A Comparison of the Effectiveness of the McCoy Laryngoscope and the C-MAC D-Blade Video Laryngoscope in Obese Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
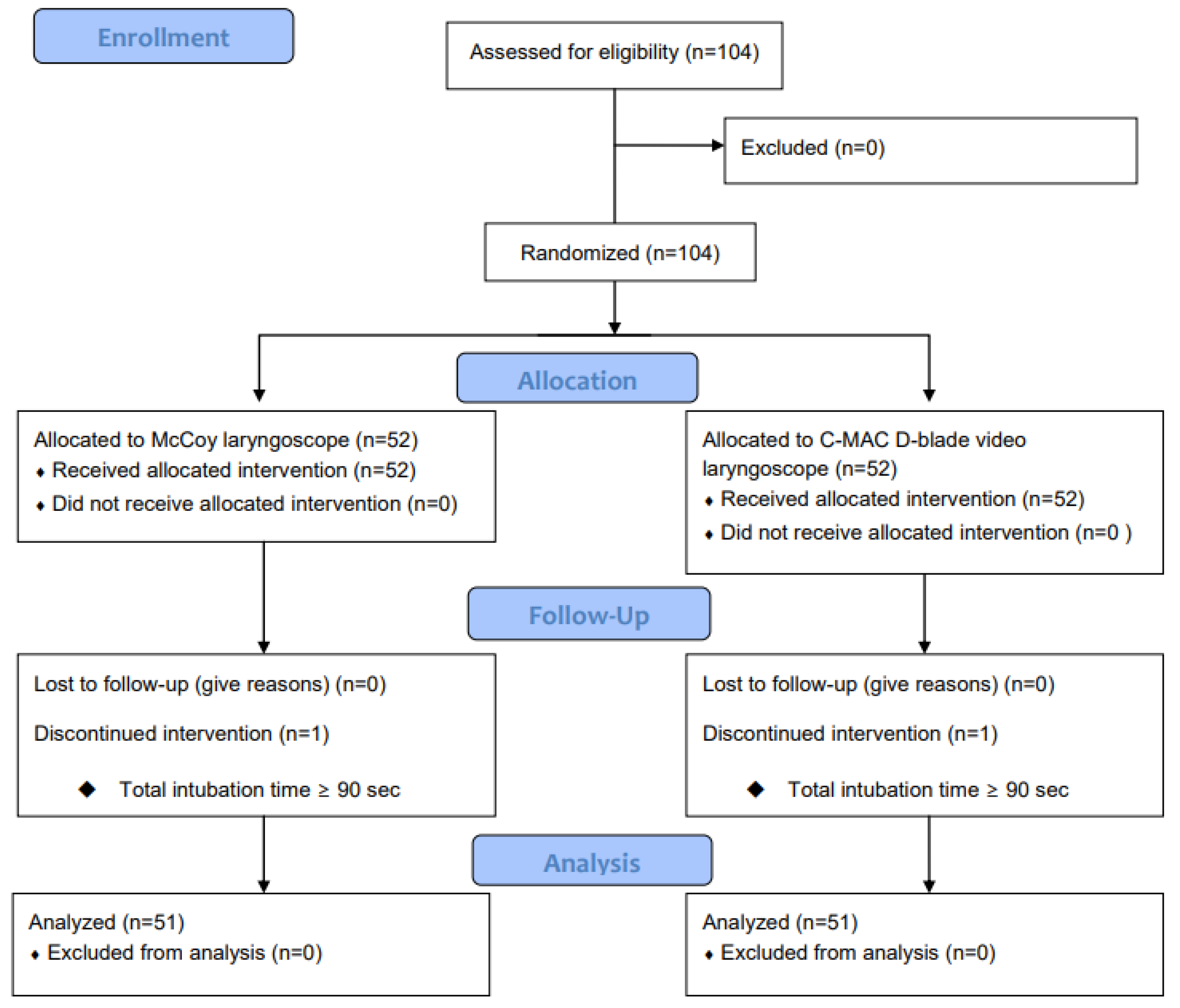
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Members of the Working Party; Nightingale, C.E.; Margarson, M.P.; Shearer, E.; Redman, J.W.; Lucas, D.N.; Cousins, J.M.; Fox, W.T.; Kennedy, N.J.; Venn, P.J.; et al. Peri-operative management of the obese surgical patient 2015: Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland Society for Obesity and Bariatric Anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 859–876. [Google Scholar]
- Kheterpal, S.; Martin, L.; Shanks, A.M.; Tremper, K.K. Prediction and outcomes of impossible mask ventilation: A review of 50,000 anesthetics. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeron, O.; Masso, E.; Huraux, C.; Guggiari, M.; Bianchi, A.; Coriat, P.; Riou, B. Prediction of difficult mask ventilation. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, P.; Perilli, V.; Modesti, C.; Ciocchetti, P.; Vitale, F.; Sollazzi, L. Airway management in obese patients. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2013, 9, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langeron, O.; Birenbaum, A.; Le Saché, F.; Raux, M. Airway management in obese patients. Minerva Anesthesiol. 2014, 80, 382–392. [Google Scholar]
- Lundstrøm, L.H.; Møller, A.M.; Rosenstock, C.; Astrup, G.; Wetterslev, J. High body mass index is a weak predictor for difficult and failed tracheal intubation: A cohort study of 91,332 consecutive patients scheduled for direct laryngoscopy registered in the Danish Anesthesia Database. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, J.B.; Lemmens, H.J.; Brock-Utne, J.G.; Vierra, M.; Saidman, L.J. Morbid obesity and tracheal intubation. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Minville, V.; Delanoue, K.; Mazerolles, M.; Concina, D.; Fourcade, O. The importance of increased neck circumference to intubation difficulties in obese patients. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.M.; Tuckey, J.P. A comparison between the Macintosh and the McCoy laryngoscope blades. Anaesthesia 1996, 51, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Hikawa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Yasuda, K. The McCoy levering laryngoscope in patients with limited neck extension. Can. J. Anaesth. 1997, 44, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidry, M.A.; Khan, F.A. Comparison of hemodynamic response to tracheal intubation with Macintosh and McCoy laryngoscopes. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 29, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, F.S.; Li, H.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yang, G.Z. Current evidence for the use of C-MAC videolaryngoscope in adult airway management: A review of the literature. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.H.; Kim, K.M.; John, H.; Jun, J.H.; Han, M.; Kim, S. Comparison of C-MAC D-blade videolaryngoscope and McCoy laryngoscope efficacy for nasotracheal intubation in simulated cervical spinal injury: A prospective randomized comparative study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dell, K. Predictors of difficult intubation and the otolaryngology perioperative consult. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2015, 33, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Tremper, K.K.; Kheterpal, S.; O’Reilly, M. Grading scale for mask ventilation. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnet, F.; Borron, S.W.; Racine, S.X.; Clemessy, J.L.; Fournier, J.L.; Plaisance, P.; Lapandry, C. The intubation difficulty scale (IDS): Proposal and evaluation of a new score characterizing the complexity of endotracheal intubation. Anesthesiology 1997, 87, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apfelbaum, J.L.; Hagberg, C.A.; Connis, R.T.; Abdelmalak, B.B.; Agarkar, M.; Dutton, R.P.; Fiadjoe, J.E.; Greif, R.; Klock, P.A.; Mercier, D.; et al. 2022 American Society of Anesthesiologists Practice Guidelines for Management of the Difficult Airway. Anesthesiology 2022, 136, 31–81. [Google Scholar]
- Frappier, J.; Guenoun, T.; Journois, D.; Philippe, H.; Aka, E.; Cadi, P.; Silleran-Chassany, J.; Safran, D. Airway management using the intubating laryngeal mask airway for the morbidly obese patient. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 96, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combes, X.; Sauvat, S.; Leroux, B.; Dumerat, M.; Sherrer, E.; Motamed, C.; Brain, A.; D’Honneur, G. Intubating laryngeal mask airway in morbidly obese and lean patients: A comparative study. Anesthesiology 2005, 102, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.H.; Rovsing, L.; Olsen, K.S. GlideScope videolaryngoscope vs. Macintosh direct laryngoscope for intubation of morbidly obese patients: A randomized trial. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2011, 55, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, K.P.; Bhalla, A.P.; Pandey, R.K.; Baidya, D.K.; Subramaniam, R.; Kashyap, L. Comparison of Macintosh, McCoy, and Glidescope video laryngoscope for intubation in morbidly obese patients: Randomized controlled trial. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2018, 12, 433–439. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, S.R.; Taghavi Gillani, M.; Tabari, M.; Morovatdar, N. Comparative analysis of the usefulness of the GlideScope®, Macintosh, and McCoy laryngoscopes for endotracheal intubation in patients with obesity: A randomized, clinical trial. Anesth. Pain. Med. 2017, 7, e57913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, P.H.; Mazumdar, B.; Skinner, S.C. Capnometer transport delay: Measurement and clinical implications. Anesth. Analg. 1994, 78, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ander, F.; Magnuson, A.; Berggren, L.; Ahlstrand, R.; de Leon, A. Time-to-intubation in obese patients. A randomized study comparing direct laryngoscopy and videolaryngoscopy in experienced anesthetists. Minerva Anestesiol. 2017, 83, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattano, D.; Corso, R.M.; Altamirano, A.V.; Patel, C.B.; Meese, M.M.; Seitan, C.; Hagberg, C.A. Clinical evaluation of the C-MAC D-Blade videolaryngoscope in severely obese patients: A pilot study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shiga, T.; Wajima, Z.; Inoue, T.; Sakamoto, A. Predicting difficult intubation in apparently normal patients: A meta-analysis of bedside screening test performance. Anesthesiology 2005, 103, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, C.J.; Shin, B.S.; Ko, J.S.; Choi, S.J.; Ryu, S.A. Neck circumference to thyromental distance ratio: A new predictor of difficult intubation in obese patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 106, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritscherova, S.; Adamus, M.; Dostalova, K.; Koutna, J.; Hrabalek, L.; Zapletalova, J.; Uvizl, R.; Janout, V. Can difficult intubation be easily and rapidly predicted? Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc Czech Repub. 2011, 155, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-Ganzouri, A.R.; McCarthy, R.J.; Tuman, K.J.; Tanck, E.N.; Ivankovich, A.D. Preoperative airway assessment: Predictive value of a multivariate risk index. Anesth. Analg. 1996, 82, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Law, J.A.; Broemling, N.; Cooper, R.M.; Drolet, P.; Duggan, L.V.; Griesdale, D.E.; Hung, O.R.; Jones, P.M.; Kovacs, G.; Massey, S.; et al. The difficult airway with recommendations for management—Part 2—The anticipated difficult airway. Can. J. Anaesth. 2013, 60, 1119–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.N.; Kim, T.S.; Park, Y.C. The relationship between the predictors of obstructive sleep apnea and difficult intubation. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2011, 60, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lundstrøm, L.H.; Møller, A.M.; Rosenstock, C.; Astrup, G.; Gätke, M.R.; Wetterslev, J.; Danish Anaesthesia Database. A documented previous difficult tracheal intubation as a prognostic test for a subsequent difficult tracheal intubation in adults. Anaesthesia 2009, 64, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.N.; Carli, F.; Cormack, R.S. Unexpected, difficult laryngoscopy: A prospective survey in routine general surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 1991, 66, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriussawakul, A.; Limpawattana, P. A validation study of the intubation difficulty scale for obese patients. J. Clin. Anesth. 2016, 33, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jense, H.G.; Dubin, S.A.; Silverstein, P.I.; O’Leary-Escolas, U. Effect of obesity on safe duration of apnea in anesthetized humans. Anesth. Analg. 1991, 72, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, G.T.; Abdalgalil, D.A.; Ibrahim, T.H. Orotracheal intubation of morbidly obese patients, comparison of GlideScope video laryngoscope and the LMA CTrach with direct laryngoscopy. Anesth. Essays Res. 2012, 6, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, N.; Katznelson, R.; Friedman, Z. Heart rate/blood pressure response and airway morbidity following tracheal intubation with direct laryngoscopy, GlideScope and Trachlight: A randomized control trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2009, 26, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkılar, G.; Sargın, M.; Sarıtaş, T.B.; Borazan, H.; Gök, F.; Kılıçaslan, A.; Otelcioğlu, Ş. Hemodynamic responses to endotracheal intubation performed with video and direct laryngoscopy in patients scheduled for major cardiac surgery. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 11477–114783. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Küçükosman, G.; Aydın, B.G.; Gülçek, N.; Okyay, R.D.; Pişkin, Ö.; Ayoğlu, H. The effect of laryngoscope types on hemodynamic response and optic nerve sheath diameter. McCoy, Macintosh, and C-MAC video-laryngoscope. Saudi Med. J. 2020, 41, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shribman, A.J.; Smith, G.; Achola, K.J. Cardiovascular and catecholamine responses to laryngoscopy with and without tracheal intubation. Br. J. Anaesth. 1987, 59, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, A.M.; Dally, F.G. Acute hypertension during induction of anaesthesia and endotracheal intubation in normotensive man. Br. J. Anaesth. 1970, 42, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.J.; Sklar, G.S.; Hill, C.H.; Villanueva, R.; King, B.D. Complications related to the pressor response to endotracheal intubation. Anesthesiology 1977, 47, 524–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshri, R.K.; Prasad, M.K.; Choudhary, A.K.; Jheetay, G.S.; Singh, Y.; Kapoor, K. Comparative Evaluation of Different Doses of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine on Hemodynamic Response during Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation in Geriatric Patients Undergoing Spine Surgeries: A Prospective, Double-Blind Study. Anesth. Essays Res. 2018, 12, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Sun, S.; Huang, S. The association of body mass index with difficult tracheal intubation management by direct laryngoscopy: A meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riad, W.; Vaez, M.N.; Raveendran, R.; Tam, A.D.; Quereshy, F.A.; Chung, F.; Wong, D.T. Neck circumference as a predictor of difficult intubation and difficult mask ventilation in morbidly obese patients: A prospective observational study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2016, 33, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| I | Ventilated using a mask |
| II | Ventilated using a mask with oral airway |
| III | Difficult mask ventilation (inadequate, unstable, or requiring two practitioners) |
| IV | Mask ventilation could not be achieved |
| Parameter | Scores | Rules for Calculating IDS Score |
|---|---|---|
| Number of attempts | N1 | N1: Each additional attempt adds 1 pt. |
| Number of operators | N2 | N2: Each additional operator adds 1 pt. |
| Number of alternative techniques | N3 | N3: Each alternative technique adds 1 pt. (e.g., patient repositioning or change in materials used) |
| Cormack grade 1 | N4 | N4: Apply Cormack grade for the first oral attempt. |
| Lifting force required | ||
| Normal/increased | N5 = 0/N5 = 1 | |
| Laryngeal pressure | ||
| Not applied/applied | N6 = 0/N6 = 1 | |
| Vocal cord mobility | ||
| Abduction/adduction | N7 = 0/N7 = 1 | |
| Total IDS = Sum of scores | N1–N7 | |
| IDS score | Degree of difficulty | |
| 0 | Easy | |
| 0 < IDS ≤ 5 | Slight | |
| 5 < IDS | Moderate to major | |
| Characteristics | Laryngoscope | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| McCoy Group (n = 51) | C-MAC Group (n = 51) | ||
| Age (years) | 43.76 ± 12.94 | 39.90 ± 10.87 | 0.103 |
| Sex (M/F) (n) | 19/32 | 26/25 | 0.163 |
| Mouth opening (cm) | 5 (4.5–5) | 5 (5–5) | 0.080 |
| Mallampati classification (n) | |||
| I/II/III/IV | 3/26/20/2 | 6/26/16/3 | 0.649 |
| Head/neck movement (n) | |||
| >90°/90°/<90° | 33/8/10 | 34/5/12 | 0.641 |
| Ability to prognath (n) | |||
| Yes/partial/no | 42/9/0 | 44/6/1 | 0.439 |
| Weight (kg) | 102.24 ± 14.76 | 107.21 ± 15.64 | 0.101 |
| Thyromental distance (cm) | 8 (7–9) | 9 (8–10) | 0.083 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 36.75 (35.5–39.75) | 36.53 (35.6–38.87) | 0.878 |
| History of difficult intubation (n) | |||
| None/questionable/definite | 26/25/0 | 17/34/0 | 0.071 |
| Neck circumference (cm) | 45.59 ± 4.51 | 46.02 ± 4.43 | 0.627 |
| ASA class (II/III) (n) | 42/9 | 41/10 | 0.799 |
| Laryngoscope | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Outcomes | McCoy Group (n = 51) | C-MAC Group (n = 51) | p-Value |
| Mask ventilation | 0.070 | ||
| I/II/III/IV | 33/15/3/0 | 27/13/11/0 | |
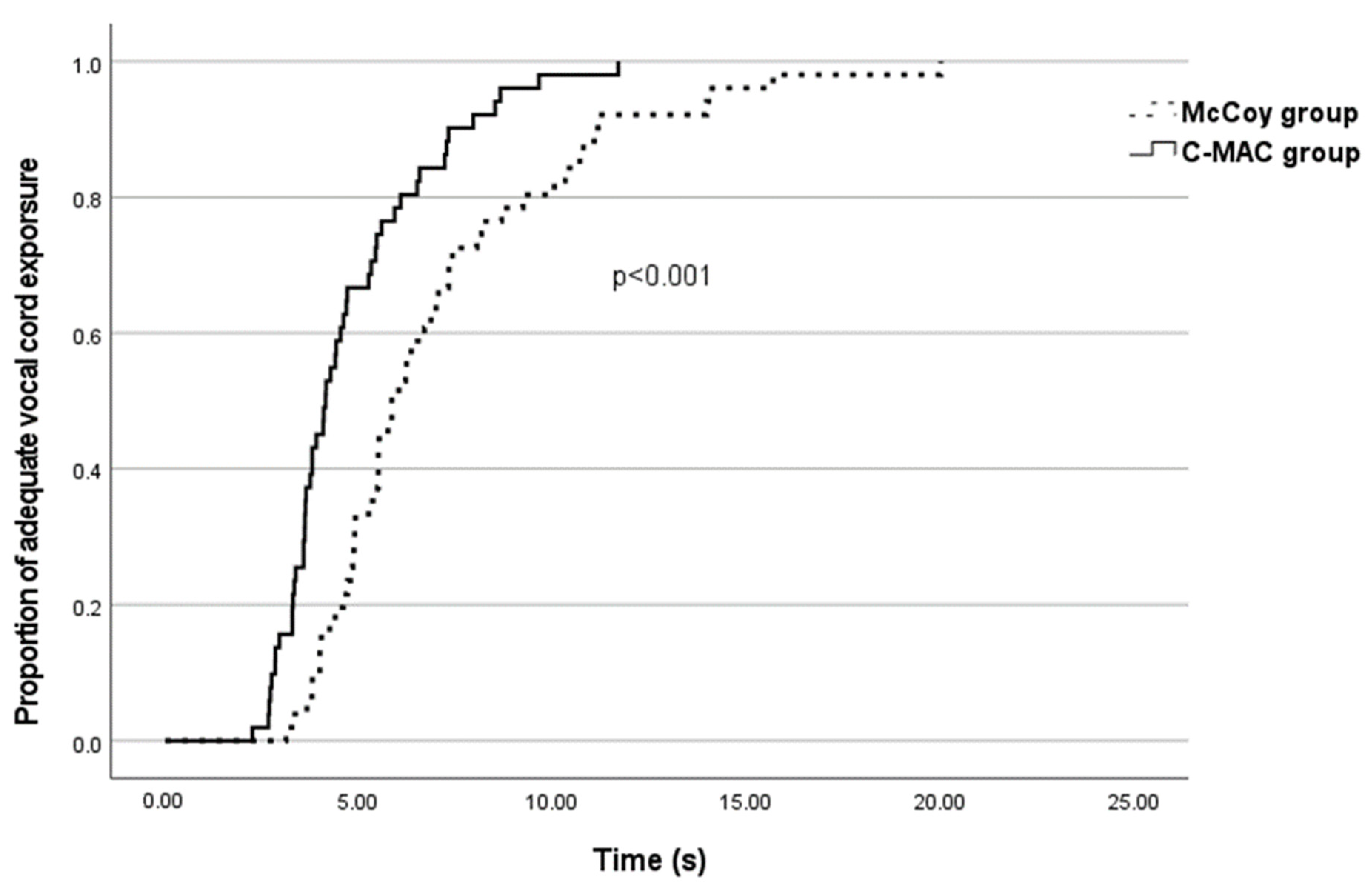
| Vocal cord exposure time (s) | 5.85 (4.81–8.10) | 4.14 (3.47–5.52) | <0.001 * |
| Vocal cord passage time (s) | 10.76 (8.75–14.39) | 10.33 (9.21–14.35) | 0.756 |
| Intubation time (s) | 32.54 (29.70–37.21) | 30.72 (28.12–32.19) | 0.499 |
| POGO score (%) | 70 (50–80) | 70 (50–90) | 0.529 |
| IDS | 2 (1–3) | 1 (0–2) | 0.046 * |
| Teeth or lip trauma (n) | 0 | 2 | 0.153 |
| Laryngoscope | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Outcomes | McCoy Group (n = 51) | C-MAC Group (n = 51) | p-Value |
| Number of attempts (1/2) | 49/2 | 51/0 | 0.495 |
| Number of operators (1/2) | 50/1 | 51/0 | 0.315 |
| Number of alternative techniques | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Cormack grade | |||
| I/II/III/IV | 12/33/5/1 | 19/30/2/0 | 0.260 |
| I,II/III,IV | 45/6 | 49/2 | 0.269 |
| Lifting force required | |||
| Normal/increased | 35/16 | 24/27 | 0.027 * |
| Laryngeal pressure | |||
| Not applied/applied | 15/36 | 11/40 | 0.363 |
| Vocal cord mobility | |||
| Abduction/adduction | 51/0 | 51/0 | NA |
| Variables | Group | Anesthesia Time | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Induction | Immediately before Intubation | Immediately after Intubation | 3 Min after Intubation | |||
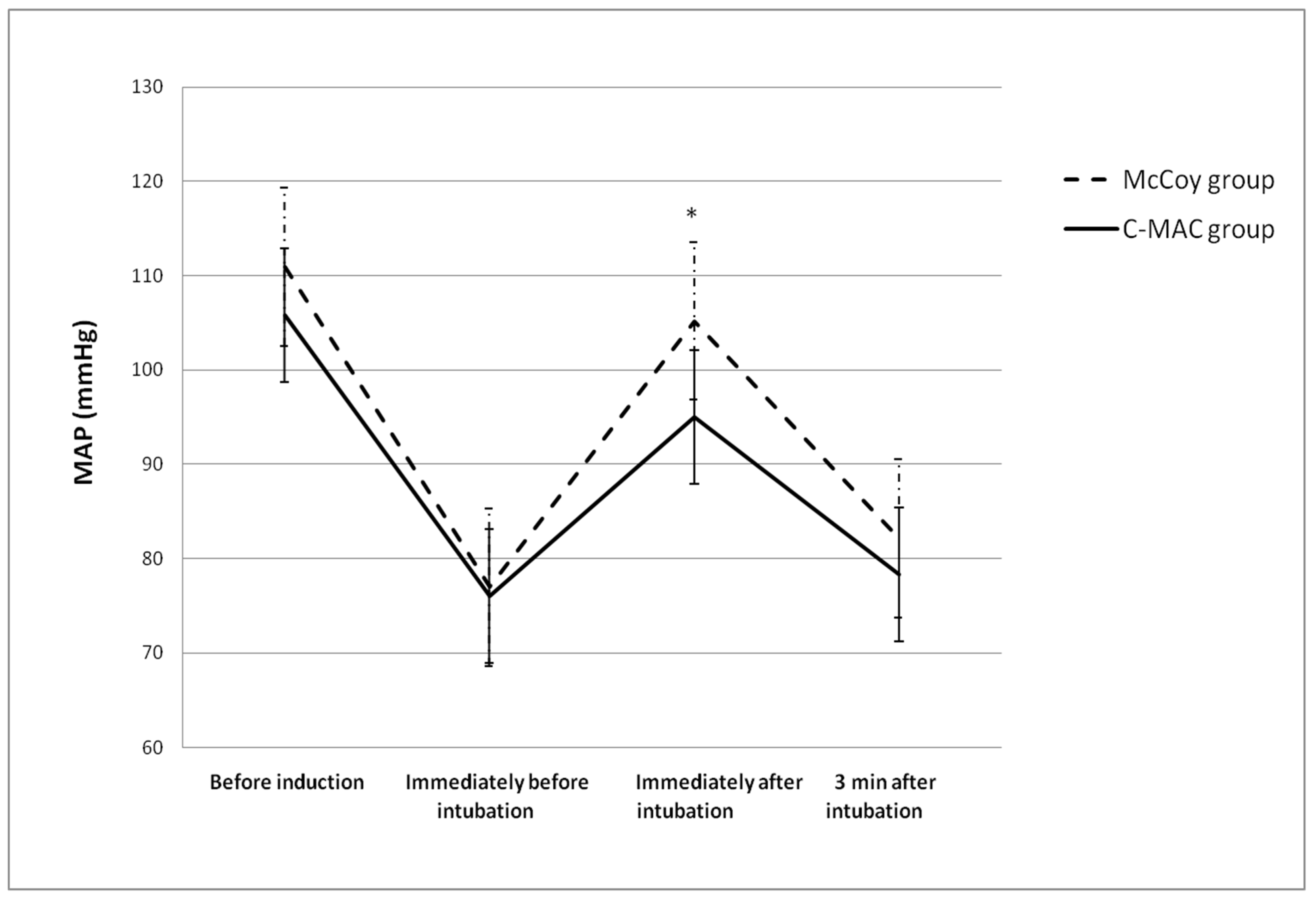
| MAP (mmHg) | McCoy | 110.96 ± 13.82 | 76.96 ± 11.24 | 105.20 ± 22.40 | 82.12 ± 14.23 | 0.042 * |
| C-MAC | 105.78 ± 19.43 | 76.02 ± 9.48 | 95.02 ± 16.79 | 78.31 ± 11.43 | ||
| HR (beats/min) | McCoy | 79.92 ± 17.93 | 76.35 ± 15.81 | 88.90 ± 12.73 | 82.14 ± 12.66 | 0.974 |
| C-MAC | 77.92 ± 13.89 | 75.82 ± 15.06 | 87.88 ± 14.62 | 81.43 ± 12.93 | ||
| SpO2 (%) | McCoy | 97 (96–98) | 100 (99–100) | 99 (99–100) | 98 (97–99) | 0.775 |
| C-MAC | 97 (96–98) | 99 (99–100) | 99 (98–100) | 98 (98–99) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-M.; Lee, S.-K.; Jang, M.; Oh, M.; Park, E.-Y. A Comparison of the Effectiveness of the McCoy Laryngoscope and the C-MAC D-Blade Video Laryngoscope in Obese Patients. Medicina 2024, 60, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60081285
Lee J-M, Lee S-K, Jang M, Oh M, Park E-Y. A Comparison of the Effectiveness of the McCoy Laryngoscope and the C-MAC D-Blade Video Laryngoscope in Obese Patients. Medicina. 2024; 60(8):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60081285
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jung-Min, Soo-Kyung Lee, Minsoo Jang, Minho Oh, and Eun-Young Park. 2024. "A Comparison of the Effectiveness of the McCoy Laryngoscope and the C-MAC D-Blade Video Laryngoscope in Obese Patients" Medicina 60, no. 8: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60081285
APA StyleLee, J.-M., Lee, S.-K., Jang, M., Oh, M., & Park, E.-Y. (2024). A Comparison of the Effectiveness of the McCoy Laryngoscope and the C-MAC D-Blade Video Laryngoscope in Obese Patients. Medicina, 60(8), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60081285





