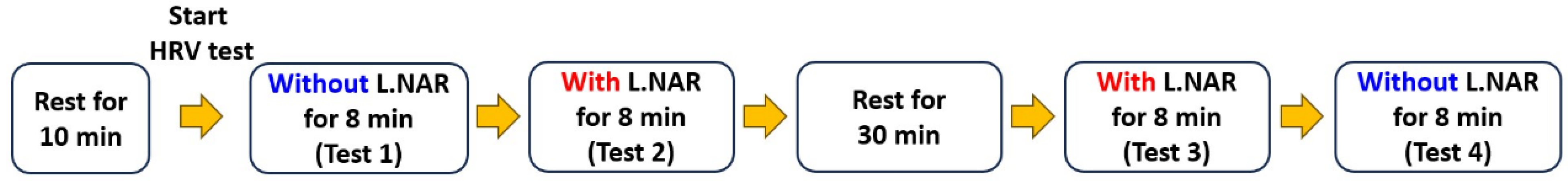
2.2. Introduction of L.NAR and Testing Procedure
2.3. HRV Measurement
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
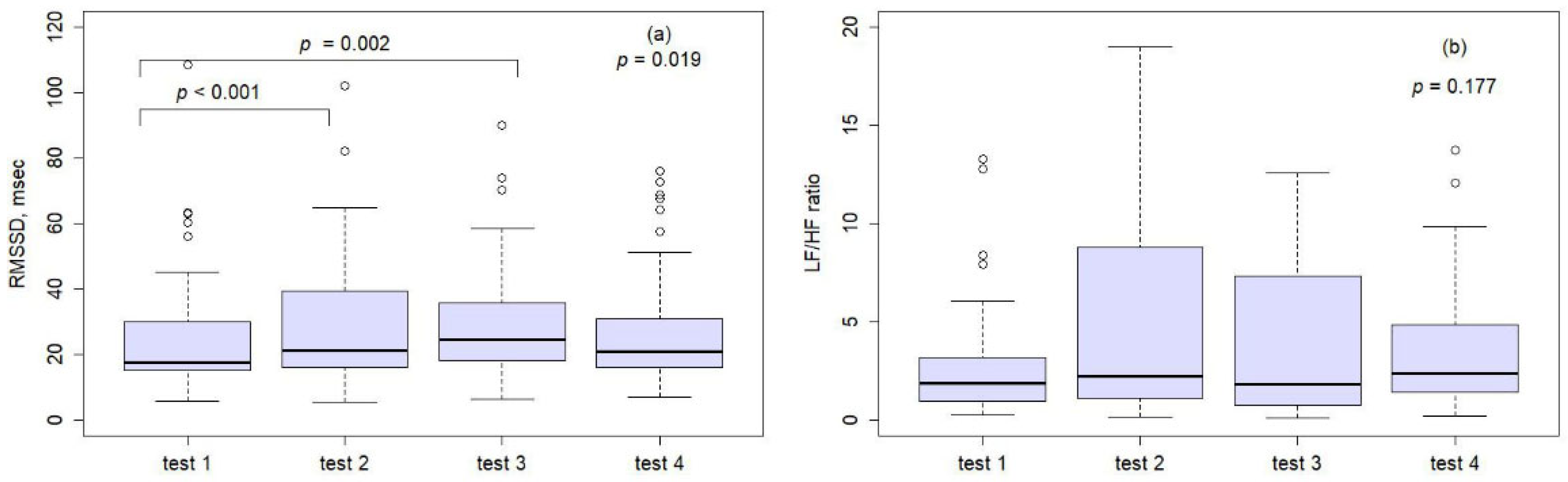
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| L.NAR | Lin Nasal Airflow Reducer |
| HRV | Heart Rate Variability |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| RMSSD | Root Mean Square of Successive Heart Beat Interval Differences |
| HRVB | Heart rate variability biofeedback |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| LF | Low-Frequency |
| HF | High-Frequency |
| LF/HF ratio | Low-Frequency Power to High-Frequency Power Ratio |
| lnHF | Natural Logarithm of HF |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| Df | Degree of Freedom |
| ges | Generalized Eta Squared |
References
- McCorry, L.K. Physiology of the autonomic nervous system. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2007, 71, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullett, N.; Zajkowska, Z.; Walsh, A.; Harper, R.; Mondelli, V. Heart rate variability (HRV) as a way to understand associations between the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and affective states: A critical review of the literature. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2023, 192, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego, M.A.; Field, T. Moderate pressure massage elicits a parasympathetic nervous system response. Int. J. Neurosci. 2009, 119, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.Y.; Watanabe, M.A.; Laddu, A.A.; Hauptman, P.J. Pharmacologic modulation of parasympathetic activity in heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2011, 16, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, P.M.; Vaschillo, E.; Vaschillo, B.; Lu, S.E.; Scardella, A.; Siddique, M.; Habib, R.H. Biofeedback treatment for asthma. Chest 2004, 126, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowder, E.; Gevirtz, R.; Shapiro, W.; Ebert, C. Restoration of vagal tone: A possible mechanism for functional abdominal pain. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2010, 35, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Xiang, Q.; Fu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Shao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T. Heart rate variability biofeedback decreases blood pressure in prehypertensive subjects by improving autonomic function and baroreflex. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kolk, B.A. Clinical implications of neuroscience research in PTSD. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1071, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patron, E.; Messerotti Benvenuti, S.; Favretto, G.; Valfre, C.; Bonfa, C.; Gasparotto, R.; Palomba, D. Biofeedback assisted control of respiratory sinus arrhythmia as a biobehavioral intervention for depressive symptoms in patients after cardiac surgery: A preliminary study. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2013, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellizzer, A.M.; Straznicky, N.E.; Lim, S.; Kamen, P.W.; Krum, H. Reduced dietary fat intake increases parasympathetic activity in healthy premenopausal women. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1999, 26, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Bermejo, P.; De La Cruz Torres, B.; Naranjo Orellana, J.; Albornoz Cabello, M. Autonomic Responses to Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Needle Electrolysis: Effect of Needle Puncture or Electrical Current? J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2018, 24, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, G.; O’Connor, R.; Johnston, N. Altitude training for elite endurance athletes: A review for the travel medicine practitioner. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2016, 14, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocherie, F.; Girard, O.; Faiss, R.; Millet, G.P. High-intensity intermittent training in hypoxia: A double-blinded, placebo-controlled field study in youth football players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerath, R.; Edry, J.W.; Barnes, V.A.; Jerath, V. Physiology of long pranayamic breathing: Neural respiratory elements may provide a mechanism that explains how slow deep breathing shifts the autonomic nervous system. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.M.; Davies, B. Physiological implications of altitude training for endurance performance at sea level: A review. Br. J. Sports Med. 1997, 31, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boning, D. Altitude and hypoxia training—A short review. Int. J. Sports Med. 1997, 18, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, S.; Allen, M.S.; Borges, U.; Dosseville, F.; Hosang, T.J.; Iskra, M.; Mosley, E.; Salvotti, C.; Spolverato, L.; Zammit, N.; et al. Effects of voluntary slow breathing on heart rate and heart rate variability: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 138, 104711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telles, S.; Desiraju, T. Oxygen consumption during pranayamic type of very slow-rate breathing. Indian J. Med. Res. 1991, 94, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nature Dental Clinic. Available online: https://alliswell.tw/?lang=en (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Muller, A.M.; Wang, N.X.; Yao, J.; Tan, C.S.; Low, I.C.C.; Lim, N.; Tan, J.; Tan, A.; Muller-Riemenschneider, F. Heart Rate Measures From Wrist-Worn Activity Trackers in a Laboratory and Free-Living Setting: Validation Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2019, 7, e14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, K.E.; Semple, S.; Naumovski, N.; McKune, A.J. Measuring Heart Rate Variability Using Commercially Available Devices in Healthy Children: A Validity and Reliability Study. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2020, 10, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinde, K.; White, G.; Armstrong, N. Wearable Devices Suitable for Monitoring Twenty Four Hour Heart Rate Variability in Military Populations. Sensors 2021, 21, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlQatari, A.A.; Alturki, J.A.; Abdulali, K.A.; Alhumud, D.A.; Alibrahim, M.A.; Alarab, Y.A.; Salem, A.M.; Yar, T.; Alqurashi, Y.D.; Alsunni, A.A.; et al. Changes in Heart Rate Variability and Baroreflex Sensitivity During Daytime Naps. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2020, 12, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Song, C.; Ikei, H.; Park, B.J.; Lee, J.; Kagawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y. Forest Walking Affects Autonomic Nervous Activity: A Population-Based Study. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M. Monitoring training status with HR measures: Do all roads lead to Rome? Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendra Acharya, U.; Paul Joseph, K.; Kannathal, N.; Lim, C.M.; Suri, J.S. Heart rate variability: A review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Lau, Z.J.; Chen, S.H.A.; Makowski, D. Heart Rate Variability in Psychology: A Review of HRV Indices and an Analysis Tutorial. Sensors 2021, 21, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashiro, K.; Min, J.; Yoo, H.J.; Cho, C.; Bachman, S.L.; Dutt, S.; Thayer, J.F.; Lehrer, P.M.; Feng, T.; Mercer, N.; et al. Increasing coordination and responsivity of emotion-related brain regions with a heart rate variability biofeedback randomized trial. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 23, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevoz-Couche, C.; Laborde, S. Heart rate variability and slow-paced breathing:when coherence meets resonance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 135, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheat, A.L.; Larkin, K.T. Biofeedback of heart rate variability and related physiology: A critical review. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2010, 35, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telles, S.; Nagarathna, R.; Nagendra, H.R. Breathing through a particular nostril can alter metabolism and autonomic activities. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1994, 38, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, G.K.; Velkumary, S.; Madanmohan. Effect of short-term practice of breathing exercises on autonomic functions in normal human volunteers. Indian J. Med. Res. 2004, 120, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Sammito, S.; Bockelmann, I. Reference values for time- and frequency-domain heart rate variability measures. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbs, W.C.; Fedewa, M.V.; MacDonald, H.V.; Holmes, C.J.; Cicone, Z.S.; Plews, D.J.; Esco, M.R. The Accuracy of Acquiring Heart Rate Variability from Portable Devices: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Total | Female | Male | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (female/male) | 49 | 29 (59.2%) | 20 (40.8%) | - |
| Age, years | 40.26 ± 10.68 | 37.63 ± 8.09 | 43.72 ± 12.81 | 0.086 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.69 ± 3.37 | 21.34 ± 2.91 | 24.04 ± 3.32 | 0.014 |
| Variables | LF | HF | lnHF | LF/HF, Mean | RMSSD, Msec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate, 1/min | −0.223 (0.002) | −0.412 (<0.001) | −0.514 (<0.001) | 0.062 (0.389) | −0.567 (<0.001) |
| LF | 0.064 (0.375) | 0.134 (0.061) | 0.514 (<0.001) | 0.268 (<0.001) | |
| HF | 0.796 (<0.001) | −0.218 (0.002) | 0.756 (<0.001) | ||
| lnHF | −0.336 (<0.001) | 0.788 (<0.001) | |||
| LF/HF, mean | −0.109 (0.127) |
| Variables | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Df | F | ges | Mauchly’s Test p Value | ANOVA | G.G. Correction p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate, 1/min | 81.7 ± 9.9 | 79.9 ± 9.6 | 77.79 ± 8.62 | 78.89 ± 7.99 | 144 | 7.10 | 0.03 | <0.001 | - | 0.001 |
| LF | 166.6 ± 202.0 | 324.2 ± 464.9 | 329.7 ± 475.6 | 195.4 ± 216.7 | 144 | 7.09 | 0.04 | <0.001 | - | 0.002 |
| lnHF | 3.8 ± 1.2 | 4.1 ± 1.4 | 4.4 ± 1.2 | 4.0 ± 1.2 | 144 | 7.23 | 0.03 | 0.229 | <0.001 | |
| LF/HF ratio | 4.3 ± 7.2 | 8.5 ± 18.9 | 7.7 ± 18.0 | 5.1 ± 10.6 | 144 | 1.85 | 0.01 | <0.001 | - | 0.177 |
| RMSSD, msec | 25.1 ± 19.0 | 29.0 ± 19.8 | 29.5 ± 17.8 | 27.8 ± 18.4 | 144 | 4.24 | 0.01 | <0.001 | - | 0.019 |
| Variables | Mean | Standard Deviation | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate, 1/min | |||
| Test 1 vs. test 2 | 1.87 | 5.68 | 0.153 |
| Test 1 vs. test 3 | 3.94 | 6.71 | 0.001 |
| Test 2 vs. test 3 | 2.07 | 6.36 | 0.165 |
| Test 1 vs. test 4 | 2.83 | 6.86 | 0.035 |
| Test 2 vs. test 4 | 0.96 | 7.35 | 1.000 |
| Test 3 vs. test 4 | −1.11 | 3.46 | 0.176 |
| LF/HF ratio | |||
| Test 1 vs. test 2 | −4.17 | 15.00 | 0.350 |
| Test 1 vs. test 3 | −3.35 | 13.46 | 0.530 |
| Test 2 vs. test 3 | 0.82 | 5.16 | 1.000 |
| Test 1 vs. test 4 | −0.78 | 8.94 | 1.000 |
| Test 2 vs. test 4 | 3.39 | 20.34 | 1.000 |
| Test 3 vs. test 4 | 2.57 | 18.56 | 1.000 |
| RMSSD, msec | |||
| Test 1 vs. test 2 | −3.91 | 6.23 | <0.001 |
| Test 1 vs. test 3 | −4.43 | 7.90 | 0.002 |
| Test 2 vs. test 3 | −0.51 | 9.79 | 1.000 |
| Test 1 vs. test 4 | −2.72 | 11.06 | 0.549 |
| Test 2 vs. test 4 | 1.19 | 12.59 | 1.000 |
| Test 3 vs. test 4 | 1.71 | 8.06 | 0.869 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-C.; Chiang, J.-K.; Kao, H.-H.; Lin, T.-H.; Hung, T.-Y.; Kao, Y.-H. The Effect of the Nasal Airflow Reducer on Parasympathetic Activity in Adults: A Pilot and Exploratory Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101772
Lin Y-C, Chiang J-K, Kao H-H, Lin T-H, Hung T-Y, Kao Y-H. The Effect of the Nasal Airflow Reducer on Parasympathetic Activity in Adults: A Pilot and Exploratory Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(10):1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101772
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yen-Chang, Jui-Kun Chiang, Hsueh-Hsin Kao, Tzu-Hao Lin, Tzu-Ying Hung, and Yee-Hsin Kao. 2025. "The Effect of the Nasal Airflow Reducer on Parasympathetic Activity in Adults: A Pilot and Exploratory Study" Medicina 61, no. 10: 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101772
APA StyleLin, Y.-C., Chiang, J.-K., Kao, H.-H., Lin, T.-H., Hung, T.-Y., & Kao, Y.-H. (2025). The Effect of the Nasal Airflow Reducer on Parasympathetic Activity in Adults: A Pilot and Exploratory Study. Medicina, 61(10), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61101772






